#literary translation experts
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
What Are Literary Translation Services? A History of Literary Translations
What Are Literary Translation Services? Literary translation services involve translating works like novels, poems, plays, and essays from one language to another. These services aim to make literary pieces accessible to a broader audience. They preserve the original work’s artistic and cultural nuances. Translators capture the essence of the text, not just its literal meaning. They focus on…

View On WordPress
#affordable literary translation#book translation services#certified literary translators#cultural translation services#experienced literary translators#literary localization#literary translation agency#literary translation experts#literary translation services#literary translator#multilingual literary translation#novel translation#play translation#poetry translation#professional literary translators#quality literary translations
0 notes
Text
I know Barry Goldstein is a bit of a controversial Yiddish translator and I haven't been able to read any of his work yet but I really appreciate his effort because he's one of the few contemporary translators working into Yiddish at all. I'm hoping to get my hands on his Tolkien and Wodehouse translations and see how he handled them.
#Yiddish#Translation#langblr#Yes under normal circumstances literary translators should be expert native/bilingual speakers#But Yiddish doesn't have a lot of those who are also willing to translate classic literature into Yiddish#We don't even have enough translators translating from Yiddish!#I'd prefer an imperfect translation to no translation for now because it might pave the way for better retranslation later
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
There is something so poetic in Carlos Centeno being the only named character in “la siesta del martes”. He was a thief in his life, and after his death that was his title. The priest tending the keys to the cemetery, his final resting place,, the last version of himself, did not know his name. No one in town knew his name, nor did they care he was just The Thief. But it is through his mother he is given a name. Just as children are named by their parents at birth in his death he is given name. It changes the story it puts him beyond the sole role of Thief and he is instead a person. Everyone remains archetypes of themselves: the Mother is a mother firm but caring, the younger sister is a younger sister shy obedient, but Carlos is named he is a complex person. In his death, he is given an agency that was taken from him through his forced role.
#Carlos centeno#La siesta del martes#gabriel garcía márquez#myrambles#yeah#idk some thoughts on him being the only person named#If I feel like torturing myself later I might translate this into Spanish and reblog this with the Spanish version#we’ll see though#Also this is fr just my interpretation!!!#I’m not pretending to be a Spanish literary expert I read this novella in my second language and I had to read it fr 4 times bc I-#-couldnt compute
0 notes
Text
*activate special interest mode* I read this poem in an undergrad class and it always makes my head spin to think about the spans of time involved—the fact that the poet describing this 'ancient ruin' is, themself, so far-removed from the present day that their English is incomprehensible to us modern speakers and requires translation.
But speaking of translation, I love this one, because it preserves a rhythm from the original that is usually lost in other translations I've seen.
There's a section of the poem where the original poet uses words that end in 'orene'/'orone' (pronounced something like 'or-uh-nuh') to emphasise the sense of destruction.
Hrofas sind gehrorene, hreorge torras, hrim geat torras berofen, hrim on lime, scearde scurbeorge scorene, gedrorene, ældo undereotone. Eorðgrap hafað waldend wyrhtan forweorone, geleorene, heardgripe hrusan, oþ hund cnea werþeoda gewitan.
And here's a typical translation of that section:
Roofs are fallen, ruinous towers, the frosty gate with frost on cement is ravaged, chipped roofs are torn, fallen, undermined by old age. The grasp of the earth possesses the mighty builders, perished and fallen, the hard grasp of earth, until a hundred generations of people have departed.
There's nothing wrong with this translation—it gets the point across.
But here's what this translator, R.M. Liuzza has done with it:
The roofs are ruined, the towers toppled, frost in the mortar has broken the gate, torn and worn and shorn by the storm, eaten through with age. The earth's grasp holds the builders, rotten, forgotten, the hard grip of the ground, until a hundred generations of men are gone.
And I think that's brilliant! Liuzza preserved those rhymes to great effect, and the 'orn' words they use are even similar to the 'orene' (remember, it's pronounced more like 'or-uh-nuh') sounds used in the original.
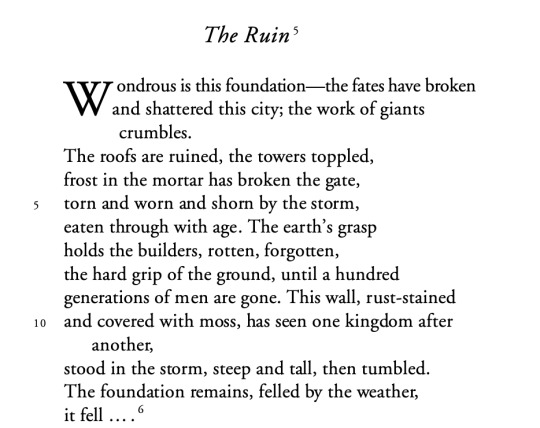


The Ruin, Anonymous Old English Poem, trans R.M. Liuzza
#the main detail i remember from the poem is those 'orene' words and how much i liked them#so when i saw this translation with 'torn and worn and shorn' i was like !!!!!!#LOVE this#also just love this poem in general but YEAH#and i can nerd out over old english/middle english any day#i'm by no means an expert I Just Think It's Neat#old english#old english literature#poetry#anglo saxon#medieval poetry#medieval literature#dark ages#literary analysis#sylvie's own nonsense#my addition#translation#literature in translation
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Tips from a former English major and English TA:
Reading the text actually does help you in the class believe it or not and we can tell when you haven’t read it. Sometimes we’re just too tired to call you out on it. Your awkward silence in class speaks volumes.
That being said, if you don’t have time because life happens read at least two different summaries or analysis pages online. Preferably more. One source will rarely mention everything your teacher asks you about.
Other tricks include reading the last sentence of every paragraph or reading every other page
The reason you’re being forced to take an English class when you’re not an English major is to help you come up with arguments when there’s no strict data set to follow and no one correct answer. If your school allows for alternatives to this sort of category like film analysis or art history that you think you’d like better, take it. The goal of GE classes is to turn you into a well rounded and educated person. Not to torture you.
If you’re reading works in translation and don’t want to take the time to learn the language but you also want to get a more accurate idea of the nuances of the original language, read three different translations of the work and compare them. Reading translators notes and reviews of translations by experts is also helpful. In some more rarely translated works translators notes and reviews may be all you have to work off of.
When you’re writing a literary essay you’re entering an ongoing conversation that’s been going on since writing has existed. A tradition that’s existed since before Aristotle. And you’re just as smart as that guy. Add something to the conversation. Participate. Bigger idiots than you have done it.
Chat gbt is really bad at literary analysis and often gets facts wrong. We can tell when you use it.
Everyone has different levels of understanding of the history of literature even within the professional world. People specialize for a reason. Nobody is expecting you to have read everything. An expert in medieval Irish literature isn’t going to have read the same things as an expert in post-colonial west African literature who won’t have read the same things as a general expert in contemporary Asian literature. Being “well-read” is subjective and means something different to everyone. English classes often show you where to start and how to research stuff related to literature and analysis. Especially if you are an English major it’s easy to get overwhelmed early on but you get used to accepting that you can’t know everything. And that’s fine. Just focus on finding your niche. Or maybe you don’t have one and just want to sample everything. Or maybe you’re just here for general knowledge. That’s fine too.
708 notes
·
View notes
Text


This post translates directly to @musas-sideblog's about how Touchstarved ties with Victorian horror and implicit/metaphorical sex, and I couldn’t stop thinking about it, so here is a lengthy theory. Enjoy :)
Note 1: Victorian era authors used an unholy amount of ways to imply sexual feelings/acts etc, so I here I will include only the ones that are of interest. Note 2: I've highlighted the "most important" parts. Note 3: I'm not an expert at this, so please bear with me and feel free to correct me. Note 4: Do I need to add a TW? I think it's obvious-
Overview: What is Victorian Horror?
Victorian horror refers to the genre of horror literature, art, and culture that flourished during the Victorian era, roughly from the mid-19th century to the early 20th century, coinciding with Queen Victoria's reign from 1837 to 1901. This period was marked by a fascination with the macabre, the supernatural, and the dark aspects of human nature, reflecting the anxieties and societal changes of the time.
Key Themes and Characteristics
Supernatural Elements:
Ghosts and Spirits: Tales of haunted houses and spectral apparitions were central to Victorian horror. Charles Dickens's "A Christmas Carol" (1843) and Henry James's "The Turn of the Screw" (1898) are notable examples.
Monsters and the Gothic: The era's literature is filled with monstrous creations and gothic settings, such as in Mary Shelley's "Frankenstein" (1818), Bram Stoker's "Dracula" (1897), and Robert Louis Stevenson's "Strange Case of Dr Jekyll and Mr Hyde" (1886).
Science and the Unknown:
The Victorian period was a time of great scientific advancement, but also of fear about the implications of these discoveries. This is evident in works that explore the dangers of unchecked scientific experimentation, like "Frankenstein" and H.G. Wells's "The Island of Doctor Moreau" (1896).
Exploration of the Human Psyche:
Victorian horror often delved into the darker aspects of the human mind, including themes of duality, madness, and the hidden, sinister side of human nature. This is seen in "Dr Jekyll and Mr Hyde" and Edgar Allan Poe’s works, such as "The Tell-Tale Heart" (1843).
Social and Moral Anxieties:
The literature frequently reflected Victorian society's fears and anxieties, including issues related to sexuality, class, and the role of women. Gothic novels often contained subtexts about societal norms and the consequences of transgressing them.
Urban Fear and Isolation:
The rapid urbanisation of the Victorian era contributed to themes of isolation, alienation, and fear of the crowded yet lonely cityscape. This is evident in the settings of many horror stories, such as Arthur Machen's "The Great God Pan" (1894).
Sexual Content: Victorian literature is renowned for its strict moral codes and conservative views on sexuality. Explicit depictions of sexual activity were considered taboo and were subject to censorship. Consequently, authors developed subtle and nuanced methods to imply sexual scenes or themes.
Literary Techniques for Implying Sexual Scenes
✧ Symbolism and Imagery:
Sexuality was often conveyed through symbolic imagery. Objects, actions, or natural phenomena could serve as metaphors for sexual activity or desire. For example, in "Dracula" by Bram Stoker, blood and biting symbolise sexual penetration and the exchange of bodily fluids, infusing the act with a sense of forbidden desire and eroticism.
Clothing and Undress:
Gloves: In Victorian culture, gloves were highly symbolic. The act of a woman removing her gloves in the presence of a man, or a man assisting her in this act, could signify a moment of intimacy or vulnerability. Similarly, a man giving a woman his gloves could be a sign of affection or a deeper connection.
Hats and Bonnets:
Corsets
Objects and Personal Items:
Locks of Hair
Jewellery
Books and Letters
Touch and Physical Contact:
Kissing Hands
Hand-Holding
Food and Drink:
Wine: Sharing wine or a meal in an intimate setting often suggested a prelude to deeper connection. Descriptions of characters drinking wine together in private could imply a romantic or sexual undertone.
Fruit: Certain fruits, like apples, grapes, or peaches, were laden with sexual symbolism. Eating or sharing fruit could represent temptation or indulgence. For instance, in Christina Rossetti’s poem "Goblin Market", the act of eating the goblin fruit is rich with sexual symbolism.
Flora and Fauna
Flowers and Gardens:
Roses: Roses were often used to symbolise love and passion. A red rose might suggest romantic or sexual attraction, while a wilted rose could imply lost innocence or sexual ruin.
Lilies: Lilies, especially white ones, represented purity but could also suggest a contrasting theme when associated with a fallen or tarnished character.
Garden Settings: Scenes set in secluded gardens or amongst lush, overgrown vegetation often hinted at secret or forbidden encounters. Descriptions of characters wandering through or tending to gardens could imply sexual exploration or awakening.
Flowers Blooming or Opening: The blooming of flowers often represented sexual awakening or the act of losing one's virginity.
Nature Imagery:
Rivers and Water: Flowing water and rivers often symbolised sexual desire and the act of lovemaking. For instance, in "Tess of the d'Urbervilles" by Thomas Hardy, Tess's encounter with Alec d'Urberville is often described with metaphors of nature and fluidity.
Storms and Weather: Storms, with their intense energy and sudden outbursts, were frequently used to symbolise sexual passion or climactic moments.
Birds and Beasts:
Animals, especially those that are wild or predatory, often symbolised primal sexual instincts and desires. The taming or interaction with these animals could imply a character’s grappling with their own sexuality.
Fire and Heat
✧ Phrases and Sayings
Euphemistic Language
Descriptive Phrasing
Dialogue and Confessions
Private Spaces:
Secluded or Dimly Lit Rooms: Scenes set in private, darkened rooms often suggested clandestine sexual encounters. The privacy of the setting allows authors to imply what could not be explicitly stated. In Wilkie Collins’s "The Woman in White", many key interactions happen in secluded spaces, hinting at secrets and hidden desires.
Dreams and Fantasies:
Dream Sequences:
Dreams and fantasies were used to explore a character’s subconscious desires and fears, often revealing their suppressed sexual longings. These sequences provided a socially acceptable way to delve into erotic themes.
Hallucinations and Madness:
Moments of madness or hallucination could serve as a metaphor for overwhelming passion or uncontrollable sexual desire. These states allowed characters to express forbidden feelings in a way that was metaphorically safe.
Physical Interactions and Horror
Touch and Proximity as Menace:
Unwanted or Forced Touch: In horror, touch that is typically a sign of affection or intimacy becomes a source of fear.
Physical Closeness in Horror Settings: Close proximity in dark, secluded places amplifies the sense of claustrophobia and vulnerability, turning what could be an intimate setting into one fraught with terror.
Undress and Exposure in Horror:
Loosening Corsets and Vulnerability: The act of undressing or loosening clothing, which can be a prelude to intimacy, in horror often leaves characters vulnerable to attack or exposure of their deepest fears.
Food and Consumption in Horror
Cannibalism and Vampirism:
Blood as Sexual and Vital Fluid: The act of consuming blood, as in vampirism, blends the themes of sustenance and sexual exchange. The vampire's bite becomes a metaphor for both sexual penetration and the transfer of life force.
Example: "Dracula" is a prime example where blood consumption is deeply eroticized, with Dracula’s victims often portrayed in a state of ecstatic submission as he drains their blood.
Food as a Lure: Food and feasting, typically symbols of pleasure and indulgence, in horror contexts can be used to lure victims into dangerous situations.
Example: In "Goblin Market" by Christina Rossetti, the goblins’ fruit is both irresistibly tempting and dangerous, representing a forbidden and potentially fatal indulgence.
Plot and Character Dynamics in Horror
Power and Domination:
Common Dynamics with a Dark Twist
Predators and Victims: Characters who prey on others are often literal monsters in horror, representing the loss of control or innocence.
Secrecy and Concealment:
Hidden Desires and Monstrous Revelations: Characters who conceal their true identities or desires often find these hidden aspects manifesting as monstrous or terrifying in horror narratives, suggesting that repression can lead to dire consequences.
Clandestine Meetings and Forbidden Encounters: Secret meetings and forbidden relationships, often tinged with sexual implications, add an element of danger and fear, suggesting that transgressing social norms leads to horror.
Common Themes in Victorian Horror
Duality and the Doppelgänger:
Theme: The concept of duality, where a character has a hidden, darker side, or encounters a double (doppelgänger), often symbolises the internal conflict between good and evil within individuals.
Connection: This theme reflects Victorian anxieties about identity, morality, and the consequences of repressing one’s darker impulses.
Gothic and Supernatural Elements:
Theme: Victorian horror is rich with Gothic elements such as haunted houses, dark landscapes, and supernatural beings. These elements create a sense of dread and evoke the mysteries of the unknown.
Connection: The Gothic setting often serves as a backdrop for exploring human fears, isolation, and the impact of the supernatural on everyday life.
Decay and Degeneration:
Theme: The fear of decay and degeneration, both physical and moral, is a recurring motif. This theme often examines the decline of individuals, families, or societies and the consequences of corruption and vice.
Connection: This theme mirrors Victorian concerns about the erosion of social and moral values amidst rapid industrial and social changes.
Madness and Psychological Horror:
Theme: The exploration of madness and psychological horror delves into the fragility of the human mind and the terror of losing one's sanity. This often includes hallucinations, obsessions, and the thin line between reality and delusion.
Connection: This theme resonates with Victorian fears of mental illness, the limitations of medical knowledge, and the impact of societal pressures on mental health.
Forbidden Knowledge and the Faustian Bargain:
Theme: The pursuit of forbidden knowledge and the resulting consequences is a central theme. Characters who seek power, immortality, or forbidden truths often pay a heavy price, reminiscent of the Faustian bargain.
Connection: This theme highlights Victorian anxieties about scientific progress, moral boundaries, and the potential hubris of human ambition.
The Uncanny and the Unknown:
Theme: The uncanny involves the strange and unfamiliar becoming eerily familiar, often unsettling the reader and characters. It blurs the lines between reality and the supernatural, invoking fear and discomfort.
Connection: This theme taps into Victorian fears of the unknown, the foreign, and the otherworldly, reflecting broader anxieties about social and cultural boundaries.
Death and the Afterlife:
Theme: Victorian horror frequently grapples with themes of death and the afterlife, exploring the fear of mortality, the possibility of an afterlife, and encounters with the dead or undead.
Connection: These themes reflect Victorian preoccupations with death, the spiritual realm, and the possibility of life beyond death, often intensified by the era's high mortality rates and interest in spiritualism.
Isolation and Alienation:
Theme: Isolation and alienation are prevalent themes, often highlighting characters who are physically or emotionally detached from society, leading to their vulnerability and descent into despair or madness.
Connection: This theme resonates with the Victorian experience of industrialization and urbanization, which often led to feelings of disconnection and loneliness.
Class and Social Anxiety:
Theme: Victorian horror often explores themes of class and social anxiety, including the fear of losing social status, the consequences of poverty, and the tension between different social classes.
Connection: This theme reflects the rigid class structures of Victorian society and the fears and tensions that arose from social mobility and economic disparity.
Moral Corruption and Hypocrisy:
Theme: Victorian horror frequently critiques the era’s moral standards and exposes the hypocrisy of societal norms. Characters who appear virtuous often harbor dark secrets or engage in morally dubious activities.
Connection: This theme mirrors the Victorian concern with appearances and the underlying tension between public propriety and private desires.
The Five Pillars of Victorian Horror & The Five Love Interests
The Supernatural and the Gothic (Ais)
Essence: Victorian horror often revolves around the supernatural, blending Gothic elements to evoke a sense of dread and otherworldly terror. This includes ghosts, vampires, haunted houses, and curses, which create an atmosphere where the boundaries between the natural and the supernatural blur.
Impact: The use of Gothic settings and supernatural phenomena provides a backdrop for exploring deeper themes of fear, mortality, and the unknown.
Psychological Depth and Madness (Vere)
Essence: Victorian horror delves into the complexities of the human mind, exploring themes of madness, obsession, and the psychological effects of fear and trauma. Characters often grapple with their sanity, facing inner demons as terrifying as any external threat.
Impact: This focus on psychological horror allows for a deeper exploration of character motivations and the impact of societal pressures.
Moral Corruption and the Double Life (Leander)
Essence: Themes of moral corruption and the duality of human nature are central to Victorian horror. Characters often lead double lives, presenting a veneer of respectability while concealing dark, sinful secrets. This tension between outward appearances and hidden truths reflects the era’s social hypocrisy and fear of scandal.
Impact: These themes critique Victorian society’s emphasis on propriety and the dangerous consequences of repressing one’s true nature. The idea of a double life or hidden self adds to the horror by suggesting that evil can reside within anyone, masked by a facade of normalcy.
Decay, Degeneration, and Disease (Kuras)
Essence: The themes of physical and moral decay, societal degeneration, and disease permeate Victorian horror. These motifs symbolise the fragility of human life and the inevitability of decline, reflecting the anxieties of a society grappling with rapid change and uncertain futures.
Impact: By focusing on decay and degeneration, Victorian horror underscores the transient nature of life and the ever-present threat of corruption and decline, whether through ageing, moral compromise, or societal breakdown.
Isolation and Alienation (Mhin)
Essence: Isolation and alienation are pervasive themes in Victorian horror, often depicted through characters who are physically or emotionally cut off from society. This separation heightens their vulnerability to external threats and internal fears.
Impact: Isolation serves to intensify the psychological tension and sense of dread, as characters confront their fears alone. It also reflects the era’s social and existential anxieties, including the fear of being disconnected or outcast from society.

Generally, I believe each LI connects with a pillair (as seen above). Perhaps by looking at the archetypes we could deduce propable endings and route elements.
Forgive me, for the following part is MESSY;
Ais

Vere

Leander

Kuras

Mhin

#THIS TOOK ME AGES#but it was worth it#vereletters#touchstarved theory#touchstarved theories#touchstarved ais theory#touchstarved vere theory#touchstarved kuras theory#touchstarved leander theory#touchstarved mhin theory#red spring studios#touchstarved#ts#touchstarved headcanons#touchstarved game#touchstarved oneshot#ais#ais headcanons#ais ts#ts ais#ais touchstarved#touchstarved ais#ais oneshot#vere#vere headcanons#vere ts#ts vere#vere touchstarved#touchstarved vere#vere oneshot
196 notes
·
View notes
Text
Make the Exorcist Fall in Love – Witches Part One
Ok, I finally finished this meta! I've broken it into two posts because it was getting a little too long. I’m covering some of the literary and historical references that Ekuoto plays with in regards to its witches hehe.. Regardless of whether Arima Aruma and Fukuyama Masuku are engaging with the actual history of witchcraft beliefs or the way it’s been filtered down into the contemporary cultural consciousness, I think it’ll be fun to present the real-life inspirations behind these ideas. Scholarly sources are cited so you can feel free to check out the information I discuss, and links are provided occasionally when I got lazy. All citations are in MLA form at the end of the second part because I didn’t feel Chicago footnote format would function well on Tumblr, so I apologize for any issues with the citations as I’m rusty with MLA. Take this all with a grain of salt, as I’m not an expert and also had to cover a lot of regions/periods of time. Hope you enjoy!
Content warnings for discussion of sexual violence, execution, images of cartoon nudity and violence (all Ekuoto panels), also major spoilers for Ekuoto and minor spoilers for Berserk, the movie Perfect Blue, and the movie The Craft
Link to Part Two of the meta (including works cited)
Witches – what did it mean to be a witch? Demonic Pacts, witch marks, and more
First off—what is a witch? This question is actually deceptively difficult to answer. For example, you can’t simply say that a witch is someone who practices magic: that’s too broad. “In September 1398 the theology faculty at the University of Paris approved a set of twenty-eight articles condemning the practice of ritual magic”—the targets of this were largely clerics (Levack 49), and there seems to have been a decent number of them (Apps and Gow 126). Those accused of witchcraft were considered distinct from these magic using priests for whom “this magic was practiced with grimoires or books of learned enchantments” (not that this was approved of by the church either) (Mackay 30-31).
What a “witch” was, is also something that could be wildly different depending on time and place. There was, however, a coalescence of ideas during the 15th century in Europe, followed by the “witch craze” of the Early Modern period (16th-18th centuries), in which there were an uptick in witch trials, provides an answer to what a witch is that has had a lasting impact in our present cultural consciousness (Witch Trials in Early Modern Europe and New England). This definition of witchcraft, then, I think, is the most relevant one to consider in this meta, although it will require a bit of generalization.
Essential to understanding this coalescence of ideas about witches is a book known as the Malleus Maleficarum, or “The Hammer of Witches,” a text on witchcraft published in 1486 by two Dominican friars, an order that focused on heresy (Mackay 1-2). Please note that mention of heresy, as it will be relevant later. How, then, did it imagine witches?
Christopher S. Mackay, in the introduction to his translation of the Malleus Maleficarum, calls this construction of witchcraft “the elaborated concept of witchcraft,” and defines it as follows (this is a direct quotation I just can't format it right on Tumblr LMFAO):
A pact entered into with the Devil (and concomitant apostasy from Christianity)
Sexual relations with the Devil
Aerial flight for the purpose of attending:
An assembly presided by Satan himself (at which initiates entered into the pact, and incest and promiscuous sex were engaged in by the attendees),
The practice of maleficent magic
The slaughter of babies. (Mackay 19)
The Malleus’s construction of witchcraft “represented a special form of heresy that played an important part in Satan’s plans for the Final Days” (Mackay 33) and borrowed elements from accusations made against earlier heretical groups (Saunders 85-86). It focused on women from the lower classes as opposed to priests who were practicing magic (Mackay 30-31). Heresy is key then to understanding witchcraft in this period. The Malleus’s construction of witchcraft also had a sexual focus, repeatedly bringing up the impact of demons on the genitals (Garrett 38). For example, there’s a whole section that details whether or not witches can take your penis away. The Malleus’s findings? No, but they can cast an illusion that makes it appear as though your penis is gone (Mackay 323-329). Breathtaking.



In Ekuoto, we see that the what makes someone a witch is a demonic convent, which involves erasing their names from the book of life and writing it in the demon lord’s book of death (which I will go further into depth on in the section on Sabbaths!), receiving a seal on their body, and merging bodily fluids through kissing or sex.
This process actually is pretty faithful to early modern beliefs about how one became a witch. The Malleus describes the process as involving a “sacrilegious avowal,” in which witches either make this vow to serve the demon ceremonially “when the sorceresses come to a certain assembly on a fixed day and see the demon in the assumed guise of a human as he urges them to keep their faith to him, which would be accompanied by prosperity in temporal matters and longevity of life.” While there, a new witch-to-be would be presented, and if determined to be “ready to renounce the Most Christian Faith and Worship,” signs themselves over (as in with a literal signature) (Mackay 281, 283). Non-ceremonially, a demon might just pop up when someone is in trouble and promise to help them if they help him (Mackay 286-287). So, here we see the idea of witchcraft granting long life and a physical signing over of the self to a demon.
But, witchcraft beliefs weren’t only constructed by books like the Malleus Maleficarum—those accused of witchcraft also contributed to these beliefs in their confessions (Roper Witch Craze 117). As historian Lyndal Roper in her book Witch Craze describes of Early Modern witch confessions from Germany, “Intercourse with the Devil was the physical counterpart of the pact with him—and it was sex with the Devil which many accused witches talked about at length, rather than the pact which, according to demonological theory, actually made them Satan’s own” (Roper Witch Craze 85). Roper speculates that a large reason for this that many accused during this time period were illiterate, and so in their confessions, sex as the form of pact appears far in confessions than physical signatures (Roper Witch Craze 85). Regardless, we can see this as where Ekuoto borrows the idea of sex or kissing as a part of the demonic convent.

Sometimes, in these confessions, we also saw that the Devil would “give the witch a special diabolical name” as a sort of reversion of the baptismal process where a Christian name would be gained (Roper Witch Craze 116). Vergilius taking a new name as a part of his demonic pact then is completely in line with historical views of witchcraft, which I think is very fun of Arima Aruma.
Another idea of that shows up regarding people becoming witches is the idea of witch’s marks and devil’s marks, which were pretty significant in English witch trials. A Devil’s mark was a mark that was believed to have been left by the Devil when the witch becomes his, while the witch’s mark was believed to be a teat that the witch would use to nurse familiars their blood, although the terms were often conflated (Garrett 49-50). In England, searching for these marks was a major part of trials, and the experience was violating, the marks often being found near women’s genitals after they had been stripped of all their clothes, and pricked repeatedly on any mark that might be a witch’s or devil’s mark (Garrett 37).
Devil’s marks have been mentioned in Ekuoto, as seen in the earlier image, although we have not had any specifically pointed out. Vergilius’s heart under his right eye is likely a devil’s mark in my opinion, as he did not have it as a child when he was not a witch. I’ll be interested in seeing if it comes up and if there’s any significance to its shape. I could totally be wrong and it could just be like make up or a tattoo or something. This under the eye heart mark isn’t original to Ekuoto—heart patches for facial application have existed at least since the 17th century (not citing out of laziness but look up beauty patches), and under the eye heart make up was like a trend back in 2019 on Tiktok—but hilariously, 2012, when Marina and the Diamonds released Electra Heart, featuring MARINA with a heart mark under her eye, is also is presumably the year Vergilius became a witch (based on Daniel’s statement in one of the chapters that he’s been active for a decade). Maybe he’s just a really big Electra Heart fan lol.
The Witch’s Sabbath
A witches Sabbath was “where witches gathered to worship the Devil, dance, feast, indulge in sexual orgies, and practice cannibalism and infanticide” (Apps and Gow 120). As previously mentioned, the book Malleus Maleficarum set the stage for a lot of early modern witch beliefs within Western Europe. This text was written within a school known as demonology, “Commonly viewed as a branch of theology, philosophy and metaphysics” (Roper “Witchcraft and the Western Imagination” 119). Demonological descriptions of the witches Sabbath are an example of elite construction of witchcraft beliefs, and they focused on Christianity inverted: “The witches were bent double, candles in their anus, and in the place of the kiss of peace in the Mass, they had to kiss the Devil’s anus (Roper Witch Craze 113).
Of course, as also has been mentioned before, Early Modern witchcraft beliefs were also shaped by those accused of witchcraft drawing from their own experience in confessions. The dance, an element of the witch’s Sabbath, appeared in Witch’s confessions as an inversion of their village dances (Roper Witch Craze 107-108, 111, 116). At these dances it was said that music might be played on the fiddle and the bagpipes (Roper “Witchcraft and the Western Imagination” 128).
Make the Exorcist Fall in Love both presents the witches Sabbaths using ideas of inversion of Christian doctrine and of social gatherings with dance and music. For one, the witches set up shop in an abandoned church in France, where they place a statue representing Beelzebub in the sanctuary. Symbolically, then, they’ve inverted the worship of God to the worship of a demon.

Additionally, you can see the Witches lined up to kiss the statue on what seems to be a phallic protrusion. They’re inverting, then, the kiss of peace the same way historically witches were thought to kiss the Devil’s anus. Roper has a description of a woodcut that bears similarity to this image, describing it like so: “At the centre of the image, witches perform the anal kiss on a giant goat, while long lines of assorted pairs of Devils and witches wind their way in a snake like spiral around the picture, playing phallic-looking bagpipes and horns” (Roper “Witchcraft and the Western Imagination” 137-138). Now, traditionally this kiss is delivered on the anus rather than the phallus, but I’m not an expert so I can’t speak to whether there were regional descriptions of Witch’s Sabbaths that varied that Make the Exorcist Fall in Love is drawing from. I can say, though, that Berserk’s portrayal of a witch’s Sabbath, which imagery-wise definitely seems to draw from woodblock representations, does feature the diabolic kiss being received on the phallus rather than the anus. It is possible that this scene was visual inspiration for Ekuoto’s witch’s Sabbath. For those who are interested in independently checking what I’m talking about, it’s in chapter 139 of Berserk.
Now, in the same above panel in Ekuoto, we also see that the witches are singing a song. This song is an inversion of the Anglican hymn “Holy Holy Holy”—the original lyrics, that the witch’s invert, are “Holy, Holy, Holy! Though the darkness hide Thee, Though the eye of sinful man, thy glory may not see: Only Thou art holy, there is none beside Thee, Perfect in power in love, and purity.” The hymn is originally about the trinitarian god, so this inverted version becomes a worship of Beelzebub.
If you want to give the original song a listen, here’s a link to a recording:
youtube
This song later also appears in the flashback to the 2011 Beelzebub fight (where, interestingly enough, an eclipse is featured very prominently. Eclipses are pretty common “ooh spooky eek” imagery but it also made me wonder if there’s potential visual influence from Berserk). This also further establishes it as a song associated with Beelzebub.



Inversion also shows up outside of the Sabbaths in Ekuoto. Dante in the below images is invoking the Trinitarian formula: “in the name of the Father, and of the Son, and of the Holy Spirit,” which is from Matthew 28:19 in the Bible. Verge, and other witches in Ekuoto, invert the Trinitarian formula: “in the name of the mother, the daughter, and the evil spirit.” Not only is this an example of inversion, but it also aligns with a neopagan concept, the Triple Goddess (although usually the triple Goddess is expressed as the Mother, the Daughter, and the Crone). I’m not going to cite this because I’m lazy, but if you want you can check this one out on Wikipedia. The Triple Goddess in neopagan beliefs harkens back to older religious forms where goddesses appeared in groups of three—one of these, from Hellenistic religious beliefs, is associated with witchcraft: Hecate was associated with magic, and often depicted in a triple form (Also too lazy to cite this but you can check this out also on Wikipedia in both the Triple Goddess (Neopaganism) page and the Hecate page. You can also check it out on Encyclopedia Brittanica). Interestingly, and as I’ll touch on later, Baba Yaga also sometimes appears in three forms in folklore (Forrester xxxiv).


Walpurgisnacht


Now, the description of the woodblock of a witch’s Sabbath mentioned in the previous section wasn’t of just any Sabbath—it was a Sabbath on the Brocken, where according to legend witches would have a Sabbath every year on Walpurgisnacht (Roper “Witchcraft and the Western Imagination” 137-138).
Walpurgisnacht is on April 30 into May 1st, and is an actual real life religious holiday, celebrating the canonization of Saint Walpurga. It’s celebrated through festivals, some of which involve dancing around bonfires. In the 17th century, a book written by Johannes Praetorius cited the peak of the Harz mountains in Germany, the Brocken, as a site in which witches would meet for a Sabbath on the eve of May 1st (Weishaupt). It was this book, the Blockesberges Verrichtung, that features the woodblock mentioned in the Sabbath section, and would inspire some of Johann Wolfgang von Goethe’s drama of the mind, Faust (Roper “Witchcraft and the Western Imagination” 135-138). Faust also has a famous presentation of Walpurgisnacht on the Brocken (Weishaupt).
So yeah, Ekuoto’s mention of Walpurgisnacht is in reference to this! Moving on to what they’ve also mentioned in conjunction to Walpurgisnacht:
Baba Yaga
First and foremost, Baba Yaga has nothing to do with Walpurgisnacht in folklore, this is an invention of Ekuoto. The Harz mountains are in Germany, whereas Baba Yaga is a figure in Slavic folklore.
Stories in which Baba Yaga appears often have several themes: “she lives in the forest, which is her domain” (Zipes VIII); that her house has chicken legs (Forrester XXVII); that her “house may be surrounded with a fence of bones, perhaps topped with skulls (Forrester XXVIII). She sometimes also has a black cat (Forrester XXVIII). Jack Zipes, in the foreword to Baba Yaga: The Wild Witch of the East in Russian Fairy Tales, describes her as “not just a dangerous witch but also a maternal benefactress, probably related to a pagan goddess” and “inscrutable and so powerful that she does not owe an allegiance to the Devil or God or even to her storytellers” (Zipes VIII). Sibelan Forrester, in that same book, describes her as “both a cannibal and a kind of innkeeper, a woman who threatens but also often rewards” (Forrester XXXV). Skulls with light coming out of their eye sockets shows up in the fairy tale Vasilia the Beautiful—“the eyes of all the skulls on the fence lit up, and the whole clearing became light as midday” (Forrester XXXVIII, XLIV, 175).
Now, so far in Make the Exorcist Fall in Love, we’ve been presented with Baba Yaga as a witch who Satan calls different from the other witches, who tried purifying the angry souls of those killed by the church until she became corrupted by their rage and desired the power to kill god, and has at least three contracts with Satan, Asmodeus, and Beelzebub (but not Leviathan). She also appears as a black cat.


The parts that most clearly draw upon traditional Baba Yaga folklore are the skulls, the chicken legged house in the middle of the woods, and the idea of her being a total wildcard. As far as I can tell, the backstory they’ve given her about purifying souls killed by the church is completely original to Ekuoto, although it could be in reference to either some piece of folklore or literature that I’m not familiar with. Traditionally, the bones and skulls in Baba Yaga’s home are presumably a threat that the hero might next be a victim of hers (Forrester XXIX). Here, they are victims of the church.
The closest thing I have been able to find is the invented backstory is from Dubravka Ugrešić’s book, Baba Yaga Laid an Egg, published as part of the Canongate Myth Series (themed around reinterpreting international mythology): “That they would finally stop bowing down to men with bloodshot eyes, men who are guilty of killing millions of people, and who still have not had enough. For they are the ones who leave a trail of human skills behind them, yet people’s torpid imaginations stick those skulls on the fence of a solitary old woman who lives on the edge of the forest” (Ugrešić’ 243). Here also the skulls are affiliated not with her cannibalism but the killings of patriarchal power. The book was originally published in Croatian and has several different languages it is available in translation, although, as far as I can tell, Japanese is not one of them, so I don’t know how familiar Arima Aruma would be with it.

I’m also fascinated by the beheaded, veiled skeletal figure with the large stomach wound we see who points towards Baba Yaga’s house. Baba Yaga is sometimes presented as a mother (Forrester XXXVIII) and the large stomach opening to me almost looks like the surgical removal of a child from the womb, although that may be a stretch.
Contemporary c-sections are also often horizontal, although historically in Europe and the Americas, up until developments in surgery and gynecology in the nineteenth century, they were only performed when the mother was dead or had no hope for survival. The images I’ve seen depicting c-sections in the 15th and 16th centuries seem to depict vertical incisions though, which lines up more with this figure’s wound. (I’m not citing these but will provide links: https://www.webmd.com/baby/what-happens-during-c-section; https://www.nlm.nih.gov/exhibition/cesarean/part1.html ). I think it would also line up with some of the other imagery that’s been established in series, such as the wound/vagina/pregnancy image combo we got in the first chapter with Asmodeus.
It's also been implied that she had something to do with binding Beelzebub from entering Germany:



That file really closely follows the contours of a Baba Yaga fairy tale—getting lost in the forest, the flaming bone torch like in Vasilia the Beautiful. I’m extremely fascinated by the way in which Baba Yaga is being presented in Ekuoto and can’t wait to see more about her motivations.
Continued in Part Two
44 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hey there, I read your first chapter of Moby Dick in modern idiom and I’ve been thinking about it pushing it at people for days. IN THEORY, have you considered writing the whole thing? They said, knowing full well the awful project they were proposing.
In reference to the Moby Dick post: https://www.tumblr.com/elodieunderglass/761181987124969473
You’re so kind to ask, and I couldn’t be more flattered by the question. I’ve answered the question recently here: https://www.tumblr.com/elodieunderglass/761216179802161152/do-you-have-more-moby-dick-modern-translation
Boils down to:
After a banger of a first chapter that really sets Ishmael up as an energetic and unusual literary character, Moby Dick goes on to have some tricky pieces, involving things like unsavoury racial stereotypes from Ishmael POV, which don’t feel right to playfully translate into insufferable modern idiom, even for educational purposes; and I’d hate to put my name to it on the piss-on-the-poor website, because a) unsavoury and b) not an expert and wouldn’t want to be fighting on so many fronts of “well actually”.
I’m a moderately quick-witted biologist who is broken enough to want to be perceived as “funny,” so likes regularly being told they’re funny on Tumblr; I’m eminently not an experienced 1800s historical fiction academic who passionately wants to communicate nuanced racial and political analysis to a thoughtful public. And again, it would probably involve so many people going “well actually” at me, pointing out how I’m not an experienced 1800s historical fiction academic qualified to properly interpret a problematic work etc. And, knowing myself, I’d probably start biting people in the notes.
And there are two immediate chapters about an interminable church sermon that I think are stupid and would skip. I don’t feel I’d like to tackle this for fun. It’s homework-coded and I’m not being paid or graded or trained in any way so my brain goes “humph” and picks daisies instead.
So I’ve considered it and I’m grateful to be asked! and I will definitely tell you if I ever do it! But for now it’s low down on the list, after finishing some commissions, a big fanfic that currently makes me very sad, and apparently writing my own story about weasels.
And of course I don’t own the work, so if anyone else wants to tackle it I’d be delighted to signal-boost and so on.
99 notes
·
View notes
Text
Kiss Distance: When Feelings Can't Reach | Linguistic Analyses on Rick & Rachel's lines foreshadow for TwiYor, DamiAnya, and Marthanderson from Ch. 105.5 (PART 1)
This is gonna be a take from the linguistic + literary lens regarding Rick and Rachel's lines from Spy x Family's Ch. 105.5.
Spoilers beware.

So let's talk about the film: Kiss Distance.
On X/Twitter, all I said was my analysis senses were tingling. There was a strong linguistic and creative writing/literary devices indicating foreshadow from the movie, and this just surprisingly got attention.

So now, I'm finally addressing this specific section in a long analysis post.
I cannot stress how much I love Endo-san's short chapters. There are so many things going on in terms of literary devices, and now, I think he plays with linguistics in them. I believe that the last time he did this was during Ch. 90.1 when we learned that Ania's name turned into Anya. I remember freaking the hell out that linguistics was touched upon, cuz honestly, what manga does that? Someone is finally paying attention to linguistics in a story, and it's just further pulling me into my rabbit-hole fixation and obsession with Spy x Family.

Although the chapter is only 5 pages long, it has SO MANY THINGS TO COVER. I won't be able to do that in this post, but I DID cover the entire thing in a video analysis that you can watch here:
What I will mainly cover in this post will be the film: Kissing Distance and the characters (Yor, Anya, Becky, and Martha) watching it + post-watching it. I cannot stress the ridiculous efforts embedded in just 3 pages, so I need to divide these sections into a linguistic lens (part 1) and a literary lens (part 2).
Let's start with the linguistic lens.
Spelling reflects language association + cultural history + maybe it's a meme too.
Spelling reflects language association
At the top right corner of page 2, we've got some English texts on the movie's billboard. "Interesting" and "Entertaining" are stacked on the left while "Movie" and "Theater" are stacked on the right.
Of these words, the word that stands out the most to me is Theater. English experts recognize that there are 2 spellings of this word: theater and theatre. These spelling tell you that it is either American (theater) or British (theatre).
I'm no expert on geography, but I believed that Ostania and Westalis were loosely based in Europe. I think I read someone talk about the architecture in Berlint also reflected European style houses--I'm so sorry that I can't recall who addressed it. The wars also felt like they were influenced by WWI and WWII. But what I do know is English it's my goddamn expertise. I'm not gonna be an uptight ass about pointing out every nook and cranny of inconsistent English, because that's just a whole lot of work for a creator and his team can do, realistically speaking. If Endo-san wanted perfect control in the language he's portraying in SxF, then he would need a dedicated team of linguists to help with translations. It may surprise you but there are many variations of a language (ex: English has AAVE. It's still English but used by this group of speakers--more on this later). But this is a hell hole of work, so I'm giving him so much slack on it as well as the translators handling the translations (like, really. No hate. Thank you for your services <3).
Another caveat: the English translation may also be a reflection of the translators. Maybe they favor American English than British English--who really knows? But I digress.
I'll stick to what I already know of the Ostanian language: It's English (variety is unspecificed, feels American) + Japanese.

Spelling shows cultural history
Next, let's address that these are adjectives slapped on a movie billboard. Normally, American movie theaters do not post adjectives. They post about the movie, the actors, etc. Comments about movies theaters being "family friendly" are subtext under the current film, etc. Here's an example of a movie theater from the 1950s found on gettyimages:

So this brings me to consider that English is being used as kazari eigo which means 'decorative English' in Japanese. In Chris Broad's (AbroadinJapan) words:
"... English in Japan is most commonly used as a form of cheap decorations and prestige, or value to a product and because so few people here understand it, the companies that plaster English all over their products and items rarely bother to check that it makes any sense." Reference:

Maybe it's a meme
This chapter, overall, felt really silly. There were silly drawings, silly play on words, silly foreshadows, etc. I couldn't help but think that maybe Endo-san was throwing in something amusing in these small things (cuz he's got attention to detail). Is it:
Interesting Entertaining Movie Theater OR Interesting Movie Entertaining Theater
It reminds me of:

Endo-san does have a tendency to incorporate memes into his manga/anime. Like... was Anya's jump not a Jojo's meme...? //sweats
youtube
youtube
I don't know if I'm severely poisoned by JJBA memes but, yeah, I saw it since the day this chapter came out. I just thought:
ANYA = DIO BRANDO
Anyway... whether it was intentional or unintentional (for this section), I love when mangakas incorporate something meme-y

2. Ricky's English Variety

This is where I went berzerk in this chapter with all of these small linguistic details. Ricky's speech says so much about him.
His introduction of himself is that he's a broken razor. Essentially, he's painting the bad-boy ML image. But he's not just any bad boy. He's a bad boy with issues controlling himself/the situation. In other words he's toxic and not good for us healing men/women //joking. However, out of all of these words, the one that stands out to me is shaddup. His speech suddenly changed because romance conflicts need to have a wall between the main couple. In this case, other than Ricky's pompadour, it's his speech. What we have here is a clash between English varieties.
To understand what is variety in linguistics, you might be familiar with these words: language, dialect, vernacular, and accent. Language is the most obvious, but dialect, vernacular, and accent can be a lil confusing to distinguish. So here's a definition and a chart I made to help distinguish them:
- Language: a system of communication that uses words, grammar, and spelling to convey meaning, languages can be spoken, written, or signed-- Ex: English, Spanish, Arabic, etc. - Dialect: is a variation of a language that is spoken by a specific group of people, such as a community, culture, or region. It includes differences in vocabulary, grammar, and how the language is used -- Ex: American English vs. British English vs. Australian English - Vernacular: is a type of dialect that's used by the "common people" of a region. It's a non-standard dialect that's spoken rather than written. Vernacular language is often made up of slang or regional terms -- Ex: African American Vernacular English (AAVE) - Accent: is the way people in a specific group pronounce words, which is also know as the prosody of speech. Prosody refers to the tone and musicality of someone's speech -- Ex: Boston accent

In Summary (a simplified version of the above info): Language is the standard language (aka what you learn in grammar class and in public speaking class) Dialect is born from language where it becomes variations of the language and adopts different grammar, vocabulary, and language use (like American English vs. British English vs. Australian English) Vernacular is a type of dialect used by "common people" and often include slang words and regional terms (think African American Vernacular English, or AAVE) Accent is a type of dialect that is mainly focused on prosody, or how a person pronounces a word (think Boston accent)
Now that you understand the linguistic terminologies, here's a fun exercise to show you what I see:
Ricky predominantly uses the standard English language in the film:



The moment a language's word has a (legitimate) spelling change, it automatically turns into a dialect (which touches on my previous topic about theater vs. theatre).
These are Ricky's English accents:


Finally, this is Ricky using an English vernacular:

POP QUIZ!
Now that you know what English variety is, can you guess which one Ricky has? If you guessed dialect, then you're half a step there. If you guessed accent, you're so close! But the correct answer is vernacular. This is because accent overlaps with vernacular, but accent stops at word pronunciations. Vernacular has accent and slang.
3. Discourse Analysis on Ricky's Vernacular
You should now have a good understanding of Ricky's vernacular, but now let's talk about why this is significant in discourse analysis.
Linguists who specialize in discourse analysis are responsible for analyzing why and how people speak a certain way. Many linguistic features are observed (lexicons, syntax, phonology, semantics, etc.) but what they share in common is who it's presented to. They're looking at the relationship between interlocutors (people who take part in the dialogue/conversation). In other words, depending on who you converse with, the way you speak is affected.
You may have already realized that Ricky is code-switching (a speaker switches between one or more languages and/or varieties) between standard English and his English vernacular.
Now, pay attention to who Ricky speaks to and when he code-switches.

We can observe in the above panel that Ricky uses standard English when speaking to Rachel. This is because Ricky has linguistically profiled her.

How am I so sure that he's linguistically profiled her? Well, because the majority of human beings unconsciously linguistically profile their appearances. Linguistic profiling does have a similar general word: stereotype. The only difference is that based on appearance, we make a split-second assumption and decision on how we talk to that person.
In this case, Ricky spoke first (exercising dominance through initiation) and used standard English. From a linguistic lens, Ricky is telling me: hey, I know I look like a bad boy, and you may have linguistically profiled me as someone who didn't have good education, which would have reflected in my speech, but I'm more than competent to use standard English. And because I can use standard English, I'm on the same equal playing field (metaphorically and linguistically speaking) as Rachel.
But then, notice the moment, Rachel tells him that she hates Ruffians like [him], Ricky's replies with an accent of shuddap (shut up). Linguistically, he's drawing a line between them. This also indicates that they're no longer on the same side before adding his threat: "I'll cut you!"

In this scene, notice Ricky's accent comes back again, but who is it directed to? An enemy or someone from his linguistic background. He uses this accent with an interlocutor of the same English variety background to make it clear to the person he's beaten up that he's speaking in the "language" that they both completely understand.
But, the moment Ricky speaks to Rachel, he reverts back to standard English. What this means is that Ricky is linguistically assimilating/aligning himself with Rachel to show that he's on her side. This can also mean that he's making himself appealing to her through discourse. On the other hand, Rachel makes herself appealing through physical means (her taste in clothing has changed--more on this under literary analysis).

In this scene, Ricky changes appearance (more on this under literary analysis) and he speaks using standard English. But the moment he loses his pompadour, guess what happens?

Ricky goes back to his true self and shows it through using English vernacular.
Rachel has never changed in her English, so she's always been true to herself. It's Ricky who goes through these changes. And it becomes a beautiful and romantic moment of a man undergoing change not only visually but linguistically.
4. Language parallel/mirroring between the anime and the manga
The fact that Endo-san decided to give Ricky an English vernacular in the English translation of the manga reflects his attention to details between the manga and the anime adaptation.
Linguistics in Anime (what you hear)
Maybe you've noticed, maybe you haven't, but Takuya Eguchi, Loid's voice actor, ingeniously incorporated different prosodic features when assuming roles for [redacted], Loid Forger, Twilight, and Robert. Catte-b covers this in her Leitmotifs in the Spy x Family soundtrack. Piracytheorist also provided a video demonstrating Loid, [Redacted], and Twilight's voices. In both posts, Eguchi's changing voice is called timbre (Catte-B and Piracytheorist have a music background). Timbre is defined as:

In other words, timbre is an individual's voice quality or vocal signature. It's how listeners can recognize a singer regardless of what song they sing and how anime watchers can identify a VA's voice by the character's name in another anime--there's just a certain quality in a person's voice that makes them identifiable.
Because of this definition, timbre is unfortunately not the correct terminology. Using vocal/voice timbre when describing vocal register, at the end of the day, is just pitch. Catte-B and Piracytheorist, however, are not wrong in their analyses. They have correctly identified one of the characteristics of speech and even provided vocal qualties (sharp, flat, soft, etc.) but the more appropriate term should be prosodic features.

I want to highlight the most important thing about prosodic features and it's the features that make it up: intonation, stress, rhythm, pitch, and pauses.
Intonation: is the variation of pitch across a phrase or sentence. > in a way, it's creating a melody when speaking. > its purpose in spoken language is to convey meaning. This is usually the case in tonal languages that require a specific pitch to indicate a word. However, in English, intonation is present when we ask a question (the last few words tend to be higher-pitched) vs. a statement which is either consistent in pitch or can sometimes be lower-pitched. Stress: involves giving prominence to one or more syllables in a word. This is achieved through increasing the length, volume, or pitch of a syllable, or by changing the vowel quality. > stress is important for helping listeners understand meaning / word class and distinguish words during rapid speech (ex: address, graduate, permit etc.) > it can be used to emphasize a specific word of a sentence (ex: Where did you go last night? vs. Where did you go last night? vs. Where did you go last night?) Rhythm: refers to the sense of movement and flow of speech. It's a combination of stress, length, and number of syllables. > mostly concerned with syllables and larger parts of speech rather than phonetic segments like consonants or vowels > important for making speech sound flow well and helps us understand what's being said > 2 most common types of rhythm in language are stress-timed and syllable-timed (English typically uses a stress-timed rhythm) Pitch: indicates highness or lowness of sound. > A person's pitch can reflect friendliness and warmth from the upper register (higher pitch spectrum) to mysterious and sexy with the lower register (lower pitch spectrum)--or at least, this is a consensus opinion that I've heard in English-speaking communities when it comes to the opinion of an individual's vocal pitch for both men and women. Pauses: a break in speaking or a moment of silence that can help add structure to the speech. Pauses have several functions: > gives listeners time to comprehend and digest the information > can be used to emphasize words or ideas > helps speakers transition between ideas > prevent rambling > can signal speech breaks, especially in languages that utilize pausing as a prominent cue > can denote high-information content
There are more prosodic features listed like juncture, loudness, duration, and tempo, but this is where it'll get too specific. Rhythm kinda already accounts for duration and tempo. Juncture is relating to annotating pauses (like indicate when a pause is greater than a certain milisecond), and loudness could kinda fall under the category of rhythm.
Timbre isn't listed as a feature, but I think it should simply because timbre is what makes your voice your voice. And because timbre is the "vocal signature", the shouldn't change--not unless you're as vocally talented as Tara Strong, who can easily change her timbre with different characters.
youtube
Eguchi-san does, however, have some roles where his timbre does change, specifically as Shuuji Hanma from Tokyo Revengers and Kazuya Kujou from Gosick (he does have some moments when he slips back to his familiar timbre).
youtube
Now that you have an understanding of what prosodic features are, you'll be able to hear that Eguchi-san's timbre doesn't change as [redacted], Twilight, Loid, or Robert. I believe Eguchi-san intentionally kept the same timbre for [redacted], Twilight, Loid, and Robert because they're all staying close to home. You can still recognize it's still the same person. But what changes are other prosodic features (intonation, pitch, rhythm, stress, and pauses). The following video is from Piracytheorist's post and the YouTube video is from Calle-B.
youtube
youtube
Here are my descriptions of the 4 voices:
[Redacted] - Intonation: N/A. Japanese is not a tonal language. - Stress: vowels and consonants are even for syllables - Rhythm: slow and steady - Pitch: low register, feels like it can be the middle (makes sense since this is the voice he's born with) - Pauses: frequent pauses (also, no way in hell you can convince me to measure the mili-second of his pause) - Tone: warm and soft - Other quality(-ies): reminds me of slight head-mix dominant (60% - 70%). In singing, a mixed voice is when a singer mixes his/her/their head voice and chest voice together (you might commonly know this as belting). But with mix voices, the singer can choose to make it an even mix of both head and chest, or leaning to either more head or more chest. Twilight - Intonation: N/A. Japanese is not a tonal language - Stress: consonants, vowels, syllables, and long phrases are rushed - Rhythm: his speed is fast. it's like water gushing out - Pitch: low(est) register. This is probably the deepest voice he can go while maintaining his timbre - Pauses: They only exist when a completed thought is finished. Twilight, BREATHE, man - Tone: cold and sharp - Other quality(-ies): sometimes his low register have a bassy quality to it Loid Forger - Intonation: N/A - Stress: His consonants and vowels are spoken fast in some syllables but also have a slight elongation typically towards the last few words of a completed thought - Rhythm: fast like Twilights, but has an upbeat rhythm to it - Pitch: upper register (it's the customer service voice lol) - Pauses: It's a mix of Twilight and [Redacted]'s. He has moments where he pauses after a long completed thought. Sometimes, he pauses in between a few words/syllables. Pauses feel irregular here--like he doesn't know if he should relax of speed up (as if he's being pulled to either Twilight or [redacted]'s pause pacing) - Tone: sounds cheerful - Other quality(-ies): 80% head-mix voice. The chest voice is still there, but head voice stands out Robert - Intonation: N/A. Japanese is not a tonal language. - Stress: elongated vowels and consonants -- similar to [redacted]. - Rhythm: originally slow and drawl. But as soon as he realizes that "Robert's mission is over", he starts speaking fast like Twilight - Pitch: low register and soft - Pauses: He has similar pauses to [redacted]. There seems to be a lil bit of longer pauses to indicate passiveness (reinforce the boring image of Robert) - Tone: monotone and soft - Other quality(-ies): head voice. The chest voice seems to be absent (chest voice is perceived as the power in singing and speech) as to reflect Robert as someone who is small and doesn't have much personality (as to not stand out during this identity). This voice is achieved by keeping your voice low but above a whisper. When "Robert's mission is over", the chest voice emerges and his head voice becomes head-mix.
Prosodic features are best accurately portrayed in discourse, meaning it's exclusively for speaking, not writing. So, how can Endo-san incorporate any linguistic feature in writing? We've already answered that with the analyses above: spelling.
Linguistics in the manga (what you read)
I've already went into great detail about spelling reflecting dialect, so I won't regurgitate what I've already covered. Instead, I want to focus on the fact that Endo-san actually acknowledges and uses prosodic features to mirror the 2 mediums of Spy x Family. This is significant because it reinforces the mirroring characters between Ricky and Loid. After all, it's going to be a foreshadow. Normally, I'd talk more about foreshadow under a literary lens, but for once, foreshadow is illustrated through linguistics.
In discourse analysis, the way you speak almost always portrays your identity.
Ricky's English vernacular is his real speech. > [Redacted]'s voice is Loid/Twilight's real speech, which often came out in the presence of Yor Forger.
Ricky speaks in standard English to mask his real voice and make himself more appealing to Rachel. > Loid's voice is used to mask both Twilight and [redacted].
Ricky gives up his pompadour (the most important thing in his life--which also happens to be a part of his identity) to destroy the "barrier" between him and Rachel. In doing so, he goes back to speaking with his English vernacular. > FORESHADOW: Loid will give up one or two of his identities for Yor (it might be Twilight and/or Loid). In exchange, [redacted] will come back.
Another possible foreshadow is what Rachel says about recognizing the importance of Ricky's pompadour to him. Because Rachel is a parallel character to Yor Forger, it can be implied that Yor would recognize how important Loid's identity is to him. In a previous analysis, I mentioned that Ch. 90.1, is the closest thing to an identity reveal. When Yor carved out Anya's name as Ania, she never once questioned it. She also didn't question when she had to carve another sign and spelled it with Anya. I'm aware of the caveat in this claim, such as Yor lacking education in Ostanian orthography which is why she doesn't react.
Be it grasping at straws or not, Yor has the emotional maturity to bounce back from the shock of an identity reveal. Yes, Yor would be sad and hurt to find out that Twilight is a spy from the opposition, but she would understand. They know they're both orphans because of the war. Yor already has a positive bias towards Loid based on observing his behavior at home, in his efforts to provide a better future for Anya, regardless of blood relationship. The point is, Yor is already infatuated with him and her feelings for him will influence her compassion and understanding for the person he's become, so bouncing back from feeling betrayal (not the romantic kind) would be faster for her than Loid.
Loid, on the other hand, may have more reluctance towards accepting the identity reveal (this is also mentioned in my Ch. 90.1 analysis). This is mainly because he's been conditioned to be skeptical and overanalyzing. So, he'll definitely need time to brood and reflect on their situation. Or, maybe he just might have already reached a point where he's just tired, and deflatingly accepts the situation. He'll self-loathe himself for being Westalis's best spy only to have married a legendary Garden assassin--seeing both as a win and loss (he'd be the type to say that he should be dead right now because his identity was revealed to the deadliest enemy). The confession of their love for one another just might be the thing to smooth out the wrinkles.

Someone once commented that, technically, losing Twilight as an identity isn't technically a loss. Twilight was born from a sacrifice. Loid technically isn't a loss either since he was born as a role for Twilight to play. Which leaves [redacted]. Like the film for Ricky, [redacted]'s foreshadowed arrival is just an opportunity for him to come in full circle.
PHEW.
This was a long linguistic analysis of these few pages, and in real-time this took me 8 hours to write. I did lose a night of sleep cuz my brain hyper-fixated on writing this. Help. But we're not done yet. The knowledge that you've acquired will definitely be beneficial through a literary lens in part 2.
I'll update this post with a link when Part 2 is finished.
#spy x family#spy x family ch. 105.5#spy x family manga#linguistic analyses#linguistics#discourse analysis#orthography#English#English variations#scarlywroteathing#yor forger#anyaforger#becky blackbell#martha marriott#twiyor#damianya#marthanderson#Youtube
57 notes
·
View notes
Text

Is it still a fanart if there's no canon characters? 🤔
Christmas gift for my friend and partner in literary crimes, @whosayscrimedoesntpay! This is a fake poster for a hypothetical movie starring our Lupin III OCs!
🦊The Secret of the Fox🦊
The Meiwaku Gang, lead by Goemon's pupil Naomi, is targeting a duo of mystical fox-shaped statues that supposedly lead to a hidden treasure. On the way, they butt heads with a mysterious masked thief and his gang, who stole the second statue and challenges them to a thieving duel. Unbeknowst to either gang, Naomi and the fox thief know each other very well...


Renjiro Jigen-Ishikawa: Jigen and Goemon's adopted son. He leads a gang of conmen and thieves. He's sly and very creative, and takes after his parents when it comes to causing problems on purpose.
Naomi Jigen-Benson (alias Motosuki): Jigen's niece, and Goemon's pupil. She is part of a group of thieves called Meiwaku. She's adventurous and hides a love of shenanigans behind her obsession for Bushido.
Ren and Naomi are aware of their relation, and although not very close, they have a friendly rivalry (and a shared tendency to keep their family history a secret from their friends).




Renjiro's gang!
Axel: the translator and puzzle geek. Is always learning a new language.
Sammi: the tech guy, a genius with an uncanny ability to find any information.
Kasumi: Keiko's twin. The muscles and occasional face of the group when Ren is busy.
Keiko: Kasumi's twin. A fashion major who specializes in making the gang's disguises.



Naomi's gang!
Kanako: Naomi's girlfriend. Expert with explosives, with a personality to match.
Hiro: Milo's boyfriend. Hacker from a long line of ninjas.
Milo: Hiro's boyfriend. Medic with a punch, a human golden retriever.
Renjiro, his gang, and Milo belong to @whosayscrimedoesntpay, the rest are mine!
You can also learn more about this bevy of idiots (affectionate) from my other fake movie projects: Lupin the Fourth, and The Geneva Conspiracy!
#lupin iii#lupin the third#lupin iii ocs#my ocs#meiwaku gang#meiwaku#naomi jigen benson#kanako misuki#hiro kimura#milo clarke#renjiro jigen ishikawa
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
li lianhua's final letter to di feisheng
i hear the official eng subs weren't great so here's my own attempt at a translation (under a read more bc fuck it's Long)
edit: translated qiao wanmian’s letter to li xiangyi as well, which mirrors this one!
十年前
Ten years ago,
东海一决
during the duel of the eastern sea,
李某蒙兵器之利
this unworthy Li made benefit of whetted blade
借沉船之机与君一战犹不能胜
and capsizing boat whilst battling thee but was yet unvictorious.
君武勇之处
Thy martial prowess and valiance
世所罕见
are unexampled in this world.
心悦诚服
Mine heart delights in it, and by mine own will yields to thine eminence.
今事隔多年
The affairs of today are by many years separated.
沉疴难起
By pains alone would a lingering malady be cured.
剑断人亡
The sword hath broken—the man hath perished,
再不能赴东海之约
and can no more honour the accord to duel by the eastern sea.
谓为憾事
Such is the cause for most sincere regret.
余感念君所赠之忘川
I recall in deepest gratitude the flower of oblivion bequeathed by thee,
然终有负君之所望
yet did forsake all thou hadst longed for in the end.
江山多年
The rivers and mountains of this land have many years endured,
变化万千
their changes reckoned in the tens of thousands.
去去重去去
Partings upon partings, farewells upon farewells;
来时是来时
the coming times shall be the coming times.
方多病习我之功法
Fang Duobing hath been studied in my skills,
资质上佳
and his own endowments of the utmost excellence.
不暇多日
Shouldst he not keep idle days,
定不在明月沉西海之下
he shall surely be not beneath the bright moon sinking into the western sea.
君今无意逐鹿
Thou hast not now any desire to pursue the throne,
但求巅峰
but instead to seek the height of skill.
李某已去
This unworthy Li hath since gone;
若君意不平
if thy desire be not appeased,
足堪请其代之
he shall suit, shouldst thou bid him succeed me.
李相夷绝笔
Thus end the last words of Li Xiangyi.
footnotes
i've translated this letter into (my best attempt at) early modern english to try and reflect the formality li lianhua is writing in. also because he uses 君 for di feisheng throughout, which is a literary second-person pronoun, and i wanted to emphasise that. i know thou is actually the informal pronoun, but given how archaic it sounds in comparison to you, the actual formal pronoun in early modern english, i thought it a better fit. (for all the feihuas out there: 君 was also used by women to address their husbands, so actually i thought the informality might work in my favour here LOL)
if you saw this post before, you might have noticed that my translation of the third and fourth lines changed slightly lmao. ty to @/presumenothing for the reminder and ofc my fav @/bat1lau4can4 for talking through it with me and being the 文言文 expert i need <3
for the purposes of my goal in the above footnote, i've had to take some creative liberties in my choice of vocabulary. for example: unexampled is not quite an accurate translation of 罕见, which actually means rarely seen.
i phrased 心悦诚服 as mine heart ... yields but that's a somewhat liberal interpretation of the phrase lol. there is a heart in it; it's just maybe not the thing that's yielding, to be precise. close enough imo though!
江山 literally translates to rivers and mountains but is often used as a metaphor for a country as a whole, hence my translating it as the rivers and mountains of this land.
grammar is not as important as Vibes.
逐鹿, which i've translated as pursue the throne, literally means to chase the deer, and stems from the 《史记》 / records of the grand historian.
绝笔, rendered here as last words, specifically refer to the last words written by one before their death.
#mysterious lotus casebook#li lianhua#li xiangyi#di feisheng#fang duobing#lhl#莲花楼#rui rambles#look i'm just incredibly impatient okay#this translation may very well change by the time i get around to subbing ep 40 but for now i'm satisfied#mlc fansub
215 notes
·
View notes
Text

Have an unpopular opinion about a BL? Don't worry, we probably do too. Saying all the things you do or don’t wanna hear Part 5 (of 4) is here to engage with BL media from Japan, Thailand, China, Korea and more. We're talking film-making techniques, narrative analysis, fandom woes, while asking questions like, hey why don't the bottoms move their arms? We may not be experts, but we are loud, chaotic, and full of opinions.
In today’s episode we’re discussing the origins of our hosts De and Sinna’s friendship and Only Friends! Mainly Only Friends cause, whew, is there a lot to talk about. Anyone else still salty over that ending? Or just us?
Show Description: Mew, Ray, Boston and Namchueam; a group of business students running a hostel together-blur the lines between friendship and romance.
Where to Watch: Only Friends
Check out the read more below for further reading resources on topics we discussed in today's episode like framing devices, and color theory in film. Along with a list fanworks we loved from the fandom! Add any fanworks you loved as well, give the people their stars.
Listen to this podcast on: Spotify | Soundcloud | Youtube
References:
Framing Devices
EVERYTHING YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT FRAMING DEVICES
A Story Inside a Story: Using Framing Devices in Fiction
10 Films that Utilize a Frame Narrative
Color Theory in Film
Color Theory in Film — Color Psychology for Directors
What Is Colour Theory In Film?
Color Symbolism in Literature: Examples and Meanings
Stain: Phenomenal and Literary Approaches to Color Studies
BL Budgets
The Storyboard: Interview with the Dee Hup House director Tee Bundit - Original Interview | Translation
BL Production Info from Strongberry - Original Interview | Translation
Fanworks We Loved:
ONLY FRIENDS as SZA Lyrics 2/? -> SMOKING ON MY EX PACK by @firelise Run away fast as you can by @iwantoceans GIF Set BostonNick by @taeminie Boston GIF Set by @khaotunq Top x Boston | Only Friends | Crazy in Love by stb Boston & Nick | Angels like you can't fly down hell with me by Scodders sand x ray | ''i need somewhere to begin by thanxxjessie “Compared to Boston, you're a saint” by @rabbiitte If Boston has a million fans by @no2tinngunshipper Only Friends FMV | Cardigan | BostonNick by @technicallyverycowboy Told You So by CaffeineAddict94 You’re On Your Own by technicallyverycowboy “Boston was ostracized, isolated and berated to the point that it completely shattered his sense of self” and “Boston and his “friends”” by @neuroticbookworm “Dear Boston” by @lurkingshan "go for it." by @gunsatthaphan
Goodbye Forever (Until Next Time) by Anonymous
Credits:
Chaotic Hosts: Dé & Sinna Beloved Editor: Bones Creative Kingpin: Libby
Support the podcast
32 notes
·
View notes
Text

Mary Shelley’s classic novel, presented in its original 1818 text, with an introduction from National Book Critics Circle award-winner Charlotte Gordon Nominated as one of America’s best-loved novels by PBS’s The Great American Read The original 1818 text of Frankenstein preserves the hard-hitting and politically-charged aspects of Shelley’s original writing, as well as her unflinching wit and strong female voice. This edition also emphasizes Shelley’s relationship with her mother—trailblazing feminist Mary Wollstonecraft, who penned A Vindication of the Rights of Woman—and demonstrates her commitment to carrying forward her mother’s ideals, placing her in the context of a feminist legacy rather than the sole female in the company of male poets, including Percy Shelley and Lord Byron. This edition includes a new introduction and suggestions for further reading by National Book Critics Circle award-winner and Shelley expert Charlotte Gordon, literary excerpts and reviews selected by Gordon, and a chronology and essay by preeminent Shelley scholar Charles E. Robinson. Penguin Classics is the leading publisher of classic literature in the English-speaking world, representing a global bookshelf of the best works throughout history and across genres and disciplines. Readers trust the series to provide authoritative texts enhanced by introductions and notes by distinguished scholars and contemporary authors, as well as up-to-date translations by award-winning translators.
buy here
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
we're 99.9% sure that portuguese poet Fernando Pessoa was plural.
okay uh disclaimer. we're not a psychology or literature expert by any means. we rarely even read poetry. we only heard of this guy in high school literature class and the thought stuck with us and then we found plausible evidence lmao. also, as a plural system ourselves, we're clearly biased.
and a considerable amount of this post will be sourced from wikipedia. and this is the first time we've made a post like this. please don't come after us I'm just writing this for fun lmao
huge ramble ahead!
who even was that man
Fernando António Nogueira Pessoa (Portuguese: [fɨɾˈnɐ̃du pɨˈsoɐ]; 13 June 1888 – 30 November 1935) was a Portuguese poet, writer, literary critic, translator, publisher, and philosopher, described as one of the most significant literary figures of the 20th century and one of the greatest poets in the Portuguese language. He also wrote in and translated from English and French.
yeah that's who the man was. but what really sparked our interest in him during class and made us wonder if he was plural were his...
✨heteronyms✨
y'know pseudonyms? when someone writes under a different name than their own for whatever reason? these are similar, but the catch is that the different names have different personalities, supposed appearances, philosophies, all that shit.
the term was coined by Pessoa himself, and his heteronyms were written as if they were real people. they had detailed careers, histories, etc. he had at least 70, although I vaguely remember some other source estimating it at around 100.
"but eva, these could just be OCs or something!",
he had 3 main ones though, being Alberto Caeiro (known for interpreting the world as-is, without greater meaning or anything, like some sorta anti-poet), Álvaro de Campos (a naval engineer who even had multiple phases in his philosophy) and Ricardo Reis (who wrote with a lot of structure and rationality, and was very pessimistic).
I predict someone typing. to that, I begin my endless copy-paste + ramble about all the things that make us think the heteronyms were headmates.
I'll throw in a section of a letter Pessoa wrote to some other poet (bolding the parts I find relevant because I don't love walls of text lmao)
How do I write in the name of these three? Caeiro, through sheer and unexpected inspiration, without knowing or even suspecting that I'm going to write in his name. Ricardo Reis, after an abstract meditation, which suddenly takes concrete shape in an ode. Campos, when I feel a sudden impulse to write and don't know what. (My semi-heteronym Bernardo Soares, who in many ways resembles Álvaro de Campos, always appears when I'm sleepy or drowsy, so that my qualities of inhibition and rational thought are suspended; his prose is an endless reverie. He's a semi-heteronym because his personality, although not my own, doesn't differ from my own but is a mere mutilation of it. He's me without my rationalism and emotions. His prose is the same as mine, except for certain formal restraint that reason imposes on my own writing, and his Portuguese is exactly the same – whereas Caeiro writes bad Portuguese, Campos writes it reasonably well but with mistakes such as "me myself" instead of "I myself", etc.., and Reis writes better than I, but with a purism I find excessive…)
so not only does he describe writing Caeiro completely unexpectedly, he also gives the same sort of opinion about his heteronyms' writings that we've seen (and experienced) plural folks give about their headmates' typing or drawing styles.
hell, "writes better than I but with a purism I find excessive" is exactly my opinion of lynn when he does our assignments lmao
the semi-heteronym surfacing when Pessoa is sleepy could be some sorta dissociative state that lets a headmate come through, be it straight-up fronting or passive influence... but I'm probably forcing it too much here.
uhhh here's something on the heteronym thing from some guy called richard zenish. I bolded some parts again
For each of his 'voices', Pessoa conceived a highly distinctive poetic idiom and technique, a complex biography, a context of literary influence and polemics and, most arrestingly of all, subtle interrelations and reciprocities of awareness. [...] Pessoa was often unsure who was writing when he wrote, and it's curious that the very first item among the more than 25,000 pieces that make up his archives in the National Library of Lisbon bears the heading A. de C. (?) or B. de D. (or something else).
"okay.... they could still be characters though"
the heteronyms were aware of and sometimes interacted between themselves. wikipedia's list of Pessoa's heteronyms even has the man himself as a heteronym and pupil of Alberto Caeiro, although I don't feel like going after the source for that bit.
dear hypothetical person I'm quoting here, you're entitled to your opinion. but how about we take, say... a more DID/OSDD-y approach to things? because there's things that hint that Fernando Pessoa's plurality could be traumagenic and/or disordered too.
When Pessoa was five, his father, Joaquim de Seabra Pessôa, died of tuberculosis and less than seven months later his younger brother Jorge, aged one, also died (2 January 1889).
(written by himself about himself:) Nothing had ever obliged him to do anything. He had spent his childhood alone. He never joined any group. He never pursued a course of study. He never belonged to a crowd. The circumstances of his life were marked by that strange but rather common phenomenon – perhaps, in fact, it's true for all lives – of being tailored to the image and likeness of his instincts, which tended towards inertia and withdrawal.
(written by a schoolfellow:) For one of his age, he thought much and deeply and in a letter to me once complained of "spiritual and material encumbrances of most especial adverseness". He took no part in athletic sports of any kind and I think his spare time was spent on reading. We generally considered that he worked far too much and that he would ruin his health by so doing.
so childhood trauma, check...? at the very least this stuff doesn't sound very good for a child's mental health.
Pessoa's earliest heteronym, at the age of six, was Chevalier de Pas. Other childhood heteronyms included Dr. Pancrácio and David Merrick, followed by Charles Robert Anon, a young Englishman who became Pessoa's alter ego.
"I can remember what I believe was my first heteronym, or rather, my first nonexistent acquaintance — a certain Chevalier de Pas — through whom I wrote letters to myself when I was six years old, and whose not entirely hazy figure still has a claim on the part of my affections that borders on nostalgia. I have a less vivid memory of another figure . . . who was a kind of rival to the Chevalier de Pas. Such things occur to all children ? Undoubtedly — or perhaps. But I lived them so intensely that I live them still; their memory is so strong that I have to remind myself that they weren’t real."
oh I just found some spiritual stuff too
the appearance of the first heteronym was after his family members died so that's one thing... and like, that's not just one childhood heteronym but at least four. and well, to me they sound a bit too vivid for your average imaginary friend.
Pessoa's interest in spiritualism was truly awakened in the second half of 1915, while translating theosophist books. This was further deepened in the end of March 1916, when he suddenly started having experiences where he believed he became a medium, having experimented with automatic writing. [...] Besides automatic writing, Pessoa stated also that he had "astral" or "etherial visions" and was able to see "magnetic auras" similar to radiographic images. [...] Mediumship exerted a strong influence in Pessoa's writings, who felt "sometimes suddenly being owned by something else" or having a "very curious sensation" in the right arm, which was "lifted into the air" without his will. Looking in the mirror, Pessoa saw several times what appeared to be the heteronyms: his "face fading out" and being replaced by the one of "a bearded man", or another one, four men in total.
........
man, this wikipedia article is extensive and full of stuff that supports our silly little theory, huh.
yeah, so he attributed it to spiritual reasons which is fair and valid, but... "owned by something else" all of a sudden? the thing with the right arm sounding a lot like partial possession in tulpamancy? seeing his heteronyms' faces in the mirror?
yeahhhh.
(I'm guessing the magnetic aura thing could be some sorta derealization, contributing to the he-was-a-dissociative-system hypothesis, but that's yet another stretch on my part.)
(plus, spiritual plurality is a thing.)
oh! this thing he wrote sounds a lot like it too.
"This tendency to create around me another world . . . began in me as a young adult, when a witty remark that was completely out of keeping with who I am or think I am would sometimes and for some unknown reason occur to me, and I would immediately, spontaneously say it as if it came from some friend of mine whose name I would invent, along with biographical details, and whose figure — physiognomy, stature, dress and gestures — I would immediately see before me."
let's just do a quick google..
am I biased? yes, very much so. but y'know. you can see I have my reasons.
to see if any people with more qualifications than we have think the same about Fernando Pessoa possibly being plural lmao.
...oh, yes. contrary to what we thought a couple years ago when we had that class about the guy, other people have indeed thought the same. and written about it.
keywords "fernando pessoa mpd" give us:
this paper from 2012 (in portuguese) that... well, I *think* it claims he had mpd but it's very convoluted and abstract about it
this little... forum post? from 2009 that quotes a dead link :v
this one seems kinda cool. it regards Pessoa's positive approach to his heteronym-having as a creative condion called Pessoa Syndrome, and later mentions some Multiple Personality Order (not disorder). don't love some of its wording about mental disorders and madness... it's good to see someone consider healthy multiplicity as a thing that exists, though. it also claims Pessoa became someone with multiple personalities through his heteronymic writing, which is yet another possible origin I hadn't considered before for some fucking reason.
this one cites a dissociative process
this one straight up calls it "subject plurality"!
conclusion ig. I'm pretending to be organized here.
other keywords (like "fernando pessoa dissociative") provide some more results :0 but I've been writing this post for far too long now and would rather not read through more odd wording lmao
it really surprises me that wikipedia doesn't mention the possibility at all from what I've read and ctrl+F'ed. I thought we were being a conspiracy theorist about it but then I found even more stuff to back us up, including other people's analyses. so that's nice.
and I think this kind of thing, of plurals of the past, should be talked about more in the community. it's really interesting to say the least.
...
how does one even end a post like this one.
uhh thanks for reading!!
62 notes
·
View notes
Note
Howdy! I'm taking a translation class this coming quarter. Any tips for beginners at translating? Thank you and have a lovely day!
This is the best ask I could have possibly gotten. I want to talk about this so bad.
So I am not an expert by any means but I love to talk about translation so:
For beginners, I would say translate everything as literally as possible so you don’t lose points for misunderstanding. Something I do in all my classes is when I translate a singular third person as “they” I always write “they(plr)” so I don’t lose points.
So if I was translating let’s say the beginning of the Aeneid in an Aeneid class I would translate “I sing of arms and a man who came first from Troy, over the high sea as a refugee from fate seeking lavinian shores” so that I got all the possible points (that translation is from memory so I’m sorry if I missed anything)
But now the fun stuff! Literary translations! I’m of the opinion that the job of the translator is to make you feel something. Not necessarily what the poet wanted you to feel, but what the translator feels. I always go into translation trying to use the text to explain what made me want to translate it.
Translation for me is a fun hobby and not yet a job (one day) so I don’t ever force translations. I have something I want to translate and then I agonize over it for months and months until I’ve exorcised the original from my mind. I do actually call my translation projects my “poetry demons” which sometimes confuses my roommates.
I also don’t try and make my literary translations completely accurate. Taking the beginning of the Aeneid, this is my favorite translation I have of it: “I sing of a man and his weapons/Who came from Troy, chased by fate,/Looking for Lavinia’s shoreline. /The war is over,/But Juno’s still angry. /He went through so much, /Down in the ocean,/Ilium’s war…”
I’ve mixed up bits- the Juno’s anger bit is before the “iactatus ab alto.” Im listening to Jesus Christ superstar so I can’t recite the Aeneid to try to remember the actual bits right now but my thing with the Aeneid is I want to make you love Aeneas as much as I do and I want you to hate him as much as I do because he’s both the best man you will ever meet and an absolute shithead. I also want to keep at least some rhythm in there, which is always the hardest bit of poetry translation. I translated the “who came from Troy, chased by fate” bit like that because the stress goes who CAME from TROY, CHASED by FATE, and the parallel stress was important to me. Same with down in the ocean/iliums war. I’m trying to keep some semblance of poetry even at the risk of sacrificing some of the meaning because the poetry, in my opinion, is more important than the exact words.
Also! I’ve been told my translation is very simplistic which I don’t deny but I think that if you’re reading classics in order to read very difficult poetry/prose, cicero is right there. Lucretius is right there. You cannot translate Catullus into difficult prose and keep consistent with the poetry- it’s easy poetry not difficult prose.
Anyway thank you for this ask it was so fun to talk about and this is possibly my favorite thing in the world. Right now I’m thinking about Sappho as marginalia- I’d need to find the right text to make it the marginalia to, but it would be good fun, maybe a combined Sappho and Trojan women? I think that would be cool.
#asks#translation#thank you for the ask I daydream about getting to explain this sometimes#not to sound lame
9 notes
·
View notes
Note
BREAKING NEWS: Atlas Vanserra Creates Jobs, Fulfils Campaign Promise Ahead of Polls
Prythian: ‘The People’s Prince’ and crowd favourite contender for the 2024 Presidential Elections, Atlas Vanserra (02), the youngest presidential nominee has already begun fulfilling his campaign promise of solving the unemployment crisis. Vanserra, pictured below conferring with his future VP Pumpkin Vanserra (02) between public appearances, has brought a whole slew of previously unemployed or underemployed people into the workforce for their expertise in “baby talk.”A panel of linguists, speech specialists, and parents have been added to virtually every news outlet in town (with the exception of Fox and co, who already had them) and everyone from cat owners to older siblings have been hired as consultants. “I never thought I’d be able to do this,” said a young mother who wishes to remain anonymous, “I got married so young - right after I learned to read and write too - I had no experience or references, no understanding of the job market - and I love being a mother so I’m glad I’m getting paid to do just that.” Many parents of young children, who may have been struggling with the cost of living crisis, income insecurity, rent hikes etc, have found a saviour in Vanserra. “I was a little sceptical at first,” says Tom, a software engineering graduate from Stanford, “I was like, I got the employable degree and still got replaced by AI, what’s a baby gonna do, babble? Turns out, yeah!” Tom has had to move in with his long time girlfriend’s parents to better provide for their infant son as rent prices go up and home ownership remains a pipe dream. “We saved up to get married, we saved up to buy a house. We planned for our baby - we knew it was a big undertaking - but then I lost my job and I was working any minimum wage job I could find so my girl didn’t have to worry about nothing… at one point we considered other options but we had none, and prenatal care is so expensive… it was a nightmare. I’m glad that the public have started caring for mothers and babies postpartum though.”
So how has Vanserra helped? The vested interest in translating the nominee’s speeches has not only employed parents, but secured parents of young children stipends for their cooperation in helping researchers study child behaviour in a non invasive environment. “It’s not just videos or observations,” says a lead scientist with the Babble Initiative, “parents spend all of their time watching children, their wealth of knowledge is priceless. Given how often other animals mimic babies - like cats - we’ve been able to decentralise our input sources. We’re not looking at languages or fiction alone, but trying to ascertain if there are commonalities in these vocalisations. Essentially, if there is a baby language.” Fields like anthropology, archaeology, primatology etc have also received much attention and funding as fascinated patrons realise just how much goes into “understanding what we should but don’t.” “I thought it was just digging,” an anonymous donor remarks “but these guys are tracing language back centuries, connecting history with the present - I was thinking how I used to be a baby once and should understand one, you know? That’s what got me hooked.”
Many wonder if the arts will finally get the respect they deserve as more and more people recognise the important work critics, historians, and especially students do in interpreting, indexing, and interacting with media and information of all kinds. Atlas Vanserra’s manifesto, a 17 page document of artistic impressions, was deciphered by a team of artists - including writers, literary critics, art hostorians etc - after three months of rigorous study. “Several independent readings exist in the mainstream and experts disagree on exactly what each blob means, but that’s part of the work - and I hope it’s at least become clear to all that it is - as a matter of fact - a lot of work!” said a graduate student when asked why Project Demanifest is important today. “Media literacy is dead and intellectualism is dying. I didn’t know what change would look like but it definitely wasn’t an adorable ginger baby, but I’m so glad it’s not another tangerine.”
The People’s Prince has not yet secured the Presidency, and it is unclear at this stage if he will. Though a fan favourite, many have wondered if Atlas is just a fresh new fad the public is obsessed with than a valid contender. “I don’t think it matters,” said an ‘Atlas Truther’ “A democracy is only valid insofar as the people believe the ones in power will act in their best interests. I can’t say that with a good conscience right now, and I’m sure that’s true for a lot of others. When a toddler has a record of fewer tantrums than other contenders - shouldn’t that be a wake up call? People like to call us baby brained anarchists for wanting Atlas to win. I disagree. If a baby can win an election that’s a problem. If the baby has you thinking he should win the election, that’s also a problem. At least Atlas is cute and apathetic to monetary bribes.” Regardless of if we are set to have the youngest president to date, one cannot ignore how easily the youngling was able to affect and enact changes that the last several presidencies have been unable to do - before even coming into power. Atlas has raised the bar, let’s hope this becomes the standard. •
I am 100% invested in this political thriller of a baby becoming president
This ask is why ask boxes were invented
10 notes
·
View notes