#linguistics study
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
So if I’m speaking Spanish, and I need to say an English word — like a name, brand, website, etc — I say it like a Spanish speaker
However, I hear a lot of speakers drop into a very native English accent in the middle of a sentence to say “el Starbucks” and whatnot (I love hearing it. Just a random completely English-sounding word in a Spanish sentence)
So I’m wondering…
From my personal observations I think native bilinguals do this more, but I’m interested in more data. Feel free to reply or reblog for a more detailed answer!
(EDIT: sorry the poll is so confusing. “YES” means yes, you do the thing I described, changing your accent to a different one in the middle of a sentence)
#resisting the urge to ask people to reblog for more results but like#I want to know#I have heard that it’s easier to switch between languages when you’re more fluent so my hypothesis makes sense#Quinn polls#quinn posts#langblr#language#linguistics#linguistics study#poll
580 notes
·
View notes
Text
Every single person studying a language when they recognize the most basic word of the language in a text or a video

61K notes
·
View notes
Text
Found an interesting study I thought I would signal boost.
Call for Linguistic Study Participants
Are you a Native English speaker? (of any dialect/variety)
Are you over 18 years old?
Do you want to help my best friend with their MA study?
Can you spare 20 minutes to do an online experiment where you learn some words in a new language? (preferably on a Windows laptop)
For more information follow this link:
please also reblog this if you can!
412 notes
·
View notes
Text
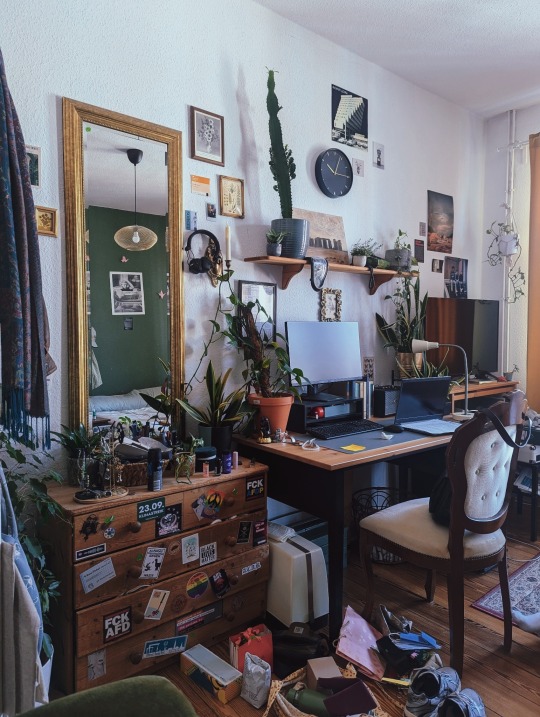
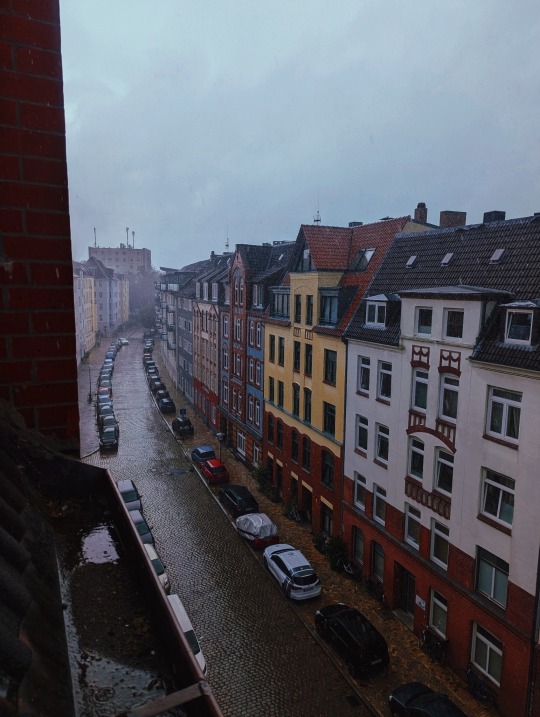
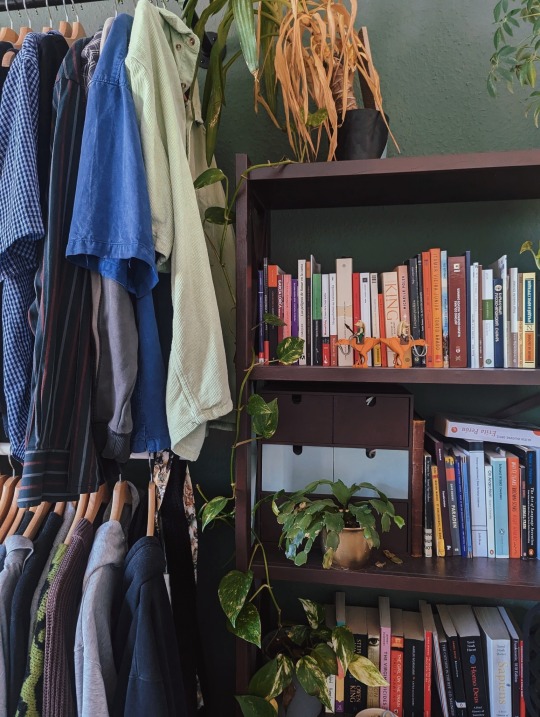




23.08.24 i am currently enjoying my exam/term paper-free life by working too much, cleaning to de-stress and finally getting back into reading (bought piranesi by susanna clarke yesterday, very excited). my first master's semester is slowly approaching and the courses all look promising. also, looking forward to autumn!
🎧 - the wolf by siamés
#it's hard to make study posts when i'm not studying#studyblr#langblr#aesthetic#study aesthetic#study inspiration#studying linguistics#studying english literature#studyspo#academia#jaystudies
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Rare Language Learning: Polari
If you have ever used the words:
- Naff
- Butch
- Camp
You have unknowingly been speaking the sociolect known as Polari, the language of queer people primarily used in the 30s to the 70s. Polari is now an endangered language, as labelled by the University of Cambridge
Something of note: Many resources out there imply (or state) that Polari was a language invented and used solely by white cis gay men, which is decidedly untrue. Many words of Polari come from drag culture, lesbians, and the Romani people and their language. The use of ‘the language of British gay men’ may be a more palatable title to the general public, but it is not to me. I did my best to curate a variety of resources, but unfortunately much of queer history has been lost many more decades than I’ve been alive, if you have any other resources for studying Polari I would love to read them, message me or leave a link in the replies.
Articles
Learn Polari, the Secret Language of the Gays ⚢ Out Magazine
Polari: The code language gay men used to survive ⚢ BBC
Polari and the Hidden History of Gay Seafarers ⚢ National Museums Liverpool
The Story of Polari, Britain’s Secret Gay Language ⚢ Fabulosa!
Polari People ⚢ Fabulosa!
Polari: a language born from prejudice ⚢ Englishpanish
The secretive gay language that gave LGBTQ people a voice ⚢ GAYTIMES
A brief history of Polari: the curious after-life of the dead language for gay men ⚢ The Conversation
Study Material
The Polari Bible ⚢ Internet Archive
Fantabulosa: A Dictionary of Polari and Gay Slang ⚢ Internet Archive
Sociolinguistics / Polari ⚢ StudySmarter
FlashCards ⚢ Quizlet
New Polari Translator ⚢ LingoJam
Polari: A sociohistorical study of the life and decline of a secret language. ⚢ Dissertation, University of Manchester
Polari: a language born from prejudice ⚢ Englishpanish
Simon Bowkett: a short blog in Polari for LGBT+ History Month ⚢ Civil Service LGBT+ Network
#academia#studyblr#university studyblr#uni#university#student#linguistics#language study#language learning#langblr#languages#endangered languages#queer history#queer history month#lgbtq community#lgbtq history#lgbtq history month#lgbt#lgbt history month#queer academia#queer community#linguistic#Polari#Polari language#dialect#sociolect#pride#uk history#English history#university student
739 notes
·
View notes
Text
if I asked very nicely would you all be willing to take a one minute anonymous survey for my linguistics class. if the answer is yes, please click here. thanks :)
(sharing for a better response size would also be very appreciated)
#linguistics#quil's unholy underworld#i have no clue how to tag this#it is quite literally 2 multiple choice questions#keeping it real simple#it's a required project in an intro class#we didn't even get to choose the topic#anyway#it's less important the results#it's intended to teach us the scientific method in practice#which I have done. like 5 times now in different classes it feels#i literally studied the demographic of the library by age an entire summer once#anyway. here's hoping this is worded and structured well enough to do what I need it to#take my survey boy#please
1K notes
·
View notes
Text


languages study schedule
daily
write 1 or 2 sentences to sum up my day
learn 5 new words
listen to a song, watch a short video, conjugate a verb, read and attempt to say out loud a tongue twister, count from 1-100, sing the alphabet, read a page in a book, talk to my reflection, vocabulary flashcards (pick one)
weekly
watch a movie, episode, documentary or follow a cooking tutorial in the target language
grammar exercises
translate a short text
monthly
write an essay or report, on a chosen topic
#that girl#becoming that girl#student#nenelonomh#productivity#student life#chaotic academia#study blog#academia#study#language#language study#spanish#french#german#italian#language resources#language stuff#linguistics#study schedule#study notes#study motivation#studying#100 days of studying#study aesthetic#study community#study hard#study inspiration#study inspo#study space
375 notes
·
View notes
Text
As we approach halloween, I would love to remind people of Samhain. Samhain is not pronounced "sow-ay-n", "sam-hay-ne", or anything similar. Its SOW-IN. And because I can practically smell the thoughts of "that doesn't make sense", it's not an English word. Irish is not closely related to English. It does not have the same grammatical rules or pronunciation.
Please I am BEGGING people to stop complaining about how irish words/names don't make sense. They make perfect sense if you know the Irish language at all. I'm far from good at irish but even a basic understanding permits you to know how names such as Tadhg or Róisín work.
Anyway, happy Samhain everyone!
#irish language#irish langblr#irish history#langblr#language learning#language study#linguistics#gaeilge
219 notes
·
View notes
Text
接続詞(せつぞくし)
conjunctions - words that are used to link phrases together
情報を加える // Adding information:
しかも besides そのうえ moreover, on top of that さらに moreover, on top of that そればかりか not only that, but also... そればかりでなく not only that, but also...
情報を対比する // Putting into contrast:
それに対して in contrast 一方 whereas
他の可能性・選択肢を言う // Giving alternatives:
あるいは or perhaps (presenting another possibility) それとも or (presenting another option within a question)
結論を出す// Drawing a conclusion:
そのため for that reason したがって therefore そこで for that reason (I went ahead and did...) すると thereupon (having done that triggered sth. to happen) このように with this (adjusting a conclusion to the arguments given beforehand) こ��して in this way
理由を言う // Giving a reason:
なぜなら...からだ the reason is というのは...からだ the reason is
逆説を表現する // Expressing a contradiction:
だが however, yet, nevertheless (contradicting what one would have expected) ところが even so (spilling a surprising truth) それなのに despite this, still それでも but still (despite a certain fact, nothing changes)
説明を補う // Amending one's explanation:
つまり that is, in other words (saying the same thing using different words) いわば so to speak (making a comparison) 要するに to sum up, in short
説明を修正する // Revising one's explanation:
ただし however (adding an exception to the information stated beforehand) ただ only, however もっとも however (obviating any expectations that might arise through the previous statement) なお in addition, note that (adding supplementary information)
話題を変える // Changing the subject:
さて well, now, then (common in business letters after the introductory sentence; is often ignored in tranlations) ところで by the way
#文法#grammar#conjunctions#japanese grammar#jlpt n2#japanese langblr#japanese language#language#japan#japanese#japanese vocabulary#langblr#linguistics#studyblr#study blog#studyspo#study motivation#study aesthetic#study notes#learning japanese#nihongo#日本語#日本語の勉強#light academia#light acadamia aesthetic
933 notes
·
View notes
Text

tuesday 23/07/2024
german! went over B2 grammar for recapping purposes since i never ended up writing notes! plus this is super helpful with reading comprehension
♫ sunburn - almost monday ♫
#studyblr#studyspo#study aesthetic#stem#studying#women in stem#aesthetic studying#study motivation#aesthetic#studystudystudy#study vibes#study study study#soft academia aesthetic#dark academia aesthetic#soft academia#academia#chaotic academia#poc dark academia#stem academia#light academia#dark academia#academia aesthetic#german language studies#learning a language#linguistics#langblr#german language#learning german aesthetic#learning german#b2 german
203 notes
·
View notes
Text
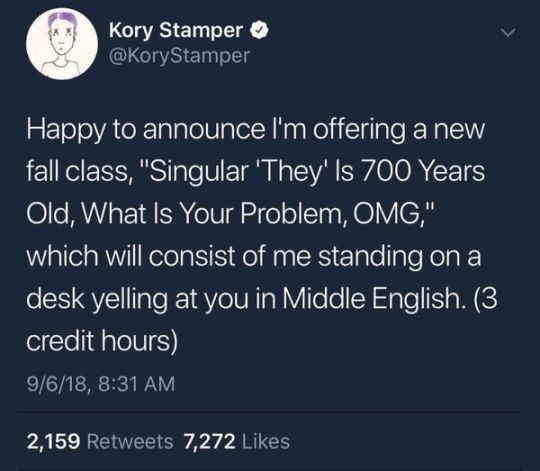
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Every now and then I think about how subtitles (or dubs), and thus translation choices, shape our perception of the media we consume. It's so interesting. I'd wager anyone who speaks two (or more) languages knows the feeling of "yeah, that's what it literally translates to, but that's not what it means" or has answered a question like "how do you say _____ in (language)?" with "you don't, it's just … not a thing, we don't say that."
I've had my fair share of "[SHIP] are [married/soulmates/fated/FANCY TERM], it's text!" "[CHARACTER A] calls [CHARACTER B] [ENDEARMENT/NICKNAME], it's text!" and every time. Every time I'm just like. Do they though. Is it though. And a lot of the time, this means seeking out alternative translations, or translation meta from fluent or native speakers, or sometimes from language learners of the language the piece of media is originally in.
Why does it matter? Maybe it doesn't. To lots of people, it doesn't. People have different interests and priorities in fiction and the way they interact with it. It's great. It matters to me because back in the early 2000s, I had dial-up internet. Video or audio media that wasn't available through my local library very much wasn't available, but fanfiction was. So I started to read English language Gundam Wing fanfic before I ever had a chance to watch the show. When I did get around to watching Gundam Wing, it was the original Japanese dub. Some of the characters were almost unrecognisable to me, and first I doubted my Japanese language ability, then, after checking some bits with friends, I wondered why even my favourite writers, writers I knew to be consistent in other things, had made these characters seem so different … until I had the chance to watch the US-English dub a few years later. Going by that adaptation, the characterisation from all those stories suddenly made a lot more sense. And the thing is, that interpretation is also valid! They just took it a direction that was a larger leap for me to make.
Loose adaptations and very free translations have become less frequent since, or maybe my taste just hasn't led me their way, but the issue at the core is still a thing: Supernatural fandom got different nuances of endings for their show depending on the language they watched it in. CQL and MDZS fandom and the never-ending discussions about 知己 vs soulmate vs Other Options. A subset of VLD fans looking at a specific clip in all the different languages to see what was being said/implied in which dub, and how different translators interpreted the same English original line. The list is pretty much endless.
And that's … idk if it's fine, but it's what happens! A lot of the time, concepts -- expressed in language -- don't translate 1:1. The larger the cultural gap, the larger the gaps between the way concepts are expressed or understood also tend to be. Other times, there is a literal translation that works but isn't very idiomatic because there's a register mismatch or worse. And that's even before cultural assumptions come in. It's normal to have those. It's also important to remember that things like "thanks I hate it" as a sentiment of praise/affection, while the words translate literally quite easily, emphatically isn't easy to translate in the sense anglophone internet users the phrase.
Every translation is, at some level, a transformative work. Sometimes expressions or concepts or even single words simply don't have an exact equivalent in the target language and need to be interpreted at the translator's discretion, especially when going from a high-context/listener-responsible source language to a low-context/speaker-responsible target language (where high-context/listener responsible roughly means a large amount of contextual information can be omitted by the speaker because it's the listener's responsibility to infer it and ask for clarification if needed, and low-context/speaker-responsible roughly means a lot of information needs to be codified in speech, i.e. the speaker is responsible for providing sufficiently explicit context and will be blamed if it's lacking).
Is this a mouse or a rat? Guess based on context clues! High-context languages can and frequently do omit entire parts of speech that lower-context/speaker-responsible languages like English regard as essential, such as the grammatical subject of a sentence: the equivalent of "Go?" - "Go." does largely the same amount of heavy lifting as "is he/she/it/are you/they/we going?" - "yes, I am/he/she/it is/we/you/they are" in several listener-responsible languages, but tends to seem clumsy or incomplete in more speaker-responsible ones. This does NOT mean the listener-responsible language is clumsy. It's arguably more efficient! And reversely, saying "Are you going?" - "I am (going)" might seem unnecessarily convoluted and clumsy in a listener-responsible language. All depending on context.
This gets tricky both when the ambiguity of the missing subject of the sentence is clearly important (is speaker A asking "are you going" or "is she going"? wait until next chapter and find out!) AND when it's important that the translator assign an explicit subject in order for the sentence to make sense in the target language. For our example, depending on context, something like "are we all going?" - "yes" or "they going, too?" might work. Context!
As a consequence of this, sometimes, translation adds things – we gain things in translation, so to speak. Sometimes, it's because the target language needs the extra information (like the subject in the examples above), sometimes it's because the target language actually differentiates between mouse and rat even though the source language doesn't. However, because in most cases translators don't have access to the original authors, or even the original authors' agencies to ask for clarification (and in most cases wouldn't get paid for the time to put in this extra work even if they did), this kind of addition is almost always an interpretation. Sometimes made with a lot of certainty, sometimes it's more of a "fuck it, I've got to put something and hope it doesn't get proven wrong next episode/chapter/ten seasons down" (especially fun when you're working on a series that's in progress).
For the vast majority of cases, several translations are valid. Some may be more far-fetched than others, and there'll always be subjectivity to whether something was translated effectively, what "effectively" even means …
ANYWAY. I think my point is … how interesting, how cool is it that engaging with media in multiple languages will always yield multiple, often equally valid but just sliiiiightly different versions of that piece of media? And that I'd love more conversations about how, the second we (as folks who don't speak the material's original language) start picking the subtitle or dub wording apart for meta, we're basically working from a secondary source, and if we're doing due diligence, to which extent do we need to check there's nothing substantial being (literally) lost -- or added! -- in translation?
#translation#linguistics (sorta)#I love language so much#long post#subtitling#dubbing#transformative work#if you read all the way to the end - THANK YOU I am so impressed#localisation#this is not an academic essay but I still feel bad for not citing sources#low vs high context cultures and languages are concepts from intercultural communication studies#but idk how up to date that is or whether folks even still actually use them#I know they oversimplify things#but it helped me say what I was trying to here so shrug#languages#language soup#meta#language meta#fandom meta of sorts#thanks for the help sorting this out kayla <3#my nonsense
1K notes
·
View notes
Text


Day 2/100 of productivity
Hello everyone!
So many things happened in life recently but I'm here again posting about my language learning progress.
I've been catching up Korean Grammar in Use book. I've noticed that I can understand simple Korean sentences here but it took me awhile to make/create sentences. So I'm going to work on that too.
My goal is to finish revising KGIU book before 2025. Wish me luck!
#100 days of productivity#langblr#linguistics#study blog#study motivation#studyblr#studyspo#korean language
75 notes
·
View notes
Text


study date at a friend's house 🪴
🎧 - watch what happens next by waterparks
#the friend MIGHT be an elf 🤔#studyblr#langblr#aesthetic#study aesthetic#study inspiration#studying english literature#studying linguistics#studyspo#academia#jaystudies
2K notes
·
View notes
Note
You actually CAN use different words to muffle emotional effects! we've been making euphemisms for death for as long as we've had language, that's why we say things like "passed away". even the word "die" was an old Norse euphemism for the old English word "sweltan", which itself is a euphemism for the even older word "diegan". (I really agree with your post, the origin of using "unalive" is incredibly dystopian and censorship is awful, I just wanted to infodump about linguistics)
that's actually really cool!!!! thank you for sharing!!!
also anon i'm in a linguistics fixation right now so we shall have a summer wedding
#ramble#i LOVE LANGUAGE#passing this onto my boyfriend who also loves language AND anything norse#if i could go back to uni and was actually smart i would study linguistics so i could be amy adams in arrival
327 notes
·
View notes
Text
japanese is such a kind language. like you forget a character it will hold ur hand and tell u that everything will be ok and you can just write it in hirigana and everyone will understand :)
and then chinese is like oh im sorry you forgot a character? youre illiterate. you mispronounce a word? your mother is now a horse
#japanese#kanji#hirigana#chinese#language#langblr#language memes#funny shit#funny#shitposting#memes#tweet#linguistics#cunning linguist#linguistness#linguistique#linguine#language study#language stuff
455 notes
·
View notes