#op amp circuits
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
https://www.futureelectronics.com/p/semiconductors--analog--amplifiers--general-purpose/ts393idt-stmicroelectronics-4394615
Amplifiers, General Purpose Amplifiers, TS393IDT, STMicroelectronics
TS393 Series 16 V 600 pA SMT Micropower Dual CMOS Voltage Comparator - SOP-8
#Amplifiers#General Purpose Amplifiers#TS393IDT#STMicroelectronics#power op amp#High-gain electronic#Op amp circuits#High speed voltage amplifier#a chip#applications#Operational amplifier circuit#analog devices op amps
1 note
·
View note
Text
https://www.futureelectronics.com/p/semiconductors--analog--amplifiers--general-purpose/ts393idt-stmicroelectronics-2252658
OP amp circuits, electronic voltage amplifier, Operational amplifier circuit
TS393 Series 16 V 600 pA SMT Micropower Dual CMOS Voltage Comparator - SOP-8
#STMicroelectronics#TS393IDT#Amplifiers#General Purpose Amplifiers#op amp circuits#electronic voltage amplifier#Power operational amplifier#High-Performance#High-speed voltage amplifier#voltage divider
1 note
·
View note
Text
https://www.futureelectronics.com/p/semiconductors--analog--amplifiers--low-noise-amplifier/ba4560f-e2-rohm-3414471
Low noise amplifier, Ultra low noise op amp, Microwave low noise amplifiers,
Dual Channel 30 V 6 mV Surface Mount Low Noise Amplifier - SOP-8
#ROHM#BA4560F-E2#Amplifiers#Low Noise Amplifiers#Low noise instrumentation#chip manufacturers#power operational amplifier#power amplifier#Op amp circuits#What is a low noise amplifier#Ultra low noise op amp#Microwave low noise amplifiers
1 note
·
View note
Text
https://www.futureelectronics.com/p/semiconductors--analog--amplifiers--general-purpose/ts391iylt-stmicroelectronics-5181997
Amplifiers, what is operational amplifier, op amps, Operational amplifier chip
TS391 Series 36 V 400 nA SMT Single General Purpose Comparator - SOT-23
#Operational#General Purpose Amplifiers#TS391IYLT#STMicroelectronics#Operational amplifier chip#OP amp circuit#High-gain electronic voltage amplifier#OP amp for audio#op amp headphone amplifier
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
https://www.futureelectronics.com/p/semiconductors--analog--amplifiers--general-purpose/tl084idt-stmicroelectronics-6240253
Operational circuit, general-purpose op amp, Power op amp, operational amplifier
TL084 Series 36V 4 MHz General Purpose JFET Quad Operational Amplifier - SOIC-14
#STMicroelectronics#TL084IDT#Amplifiers#Operational#General Purpose Amplifier#circuit#Power op amp#operational amplifier#audio op-amp#chip#High-gain electronic voltage amplifier#High-gain electronic#Voltage Comparator#Power amplifier
1 note
·
View note
Text
https://www.futureelectronics.com/p/semiconductors--analog--amplifiers--general-purpose/ts393idt-stmicroelectronics-1027334
Power operational amplifier, power op amp, operational circuits,
TS393 Series 16 V 600 pA SMT Micropower Dual CMOS Voltage Comparator - SOP-8
#STMicroelectronics#TS393IDT#Amplifiers#General Purpose Amplifiers#Power#op amp#operational circuits#applications#what is operational amplifier#Op amp circuit#CMOS Voltage Comparator#High-gain electronic voltage amplifier
1 note
·
View note
Text
https://www.futureelectronics.com/p/semiconductors--analog--amplifiers--low-noise-amplifier/ba4560f-e2-rohm-9106267
Operational amplifier, high-gain electronic voltage amplifier, low noise op amps
Dual Channel 30 V 6 mV Surface Mount Low Noise Amplifier - SOP-8
#Amplifiers#Low Noise Amplifiers#BA4560F-E2#ROHM#Operational amplifier circuit#low noise Op amp circuits#General purpose amplifier#high-gain electronic voltage amplifier#op amps#operational amplifiers#operational circuits
1 note
·
View note
Text
Comparator applications, NOR gate indicate, Comparator circuit, NAND gates
LM2903 Series 36 V 250 nA SMT Dual Low Power Voltage Comparator - SOIC-8
#Comparators#LM2903YDT#STMicroelectronics#comparator applications#NOR gate indicate#Comparator circuit#NAND gates#op-amp comparator#voltage divider calculator#Power comparator#logic gate#Low Power Voltage#single comparator#universal gates
1 note
·
View note
Text
Inverting comparator, comparator applications, voltage comparator
LM2903 Series 36 V 250 nA SMT Dual Low Power Voltage Comparator - SOIC-8
#Comparators#LM2903YDT#STMicroelectronics#inverting comparator#comparator applications#voltage comparator#Dual Low Power Voltage Comparator#window comparator#comparator op-amp#NOR gate indicate#Comparator circuit#Comparator Electronics
1 note
·
View note
Text
I made a VCO that covers <0.03Hz through >13KHz out of crap and sticks!
6 generic op-amps, 3 generic transistors, 3 generic diodes, 1 capacitor and 20 resistors - and you, too, can have one TODAY, since my article on Ultra-Widerange Micro VCO is now out!



It's not a very precise VCO - it tracks exponentially and CV inputs can be tuned to track 1V/Oct over 2-3 octaves, but not more than that. But it requires no fancy or obsolete parts like a VCO chip or an OTA - just the most bread-n-butter parts ever. It's also a simple circuit and an easy build. If you were meaning to build an oscillator that is something more than an atari punk console, but all designs online are too complicated and have uncommon parts, this design just might be suitable for you!
Here's a basic sweep:
And here's some gross noise it and another VCO make in tandem!
As always, all the info, including schematics, circuit notes, more sound demos and module photos, veroboard layouts, etc, are in the article on my site. I'll drop the schem here, though, because for once i really like how it looks, despite in fact being a kinda hacky design.
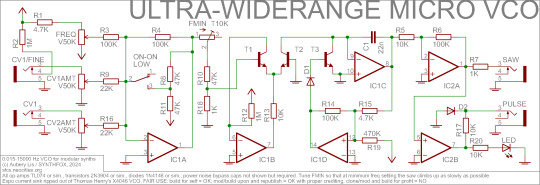
(i actually think the only reason it doesn't heat up is because TL07x are too slow for that to happen lmfao)
24 notes
·
View notes
Text


BOSS - CE-1 Chorus Ensemble
"... yeah, there’s a reason why they occupy so much Cabinet real estate. The company created the “first” of a variety of effects, and was certainly the first to offer many types in compact boxes. However, one such pedal is a stone-cold all-time classic despite never being offered in Boss’s trademark compact enclosure. That pedal is the CE-1 Chorus Ensemble.
Released one year after parent company Roland’s flagship Jazz Chorus amplifiers, Boss did what was once considered the unthinkable. Following the rapid and perhaps unexpected success of the aforementioned amp series, Roland wasted no time with ripping a circuit straight from them and putting them in a floor unit. In fact, this circuit ended up being the first pedal to bear the Boss name, and what a first it was.
Back when the CE-1 was conceptualized, the idea of mains-powered pedals was pretty commonplace. Mu-Tron effects used them, and so did MXR on some of its more ambitious models. Onboard and oftentimes custom-wound transformers ensured that voltages would be stepped down at precisely the right increments in order to preserve tonal integrity and headroom.
Of course, most pedals of the time also ran on nine-volt batteries, establishing a standard that continues today. But before these standards were established, the idea of grandiose effects thrived under the usage of mains power. Such a boundless canvas allowed companies like Boss to rip entire hunks of circuitry straight from larger silicon conglomerates and put them right at a player’s feet. These days, very few manufacturers offer such exacting circuitry, and the few that do charge exorbitant prices.
The CE-1 is one particularly exceptional example of this practice, because it expands on the original circuit, with the added bonus that you can play it through an actual tube amplifier. It also adds an extra functionality that the Jazz Chorus just couldn’t match. The Jazz Chorus gives players both Chorus and Vibrato modes, and to that end, serves up three knobs, of which Speed and Depth are two. The third knob is actually a rotary switch that chooses either mode. While the JC-120 offers a footswitch input to toggle the effect on and off, the CE-1 does one better and converts the rotary switch into a stompable button, meaning you don’t have to do the Angus Young duckwalk back to your amp mid-set to change modes. Nobody wants to do this.
Roland’s Jazz Chorus—and thusly the CE-1—couldn’t have come at a better time for end-users or commerce. Californian semiconductor company Reticon developed the first bucket-brigade device (BBD) and distributed them through the usual suspects, including Radio Shack under the store’s in-house Archer brand. The only problem—again for end-users and commerce—was that each one cost a crazy amount of 1970s dollars. Even at wholesale prices, Reticon’s SAD series of BBD chips made effects a bit on the expensive side.
Shortly after in Japan, Matsushita released the genesis of the Japanese BBD boom that ended up sinking Reticon and all pedals that relied on it. The first chip off the Matsushita line was the MN3002 and found its way into the CE-1 tout de suite. With the combination of the relatively inexpensive BBD and the full-strength brawn of the circuit itself, the CE-1 made a splash in the effects world and primed the pump for Boss’s compact series to take the effects world by storm.
The most unsung piece of the CE-1 puzzle is the onboard preamp that preps the signal for its impending modulation. While many effects and amplifiers (especially of this era) features “high” and “low” inputs, they usually correspond to a brute force approach that swaps out resistors in the signal path. However, the CE-1 preamp section starts with an op-amp preamp circuit that sweetens the signal, and switching over to high mode inserts a transistorized gain stage between the input and the op-amp section. This adds a velvety gloss to the signal before it ever sniffs the BBD chip, catapulting your tone into heights unreached by lesser devices.
It’s not often that almost 50 years later, no effect of a given type has surpassed the first one ever created, but such is the case with the CE-1. Its combination of unsurpassed tonal brilliance, component count and wacky power requirements has cemented its place in the effects hall of fame, leaving even the most modern refinements squarely in the rear-view mirror."
cred: catalinbread.com/blogs/kulas-cabinet/boss-ce-1-chorus-ensemble
47 notes
·
View notes
Text


Spock’s Brain (1990) by IS Robotics (iRobot), Somerville, MA. This hard-wired analogue brain is designed to emulate the brain of an insect, modelling how the insect gait transforms seamlessly from a slow, statically stable walk to a faster dynamic running motion. It controls the gait of a simulated hexapedal robot, represented by on-board LEDs for each leg. The legs maintain synchrony with signals flowing both longitudinally and laterally. Each leg has an identical circuit; the XR-2207 is a voltage controlled oscillator for timing, the 74123 is a dual retriggerable monostable multivibrator producing a square wave output to actuate the leg, and the smaller 8 pin TL082C is a dual op-amp.
83 notes
·
View notes
Note
I can't tell what's more impressive, your art or how clean your circuit diagrams are :0 mine were always so wobbly and the op amps were just disastrous 😭 it's so nice to see a fellow artist also in biomed eng, I really wish you all the best in both endeavours!!
THANK U SO MUCH!!! it genuinely means so much esp bcs ive been feeling sooo unsure abt my major recently :’))
and also thank u for the bme love (stem majors please dm me bcs id LOVE to be friends w u guys 😭😭)
in honor of this post i’m also gonna drop the full versions of all of my poorly drawn piastri notes LOL (bcs i am actually very proud of my notes :’))



also no one asked but yes i take my notes in procreate bcs im insane im sorry 😭
#a lot of oscar piastri#i love my major but i hate my major#guys i will send and make personalized study sheets because theres actually nothing i love more please just ask me#also i set the drawing guide size to either 33 or 44 pixels. because. im insane.#f1#formula 1#formula one#poorly drawn piastri#f1 fanart#op81#oscar piastri
29 notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
Analog Devices Op Amp #OP27GS #ADI #MAX487ESA #MC34063ABD #Chip #ICGOODFIND Electronic Components #SMT #PCBA Integrated Circuit Email and Skype: [email protected] www.icgoodfind.com
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
So this is another Eurorack patch using external devices: here, my homemade cracklebox.

I built this thing quite a while ago; it's a copy of the classic STEIM Krakadoos design. Its oscillator exploits bugs in the design of the ancient μA709 op amp chip to produce squelchy and crackling sounds when you touch the brass buttons on the left hand side. I've been intending to supplement the audio output jack on it, which is directly wired into the discrete amplifier circuit, with an output transformer; I've been told that doing that will make it so that plugging it into something doesn't couple that amplifier to the internals and change the sound.
But I decided tonight that before making any modifications, I should try plugging it into the sync input of my VCO 3340. This audio clip is the result: a solid chip oscillator being intimately tied to a weirdo.
The original zwoopy bounce is the patch as it stands without sync added, and then I turn the Cracklebox on, soft-syncing the VCO first with the ultrasonic base waveform of the Cracklebox, and then going through varying pressure on different patterns of touch knobs. I flip the Cracklebox off in the middle and switch to hard sync before going through the process again.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
DIY Dumble-like sounding MOSFET Overdrive

The Hermida Zendrive guitar pedal we will study, assemble and listen to today is a true masterpiece. Many say its sound is close to the Holy Grail of guitar amplification - Dumble Overdrive Special.
Other people are more pessimistic in their judgments. Still, the precise response to the picking dynamics, the Voicing tuning options, and the sheer beauty of this overdrive's sound are simply impossible not to love.
But before we study the Lovepedal Zendrive or its copy of the Landtone Phoenix song, or the Aion effects Azimuth dynamic overdrive, we'll study the evolution of the MOSFET overdrives that finally resulted in the development of this gem.
Fulltone OCD

Mike Fuller was one of the first to start using MOSFETs instead of diodes to limit the amplified guitar signal in 2004.
His Obsessive-Compulsive Drive overdrive-distortion pedal is built on a standard circuit with one dual op amp. The first operational amplifier, X1, amplifies the amplitude of the guitar signal by a factor from 8 to 463 times, depending on the position of the drive control X3. This is a 1-megohm potentiometer.

Further, through resistor R9, the signal is fed to the limiter, which comprises 2N7000 MOSFETs M1 and M2 connected in parallel. A germanium diode D1 - 1N34A is additionally included in series with M2, which makes the limiter asymmetrical and, therefore, makes more interesting sound.
A limiter in overdrives is usually included in the negative feedback circuit of an operational amplifier (i.e., in parallel with C6). Such a limiter is called a soft limiter.
And here, a hard limitation is applied: clipping sections are included between the preamplifier output of the gain section and the virtual ground - half of the supply voltage Vref, formed by resistors R4 and R7.
Virtual ground is used in the unipolar powering of operational amplifiers to amplify analog signals, such as audio signals. The guitar signal does not change from zero to plus but from minus to plus, passing through zero.
To prevent the signal from being limited to the circuit's ground, it is shifted in the plus direction by half the supply voltage.
Such hard limiting is typical for distortion pedals. But by using MOSFETs instead of diodes or LEDs, the top of the signal is not cut hard but softly rounded. Therefore, OCD can work as both distortion and overdrive.
Due to the smoothed peaks of the limited signal, the sound is highly dependent on the sound's attack dynamics. For rock and especially blues, this is very valuable. With modern metal pickups that compress the dynamic range of the signal, it can help make solos sounding more sweet.
The second operational amplifier X3 amplifies the limited signal by a factor of 3.8, correcting its timbre. Capacitors C6 and C9 prevent the self-excitation of operational amplifiers at high frequencies.
Next is a simple passive tone knob, which implies a treble leak circuit. Potentiometer X4 10 kilohms and capacitor C11 47 nanofarads are connected in the same way as on the pickguard of any electric guitar.
The Switch1 switch changes the circuit's output impedance as if the high-impedance and low-impedance pickups were switched. When it's open, you get a transparent overdrive like the Klon Centaur, and when it's closed, you can get a more aggressive sound like the Marshall Plexi.
Hermida Audio Zendrive

The Zendrive pedal's authors, Hermida audio technology (now produced by LOVEPEDAL LLC), have undoubtedly studied the Fulltone OCD thoroughly. Let's find the differences between the two circuits.
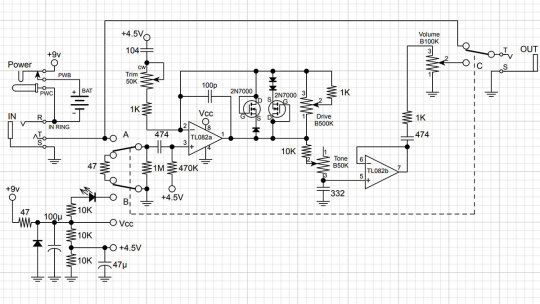
First, the limiter is included in the operational amplifier feedback, that is, between the output and the inverting input, not between the output and virtual ground. That is, here we have a soft limiter.
Secondly, one diode is added in series with each MOSFET. Clipping remains asymmetric: we have one diode in the left arm of the limiter and two diodes in the right arm.
Third, the second operational amplifier is used as a voltage repeater, aka buffer: the output is directly connected to the inverting input.
Fourth, the tone control is implemented a little differently: two OCD`s switchable resistors are replaced by a potentiometer.
And finally, the most critical, fifth difference. A potentiometer is included in the tone correction circuit between the inverting input of the first operational amplifier and the artificial midpoint.
This fourth knob, Voicing, or Character, allows you to smoothly adjust the lower frequencies in the overdrive structure over a wide range, similar to the Resonance control on many tube guitar amps.
The potentiometer is signed as a trimmer in the diagram because some pedal makers don't want to install a fourth knob on the pedal`s body. This is what Landtone did when developing the Phoenix Song Overdrive DIY kit.
The developer suggests installing the trimmer on the PCB, and to access it, you need to disassemble the pedal by unscrewing the footswitch nut and taking out the PCB.
But I will not be lazy to drill an extra hole in the pedal body and install a potentiometer with a knob, connected to PCB by wires instead of the trimmer. Because I consider this regulator simply invaluable and irreplaceable.

Before we get to assembly and testing, let's look at another pedal with a similar adjustment. However, it is based not on the Fulltone OCD but on the Ibanez Tube Screamer.
The Precision Drive

This is a signature pedal by Misha Mansour of Periphery, manufactured by Horizon Devices. Compared to the original Overdrive Pro TS808, the circuit adds a noise suppressor, which we will not consider, and an exciting ATTACK switch.
The Precision Drive scheme was studied and partially replicated by PedalPCB and PCB Guitar Mania. They are manufacturers of DIY kits for guitarists. Their products are called Dwarven Hammer and Collision Drive, respectively. A noise gate is not provided there, but the attack switch is implemented. This is the main difference between Precision Drive and many other overdrive pedals.
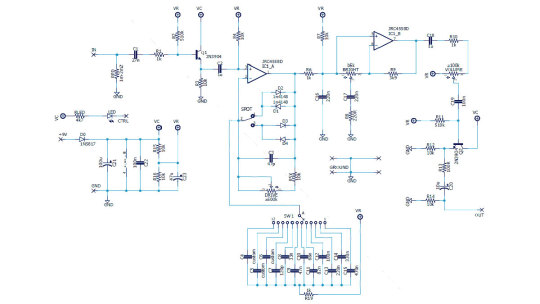
In the Fulltone OCD schematic, we saw a resistor switch at the tone shaping circuit in the output section. The Zendrive has a variable resistor in the preamp's RC circuit which is controlling the overdrive structure.
Precision Drive has a constant resistor in the same place, between the inverting input of the overdrive section operational amplifier and the virtual ground, but the capacitors are switched.
This is the same thing: we change the time constant of the RC circuit, which adjusts the audio signal's frequency spectrum. At the same time as the time constant, the complex impedance changes, thus the gain.
A resistor is a resistance to both DC and AC current. At the same time, a capacitor is only resistant to AC current because DC current does not flow through a capacitor. Since DC current does not flow through our RC circuit, there is no difference between adjusting the resistance and switching the capacitance.
But the active/reactive ratio affects the circuit's Quality factor, i.e., its resonance. It's no coincidence that the knob on guitar amplifiers, which adjusts the same frequencies as our potentiometer or switch, is often called RESONANCE. And it is used to adjust to the resonance of the electromechanical system - the loudspeakers in the cabinet, along with the masses of air in and around it.
The reactive impedance accumulates energy and gives it away, except for losses due to dielectric recharging and magnetizing the magnetic core in inductors. This is why coreless inductors are often used in high-end equipment, so-called air inductors. They weigh a lot, take up a lot of space, and are expensive because copper is more expensive than steel. But these are the laws of physics on which technology is based.

Unlike reactive impedance, active resistance converts electrical energy into heat, thus reducing the Q-factor. In some cases, it is necessary and useful. In others, it is harmful. Or it simply creates a unique sound character.
That's why switching capacitors and turning the potentiometer knob in the feedback circuit of an audio frequency amplifier is almost the same thing, but not quite. And it's great that there are such different variants of guitar overdrive pedals!
Landtone Phoenix Song Overdrive
Now you can hear how my Zendrive from the Landtone OD-1 kit sounds, with a Seymour-Duncan SH4 humbucker on a Gibson MM Explorer guitar, into an Orange MT20 with a Torpedo Captor X. And see how I assembled the pedal and also a kitten walking around the table and prancing around.
youtube
I liked the pedal, especially its fourth magic Voicing knob, which does things to the sound that other tone controls can't. I also liked the bird on the body. Because I love birds. And in the music world, the decoration of instruments and hardware plays no small role because it inspires creativity. And the fact that the pedal is assembled by my hands also warms my soul and creates inspiration.
3 notes
·
View notes