#mens headwear
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
[Hanfu · 漢服]Chinese Song Dynasty(960–1279AD)Emperor Traditional Official Hanfu











The official uniform of the Chinese Song Dynasty emperor in "Serenade of Peaceful Joy"




【Historical Reference Artifacts】:
Portrait of Emperor Taizu (21 March 927 – 14 November 976)of Song Dynasty, kept in the National Palace Museum

Portrait of Emperor Yingzong (16 February 1032 – 25 January 1067) of Song Dynasty, kept in the National Palace Museum

Many people may curious about why the emperors of the Song Dynasty did not wear the classic yellow, but instead wore white or red round-necked robes.
During the Han and Tang dynasties, yellow was exclusively associated with imperial authority. According to the theory of "the Wuxing (Chinese philosophy)"which is Fire, Water, Wood, Metal, and Earth, yellow represented the center and symbolized the legitimacy of imperial power. However, during the Song Dynasty, due to political changes, Emperor Taizong decided to shift this tradition and adopt red as the new symbolic color for the dynasty. The court officials supported this change and provided various justifications, such as the theory of fire's virtue and the idea of red being a color of celebration, among others.
During the Han and Tang dynasties, yellow was exclusively associated with imperial authority. According to the theory of "the Wuxing (Chinese philosophy)"which is Fire, Water, Wood, Metal, and Earth, yellow represented the center and symbolized the legitimacy of imperial power. However, during the Song Dynasty, due to political changes, Emperor Taizong decided to shift this tradition and adopt red as the new symbolic color for the dynasty. The court officials supported this change and provided various justifications, such as the theory of fire's virtue and the idea of red being a color of celebration, among others.
【Emperor Taizu of Song Dynasty<Zhao Kuangyin/赵匡胤>】
Emperor Taizu of Song (21 March 927 – 14 November 976), personal name Zhao Kuangyin, courtesy name Yuanlang, was the founding emperor of the Song dynasty of China. He reigned from 960 until his death in 976. Formerly a distinguished military general of the Later Zhou dynasty, Emperor Taizu came to power after staging a coup d'état and forcing Emperor Gong, the last Later Zhou ruler, to abdicate the throne in his favor.
During his reign, Emperor Taizu conquered the states of Southern Tang, Later Shu, Southern Han, and Jingnan, thus reunifying most of China proper. To strengthen his control, he lessened the power of military generals and relied on civilian officials in administration. He was succeeded by his younger brother, Zhao Kuangyi (Emperor Taizong).
Early life
Born in Luoyang to military commander Zhao Hongyin, Zhao Kuangyin grew up excelling in mounted archery. Once, riding an untamed horse without a bridle, he knocked his forehead on the wall above the city gate and fell off, but got right back up and chased the horse, eventually subduing it while going unharmed. In the mid-940s, he married Lady He on his father's arrangement. After wandering around for a few years, in 949 he joined the army of Guo Wei, a jiedushi (military governor) of the Later Han dynasty, and helped Guo quell Li Shouzhen's rebellion.
Career under Later Zhou(后周)
In 951, Guo Wei rebelled and created the Later Zhou dynasty. Because of his brilliant combat skills, Zhao Kuangyin was promoted to a palace guard commander. Chai Rong (Emperor Shizong of Later Zhou) frequently met Guo Wei and noticed Zhao Kuangyin's potential. Under his command, Zhao Kuangyin was made into a commander of the cavalry units. Under Chai Rong, Zhao Kuangyin's rise to power had begun.
Zhao Kuangyin's career started at the Battle of Gaoping, against the alliance of the Northern Han and Liao dynasties.
This rivalry started when Chai Rong ascended the throne and Liu Chong decided to work with the Liao dynasty. In the initial confrontation, the army's right flank, led by Fan Aineng (樊愛能) and He Hui (何徽), was defeated. Looking at the situation, Zhao Kuangyin and Zhang Yongde (張永德) led 4000 elite Palace troops to counter the Liao army. Zhao Kuangyin's exhortation for the loyalty to the emperor quickly strengthened morale. The small force held off the larger Liao army until reinforcements arrived. In the end, the successful counter repelled the Northern Han back to Taiyuan.
The victory raised Zhao Kuangyin up to the post of the grand commander of the palace guards, as well as reorganising and training them. More importantly, he developed the relations with other generals and officials related to the Chief of Palace, including Shi Shouxin, Wang Shenqi (王審琦), Yang Guangyi (楊光義), Wang Zhengzhong (王政忠), Liu Qingyi (劉慶義), Liu Shouzhong (劉守忠), Liu Yanrang (劉延讓), Mi Xin (米信), Tian Chongjin (田重進), Pan Mei, his brother Zhao Kuangyi, Shen Yilun (沈義倫), Lu Xuqing, Zhao Pu (趙普), Chu Zhaofu (楚昭輔). Within a few years, Zhao Kuangyin completely controlled the palace guards and even developed a set of officials under him with the people mentioned above.
Soon, he was promoted to a jiedushi (military governor), controlling most of the military power under Chai Rong. Nevertheless, he still had two rivals – Zhang Yongde (Guo Wei's son-in-law) and Li Chongjin (Guo Wei's nephew). In 959, after a trap[clarification needed] set by Zhao Kuangyin, Zhang Yongde was demoted. After the death of Chai Rong, the Later Zhou throne was left to his seven-year-old son Guo Zongxun, and the second rival, Li Chongjin, soon found himself lacking the political backing. As a result, Zhao Kuangyin was able to use his influence to transfer Li Chongjin to Yang Prefecture as a jiedushi.
Chenqiao Mutiny/陈桥兵变
Main article: Chenqiao Mutiny20th-century illustration of Zhao Kuangyin being proclaimed emperor by the army of the Later Zhou dynasty.
In 960, word reached the chancellor Fan Zhi that Northern Han and Liao dynasties were once again allied to invade them again. Without verifying the reliability of the hearsay, Fan Zhi sent Zhao Kuangyin to combat the alliance. After traveling 40 li, there was a clamour that a "prophet" saw two suns fighting, and that this meant the transfer of the Mandate of Heaven to Zhao Kuangyin. The story effectively spread around the army: there came discontent of the "command" of the young emperor and a shift of loyalty to Zhao Kuangyin. A few days later, when Zhao Kuangyin was drunk in his tent, all the troops had not slept the whole night; they got their weapons and started yelling. Zhao Pu and Zhang Kuangyi, who were guarding the tent, saw the situation and went into the tent to wake up Zhao Kuangyin. When Zhao Kuangyin came out, all the troops yelled, "The army is without a master, we are willing to make the general the new emperor." Allegedly, Zhao Kuangyin took the power reluctantly, only under the urging of his soldiers. The midnight mutiny of officers forcibly urged Zhao Kuangyin to the throne; but, when the officers presented him to the troops as their new commander-in-chief he refused the imperial nomination until they swore unconditional obedience to him as leader.[6] News of the rebellion soon reached the court and chaos erupted. The only person who thought about a resistance was Han Tong, but he was killed by one of Zhao Kuangyin's generals when he reached home.
Upon entering the capital to take his seat on the throne, Zhao Kuangyin made an executive order prohibiting the troops from looting the city or otherwise violating the rights of the population.
This coup would allow Zhao Kuangyin to become emperor in 960.With the gates opened for him, he became emperor with no resistance. Before the chancellor Fan Zhi could say anything, one of Zhao Kuangyin's generals pointed a sword at him and said, "We are without masters. Today, we must have an emperor." After the officials looked at each other and knew it was hopeless to resist; they all bowed down. With the court under control, Zhao Kuangyin was officially proclaimed emperor. The new dynasty's name, Song, was inspired by the army Zhao Kuangyin commanded in Song Prefecture.
After the declaration, Zhao Kuangyin sent the dethroned young emperor Guo Zongxun with his mother to the Western Capital (西京). He personally ordered the Zhao family to receive the Chai family into their family's care for generations.
As emperor
Emperor Taizu playing cuju with Zhao Pu, by the Yuan dynasty painter Qian Xuan (1235–1305)
In 960, Zhao Kuangyin helped reunite most of China proper after the fragmentation and rebellion between the fall of the Tang dynasty in 907 and the establishment of the Song dynasty. The plan set during Chai Rong's reign was to first conquer the north, then the south. During Emperor Taizu's reign, there was a change in strategy. He would conquer all the smaller states such as Later Shu, Southern Han and Southern Tang. The exception was the strong Northern Han in the north at Taiyuan supported by the Khitans of the Liao dynasty. Emperor Taizu's strategy was to win over the independent southern states[8] as the south was weaker than the north as the Liao dynasty supported Northern Han.
In 968, Emperor Taizu personally led the army against the Northern Han. At first, his forces tore through the defences and placed Taiyuan under siege, but was ultimately forced to retreat after he struck against the defences of the Northern Han with the Liao cavalry coming in to support.Portrait of Emperor Taizu, who founded the Song dynasty
Emperor Taizu established the core Song Ancestor Rules and Policy for the later Song emperors. He was remembered for his expansion of the imperial examination system such that most of the civil service were recruited through the exams (in contrast to the Tang where less than 10% of the civil servants came through exams). He also created academies that allowed a great deal of freedom of discussion and thought, which facilitated the growth of scientific advance, economic reforms as well as achievements in arts and literature.
Emperor Taizu is well known for bringing the power of the military under control, ending the era of the warlords, centralizing the state over regional commanders and so preventing anyone else rising to power as he did.[8] Upon becoming emperor, he invited the general officers to a lavish banquet, where he convinced them all to retire as military leaders or accept minor posts, in favour of enjoying extensive estates and generous retirement funds and benefits which he then offered them.At a certain point during the feast, the new emperor made a speech to the military officers assembled there, which he began by expressing his deep gratitude to each and all of them for placing him on the throne, and that now that he had the power to do so, he wished to reward them to the utmost of his ability; then he went on to say that he thought the present company would all understand that he could not feel at ease on his new throne, with them continuing in command of their various armies of troops: and, he said, that if they duly considered the ramifications of the matter, neither would they. He then sincerely promised that they and their families would live in happiness and harmony, if they accepted his offer to retire with the stated benefits: eventually, none of the generals refused his terms, and thus began a period of relative internal peace within the realm for the duration of the Song dynasty which he thus founded, also better securing the military forces for involvement with the rival surrounding empires.
Many Song and later sources record the story of the "Taizu's Oath", which forbade his successors from killing scholar-officials. However, this story might be a later construct.
Death and succession dispute
Tomb of Emperor Taizu in the Yongchang Mausoleum, Gongyi, Zhengzhou
Emperor Taizu reigned for seventeen years and died in 976 at the age of 49. Curiously, he was succeeded by his younger brother, Zhao Kuangyi (Emperor Taizong), even though he had two grown sons – Zhao Dezhao, the Prince of Yan (951��979), and Zhao Defang, the Prince of Qin (959–981). The traditional historical accounts place emphasis on the role Zhao Kuangyin's mother played in the decision which was made shortly after the Song dynasty was proclaimed (around 961). So for nearly his entire reign, it was known and accepted that Zhao Kuangyi would succeed him.
In folklore, the story known as "shadows by the candle and sounds from an axe" is very popular and suggests that Emperor Taizu was murdered by his brother, who was after the throne.After his death, Taizu was interred at the Yongchang Mausoleum, near Gongyi.
After Emperor Taizong, the line of succession passed on to his son and descendants rather than those of Emperor Taizu. However, when Emperor Gaozong (1127–1161) failed to produce an heir, he selected a descendant of Emperor Taizu to be his adopted heir to succeed him in 1161. After 1161, all the subsequent Song emperors were descended from Emperor Taizu through his two sons, Zhao Dezhao and Zhao Defang.
—————————–
📸Photo::©胶宗模玩jiaotoys(Chinese manufacturing historical figure model merchant)
🔗Xiaohongshu App:https://www.xiaohongshu.com/user/profile/5659f093589de33cb53e0083
—————————–
#chinese hanfu#Song Dynasty(960–1279AD)#Emperor Taizu of Song Dynasty#hanfu#hanfu accessories#hanfu_challenge#chinese traditional clothing#china#chinese#yuanlingpao#mens hanfu#mens headwear#胶宗模玩jiaotoys#漢服#汉服#中華風#Serenade of Peaceful Joy
118 notes
·
View notes
Text
OP's tags: #damn they brought the whole court....
FASCINATING, NEAT

2K notes
·
View notes
Note
Traditional hair ornaments for men?
Hi! Thanks for the question, and sorry for taking ages to reply!
For posts showcasing traditional hair ornaments for men, please check out my mens headwear tag. I also have a "men's headwear/hairstyles" section in my Q&A Masterpost - so please check that out as well.
Hope this helps!
#mens headwear#hair ornaments#hanfu accessories#hanfu#mens hanfu#tik-a#ask#reply#reference#m#x#s#chinese fashion#chinese clothing#china
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
#polls#poll#daily polls#i love polls#polladay#hat#hats#headwear#men's fashion#women's fashion#fashion#everyday fashion
365 notes
·
View notes
Text

Tintype of best buds in bowler hats enjoying a joke for two, c. 1880s
#get you a man who shares your sense of humor AND headwear#19th century#1800s#1880s#19th century fashion#1880s fashion#fashion history#historical fashion#gay interest#vintage men#19th century men#tintype#ferrotype#menswear
376 notes
·
View notes
Note
NICE
top 5 hanfu outfits hanyi 💓 - xiaosean
*SCREAMING* I jumped straight into Taobao to grab pictures for this ask I AM SO EXCITED TO REPLY IT
disclaimer: oncoming picture spam which I just couldn’t bear to hide beneath a cut
not really a specific look, but more in terms of my top 5 (listed “chronologically”) favourite hanfu styles
1. 圆领袍 (yuan2 ling3 pao2)
Literally means “round-collared robe”
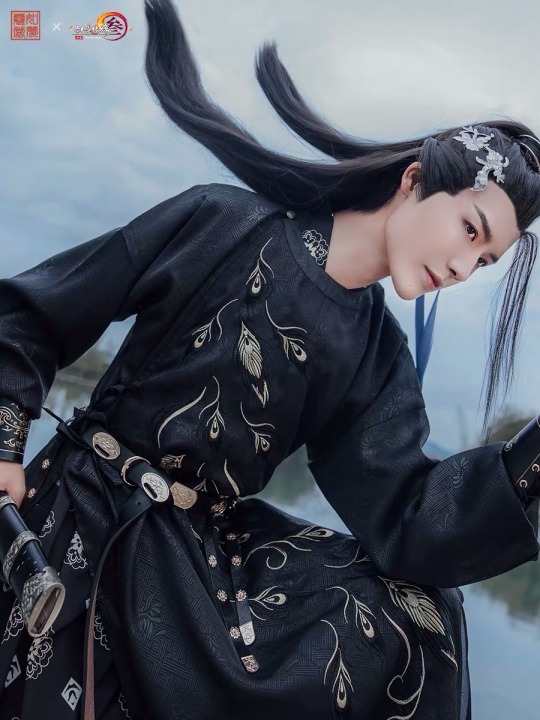

Originally for men

But became popular among women in the Tang dynasty
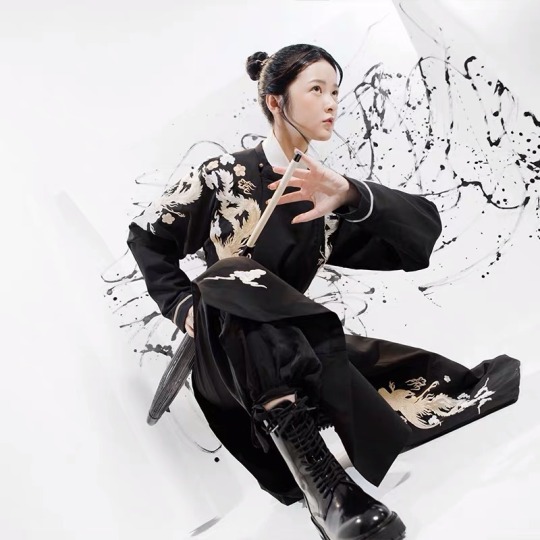


Some people also wear the collar unbuttoned so it ends up looking like this double lapel thing which is still damned cool
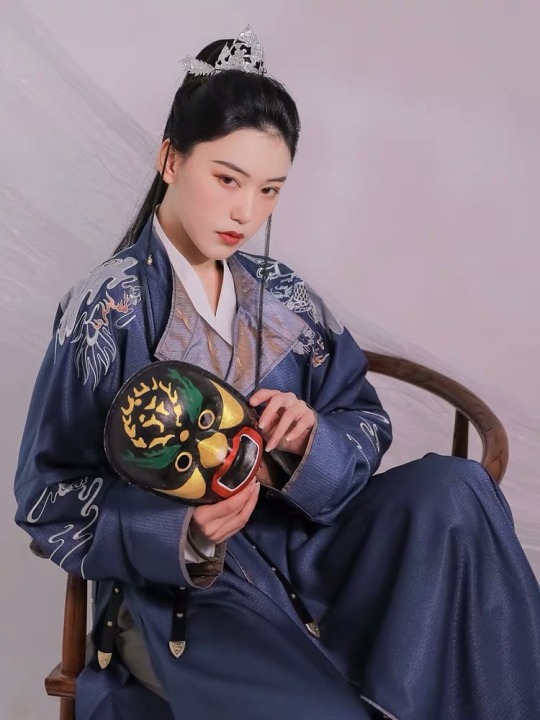

Sources:
如梦霓裳
寻景记汉服
织羽集
流烟昔泠
2. 飞鱼服 (fei1 yu2 fu2)
Literally means “flying fish clothing”
Type of clothing given from the emperor to eunuchs/ guards (e.g. the Embroidered Uniform Guard) during the Ming dynasty



帅气 x100000 although I’ll never be able to pull this cool look off
Sources:
如梦霓裳 [1] [2] [3]
3. 道袍 (dao4 pao2), bonus if it’s paired with a 披风 (pi1 feng1)
Literally means “Taoist robe” but was not restricted to only Taoists
Common full-length single robe that was worn by men in the Ming dynasty
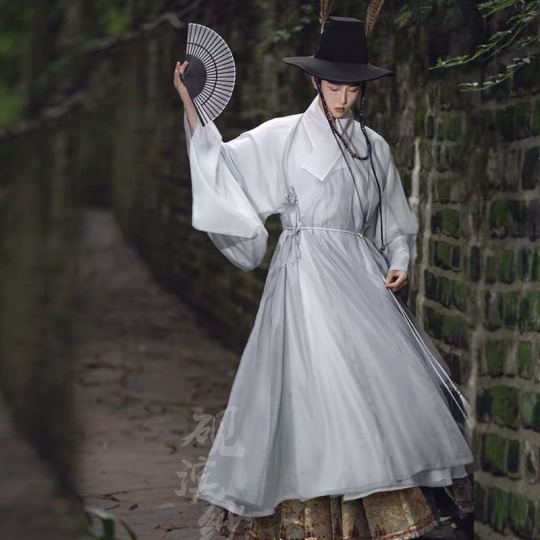


Sometimes with a ma mian qun (will talk about this later) underneath it!

LOOK AT THAT PI FENG AHHH 仙 x100000

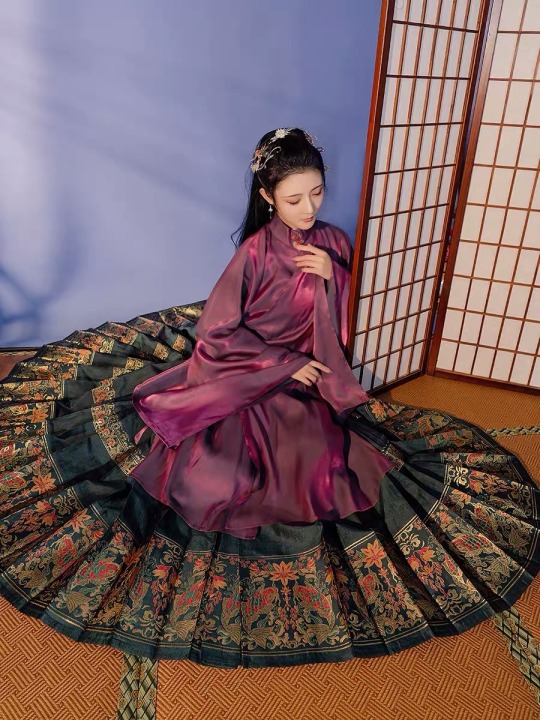
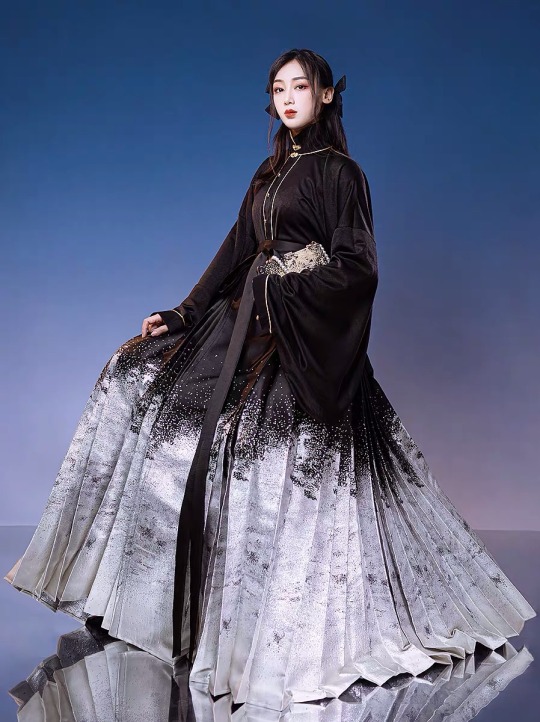
4. 马面裙 (ma3 mian4 qun2)
I LOVE THESE OMG
Literally means “horse face skirt”
Common pleated skirt worn in the Ming dynasty
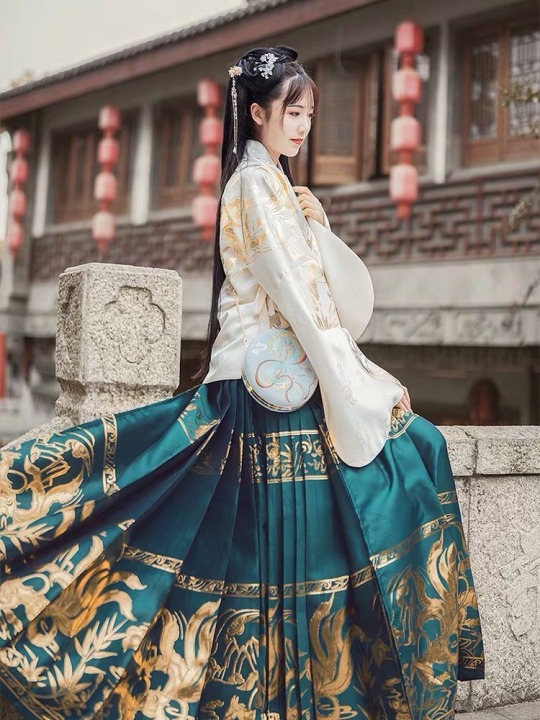


Can be traditionally worn as part of the 袄裙 (ao3 qun2), which consists of the skirt and a top worn over the skirt

But I reaaaally love the ma mian qun because it’s so damn versatile and can be paired with modern classy looks like this
(I’m getting this top and skirt on 11.11 hoho)

An even more modern look like this (I have this particular skirt hoho)
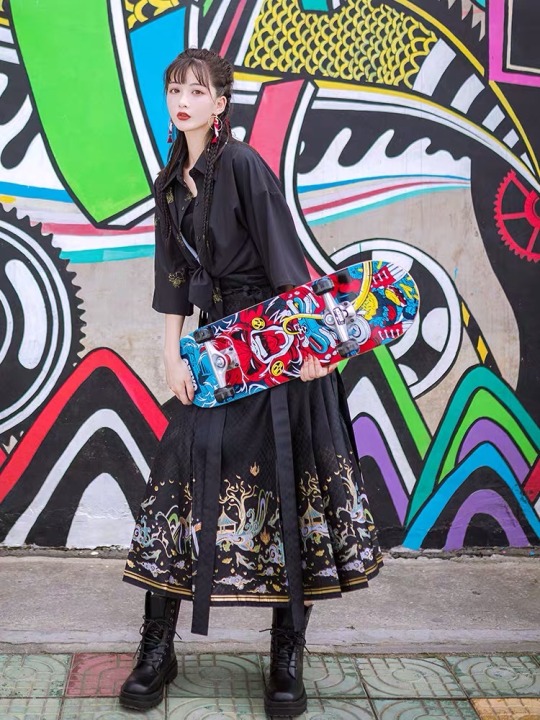

AND EVEN MODERN BADASS LIKE THIS (also getting this skirt during 11.11 hoho)
Sources:
如梦霓裳
七巧坊
拟梦汉服
华裳九州
池夏
5. 交领襦裙 (jiao1 ling3 ru2 qun2), bonus if it’s paired with a 大袖衫 (da4 xiu4 shan1) or 褙子 (bei4 zi3)
Okay I’m a bit hazy on when this started becoming popular/ commonly worn so I’ve put it right at the end instead of fitting it “chronologically” like the rest above
Some styles are from the Wei-Jin period, some are from the Song dynasty, and a lot of styles on Taobao these days don’t really stick to particular period of what a jiao ling ru qun looks like
Literally means “cross-collared short coat and skirt”, as opposed to the 齐胸襦裙 (qi2 xiong1 ru2 qun2) which is something like what jiang yanli in donghua wears
I prefer the cross-collared styles more hehe
Tho speaking of cross-collared styles, my major pet peeve is when people accidentally draw the collars crossed the wrong way (right over left instead of left over right)… because that’s usually meant for the deceased





Sources:
如梦霓裳 [1] [2]
出社
重回汉唐 [1] [2]
okay end of spam I think I might have gone a little over on this whoooopss (〃ー〃)
answering “top 5″s!! ���°。⋆⸜(ू。•ω•。) (altho I admit to being terrible with fanfics so please avoid those *nervous cough*)
#hanfu#mens hanfu#hanfu recommendations#limao#damao#yuanlingpao#feiyufu#daopao#pifeng#mamianqun#aoqun#ruqun#yichang#daxiushan#beizi#mens headwear#hats#mens hairstyles#taobao#reference#history#leonzhng
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Photos of 16th-17th century Irish clothing
Extant garments in the National Museum of Ireland
Notes: The garments in this post are all bog finds which means their current color may not be their original color. Although some of these items were found with human remains, no photos of human remains are included in this post.
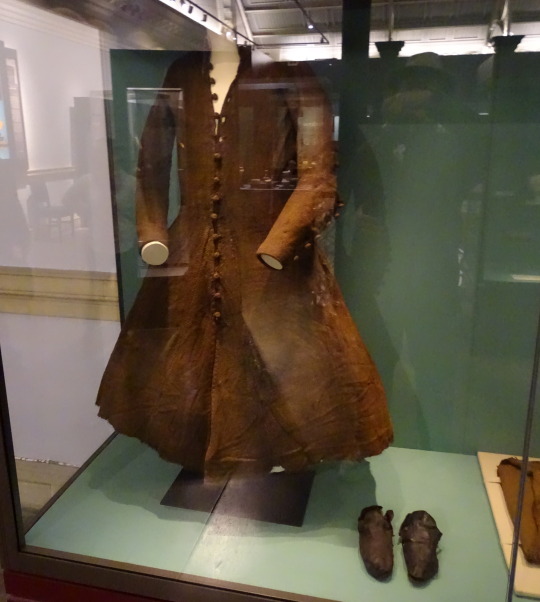
Killery Cóta Mór (great coat) and brogues:

photos by hayling billy used under non-commercial, share alike license
The Killery outfit comes from an adult male bog body found in Killerry parish, Co. Sligo in 1824. It includes a cóta mór, triús, a brat, and shoes which are on display in the museum, and a sheepskin biorraid (conical hat) which fell apart shortly after it was found (Briggs and Turner 1986).
Killery triús (trews):

photo by hayling billy
Killery outfit with and without brat:
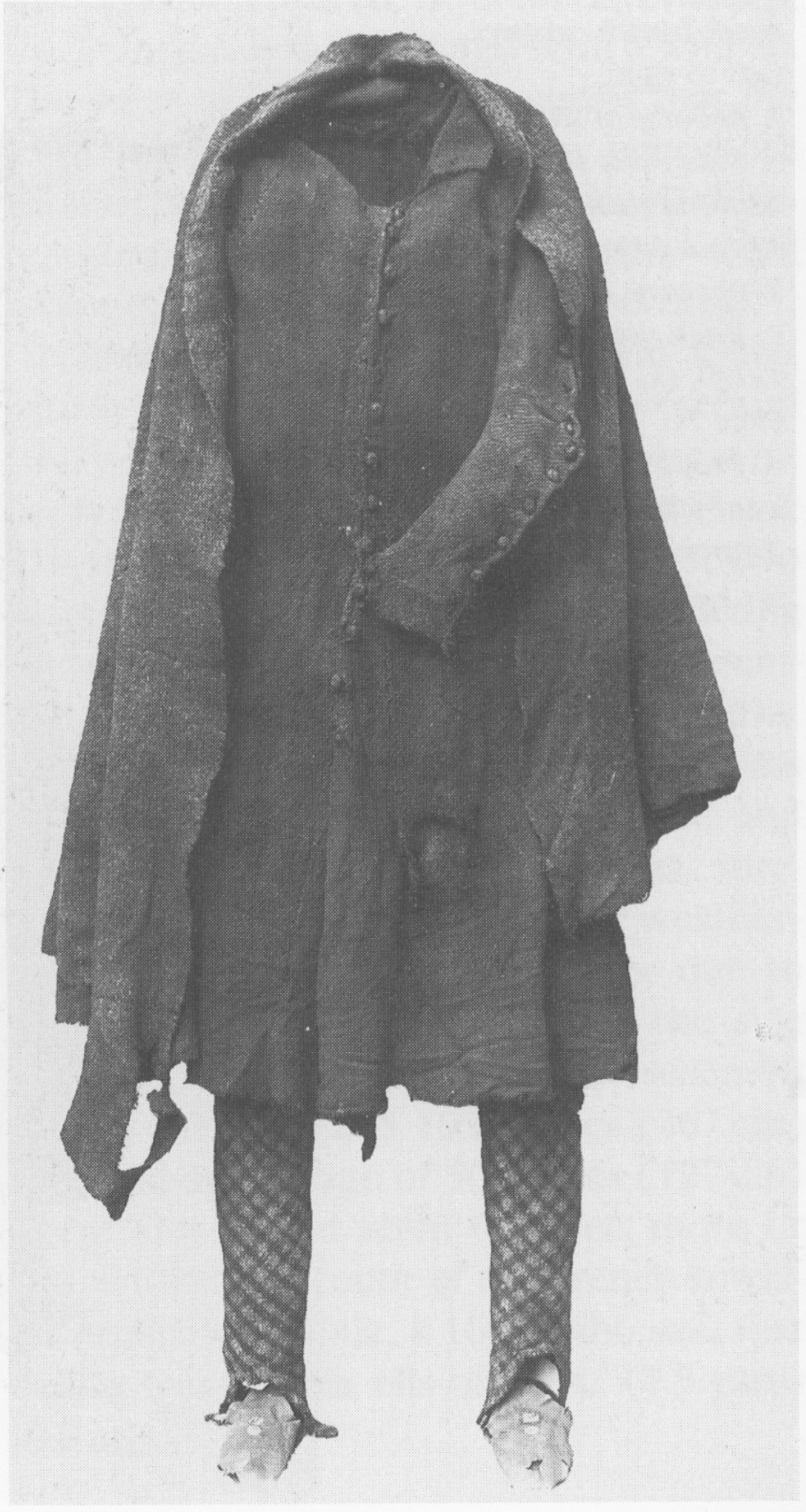


The outfit is generally dated to the 17th c. (Dunlevy 1989). It matches Luke Gernon's 1620 description of Irish men's winter apparel:
"in winter he weares a frise cote. The trowse is along stocke of frise, close to his thighes, and drawne on almost to his waste, but very scant, and the pryde of it is, to weare it so in suspence, that the beholder may still suspecte it to be falling from his arse. It is cutt with a pouche before, which is drawne together with a string."
Additional photos of the outfit: cóta front, hem, buttons, and brat.
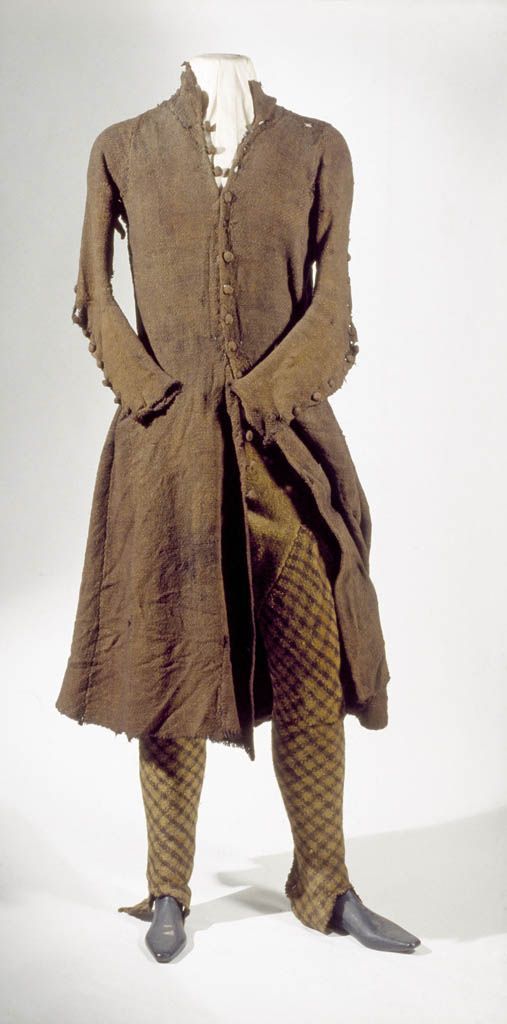
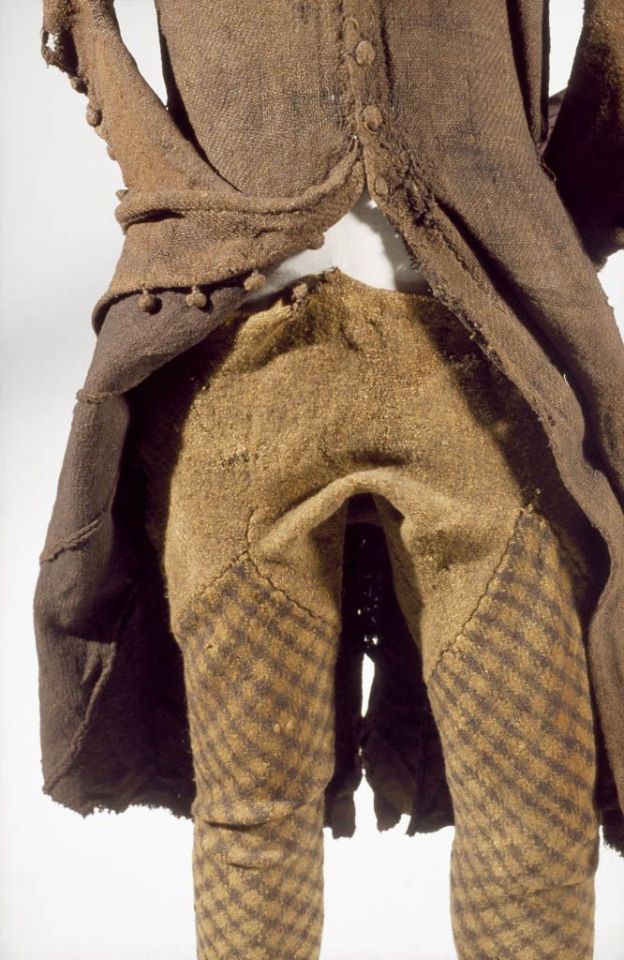
Shinrone gown:
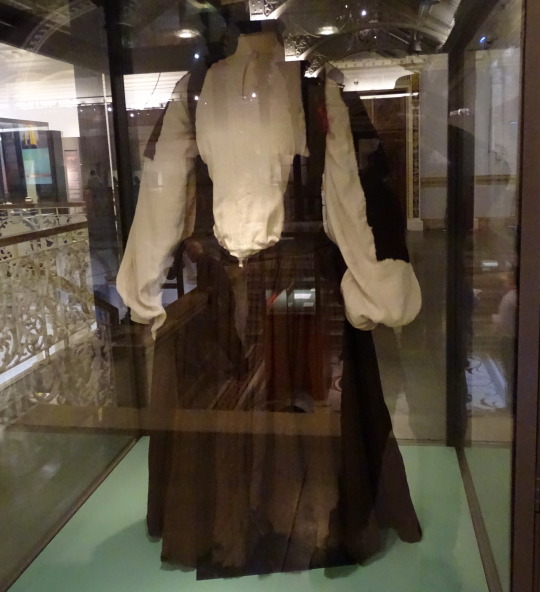

photo by hayling billy
The Shinrone gown was found in a bog in 1843 in Co. Tipperary near Shinrone, Co. Offaly. Unlike the Killery outfit, there were no human remains or other items found with it (Briggs and Turner 1986). The ends of the sleeves and possibly also the bottom of the skirt are missing. The sleeves would have had wrist cuffs or ties that allowed them to be fastened around the wearer's wrists. It probably also had loops or rings along the U-shaped center-front opening for lacing. It is typically dated late 16th-early 17th c, based on its similarity to a circa 1575 illustration by Lucas DeHeere and to the dresses described by Luke Gernon in 1620 (Dunlevy 1989, McGann 2000). It could be older however, because Laurent Vital described dresses with this type of sleeve in 1518.
Copyrighted, better quality photos: left front, right front, back Additional details: side-front, front waistline
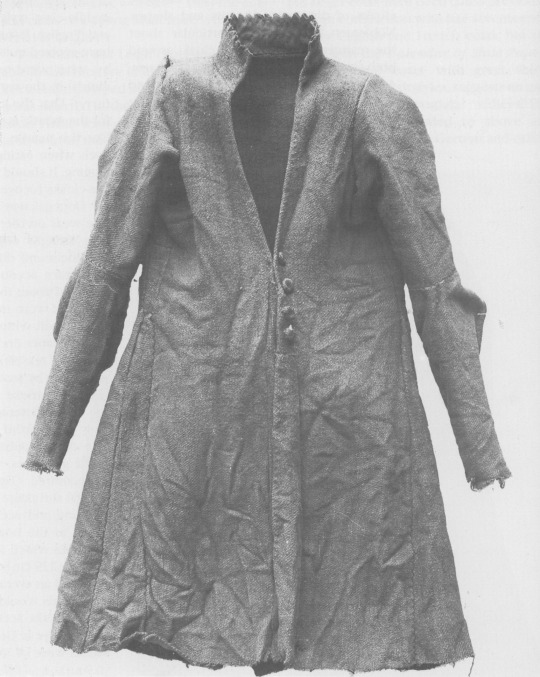
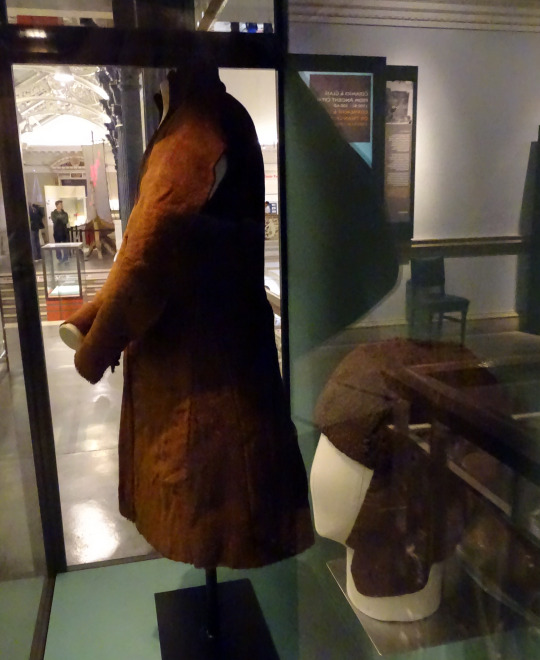
Tipperary Cóta Mór:


photos from Dunlevy 1989 and hayling billy
Another Cóta Mór. This one is from Co. Tipperary, exact find spot and date unknown. Like the Shinrone gown, it was not found with human remains or other items (Ó Floinn 1995). It is probably also from the 17th century (Dunlevy 1989).
Additional photos: front, side, front buttons, front detail, side
Brat and hats:
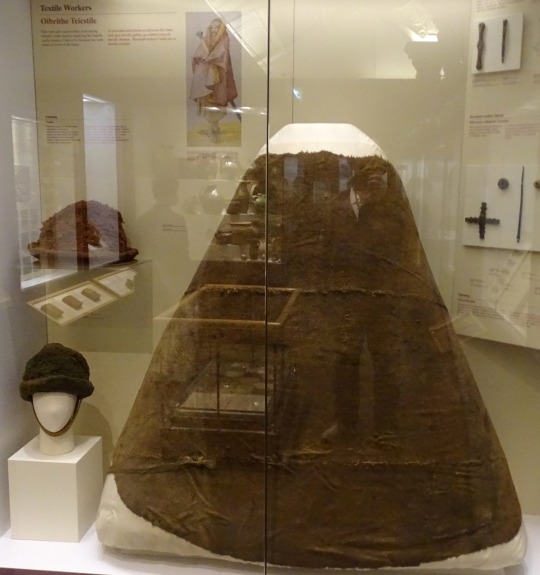

photo by hayling billy
I haven't been able to find any clear photos of the label on this display, but based on the excellent condition and the presence of the leather tie, I think this is the Meenybradden woman's brat.
Closeup of the tie:

The Meenybradden woman is a bog body found in Meenybradden bog, Co. Donegal in 1978. The brat was wrapped around her as a shroud and secured with the leather tie (Delaney and Ó Floinn 1995). No other garments or artifacts were found with her, although she may have been wearing a linen garment such as a léine when she was buried. Linen tends to not survive in bogs. The Meenybradden woman has a calibrated radiocarbon date of AD 1130-1310, but some archaeologist have suggested humic contamination from the peat may be throwing off the dating. Her brat is identical in cut to others from the 16th-17th centuries (Delaney and Ó Floinn 1995).

Meenybradden brat laid flat. (photo from Delaney and Ó Floinn 1995)
Wool hats:
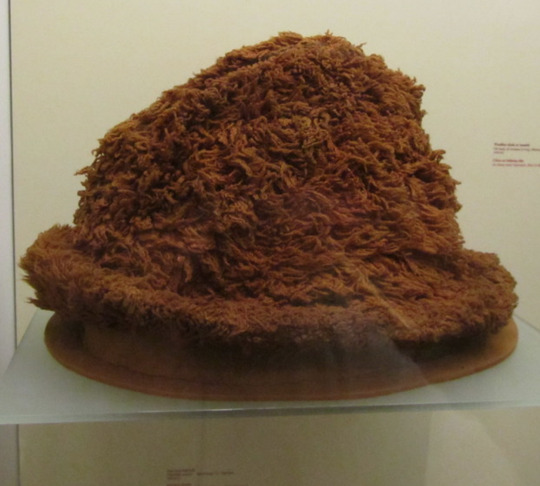
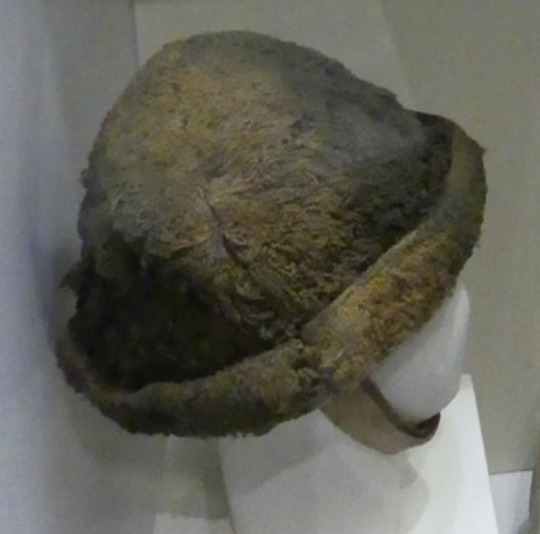


Hats from Boolabaun, Co. Tipperary made of wool felt which has been cut and sewn to form the shape. They have togs of unspun wool worked into them giving them the appearance of faux fur. Dunlevy suggests a 15th-16th c date for them (Dunlevy 1989, McClintock 1943).
Wool cloak:
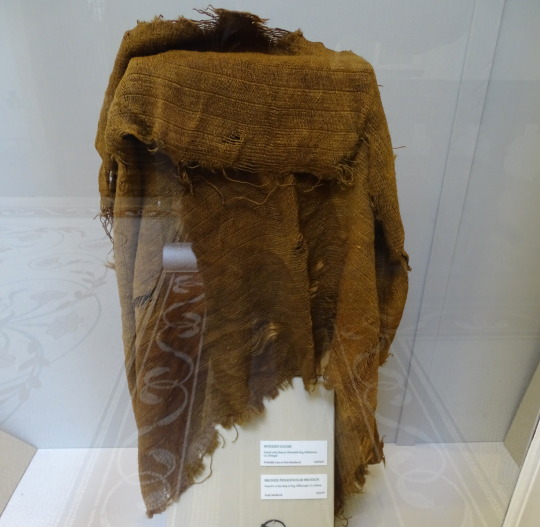

photo by hayling billy
The museum label says it's from Glenmalin bog, Malinmore, Co. Donegal, but I think this may be a mistake. According to Ó Floinn (1995), the artifact with accession number 1946:416 from Malinmore, Co. Donegal is a bale of linen. Ó Floinn's table also gives accession number 1946:416* for a group of clothing from Owenduff, Co. Mayo which includes a gown, a jacket, and a cloak. If the cloak in the photo is actually the one from Owenduff, it is probably from the 17th c (Dunlevy 1989). Alternatively, someone might have misidentified a wool cloak as a bale of linen. The museum label dates this as late Medieval to post-Medieval.
*Either Ó Floinn made a typo or this is a mistake in the museum records. Museums are not supposed to give the same accession number to 2 different artifacts. In the NMI's defense, 1946 was probably a messy year for everyone.
Bibliography:
Briggs, C. S. and Turner, R. C. (1986). Appendix: a gazetteer of bog burials from Britain and Ireland. In I. Stead, J. B. Bourke and D. Brothwell (eds) Lindow Man: the Body in the Bog (p. 181–95). British Museum Publications Ltd.
Delaney, M. and Ó Floinn, R. (1995). A Bog Body from Meenybradden Bog, County Donegal, Ireland. In R. C. Turner and R. G. Scaife (eds) Bog Bodies: New Discoveries and New Perspectives (p. 123–32). British Museum Press.
Dunlevy, Mairead (1989). Dress in Ireland. B. T. Batsford LTD, London.
Gernon, Luke (1620). A Discourse of Ireland. https://celt.ucc.ie/published/E620001/
McClintock, H. F. (1943). Old Irish and Highland Dress. Dundalgan Press, Dundalk.
McGann, K. (2000). What the Irish Wore/The Shinrone Gown — An Irish Dress from the Elizabethan Age. Reconstructing History. http://web.archive.org/web/20080217032749/http:/www.reconstructinghistory.com/irish/shinrone.html
O’Floinn, R. (1995). Recent research into Irish bog bodies. In R. C. Turner and R. G. Scaife (eds) Bog Bodies: New Discoveries and New Perspectives (p. 137–45). British Museum Press.
Vital, Laurent (1518). Archduke Ferdinand's visit to Kinsale in Ireland, an extract from Le Premier Voyage de Charles-Quint en Espagne, de 1517 à 1518. translated by Dorothy Convery and edited by me. https://irish-dress-history.tumblr.com/post/721163132699131904/laurent-vitals-1518-description-of-ireland
#16th century#17th century#irish dress#dress history#gaelic ireland#historical men's fashion#historical women's fashion#bog finds#irish history#historical dress#brog#bratanna#irish mantle#headwear#triús#cóta mór
83 notes
·
View notes
Text



#silence bottom#medieval#medieval fashion#chuckling darkly to myself whilst i take notes bc the women's headwear section is by far the longest#yeeeees YEEEEEEEEES!!!!!!!!!!#i earned this after enduring male fashion#'men dressed more richly during this period pffffft'#and its still ass‼️🗣️#u will never be glamour
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
Riverside Code at Qingming Festival (清明上河图密码) : Fashion
Small official styling reference
Inspired by the "Wen Hui Tu": Literary Gathering painting, the image of a minor clerk in Song dynasty is: hair cap, round collar robe with left lapel-over-right shirt underneath, and open crotch pants.

In the Song Dynasty, men thought that showing their hair in public was not proper, so whenever you go out, you must wrap your hair in a scarf or a hat. It was both for prevention against dust and as good manners.
.
Tuan Guan (Round Crown) styling reference
Inspired by the murals from Baisha Tomb of Song.

Zhang Qiniang's crown is silver-plated and hand- decorated by gold. This was a trendy style among wealthy Song Dynasty women. There have been various other materials used as well, such as flowers and emerald-adorned and lacquered crowns.
.
Song Dynasty Outfit-of-the-Day
Zhao Ban'er: A Part-timer Coroner "I can! I can do it! Let me try!"
Playful double bun- At first glance, she looks like a woman who is not afraid of anything!
Small crossbody bag- Decorate what you are supposed to decorate, opportunities always come to those who are prepared!
Orange top- Everywhere you go, there is a little sunshine around you~
Zhao Mo'er: A Scientific Researcher "You will know after experimenting."
Knot type futou- The hair is neatly tied up, "You can't have strands of hair when doing experiments~"
Blue and gray robe- At first glance, he looks like an iceberg guy with fashionable colors (actually he is an introvert)
Dirty little hands- Can instantly tell he's someone who is destined to do great things!
Zhao Li: A Tipsy Grandpa "If you don’t enjoy happiness now, when will you wait?"
Big red flower hairpin- He looks like a happy old man!
Cardigan coat- The slightly dipped grandpa's unruly clothes, the chill feeling is perfect!
Delicious wine- Drunk or not, I can always drink again~



Gu Zhen: A Hardworking Officer "Interesting, y'all are interesting."
Cross foot Futou- Wearing a little hat is a symbol of status and dignity
Dark pattern official robe- If you see these thieves from a distance, you will tremble and take a detour!
Black and silver- It’s a luxury product for men. If you save some money, let’s exchange it for a black gold one~
Wen Yue: A Shopkeeper "Don't mess with me if you don't have a few lives!"
Silver hairpin bun- As soon as you pull it out, it will be a life-threatening blade, hiding a little secret~
Light blue shirt- The fabric is soft and docile, and the small floral decorations make it look even more gentle~
Umbrella shop ledger- Must read it every day. With a little bit of savings, the big house is waving to her!
Zhao Buyou: A Flirt "Wife, I've secured us a good spot, come here!"
Soft cloth futou- ·Looks warm, soft and friendly~
Wearing a flower hairpin- Just to attract the other person’s first glance in the crowd~
Crew neck blouse- Gentle and elegant, the smell of a scholar can be smelled eight hundred miles away!



.
Traditional Color Palette of Wen Yue's Wardrobe











.
Riverside Code at Qingming Festival ( 清明上河图密码) : Qīngmíng shànghé tú mìmǎ Cultural Meta Masterpost
#cdrama#chinese drama#chinese history#chinese fashion#song dynasty#Riverside Code at Qingming Festival#清明上河图密码#song dynasty fashion#song dynasty headwear#tuan guan#baisha tomb#futou#men's flower hairpins
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Shiera Seastar moodboard/inspirations
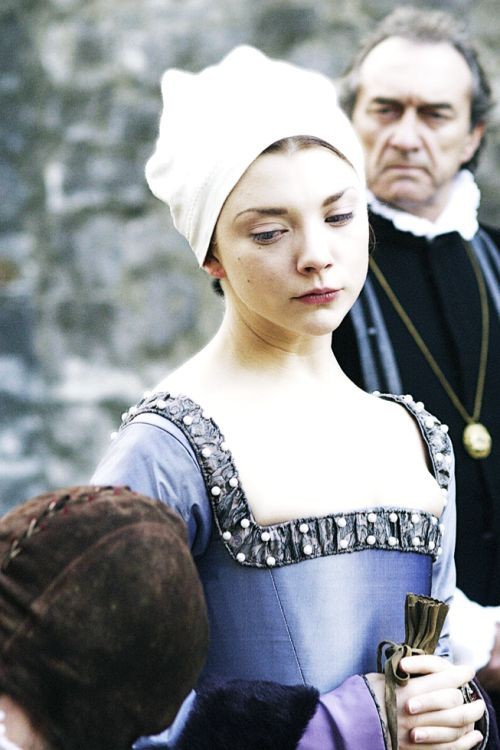
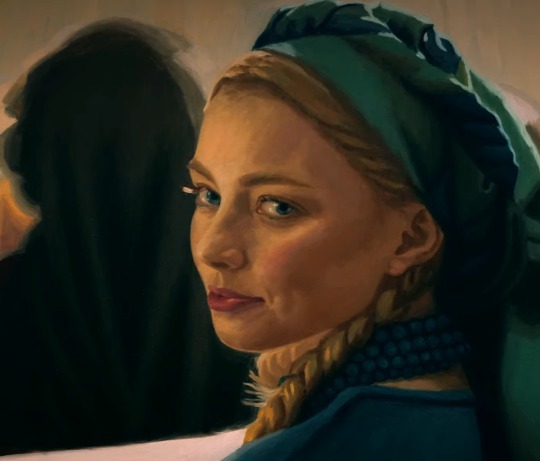
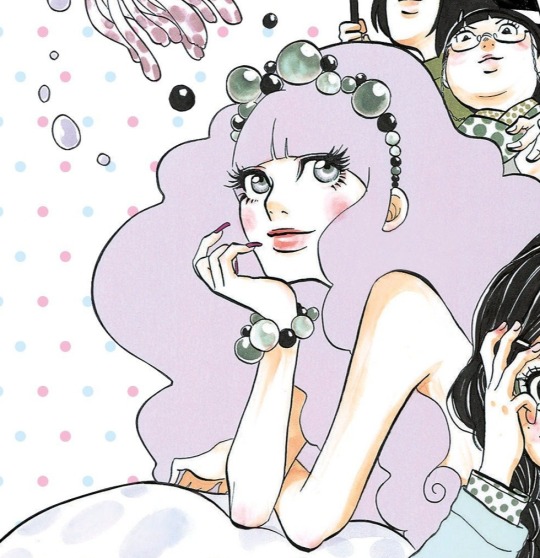










#shiera seastar#asoiaf#valyrianscrolls#house targaryen#little headcanon creeping in my head#shiera wore her hair long but liked to put it under a stylish headwear#hiding it to be more alluring#only showing it in its full glory to the men closer to her#wearing headwears dissimulating the hair inspired by queen naerys' fashion ?
27 notes
·
View notes
Text
It's called fujin/幅巾. I have a fujin tag here and there's a wikipedia article on it here.






to hanfu fans/experts, does anyone know what this headwear is called? i can't find the chinese name for it anywhere, any help is appreciated!
70 notes
·
View notes
Text
Elevate your everyday look with TRONFORM’s Men’s Beanie. Designed for those who appreciate both style and comfort, this beanie offers the perfect blend of warmth and luxury. Whether you're dressing for a casual day out or adding a finishing touch to your streetwear, TRONFORM’s Men’s Beanie ensures you stay on trend while staying cozy.
Shop now: https://www.tronform.co/products/men-s-tronform-beanie





#TRONFORM #MotivationInStyle #LuxuryEssentials #EvolveWithTRONFORM #Fashion #Style #Luxury #LuxuryLifestyle #DesignerWear #Trendy #Fashionable #FashionAddict #Fashionista #fyp #foryoupage #foryou #WinterStyle #BeanieStyle #MenFashion #Streetwear #CasualLuxury #CozyLooks #Headwear #MinimalistStyle #WarmFashion #EffortlessStyle #TronformEssentials #ChicAndComfort #SeasonalFashion #TrendingNow #TimelessStyle
#Elevate your everyday look with TRONFORM’s Men’s Beanie. Designed for those who appreciate both style and comfort#this beanie offers the perfect blend of warmth and luxury. Whether you're dressing for a casual day out or adding a finishing touch to your#TRONFORM’s Men’s Beanie ensures you stay on trend while staying cozy.#Shop now: https://www.tronform.co/products/men-s-tronform-beanie#TRONFORM#MotivationInStyle#LuxuryEssentials#EvolveWithTRONFORM#Fashion#Style#Luxury#LuxuryLifestyle#DesignerWear#Trendy#Fashionable#FashionAddict#Fashionista#fyp#foryoupage#foryou#WinterStyle#BeanieStyle#MenFashion#Streetwear#CasualLuxury#CozyLooks#Headwear#MinimalistStyle#WarmFashion#EffortlessStyle
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Attention American Viewers:

Lost Painting:
This lithograph was published in The Ulster Journal of Archaeology in 1856. It is based off a portrait of Owen Roe O’ Neill (Eoghan Ruadh Ó Néill) which is believed to have been painted before his death in 1649. The original painting was sold to an unrecorded buyer in America in about 1884, and its current location is unknown. The portrait is of great value to the cultural history of Ireland. In it, O' Neill wears a bairéad (Irish flat cap) and brat (shaggy Irish mantle), making it a rare, detailed portrayal 17th c. Irish dress.
Dr. Hiram Morgan of University College Cork is looking for the original painting. If anyone knows where it is, please email him at [email protected]. (More info) (Also, please send me a photo of it.)
The original portrait is an oil painting on wood and is approximately 12 in x 16 in (30 cm x 40 cm). According to the 1856 description of the painting, "The colour of the hair [. . .] is not decidedly red, but only approaching to it. The tinge of redness, however, is quite sufficient to have distinguished him amongst a number of dark-haired men; and the complexion is clear and ruddy." A partially illegible text on the back of the painting reads, "Owen Roe O’Neill at the Court of [. . .] by the celebrated Dutch artist, Van Brugens".
The Ulster Journal states that the lithograph was "faithfully copied" from the painting, but if it really is an early 17th c. Dutch painting, I doubt the lithograph is an exact copy of it. 17th c. Dutch paintings tend to fill the whole canvas. They don't fade out at the edges.
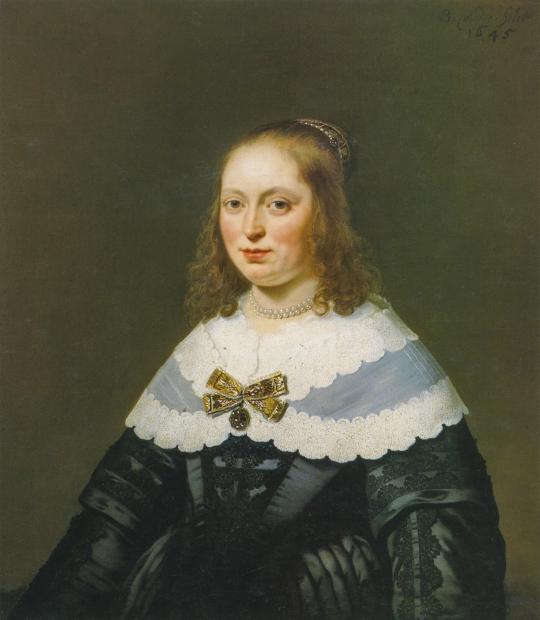

A 1645 portrait by Dutch artist Bartholomeus van der Helst. Notice how the lace on her sleeves continues all the way to the bottom edge of the canvas.
If we had the original painting, it might show us more details of the garment O' Neill is wearing under his brat.
There is also a color print of this portrait by John D. Reigh. It was originally published in 1888 and was probably made after the original painting left Ireland.

I would guess the Reigh version is less accurate to the original than the Ulster Journal version. In the Ulster Journal version, O' Neill's face looks more like a distinct individual, whereas, in Reigh's version, O' Neill looks more like a generic manly man. 17th c. Dutch portrait painters tended to excel at capturing distinct individual detail, as seen in the van der Helst example above. I'm not an art expert though.
Keep an eye out, people in America. Owen Roe O’ Neill might be hiding in an attic or antique shop somewhere in the US.
#gaelic ireland#art#historical men's fashion#irish mantle#headwear#irish history#irish dress#bairéad#17th century#lost art
29 notes
·
View notes
Text
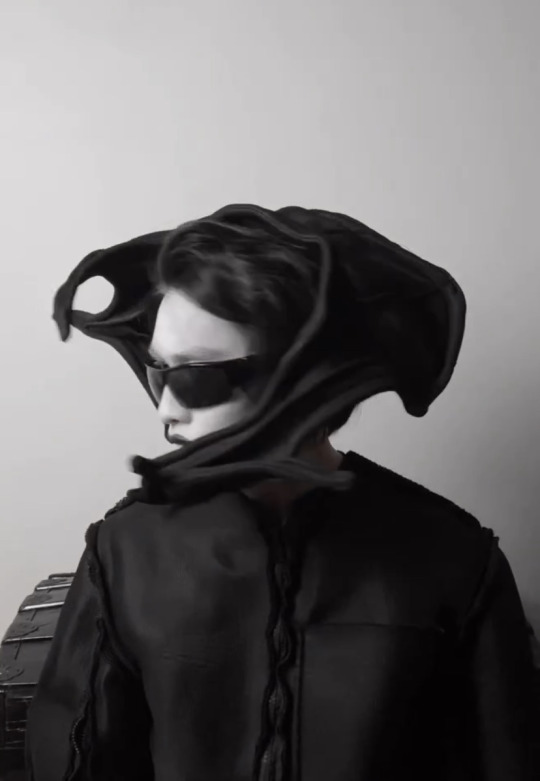
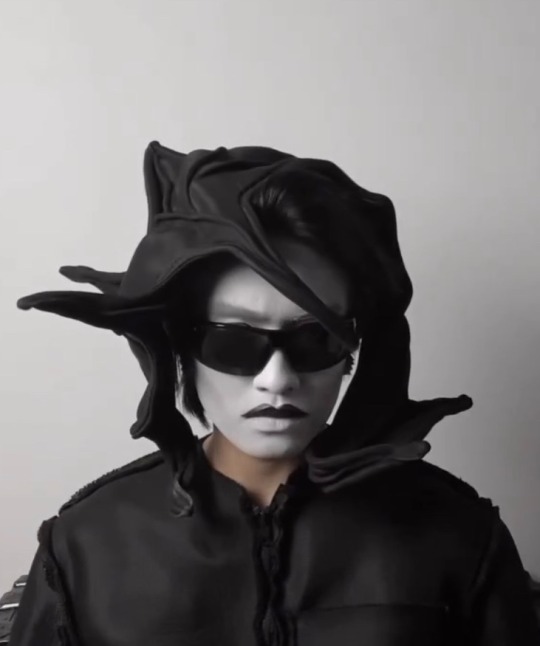


batwing headpiece, 2023
#Jean Louie Castillo#goth#goth fashion#jeanlouiecastillo#fashion designer#goth aesthetic#gothic#goth menswear#goth men#alternative goth#dark fashion#headpiece#headwear#crown#hat#hats#sombrero#fascinator#fashion#fashion design#fashion editorial#diy fashion#high fashion#couture#goth makeup#the crow#black outfit#black and white#gothgoth#gothcore
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
INTERESTING
chinese folk fashion in song dynasty
#hanfu#song dynasty#commoners hanfu#mens hanfu#mens headwear#childrens hanfu#runway#video#music#fashion
851 notes
·
View notes
Text
Get This Hat and Cap Design
Worldwide shipping

ORDER NOW
#buckethat#baseballcap#dadhat#headwear#summer#love#art#fashion#baseball#hats#travel#photooftheday#photography#streetwear#style#ootd#nyc#women#instagood#sun#snapback#men#nature#beautiful#redbubble#artists on tumblr#outfit#outfit inspiration#trends#trendingnow
3 notes
·
View notes