#regional administrative shifts
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Jharkhand Government Reshuffles Administrative Positions
7 state service officers transferred ahead of elections The Jharkhand government has announced a significant administrative reshuffle, transferring seven officers of the Jharkhand State Service to new positions. RANCHI – The Revenue, Registration, and Land Reforms Department of Jharkhand has issued transfer orders for seven critical administrative officers throughout the state. As part of the…
#administrative streamlining#मुख्य#Featured#Jharkhand administrative reshuffle#Jharkhand civil service#Jharkhand government reorganization#Jharkhand zonal officers#pre-election administrative changes#regional administrative shifts#Revenue and Land Reforms Department#state bureaucracy changes#state service officer transfers
0 notes
Text
Nearly a dozen children were working shifts cleaning meat processing equipment used at an Iowa pork plant’s so-called kill floor over a four-year period, the US Department of Labor announced.
Eleven children were using corrosive chemicals to clean as well as perilous “head splitters, jaw pullers, bandsaws, neck clippers and other equipment” at a Seaboard Triumph Foods pork processing plant in Sioux City, according to officials. This is the second time federal investigators have found children working at that particular Sioux City meat processing plant.
The most recent settlement comes with Qvest LLC, an Oklahoma-based cleaning company hired by Seaboard from 2019 to 2023. The company was fined $171,919 for violating federal law.
In September 2023, Seaboard hired a new cleaning contractor: Fayette Janitorial Services, headquartered in Tennessee. Investigators found Fayette hired 24 children to work overnight shifts – some as young as 13 and carrying glittery school backpacks – including some of the same minors who were employed by Qvest, the previous cleaning company. In May, Fayette was fined $649,304.
“These findings illustrate Seaboard Triumph Foods’ history of children working illegally in their Sioux City facility since at least September 2019,” said wage and hour midwest regional administrator Michael Lazzeri. “Despite changing sanitation contractors, children continued to work in dangerous occupations at this facility.”
The federal investigation comes after a 2023 New York Times report on migrant child exploitation, in which the paper documented children working dangerous jobs and overnight hours.
Children who arrive at the US’s southern border alone often stay in the country for years before their cases are adjudicated. While they wait, they live with sponsors. As of 2023, only one-third of migrant children went to live with their parents, a sea change from a decade ago. That can leave children vulnerable to exploitation or trafficking.
#oh upton sinclair we’re really in it still#the slaughterhouse/meatpacking industry continues to be the actual devil#food systems#immigration#lines on a map#labor rights#news#my posts
783 notes
·
View notes
Text

[Newly Declassified Document from U.S. Army Medical Corps Archives, 1944 Subject: Medical Assessment Report — Pvt. Andrew “Drew” Matthews (Service No. 5XXXX) Date: May 10, 1944 Location: Field Hospital, Western Front
Background & Context
Private Andrew “Drew” Matthews, 18, is currently serving overseas under the U.S. Army. Initial enlistment was in late 1943. He has been under periodic medical review following the discovery of an unexpected pregnancy while stationed in-theater. According to the most recent examinations, Pvt. Matthews is now at approximately seven months gestation. This update provides a detailed assessment of his physical condition, with particular focus on rectal and hip adaptations pertinent to male pregnancy.
Current Medical Evaluation
General Physical Status
Vital Signs:
Blood Pressure: 115/76 (stable)
Pulse: 84 BPM (slightly elevated but within normal pregnancy parameters)
Respiration: 18 breaths per minute
Weight Gain: 18 pounds above initial enlistment baseline (notable increase from previous month, consistent with advancing gestation).
Gestational Progress
Estimated 28 weeks (7 months). The uterine and lower abdominal growth is consistent with typical third-trimester developments in male pregnancy.
Fetal heart tones remain strong on auscultation (~146 BPM). Fetal movements reported to be frequent, especially in the evenings.
Rectal Examination
Pvt. Matthews reports periodic pressure and heaviness in the rectal canal, especially when standing or marching for extended periods.
On gentle palpation, the rectum shows increased vascularity and mild swelling, which is not unusual in the late stages of male pregnancy. However, care must be taken to prevent or manage potential hemorrhoids, given added strain in this region.
The anal sphincter demonstrates normal tone, though Pvt. Matthews describes occasional episodes of discomfort—likely linked to fetal positioning and the downward pressure exerted by the growing child.
Hip and Pelvic Girdle Assessment
Complaints of hip soreness and lower back ache have intensified since last examination (one month prior). This is attributed to gradual pelvic widening and the shifting center of gravity.
Physical palpation indicates mild ligament laxity around the hip joints—a natural adaptation in male pregnancies as the body prepares for labor.
Pvt. Matthews experiences discomfort when required to traverse uneven terrain or stand in formation for extended durations. He reports temporary relief with short seated rests and mild stretches.
Nutritional and Environmental Factors
Wartime rationing complicates access to fresh produce, but additional calorie allowances have been arranged.
Daily supplements (when available) include powdered milk, iron tablets, and occasionally vitamin-fortified biscuits. Pvt. Matthews has been instructed to remain vigilant about hydration, as dehydration can exacerbate swelling and discomfort.
Duty Restrictions and Lifestyle
Currently assigned to administrative duties at a rear-echelon facility to minimize prolonged standing and heavy lifting.
Recommended low-impact movements: occasional short walks, gentle pelvic exercises, and if feasible, daily check-ins with medical staff for observation.
Sleep remains inconsistent due to frequent nighttime fetal activity and shared barracks noise, though Pvt. Matthews states he manages intermittent rest as best he can.
Psychological Outlook
Pvt. Matthews displays a mix of resolve and concern. He expresses worry about the stigma associated with his pregnancy and the uncertainty of how the child will be cared for if deployment conditions worsen.
Reports a sense of relief in having official medical oversight. Limited but consistent morale support from select squadmates and some discreet chaplain consultations appear beneficial.
Recommendations
Rectal & Hip Care
Moderate Rest: Schedule routine seated breaks to alleviate rectal pressure.
Support Garments: A supportive belt or band around the lower abdomen may reduce strain on hips and rectal canal.
Warm Compresses: Applied to the lower back and hips can mitigate soreness; for rectal discomfort, brief sitz baths or mild topical ointments (when resources permit).
Continued Nutritional Support
Maintain priority rations and supplements. Encourage iron- and protein-rich foods to prevent anemia and support fetal growth.
Ensure hydration, especially given increased metabolic demands at seven months.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Regular monthly checks, or sooner if rectal swelling increases or if new symptoms arise (e.g., significant bleeding, severe pelvic pain).
Coordinate with field hospital staff to prepare for potential labor or complications, given the unusual deployment environment.
Emotional and Social Support
Where possible, arrange for discreet counseling. Encourage Pvt. Matthews to continue confiding in chaplain or trusted medical personnel, minimizing isolation.
If feasible, discuss postpartum logistics with commanding officers to ensure the newborn’s welfare and Pvt. Matthews’s postpartum recovery.
Conclusion
At seven months pregnant, Pvt. Matthews remains in stable condition with no immediate red flags detected aside from typical third-trimester challenges. Symptoms such as rectal heaviness, hip soreness, and general fatigue reflect the normal physiological adaptations of late-stage male pregnancy. Ongoing support, both medical and logistical, will be crucial to ensure a safe outcome for both father and child as wartime circumstances persist.
Signed,
Capt. Robert H. Nolan, M.D.
U.S. Army Medical Corps, Western Front
211 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Spanish Meteorological Agency had warned of the severity of this DANA (isolated high-altitude depression) days in advance, yet the government of Valencia–led by Mazón from the Popular Party (PP), which allied with the far-right VOX in the last election–did not raise the alert level or inform residents of the impending danger until it was too late. These climate change-denier parties made dismantling the Valencian Emergency Unit one of their first actions in power, scrapping a unit established by the previous left-wing government to coordinate emergency responses. Such a response could have saved hundreds of lives, as only after five days were fire brigades from other parts of Spain finally allowed to respond, despite being ready from day one, some stationed only a couple of hours away. The staggering dysfunction was made clear when a team of French firefighters, arriving voluntarily and without permission on Saturday, discovered they were the first responders in the area. Employees who received warnings from family and friends about river overflows upstream were not allowed to leave work. Consequently, when the worst of the flood came, countless people were trapped in their cars on the way home, many of them returning from industrial parks on Valencia’s working-class outskirts, caught at the end of their full shifts. Those workers now still lie trapped in their cars, waiting for rescue–if they survived–or decomposing. Meanwhile, the areas hardest hit by the torrent are mostly working-class neighborhoods, built on floodplains near the river’s overflow zone. Construction was permitted there for developers–many friendly with politicians–in a region known for government corruption, particularly under the right-wing Popular Party’s administrations between 1995-2015.
[...]
Capitalist employers put profits before their workers’ lives. Testimonies abound of employees spending the night at work, unable to leave until it was too late. A video has gone viral showing a Mercadona supermarket lorry, owned by a tycoon notorious for ruthless business practices, stuck in the floodwaters–though the servile Spanish media pixelated the logo to protect its reputation. The same employer, while making a show of charitable donations for the flood-affected, has forced affected employees back to work since the very next day. The underground car park of the Bonaire shopping center, one of Spain’s largest, is feared to hold many bodies, as the center stayed open despite the red alert from the Meteorology Service. Public institutions like Valencia’s University sent staff and students home hours before, as did the Valencia government, which sent its workers home because of “a high risk for the population”.
4 November 2024
177 notes
·
View notes
Text
Biden's visit has concluded. Israel has spent his entire visit trying to muddy the waters of what happened to Al Ahli Hospital and despite their cartoonish efforts, it hasn't worked
The Global South and especially West Asia know who is responsible for the bombing and no amount of AI voice recordings of 'Hamas operatives' can change that.
Israel war crimes continues to backfire on them even in America
Biden backing Israel has had an impact on America's image. Here's a Wall Street Journal article warning that America's continued support is turning countries towards Russia and China which is code for turning countries against America
An EU official said that the EU will pay a heavy price in the Global South for its continued, unabashed support for Israel
There's also speculation that the Biden administration knew about the bombing before it happened.
Countries that were/are allied with Israel continue to distance themselves from Israel like Russia. The reason I keep highlighting Russia is because the West has been running out of ammunition due to the Russia-Ukraine war and that includes Israel which is rumoured to have sent 80-90% of its ammunition to Ukraine. If this conflict lasts a long time, Israel will need to buy weapons and ammunition and Russia would be one of the countries they would turn to (same with China)
So, where are we in terms of the conflict? After days of waffling over a ground operation in Gaza, Israel postponed it until some time after Biden's visit and now we're back here again
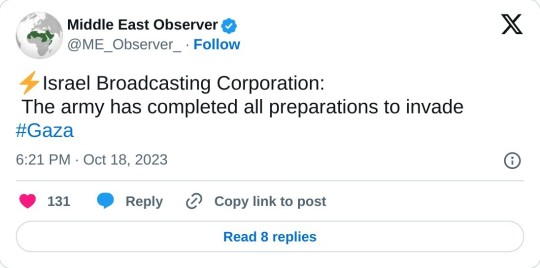

Now I'm no military expert but constantly going back and forth on whether or not you'll invade Gaza is bound to do damage to your troops' morale. No wonder they're dealing with mass desertions while their citizens demonstrate on the streets. The Israeli leadership has no plan besides bombing Gaza.

I've seen people on twitter say that the hospital bombing was done deliberately to normalise IDF soldiers to mass civilian deaths in places like hospitals, schools, places of worship, etc. I don't know if I believe that - I think they wanted to push Iran and Hezbollah's buttons before hiding behind Biden. I don't think these people are thinking strategically.
As far as the possibility of regional war is concerned, all indicators show that the West preparing for the war to escalate
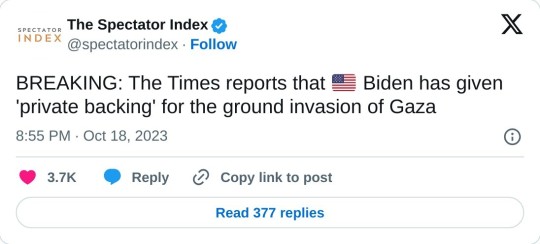

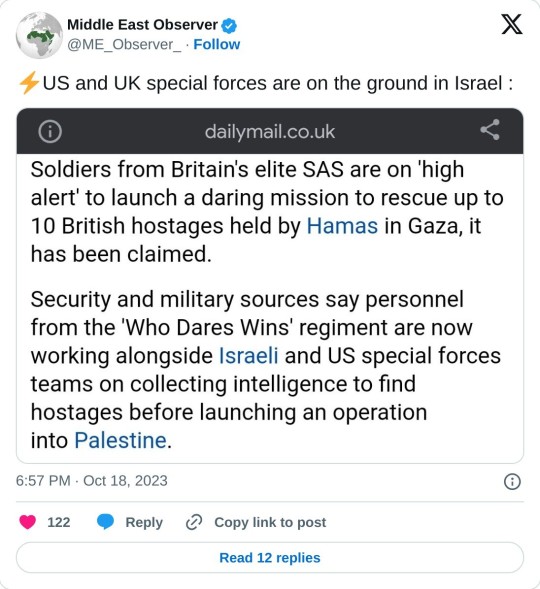
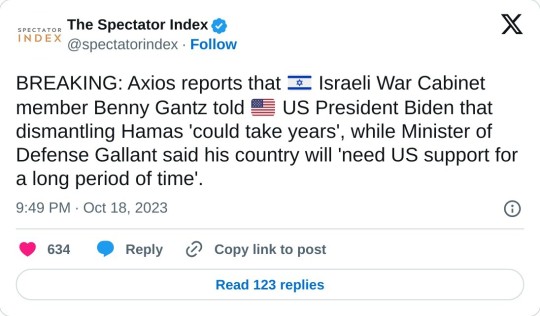
Seems to me the Israel has seen what Ukraine has received in just a year and a half of war. They're done receiving a paltry 3.8 billion every year and now prepared to drag out the conflict and I can't say I blame with Biden proposing a 100 billion package for both Ukraine and Israel. This will stretch America too thin as far as funding in concerned. Cracks are already showing
There are parts of the US government that is unhappy that the Ukraine war is losing attention. During the Ukraine war, you had parts of the government that wanted focus to shift from Russia to China. Because of that, the US government has spent the past year alternating between hostility to Russia and threatening to go to war with China over Taiwan. When Niger expelled France from within its borders, America was preparing to join that conflict until Mali and Burkina Faso declared they would fight with Niger. Now they're entering a third front in West Asia. In short, the mighty empire is expending a lot of resources right now and it is not the threat it was when it invaded Iraq and Afghanistan in the early 2000s.
At any rate, the ground invasion of Gaza won't go the way Israel and America hopes it will
The coalition of Palestinian resistance fighters are still patiently waiting for the IDF to come meet them. Their allies aren't backing down either

The reason I keep making these posts is to remind people that, while the genocide of the people of Gaza is horrifying, the war for the liberation of Palestine has not yet been lost.
Do not lose hope. From the river to sea, Palestine WILL be free
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
WORKMAN COMESENTATION CLAIM
DRC, Administration & Management Office, Human Resources Division
To: DRC Claims Review Board
From: Employee ID [REDACTED]
Date: [REDACTED]
Subject: Rise in Compound Work Injury Claims
I. Claim Summary
Mr. [REDACTED] (Employee ID# HS-137-611), assigned to the Gestational Support Command, has submitted a claim for work-related injuries sustained during routine surrogate handling duties at Paternity Compound 137. The claim outlines physical injuries attributed to interactions with surrogates during a personal monitoring session, specifically citing muscular strain, joint stress, and abrasions incurred as part of the surrogate gratification procedures.
II. Incident Description
At 13:20 on [REDACTED], Employee HS-137-611 was assigned to conduct a physical engagement of Surrogate S137-614-P, who was at +19 days gestation with sexdecuplets (16). The surrogate’s condition was flagged as an unusually high degree of prenatal nymphomania, a behavioral side effect frequently observed in most surrogates. The evaluation was intended to reduce the surrogate’s discomfort and agitated mood to return to behavioral stability.
Upon initiation of the session, the surrogate began exhibiting heightened physical restlessness and compulsive behaviors consistent with gestational hormonal surges. Employee HS-137-611 attempted to follow established engagement protocols, which required direct physical insertion to stabilize the surrogate and manage their urges. However, the surrogate’s extreme abdominal size and mobility issues created an unpredictable environment, leading to a series of complications for the employee.
III. Details of Injuries Sustained
Lower Back Strain: The surrogate's advanced abdominal distension significantly limited the employee’s ability to maintain proper ergonomic positioning during the session, resulting in sustained stress on the lumbar region. The weight and movement of the surrogate’s abdomen further exacerbated this strain, especially during heightened activity.
Abrasion Injuries: The surrogate’s unexpected movements resulted in significant friction-related abrasions to the employee's arms and chest. Mr. [REDACTED] indicated that the surrogate’s movements were both unpredictable and forceful, making it difficult to avoid these injuries.
Joint Pain in Wrists and Knees: The employee reported experiencing joint pain in both wrists and knees due to the physical responsiveness to engagement, which required the employee to repeatedly shift positioning to maintain control and ensure safety during the session. These adjustments placed excessive pressure on weight-bearing joints, contributing to localized inflammation and discomfort.
IV. Contributing Factors
The surrogate’s unpredictable reactions have been cited as a significant factor in the injuries sustained due to more vigorous and prolonged activity than is typical during surrogate gratification procedures. Despite attempts to adhere to standard protocol, the surrogate’s heightened state rendered many of these measures insufficient, forcing the employee to rely on adaptive physical engagement techniques that increased the risk of injury.
V. Statements
Employee
"Look, I was just doing what the protocol said, but this preggo was on another level. He was completely out of control—so worked up I could barely keep up. I tried shifting around to get a better angle, but his sheer size made it impossible to keep my footing. I’m just saying, if these guys are gonna get this worked up, someone’s gotta think about the toll it’s taking on us."
Surrogate
"I don’t know what the big deal is. I just… I couldn’t help it, okay? These babies are all fighting for space in there, and I can feel them all the time—kicking, squirming—it’s too much! Is he complaining about his back?! I’m the one who’s gained 210 lbs in three weeks!"
VI. Medical Evaluation
Employee HS-137-611 was evaluated by the Paternity Compound 137 medical staff, who confirmed the following injuries:
Grade II lower back strain
Bilateral wrist tendonitis
Surface abrasions on the arms and chest
The employee has requested:
Paid medical leave for two weeks to recover from the injuries.
Additional training for handling surrogates exhibiting heightened hormonal behaviors.
Sedatives to be applied to high-risk surrogates to reduce the risk during compliance procedures.
Pending further investigation, the DRC Claims Review Board will determine the validity of Mr. [REDACTED] (Employee ID# HS-137-611) workman’s compensation claim. The board recognizes the physical demands placed on staff during surrogate engagements and will consider adjustments to safety protocols to prevent future incidents.
This case highlights the need for ongoing staff training and protective measures when interacting with surrogates in advanced gestation to ensure the safety of DRC employees.
VII. Overall Employee Injury Statistics
Late-stage surrogates with high multiples exhibit a combination of extreme physical changes and heightened hormonal states, which frequently result in unpredictable and physically demanding interactions for staff.
Injury Rates
Employees handling surrogates carrying +12 fetuses report injuries at a rate [REDACTED]% higher than those managing surrogates with fewer multiples.
The most common injuries include [REDACTED], muscular strain, abrasions, [REDACTED], and joint-related stress.
Severe injuries, such as fractures or nerve damage, account for [REDACTED]% of reported cases, often attributed to surrogate-related behavioral outbursts or sudden physical engagement.
High-Risk Gestational States
Surrogates at +10 days gestation show a significant increase in hormonal behaviors, including restlessness, compulsiveness, and enhanced physical responsiveness. These factors directly contribute to the likelihood of employee injuries.
The combination of extreme abdominal distension, weight gain, and prenatal hormonal surges creates a uniquely hazardous working environment for staff.
Behavioral Challenges
Surrogates carrying +12 fetuses are [REDACTED] as likely to exhibit heightened prenatal nymphomania, leading to increased physical demands on staff.
Conclusion
Without immediate intervention, the rising trend of injuries associated with surrogate management will continue to strain compound operations. The Gestational Support Command must prioritize the development of advanced handling protocols, expanded access to protective gear, and training programs tailored to high-multiple surrogates to safeguard employee well-being and maintain operational efficiency.
These statistics underscore the urgency of addressing the physical demands placed on staff in high-risk situations to reduce injury rates and ensure a sustainable working environment.
----------------
Click Here to return to DRC Report Archives

#mpreg#mpregkink#malepregnancy#mpregbelly#pregnantman#mpregmorph#mpregcaption#mpregstory#mpregbirth#mpregart#mpregnancy#aimpreg#mpregroleplay#malepregnant
47 notes
·
View notes
Text

The daughter of a great queen, Padishah Khatun (1256–1295) fought for her rights and proved herself to be a capable and determined ruler.
A strategic alliance
Padishah was the daughter of Qutb al-Din Mohammad, a member of the Qutlugh-Khanid dynasty, which was loyal to the Mongol Empire, and his wife, Qutlugh Turkan. After Qutb al-Din’s death in 1257, Turkan seized power, ruling Kerman (modern-day Iran) in her own name.
Padishah, her mother’s favorite child, received an exceptional education and excelled in poetry and calligraphy. In 1272, she married Abaqa Khan, the ruler of the Ilkhanate. Her marriage came with a grand household, and she frequently met with her mother and acted as her representative at court. This position was vital for defending her mother’s interests and maintaining her rule over Kerman
A wronged daughter
The death of Abaqa Khan in 1282 changed everything. His successor, Tegüder Ahmad, deposed Turkan and handed the throne of Kerman to Turkan’s stepson, Suyurghatmish. Soon after, Turkan passed away. Padishah chose not to accompany her mother’s remains back to Kerman, instead remaining at court to safeguard her interests. However, she sent her sister, Bibi Terken, to represent her in Kerman.
Tegüder’s reign was short-lived. In 1284, his successor Argun summoned Suyurghatmish to court and divided Kerman between Padishah and her rival. Unsurprisingly, Padishah was disappointed by this decision. Meanwhile, Suyurghatmish strengthened his position by marrying a Mongol princess, Kurdujin Khatun, eventually regaining full control of Kerman.
Padishah later married Argun’s brother, Gaykhatu. Although she managed to recover her personal domain of Sirjan in 1289, she had to wait patiently for the tides to shift in her favor.
Queen at last
Argun’s death in 1291 paved the way for Padishah’s return to power. Gaykhatu, now head of the Ilkhanate, reinstated Padishah as ruler of Kerman in 1292. She adopted the title Safwat al-Dunya wa al-Din (“Purity of the World and the Faith”) and also referred to herself as Ḵodāvand-e ʿĀlam (“Lord of the World”), a title that appeared on her coins.
Her first act was to neutralize her opposition. She imprisoned Suyurghatmish, and, doubting his loyalty, had him strangled.
Like her mother, Padishah’s reign was marked by justice and a dedication to the welfare of her people. She encouraged charitable works and extended her influence to nearby regions. Writing under the pen name Lāla Ḵātun, she composed poetry and supported scholars and poets.

Cycle of revenge
The assassination of her husband Gaykhatu in 1295 by his successor, Baydu, placed Padishah in a precarious position. Baydu was married to Shah ʿAlam, Suyurghatmish’s daughter, who sought revenge for her father’s death. Suyurghatmish’s widow, Kurdujin, was also ready to act.
Although Padishah remained in Kerman, many of her supporters abandoned her. She sought alliances but found none. Kurdujin, with the backing of loyal amirs, besieged Kerman, forcing Padishah to surrender.
Padishah was taken to court and eventually assassinated, likely at the instigation of Kurdujin and Shah ʿAlam. Her remains were returned to Kerman, where she was buried in the seminary built by her mother.
Though Kurdujin emerged victorious, she was never formally crowned ruler of Kerman, and her triumph was short-lived. She later became queen of Shiraz in 1319 and was succeeded by her niece, Sultan Khatun, upon her death. Their authority appears to have been more symbolic than political and limited to the city.
Enjoyed this post? You can support me on Ko-fi!
Further reading
De Nicola Bruno, Women in Mongol Iran: The Khatuns 1206-1335
Lambton Ann K. S., Continuity and Change in Medieval Persia Aspects of Administrative, Economic, and Social History, 11th-14th Century
Mernissi Fatima, The Forgotten queens of Islam
“PĀDŠĀH ḴĀTUN”, Encyclopaedia Iranica
#this is probably my last post of the year :)#padishah khatun#history#women in history#women's history#historyedit#13th century#iran#iranian history#queens#powerful women#ilkhanate#mongol history#kurdujin khatun#sultan khatun#kerman#central asian history
38 notes
·
View notes
Note
I've been curious as to why in a lot of socialist states, there seems to be such a reverence of their leaders - I understand why strict adherence to the Party is necessary to oppose counter-revolutionaries and for the survival of a Dictatorship of the Proletariat but I've always had trouble recounciling the fact that there seems to always be cults of personalities around leaders.
Is this image of a cult of personality in socialist states completely fabricated by capitalists? I feel like it must at least be exaggerated by the West, and I understand that these leaders are/were popular amongst their populations for the good they have done, but I would like to know if there is more to it.
As a slight aside before the meat of the question, adherence to the party is mainly necessary because as the party of the proletariat, it should sum all of the interests of the class into a single program and a single will. Apart from the issue of survival and defense, it's mainly a political reasoning.
We should have in mind the context of these "cults of personalities". The places in which socialism has imposed itself for any significant amount of time have essentially been imperial periphery, meaning a colonized people with decades of savage exploitation weighing heavily in their minds. The case of the USSR was an imperialist country, although living conditions within the empire were nothing to be envied, and in the case of Eastern Europe, a cautious parallel can be drawn to fascist occupation and the various reactionary dictatorships of the interwar period, with the myriad of little regional wars and population transfers. To sum up, socialism has been a liberatory force, one that sided with the powerless in their most miserable times and brought them to run their own state, and enjoy the full fruits of their collective labor. Keep this point in mind for a moment.
Idolization of individuals is an attitude that has been inherited from nodes of production that benefit from taking the focus away from masses of people as classes by shifting it to extraordinary individuals. It is an aspect of psychology that is still nowadays very hard to escape because it has been conditioned so deeply into the collective consciousness, if one allows me to borrow a Freudian concept. History is taught through individuals, but we also conceive of all political leadership in terms of individuals. The administration of so and so, the such and such era, etc. Most communists also do this to an extent, for instance, when we talk about the history of the USSR or of China or Cuba, we rely on the tenure of individuals or at least use it as a crutch for compartimentalizing periods.
With these two things in mind, it's not surprising to see idolatry of individual communist leaders to happen. I'd agree with you that it's not exactly desirable, but the context in which revolutions take place are the smoldering ashes of the old, not a foundation of freshly-poured concrete. A lot of communist states also leaned into this individual worship, and while I won't get into specific examples, I will say that the ones I know of have a satisfactory explanation, or at the very least the reasoning behind the choice at the time makes sense. Regardless of this, the propaganda that comes out the mouth of the Pentagon is exaggerated and at times complete fabrications.
Let's take a modern example, for a change of pace. It is true that the Kim family has included all general secretaries of the Worker's Party of Korea, and that Korean people in the north have very positive opinions of the Kims. Did Kim Jong Un force all Koreans to have his haircut? or forbid all babies to be named after him? or force every house and establishment to have a portrait of him? Absolutely not.
All of this scare-mongering plays very deftly into the pre-conceived expectation of people in liberal democracies of politicians being polarizing figures or largely disliked. This propaganda simultaneously reinforces a normalization of this expectation, which does prevent some people from acting on their discontent, and also convinces people that there can be no such thing as a politician who genuinely does govern for the benefit of the social majority and is liked for it. "A worker's state can't possibly be so because it's impossible for a state to truly satisfy all people, they must all be under the spell of a personality cult!" thinks the worker living in a bourgeois dictatorship reading the umpteenth ridiculously exaggerated story of Kim's dictatorial whims.
43 notes
·
View notes
Text
1.20.25 • Today the United States Climate Alliance delivered a letter to UN Climate Change Executive Secretary Simon Stiell, making it clear to the global community that our climate work will continue regardless of federal action or inaction.
If you're not familiar with the U.S. Climate Alliance, they are a bipartisan climate action coalition of 24 governors representing approximately 55% of the U.S. population and 60% of the U.S. economy.
To read their letter, read more here or explore their press release on their website. Onward!
•••
Mr. Simon Stiell, Executive Secretary
United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change
P.O. Box 260124
D-53153 Bonn, Germany
January 20, 2025
Dear Executive Secretary Stiell,
We write as co-chairs of the United States Climate Alliance, a bipartisan coalition of two dozen governors representing nearly 60 percent of the U.S. economy and 55 percent of the U.S. population, to make it clear to you, and the rest of the world, that we will continue America’s work to achieve the goals of the Paris Agreement and slash climate pollution.
As you know, this is not the first time we’ve responded to this challenge in the U.S. Our coalition was launched after the President’s decision to withdraw our country from the Paris Agreement back in 2017. Since then, our reach, resolve, and impact have only grown.
In fact, our states and territories are now on track to meet our near-term climate target by reducing collective net greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions 26 percent below 2005 levels by 2025. Our recent progress reflects a wave of ambitious state policies and federal funding enacted over the last few years – and it builds on our coalition’s 15-year trend of cutting emissions while simultaneously growing our economies. We have continued to ramp up our longer-term commitments as well, pledging to reduce GHG emissions at least 50-52 percent by 2030 and 61-66 percent by 2035, below 2005 levels, in alignment with the U.S. Nationally Determined Contribution. Most importantly, this action is bringing better health, cleaner air, good-paying jobs, new economic development, and lower costs to our communities.
Our states and territories continue to have broad authority under the U.S. Constitution to protect our progress and advance the climate solutions we need. This does not change with a shift in federal administration. States across our coalition are implementing a suite of policies and programs to secure our net-zero future, including statewide and regional carbon markets, 100 percent clean energy standards, and methane reduction programs for the oil and gas, waste, and agricultural sectors, among many others. We are also deploying billions of dollars to eliminate pollution in our communities and sustain our country’s clean energy boom.
It’s critical for the international community to know that climate action will continue in the U.S. The Alliance will bring this message to the United Nations Climate Change Conference in Brazil (COP30) later this year – just as we have at every COP since our coalition’s founding – as we work to implement our climate goals. We are also committed to tracking and reporting on our progress and look forward to working with you and the global community to identify the most impactful ways to do so. The Alliance is proud to publish an annual report each year on our latest action, and we are enclosing here our most recent report for your reference.
We will not turn our back on America’s commitments. For our health and our future, we will press forward.
Sincerely,
Governor Kathy Hochul, Co-Chair
State of New York
Governor Michelle Lujan Grisham, Co-Chair
State of New Mexico
#us climate alliance#environmentalism#climate action#climate change#us politics#traumerica#good news
20 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hello bro.
What do you expect for this new trump administration? Locally and internationally?
Bro, thank you so much for this ask!!! I sincerely appreciate it 😁. I will try to keep this brief and try not to ramble lol.
I honestly don't expect to much to change both locally and internationally. Beyond all Trump's bombastic rhetoric he is just another typical cookie cutter bourgeois figurehead who only serves the interest of the ruling class. He is just a lot more obvious and transparent about it, at least he can be hilarious. To me, he is no different than any other president. He's just going to advance the same imperialism, the same agenda for u.s. hegemony and the same toxic foreign policy.
Internationally, he is going to keep giving israel unlimited funding that will enable it to continue being the rabid dog of a state that it is, and perpetuate the horrific genocide that we are witnessing. He is going to keep Ukraine on life support, maybe even more so since Ukraine has been losing badly as of late. And he is going to keep building up Taiwan to use as a bulwark against China.
The two things I am going to be watching most closely are:
1. What is the u.s. going to do in Syria now that Assad is out of the picture. During his first term the u.s. went into Syria supposedly to fight the Islamic State, but past that we saw massive plundering of Syria's oil, he even gloated about it saying "I like oil". With no more legitimate government and the destruction of Syria's military capabilities, Syria is going to be dissected and turned into a textbook failed state, truly tragic. It may also weaken Iran's position in the region.
2. How is the shadow war going to develop in Africa. u.s. involvement in Africa in the so called "War on Terror" has been significant to say the least. The u.s. is in several African countries doing "counter terrorism operations". Notably though, the u.s. lost a major foothold in Niger, when the new military government ended the agreement that allowed for 1,000 u.s. troops to be stationed in the country, the u.s. subsequently withdrew it's forces last August, this has been a major setback for the u.s. in the region. It will be interesting to see how these new governments will respond to the u.s. presence and how they will pivot towards Russia/China.
I hope this a good answer bro, I've been up since 4:00 am and I worked a twelve hour shift, but I did not want to keep you waiting for too long. Thank you so much for sending me this question, this made my day, feel free to send me asks anytime.
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
Disability is not a fixed state or attribute but exists in relation to assemblages of capacity and debility, modulated across historical time, geopolitical space, institutional mandates, and discursive regimes. The globalization of disability as an identity through human rights discourses contributes to a standardization of bodily usefulness and uselessness that discounts not only the specificity of location but also the ways bodies exceed or defy identities and subjects. The non disabled/disabled binary traverses social, geographic, and political spaces. The distinctions or parameters between disabled and non-disabled bodies shift historically, as designations between productivity, vagrancy, deviancy, illness, and labor market relations have undergone transformations from subsistence work to waged labor to hypercapitalist modes of surplus accumulation and neoliberal subject formation. They shift geographically, as varied cultural, regional, and national conceptualizations of bodily habitations and metaphysics inhabit corporeal relations differently and sometimes irreconcilably, and issues of environmental racism are prominent. They shift infrastructurally, as a wheelchair- accessible elevator becomes a completely altered vehicle of mobility, one that masks various capacities to climb stairs, in many parts of the world where power outages are a daily, if not hourly, occurrence. They shift legally, administratively, and legislatively, as rights- bearing subjects are formed and dismantled in response to health care and insurance regimes, human rights discourses, economic opportunism, and the uneven distribution of resources, medical supplies, and basic care. They shift scientifically, as prosthetic technologies of capacity, from wheelchairs to cellphones to dna testing to steroids, script and rescript what a body can, could, or should do. And they shift representationally, as discourses of multicultural diversity and plurality absorb “difference” into regimes of visibility that then reorganize sites of marginalization into subjects of privilege, indeed privileged disabled subjects.
Right to Maim: Debility, Capacity, Disability (2017, xiv-xv), Yasbir K. Puar
52 notes
·
View notes
Text
In the space of four days, the Russia-Ukraine war has dramatically shifted. The incursion of Ukrainian forces into Russia’s Kursk region has quickly turned into the largest territorial gain by either side since the successful Ukrainian counteroffensives in Kharkiv and Kherson in the fall of 2022. As of this writing, it is still unclear whether thinned-out and poorly prepared Russian forces have been able to halt the Ukrainian advance, with reports of burning columns of Russian reinforcements reminiscent of the early days of the war.
The operation demonstrates Ukraine’s ability to achieve surprise and exploit sudden breakthroughs, something at which Russia has consistently failed since the start of its invasion. It is also the first time Russia has been invaded by foreign troops since World War II, showing Russians in no uncertain terms that the bloody war they unleashed against their neighbor has come home. Ukraine’s Western supporters seem to be on board, with the White House and European Union headquarters issuing statements that it was up to Ukraine to decide on the operation.
Previously, there had been much debate in Washington, Berlin, and among a wildly speculating media about the Kremlin’s supposed red lines that would set off World War III and nuclear Armageddon, with one of the lines being taking the war to Russia with Western weapons. The latter has now occurred. The belief in uncontrolled escalation led the Biden administration and some of its partners to severely restrict both the types of weapons delivered to Ukraine and their permitted range; Ukraine has not been allowed to use Western missiles to hit military installations on the Russian side of the border, for example. Part of the effect and purpose of the Kursk operation could be to demonstrate, once again, the fallacy of the red-line argument.
As the offensive unfolds and Kyiv stays mostly mum on events, it’s still too early to say what strategic goals Ukraine is hoping to achieve. One speculation that has gained a lot of traction is that it could lead to a quicker end to the war. The operation makes it clear to Russian President Vladimir Putin that Ukraine retains significant potential to inflict pain on Russia. And if Ukrainian forces can hold on and maintain control of Russian territory—for which they appear to be digging in as they bring in more equipment and build new defensive lines—it could strengthen Ukraine’s leverage in any potential negotiations to end the war. Already, Ukraine’s lightning foray into Russia undermines the widespread idea that Putin holds all the cards to dictate the terms of a cease-fire.
Kyiv seems to be signaling that leverage in negotiations is one of the goals of the offensive. An unnamed advisor to Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky told the Washington Post: “This will give them the leverage they need for negotiations with Russia—this is what it’s all about.” This dovetails with recent hints by Zelensky that Kyiv was ready to negotiate. In an interview with BBC News in July, he said, “We don’t have to recapture all the territories” by military means. “I think that can also be achieved with the help of diplomacy.” Occupied Russia could be traded for occupied Ukraine: As former Swedish Prime Minister Carl Bildt suggested on X, “Would an idea be for both states to retreat to within their respective recognized border?”
If Kyiv seems to be preparing the ground for potential negotiations—by seeking to strengthen its hand and publicly declaring its willingness—it is also a response to several factors.
One is growing war weariness among the Ukrainian population. Although the majority of Ukrainians favor fighting on until all the territories Russia has occupied since 2014 are liberated, the number saying that Ukraine could trade some of that territory for peace has been rising.
Second, there has been growing criticism, particularly in Western Europe and the global south, of the way Ukraine has repeatedly ruled out talks with Moscow. Major substantive issues aside, with the Kremlin apparently back-channeling openness to talks, Kyiv risked being seen as intransigent in preventing an early end to the war.
Finally, Ukraine’s strategic position is risky, even if it holds back Russia and maintains the flow of Western weapons. A victory by Donald Trump in the November U.S. presidential election and a sudden stop of U.S. aid cannot be ruled out, and even a Harris administration may have trouble cobbling together future support packages if the Republicans keep their majority in the U.S. House of Representatives. Zelensky may have decided to gamble to change and accelerate the dynamics of the war, including greater leverage if negotiations end up taking place sooner than anticipated.
Without much leverage, Kyiv has had to appeal to moral, normative, and legal arguments when communicating with its foreign partners about any peace short of full liberation. In the past, this has led to highly skewed negotiations. In the talks that produced the Minsk I and II accords in 2014 and 2015, Ukraine had such a weak hand that it had to agree to impossible terms: It could only get the Russian-controlled Donbas back if it allowed Moscow’s proxies to become part of the Ukrainian polity through local elections manipulated by the Kremlin, which would have given Moscow a permanent veto over Kyiv’s politics. Previously occupied and annexed Crimea was not even included in the discussion.
In March 2022, direct talks between Ukraine and Russia on the Belarusian border were not a negotiation but Russia’s delivery of surrender terms to Ukraine. In April 2022, negotiations brokered by Turkey in Istanbul also went nowhere: Russia’s price for ending its invasion was a considerable limitation of Ukrainian sovereignty and ability to defend itself. Since then, Russia’s proposal has been for Ukraine to permanently cede, in addition to Crimea, Luhansk, Donetsk, Zaporizhzhia, and Kherson oblasts—including substantial parts that Russia has never occupied.
Not only has Ukraine lacked negotiation leverage, but Russia has also been successful in promoting, to audiences around the world, its land-for-peace approach to ending this round of the war. As Ukrainian counteroffensives after 2022 largely failed and the Russian war machine slowly but steadily took more territory in Ukraine’s east, another Minsk-type deal limiting Ukrainian territorial integrity and political sovereignty seemed to loom on the horizon.
Kyiv has not only changed the military narrative on the ground but may also be trying to change the narrative on negotiations—from a “land for peace” deal to a “land for land” deal. This puts Putin in a bind: Loss of control over parts of Russia proper is an enormous embarrassment for the Kremlin. But since their illegal annexation by Russia, the Ukrainian territories Putin seeks to keep are also part of the state territory he is obliged to defend. That said, in terms of Russian elite and popular perception, the restoration of Russia’s legitimate state territory will take precedence over continued occupation of recently conquered domains—especially if a land swap opens an avenue to the end of Western sanctions.
In a way, the new Ukrainian strategy may provide an opening for doves in the Russian leadership—assuming they exist and have any influence over Putin—to argue that the annexations should be reversed in order to restore Russia’s territorial integrity. As long as Ukraine can hold on to its captured territories in Russia, there will a strong pressure on Putin to return them under Moscow’s control.
None of this, however, changes the most fundamental problem with a negotiated outcome: the fact that Russia has ignored just about every agreement it has signed with Ukraine. But for Ukrainians and their Western supporters hoping for an end to the war, some intriguing possibilities may soon be on the table.
34 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Byzantine-Armenian Relations
The relationship between the Byzantine Empire and ancient Armenia was a constant and varied one with an equal mix of wars, occupations, treaties of friendship, mutual military aid, and cultural exchange. Regarded as a vital defence to the Empire's eastern frontiers, emperors used various means of influence from outright takeover to gifts of titles and lands to Armenian nobles. Influence went in the other direction, too, with several important Byzantine emperors being of Armenian descent, as well as many individuals who held key military and administrative positions in Constantinople and beyond.
Sources
There are several difficulties in assessing the relations between Byzantium and ancient Armenia. Aside from the usual problem of ancient historical sources having an inherent bias towards rulers, noble families, and high politics, account must be taken of the shifting geographical location of Armenia over the centuries and its regular division and redivision by successive empires in the region. There are problems, too, with primary sources which can be coloured by nationalism and left incomplete with deliberate omissions. There are also long silences in the historical record, notably from 730 to 850 CE and 925 to 980 CE. Nevertheless, a reasonable picture of relations between the two states can be drawn and the historian T. W. Greenwood, by way of a summary, highlights three stand-out features of this relationship:
In the first place, relation were continuous…Secondly, they were multi-layered…it seems very likely that lesser lords and individual bishops were also in contact with Byzantium throughout…Thirdly, they were reciprocal. Byzantium was eager to secure its eastern flank and therefore sought to attract Armenian clients into its service. At the same time Armenian princes looked to Byzantium to bolster their own status within Armenia through the concession of titles, gifts and money…It is no coincidence that the Byzantine army - and then the state - came to be filled with men of Armenian origin or descent. (Shepard, 363-4)
Continue reading...
41 notes
·
View notes
Text
https://t.co/J3fEqiIOIk
Since June 2019, Sudan has been caught in a whirlwind of revolution, descending into a profound economic and political crisis. The initial optimism that followed President Omar H. al-Bashir's ousting has led to chaos, influenced by powerful international actors with their respective political agendas. The geopolitical quagmire is further complicated by the involvement of neighbouring countries.
Prime Minister Abiy Ahmed's (PhD) recent visit to Port Sudan, where he met with Abdel Fattah al-Burhan (Gen.), the head of the Sudanese army and the Saudi- and Egyptian-backed Sovereign Council of Sudan, evidenced Ethiopia’s vested interests. The visit should be particularly important given Abiy’s prior engagement with Mohamed Hamdan Dagalo, the Rapid Support Forces (RSF) leader, whom he hosted in Addis Abeba in December 2023 to advocate for peace in Sudan.
Ethiopia's economic ties with Sudan are substantial. The slowdown in the 211.5 million dollar investment circuit between Khartoum and Addis Abeba has adversely affected both countries. Small businesses along the Sudan-Ethiopia border have borne the brunt of the ongoing conflict. Prime Minister Abiy’s visit can be seen as an effort to stabilise these economic ties and promote peace for mutual benefit. However, if influenced by Western countries or Saudi Arabia, Abiy’s administration may face political backlash from its ally, the United Arab Emirates (UAE).
The role of international players was evident early on. The UAE was among several countries, including the United States (US), Israel, Saudi Arabia and Egypt, that expressed solidarity with the Sudanese people. Saudi Arabia and the UAE notably provided three billion dollars in economic aid to Al-Burhan’s leadership, signalling their approval of the political shift in Khartoum. However, the situation in Sudan soon deteriorated into an ongoing civil war, leading to accusations of ethnic cleansing and further international scrutiny.
Sudan's civil war, however, extends beyond regional dynamics. Recent reports have uncovered the involvement of external actors in perpetuating the conflict.
In May this year, American Senator Ben Cardin, chairman of the Senate Foreign Relations Committee, raised concerns about a UN Panel of Experts' report from the previous year, which provided evidence of the UAE supplying weapons to the RSF, a group notorious for its brutal tactics. US Ambassador to the UN, Linda Thomas-Greenfield, echoed these concerns, calling for “external actors" to stop "fueling and prolonging this conflict and enabling these atrocities by funnelling weapons into Sudan.”
Abu Dhabi has been working vigorously to clear its name in response to these accusations. Through diplomatic channels and humanitarian aid, the UAE has sought to counter allegations of its involvement in the Sudanese civil war. Hundreds of millions of dollars have been funnelled to humanitarian organisations operating in Sudan through various UN agencies, a move seen by many as an attempt by Abu Dhabi to portray itself as a force for good amidst the chaos.
Despite these efforts, a recent UN report has further implicated the UAE. The report exposed that the RSF, supported by Abu Dhabi, committed international crimes by receiving and laundering gold illegally exported from Sudan. The UAE has vehemently denied any involvement in Sudan’s political turmoil or illegal gold trade practices, calling the allegations a political mockery of its humanitarian generosity.
While these revelations add layers of complexity, the international community’s response remains lacklustre. The US and the UN have the political and diplomatic clout to influence the situation, but the resolution of Sudan’s crisis ultimately lies in the hands of its people. The international community can only play a supportive role in the Sudanese-led efforts to resolve the political disorder, providing the necessary space and resources for Sudan to shape its destiny.
Although belatedly, the Addis Abeba-based African Union (AU) has also begun addressing the dire humanitarian situation in Sudan. The Chairperson of the AU High-Level Panel on Sudan, Mohamed Ibn Chambas (PhD), has begun to speak out about the severe impacts of the ongoing civil war. However, stronger official condemnations from the AU were expected, holding all groups and countries involved in the war accountable.
Ironically, Sudan’s revolution is no longer a story of a failed uprising but an ongoing civil war marked by international intrigue and regional power struggles.
43 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hunter Walker at TPM:
President-elect Donald Trump has been filling out his administration in the week since his landslide election. On Tuesday, he announced that former Arkansas Gov. Mike Huckabee is his choice to serve as U.S. Ambassador to Israel. The pick is notable because Huckabee has a long history with the country, including statements that indicate he doesn’t necessarily believe in the two state solution to the country’s conflict with the Palestinian people.
In multiple posts on the site once known as Twitter, Huckabee has suggested the nation of Palestine does not exist at all. For example, in 2019, Huckabee tweeted “there has NEVER been a nation called Palestine.” That comment came as a response to reports about the first Palestinian-American congresswoman, Rep. Rashida Tlaib (R-MI), including a new report at the time about a map in her office that was branded with a post-it note saying Palestine placed next to Israel. Huckabee offered a similar perspective in a 2020 tweet where he endorsed former Georgia Sen. Kelly Loeffler (R) against the man who ultimately won her seat, Raphael Warnock. “Until terrorist Yassar Afafat ‘invented’ a ‘Palestinian nation’ in 1962, the term applied to ALL who lived in the region, including the Jews,” Huckabee wrote.
Huckabee did not respond to a request for comment. His contention that Palestine has never been a country and that the term “Palestinian” has applied to everyone in the region is a decidedly ahistorical one. The modern nation of Palestine, which includes the territories of the West Bank and the Gaza Strip, is recognized by over 140 other countries. That list does not include Israel, which has been engaged in a decades long conflict over borders with the Palestinians since its own founding in 1948, and the United States. The Palestinian people, a group that includes Arab Christians and Muslims, have been described as inhabiting the region since the Biblical times. English translations of the Torah and Bible translate the Arabic and Greek references to the group by calling them Philistines. In the relatively modern era, the region was ruled by a series of colonial powers, including the Ottoman Empire and the British, who left the territory in 1948, setting off a conflict between the newly-declared Jewish State of Israel and Arabs in the region.
However, in Huckabee’s telling, any notion of a Palestinian state seems to be totally illegitimate. He reiterated this view in February when President Joe Biden visited the town of East Palestine, Ohio. On Twitter, Huckabee quipped that Biden made a mistake and thought it was “actually a visit to the mythical land of ‘Palestine’ where Jew-hating genocidal Hamas & Fatah rule and celebrate murder of Jews.”
The long simmering Israeli-Palestinian conflict reached a new level of urgency in the aftermath of the Oct. 7, 2023 attack staged by Hamas, which controls the Gaza Strip. During the violence, Hamas militants invaded southern Israel, killed over a thousand people and took more than 200 hostages. The Israeli government of Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu responded by staging an invasion of Gaza, which is ongoing and has left over 40,000 people dead, so far. Fighting has also spilled over into Lebanon, Israel’s Northern neighbor. President Biden’s support for Israel despite an invasion that many on the left view as a genocide is one of the issues believed to have helped erode support for Vice President Kamala Harris as she lost last week’s election to Trump. While some Democrats and leftists may have been unhappy with Biden’s support for Israel, during the election, Netanyahu displayed a clear preference for Trump. And, despite shifting comments on the conflict, Trump has increasingly indicated he would be open to a so-called one-state solution that saw Israel take control over the Palestinian territories.
Mike Huckabee, who is set to serve as US’s Ambassador to Israel, has repeatedly pushed the pro-Israel Apartheid apologist false notion that Palestine doesn’t exist. Well, Mr. Huckabee, various agencies and several countries would beg to differ there.
#Mike Huckabee#Israel#Palestine#Occupation of Palestine#Israel Apartheid#US/Israel Relations#Trump Administration II#Israel/Palestine Conflict
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
Democrats are rolling out a new plan to appeal to rural voters after major losses in the 2024 elections. They hope to convince rural Americans that President Donald Trump’s policies are hurting their communities, especially when it comes to healthcare, economic opportunities, and infrastructure support.
Key Facts:
Outgoing DNC Chair Jaime Harrison discussed a new approach aimed at rural America.
Democrats lost the 2024 presidential race and now want to win crucial seats in the 2026 midterms.
The strategy focuses on labeling Trump’s actions as harmful to rural families.
They plan to highlight policy successes under Joe Biden, including environmental protections and federal program funding.
The Rest of The Story:
The Democratic National Committee, under the leadership of Jaime Harrison, is turning its attention to rural voters.
Harrison believes Trump’s second-term plans place healthcare and economic benefits for these regions at risk.
By showcasing programs launched under the Biden administration—such as investments in clean energy, PFAS contamination crackdowns, and potential expansions in healthcare access—Democrats are trying to remind rural voters of what they have to lose if Trump fully implements his proposed policies.
This rural-focused push comes at a time when Democrats are reeling from defeats at both the presidential and congressional levels.
Party leaders say their new approach is a long game that involves local outreach, better candidate recruitment, and persistent efforts to shift public opinion in predominantly red states.
Commentary:
Trump’s landslide victory in the swing states proves many Democrat leaders are more out of touch with everyday folks than they would like to admit.
Their latest scheme to win rural support sounds desperate, especially since they show little sign of honestly revising the big-city policies that drove away farm-country voters in the first place.
Rural Americans have made it clear that they value personal freedoms, job security, and lower taxes—ideas the Democrats often challenge with heavy regulation and social spending.
It’s hard to see how they can suddenly flip the script without seeming insincere.
Even if they do overhaul their platform, many rural families will be suspicious of a party that once wrote them off.
Winning back trust is tougher than simply changing campaign talking points.
Still, it’s entertaining to watch them try.
It would be nice if they stayed on this path, so we can see just how far off-base they will go before waking up to reality.
8 notes
·
View notes