#studying andrew loomis
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

cooldown 20s photo study from pinterest
#original art#sketchbook#digital art#artists on tumblr#1920s#procreate#studying andrew loomis#if you haven’t read figure drawing for all it’s worth#and creative illustration by andrew loomis#pls do
10 notes
·
View notes
Text

Exchange #11: Rose's gift for Arturo!
#danganronpa despair time#drdt#drdt secret santa saga#rose lacroix#arturo giles#fanganronpa#i fucking hated studying the andrew loomis ideal male and female proportions in school#yeah yeah they made my anatomy better whatever#can we talk about how his “ideal female proportions” includes her WEARING THREE INCH HEELS?????#i hate beauty standards. anyways. i hope this makes sense to non art students#my art#comic#fanart
160 notes
·
View notes
Text
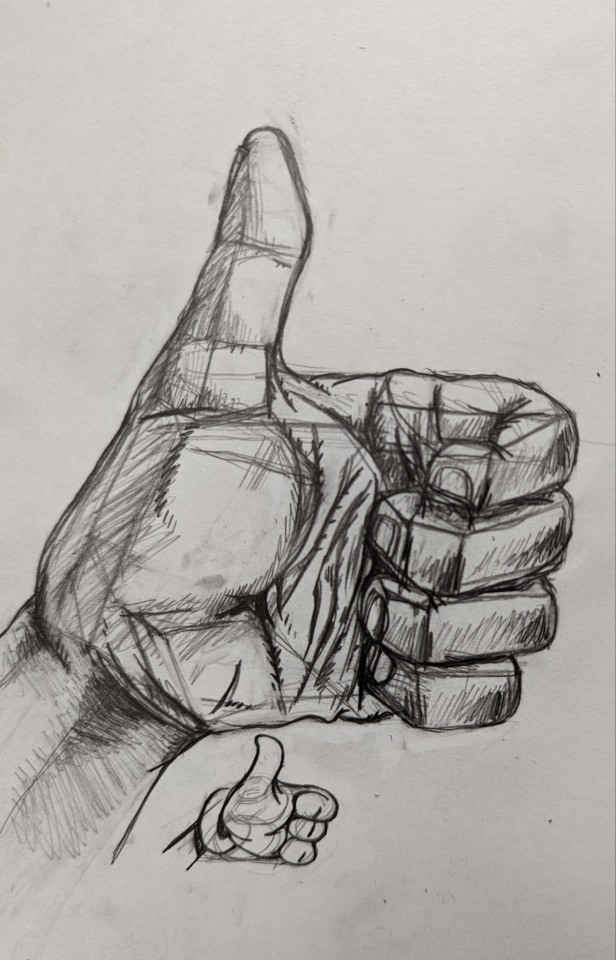
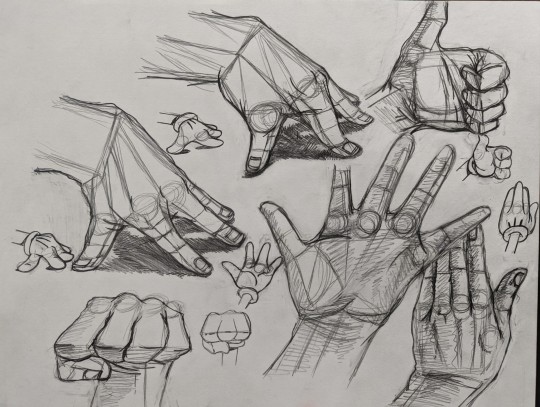

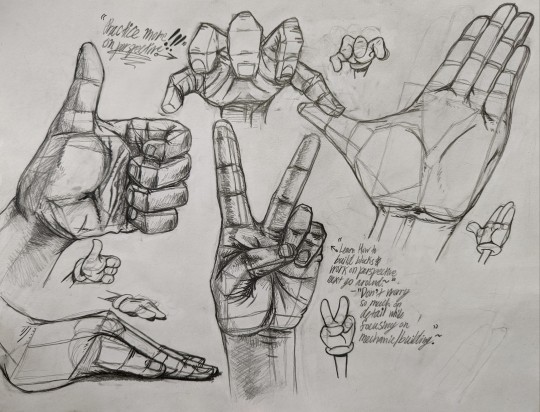
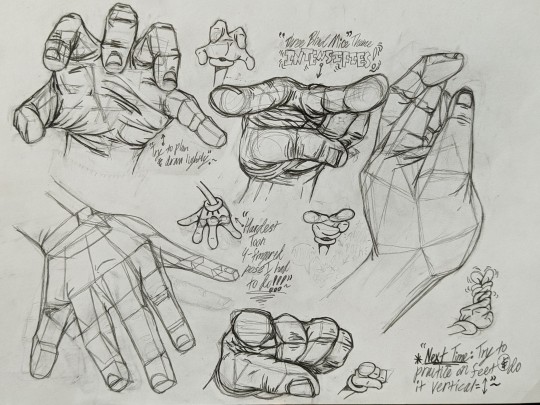
Some of my arm/hand anatomy practices from 2022. The Loomis Method has been a great way for me to practice a lot of my proportions and angles on my character designs. This was surprisingly the first time I ever practiced on doing realistic hands like this by photo reference along with studying my surroundings by breaking them down in their basic shapes. This also inspired me to draw a few Popeye forearm studies at the time.
#jay's art#jay's post#black and white#pencils#anatomy#loomis method#andrew loomis#practice#studies#sketches#pencil sketch#photo reference#realistic#angles#proportions#doodles#cartoon gloves#sketch base#realism#three dimensional
5 notes
·
View notes
Text

no Loomis? old study sheet
#digital art#digital illustration#art#bye#photoshop#illustration#study#doodles#anatomy#faces#heads#no bitches#artwork#artist#form#sketch#color#animated#andrew loomis
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
andrew loomis has me out here drawing rocks past my bedtime

#didnt wanna draw#but hadnt drawn in ten days#so i had to draw#decided to just look at my copy of Succesful Drawing by king Andrew Loomis#decided to do a light study of a rock#the rock turned out nice i think#so proud of my rock#look at my rock boy#going to bed now
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Successful Drawing by Andrew Loomis
"For those who have an understading of nature's laws, plus vision, the greatest teacher is nature itself. If the artist has the technique of depiciting the construction and contours of an object set in space, plus the knowledge of how light operates on the forms we consider basic, he has acquired the springboard to his own individual expression, which, after all, is of greater value than anything else" (p. 13)
Tip: Frame your object to decide which angle makes it look better.
"What a good drawing is?"
The five P's
Proportion
Placement
"When a viewoint has been selected and a placement decided upon, we start to draw" (p. 13)
Perspective
"Since perspective is the first main problem that arises, it is the first thing the artist should learn".
Planes
Light, halftone and shadow.
Pattern
"Placement relates to composition in terms of line, pattern relates to it in terms of tonal areas".
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Photo


Another trace and color for my art class - this time tracing Andrew Loomis and coloring on a monochromatic scale.

#andrew loomis#master copy#master study#my art#but yaknow - traced#but ya girl is coloring#and.....STRUGGLING AND DYING#I WANNA RENDER FACES GUD
1 note
·
View note
Note
What are the questions you hate??
Okay so I don’t really HATE anything (so far) but how bout an FAQ? There are some asks I’m kind of tired of answering lol. Such as;
• “FEED ME” For one thing, it’s not even an ask 💀 So I don’t love this energy, it’s -2 charm for me. Whilst I’m grateful that folks really like the art I share (like SUPER GRATEFUL!!) I am not particularly enchanted by a demanding aura
• “when is ____ coming out”? The answer is always “I don’t know” because I draw for FUN and I draw in my FREE TIME and that varies. So for the foreseeable future, unless I EXPLICITLY state otherwise, you can expect my next post to appear on your screen whenever I post it 🥰😘
• “what programs do you use”? I don’t have a problem AT ALL with inquiring minds, I just get this ask a lot and I’ve already answered it a few times (for the inquisitive minds, please consider checking the tag ‘answers’ on this blog to find information. I’ll tag this ‘faq’) Anyway, I use pens, paper, my iPad, Apple Pencil, and Procreate. I often use brush packs made by Shiyoon Kim and Kyle Webster. I find brush packs on the creative market as well. wanna learn Clip Studio Paint, but haven’t gotten to it.
• “advice on improving in drawing”? This is a beautiful question, and I’m happy there are people who want to improve their drawing skills! I am one of you. I frequently use “YouTube university” where I will find drawing focused channels that teach you this very thing. Andrew Loomis books on drawing are like textbooks that break down the fundamentals really effectively. Like any skill, you have to research, study, and practice. The more you do of each, the better you will get. I’m trying my best to improve and master the craft eventually. (A fool’s errand haha) anyway, have fun!
• “can I fandub this”? The answer is yes!! And I hope you have a lot of fun!!! Please credit me and no monetizing. 🥰 Also, please no posting on twitter (X) or meta (instagram, facebook), as I feel uncomfortable with the Gen AI social media platforms.
• “can I make fanfiction/fanart/cosplay based on your fanart?” FUCK YEAHHHHHH!!! I LOVE people being creative. We’re all having fun in this fandom and I think it makes life more exciting when we create! Same with fandubs, please credit and no monetizing 🥰
• “do you do commissions”? I am not accepting any right now, but that can change! Please trust that if/when I do start taking commissions, I will be letting y’all know!! And I really appreciate that you’d want to commission me 🥹♥️
• “in your comic, will ____ happen?” I’m not just gonna TELL you that lol. But clarifying what’s ALREADY happened is always a welcomed ask :)
I just want to thank everyone who tunes into this blog!! I really have a great time creating fanart, fanfiction, and comics and I’m VERY SHOCKED that what I’ve made has had the reception it has. It’s fun to be in this fandom with you all!
THANK YOU TO EVERYONE WHO SENDS ME SWEET ENCOURAGING MESSAGES ILYYY 🥹💖💘💞💓💝
750 notes
·
View notes
Text

medic , study of a loomis painting shoutout andrew loomis
283 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hi, I found your work on Twitter last year and I really love and look up to your art. If you have the time, I wanted to as if there are there any study topics, artists or techniques that have significantly influenced you :')
I'm at a bit of a complete loss on what to study presently so I thought I'd ask my favorite artists, thank you for reading and I completely understand if this is too open ended a question
Thank you!
This isn't the first time I have been asked this question and I suspect this won't be the last so I'll just lay everything out here. Go to a cafe or get a blanket or something because this will not be a short read:
Foundational:
Anatomy: A lot of my foundational anatomy and clothing illustration knowledge was gained from taking classes and doing observational drawing. Because of this, I'm not going to have the best book recommendations but top 2 books I can recommend for getting Started started are Andrew Loomis or RockHe Kim's books on anatomy (huge asterisk here: they're good at teaching you Basics basics like muscle groups and turning forms and extremely general proportions but will not help that much with making your figure drawings less stiff or how to draw fat or especially in the latter's case how to draw women not built like stick bug anime girls but uh I heard the Morpho books are pretty good. genuinely everything I know about drawing fat is from observational drawing/studies because at some point I got sick of my school for only hiring skinny models in their 20s-30s). I have some diagrams drawn by my friend who studied the hell out of these guys below:

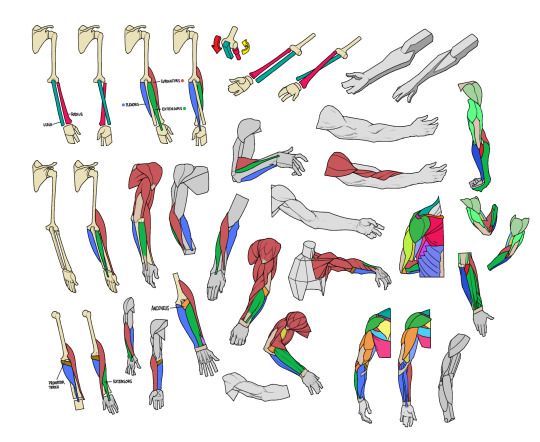


Clothing: I don't know any books that can really help on this front I apologize if I find any I'll update this post but pretty much all of my knowledge on drawing clothes boils down to the following rules: Where are the tension points, how stiff or soft is the textile, how is the form underneath the section of clothing behaving, and don't make even spaces between fold groups
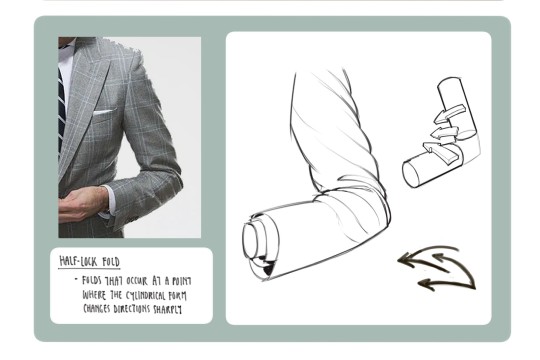
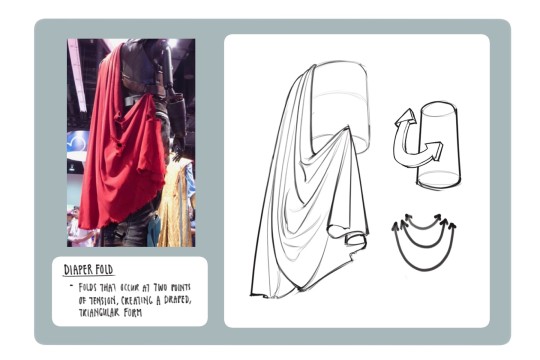

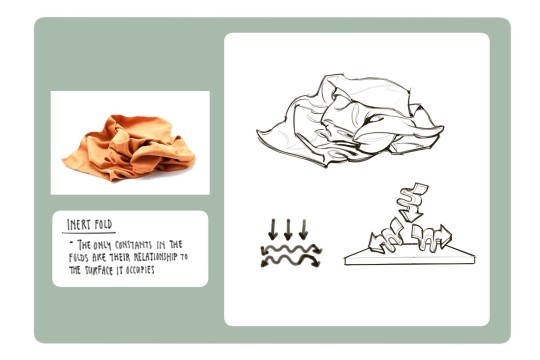
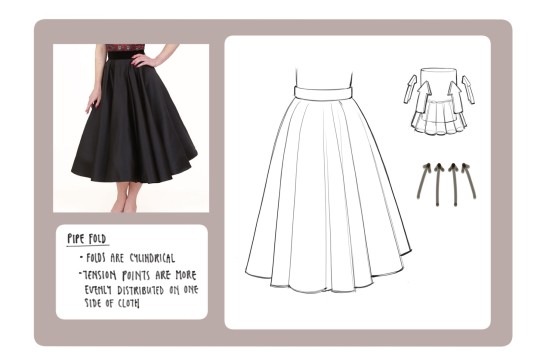
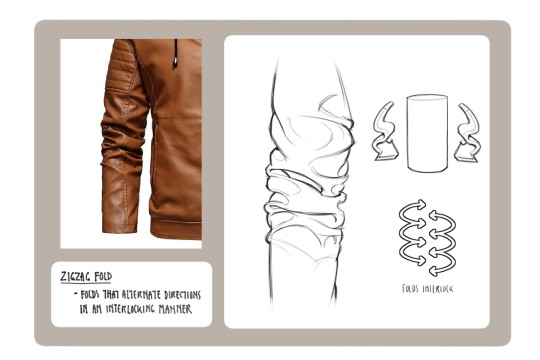
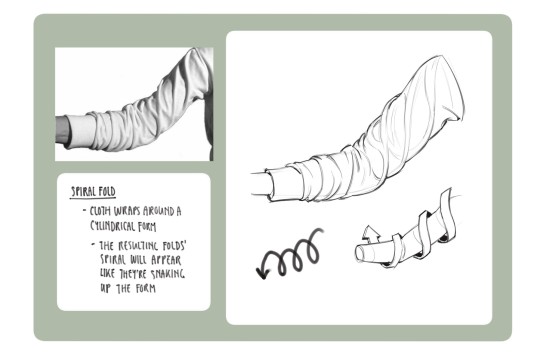
All of this is kind of moot though if it isn't applied through study or observational drawing though
Design:
I have to be really careful here because I don't want to deal in absolutes, the only absolute I'm confident espousing is that anyone who tells you there is only a small selection of methods you should follow to execute a specific type of design are objectively incorrect and just haven't figured out alternative if not more effective design solutions to a common problem. The only real Worst Thing I think you could do as a designer is create a pinterest mannequin devoid of a story, disconnected from its context in the world, and lacking in a clear purpose/personality but this too could be easily be disputed if maximising a character’s aesthetic appeal serves a purpose in its context, and my opposition to this design approach is my personal bias as a character designer for entertainment where emphasizing a character’s function and their relationship to said function is usually the goal
I think the 5 best pieces of advice I've ever received when it comes to designing characters are the following:
Try and follow the rule of thirds/general gestalt design principles of contrast
Always consider what it is you're trying to communicate with the character
Create believable transitions and reinforcements between points of interest
(Entertainment related) KISS principle/Keep It Simple, Stupid is your friend, the way a character wears or wields what they wear or wield will communicate their role in the world (who are they?), their relationship to their role (do they like their job? are they good at it? are they a part of an organization with the means to provide them things to perform their role more effectively?) effectively enough. Excessive information that bloats and conflicts with the communication objective weakens design (example: My favourite childhood toy for years was a pokemon plushie. Would I as a stay at home digital artist be wearing it as a keychain on my crusty paint stained polyester pajama pants when I'm at my desk working my job? is wearing it relevant to my character as a person who both no longer is invested in pokemon and is in this context focused entirely on comfort and doing my job? (no)). I think Elden Ring is an excellent example of a game that has visually complex designs but pretty expedient storytelling with its characters for worldbuilding
Study things that aren't just character design, to borrow from Lynn Yaeger borrowing from Sally Singer "If you're interested in fashion learn everything except fashion... Politics, art, painting- anything except fashion". Because people in different disciplines who work with different mediums or fields of study approach problems in different angles you may not have considered which can help give new ideas + often times the stuff you like was inspired by stuff that isn't at all what you would expect or enjoy yourself (To pull from a very popular example, Arcane is a League of Legends joint which was highly influenced by Warcraft which was highly influenced by Warhammer which was basically a giant response to western pop culture of the 1960s and the history of European warfare something something coconut tree).
Character design is kind of a hard thing to Get Good at considering how much of the actual process is super psychological/not bound by a *ton* of absolutes and has to account for medium and function (you kind of just have to have The Sauce) so I don't recommend Just studying independently only (possible, just very difficult). If you can and are interested in learning more about the specifics take some classes taught by people whose styles you fw who both know what they're doing and are good at explaining their process. For design for entertainment you can always check out Concept Design Academy or The Workshop Academy and see who's teaching there
As far as artist inspirations are concerned I think looking up the artists who worked on projects you like are a good starting point to figure out how you want to stylize. Going off of that at least currently my favourite designers/illustrators for entertainment with The Sauce are probably Evening Monteiro, Sergey Kolesov, Mindy Lee, Tonci Zonjic, Sasha Tudvaseva, Claire Hummel, and Yoshitaka Amano
My favourite book currently for tackling character design at least from a narrative consideration is probably Talking Threads: Costume Design for Entertainment Art (one of the authors is my friend and an excellent teacher!) and a lot of the stuff they espouse really helps to take into consideration individual and external factors when designing a character/how they can be used as vehicles for both individual storytelling and worldbuilding, gigantic reference point for my most recent casual project
Besides that the only other way I can really recommend studying character design is to just look at art, history, architecture, nature (pretty much Everything) and think about how ideas and concepts from those things can be applied to or communicated through a design or figure out what it was about a design or designs you like made it appealing
uhh tldr this is just how i as one among millions of artists got to where i am today as of January 16th 2025 my word is not gospel the advice I espoused here may very well spell my downfall tomorrow
133 notes
·
View notes
Text
i often get asked how to draw fat bodies, and my advice is to start by studying volumes and forms. before tackling full bodies, it is important to build a strong foundation. take a 3d shape (cube, sphere, whatever) and use it to learn how weight sits, moves, and interacts with gravity. in animation, we used the ball and sack bag test to study volume and weight, which also introduced principles like squash and stretch, spacing, and timing. as you get comfortable with these concepts, you can start applying them to drawing bodies. and as you get even more comfortable, you can begin to exaggerate your drawings.


even if you never plan to animate, studying cartooning can teach you a lot about volume, movement, and weight. all that good stuff.


there are so many great art books out there too. morpho by michel lauricella is a popular recommendation and a great reference to have on hand. i also love the animator's survival kit by richard williams (MY GOAT), anything by andrew loomis (THE GOAT), FORCE: dynamic life drawing by michael d. mattesi, and atlas of human anatomy for the artist by stephen rogers peck. there are plenty more, but these are the ones that come to mind.
i apply the same idea when drawing hard surfaces like vehicles, armor, and mecha. understanding perspective and form is important. i break down complex shapes into simpler ones, like cubes, cuboids, or cylinders. this makes it easier to visualize how they sit in space and how light interacts with them. studying the fundamentals of form, volume, and weight applies to almost anything you draw.
AND MOST IMPORTANTLY....get really really really really really super into golden kamuy and disco elysium. you will not regret it. here are my befores and afters...






#ive gotten this ask so many times so i will refer to ppl to this in the future haha#may make another post thats more thought out tho but this is just for now#i am a lil rusty and i need to go attend a life drawing class again someday lol#and if u just wanna jump right into drawing bodies go ahead#but try to understand volume and forms when u do#personally i like understanding how things work it makes learning easier
34 notes
·
View notes
Text
Successful Drawing by Andrew Loomis
"Drawing is vision on paper. More than that, it is individual vision, tied up with individual perception, interest, observation, character, philosophy, and a host of other qualities all coming from one source. It cannot, and to be successful should not, be anything else" (p. 11).
A successful drawing is a drawing that shows a vision.
Intelligent perception + emotions
"When drawing is convincing to the intelligent perception of the spectator because of its rightness of from, texture, space, and lighting, and at the same time appeals to hisemotions, the artist can depend upon a favorable response" (p. 12).
Why my art does not appeals to the public? And more than that, why my art does not appeal to me? At first I thought it was a technique problem, but I look at the drawings I made when I was child or as a teenager and they seem so full of life and joy that sometimes I fell I grow up broken and that's why my art is broken. I've learned a lot over the past years and still feel like I've lost something. I want it back so desperately that sometimes I cry thinking about it. And I can't even tell what I lost.
What emotions I want to express with my art?
Love, deeply love and passion. Warmness as a hug. Sexyness and fun. Femininity. Comfort. Desire of have it or live on it. Sweetness. Cuteness.

How to do that?
I'm trying to discover!!! (I'm full of hope)
0 notes
Note
It's may be an odd question but do you think you could maybe post a couple tips of anatomy and/or proportion that helped you sometime? I notice I have a hard time learning from videos or guides, but sometimes when I learn on my own or hear someone else's personal experience it just clicks and it's nice.
I know this may sound strange, but for me it was a class I took with Matt Faulkner, who had a very refreshing approach to mark making and drawing from life. We did have a live model, and drawing people from life teaches you two important things that books cannot: textbook anatomy is idealized, not everybody will look like that and foreshortening and perspective are things that are easier to see in person (at least, for me they were).
As you draw things like that over and over, you will build a mental library that will help you draw those tougher perspectives from imagination. I still use a reference, because the human body can bend and distort in a lot of ways and I am nowhere near having all of that memorized, and WE DON’T HAVE TO! If it gets committed to memory, great! But artists should never feel shame from using a reference because that is how we learn and that is how we improve. Even professionals use a reference.
The mark making that Matt taught us was a little different than some of the other classes I had been through in the past. I typically would draw a human with basic shapes and a “wire-frame” skeleton for my foundational rough sketch, but Matt would have us start drawing our figures with different lines. Contour lines, is just drawing the outside of what you’re observing, while periodically flashing your eyes at the paper. Blind contour would have us looking only at our subject and drawing what we were seeing without ever picking up the pencil (some of these actually turn out pretty cool).
Volumetric drawing was the one that I had never come across before. Matt uses a lot of crosshatching and volume lines in his work. See the below example:

The way this applies to anatomy is that his way of volumetric drawing is helpful in finding the space that your figure takes up. Sometimes Matt would have us draw our figure with ONLY volumetric lines. It would look like a tornado person, but this practice wasn’t to make something visually appealing, it was to help us train our brain and our eyes to see the volume. In that volumetric study we would be wrapping lines in a width and curvature that followed the subject. Here is a visual example of a volumetric drawing by Monika Zagrobelna that shows what I mean:
The volumetric drawing helps to grasp how much space something takes up, whereas the wire-frame doesn’t really convey that kind of information. A lot of people reference the Andrew Loomis books and Figure Drawing For All It’s Worth [ISBN: 978-0857680983] is a good resource to learn from. But Loomis does idealize the standard figures in his works and books. I am not saying don’t draw like him! There is nothing wrong with his style! Just don’t fall into the assumption that every body type will align exactly with the proportions and measurements that he covers. For example, he usually has a standard height that male and female figures are drawn at and certain points where knees are expected to reach and other body part milestones:
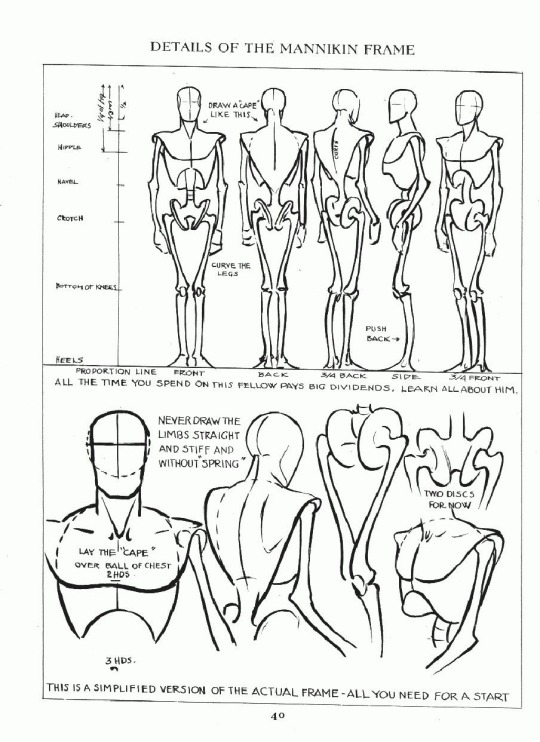
It is a guideline, and it is useful, but I found that the best exercise that you can do is to do a study on separate pages. No one taught me this, I just did it out of curiosity to see how it would go. Set one aside for male and one for female. First, draw your standard Loomis figure, then get five other male/female reference photos (or drawn from life if you can) of people with different body types. Try drawing them from observation and see how much of the Loomis concept applies to them. You’ll find that you can bend a lot of the Loomis ideas to fit, but you have to throw out some things entirely in order to accurately portray your subject (like the number of heads tall something has to be, or posture, for example).
Hopefully, despite that being a little long-winded of me, you found this experience helpful? Everyone learns differently, so I feel your struggle. I am a big visual learner and need to see what is happening with something to understand it. I also learn best by struggling. So what were the “aha” moments for me, may not necessarily work for another, but it is here if you can find any value or use in it.
#art#anatomy#perspective#draw from life#use a reference#Matt Faulkner#Andrew Loomis#Monika Zagrobelna#volumetric lines#drawing volumetrically#volumetric drawing#figure drawing#art advice#art help#art asks
41 notes
·
View notes
Note
Do you have any advice on how to get over lack of skill? I want to do the Astarion Lestate trend but I don't think my skills are ready for it. I have references pictures of Astarion pulled up when I'm working, and even have the game launched so I can turn him if I need to (mostly for the attempts I did at his hair) but everytime I tweaked something or started over nothing looked right. I keep getting frustrated 😭
Hi anon- Sorry this took me a while to get to, i hope you and others can still find this useful! While the basic advise to get over 'lack of skill' is PRACTICE, PRACTICE, PRACTICE! i hope this will help you knowig where to get started with that!
I'm going to put my teacher pants back on, this might be a bit long so buckle up- I'll go over a few areas:
Primitive Shapes
How to Use References
Delete your work (hear me out)
--------------------------------------
Primitive Shapes:
This is your foundation. Everything starts with this, and while you may find it boring to think of your art in terms of cubes and spheres- i kid you not it will help elevate your work.
If/when you are stuggling to draw a complicated pose, or a specific perspective, refering back to the form in these basic shapes can really help to simplify your process and help you problem solve.
A chill/silly watch for a more in depth discussion on what i mean / how this can help - Give Pikat's 'Draw boxes (correctly) to improve your art' a watch. They also mention this in the video but @/Uncomfortable on youtube also has some great fundermental videos.
-------------------------------------
How to use references.
Okay so references are great 10/10 very useful. But, unless you know WHAT to study from a reference, they can sometimes fall flat of their usefullness.
Anatomy studies are something a lot of us will be recommended as artists, but actually knowing what to pay attention to can boost your confidence in your work. Start with a goal, what do you want to get out of this sketch session? Do you want to get better at understanding the 3D form of a specific part of anatomy? Better at poses? Try to narrow down your learning each session to make it less overwhelming.
In this i'll focus on understanding the form so, lets start with a reference. Linking back to Primitives again, start off by braking down your anatomy into forms. Sketching over the top of your references is totally fine. But make sure you are doing so critically, otherwise it may look like a flat/unnatural trace and you're not really learning from it. Via the first sketch you can see where the primitive shapes fall on the body - think of it like a ball-jointed-doll, hips, knees, shoulders ect are ball socketed whereas arms, legs ect can be made up of tubes. (See the first image, when sketching your tubes, sketch your contour lines too- this can help determind how clothing / hair will fall over the body, and can help you understand the 3D Form.)
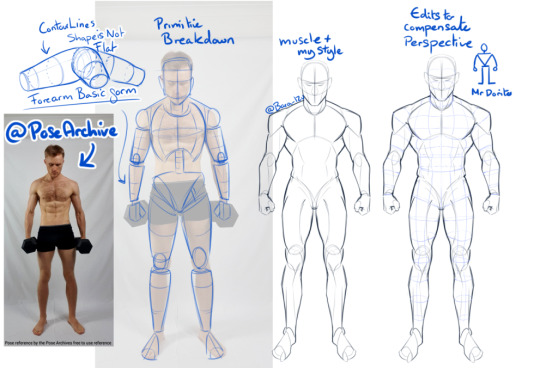
A BIG IMPORTANT SIDE NOTE - When using photo references, do be very aware that they may be distorted due to the height of the camera, or camera focal length - (you can see in my sketch i had to edit the torso and head because the reference was a little top heavy)
A few artists/books for some extra reading / reference : - Andrew Loomis (OG for body proportions, books are a little outdated but fundermentals are still useful), - Tenten云画画 (his stylised anatomy breakdowns are very interesting to me) - Anatomy Essentials (I've had this book for years, it covers lots of areas, is a bit complex though, i myself should reread it again 😅
Also, if you can't find a reference for a specific pose, don't be afraid to use 3D programs! Anatomy 360, DesignDoll, Clip Studio, Magic Poser - all nifty options~
SO taking when we've learnt from the primitive forms, you can now try applying that to the Lestrat Picture. (which, granted is a complicated pose, as it also has forshortening and an odd top down perspetive of the bottom character- so don't panic if you don't get it the first time!)
-------------------------------------
Final points- Delete your art (hear me out)
What i mean by this is, sometimes reworking the same face over and over again can bog your down. It can make it very difficult to actually see whats wrong. So, get rid of it and start again. (hide the layer/use a different piece of paper, please don't actually bin it (yet))
Next, redraw it. Use what you've learned the first time, and redraw it from scratch. (in this case, that might be just specifically the head, or the hair, or the eyes ect - you don't have to bin the whole thing, but sometimes it can really help give you a new perspective)
Once you've done this, unhide your original, compare, this may help you understand what you were doing wrong the first time. Or if there are areas of one that you like- its an opportunity to combine them as you see fit! :)
On a side note for Astarion's Hair, the lovely @mistercrowbar actually posted a breakdown yesterday! (i use p much the same method so-)
I HOPE this was of some use- do feel free to ask any questions if you've got them! i'll try to answer in a more timely manner next time 😅
95 notes
·
View notes
Text
art credit from left to right up and down btw :3
Tristan and Iseult by August Spiess
Study for Butterfly Couple by Joseph Christian Leyendecker
The Kiss by Francesco Hayez
The Kiss by Silvio Allason
Adoration by Ste Phan Sinding
The Meeting on the Turret Stairs by Frederic William Burton
The Piano Man by Robert Mcginnis
Le Vertige by Hubert-Denis Etcheverry
The Wedding by Andrew Loomis
#lisa frankenstein#lisa swallows#the creature#lisa x creature#lisa x the creature#the creature lisa frankenstein#imsillyimsillyimsillyimsillyimsillyimsillyimsillyimsilly#genuinely tweaking over this movie#over them#bruh i FUCKING LOVE THEM#eveything is a lisa frankenstein refrence at this point tbh#yknow how eveything is a jojo reference#yeah that’s how i feel about this movie#anyways they fuck like rabbi- *gunshot*#WHO THE FUCK SAID THAT ⁉️⁉️⁉️#(i’m right tho)#i use the word “semi-famous very loosely cause some of these are pics i thought were cute from pinterest sorry not sorry xoxo
51 notes
·
View notes