#particularly in the global north
Text
also people talking about how few third spaces men have.... look around you. how many third spaces do any of us have? for every demographic you can think of, there are complaints about the lack of third spaces. think about how often this comes up in reference to teenagers, to queer people, to young families, etc etc etc. what this tells me is that it simply is not a demographic problem. it's a capitalism problem. that doesn't mean it's not a problem. it absolutely is! but you cannot say with a straight face that men are suffering from a lack of third spaces as if this is a problem unique to men. and the fact that this is yet another conversation that has come to centre men and men's feelings. well. that really says something about the value we place on men's problems as compared to. literally anyone else. lol
and before anyone starts with TERF shit: this post is covered in trans cooties fuck off
#annoyed by people acting like men uniquely suffer from capitalism#the ability to believe that your problems are unique is a form of privilege. btw#abled cishet white men have the privilege to believe that when they encounter a problem they are the first to encounter it#particularly in the global north#think about the way USAmericans talk about America Problems as if nobody else in the world has ever experienced those problems before#well. it's that. but for every dimension of privilege you can think of
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
South Africa’s genocide case has put the spotlight on a deeper fault line in global geopolitics. Beyond the courtroom drama, experts say divisions over the war in Gaza symbolize a widening gap between Israel and its traditional Western allies, notably the United States and Europe, and a group of nations known as the Global South — countries located primarily in the southern hemisphere, often characterized by lower income levels and developing economies.
Reactions from the Global North to the ICJ case have been mixed. While some nations have maintained a cautious diplomatic stance, others, particularly Israel’s staunchest allies in the West, have criticized South Africa’s move.
The US has stood by Israel through the war by continuing to ship arms to it, opposing a ceasefire, and vetoing many UN Security Council resolutions that aimed to bring a halt to the fighting. The Biden administration has rubbished the claim that Israel is committing genocide as “meritless,” while the UK has refused to back South Africa.[...]
As a nation whose history is rooted in overcoming apartheid, South Africa’s move carries symbolic weight that has resonated with other nations in the developing world, many of whom have faced the burden of oppression and colonialism from Western powers.
Nelson Mandela, the face of the anti-apartheid movement, was a staunch supporter of the Palestine Liberation Organization and its leader Yasser Arafat, saying in 1990: “We align ourselves with the PLO because, akin to our struggle, they advocate for the right of self-determination.”
Hugh Lovatt, a senior policy fellow with the Middle East and North Africa Programme at the European Council on Foreign Relations, said that while South Africa’s case is a continuation of its long-standing pro-Palestinian sympathies, the countries that have rallied behind it show deeper frustrations by the Global South.
There is “a clear geopolitical context in which many countries from the Global South have been increasingly critical over what they see as a lack of Western pressure on Israel to prevent such a large-scale loss of life in Gaza and its double standards when it comes to international law,” Lovatt told CNN.
Much of the non-Western world opposes the war in Gaza; China has joined the 22-member Arab League in calling for a ceasefire, while several Latin American nations have expelled Israeli diplomats in protest, and several Asian and African countries have joined Muslim and Arab nations in backing South Africa’s case against Israel at the ICJ.
For many in the developing world, the ICJ case has become a focal point for questioning the moral authority of the West and what is seen as the hypocrisy of the world’s most powerful nations and their unwillingness to hold Israel to account. [...]
Israel sided with the West against Soviet-backed Arab regimes during the Cold War, and Western countries largely view it “as a fellow member of the liberal democratic club,” he added.[...]
“But the strong support of Western governments is increasingly at odds with the attitudes of Western publics which continue to shift away from Israel,” Lovatt said.
Israel has framed the war in Gaza as a clash of civilizations where it is acting as the guardian of Western values that it says are facing an existential threat.
“This war is a war that is not only between Israel and Hamas,” Israeli President Isaac Herzog told MSNBC in December. “It’s a war that is intended – really, truly – to save Western civilization, to save the values of Western civilization.”
So far, no Western countries have supported South Africa’s case against Israel.
Among Western states, Germany has been one of the most vocal supporters of Israel’s campaign in Gaza. The German government has said it “expressly rejects” allegations that Israel is committing genocide in Gaza and that it plans to intervene as a third party on its behalf at the ICJ.
An opinion poll by German broadcaster ZDF this week however found that 61% of Germans do not consider Israel’s military operation in the Gaza Strip as justified in light of the civilian casualties. Only 25% voiced support for Israel’s offensive.
But it is in Germany’s former colonial territory, Namibia, that it has attracted the fiercest criticism.
The Namibian President Hage Geingob in a statement on Saturday chided Berlin’s decision to reject the ICJ case, accusing it of committing “the first genocide of the 20th century in 1904-1908, in which tens of thousands of innocent Namibians died in the most inhumane and brutal conditions.” The statement added that the German government had not yet fully atoned for the killings.
Bangladesh, where up to three million people were killed during the country’s war of independence from Pakistan in the 1970s, has gone a step further to file a declaration of intervention in the ICJ case to back South Africa’s claims, according to the Dhaka Tribune.
A declaration of intervention allows a state that is not party to the proceedings to present its observations to the court.
“With Germany siding with Israel, and Bangladesh and Namibia backing South Africa at the ICJ, the geopolitical divide between the Global South and the West appears to be deepening,” Lovatt said.
Traditionally, the West has wielded significant influence in international affairs, but South Africa’s move signals a growing assertiveness among Global South nations that threatens the status quo, says Adekoya.
“One clear pattern emerging is that the old Western-dominated order is increasingly being challenged, a situation likely to only further intensify as the West loses its once unassailably dominant economic position,” Adekoya said.
19 Jan 24
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
A group of journalists held a public appeal yesterday for an end to Israel’s siege of the northern Gaza Strip, where practically no food aid has entered since October 2023. People in the north are living and dying in famine due to the complete blockade by the IOF.
To make matters worse, most mainstream media outlets are ignoring the plight of north Gaza, as the journalists and other people remaining in the north are predominantly Arabic-speaking. The north of Gaza is starving in silence.
Instagram user faridaek has been kind enough to repost the appeal with English subtitles added. This is a significant undertaking that we greatly appreciate, and we ask everyone with an Instagram account to share the video.
The journalist speaking is Islam Bader. He and his colleagues are making this appeal on behalf of the people of northern Gaza. The journalists present include Abed Alqadr Sabbah, Mahmoud Al-Awadia, Momin Abu Owda, Mahmoud Sabbah, Mahmoud El-Shareef, Anas Al-Sharif, Islam Bader, Mohammed Ahmed, and Fadi Al-Whidi, among others. The subtitles read
From the north of the Gaza Strip, we, as journalists still stationed here in the north stand today driven by our ethical responsibility and national duty as a voice for all those who remain steadfast in Gaza and its north who are being subjected to a policy of extermination and a policy of starvation which is no less than extermination. The markets have been emptied of all essentials, and there is no flour available except in rare instances. The occupation does not allow aid to enter, maintaining its obstinate siege against our people and our families. We are of this people, and today we speak for Palestinians, for the besieged and for those denied life’s essentials. The most basic necessities have now become extremely rare in Gaza.
Therefore, we issue this call as a final warning, about a severe famine that is unprecedented on a global scale and impacting all facets of life, particularly children, individuals with chronic conditions and society’s most vulnerable groups. We hold the Israeli occupation and the international community especially the United States responsible for this starvation because it is happening in front of the eyes and ears of the entire world without any concrete action [on the ground] to stop it. The occupation’s claims of aid delivery are deceptive and unfounded. In reality, nothing has entered the north of the Gaza Strip.
Therefore, this final call, on behalf of all these people, on behalf of our fellow journalists, on behalf of our families and on behalf of Palestinians and the displaced in the north of the Gaza Strip is for the world to uphold its responsibility. North Gaza is starving, and this famine must be stopped.
Source: Islam Bader et al via faridaek on Instagram
instagram
#north gaza#gaza#gaza genocide#gaza strip#gaza under attack#free gaza#from the river to the sea palestine will be free#palestinian genocide#gaza journalists#video#islam bader#abed alqadr sabbah#Mahmoud sabbah#Mahmoud al awadia#momin abu owda#Mahmoud el shareef#anas al sharif#mohammed ahmed#fadi al whidi#11 February 2024#10 February 2024#free palestine#free free palestine#save palestine#save gaza#stop genocide#stop the genocide#stop israel#gaza under siege#Instagram
3K notes
·
View notes
Text

stealing this screenshot from a post correcting people about what liminal spaces are, because I want to say something kind of unrelated and don’t want to bother the op - it’s funny this wiki article identifies airports as one of these non-places, and one of the “criteria” for a non-place is somewhere where you are able to remain anonymous, because (at least in north america, I can’t speak globally), one of the primary terrors of airports is its ability to render you a known quantity at basically any time, to bring you into public attention specifically by cops and security people identifying who you are. Airport security, bag inspections, police, surveillance cameras, etc do this security theatre routine at airports in a way that is more intense than other public spaces. Like I just don’t think this state of remaining anonymous in the airport applies to muslims or other religious and racial minorities the state deems to be a “high risk population” vis a vis border security, I think if you want to make the argument that these places allow anonymity, a fundamental part of this analysis has to include the fact that this anonymity is premised on visiting state violence, surveillance, and coercion on largely non-white and religious minorities, particularly and especially muslims, to “protect” and secure this space of (largely white) public anonymity
#the guy who coined it is a white French anthropologist so . well actually I don’t need to say anything else#book club#not really I’m reacting to a partial summary of a Wikipedia page this is kind of a fish in a barrel situation#geography#<- for place discussion
1K notes
·
View notes
Text

Submissions open through June 30, 2024 - Mad Dykes, Queer Worlds
Hello all! I'm editing a special issue of the literary magazine Sinister Wisdom titled Mad Dykes, Queer Worlds. If you're Mad –– regardless of personal label or diagnostic status –– and identify with some aspect of dyke experience (in all its multiplicities!), I want to consider your work for publication.
The title links to Submittable, the platform Sinister Wisdom (and most other magazines) use to process submissions. It's free to use, but can be inaccessible for visually disabled people. If that's you, email Sinister Wisdom for alternative submission options.
I am particularly interested in reading work by young/new/emerging creatives, survivors of psychiatric/medical incarceration, and/or those living outside the Global North/West. Visual art and written work are all welcome!
Note: Sinister Wisdom can't pay $; they compensate in a year-long print subscription and complementary copies of the journal. If you only submit to magazines that pay, consider checking out mine, manywor(l)ds.place; we reopen for general submissions June 1.
Feel free to email me with any further questions. Don't self-reject. ID for the image both in the alt text and below the cut.
Mad Dykes, Queer Worlds
What is Madness, and how do we, as lesbian/queer creatives, wield it? Amid much feminist discourse around the figure of the “madwoman,” mostly as an archetype to be avoided or, in some instances, appropriated, in reaction to rational distress under violently cisheteropatriarchal conditions, comparatively little discussion has focused on the lived experience of psychiatric survivorship, iatrogenic harm, and abuse under the sign of “mental illness” or psychiatric disability. Behind and beyond the figure of the madwoman, or the specter of “hysteria,” are the lived (sur)realities of Madpeople of all marginalized genders.
This issue of Sinister Wisdom seeks contributions by lesbian, queer, and/or trans people self-identified as Mad, mentally disabled, and/or psychiatric survivors. Following the portmanteaue coinages “transMad” (Cavar), “neuroqueer” (Walker, Yergeau, and Michaels-Dillon), and “neurotrans” (Smilges), Madness and (gender)queerness are deeply entangled and often inextricable from each other, both as they manifest “inside” us and in our ways of relating to our words, world(s), lovers, and friends.
What, who, and where are Mad dykes, and how do we find each other in a world increasingly oriented toward cisheteronormative, whitewashed wellness? What are the legacies and ongoing violences of queer/trans pathologization in our communities and beyond? How do we live as transMad people amid cissexist, saneist attacks from the reactionary Right? And how do we share, negotiate, or conceal our experiences of trauma, altered realities, and unfamiliar access needs while also building community?
Please submit works of any, all, or no genres, including reviews and interviews, up to 5,000 words, and a short contributor biography between 25 and 125 words. We are also seeking illustrations and photographs (.jpg or .tif files only, print resolution size at least 300 ppi). Please do not send previously published work.
Deadline for submissions: June 30, 2024
-
-
[tagging for spread hopefully! @closet-keys, @rebirthgarments, @fluoresensitive, @heavenlyyshecomes, @trans-axolotl, @fatehbaz @sawasawako @felgueirosa @bioethicists @campgender @candiedsmokedsalmon @sadhoc @osmanthusoolong @boykeats ]
#tia to everyone for sharing!!! i want to get this seen by as many ppl as possible#mine#call for submissions#madness
323 notes
·
View notes
Text
The way environmental justice feels so isolated from other forms of justice pisses me off.
Rising temperatures effect the global South more than anyone. Oil pipelines and their spills effect Indigenous communities the most. The pollution from fast fashion is dumped in Kenya, Uganda, and Tanzania. Bombings like that in Ghazza are causing wild spikes in emissions (and this point is used so that white people may start to care, which sucks, and conservationists still aren't mentioning the Palestinian genocide). The Hawa'ii fires?? The flooding in Brazil right now and previously so Pakistan and so many other places?? Heatwaves. Earthquakes. Tsunamis. Hurricanes. Typhoons. Who do you see being effected by these the most, really? Don't even get me started on how """green technology""" uses slave labor from Congo, whose people and CHILDREN are being forced to mine for battery materials. And nobody—particularly and especially institutions—who fights for the environment ever really mentions this stuff. Because they care more about securing this sanitized idea of climate activism that tries to work with capitalism rather than focusing on intersectionality and solidarty and fighting the system causing the problems.
White and other priveleged people honestly only really care about environmental justice because it has the potential to harm them too. Either that or they feel bad for animals that are more palatable to them than actual people, as mentioned in a prev post I rbed. It's part of the "humans are the virus" eco-fashy sentiment that is frustratingly pervasive. I have been persuaded by that thinking in the past. It's possible to stop it, and you must stop it in yourself. You can care about animals obviously but don't forget people.
My point is. The movement of environmental justice is SO focused on the global North/the West/whatever else u wanna call colonial powers. We have to change that. Care about the people in "far away" countries who are being effected by climate change. Care about people of color and poor people in your communities effected by these things. Care about indigenous people worldwide. Fight for them. Listen to them. And fight against the ruling class that marginalizes and oppresses them. Everyone needs an Earth without colonial & capitalist caused environmental disaster.
#im not apologizing for this post coming from out of the blue this is My House#original post#free congo#free palestine#environmentalism#climate justice#if any1 wants to plug fubdraisers and talk about their own stories pertaining to this pls do so#this isnt worded all that great but whatever. read it anyway.
315 notes
·
View notes
Text
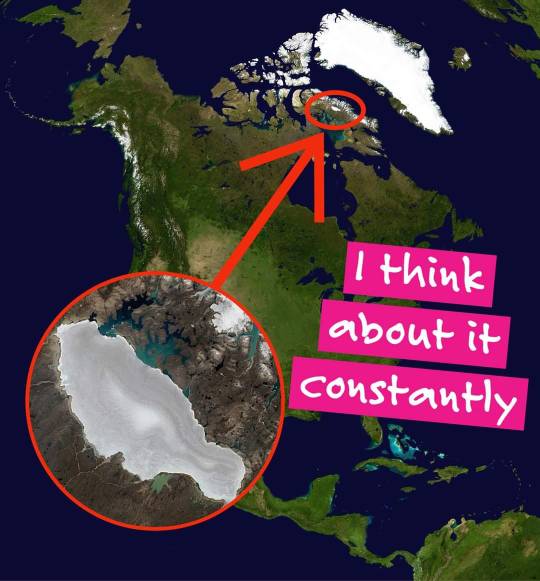
Did you know the “ice age” never completely finished?
By that I mean… you know the ice sheet that grinded Canada down to bedrock? The one that sat a mile high over Boston? The one that dug out the Great Lake basins? The one that pushed deep into North America, forming massive proglacial lakes and changing the courses of river systems?
That ice sheet still exists.
Sort of.
In Inuit territory, on the great island known as Qikiqtaaluk, you can lick the last, ancient icepop left from that continent-sized ice sheet that once smothered North America like a blanket.
Known as the Barnes Ice Cap, it’s the last fragment left of the mighty Laurentide Ice Sheet. And it’s melting FAST.
It will likely outlive me- but not by much. It’s like a 20,000-year-old ice cream cone, and we’ve dropped it on the hot pavement. In our rapidly warming world, it will likely be completely gone within a century or two.
Its contribution to global sea level rise won’t be particularly significant- it’s a rounding error compared to the Antarctic and Greenland ice sheets.
But to me, it’s like some kind of impossibly ancient alabaster tortoise;
a witness of unknown epochs of history;
critically endangered;
the last living of its kind;
doomed to perch up high on its mountain, drooling, panting, feverish, baked by the sun in a carbon blanket;
until it finally expires, leaving only bare rock and gravel for a grave:
no trace left of an ice age that covered a continent.
Found here on Facebook.





160 notes
·
View notes
Text
Things Biden and the Democrats did, this week #4
Feb 2-9 2024
The White House announced that a landmark 23 million Americans, 1 in 6 households, have been connected to affordable high speed internet with the help of the Affordable Connectivity Program, saving Americans between $30 and $75 every month on their internet bill. 4 Million ACP users are seniors, 1/4th of households on the program are African American and 1/4th are Latino, and it supports 320,000 households on Tribal lands. Sadly the program will be forced to end if Republicans in Congress continue to block new funding
The White House announced $5 billion for a National Semiconductor Technology Center, focusing on research and development as well as workforce needs. This is part of an effort under the CHIPS and Science Act to make America a world leader in science and grow jobs for the 21st century. This will include hundreds of millions of dollars of investment in workforce development
The EPA announced finalized rules that will strength air quality standard around fine particle pollution, AKA soot. The new stronger rules are projected to prevent 4,200 premature deaths and save Americans $46 billion in health costs by 2032. Soot is particularly harmful to those with lung and heart illnesses, children and those with asthma. Industrial soot is more common in low income communities
The Department of Transportation announced $1.5 Billion investment in America's bus systems. The bulk of the money will go helping local transport authorities buy low or no emission buses. There will also be investment in bus facilities.
President Biden signed a memorandum directing a strengthening of human rights safe guards around weapons transferred from US stockpiles to allied nations. The directive seeks to guarantee no arms are transferred that might be used to violate human rights.
HHS and HUD announced a join program partnering with 8 states and DC to help streamline an all of government response to homelessness. This is an off shoot of the $3.16 billion dollar investment amounted by HUD last week to end homelessness in America
The Department of Energy and FEMA released the findings of a two year study that projections Puerto Rico will be able to be 100% renewable energy by 2050. DoE also announced that by the end of the 30,000 low income Puerto Ricans will be able to apply for a solar power program, the first investments in a billion dollar DoE program for the island's renewable energy future
Department of Transportation announced $417 million dollar loan to the North Carolina Turnpike Authority to complete a major transportation overhaul in the greater Raleigh area
The EPA and Department of Energy announced a joint plan to invest federal funds to help measure and reduce methane emissions from the oil and gas production. Methane is the second largest green house gas after CO2 and is responsible for 30% of global warming in the last 200 years. This comes after the EPA pushed new rules to fine oil and gas manufacturers for excess methane emissions.
The Senate confirmed 2 more Biden nominated federal judges. This brings the total number of Biden judges to 177 For the first time in history a majority of a President's judicial nominees are not white men, Biden has nominated a majority women and people of color Biden also nominated 4 more federal judges, including two LGBT candidates. If they are confirmed it'll bring Biden's LGBT judge total to 11 tying with President Obama for the most LGBT people put on the federal bench
#Joe Biden#Thanks Biden#democrats#good news#politics#us politics#climate change#climate crisis#public transport#buses#puerto rico#clean energy
376 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Proving that change is possible if the will to create it is present, Chinese megacities like Beijing that were once famous for their apocalyptic grey skies are enjoying the lowest levels of air pollution they’ve experienced in the 21st century.
Falling 42% from an average high in 2013 when Chinese air pollution was higher than 50 particles per cubic centimeters of city air, the change has increased the lifespan of Chinese urbanites by 2.2 years.
The news comes from a report published by the University of Chicago called the Air Quality Life Index which listed some of the actions taken by the Chinese government to reduce air pollution, described by the CCP as a “war on pollution.”
This has included reducing the presence of heavy industry like steel production in city centers, as well as restricting coal power plants from being built inside cities while shuttering those that were already there.
Some cities like Beijing have reduced the number of cars allowed on the roads during peak hours, similar to London’s congestion charge. Lastly, China’s mass urban tree-planting campaigns have been well documented.
While the life expectancy has risen on average 2.2 years, some cities have seen far more drastic increases. Citizens living under the new “Beijing Blue,” are predicted to live 4 additional years, while those 11 million in the north-central city of Baoding are predicted to gain 6.
“At the foundation of those actions were common elements: political will and resources, both human and financial, that reinforced each other,” the report said. “When the public and policymakers have these tools, action becomes much more likely.”
In fact, the decline in China’s pollution levels has been so drastic that it lowered the world average, which the report says would have increased if not for the Middle Kingdom’s war on pollution.
Although Chinese city air is still several times higher than the WHO’s recommended minimum, it shows what’s accomplishable with political and civic effort—particularly to its neighbors in South Asia where the report warns air quality is worsening."
-via Good News Network, September 1, 2023
#china#pollution#air pollution#coal#carbon emissions#pollution reduction#tree planting#beijing#air quality#aqi#life expectancy#asia#south asia#good news#hope#hope posting
803 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hello I am going on a holiday to Eryri next month & I like to read up about an area before going there... do u have any reading or documentary or podcast recs? I'm particularly interested in the ecology & minority language activism & like. Peoples history & rural lives! I know this is stuff u know about in Wales but idk if north Wales is ur region! Míle buiochas ón Eireann!
Fáilte go dtí an Bhreatain Bheag! Or croeso i Gymru. Exciting! Keep an eye on the notes for others chiming in with good recs for documentaries and the like, I'm going to just give a super quick guide
Okay, pronunciation guide for place names and that is here in written form and here in video form. I cannot recommend strongly enough that you try to use the Welsh place names rather than the English translations. Duolingo is flawed but serviceable if you want to hear and learn some basic phrases. If you can at least throw out a 'bore da' to people you pass/shopkeepers, you'll be very well liked. You don't need to be fluent by any means, but Making An Effort is seen as, like, the nicest and politest and most wonderful thing in Wales, and particularly in regions like Eryri.
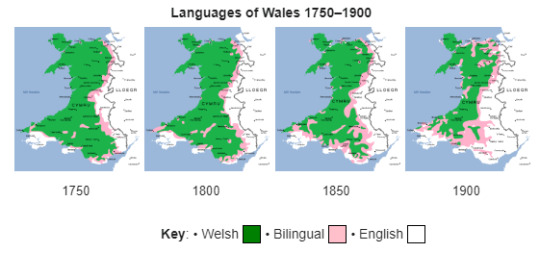
Because! It's one of the biggest remaining Welsh language strongholds. If you look at language maps over time in Wales, a pattern emerges:
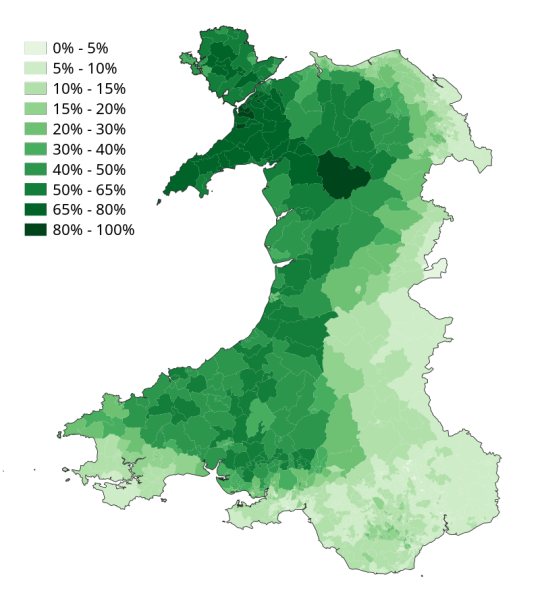
And the current (2021) figures show this:
And you are going to this bit:
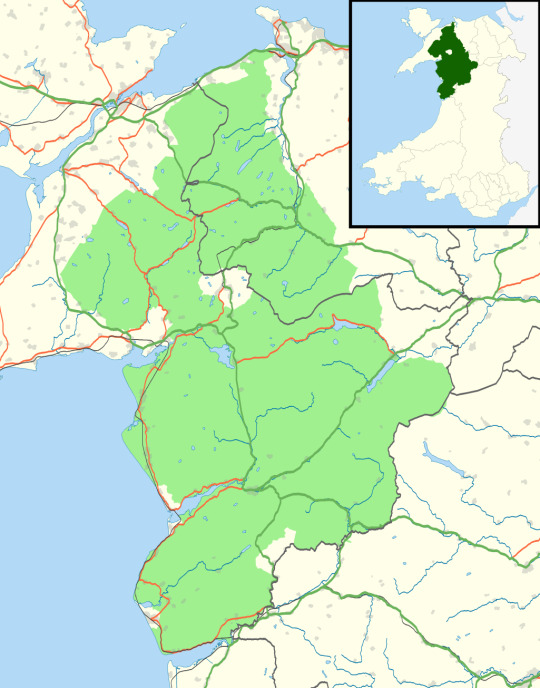
So you're heading into the Welshest bit in all of Wales! And the bit with the strongest and longest history of Welsh, too.
Which also means there's a lot of activism-related stuff in that area. It's probably worth you reading up on the history of Tryweryn (which was a bit further east, but sets the scene well); there was also a BIG thing a couple of decades ago where activists would burn down English-owned holiday homes (while they were empty in winter, not, like, with the English in them). This is because, in addition to the usual issues with the social impacts of holiday homes (driving up prices meaning locals can't live there, eroding communities, etc), holiday homes in Welsh language heartlands are a significant and tangible threat to the language. Even today, the issue of holiday homes is an extremely touchy subject, as is the issue of (mostly-English) people moving into the area because "It's so pretty!!!" and then not learning the language.
(Yet another reason they will love you if you Make An Effort)
Historically speaking, you'll be in a chunk of the country that was the ancestral seat of the last kings of Wales (Gwynedd). The final one, Llywelyn ein Llyw Olaf, was ambushed and murdered in 1282, which was the beginning of the end for fighting off English rule. In fact, Owain Glyndŵr later crowned himself king of Wales for about two years, but weirdly, no one acknowledges this as real kingship for some reason - if you google his name, he's always listed as a soldier or military commander, which really opens up a whole "Who gets to say when someone is royalty" debate, but he did actually claim descent from the House of Aberffraw anyway, so ultimately it still links back to Llywelyn.
Ecology! Temperate alpine. There actually isn't a global scientific distinction between hill and mountain, but most countries set an arbitrary height standard. This means it varies from country to country depending on how tall their topology is. Wales, however, bucks this trend, and instead decides based on what is formally referred to as 'land use' and colloquially referred to as 'Vibes'. If it's a hill, it's tamed - if it's a mountain, it's wild. This means Eryri is fairly short by the standards of tedious foreigners who regard mountains as a sort of geological dick waving competition, but it's in fact a whole mountain range; it's also older than Saturn's rings. And, crucially, it's very much sufficiently above sea level to have an alpine ecosystem.
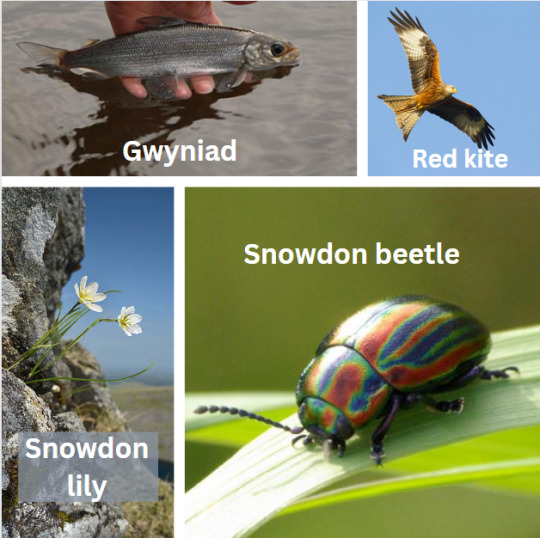
There are three endemic (i.e. not occurring anywhere else in the world) species in Eryri, to whit:
The Snowdon lily. A small and delicate flower growing in protected and inaccessible spots on yr Wyddfa (formally known as Snowdon). Excessively vulnerable to trampling, so the national park keeps sections where it grows fenced off.
The Snowdon beetle. RAINBOW BEETLE.
The gwyniad. A sub-species of whitefish until recently exclusively found in Llyn Tegid (Bala Lake), trapped there after the ice age and now developing its own genetic profile distinct from other whitefish. Some dickhead in the 80s introduced the ruffe to the lake for fishing, and the ruffe eats the gwyniad's eggs, so they've now transplanted eggs to Llyn Arenig Fawr nearby as a conservation measure.
There's also feral goats. And Welsh mountain ponies. Ooh, and, red kites - in the UK red kites were so heavily persecuted they eventually fell to just 7 breeding pairs in Wales. We established a protected zone and hired Nepalese Gurkhas to guard the nests and thus saved it from extirpation so successfully they later translocated Welsh birds to other spots in the UK. It's a big conservation success story, and now red kites are considered to be the national bird of Wales. They have a very distinctive silhouette, too, look for the forked tail.
Oh, and, we have a unique habitat type called ffridd, which you see a lot of in Eryri.
Final wildlife pictures to close:

Anyway - have a great time! Enjoy muchly.
293 notes
·
View notes
Text
Climate denial may be on the decline, but a phenomenon at least as injurious to the cause of climate protection has blossomed beside it: doomism, or the belief that there’s no way to halt the Earth’s ascendant temperatures. Burgeoning ranks of doomers throw up their hands, crying that it’s too late, too hard, too costly to save humanity from near-future extinction.
There are numerous strands of doomism. The followers of ecologist Guy McPherson, for example, gravitate to wild conspiracy theories that claim humanity won’t last another decade. Many young people, understandably overwhelmed by negative climate headlines and TikTok videos, are convinced that all engagement is for naught. Even the Guardian, which boasts superlative climate coverage, sometimes publishes alarmist articles and headlines that exaggerate grim climate projections.
This gloom-and-doomism robs people of the agency and incentive to participate in a solution to the climate crisis. As a writer on climate and energy, I am convinced that we have everything we require to go carbon neutral by 2050: the science, the technology, the policy proposals, and the money, as well as an international agreement in which nearly 200 countries have pledged to contain the crisis. We don’t need a miracle or exorbitantly expensive nuclear energy to stave off the worst. The Gordian knot before us is figuring out how to use the resources we already have in order to make that happen.
One particularly insidious form of doomism is exhibited in Kohei Saito’s Slow Down: The Degrowth Manifesto, originally published in 2020 and translated from Japanese into English this year. In his unlikely international bestseller, Saito, a Marxist philosopher, puts forth the familiar thesis that economic growth and decarbonization are inherently at odds. He goes further, though, and speculates that the climate crisis can only be curbed in a classless, commons-based society. Capitalism, he writes, seeks to “use all the world’s resources and labor power, opening new markets and never passing up even the slightest chance to make more money.”
Capitalism’s record is indeed damning. The United States and Europe are responsible for the lion’s share of the world’s emissions since the onset of the Industrial Revolution, yet the global south suffers most egregiously from climate breakdown. Today, the richest tenth of the world’s population—living overwhelmingly in the global north and China—is responsible for half of global emissions. If the super-rich alone cut their footprints down to the size of the average European, global emissions would fall by a third, Saito writes.
Saito’s self-stated goals aren’t that distinct from mine: a more egalitarian, sustainable, and just society. One doesn’t have to be an orthodox Marxist to find the gaping disparities in global income grotesque or to see the restructuring of the economy as a way to address both climate breakdown and social injustice. But his central argument—that climate justice can’t happen within a market economy of any kind—is flawed. In fact, it serves next to no purpose because more-radical-than-thou theories remove it from the nuts-and-bolts debate about the way forward.
We already possess a host of mechanisms and policies that can redistribute the burdens of climate breakdown and forge a path to climate neutrality. They include carbon pricing, wealth and global transaction taxes, debt cancellation, climate reparations, and disaster risk reduction, among others. Economies regulated by these policies are a distant cry from neoliberal capitalism—and some, particularly in Europe, have already chalked up marked accomplishments in reducing emissions.
Saito himself acknowledges that between 2000 and 2013, Britain’s GDP increased by 27 percent while emissions fell by 9 percent and that Germany and Denmark also logged decoupling. He writes off this trend as exclusively the upshot of economic stagnation following the Lehman Brothers bankruptcy in 2008. However, U.K. emissions have continued to fall, plummeting from 959 million to 582 million metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent between 2007 and 2020. The secret to Britain’s success, which Saito doesn’t mention, was the creation of a booming wind power sector and trailblazing carbon pricing system that forced coal-fired plants out of the market practically overnight. Nor does Saito consider that from 1990 to 2022, the European Union reduced its emissions by 31 percent while its economy grew by 66 percent.
Climate protection has to make strides where it can, when it can, and experts acknowledge that it’s hard to change consumption patterns—let alone entire economic systems—rapidly. Progress means scaling back the most harmful types of consumption and energy production. It is possible to do this in stages, but it needs to be implemented much faster than the current plodding pace.
This is why Not the End of the World: How We Can Be the First Generation to Build a Sustainable Planet by Hannah Ritchie, a data scientist at the University of Oxford, is infinitely more pertinent to the public discourse on climate than Saito’s esoteric work. Ritchie’s book is a noble attempt to illustrate that environmental protection to date boasts impressive feats that can be built on, even as the world faces what she concedes is an epic battle to contain greenhouse gases.
Ritchie underscores two environmental afflictions that humankind solved through a mixture of science, smart policy, and international cooperation: acid rain and ozone depletion. I’m old enough to remember the mid-1980s, when factories and power plants spewed out sulfurous and nitric emissions and acid rain blighted forests from the northeastern United States to Eastern Europe. Acidic precipitation in the Adirondacks, my stomping grounds at the time, decimated pine forests and mountain lakes, leaving ghostly swaths of dead timber. Then, scientists pinpointed the industries responsible, and policymakers designed a cap-and-trade system that put a price on their emissions, which forced industry into action; for example, power plants had to fit scrubbers on their flue stacks. The harmful pollutants dropped by 80 percent by the end of the decade, and forests grew back.
The campaign to reverse the thinning of the ozone layer also bore fruit. An international team of scientists deduced that man-made chlorofluorocarbons (CFC) in fridges, freezers, air conditioners, and aerosol cans were to blame. Despite fierce industry pushback, more than 40 countries came together in Montreal in 1987 to introduce a staggered ban on CFCs. Since then, more countries joined the Montreal Protocol, and CFCs are now largely a relic of the past. As Ritchie points out, this was the first international pact of any kind to win the participation of every nation in the world.
While these cases instill inspiration, Ritchie’s assessment of our current crisis is a little too pat and can veer into the Panglossian. The climate crisis is many sizes larger in scope than the scourges of the 1980s, and its antidote—to Saito’s credit—entails revamping society and economy on a global scale, though not with the absolutist end goal of degrowth communism.
Ritchie doesn’t quite acknowledge that a thoroughgoing restructuring is necessary. Although she does not invoke the term, she is an acolyte of “green growth.” She maintains that tweaks to the world’s current economic system can improve the living standards of the world’s poorest, maintain the global north’s level of comfort, and achieve global net zero by 2050. “Economic growth is not incompatible with reducing our environmental impact,” she writes. For her, the big question is whether the world can decouple growth and emissions in time to stave off the darkest scenarios.
Ritchie approaches today’s environmental disasters—air pollution, deforestation, carbon-intensive food production, biodiversity loss, ocean plastics, and overfishing—as problems solvable in ways similar to the crises of the 1980s. Like CFCs and acid rain, so too can major pollutants such as black carbon and carbon monoxide be reined in. Ritchie writes that the “solution to air pollution … follows just one basic principle: stop burning stuff.” As she points out, smart policy has already enhanced air quality in cities such as Beijing (Warsaw, too, as a recent visit convinced me), and renewable energy is now the cheapest form of power globally. What we have to do, she argues, is roll renewables out en masse.
The devil is in making it happen. Ritchie admits that environmental reforms must be accelerated many times over, but she doesn’t address how to achieve this or how to counter growing pushback against green policies. Just consider the mass demonstrations across Europe in recent months as farmers have revolted against the very measures for which Ritchie (correctly) advocates, such as cutting subsidies to diesel gas, requiring crop rotation, eliminating toxic pesticides, and phasing down meat production. Already, the farmers’ vehemence has led the EU to dilute important legislation on agriculture, deforestation, and biodiversity.
Ritchie’s admonishes us to walk more, take public transit, and eat less beef. Undertaken individually, this won’t change anything. But she acknowledges that sound policy is key—chiefly, economic incentives to steer markets and consumer behavior. Getting the right parties into office, she writes, should be voters’ priority.
Yet the parties fully behind Ritchie’s agenda tend to be the Green parties, which are largely in Northern Europe and usually garner little more than 10 percent of the vote. Throughout Europe, environmentalism is badmouthed by center-right and far-right politicos, many of whom lead or participate in governments, as in Finland, Hungary, Italy, the Netherlands, Serbia, Slovakia, and Sweden. And while she argues that all major economies must adopt carbon pricing like the EU’s cap-and-trade system, she doesn’t address how to get the United States, the world’s second-largest emitter, to introduce this nationwide or even expand its two carbon markets currently operating regionally—one encompassing 12 states on the East Coast, the other in California.
History shows that the best way to make progress in the battle to rescue our planet is to work with what we have and build on it. The EU has a record of exceeding and revising its emissions reduction targets. In the 1990s, the bloc had the modest goal of sinking greenhouse gases to 8 percent below 1990 levels by 2008-12; by 2012, it had slashed them by an estimated 18 percent. More recently, the 2021 European Climate Law adjusted the bloc’s target for reducing net greenhouse gas emissions from 40 percent to at least 55 percent by 2030, and the European Commission is considering setting the 2040 target to 90 percent below 1990 levels.
This process can’t be exclusively top down. By far the best way for everyday citizens to counter climate doomism is to become active beyond individual lifestyle choices—whether that’s by bettering neighborhood recycling programs, investing in clean tech equities, or becoming involved in innovative clean energy projects.
Take, for example, “community energy,” which Saito considers briefly and Ritchie misses entirely. In the 1980s, Northern Europeans started to cobble together do-it-yourself cooperatives, in which citizens pooled money to set up renewable energy generation facilities. Many of the now more than 9,000 collectives across the EU are relatively small—the idea is to stay local and decentralized—but larger co-ops illustrate that this kind of enterprise can function at scale. For example, Belgium’s Ecopower, which forgoes profit and reinvests in new energy efficiency and renewables projects, provides 65,000 members with zero-carbon energy at a reduced price.
Grassroots groups and municipalities are now investing in nonprofit clean energy generation in the United States, particularly in California and Minnesota. This takes many forms, including solar fields; small wind parks; electricity grids; and rooftop photovoltaic arrays bolted to schools, parking lots, and other public buildings. Just as important as co-ownership—in contrast to mega-companies’ domination of the fossil fuel market—is democratic decision-making. These start-ups, usually undertaken by ordinary citizens, pry the means of generation out of the hands of the big utilities, which only grudgingly alter their business models.
Around the world, the transition is in progress—and ideally, could involve all of us. The armchair prophets of doom should either join in or, at the least, sit on the sidelines quietly. The last thing we need is more people sowing desperation and angst. They play straight into the court of the fossil fuel industry.
118 notes
·
View notes
Text

A global food monitor has found that famine has taken hold at a camp for displaced people in Sudan ’s North Darfur and is likely to spread to other parts of the region.
In its report, the Famine Review Committee (FRC) concluded that famine was occurring in the Zamzam camp that shelters an estimated 500,000 International Displaced People (IDPs), and is likely to persist there at least until October.
According to the report, famine conditions have prevailed at the camp as of June and July in Zamzam, which lies near North Darfur’s capital, El-Fasher.
“The FRC found that two out of three critical requirements to classify Famine - acute malnutrition and mortality rates - have been surpassed, confirming Famine, based on reasonable evidence,” the report read.
Famine is determined by the Integrated Food Security Security Phase Classification (IPC), the UN’s hunger monitoring body and the main global reference for assessing the severity of food crises.
This is just the third time the IPC has made a famine determination since the system was implemented 20 years ago.
According to the report, the population of Zamzam has swelled to half a million in just a few weeks, after the camp absorbed almost half of the 320,000 people believed to have been displaced in El-Fasher since mid-April.
The experts identified conflict and restricted humanitarian access as drivers of the famine conditions.
The designation comes over a year after the start of a war between the Sudanese Armed Forces (SAF) and the paramilitary Rapid Support Forces (RSF), which has caused mass displacement and a rapidly deteriorating food security situation.
“Famine conditions will only worsen and be further prolonged if conflict continues and humanitarian and full commercial access is not made possible,” the report warned.
The experts said their analysis was limited to Zamzam due to limited data but emphasised that other areas of the region, particularly the Abu Shouk and al-Salam camps, were also potentially experiencing famine and would remain at risk as long as the war continues.
76 notes
·
View notes
Text

Cannot stop thinking of Palestine and how horrific the situation keeps getting, just... god... we've known the true nature and cruelty of world leaders (particularly the global north and those backed by it tbh) for forever but to see it all so blatantly in action is still heartbreaking and infuriating as hell
so... Here's something
165 notes
·
View notes
Text
The link between warfare and technological innovation has been well documented [...]. World War II was a particularly intense crucible of technological change, and the repurposing of military technologies and industries in the forging of a new post-war consumer [economy] is crucial [...]. Processes of technological bricolage turned the machines of war onto the natural world as global powers competed to cement their economic and imperial hegemony. In Great Britain’s post-war “groundnut scheme” in its East African territories (1946-51), this collision of nature, military hardware, and technical expertise was part of efforts to both produce more fats for the British diet and to demonstrate to the world (most importantly the United States) that, through a newly energized science-led developmentalism, British colonialism still had a “progressive” role to play in the postwar world.

The aim was to produce millions of tons of peanuts across Tanganyika using the latest methods of advanced scientific agriculture. The environmental conditions in the north, where the scheme was to begin, were known to be especially trying, not least the dry climate [...]. But faith in the power of mechanized agriculture was such that any natural limits were thought to be readily surmountable.
The groundnut scheme was to be, as its Director put it in an interview with the Tanganyika Standard, a “war” with nature, and an “economic Battle of Alamein” waged over some three million acres by an army of colonial technicians - many recruited from military ranks - and local laborers, for many of whom the scheme represented their first entry into the wage labor market.
But it wasn’t just the rhetoric of war that was repurposed.
Lancaster bombers were kitted out to survey and discover “new country” in East Africa for agricultural development. [...] [T]ractors and bulldozers from military surplus stores in Egypt proved unable to tackle the hard ground and tough vegetation, so the planners turned to a novel solution: repurposing surplus Sherman M4A2 tanks. The Vickers-Armstrong factory in Newcastle-Upon-Tyne set about rearranging key elements of the tanks’ construction [...]. The tractors, christened “Shervicks” for their hybrid origins, were [...] thought to be particularly suited to large-scale earth-moving and to the kind of heavy duty “bush clearing” that was required in Tanganyika.


Officials sought to dismiss concerns that large-scale bush clearing would have wider environmental consequences, using the well-worn colonial trope that any observed changes in local climate or erosion patterns were due to the “primitive” agricultural practices of the locals, not to the earth-moving practices of the colonists. [...] As the plants continued to wilt in the sun, [...] [t]he stakes were high. As [J.R.] of the Colonial Development Corporation put it in a letter: “Our standing as an Imperial power in Africa is to a substantial extent bound up with the future of this scheme. To abandon it would be a humiliating blow to our prestige everywhere.” The only option left was to try and bend the weather itself to the scheme’s will, by seeding the clouds for rain. [...] “Balloon bombs” (photographic film canisters tethered to weather balloons) and a repurposed Royal Navy flare gun were used to target individual clouds [...]. The scheme itself has survived as a cautionary tale of governmental hubris, but it is instructive too as a case study of how technologies of war have been turned against other foes.
---
All text above by: Martin Mahony. “The Enemy is Nature: Military Machines and Technological Bricolage in Britain’s ‘Great Agricultural Experiment.’“ Environment and Society Portal, Arcadia (Spring 2021), no. 11. Rachel Carson Center for Environment and Society. doi:10.5282/rcc/9191. [Bold emphasis and some paragraph breaks/contractions added by me. Images and their captions are shown unaltered as they originally appear in Mahony's article. Public Domain Mark 1.0 License for images: creativecommons dot org/publicdomain/mark/1.0/]
165 notes
·
View notes
Text
The main effort in a process of planetary degrowth must be made by the countries of the industrialized North (North America, Europe, and Japan) responsible for the historical accumulation of carbon dioxide since the Industrial Revolution. They are also the areas of the world where the level of consumption, particularly among the privileged classes, is clearly unsustainable and wasteful. The “underdeveloped” countries of the Global South (Asia, Africa, and Latin America) where basic needs are very far from being satisfied will need a process of “development,” including building railroads, water and sewage systems, public transport, and other infrastructures. But there is no reason why this cannot be accomplished through a productive system that is environmentally friendly and based on renewable energies. These countries will need to grow great amounts of food to nourish their hungry populations, but this can be much better achieved—as the peasant movements organized worldwide in the Vía Campesina network have been arguing for years—by a peasant biological agriculture based on family units, cooperatives, or collectivist farms. This would replace the destructive and antisocial methods of industrialized agribusiness, based on the intensive use of pesticides, chemicals, and genetically modified organisms. Presently, the capitalist economy of countries in the Global South is rooted in the production of goods for their privileged classes—cars, airplanes, and luxury goods—and commodities exported to the world market: soya beans, meat, and oil. A process of ecological transition in the South, as argued by ecosocialists, would reduce or suppress this kind of production, and aim instead at food sovereignty and the development of basic services such as health care and education, which need, above all, human labor, rather than more commodities.
Michael Löwy, Nine Theses on Ecosocialist Degrowth
237 notes
·
View notes
Text
In 1975, civilian nuclear technology was part of a worldwide strategy to bring the Organization of Petroleum-Exporting Countries (OPEC) to heel. That body’s power seemed unprecedented, given that most of its countries were historically impoverished or “backward” peoples. [...]
Many developing countries did adopt nuclear technologies, often with crucial parts of their national infrastructures relying on American and European expertise, equipment, and fuel. Rather than seeing liberation from nature, such countries faced renewed forms of dependence. Iran certainly never gained reliable access to uranium and did not become the economic miracle envisioned by Ansari back in 1975. Instead of lifting up the poorer nations of the world, the global nuclear order seemed structured in ways reminiscent of the colonial era. The most heated debates within the IAEA pitted the nuclear weapons states against the so-called LDCs—less developed countries. The agency never became a storehouse for fission products. Instead, one of its primary functions was to monitor an arms control treaty—the Treaty 4 on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons. By the end of the century, the IAEA was referred to as a “watchdog,” known for its cadre of inspectors. In 2003, IAEA inspections were crucial talking points in public debates about the invasion of Iraq by the United States [...] evidence gathered over the years by the agency created for the peaceful atom was being interpreted by the United States government as justification for military intervention. [...]
Focusing only on arms control glosses over the domestic politics of nuclear programs, particularly the role of high technology as symbols of state power and legitimacy. But it also does not square with what scholars of the Cold War have been pointing out for decades—that governments, especially the United States, deployed science and technology as diplomatic tools, to achieve feats of prestige, to shape business arrangements, to conduct clandestine surveillance, or to bind countries together with technical assistance programs. Poorer countries’ dreams of modernization, of using advanced technology to escape hunger, poverty, and the constraints of nature—these were the stock-in-trade of US diplomacy. Why, then, should we imagine that the promises connected to peaceful uses of atomic energy were any less saturated with geopolitical maneuvers and manipulation? [...]
American officials in the late 1940s and early 1950s were very worried that commercial nuclear power would siphon off supplies of uranium and monazite needed for the weapons arsenal. So they explicitly played down the possibility of electricity generation from atomic energy and instead played up the importance of radioisotopes for medicine and agriculture—because such radioisotopes were byproducts of the US weapons arsenal and did not compete with it. The kinds of technologies promoted in the developing world by the United States, the USSR, and Europeans thus seemed neocolonial, keeping the former colonies as sites of resource extraction—a fact noticed, and resented, by government officials in India, Brazil, and elsewhere. Mutation plant breeding, irradiation for insect control or food sterilization, and radioisotope studies in fertilizer—these were oriented toward food and export commodities and public health, problems indistinguishable from those of the colonial era. These were not the same kinds of technologies embraced by the global North, which focused on electricity generation through nuclear reactors, often as a hedge against the rising political power of petroleum-producing states in the Middle East. By the mid-1960s and 1970s, the United States and Europe did offer nuclear reactors even to some of the most politically volatile nations, as part of an effort to ensure access to oil. Convincing petroleum suppliers of their dire future need for nuclear reactors was part of a strategy to regain geopolitical leverage. Despite the moniker “peaceful atom,” these technologies were often bundled in trade deals with fighter jets, tanks, and other military hardware [...]
By the close of the century, two competing environmental narratives were plainly in use. One was critical of atomic energy, drawing on scientific disputes about the public health effects of radiation, the experience of nuclear accidents such as Three Mile Island (1979) and Chernobyl (1986), or the egregious stories of public health injustice—including negligence in protecting uranium miners or the wanton destruction and contamination of indigenous peoples’ homelands. In contrast was the narrative favored by most governments, depicting nuclear technology in a messianic role, promising not only abundant food, water, and electricity, but also an end to atmospheric pollution and climate change. [...]
As other scholars have noted, the IAEA tried to maintain a reputation of being primarily a technical body, devoid of politics. But it had numerous political uses. For example, it was a forum for intelligence gathering, as routinely noted by American Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) documents. It also outmaneuvered the World Health Organization and Food and Agriculture Organization in the early 1960s and was able to assert an authoritative voice playing down public health dangers from atomic energy. Further, it provided a vehicle for countries to stay engaged in atomic energy affairs even if they did not sign on to the non-proliferation treaty—India, Pakistan, and Israel most notably. It provided apartheid-era South Africa with a means of participating in international affairs when other bodies ousted it because of its blatantly racist policies. By the same token, it gave the Americans and Europeans political cover for continuing to engage with South Africa, an important uranium supplier.
Introduction to The Wretched Atom, Jacob Hamlin
53 notes
·
View notes