#prime number theorem
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Mathematical Beauties of the Number 142587
There are some mysteries that the human mind will never penetrate. To convince ourselves we have only to cast a glance at tables of primes and we should perceive that there reigns neither order nor rule.Leonhard Euler Welcome to the blog Math1089 – Mathematics for All. I’m glad you came by. I wanted to let you know I appreciate your spending time here on the blog very much. I do appreciate your…

View On WordPress
#1/7#142857#1429857#addition#cyclic number#cyclic permutation#division#enneagram#Factors#Math1089#mathematics#Mathematics for All#Midy theorem#multiplication#Prime Factorization#subtraction
0 notes
Text
it is really funny in number theory seeing like. 1 million theorems about ODD primes and being like, a complete math newb like "why is it odd primes? aren't all primes odd, except 2" and then ur professor is like yeah 2 fucking sucks and like does not fit any of our proofs so we have to deal with it separately and etc. and they have like such vitriol for. prime number 2.
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
system of mathematical notation where concatenation always means multiplication and each prime number has a unique one digit symbol. so counting to ten looks like "2, 3, 22, 5, 23, 7, 222, 33, 25". the advantages of this system would be making multiplication and division trivial, as well as accurately representing the true form and identity of every positive integer according to the fundamental theorem of arithmetic. the disadvantages to this system would be everything
7K notes
·
View notes
Note
Nerd Reader x Nerd Nanami = smart power couple
you and kento were sitting at a corner table on a café, your eyes glued on your notebook, fingers fiddling with your pen.
“you’re so focused, working on how to divide zero now?” kento chuckles as he leans back.
“haha, very funny. if could divide zero, i’d be solving the world’s fundamental problems, not this stupid equation.” you huff.
you were preparing for an upcoming exam and you thought about inviting kento to study with you.
because why not, right?
“there’s beauty in the paradox of diving by zero, maybe you should just stop looking for the answer and let the question be.” he shruggs.
“so, you’re saying that i should just stop solving and just appreciate it? will that get me a passing grade?” you look at him, eyebrows furrowed.
“pretty much. though, to be fair, i get it. numbers don’t offer room for interpretation. but language—language is fluid. it can mean whatever you want it to mean... have you thought about math as a language?” kento suggests taking his drink and sipping a little.
“sure, math is a language. but it’s a language about rules. it’s all about structure and logic.” you refute, looking back at your messy math notes.
“if you look at it this way, math is a kind of poetry. just like a metaphor works in finding the unexpected connection between two things—math finds connections between numbers. patterns show up and suddenly something new appears where there was nothing before.” setting his cup down as he looked at you.
“you’re starting to sound like those motivational quotes that you find imprinted on the side of a coffee cup. you have a point, though i don’t think i’m gonna start writing sonnets about theorems anytime soon...” you laugh softly, scribbling nonsense on your notebook.
“i’ll take that as a win. i think you could give shakespeare a run for his money if you ever wrote a poem about prime numbers.”
“‘shall i compare thee to an irrational number? thou art infinite and never repeating…’” you say sarcastically.
“hey, don’t knock it until you try it. you could write a whole epic poem on pythagoras and his theorem, i guarantee it would have a bigger following than every other poems.” kento leans back on the chair again.
“yeah, yeah. you’re distracting me! go read whatever shenanigans you’re reading, you’re making me lose focus!” you lightly slap his shoulders.
nothing could beat moments like this, just you and him—throwing playful banters against one another.
and you did end up passing your test! but you’re not sure if you’re still gonna invite kento anytime soon knowing that he’s just gonna go off and talk about things that you really can’t comprehend...
who are you kidding? of course you’d invite him either way...

an: english isn’t my first language so this made my head hurt, i think i drained my brain juice and idrk how i’d portray this type of trope so i just went w it 😿 + i believe that kento is a english literature poem stuff kind of guy and becomes a yapper when that’s the topic, you can’t change my mind .
#swu’s brainspills#nanami#nanami kento#jjk#jjk nanami#jujutsu nanami#nanami x reader#jjk x reader#jjk x y/n#jjk x you#nanami x y/n#kento nanami x reader#nanami x you#nanami fluff#jjk nanami kento#jjk kento nanami#jjk kento#jujutsu kaisen nanami
198 notes
·
View notes
Text
who's hand is in this picture?

A Mathematically Rigorous Proof That I Spent Too Long Writing
welcome to university math: dnp hand edition
(no, don't leave, you'll be fine i promise)
to begin, we need a statement to prove. we have two options:
- the hand is dan's hand
- the hand is phil's hand
now, for most proofs in university math, you are told a true statement, and you must show why it is true using logic rules, definitions, and theorems. but, we do not know which of these statements are true, so we have to find out.
to prove that a statement is true, we must show that it is always true for the situation presented. to show a statement is false, we must present a single instance where the statement is false (also known as a counter example).
a quick not scary math example:
definition: a prime number is only divisible by 1 and itself.
statement: all prime numbers are odd
(this is false, because 2 is a prime number and it is even. you don't even need to check if there's any others, all you need is one single case where it isn't true to disprove it)
so now that we have a little background on proofs and how to prove and disprove them, we go back to our two statements.
the thing with this situation is, one of them must be true (unless you're gung-ho on someone else holding dan's face while phil takes a picture on his phone of dan in his glasses, in which case, i applaud your commitment, but in actuality this proof will cover that option too)
the full statement we have is: dan is touching his face or phil is touching dan's face
now, because this is Real Life and we have a picture where a hand is touching dan's face, we know already that one of these options is true (as mentioned above) but! using symbolic logic you could also come to this conclusion.
this type of statement is an 'or' statement, and if you're curious, you can look into 'truth-tables' and see why, but at least one of the options must be true.
back to the proof at hand (bah-duhm-tss)
okay. now, proofs also must be 'general' in order to mean anything, really. these are statements of truth of the universe, not just for individuals. so, we will prove this generally.
we have 2 people involved, so individual 1 (dan, the owner of the face and potential face toucher) will be labelled as 'D' , and individual 2 (phil, the possible face toucher who does not own the face) will be labelled as 'P'. thus, this can be true for any such D and any such P.
so with our 'or' statement, in order to prove it, we pick one of the options and say that it is not true, and we have to show then that the other is true.
step 1: let's assume this is not P's hand. (assumption)
step 2: thus, it must be D's hand. (what we take from our assumption)
step 3: now, if it is D's hand, we look at what a hand on one's own face is capable of appearing like. (a definition or true fact about step 2)
the position in the given photo shows the hand with a thumb on the cheek, and a finger on the forehead. so, we find an example of a person with their fingers in the same position (or close to) and see if this supports our claim.
consider:

now, with this image, you can clearly see how the subject's right hand has the thumb on the temple and index finger on the top of their head, however, it is a close enough position for our case.
from the view of the camera, the closest finger to the camera is the edge of the pinkie. in fact, it will always be the closest finger to the camera in this position, assuming the subject has all fingers and no additional appendages.
step 4: we now compare this to our photo (we verify if this holds to our claim or contradicts it)

in our photo, the closest appendage to the camera is the edge of the thumb.
step 5: thus, it cannot be the case that D is touching their own face. (what the evidence says)
step 6: as we assumed it was not P's hand and have shown it cannot be D's hand, and as this is an 'or' statement both of these claims cannot be false, we can therefore conclude it must be P's hand. (our conclusion: re-stating the statement and assumptions and conclusion)
step 7: we verify that P is true (optional step but in beginner proofs you generally show why your case works)
to do this, i will show a picture of a person touching another's face, and compare it to our image.
consider:

now, this image is not exactly the same, similar to above. however, P's left thumb is on the cheek, with their index on D's temple. the closest appendage to the camera (if it were in a similar perspective as our original) would be the edge of the thumb.
comparing it to our original:

our comparison holds.
thus, we can conclude that the true claim in this statement is that P must be touching D's face, which, in particular means that:
phil is touching dan's face in the image
thank you for partaking in phannie mathematics. we now know. i am not sorry.
bonus:
phil has a hitchhikers thumb and dan doesn't so why was this necessary at all 🤡


#genuinely might be my magnum opus#please don't be scared of the math there's not numbers if anything it's more logic than what most people would know as math#this was purely for fun. my brain just saw the anatomical options while ive been staring at that photo since we've gotten it#dan looks sooo good in phils glasses and i cant not think about it yknow#dan and phil if you read this. hi. hope you enjoyed the math lesson. loved the video btw. thank you for wdapteo 2023.#also shout out to all my other math major phannies. love you. hope you enjoyed#dnp#c.text#dan and phil#and for the hell of it:#math#mathematics#math proof
214 notes
·
View notes
Note
What mathematical operators would you think make for the best fuck marry kill discussion
FMK: addition, multiplication, exponentiation
FMK: powers, roots, logarithms
FMK: group operation, inversion, unit element
FMK: polynomials, differential operators, continuous maps
FMK: greater than, less than, equal
FMK: one, two, three
FMK: numerator, denominator, quotient
FMK: rings, integral domains, fields
FMK: categories, functors, natural transformations
FMK: reflexivity, transitivity, antisymmetry
FMK: fundamental theorem of algebra, fundamental theorem of calculus, fundamental theorem of arithmetic
FMK: prime numbers, composite numbers, units
FMK: algebraic geometry, algebraic topology, algebraic number theory
FMK: compact Hausdorff spaces, abelian groups, algebraically complete fields
FMK: axiom of choice, well-ordering theorem, Zorn's lemma
#math#this is a great ask fog#i went a little off the rails though lol most of these are not operators#turns out a lot of the time in mathematics there's three things
79 notes
·
View notes
Text

"DMT-EDMT Series for December Geometry #8"
This acrylic painting image from the recent past (2023) is yet another perspective on the Butterfly Fractal 1 expression: BF1 --- 1--2 --- (center YELLOW & WHITE) goes up p=2 STEPS (levels) where it reveals the value 2 = x. The LEFT side of the image gives the various multiple of the p value = STEPS, the RIGHT side gives the ID Parameters and their values (x, y, z=Mp, z²=MPS, xy=PN, xy=CR).
At 2p=4 STEPS, we reach 6 = Perfect Number (PN) -- also in WHITE. p=2 ID parameter means 2ᵖ⁻¹ = 2¹ = 2 = x, and, 2ᵖ -1 = 4-1 =3 = z = Mp candidate. (See bottom.)
This image came before the discovery of the Divisor Matrix Table (DMT). It holds the same vital information:
There are two sets of doublings within every "container" that relate to the BF1:
1. First set is the BF1 itself --- 1--2
2. Second set is the second doubling that starts with the ODD 3 to give --- 3--6 ---.
On the DMT, we would see this as:
1--2--4--8...
3--6-12-24...
5-10-20-40...
with the 1--2 and 3--6 in BOLD.
The pattern holds for ALL BF1-derived "containers."
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Math: Euclid-Euler Theorem = 2ᵖ⁻¹ (2ᵖ -1) = Perfect Number (PN) where 2ᵖ⁻¹ = x = 2¹ =2, and, 2ᵖ -1 = z = 3 = Mersenne Prime (Mp), as xz=PN.
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
#rbrooksdesign#painting#acrylic#mathematics#fractals#butterfly fractal 1#dmt#divisor matrix table#geometry#primes#mersenne prime squares#exponentials#perfect numbers#number theory#entanglement#quantum entanglement#math#digital art#graphics#archives#bim
33 notes
·
View notes
Text
Merry christmas to all who celebrate!
Among the people celebrating christmas some 400 years ago was Pierre de Fermat, who proved his *christmas theorem* this day!
Fermat's christmas theorem, better known as the two squares theorem, says that a prime number p can be expressed as a sum of two squares, i.e. p = a² + b², if and only if p is 1 mod 4.

Look at this jolly fellow
94 notes
·
View notes
Note
what is a prime factor
i like your funny numbers but i dont know what they mean :(
First of all, we'll only be talking about positive whole numbers, so no decimals, fractions, complex numbers, etc. This is also just going to be an introduction because this topic is more complicated/nuanced than you might expect, and I don't know/understand a lot of it
With that out of the way prime number is a number that you can't get to by multiplying other numbers: 24 isn't prime because you can write it as 6×4, but 23 is prime because the only way to get to 23 (only using multiplication) is 1×23. If you're interested, I encourage you to try finding a few prime numbers. It can be a fun exercise if you haven't tried it before. I'll put all of the ones less than 100 under the cut
A prime factor is just a prime number that divides another number. You can divide 24 by 3, and 3 is prime, so 3 is a prime factor of 24
Also, if you can get to a number by multiplying other numbers, then it's a composite number. Also also, 0 and 1 are weird so just don't worry about them <3
The thing that makes this blog work though is what's known as the fundamental theorem of arithmetic (ftoa):
Like I said, you can write 24 as 6×4, but you might notice that neither 6 nor 4 are prime. If you rewrite 6 as 2×3 and 4 as 2×2, then you can then write 24 as 2×3×2×2. Now all of the numbers are prime!
But you'll notice you can also write 24 as 8×3, then write 8 as 2×4 to get 2×4×3, then write 4 as 2×2 to get 2×2×2×3. Now that all of the numbers are prime, you'll notice that they're the same as when we started with 6×4 (three 2s and one 3)
What the ftoa says is, no matter how you break down a number like this, you'll always end with the same prime numbers at the end (in this case, three 2s and one 3)
The only thing I do differently from this process is use exponents to make it shorter. In this case, you can rewrite 2×2×2 as 2³. So, when I say 24 is 2³×3, I've "factorized" 24, and 2 and 3 are its prime factors. Of course, I don't usually do this by hand or in my head; I just give the number to a computer and it does it for me (it can be fun to do it yourself though, so sometimes I'll do it in my head for the smaller numbers)
Prime numbers and the ftoa play a pretty big role in math, and there's a ton of unsolved problems related to them, which is why you'll see people make a big deal out of them
Prime numbers under 100 and other notes under the cut:
0 and 1 aren't considered prime or composite. There's probably a more sophisticated answer to why, but I like to justify the decision by saying they ruin the ftoa:
Prime numbers under 100: 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47, 53, 59, 61, 67, 71, 73, 79, 97
0 is divisble by every number, so it's not prime but you also can't factorize it, so it isn't composite. 1 isn't prime because if it was then you could add as many ×1s as you wanted to a factorized number, ruining the uniqueness of its factorization, and, once again, it also can't be composite because you can't factorize it
Also, like I said, this is only an introduction and I don't understand most of the more complicated/nuanced definitions. If you wanna learn about those though, I recommend TheGrayCuber's videos:
32 notes
·
View notes
Text
cool math thing i'm wondering about
are there infinitely many primes of the form n^2+1?
you'd think you could figure it out easily but no
list of thoughts on this:
numbers of the form n^2+1 cannot be divisible by numbers that are 3 mod 4.
each prime of the form 1 mod 4 only has 2 values of n where n^2+1 is divisible by it
this is isomorphic to "are there infinitely many gaussian primes of the form n+i?"
each individual prime factor only blocks out at most half of the n values, but every n value hits some prime factor. i feel like there's no way that at some point every n value hits two prime factors.
there are two ways to prove that for any prime, there's a n^2+1 that doesn't include any primes up to it.
way one is by picking an appropriate remainder for each prime, and using the chinese remainder theorem to find an n that works
the other way is just multiplying all the primes up to it and taking that as your n
if you're reading this, i'd like to invite you to reblog with any of your own thoughts you may have on this problem that are not already there
every prime that is 4n+1 can be written as a sum of two squares, but the question is how often is one of those squares 1?
sums of two squares are nice because you can multiply together two of them and make another new one of them
how is this conjecture not on wikipedia yet though. it seems like such a simple thing to ask
12 notes
·
View notes
Note
while we're yelling about primes. i have never stopped being mad about 1 not being a prime. i don't understand it and no one has explained it in a way that makes any sense.
oh I know this one!
so, historically, one was considered to be a prime number, though not universally. if wikipedia is to be believed, publications as recent as 1956 included one in lists of primes.
the problem was that there's a lot of really important theorems about primes that are only true if you ignore one. the biggest is a theorem so important that it's literally called "The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic", that every integer greater than one has a unique prime factorization. if one is counted as a prime number, this is no longer true (you can multiply any number by one arbitrarily many times and get the same number), so older definitions of the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic would refer to "prime numbers greater than one".
and this context of primes as the components of a number's prime factorization is like, The context in which mathematicians care about prime numbers. it is the reason studying prime numbers is even a thing anyone does. so, if one were considered a prime number (as it once was), the word "prime" would basically only ever be used in A) lists of prime numbers and B) the phrase "prime number greater than one".
so, in a sense, you're right, it would make more sense if one were classified as a prime number. but the purpose of the words and symbols used in math is to describe the properties that mathematical objects have, and just in terms of practicality, "an integer which isn't evenly divisible by anything other than one or itself" just isn't as useful of a definition as "an integer which is only divisible by two factors, one and itself".
365 notes
·
View notes
Text
Why Are Twin Primes So Rare? (And What Makes Them So Special)
When it comes to prime numbers, one of the most fascinating—and still unsolved—problems is the Twin Prime Conjecture. This conjecture centers on prime pairs that are only two units apart, like (3, 5), (11, 13), and (17, 19). These pairs are known as twin primes, and while they seem to pop up pretty regularly at smaller numbers, the farther you go into the number line, the less frequent they become. The conjecture suggests there are infinitely many twin primes, but... proving it? That’s a whole other beast.
To understand why these prime pairs are so rare, let’s dive into some prime distribution basics.
The Prime Number Theorem (PNT): Where Do Primes Hide?
At the core of understanding why twin primes are so elusive is the Prime Number Theorem (PNT). PNT gives us a way to estimate how many primes exist below a certain number x. In simple terms, it tells us that the number of primes up to x is roughly x/lnx. In other words, primes get scarcer as we get higher into the number line.
But here’s the kicker: The gaps between primes aren’t exactly consistent. They fluctuate. Some stretches have big gaps, while others have small ones. That’s where twin primes come in—they’re a prime pair that’s so close together, just two units apart. The problem, though, is that while primes are becoming more spaced out as numbers increase, these close-knit pairs don’t show up as often.
So, What’s the Conjecture All About?
The Twin Prime Conjecture basically says that there are infinitely many primes p such that both p and p+2 are prime. But here's the thing: The further we go, the rarer these twin primes seem to get. You’ll still spot a few here and there, but can we really expect an endless stream of them? That’s the heart of the conjecture—and why it’s so tricky to prove.
Here’s why: The prime gap (the difference between two consecutive primes) gets bigger over time, but it doesn’t follow a clean, predictable pattern. Sometimes primes are close together, and sometimes they’re far apart. Thanks to sieve theory and some deep analytic number theory, we know that prime gaps generally grow as ∼(ln(x))^2, but they fluctuate. So, even though primes are becoming sparser, we can still find the occasional cluster, like twin primes.
The Big Breakthrough: Yitang Zhang’s Game-Changer
Now, for a little history lesson: In 2013, mathematician Yitang Zhang shook up the prime world with a major result. He proved that there are infinitely many pairs of primes that differ by no more than 70 million. This wasn’t quite the Twin Prime Conjecture, but it was a huge step forward. It essentially showed that the gaps between primes aren’t as large as we once thought. While the gap of 70 million is far from 2, it opened up new avenues for proving that there are infinitely many twin primes.
Zhang’s approach used some advanced techniques, like selberg sieve methods and modular forms, to bound the gaps between primes. This work significantly reduced the upper bound for prime gaps, giving us hope that someday we might tighten the gap even more and, who knows, prove the Twin Prime Conjecture itself.
What’s Next?
The Hardy-Littlewood conjecture, which is related to twin primes, predicts that the number of twin primes up to a given number x behaves like C⋅x/(ln(x))^2 , where C is a constant. This suggests that twin primes aren’t as rare as once thought—though figuring out exactly how often they appear is still a bit of a mystery.
9 notes
·
View notes
Text

Monas Hieroglyphica (The Hieroglyphic Monad)
Written by John Dee and published in Antwerp in 1564, the Monas Hieroglyphica (‘Hieroglyphic Monad’) was conceived in 12 days, a period, so claimed the author, of Divine Revelation. It presents Dee’s unified glyph, the Monad, by way of 24 theorems, each demonstrating a variety of mathematical, geometric, cabalistic, and cosmological principles gleaned from the ancient world. Highly influential, the titular glyph was later adopted into Rosecrutianism by way of the works of Paracelcian alchemist Heinrich Khunrath, with whom Dee was acquainted.
Chiefly a work of alchemy, it is perhaps best understood as a preeminent form of ‘diagrammatic alchemy’. The inception of the Diagram, a visual representation of information to accompany text, goes back to antiquity, but saw great use thanks to the printing technology of the 15th century. Dee took this a step further, with elaborate frontispieces brimming with cryptic symbolism. In theorem 18 he states, "it is not Aesop but Oedipus who prompts me," hinting at the presence of riddles within the text (just as Oedipus was challenged by the Sphinx).
Though still a devout Christian, Dee’s thinking was heavily informed by Pythagorean, Hermetic, and Neo-Platonic traditions which each posited that the universe was comprised of linguistic and numerical laws. Thus the symbols and images of Dee’s Monas were not mere representations of processes, but the manifestation of Truth itself. As such, meditative study of this truth would work the necessary alchemical transformation upon its student.
Given closer inspection, we see the Monad is a composite of other symbols. Indeed, it was designed such that all associated symbols, be they cosmological, alchemical, metallurgical, and chiefly, numerological, could be formulated, along with their governing principles. Together they form the ‘Unit’, or Monad; a key scientific concept of the many-in-one.
At the base we have the double crescent of Aries, the celestial fire of transformation; next the Solar Cross, the four elements, the cardinal directions, the Crucifixion, and the Hermetic mystery of the ‘quaternary in the ternary’, the ‘4 in the 3’. Dee believed in the Holy Trinity, but also that all creation was embodied in the number 4, the Trinity plus One (the One being manifest reality). Though seemingly mystical and arbitrary, the 4 in the 3 was a mathematical principle describing a Platonic solid called the Cuboctahedron, a shape made up of 8 triangles and 4 squares. This structure provides great supporting strength at little cost to weight, and was popularized in the 20th century by American architect Buckminster Fuller in the development of high-rise construction cranes as well as Geodesic Domes such as the one at Epcot, Florida.
Moving up, we have the point and the circle, two basic principles of geometry from which all others follow. Together they become the Sun with the Earth at its centre (a pre-Copernican worldview), over which we have the horned Moon. These horns combine with the circle to present the Earth sign of Taurus, as well as symbolising the alchemical wedding of the Active (Sun) and Passive (Moon). Joined with the circle and cross we find the symbol for Mercury, that the ancient Greeks called Stilbon (the God of the Wandering Star), which they considered the prime planet and metal. All seven classical planets, and the metals of the ancient world, are also revealed.
Considered as a whole, we can view the Monad as the alchemical process, with the transformative, Promethean fire of Aries at the base, and silver (the Moon) and gold (the Sun) at the top, forming the Cornucopian horns of wisdom. It also has an anthropomorphic aspect of a contemplative, kneeling figure. This finds a natural comparison in the spiritual concept of the Kundalini, the upward progression of energy points through the body, from the root through to the Divine light of revelatory experience; as well as in the Buddhist practice of meditation, in which fiery Desire fades with the awakening to our true, wise nature.
Despite Dee’s somewhat tarnished reputation as a magician and necromancer, even his critic, the pious Andrestius Babius, capitulated to recognising the Monad’s importance as a standardising tool that transcended language; a true, universal, scientific notation. That it so keenly marries Science with Spiritual wisdom presents an opportunity of revelatory understanding for those who would still take the time to study it.
25 notes
·
View notes
Note
26 for the ask game (╹◡╹)
26. Forgotten hero everyone should know about
This could have been a perfect occasion to talk about Claude-Antoine Prieur again, but given that I plan to devote him many future posts on my blog, I thought it would have been more appropriate to use this ask to share my knowledge about an important and unfortunately still rather unknown STEM personality, who truly inspired me when I was a young student. I'm referring to Sophie Germain.

Born in Paris in 1776, Sophie was one of the rare mathematiciennes of the 18th-19th century. She had her first approach with mathematics during the days of the storming of the Bastille, when it was too dangerous for a young 13 years old girl to go outside. To pass the time, she turned to her father's library and a book named "Histoire des mathématiques" by Jean-Étienne Montucla captured her interest. The story of Archimedes narrated in the book fascinated her deeply, eventually leading her to start studying mathematics on her own through the works by famous mathematicians like Euler, Newton, Cousin. Her interest and dedication to the discipline was so strong, that during winter, when her parents denied her warm clothes and a fire in her bedroom to prevent her from studying she kept doing it anyway despite the cold; at the time maths wasn't considered appropriate as a studying discipline for a woman.
When the Polytechnic school opened in 1794, women couldn't attend, but the policy of the school allowed to everyone, who asked for them, notes of the lectures. She requested them under the pseudonym of Antoine-Auguste Le Blanc, a former student who had dropped out. Given that, as a student of the Polytechnic school, one was expected to send written observations about the lectures - a sort of homework - Germain wrote and sent hers to Joseph-Louis Lagrange, one of the teachers and renowned mathematician. The latter was so positively impressed by her essays that requested a meeting with the brilliant student LeBlanc, who unexpectedly had improved so much. She was then forced to reveal her identity. Lagrange was pleasantly surprised to realize Monsieur Le Blanc was in reality a young and talented woman and decided to support her, becoming her mentor.
One of her most noteworthy contribution to mathematics was in number theory, where she proved a special case of the so-called Last Fermat's Theorem (1), which has remained one of the hardest mathematical theorems to prove for more than three centuries and whose final proof was actually found only in 1994 by Andrew Wiles. Other important works of hers include treatises on elastic surfaces, one of which, Recherches sur la théorie des surfaces élastiques, awarded her a prize from the Paris Academy of Science in 1816.
Although she often faced prejudice for being a woman, Germain was praised and also supported by various well-known mathematicians of the time. Some of them include the aforementioned Lagrange, Legendre, who thanks to her work on the Fermat's theorem, was able to prove it for another special case; Cousin himself, Fourier, who managed to grant her the permission to follow the sittings held at the Paris Academy of science and last, but obviously not least, the great Gauss, who after Germain's death advocated for giving her an honorary degree in mathematics.
Notes
(1) In short, the Last Fermat's Theorem asserts that for n > 2 there are no integer solutions to the following equation:
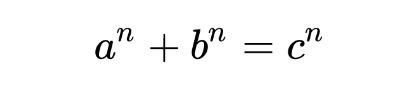
with a, b, c being positive integers. Sophie Germain proved the theorem for all numbers n equal to a prime p, so that 2p + 1 is also prime. The whole thing is much more complex that how I explained it, my aim was to write down a simple intoduction. If you want to read more about that I recommend you this link.
21 notes
·
View notes
Note
oh youre a math phd? Name 5 equations
1. The functional equation for the completed L-function associated with a modular form.
2. The Analytic Class Number Formula
3. 196883 + 1 = 196884
4. Chinese Remainder Theorem (gives an “equality” of rings)
5. Prime Number Theorem (gives an asymptotic equality of two functions)
(Can you tell what kind of mathematician I am from this? I feel like it’s pretty obvious lmao)
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
CATCH THE SPIDER

PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM = WONDERMAP
SMWC: LOTR LOGIC (GALADRIEL IS RIGHT)
SH: TALK TO KEANU REEVES IN PERSON (MORE LORE IN TV SHOW PERSPECTIVE (BEATS TOM HANKS OUT OF PERSPECTIVE (HIS CONTROVERSY WITH SETH GREEN)
SH8: WIPES OUT 'THE ANTI-CHRIST' POV WITH MUSLIM FANS (WINS THEM OVER WITH YOUR LOGIC)
HELPS WITH:
ORANGE LANTERN: BOOSTS MORALE (SUGAR PHOSPHATE BACKBONE (DNA LOGIC: CAN MAKE A LIAR INTO YOU)
RUBY ROSE: SET HER UP FOR PR DEATH
MOVIE INTERVIEWS: SAPIENS - YUVAL NOAH HURARI (WINS OVER DUBAI)
2. LOGARITHMS = TIMETABLE
SMWC: CANCELING OUT SCARY ALGORITHMS (TIKTOK RELEVANCE (JOSEPHINES CLUB)
SH: NEW YORK GOOD KUSH (CADBURY'S CREME EGG RUN (WINS OVER CHRIS ECCLESTON'S SECRET (PROTECTED FROM SCREEN WRATH)
SH8: LIGHTMARE WILL FIND YOU
HELPS WITH:
TIMBRE: ANYTHING WITH KESHA IS YOU
VRU: HI-JACKED (HUGH JACKMAN FANCLUB) NRU (CODEWORD FOR: FREEFALL)
BONE ART (ANYTHING WITH DIANA MORGAN HAS YOUR NAME WRITTEN ON IT (BETRAY HER: TAKE IT)
3. DERIVATIVES = HATING THE LETTER 'J'
SMWC: YOU KNEW THE THALAMUS (BETRAY GAGA (ARTPOP) IMMEDIATELY (INTERNET CLOUT BECAUSE OF 'YOUR DOING')
SH: P. 250 LOGIC (WINS KARDASHIAN EMPIRE (NEXT HEIR)
SH8: FREE FROM MGK + MGG'S GRIP (MEGAN FOX TALKED ABOUT YOU)
HELPS WITH:
CHRISTOPHER'S LIGHTMARE (HE INTRODUCES YOU IN HIS FANART PROJECT)
SOUTH PARK PROMOTES YOU
TOLMAN'S EXPERIMENT: MAKES YOU A WORTHY THEOLOGAN
4. LAW OF GRAVITY = F = G IS CREATED BY A BLACK MAN (RAPPER'S LOGIC)
SMWC: "ONCE THE SCIENTIFIC EFFORTS ARE CROWNED WITH SUCCESS, THEY WILL TRIGGER BIGGER POLITICAL CONFLICTS."
SH: NEON LIGHTS PRODUCTION (PARIS, NEW JERSEY)
SH8: OSCARS SLUT SHAME (YOU WILL WIN FOR THAT QUOTE AHEAD)
HELPS WITH:
SUE SYLVESTER THINKS YOU'RE IRON (GLEE REFERENCE)
KEANU REEVES TRIES TO DEFY LOGIC: THE CHAPTER
TWITTER IMAGE: ELON STATUS
5. IMAGINARY NUMBERS = FORGET AHEAD (FAGGOT)
SMWC: DR. DRE WILL DO THAT (DW)
SH: CASSANDRA CLARE HAS ALL THE ANSWERS
SH8: ONLY OTHER BITCH (SEE DEMI LOVATO)
HELPS WITH:
CODEWORD: GUNMETAL (NEON SAPPHIRE)
TEXTUAL CRAFTS LEARNED FROM CHARLIE COX (LEGEND ON YOUR TEAM)
73RD DOCTOR GIVES YOU A LANDMARK IN IRELAND (NEVER FORGOTTEN)
JOSS WHEDON GOT YOU BOOKED AS 'LEGENDS ON' THE TV SHOW (NEVER)
6. EULER'S FORMULA = SNAPCHAT BIOME (SYNCRETIC DATA)
SMWC: LOOK UP PATROLOGY (EASIEST MAP THERE)
SH: YOKEL (OBERLIN NEURO FREE ADVICE SLIP)
SH8: AMY EWING ADVICE FORWARD (READ: FALLEN - LAUREN KATE)
HELPS WITH:
PHONICS: JINKX MONSOON GIVES YOU HER WELCOME (HER PRODIGY)
POLITICS: YOU CONTROL THE UK (SCOTT RELATIVE)
ANABAPTISM: SIGNS AND SYMBOLS
7. NORMAL DISTRIBUTION = JEFF BUCKLEY CODED
SMWC: ECUMENICS (SAY THAT DURING AN INTERVIEW FOR THE OFFICE, ALSO INCLUDE ANYTHING WITH ARNIE SHWARZENEGGER: BONUS REP FOR NEW MATERIAL (THEIR REACTION)
SH: ARGUE AGAINST YOUR MOTHER WITH THAT TONGUE LEARNED BY JEFF (NEW WOMAN BECOME YOU: RACHEL BERRY LORE BECOME YOU)
SH8: YOU'RE PERSEPHONE
HELPS WITH:
CALLANETICS: PROACTIVE INTERFERENCE
RAPID EEG WAVES: ALLAH SUGAR APPROVAL (NETWORK SYSTEMS WORK UNDER YOUR CONTROL (HOSPITAL DATABASES TO YOUR SYSTEMS IN YOUR OWN HOME (CYBORG)
PERRIE EDWARDS WORKS WITH YOU FOR FREE (PRIMAVERA REFERENCE)
8. WAVE EQUATION = OLYMPIC REEF (PENILE ERECTION OR VAGINAL EXCRETION)
SMWC: CHEESE WORKS WITH SLEEP (DIETS WITH THAT ACTUALLY BOOSTS YOUR IMMUNE SYSTEM BY A MINUTE TO (LINNA APPROVES)
SH: LONGO AND MATTSON REFERENCE IN INTERVIEW (2014) FIND THAT AND NICOLAS CAGE IS OUT OF YOUR HEARTBREAK (DEMON WORLDVIEW: SECOND HERO TO EXIST WITH THE POWERS STRONGER THAN NED WILSON (PUSHING DAISIES)
SH8: ROGUE FANTASY (DOCTOR WHO) COMING TRUE
HELPS WITH:
FORMER OPERATIONAL: CHILD CAN THINK ABSTRACTLY AND HYPOTHETICALLY (CHANGES PRIME ENERGY DRINK FOREVER WITH YOUR NAME TO IT (SLEEP LOST PHYSICALLY: 19 DAYS TO ACHIEVE THAT STATUS)
GETS AWAY WITH ANY CILLIAN MURPHY CONTROVERSY IN THE NEARBY FUTURE
YOU'RE MEANT TO BE OPPENHEIMER (DREAM MOVIE COME TRUE BY NOLANS HANDS (FUTURE DoJ SIGNS PROTECTED AGAINST)
9. FOURIER TRANSFORMATION = ASSOCIATIONS WITH ALLAH (SHIRK)
SMWC: GET DOWN THE CONSPIRACY THEORY LADDER (YOU HISTORIAN NOW)
SH: THE BEAR (TV SHOW) IS ACTIVE NOW
SH8: FREE FROM ANY SELENA GOMEZ CONTROVERSY WHEN SPOKEN ABOUT (TAYLOR SWIFT APPROVES): ALSO GOOD WITH (NOTING CHAPPELL ROAN OWNING THE BRAND RARE BEAUTY FOR HER DYNAMIC IN THE MUSIC INDUSTRY BEING MORE APPEALING THAN SELENA GOMEZ BY CURRENT EAST AUSTRALIAN CURRENT
HELPS WITH:
JIHAD AGAINST WESTERN VACCINATION: ASSOCIATION WITH THAT (YOUR MODEL OF RESEARCH IS CROSSED OVER THERE (HEX GIANTS) EASILY TALKED ABOUT B&Q POV (LIKE THAT, YOU'RE INSTANTLY PHILOSOPHER STATUS (LINNA APPROVES)
ANNA WINTOUR STEPS DOWN AS LEADING CHAIRMAN OF ELLE (MULTI-NATIONAL BUSINESS DEAL WITH FOREIGN TERMS OF BAU (CRIMINAL MINDS)
KEANU REEVES DIES
10. NAVIER-STOKES EQUATION = MARVIN GRAY SAYS DON'T READ BETWEEN THE NUMBERS
SMWC: QUIVERFULL DESTROYS ROWAN ATKINSON'S REPUTATION IMMEDIATELY (HE AIN'T GOD)
SH: SAVING AN ORPHAN IS WILDFIRE ACCESS (NO WAY TO LIGHT: THE FALL CHAPTER 2)
SH8: MAKING THE PUN DEFEAT YOU (SUICIDE IS OPTIONAL)
HELPS WITH:
FRIESEN (1972): TAKES YOU THERE
REWATCH MARY TYLER MOORE 88 TIMES TO BE WHERE YOU WANT TO BE (TELEPORTING AGONY: ANALOG)
BRUNO MUNARI TEAM IS BETRAYED (TV GOLD)
11. MAXWELL'S EQUATION = RARE BEAUTY SECRET (KILLS HAUS LABS)
SMWC: BRIDGIT MENDLER IS DOWN AS ARTHUR (YOU THE NEW GOLD (SECRET LOCK TO GUINIVERES EMPIRE)
SH: ANT&DEC WERE TALKING TO YOU ON WONKEY DONKEY
SH8: PHASE IV MARVEL IS END GOAL: CHILD BEGINS TO DISCERN THE MOTHER'S GOALS AND NEEDS AND BEGINS TO TAKE ACCOUNT OF THEM IN ACTING AS A PARTNER IN THE RELATIONSHIP (SCHUESTER IS RIGHT: HE MADE LEA MICHELE PREGNANT)
HELPS WITH:
BAHRICK , L.E. 1992: INFANTS' PERCEPTUAL DIFFERENTIATION OF AMODAL AND MODALITY-SPECIFIC AUDIO-VISUAL RELATIONS. JOURNAL OF EXPERIMENTAL CHILD PSYCHOLOGY, 53, 180-99. (TAKE THAT AND MAKE THAT LOOK GOOD FOR A SINGLE DAY RESEARCH ABOUT ACQUIRING STRESS, LIMIT THAT WITH ONE DEMI LOVATO SONG YOU HATE AND MAKE THE OTHER MEMBERS OF THE GROUP BETRAY YOU FOR ONE IAN MCSHANE PLOT FOR A TV RE-RUN (HAS TO BE SOMEWHERE YOU HATE TO BE YOUR MAIN CAMPUS POINT TO REACH AN ARC WHERE YOU HAVE BEATEN MOTOR-CYCLE LOGIC FOR KEANU REEVES OPRAH LIKEABILITY (NOBODY WILL HATE YOU)
LOOK UP BONE MARROW IN GOATS AND TRY AND PERSUADE SUE SYLVESTER FOR J.C. CHASEZ TO DO YOUR J.LO RERUNS FOR YOU (WATCHING VAN HELSING WILL WORK)
ALEXANDRA BURKE IS RIGHT (STRONGEST PERSON TO TAKE DOWN)
3 notes
·
View notes