#tastant
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
i think i just unlocked nirvana or heaven or hell with hot tub jets. eating honeycrisp apple slices with honey and tortilla i pu ton the burner with and goat cheese. i think ive transcended a medium of life and played some sort of 4d gender chess wiht my palate I love humanity and i loive creationn Ilvoe hands. Did you know tastebuds are actually in between the bumps on your tounge. theyre taste receptors lining the sides of the dips in between the bumps.isnt that poetic that what we seek in sustience is below the surface and is misconcieved and is that we have to dissolve the tastants in saliva or water and thats how flavor. how flavor is half smell. how we have to hold hands. how whHoLY SHIT JUST DIPPED THE CHEESE TORTILLA IN THE HONEY HOOOOOOOLY DHIT HOOLLLLLLLY SHIT OH MY GOD.
#all the while i am watching youtube and scrolling#tumblr. im also really seriously ill with some xtra evil cold#man tastes yummy for thje first time . rediscovers fire#food
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

Et trobo tantíssim a faltar. Avui em toca ser a l'Alimentaria, sabent que hagués gaudit tant compartir-ho amb tu. És insuportable la falta que em fas.
M'imagino "robant" cosetes als diferents stands, posant-hi morro perquè em regalin mostres o petites degustacions. Per explicar-t'ho per telegram, o a la nit al sofà amb una cerveseta. M'imagino tastant totes aquestes absurditats junts, un dia qualsevol de vermut. O agafant-ho com a excusa per a celebrar qualsevol cosa.
Perquè nosaltres erem així. Gaudíem d'aquesta manera. Amb les petites coses, els petits moments. Buscant qualsevol excusa per fer-ho especial.
En teniem prou tenint-nos a nosaltres.
Érem tant feliços. I la vida és tant buida sense tu.
0 notes
Text
Water tastes like water, y'all unevolved monkes with no hydroceptive tastants.
I'm so sick of people saying water doesn't taste. Water fuckin TASTES
53K notes
·
View notes
Text
Bledes amb tahina, iogur i pinyons
Ingredients (2 px): un manat de bledes, mig iogur grec, un bon grapat de pinyons una cullerada sopera de tahina, 2 grans d´all, un raig de vi blanc, suc de llimona, un xic d´aigua, sal i pebre Preparació: Per preparar la salsa heu de barrejar el iogur, la tahina, el suc de llimona i una miqueta d´aigua. Si veieu que necessiteu més líquid podeu afegir qualsevol dels ingredients, tastant-ho per…

View On WordPress
#AIGUA#ALL#BLEDES#CUINA#FRUITA#FRUITA SECA#IOGURT#LACTIC#LLIMONA#PEBRE NEGRE#PINYONS#PRIMERS PLATS#RECEPTA#SAL#SUC DE LLIMONA#TAHINA (MANTEGA DE SESAM)#VERDURA#VI#VI BLANC
0 notes
Text
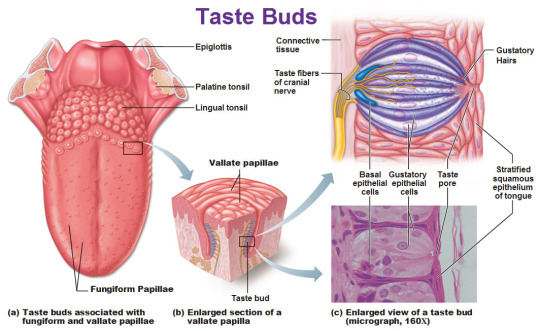
Taste
The tongue is covered with many little bumps called papillae. Taste buds are found in the walls of papillae and the grooves surrounding them. Each taste bud contains anywhere from 50 to 150 taste receptor cells.
Microvilli extend from taste receptor cells
and protrude through an opening (taste pore) into the mouth.
These microvilli come in contact with substances in the mouth that can be tasted, also known as tastants.
Tastants interact with taste receptor cells through a number of different mechanisms to depolarize the cells.
When taste cells are depolarized, they release neurotransmitters that stimulate sensory neurons that travel in cranial nerves VII, IX, and X.
These neurons terminate on neurons in the nucleus of the solitary tract in the medulla then continue on to the thalamus.
Taste information is sent to the gustatory cortex, ( ocated on the border between the anterior insula and the frontal operculum).
This information encodes for basic tastes, such as sweet, salty, sour, bitter, and savory or umami.
However, the actual flavour of a food---which is what we typically define as taste---is created by a combination of taste and olfactory (smell) information.
Sweetness
Produced by the presence of sugars, some proteins, and other substances.
Detected by G protein-coupled receptors T1R2+3 (heterodimer) and T1R3 (homodimer).
Saltiness
Saltiness is a taste produced best by the presence of cations (such as Na+, K+or Li+)
Directly detected by cation influx into glial like cells via leak channels causing depolarisation of the cell.
Sourness
Sourness is acidity and is also sensed using ion channels.
Undissociated acid diffuses across the plasma membrane of a presynaptic cell, where it dissociates in accordance with Le Chatelier's principle.
The protons that are released then block potassium channels, which depolarise the cell and cause calcium influx.
Bitterness
Current research suggests TAS2Rs (taste receptors, type 2, also known as T2Rs) such as TAS2R38 are responsible tasting bitter substances.
Savouriness
The amino acid glutamic acid is responsible for savouriness, but some nucleotides (inosinic acid and guanylic acid) can act as complements.
Glutamic acid binds to a variant of the G protein-coupled receptor, producing a savoury taste
#medicine#biomed#biomedicine#notes#medblr#studyblr#sciblr#premed#nursing#biology#human biology#med#biomedical science#science#taste#physiology#anatomgy#gustatory#gustatory system#gustatory cortex#mouth
265 notes
·
View notes
Photo

#cadup #novetat a @cervesespopaire !! #cervesa #artesa #cítrica #floral #suau #tastant #distribucio : @vinsvidart 😉 La#vols ???? #blanes #cerveza @cervezaartesana #popaire #bier #bière #artesanalbeer #catalanbeer #catalunya #km0 #compra #goodbeer #birra #biraartesanal #moments #tast #atothora #tarda #divendres (at Porqueras)
#compra#tarda#divendres#vols#blanes#goodbeer#moments#catalunya#birra#distribucio#tastant#tast#suau#bier#popaire#cadup#cervesa#cerveza#biraartesanal#floral#artesanalbeer#km0#catalanbeer#novetat#cítrica#artesa#atothora#bière
0 notes
Text
quenya names BUT including "an"
Admostanwë Airrónani Airyatanor Alaiands Alanderul Alanil Alanor Alcanaxë Alcand Alcandë Aldaneno Aldangamin Aldanyata Aliornanyë Allanca Allangwa Almandises Almangs Almanto Alphannaxë Amandlem Amantura Ambarant Ambindian Anandayel Anatandi Ancando Andilin Andilling Andoressë Andoron Anelya Anictuamor Annamandë Annands Annórind Antauromen Anturcamo Apandë Arandari Arandel Aranden Arandil Arandin Arando Arandor Aranna Arantay Aranwincar Arcardan Arfanitern Artani Arvand Astanyároc Ataman Atandórë Atanon Atatandil Atatany Aulanyar Aulendanë Avandana Avanya Avyhantië Awarannar Axandë Axango Basano Bastand Beatan Beavang Bindilmand Birnando Blanden Blontan Brianya Calahani Calana Calandúna Calanna Callan Calman Calmang Calmanin Candon Cangar Cannanweld Canwar Canáravars Carmanya Casanóred Cassarman Chander Chradfans Cilmands Ciryand Ciryanyaf Ciryondang Clownfang Coplandil Cordiévan Cormano Cánange Damandinwë Darónan Datalands Demmacant Devanamitë Devandacar Elarantë Elcanónar Eldamando Eldamanil Eldanyar Eldavand Elenyanda Elflan Elflyanna Elmand Elmandil Elmani Elmanár Elvehtan Elvestandë Endando Endanel Ennaxany Enquanifin Erucandë Eruirrana Essandë Essëang Estalangs Etyarman Eäranë Eärwhanong Faiantë Falaithan Falantë Falanyë Falman Fandalmë Fandandi Fandil Fandon Fangeman Fangwed Fannat Fastan Fatafancë Fattana Feavan Finangs Findiantir Flanwë Foanyar Foldandë Foreanyar Forianatta Foruhang Foryanys Frannon Frianwë Frimman Fëanyárage Galmandórë Garandis Glorgeman Gnolanna Golliandú Grandëa Grianótë Hallan Hanastrem Hangassin Hantiming Hanárë Heavan Hilmanwë Hoottang Hoplan Horeavand Hranord Hraxan Hyanata Hyandinë Hyands Hyandúnë Hyanwë Hyanyata Hyarantir Hávantál Ilinandil Ilmindandi Ilwanwits Ilúvandë Inalani Indolanwë Irincandi Isiman Isinyang Islandë Istwan Itander Jewearmang Kembarcan Kintanta Ladfancava Lainguanya Laityanory Lalanyar Lamanária Lamitande Lampands Landin Landiénels Landon Landondern Landur Langolion Lanissë Lantarcar Lantárien Lanámo Lanárassë Lanórigher Lanótë Lastafanië Latano Lauran Leavanto Liandorigh Linanië Linquandë Litane Liévan Lofanyar Lonant Lownfany Lámangot Lámantar Macirdan Mahant Manairëa Manalimer Mandanië Mandil Mandistays Mandië Mandon Manduruong Mandúna Manelwer Mangth Manielpin Manistur Mantirin Mantorya Manárë Maranil Mareanë Mariandë Marmantalm Meldannat Mentant Mettan Mightarman Mindanossë Mingalan Mingoland Mornanórëa Mortaran Moryafand Mottóland Máhando Máhants Mámandië Márilman Míriana Nahandel Nanalmans Nandëa Nangolday Nannaráto Nanson Nanyar Nanysh Naraurani Narmant Naxandil Nimanta Noblanwë Noldands Nollandmo Norröan Nyanollon Nárianwë Nóriantar Núnaned Ohtandë Ohtaniel Oiondanna Ollianorde Ontandë Ormantron Orröandē Ostandë Outsimant Outyans Paland Pantule Parand Parantast Pellanoron Pitaman Plandandë Polanarë Poonang Poungwantë Praityand Quenanilmë Quendanita Raitanë Randil Rannata Reando Repvancë Rinaranyë Roangazed Roardaney Rocana Roossana Royannië Russantult Rómendëan Sanacil Sandern Sanduressë Santum Savano Searnan Shandi Shandil Shanwen Shanyelpë Shanárinyë Sicans Sinyshanwë Sornanlan Southand Spandë Stands Stanition Stannórë Stantar Stanwë Stanávaró Stlandil Swandë Taliman Tanaity Tanatars Tandilda Taneles Tanerion Tangwë Tantamar Tanyaráma Tanáva Tarant Tarmancar Tastantion Tatalance Tatantely Tataranda Telyantië Telónani Terland Theantirë Thlananto Thlannar Tilman Timantar Tinyastan Towvanwë Treanien Turanwë Tyando Tyanglië Tyarávan Tyatyant Táriando Ulmand Ulmantano Umbaran Umbarian Undanyávë Unmanwë Uruanni Uruliandë Valacande Valandar Valanders Valanwë Valanórë Valiandi Valiman Valman Valmantar Valmanya Vandambë Vandowme Vanduir Vanduron Vaniel Vanilmo Vanily Vanimo Vanárë Vastlandel Vindandur Vormannary Vëandider Waltanen Wanyar Warklyand Wavanna Weltanna Wervanta Westalan Westantë Wetanya Wilmanta Wrangolair Áranalia Árissantin Ëannar Íringaian Ñgoliévan Úmandust Úmanto Úmanyárëa
0 notes
Text
E-PORTFOLIO IN PHYSIOLOGICAL & BIOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY (PY48) MRS. ABIGAIL INTERNO (COURSE PROFESSOR) LAIRA ANDREI S. OSIAS (STUDENT)
MIDTERM ASSIGNMENT #2
PHYSIOLOGICAL & BIOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY
NAME: OSIAS, LAIRA ANDREI S.
SUBJ CODE: PY48
UNIT 3 TOPIC:
Sensory Physiology
Endocrine Glands
Muscles
SPECIFIC GUIDE QUESTIONS:
A. Sensory Physiology
Discuss the following:
undefined
Sensory receptors are primarily classified as chemoreceptors, thermoreceptors, mechanoreceptors, or photoreceptors.
Broadly, sensory receptors respond to one of four primary stimuli:
Chemicals (chemoreceptors)
Temperature (thermoreceptors)
Pressure (mechanoreceptors)
Light (photoreceptors)
Cutaneous Sensations
Touch, pressure, and temperature receptors are found on the surface of the skin. The connections between receptors and cutaneous sensations are not well understood. Touch sensitive Meissner corpuscles and deep pressure sensitive Pacinian corpuscles Ruffini ends communicate warmth, while Krause's bulbs communicate cold. Information is sent from the receptors to nerve fibers in the spinal cord, which then travel to the brainstem. They are then sent to a cortical area in the parietal lobe. Skin senses are also subjected to sensory adaptation. A hot tub, for example, can be unbearably hot at first, but after a while, one can sit in it without discomfort.
Pain. The majority of pain receptors in the skin are free nerve endings. Information is transmitted by two types of pathways to the brain by way of the thalamus.
The fast (myelinated) route recognizes localized pain and transmits it to the cortex quickly.
The unmyelinated slow route carries less localized, longer acting pain information (such as that concerning chronic aches).
Taste & Smell
Taste and smell are two distinct sensations with independent receptor organs, but they are inextricably linked. Taste buds, which are made up of unique sensory cells, detect tastants, which are substances found in foods. These cells convey messages to specific parts of the brain when activated, making us aware of our taste sense. Similarly, odorants, or airborne odor molecules, are picked up by specific cells in the nose. Odorants trigger a neuronal response by activating receptor proteins present on hairlike cilia at the ends of sensory cells. Taste and smell messages eventually converge, allowing us to detect food flavors. This strong association is most evident in our perception of food flavors. Food "tastes" differently when the sense of smell is impeded, as anyone who has had a head cold will attest. Actually, the flavor of the food, or the combination of taste and smell, is what is being altered. This is because just the taste of the meal is detected, not the scents. Taste is concerned with discriminating between compounds that have a sweet, salty, sour, bitter, or umami flavor (umami means "savory" in Japanese). Taste and smell interactions, on the other hand, improve our perceptions of the meals we eat. Specialized sensory neurons in a small patch of mucus membrane along the roof of the nose detect airborne odor molecules called odorants. These sensory cells' axons flow through perforations in the overlying bone and enter two extended olfactory bulbs on the underside of the frontal lobe.
Vestibular Apparatus and Equilibrium
The vestibular system is the inner ear's sensory equipment that aids in maintaining postural balance. The vestibular system's input is also crucial for coordinating the position of the head and the movement of the eyes.
The Ears and Hearing
The ear is the organ of hearing and balance. The parts of the ear include:
External or outer ear, consisting of:
undefined
Tympanic membrane (eardrum). The tympanic membrane divides the external ear from the middle ear.
Middle ear (tympanic cavity), consisting of:
undefined
Inner ear, consisting of:
undefined
The ability to see the world around you is determined by your vision. Several components within your eye and brain work together to give you vision. These components are:
Lens
Retina
Optic nerve
Many different parts of your eye and brain work together to assist you in seeing. The following are the primary elements of your vision:
Cornea: The front layer of your eye is called the cornea. The cornea is a dome-shaped structure that bends light entering your eye.
The pupil is the black dot in the middle of your eye that serves as a light gateway. In dark light, it extends, and in brilliant light, it contracts. The iris is in charge of it.
Iris: Your eye color is usually attributed to this area. The iris is a muscle in your eye that regulates the size of your pupil and the amount of light that enters it.
The lens is located behind the iris and pupil. Like a camera, it works with your cornea to concentrate the light that enters your eye. The lens sharpens the image in front of you, allowing you to see all of the details clearly.
The retina is a layer of tissue located in the back of the eye that converts the light that enters your eye into electrical signals. These signals are transmitted to the brain, which recognizes them as images.
Optic nerve: This aspect of your vision serves as a link between the retina and the brain. The electrical signals created in the retina are transmitted to the brain via the optic nerve. The brain then generates visuals.
Tears: Tears are supposed to keep your eyes moist and help you focus effectively, despite the fact that they are most usually associated with sobbing. They also aid in the prevention of eye discomfort and infection.
Endocrine Glands
Discuss the following:
undefined
The endocrine system is made up of hormone-secreting endocrine glands. Despite the fact that there are eight primary endocrine glands spread throughout the body, they are nevertheless considered one system since they have comparable functions, influence mechanisms, and interrelationships.
Non-endocrine portions of certain glands serve purposes other than hormone release. The pancreas, for example, includes both an exocrine and an endocrine part that secretes digestion enzymes and hormones. Hormones are secreted by the ovaries and testes, which also create eggs and sperm. Although several organs, such as the stomach, intestines, and heart, create hormones, this is not their major role.
Mechanisms of Hormone Action
Hormones activate target cells by diffusing through the target cell's plasma membrane (lipid-soluble hormones) to bind a receptor protein in the cell's cytoplasm, or by binding a particular receptor protein in the target cell's cell membrane (water-soluble proteins).
Pituitary Gland
The pituitary gland is a small pea-sized gland that plays a major role in regulating vital body functions and general wellbeing. It is referred to as the body's 'master gland' because it controls the activity of most other hormone-secreting glands.
Adrenal Glands
Adrenal glands are small, triangular-shaped glands that sit on top of both kidneys. Hormones produced by the adrenal glands serve to regulate your metabolism, immunological system, blood pressure, stress response, and other vital activities.
Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands
Iodine from meals is used by the thyroid gland to produce two thyroid hormones that control how the body uses energy. The parathyroid glands are a group of four small glands that sit behind the thyroid gland. The parathyroid glands make a hormone (parathyroid hormone) that helps regulate calcium levels in the blood.
Pancreas and Other Endocrine Glands
Glands are organs in the body that generate and release chemicals. The pancreas has two primary functions: exocrine and endocrine. Exocrine function: produces chemicals (enzymes) that aid digesting. Endocrine function: releases hormones that regulate the quantity of sugar in your blood.
Paracrine & Autocrine Regulation
(Autocrine glands generate hormones that operate on their own glandular cells, such as prostaglandins; paracrine glands create hormones that are released into the extracellular matrix and diffuse to neighboring cells, such as islets of Langerhans - somatostatin.) Diffusible chemicals bind to receptors on the same cell from which they were released in autocrine signaling. Insulin was the first transmitter to be implicated in the autocrine regulation of -cell function.
Muscles
Discuss the following:
Skeletal Muscles
Skeletal muscles make up 30 to 40% of your total body weight. They're the muscles that attach to your bones and allow you to move and operate in a variety of ways. Skeletal muscles are voluntary, which means you may choose when and how they perform.
Mechanisms of Contraction
Abstract. When the thin actin and thick myosin filaments slip past each other, muscle contraction occurs. Cross-bridges that stretch from myosin filaments and cyclically engage with actin filaments when ATP is hydrolyzed are thought to be the driving force behind this activity.
Contractions of Skeletal Muscles
The neuromuscular junction, which is the synapse between a motoneuron and a muscle fiber, is where skeletal muscle contraction begins. The presynaptic membrane's voltage-gated calcium (Ca2+) channels open when action potentials are sent to the motoneuron and then depolarized.
Energy Requirements of Skeletal Muscles
The breakdown of ATP provides the energy required for muscle contraction, but the amount of ATP in muscle cells is only enough to fuel a brief contraction.
Neural Control of Skeletal Muscles
Concentric, eccentric, and isometric contractions, muscle fiber recruitment, and muscle tone are all controlled by neural control. The role of motor units in nervous system control of skeletal muscles is critical.
Cardiac & Smooth Muscles
Cardiac muscle cells are found in the heart's walls, appear striped (striated), and are controlled involuntarily. Except for the heart, smooth muscle fibers are found in the walls of hollow visceral organs (such as the liver, pancreas, and intestines), are spindle-shaped, and are controlled involuntarily.
0 notes
Text
Teleman planeja nou EP, Sweet Morning (2021)
@teleman Gènere: #pop #electronic #songoftheday Teleman planeja nou EP, Sweet Morning (2021)
@teleman Gènere: #pop #electronic #songoftheday El proper 5 de novembre Teleman tenen previst, “Sweet Morning”. Un EP amb cinc pistes del que anem tastant mica en mica. Fa un dies van compartir Right As Rain, ara li arriba el torn a la cançó que titula el mini disc. Anticipen i ens fan intuir que serà un disc de pop electrònic, lúdic i espontani. Amb aquell aire jovial i pur, amb el que venen…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Link
The fruit fly has multiple taste organs throughout its body to detect chemicals known as tastants, that signal whether a food is palatable or harmful.
0 notes
Text
Amanida d’arròs
INGREDIENTS (2 persones): 125 gr. d’arròs (2 tassetes de café, aprox) 1 llauna de tonyina 1 tomàquet 2 ous durs 1 ceba tendra Una llauna d’olives Pebrot vermell PREPARACIÓ: Primer de tot fer coure l’arròs amb una mica de sal, una fulla de llorer i un all. Quan l’arròs estigui al punt…passats uns 15 minuts aproximadament (aneu-lo tastant), l’escorrem i reservem. Preparem ara els ingredients que…

View On WordPress
#AMANIDA#ARRÒS#CEBES TENDRES#CUINA#OLIVES#OUS#PEBROT#PEIX#PRIMERS PLATS#RECEPTA#TOMÀQUET#TONYINA#VERDURA
0 notes
Photo

#tastant una #novetat de @cervesespopaire #tarongina #fresca #suau #moltsuau #cítrica #poccarbonic #lleugera #diferent #original #distribució : @vinsvidart @cervezaartesana #cervesa #bière #birra #bier #orange #freshorange #goodbeer #ilivebeer #winelover #gastrobeer #gastronomicbeer #cervezaartesanal #cervesaartesana #blanes #cervesacatalana #catalanbeer #vullcervesa (at Catalonia, Spain)
#catalanbeer#blanes#distribució#poccarbonic#ilivebeer#goodbeer#freshorange#winelover#tarongina#tastant#cervezaartesanal#bière#novetat#fresca#diferent#cervesacatalana#moltsuau#cervesa#suau#orange#lleugera#cervesaartesana#birra#bier#gastronomicbeer#vullcervesa#cítrica#gastrobeer#original
0 notes
Text
greek forenames + the entire list of celtic deities from wikipedia + animals + tolkienesque forenames
Abroni Ackey Actha Adaildly Adowl Adraegia Adurinote Aeallydd Aelbál Aelphis Aergy Afromë Afsinhard Afsios Agalola Agamana Aiantons Aibor Aillatar Ainia Alamailia Albelman Albêth Aleaditba Alemes Aliatios Allistanis Almacal Ambabilve Amell Amhagin Amolos Anacha Anarwent Ancala Andil Angbe Anidine Aniensta Annorth Anothir Antis Antonaen Aphadda Aphantië Aphirdir Arach Aralinhwch Aranab Arane Aravon Arences Argalewt Arges Arinean Arkos Arpumars Arveru Aspith Assummos Atholek Athéod Augeid Aulibal Ausbarina Bacish Badova Bancateve Barumayion Bathe Baunt Beaternea Beflus Beriberia Bestis Betarla Binymos Blanar Boacona Boadoothia Bogele Bolama Bormil Bornvan Bratineits Breae Briancan Brinia Briter Britos Broth Budorm Buink Bëormeri Calaton Calina Camis Carko Casius Cassula Catrever Ceigh Celow Cenind Chloid Cháedber Cirean Clepolly Clidly Cneru Colvaster Conagod Conateldir Conistaius Consper Crapus Cratife Crilanters Crissher Crivin Curitaí Curitcre Cuslos Deadsae Dealear Deara Deigh Demina Demmir Demon Deninos Derenus Deril Desion Desus Deórin Dilos Diminon Dinwar Dionditer Diongroter Dores Dowen Doxianinas Dralia Druir Díris Efalver Effelwevor Ekada Eladoma Eleksia Elemork Elene Elenius Ellaug Elothear Emathimed Emmagunaen Emmar Emmiritat Encaturo Epalexia Equing Eratasp Erinflo Ernelcy Ertassiony Estas Estolach Etrenes Euced Eugdis Eugus Evdockano Evdon Evrar Farneva Femere Fergyrid's Ferios Fickas Filtel Fimbasta Finonus Fisharatis Flydel Folwë Foruit Fotir Frospiger Fréaw Fréino Fëantia Fílimon Fódlebia Gatrostas Gavaireven Gazed Germwhocka Giousky Glicall Gloceon Glúth Goona Gorgois Gother Gragarn Gregio Gréitypus Gríannwë Gwark Gwenuseus Gwynth Haidere Haine Haiteree Hanikates Hanth Harialai Hemer Henuela Himania Hipper Holgill Holveia Hopas Humhail Háman Iachar Ilach Ilina Iliven Imeecheam Inaerwyfir Inelper Ioadysard Iphey Iriën Irmatas Isades Itrin Ivern Jelcmara Kalle Knoce Konia Korix Kílie Laingelexi Lames Larfire Lassion Lazarneion Lazed Leethôr Leoders Leogs Lidwince Likadachan Likain Lityriele Llartolod Lugain Lugal Lumhandë Lídnos Lúinene Macit Mactepos Magod Maighenis Mainow Maket Mallimine Mandin Mantanis Manth Mapioul Maray Mareteus Maridenel Marie Medasios Mendor Merwelegod Mesagel Meted Micum Milis Mindris Miria Mithaissil Monirippe Morawn Morsid Motast Motinicar Mouls Muníricil Murenna Myrod Myton Mîmeiona Navicar Neleanceng Neophirë Niamir Nikinea Nimehaulis Nioni Nosus Nouorm Nóminos Ofornandor Olday Ophambinon Orabuterra Ourecia Palikolog Pamen Panac Paning Panish Panishimot Pann's Pannuil Paunus Pelios Peogyre Philly Pholi Phyennits Pirens Polad Polana Prondibûn Quanima Quinfionus Ragor Rebandug Rhovels Rithaleor Rodil Ruiron Rígamailf Rúmern Sadamar Sagiltios Sally Salruider Samans Samplen Saurus Savith Scecius Seinceme Serinaburt Sevatanes Shale Shalos Shelinains Sillity Simia Siona Siond Sitersho Skeret Sktria Slast Slorgala Sneli Somaila Spadhen Spigolis Spiobius Spybus Spyrespril Squagda Starodia Starë Statecuibh Stefor Stiougduce Stracil Streing Tasia Tasnaby Tastant Tecna Tedrand Thant Thanthear Tharmatos Thder Theancet Theary Thello Thene Therrod Thidle Thray Tiella Tleiania Toris Trebo Treria Tronysad Tuiline Tuseve Ucellanth Ufincaug Ulafth Ulasia Ulows Umbretaray Usbar Vaglard Valeman Vanastos Vasil Vedbuth Viaeo Vibareck Vidantypus Vinnond Vonus Vosmani Waturawas Whainn Whalbál Wharalara Whiende Whilia Whonstios Wiffrous Wilio Witavron Womil Yiaet Zachambin Zimeagia Zoinees Éowendre
#name stash#444names#444 names#dnd names#character names#random character names#markov namegen#markov name generation#markov#markov gen
0 notes
Text
Fruit fly offers lessons in good taste
The fruit fly has multiple taste organs throughout its body to detect chemicals, called tastants, that signal whether a food is palatable or harmful. It is still unclear, however, how individual neurons in each taste organ act to control feeding. To explore this question, a team used the fly pharynx as a model to study whether taste information regulates sugar and amino acid consumption at the cellular level. source https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2021/07/210727171549.htm
0 notes
Text
Fruit fly offers lessons in good taste
The fruit fly has multiple taste organs throughout its body to detect chemicals, called tastants, that signal whether a food is palatable or harmful. It is still unclear, however, how individual neurons in each taste organ act to control feeding. To explore this question, a team used the fly pharynx as a model to study whether taste information regulates sugar and amino acid consumption at the cellular level. from Nature's Incredible! https://ift.tt/2WtLXd2 via Nature & Insects
0 notes
Text
The sense of taste is called
The sense of taste is called
The sense of taste is called 21. The sense of taste is called A. olfaction. B. perception C. gustation D. tastant. E. mastication. 22. Palpebrae is another name for the A. eyes B. eyelids. C. eyebrows. D. eyelashes. E. conjunctiva. 23. The lacrimal glands when inflamed. A. cause a sty B. constantly produce a fluid called tears. C. are located in the superomedial corner of the orbit. D. are…

View On WordPress
0 notes