#late 19th century -today
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
The Squando Ghostship
The Squando a Norwegian merchant ship docked herself 1890 off Embarcadero in San Francisco. A short time later a headless corpse was found floating in the bay and after investigation it was determined that this was the 1st Mate of the Squando who had been decapitated and disposed of by the Captain and his wife. They had hidden the head in a box under the bunk of the couple as a precaution. How had it come to this ? There are two versions, the first says that the wife of Captain Nels Erikson, the 1st Mate Lars Gunderson made beautiful eyes and they committed an affair. Her husband found out and forced her to assist him in the murder. To do this, she lulled her lover with liqueur and held his hands together behind his back as her husband rushed in and cut off the drunken man's head with an axe.
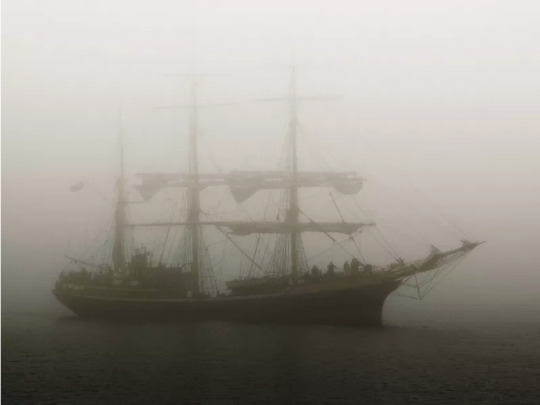

The other version was that he called the lover into his cabin and cut off his head with a saber in front of his horrified wife. In other versions, the wife does not have an affair with the 1st mate at all, but the 1st mate is stalking the captain's wife and was beheaded by the captain. However the couple was captured and sentenced to death. But the story doesn't end here, the Squando were equipped by her owners with a new crew and the tragedy took its course.
After only a month, 4 crew members mutinied and killed their captain. The next two captains also died unnaturally. One died from poisoning by a cut in the hand and the other from a violent squall at night, another version reports that both died violently in the cabin under mysterious circumstances.
In 1893, the entire crew, fed up with the ship's curse, left the ship in Bathurst, New Brunswick. The ship's reputation as a haunted and cursed ship made it impossible for the owners to hire a new crew. The Norwegian consul finally stepped in and hired two night watchmen to guard the ship until it was decided what to do with the cursed vessel. The night watchmen left the ship on the first night and fled in fear after encountering a headless apparition running around in the corridor outside the captain's cabin.
This is what happened to the next six night watchmen, who were all hired and quit again in the next few weeks. Unable to hire workers for the ship, the owners were forced to tear it down. Another legend has it that the Squando wanted to make one last transatlantic voyage in 1901, but completely disappeared on her journey and never arrived at her final destination - on the contrary, she is said to be still looking for a new crew today. So you could call her a spiritship rather than a ghost ship.
But how do you come to that? considering that spiritships are quite rare, if you believe the superstition. Well, the Squando is said to have been involved in a curse. Several workers were killed during the construction of the ship, and one of the widows cursed the ship and all who were to sail on it, and then committed suicide to make the curse effective. Another version says that the widow desperately turned to the ship for help after the owner refused to help her after the death of her husband. The ship itself is said to have offered to carry out her revenge if the widow spilled her blood on it. No sooner said than done, the widow sacrificed herself and the revenge took its course, as already detailed above.
All in all, an evil ship which, when it goes hunting in the fog off the coast to look for a crew, soon kills them and then looks for a new one. My dear friends, I warn you to stay away from an older Norwegian ship that calls you as a crew member in the fog, she does not mean well with you.
#naval history#ghostship#spiritship#norway#squando#late 19th century#age of steam#something spooky today#history
79 notes
·
View notes
Text
it's fascinating to me how many women there are in the history of science and people just... don't know!
#💖.txt#there is such a pervasive myth that prior to like. ~1850 ish no women did anything but be mothers#which is such nonsense. women of the past are just as complex and multifaceted as anyone today is#dont even get me started on the 'women werent really in the workforce until the late 19th/early 18th century!' nonsense#you are falling for the propaganda of those eras.#women worked. not just bc being a housewife is work but because they outright had jobs
1 note
·
View note
Text
I don't know who needs to hear this today but:
most adult women wore their hair up, on a normal day when going out in public, for most of western history from at least the late Middle Ages until the 1920s. even after that, wearing truly long, unstyled hair entirely loose was not common until the 1960s
not half-up. not in a ponytail. not braided with the braid hanging loose. at times trailing elements were involved, but the majority of the hair would still be pinned up. at times it was also a social norm that the hair would always be mostly or entirely covered when out of the house
and until around the early 19th century, little girls usually wore their hair up too, if it was long
when "putting one's hair up" became a specifically adult thing, around the 1830s or 40s, it was not related to marriage. it was something teen girls did around age 16 as a marker of social adulthood. even if she was unmarried, she'd wear her hair up. this attitude remained until the bob took over hair fashion in the 1920s, and even then, long hair was usually still worn up
obviously people can do what they want with their art but like. just. just please be aware of this
I have not reblogged so much Dracula fanart because the artist inadvertently made Mina and/or Lucy look uncomfortably young, hair-wise
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
missing the soft art of men. who are our modern day henry scott tukes, our modern day john singer sargents. where are they??? i need to know
#art#gay#gay art#questions#seriously though i know this kind of softness is NOT reserved for the late 19th and early 20th century. i know it's possible today.
1 note
·
View note
Text
The Forgotten History of the World’s First Transgender Clinic
I finished the first round of edits on my nonfiction history of trans rights today. It will publish with Norton in 2025, but I decided, because I feel so much of my community is here, to provide a bit of the introduction.
[begin sample]
The Institute for Sexual Sciences had offered safe haven to homosexuals and those we today consider transgender for nearly two decades. It had been built on scientific and humanitarian principles established at the end of the 19th century and which blossomed into the sexology of the early 20th. Founded by Magnus Hirschfeld, a Jewish homosexual, the Institute supported tolerance, feminism, diversity, and science. As a result, it became a chief target for Nazi destruction: “It is our pride,” they declared, to strike a blow against the Institute. As for Magnus Hirschfeld, Hitler would label him the “most dangerous Jew in Germany.”6 It was his face Hitler put on his antisemitic propaganda; his likeness that became a target; his bust committed to the flames on the Opernplatz. You have seen the images. You have watched the towering inferno that roared into the night. The burning of Hirschfeld’s library has been immortalized on film reels and in photographs, representative of the Nazi imperative, symbolic of all they would destroy. Yet few remember what they were burning—or why.
Magnus Hirschfeld had built his Institute on powerful ideas, yet in their infancy: that sex and gender characteristics existed upon a vast spectrum, that people could be born this way, and that, as with any other diversity of nature, these identities should be accepted. He would call them Intermediaries.
Intermediaries carried no stigma and no shame; these sexual and Gender nonconformists had a right to live, a right to thrive. They also had a right to joy. Science would lead the way, but this history unfolds as an interwar thriller—patients and physicians risking their lives to be seen and heard even as Hitler began his rise to power. Many weren’t famous; their lives haven’t been celebrated in fiction or film. Born into a late-nineteenth-century world steeped in the “deep anxieties of men about the shifting work, social roles, and power of men over women,” they came into her own just as sexual science entered the crosshairs of prejudice and hate. The Institute’s own community faced abuse, blackmail, and political machinations; they responded with secret publishing campaigns, leaflet drops, pro-homosexual propaganda, and alignments with rebel factions of Berlin’s literati. They also developed groundbreaking gender affirmation surgeries and the first hormone cocktail for supportive gender therapy.
Nothing like the Institute for Sexual Sciences had ever existed before it opened its doors—and despite a hundred years of progress, there has been nothing like it since. Retrieving this tale has been an exercise in pursuing history at its edges and fringes, in ephemera and letters, in medal texts, in translations. Understanding why it became such a target for hatred tells us everything about our present moment, about a world that has not made peace with difference, that still refuses the light of scientific evidence most especially as it concerns sexual and reproductive rights.
[end sample]
I wanted to add a note here: so many people have come together to make this possible. Like Ralf Dose of the Magnus-Hirschfeld-Gesellschaft (Magnus Hirschfeld Archive), Berlin, and Erin Reed, American journalist and transgender rights activist—Katie Sutton, Heike Bauer. I am also deeply indebted to historian, filmmaker and formative theorist Susan Stryker for her feedback, scholarship, and encouragement all along the way. And Laura Helmuth, editor of Scientific American, whose enthusiasm for a short article helped bring the book into being. So many LGBTQ+ historians, archivists, librarians, and activists made the work possible, that its publication testifies to the power of the queer community and its dedication to preserving and celebrating history. But I ALSO want to mention you, folks here on tumblr who have watched and encouraged and supported over the 18 months it took to write it (among other books and projects). @neil-gaiman has been especially wonderful, and @always-coffee too: thank you.
The support of this community has been important as I’ve faced backlash in other quarters. Thank you, all.
NOTE: they are attempting to rebuild the lost library, and you can help: https://magnus-hirschfeld.de/archivzentrum/archive-center/
#support trans rights#trans history#trans#transgender#trans woman#trans rights#trans representation#interwar period#weimar#equality#autistic author#nonbinary#lgbtq representation#lgbtqia#book news#book#books#new books#thank you#neil gaiman#for your support
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
So much for Legends Celebi or B3W3, lmao.
But for real, before anyone starts theorizing about ultimate weapons or ancient wars in Pokémon Legends ZA, there are a few important things to consider first:
1. The game will be set entirely in Lumiose City.

A bit disappointing, though Lumiose is already a big place, and it’ll only be bigger now that it’s the central focus. A smaller scope will also probably mean a higher-quality product in the end, too. Though it does makes me wonder how catching wild Pokémon will work within an urban city. Maybe the game will be more battle-focused, as opposed to the catching-focused Legends Arceus.
2. The game will (almost certainly) not be about the events of 3,000 years ago.
If it wasn’t already obvious by the limited setting, Legends ZA will most likely have little to do with the events of the ancient war and ultimate weapon. If it’s anything like Legends Arceus, Legends ZA will instead be set in a period based on the latter half of the 19th century, soon after the invention of Poké Balls. Anything set before this period would predate the invention of Poké Balls, and thus have to have drastic changes to its gameplay, which is something I just don’t see happening.
And we know that Legends Arceus is set during the mid-to-late 1800s because of the events it is based on, i.e. the Japanese annexation of Hokkaido in 1869, as well as the subsequent colonization efforts.
Similarly, we can guess that Legends ZA will be set during this same period because of the event it is seemingly based on, Georges-Eugène Haussmann’s renovation of Paris from 1850 to 1870.

For those unaware, Haussmann’s renovation was an urban renewal project, commissioned by Emperor Napoleon III, that included the demolition of old medieval neighborhoods, the annexation of surrounding suburbs, the construction of new sewers, etc. The renovation was extremely unpopular, what with the whole bulldozing thousands of houses and replacing them with standardized streets and buildings thing, resulting in Haussmann’s dismissal in 1870. However, work on his plans continued until 1927, and ultimately are what made Paris what it is today.
While Legends ZA likely won’t go too far into the nitty-gritty of the real-world events, knowing what the game will be drawing from is essential for any speculation on what we can expect to see.
In fact, using this same method, we can probably even guess what future Legends games will be like by looking for historical events during the mid-to-late 1800s period. Take Unova, for example, which could…

Oh.

Oh no.
#honestly this could all be just blatantly wrong#but it was still worth it for the setup#pokemon#pokemon legends#pokemon legends za#pokemon legends z-a#pokemon legends zygarde#pokemon legends arceus#game freak#nintendo#theory
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
The Romanticism of One Piece I: Definition
Part II Full essay posted on AO3 here
“Romanticism is the star which weeps” —Alfred de Musset
One Piece is a Romance. It’s the title of the opening chapter as well as the first volume, and was liked enough by Oda that he recycled it for the first chapter and volume after the time skip. Sprinkled throughout the story Luffy and others will declare certain moments to be romantic. But what does that actually mean?

If you go to website for Mirriam-Webster and scroll down to the fourth definition, you’ll read that romance is “a: marked by the imaginative or emotional appeal of what is heroic, adventurous, remote, mysterious, or idealized
b: often capitalized : of, relating to, or having the characteristics of romanticism”
It’s this second aspect of romance that I want to focus on today, because while One Piece is imaginative, and emotional, and adventurous, the roots of the manga dig much deeper than these superficial traits and tap into the much bigger movement that at one point dominated the Western World.
As with many things, Romanticism is a concept that at its face seems quite simple, but the more you try to pin down specifics the more it squirms into something amorphous and difficult to define. In his lectures on Romanticism, Isaiah Berlin described it as, “the greatest single shift in consciousness of the West” before spending an entire hour of his introductory lecture trying to distill it down to its purest essence. In the Romantic movement we find our modern ideas of imagination, childhood, and sentimentality. Its influence dominated everything from politics, philosophy, poetry, literature, art, music and architecture. From the Romantics was born the Nationalism of the late 18th and early 19th centuries, which would lead to tragic results in the 20th. It spanned Europe and America, the Western world alight with hope after the French Revolution only to watch with horror as it was followed by the Reign of Terror, Napoleon, and the wars he brought to the rest of the continent.

Pinpointing dates is difficult, but for simplicity’s sake it’s easiest to put it as lasting from approximately the mid 1700s through the mid to late 1800s. As Romanticism was a pan-European movement, it didn’t hit every place at the same time. It swept from France through Europe and eventually America at its own pace, blooming and dying independently of one another, with various precursor movements such as the Storm and Stress era in Germany, as well as holdovers lasting well after the golden age ended, the last embers clinging on until the First World War. Romanticism picked up the local flavor of wherever it went, the Romantic ideals of France related but not identical to the Romantic ideals of Germany, just as the Romanticism of William Wordsworth wasn’t the same as the Romanticism of Lord Byron.
When attempting to define Romanticism, it is perhaps easiest to see it in what it was trying to push back against. As with every movement, the Romantics were in conversation with the past, in their case the Enlightenment thinkers of the 17th and early 18th centuries. The Enlightenment as a movement is just as difficult to pin down as the Romantics, but on the whole it said that there was one, specific way men should live their lives, that there was a formula for happiness and improvement of the human condition using reason, science, and an appropriate methodology. While the various Enlightenment figures all disagreed what that methodology was, for the most part they all agreed that it existed. It favored cold, hard logic, a celebration of science and of learning, and was hopeful for a future where humanity could better itself through its own effort by understanding the universe in which it lived.
The Romantics looked at all of this, and said…no.

There are other factors to consider when discussing Romanticism, such as the increase in urbanization following the Industrial Revolution and the political instability brought on by corrupt, crumbling monarchies and the revolutions they spurned, but in my mind this defiant no is the beating heart of Romanticism. It’s a philosophy that emphasizes the self over all, prioritizing feeling over reason and experience over logic. In fact, to the Romantic, there was no knowledge without feeling.
Institutions such as the church lost some of their power even as the Romantics became more obsessed with spirituality and the occult. The idealized, pastoral past of their beloved romantic ballads was yearned for even as revolts broke out against the monarchies that ruled in those stories of old. There was veneration of the child and the so-called Noble Savage, who were free from the corrupting forces of society and civilization. Freedom was the rallying cry, with abolition, women’s, and animal rights movements all stirring within this time period, but there was no greater freedom than the freedom of self. To do what you wanted when you wanted to do it.
There was a preoccupation with individual genius, and there was little that could bolster one’s career more than living fast and dying young. The Romantic world was one where death was frightfully common, with the increased density of the rapidly growing cities leading to frequent breakouts of disease even as populations boomed. Nearly half of children didn’t live to see their fifth birthday, and for those who did survive to adulthood, the political instability of the time made the future seem uncertain. Better then, to reject the all-consuming industry of the modern age and the cities that seemed to destroy more than they built in favor of spending time alone in the glories of nature and their own imagination, living as they pleased, beholden to no one but their own conscience.

You’ll notice in the examples that I quote that most are white men and most of these men were well-educated. It’s a simple fact that the opportunities they were afforded were different than women and people of color, and their voices were amplified as a result. While there’s been increasing scholarship in recent years to diversify the canon, and there’s good fruit to be found in that regard, it must be acknowledged that the worldview shaped by the most famous Romantics is limited by this singular perspective.
That being said, there can be a more universal application to Romanticism, and One Piece proves that. The defiant no to the binding chains of society and the enthusiastic yes of personal freedom is something that we all feel at one point or another, and it’s what makes up the core of One Piece. Romanticism is a cosmic wanderlust, the ability to poeticize everything both great and small, the neverending search for, well…that depends on the person. But the important part is that they do search and they do dream. And it’s that search that I want to explore in more detail as I dig into specific aspects of Romanticism, and how One Piece applies.

260 notes
·
View notes
Text

Monte Melqonyan/Մոնթե Մելքոնյան (1957-1993)
Honestly, I don't even know where to begin. He's one of those extraordinary individuals about whom countless books could be written and numerous movies could be made, yet still, so much would remain untold. You might wonder, "He's a National Armenian Hero—cool, but why should I know about him?" My answer is simple: if the world had more people like him, especially in today's times, it would be a much better place. He fought for justice, embodied culture and education, and radiated a deep love for his people and humanity as a whole. I believe everyone should aspire to have a little bit of Monte's spirit within them, regardless of their nationality.
Now, it's important to note that some things written about him in the Western press can be questionable and inaccurate. So, I would advise taking most of the information from those sources with a grain of salt.

Monte was born on November 25, 1957, into an Armenian family in Visalia, California, that had survived the Armenian Genocide. From 1969 to 1970, his family traveled through Western Armenia, the birthplace of his ancestors. During this journey, Monte, at the age of twelve, began to realize his Armenian identity. While taking Spanish language courses in Spain, his teacher had posed him the question of where he was from. Dissatisfied with Melkonian's answer of "California", the teacher rephrased the question by asking "where did your ancestors come from?" His brother Markar Melqonyan remarked that "her image of us was not at all like our image of ourselves. She did not view us as the Americans we had always assumed we were." From this moment on, for days and months to come, Markar continues, "Monte pondered [their teacher Señorita] Blanca's question Where are you from?"
In high school, he excelled academically and struggled to find new challenges. Instead of graduating early, as suggested by his principal, Monte found an alternative - a study abroad program in East Asia. The decision to go to Japan was not random. He had been attending karate clubs and was the champion of the under-14 category in California. He also studied Japanese culture, including taking Japanese language courses. After completing his studies at a school in Osaka, Japan, he went to South Korea, where he studied under a Buddhist monk. He later traveled to Vietnam, witnessing the war and taking numerous photographs of the conflict. Upon returning to America, he had become proficient in Japanese and karate.

Having graduated from high school, Monte entered the University of California, Berkeley, with a Regents Scholarship, majoring in ancient Asian history and archaeology. In 1978, he helped organize an exhibition of Armenian cultural artifacts at one of the university's libraries. A section of the exhibit dealing with the Armenian Genocide was removed by university authorities at the request of the Turkish consul general in San Francisco, but it was eventually reinstalled following a campus protest movement. Monte completed his undergraduate work in under three years. During his time at the university, he founded the "Armenian Students' Union" and organized an exhibition dedicated to the Armenian Genocide in the late 19th and early 20th centuries in the Ottoman Empire and the Republic of Turkey.
Upon graduating, he was accepted into the archaeology graduate program at the University of Oxford. However, Monte chose to forgo this opportunity and instead began his lifelong struggle for the Armenian Cause.

In the fall of 1978, Monte went to Iran and participated in demonstrations against the Shah. Later that year, he traveled to Lebanon, where the civil war was at its peak. In Beirut, he participated in the defense of the Armenian community. Here, he learned Arabic and, by the age of 22, was fluent in Armenian, English, French, Spanish, Italian, Turkish, Persian, Japanese, and Kurdish.
From 1980, Monte joined the Armenian Secret Army for the Liberation of Armenia (ASALA – I promise to tell you more about them later) and quickly became one of its leaders. In 1981, he participated in the planning of the famous Van operation. In 1981, he was arrested at Orly Airport in France for carrying a false passport and a pistol. During his trial, Monte declared, "All Armenians carry false passports—French, American—they will remain false as long as they are not Armenian." Over the following years, he perfected his military skills at an ASALA training camp, eventually becoming one of the group's principal instructors.

Monte with his wife Seda
After being released from a French prison (once again) in 1989, Monte arrived in Armenia in 1991, where armed clashes between Armenians and azerbaijanis had already begun. He founded the "Patriots" unit and spent seven months in Yerevan working at the Academy of Sciences, writing and publishing the book "Armenia and its Neighbors." In September of the same year, he went to the Republic of Artsakh to fight for his fatherland and its people. Due to his military expertise, he was appointed Chief of Staff of the Martuni defense district in 1992. His sincerity and purity quickly won the love and respect of the local population and the Armenian community as a whole.
Throughout his conscious life, Monte fought for the rights of Armenians, recognition of the Armenian Genocide, and the reclamation of Armenian homeland.
There are various versions of Monte Melqonyan's death circulating in both Armenian and azerbaijani media. According to official Armenian information, Monte was killed on June 12, 1993, by fire from an azerbaijani armored vehicle.
Monte remains a lasting testament to the incredible potential unleashed when the Armenian patriotic heart unites with sharp intellect.
youtube
In case you'd like to put a voice to the face and hear about the Artsakh struggle directly from Monte, here he is speaking about it in English.
#so many things have been left out#but I guess this is a good starting point#I promise to tell you more about ASALA and Van Operation in near future#monte melqonyan#armenia#armenian history#armenian culture#world history#artsakh#artsakh is armenia#translated literature#մոնթե մելքոնյան
288 notes
·
View notes
Note
why do the children seem to often ask for fruit and/or nuts from santa?
Fruit and nuts are by far the most commonly requested stocking stuffers I see in Dear Santa letters in the late 19th/early 20th century - even more so than candy. Apples and oranges are the fruits you see asked for most often, but in the Southern part of the US you also see bananas and coconuts requested.
As for why (at least where fruit's concerned) - consider the difference in how easy it is for us to get fresh fruit in December vs what it was like 120 years ago. Today we can put fresh produce on a plane, overnight it and have a semi drive it to a store within 24 hours. When many of these letters were written fruit had to be loaded it on a steam ship, sail across the ocean for a week, put on a coal-burning train and then delivered by horse-drawn wagon - often without the benefit of modern refrigeration.
Oranges in the middle of the winter were a treat.
When I was growing up I still usually got an orange in the toe of my stocking, because that’s what my mom got when she was little, and I’m assuming the tradition had been passed down from previous generations.
I think another factor as to why you see fruit and nuts mentioned so often is that back when kids only got two or three Christmas presents - stocking stuffers warranted a mention in a Dear Santa letter. Now that kids lists are considerably longer - I think candy and treats for your stocking are just kind of implied in most modern Xmas lists and not specifically spelled out.
152 notes
·
View notes
Text



19th century fashion plates, designs, etc.
(with late 18th and early 20th century plates)
Tagged by decade:
1790s | 1800s | 1810s | 1820s | 1830s | 1840s | 1850s | 1860s | 1870s | 1880s | 1890s | 1900s | 1910s | 1920s | 1930s | 1940s
Check out today’s plates.
Or check out the art, design, and fashion posts I reblog.
#fashion#fashion plate#collage#1790s#18aughts#1810s#1820s#1830s#1840s#1850s#1860s#1870s#1880s#1890s#1900s#1910s#1920s#1930s#1940s
727 notes
·
View notes
Text
Today I learned that the term "sugarloaf" is not figurative; until the late 19th Century, sugar was most commonly sold in enormous cone-shaped masses, some up to three feet in length and thirty pounds in weight, and in order to use it you had to break off a piece of the desired size using a specialised pair of iron pliers called "sugar nips".
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Etiquette of the Edwardian Era and La Belle Époque: Ball

This is a new set of posts focusing on the period of time stretching from the late 19th century to the early 20th Century right up to the start of WWI. I'll be going through different aspects of life. This series can be linked to my Great House series as well as my Season post and Debutant post.
Let's throw a ball, my darling. It is the age of elegance and opera gloves. Etiquette during these events was as intregal as the music. So let's delve in and dance the night away.
Preparing to host a Ball

Balls in this period weren't just little get-together with a little music in the corner. These were large productions and required the entire household to pitch in. The ballroom would have to be cleaned, chandeliers would need polishing. Any large halls would need to be cleared of any furniture to accommodate a large crowd. If throwing a ball, you need to set aside more rooms than just the ballroom. You will need a room to store any cloaks, coats and hats (a valet and lady's maid would have charge of this), a room for refreshments and sometimes a room set up for any other entertainment such as cards. The dining room would also be needed for a supper (yes, suppers are expected). A ball requires the best of the best. Musicians would be hired, the kitchens will be slaving all day, butlers will be decanting the best wines and select the finest liquor, and rooms made up for anybody thinking of staying the night. The kitchens will have to prepare light snacks as well as the late supper, so everything must be cooked at exactly the right time and kept in optimum condition until needed. A red carpet would be laid from the front door right down to the pavement with an awning to keep the worst of the weather off. Invites should be sent out a few weeks prior and should attempt not to clash with any other event, you may compete who has the best ball but you should never force guests to snub another to go to your ball. Servants should be prepared for a long night, so they may dine earlier in the day to sustain them. Footmen would wait outside to open carriage doors and direct guests to the door. The butler would have to greet them, announce their arrival (not by order of rank but simply in the order they arrive) in the hall and then toward the coat rooms to relieve themselves of any coats or hats. These balls were very expensive affairs. Between food, drink, entertainment, their clothes, wages and getting their house up the snuff, a host could expect to fork out thousands if not more. Alva Vanderbilt's great costume ball cost her $6 million in today's valuation ($250,000 in her era).
The Hosts on the Night of the Ball
The hosts of the ball should be ready to recieve guests promptly. The lady of the house should be downstairs an least an hour before kickoff to check the work of the servants and provide last minute commands. The hosts would wait in the hall and greet guests. The butler will announce every guest while valets and lady's maids take charge of any coats. After guests have shed their coats, they would then greet the host, usually exchanging a few words and thanking them for the invitation before being escorted into the ballroom. The hosts would usually begin the ball themselves or if there was a guest of honour, they would allow them to open the ball. Dancing is only meant to begin with the invitation of the hosts. If there's music playing, it's not an invitation to dance. Hosts have a duty to ensure everyone is having a good time. They will be expected to dance and ensure people are partnered.
Guests
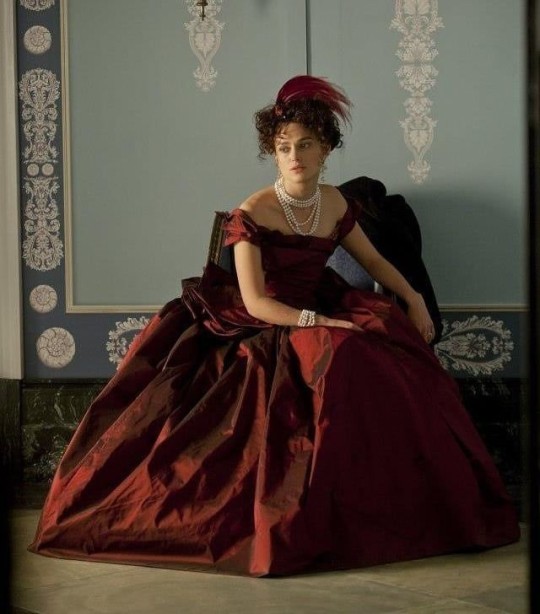

Guests are expected to arrive in a certain time frame. Balls usually begin quite late into the night, usually around 10pm. It would do no good to arrive too early and ride to arrive midway without a viable reason. There may have been a previous event, such as a theatre engagement or an opera so if you are coming from there and everybody eksevgas arrived on time and you show up late, you had best apologise. Guests must only attend if they have been invited by the hosts. You can't just rock up to a ball and expect to be admitted. If a guests wishes to have a friend who is a stranger attend the ball, they can request for the host to invite them. Guests will arrive by carriage or on foot if they live nearby. If arriving by carriage, one must allow for appropriate space between coaches and room for them to pull out. Also, it is a good idea to remind your driver when to collect you. Guests are always expected to greet the hosts as soon as they can, thank them for the invitation and be courteous at all times. Guests should not comment negatively on anything the hosts have provided such as the food or music, it's better to reserve opinion until another less public event. Guests are encouraged to mingle but strangers must be introduced by a mutual acquaintance or even the host. Wandering off through any section of the house not designated as part of the ball is prohibited as is sneaking off into the gardens. Also if one expects to stay for the night (say you live far away and have travelled to get there) you must have requested it of the host a few days at least before.
Dancing Etiquette

Dancing is one of those things in this era that isn't just a pastime but a ritual. Men asked women for the privilege of a dance, a waltz perhaps. Women would not ask a man. Women would have dance cards where gentlemen could request to partner them for certain dances. If a woman has turned down a gentleman for any reason but has no designated partner for the dance, she must sit that particular dance out. A lady should limit dances with the same partner lest it be a root of scandal: it is not considered terrible to dance two dances with the same partner but questionable if you were to dance with the same partner for multiple dances in a row. It is frowned upon for a lady to reject a dance partner when it is his honour after accepting him earlier. And also highly insulting for a man to spurn a dance partner he has sworn to dance with. It is usually customary for the man to ask whether his partner would like a refreshment, wherein he can escort her to find it. They may chat until the next dance whereupon he must excuse himself with a bow and relieve her of his company so she may dance with her next partner. When supper is announced, the last partner is ecoected to escort his lady into the dining room.
Timeline of a Ball

As stated above, Balls usually start around 10pm (but can be held earlier). Once all the guests have arrived and the hosts enter the ballroom, the dancing can go on. Around 1am there would be a light supper. Small refreshments such as canapés would be available throughout usually offered by footmen stationed around the house. Servants would stay up around the clock to unsure that everything runs smoothly, fetching drinks and later after the ball studying up. Balls would end about 3-4am, whereupon carriages would return to fetch guests and ferry them home. Guests staying would head upstairs. Anybody staying over would be treated to a breakfast in the morning.
Theme
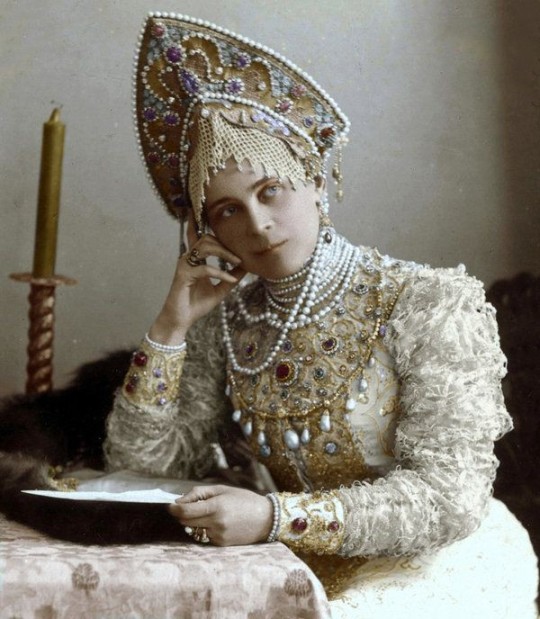

Many balls were themed. Themed balls were usually announced months in advance to allow costumes to be made. A guest should not arrive without having paid attention to the theme as it not only can show poor time management but may be seen as an insult to the host. All guests were expected to adhere to theme where it be a "servant's ball" where they would dress as servants or even a Costume balls are all about extravagance but it's better to rein yourself in (we're side eyeing you, Kate Strong). The grandest costume ball of all time was of course Alva Vanderbilt's grand affair of March 26, 1883. Costume balls were very expensive affairs, with some guests spending up close to thousands of pounds/dollars on their looks. At one ball in 1893, the infamous Bradley-Martin affair, guests spent nearly $400,000 on their costumes - during a particularly bad financial crisis. The overall party cost $10 million.
Dressing for a Ball

Dressing as you know from the previous post is a large part of etiquette of this era. The right costume for the right event is paramount if one wants to make the right impression. Newspapers often wrote about who wore what so it was important to dress your best.
Men must wear a suit or tailcoat, always black. A ball is white tie so he must dress accordingly. He would arrive with a top hat which he would surrender to a valet. He would keep his gloves on when dancing.
Ladies are encouraged to wear a gown usually of a subtle colour with with a décolleté that leaves the upper arms snf shoulders bare. A woman's gown was important as it not only helped her stand out.
A sensible woman for goes her heels and wears pumps to dance as she will be on her feet all night.
Tiaras are beautiful but when dancing all night, it's perhaps best to pick the lightest or go for a simpler headpiece such as a feather or a broach. Wearing a heavy tiara all night while dancing will give you a migraine (it's painful).
Also it's better not to over accessorize. You don't want to be mid spin and all your pearls go scattering across the floor or catch a bracelet in your partners' jacket. Minimalism is best.
A woman may even chose to decorate her gown with fresh flowers.
How to Behave at a ball

Gloves are to be worn at all times when dancing. You only remove your handling food or playing cards. White gloves are preferred but light shades can be forgiven. Gloves for women are worn to the elbow, men's to the wrist.
No lady should arrive at a ball without an escort, either an older woman or a family member.
Men who come to the dance and are unwillingly to dance despite being able to should stay away (I'm not kidding, this is in several etiquette books)
Married couples are not expected to dance together but it is not barred.
A man should always be careful of his lady's train and that of any other. Do not stand on them.
Outward PDA is not permitted. A kiss on the hand or kiss on the cheek is permitted, as is a hand tucked into the crook of an arm but one must swing out of people.
Don't hurry onto the dancefloor (even if it is your song)
When a gentleman seats a lady at the table, he must offer her thanks for her favour.
If a lady does refuse to partner a gentleman but then dances that dance with another without prior agreement, the gentleman is expected to restrain himself from confronting her. He is permitted to never offer her a dance again if this happens.
No lady should ever be unaccompanied at any time. They should have a companion or an escort to make sure they are kept in the loop at all times.
If dancing a set, your choices must be made swiftly and wisely.
A gentleman is without saying barred from going into the women's coat room. That's a no no, stay out of there.
If a gentleman wishes to partner a woman he doesn't know, he must have a mutual friend to introduce themselves and if they don't have one, the host would be on hand to introduce them.
When attending a ball, it's better to avoid heavy topics of conversation. It's better to stick to neutral smalltalk. No party is enjoyable with people standing on soap boxes.
When dancing, good posture is not only favourable but stops the body from any undue movements.
Try not to join in when the dance is midway or almost over. Be prompt.
If your partner is missing, you should not replace them. You should sit the dance out.
The hostess is in charge of ensuring that her female guests are provided with a partner if they wish to dance and gave not been asked.
If a man accompanies a woman to the ball, he's expected to dance with her on her first and last dances of the evening.
If one invites a lady to a ball, a carriage must be provided to ferry her.
Popular dances of the era
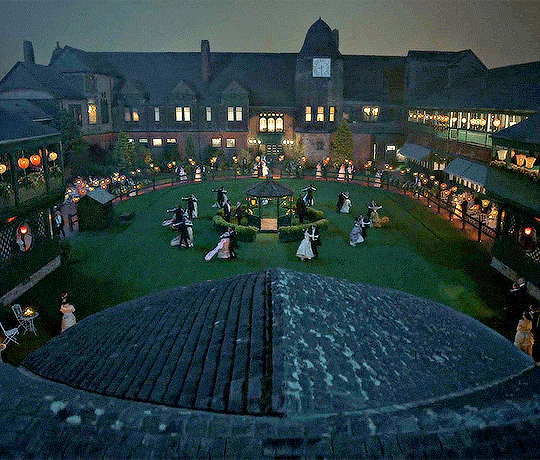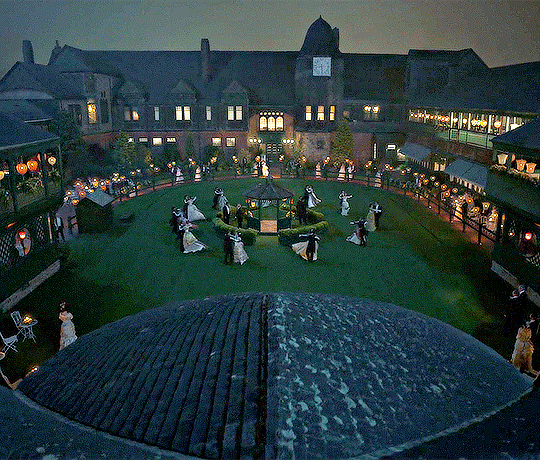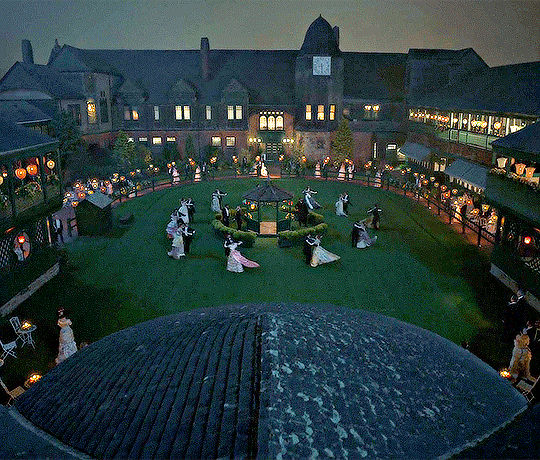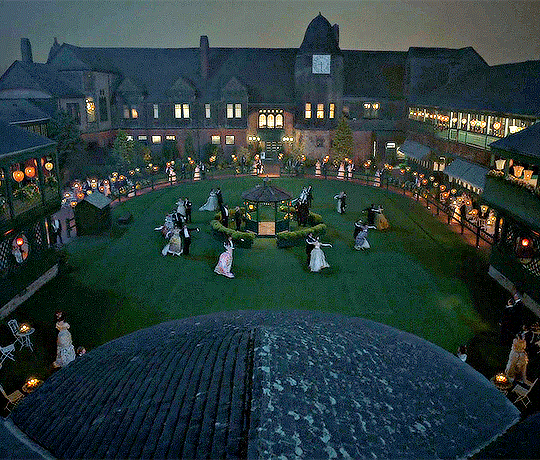
Waltz: The Waltz is seen by many as a reserved dance nowadays but in this era it struck many as a questionable dance because of how close the couple must get. It is a simple dance, requiring 6 steps all with a "box step". It's an elegant and popular dance of the time. A gentleman or whoever is leading should place their hand on the waist of their partner and their partner should rest their hand upon their shoulder.
Cakewalk: The Cakewalk had it's beginnings with enslaved peoples on American plantations. It was a satire poking fun of white plantation owners, mimicking the way they behaved at their own balls. It was later adopted into white society who did not get the joke. It was a group dance where multiple couples set themselves in a square (men on the inside), stepping and strutting to the music. In some instances, a cake was awarded to the most impressive couple which gives the dance it's name (also because it was a piece of cake to perform). The Cakewalk is seen by many as the seed of many of the jazz dances that would dominate the 20s.
Polka: A Polish dance. It requires 3 swift steps followed by a hop. The music is at is 2/4. The couples circle about the dance floor.
Krakowiak: A Polish dance for multiple couples. The leading male dancer (from the first pair) leads the steps for all the couples, and on approach to the band must tap his geeks and sing an improvised verse to his partner, the rhythm the band must match. The couples break up to form a circle. The leading couple will remain before the band. The couples would then dance around the room during the rest of the tune.
Mazurka: This is a lively dance, with it's beginnings in Polish folk dance. Couples gather in circles. The dance requires music with a forceful accent on its second beat, in time at 3/4 or 3/8. This dance has no set figure, relying on the skills of the couple yo improvise. However there are over 50 different steps.
Redowa: A Czech dance. The dance begins with a closed position, their clasped hands pointing the direction they will dance. A leader (the first couple) will take a slight leap around his partner with their left foot tmfollowed by a gliding step with their right. This foot must be pointed, the left leg slightly bent and the back straight. The next set turns the leader about toward the front line again, their left leg is now forward and straight, the right now bent. The left leg is now meant to tuck beneath the right leg with is extended backwards. Another leap to the right leg finishes the pattern. The next couple, the follower, begins movement on the early beats where the leader makes moves on the second set of beats
Castlewalk: The leader moves forward while their partner goes backward. The partner is guided around the room, the leader's arm around their right side under whilst their lest hand rests on the leaders opposite shoulder. Their other arms are clasped, held aloft. The leader begins on their left foot, their partner on their right. They will move with gliding steps, stepping on each beat of the music. They will dance in a circle, moving about the room with other couples, their circle gradually growing smaller and smaller on three very quick turns.
Quadrille: The Quadrille is an older dance but still very popular in Gilded Age America. It is made up with a series of 4-6 contredanses (country dances). The Quadrille is a group dance, made up of sets. The standard Quadrille is five parts, the Viennese contains six. Each section is danced with a combinations of figures. A combination was a set of steps and movements. Examples would be the ladies chain (chaîne des dames) or the two hand turn (tour de deux mains).
#Balls#Etiquette of the Edwardian Era#Etiquette of the gilded age#Etiquette of the belle epoque#belle epoque#Edwardian era#The gilded age#How to write a ball#ballroom#Fantasy Guide to writing a ball#Fantasy Guide#Writing reference#writing resources#Writing research#writing#writeblr#writing reference#writing advice#writer#writers#spilled words
618 notes
·
View notes
Text
Not Flirting

This is NOT FLIRTING.
The very fact that the media say "flirting" is indicative of the fact that the cultural ideas we have around value, improvement, morality, ability and functionality are *rooted* in a a framework which is ableist and eugenic in nature.
Fundamentally, the idea that there are "good genes" and "bad genes" is saying there are "good" forms of embodymindedness and "bad" forms, and that we should remove or reduce the bad and increase the good.
This is biopolitics which is at the root of 19th, 20th and 21st century processes and horrors, and is not *just* racist, but is one of the major ORIGINS of racism as it manifests today, as well as a wellspring of sexism, homophobia, transphobia, antisemitism, colonialism and capitalism.
We are enmeshed in the world eugenics and its proponents thought up, and wrought. It is so prevalent beneath the surface of how we relate to the world in terms of growth, progress, science etc, that we are like fish swimming in it.
This IS NOT JUST TRUMP. This is the ongoing pandemic, the manfacture of debility in marginalised populations for the benefit of those at the levers of power. This is the dismissal of Appalachian lives and folks in rural areas as low-intelligence inbred hicks who "should have known"/"should have moved" in the face of hurricanes. This the way standardised testing structures education on pass fail and grade curves. On and on, with countless more manifestations and iterations.
**We live in a eugenicised society.**
One that frames who should be improved, and how, on the basis of trajectories which begin by evalulating a being on how much it conforms to a certain set of criteria. We never ask where those criteria come from. We never consider that the liberal humanist agenda might also create folks who *don't fit*, in order to mark those who do.
We should. We should ask ourselves where "the human" even comes from.
[ID :A screenshot from The Guardian's liveblog coverage of the US Election, which reads: "Flirting with eugenics, Trump says: ‘We got a lot of bad genes in our country right now’ In an interview earlier today with conservative broadcaster Hugh Hewitt, Donald Trump used terminology associated with eugenics to attack migrants. The remark came as the former president discussed the alleged harm done by new arrivals to the United States, saying many were “murderers”. “Now, a murderer, it’s in their genes,” Trump continued. “And we got a lot of bad genes in our country right now.” It was language similar to the beliefs of eugenics, which emerged in the late 19th century and held that human ills could be combatted through selective breeding. The theory is today regarded as both inaccurate and racist."]
148 notes
·
View notes
Text
Why I fucking hate "The Handmaid's Tale" comparisons to real life (ie "this means THT is going to come true!!!")
that was not an elected government in the story. it was a fringe group that slaughtered the entire US government and took control by force. which makes little sense if you think about it, but that's because it doesn't matter HOW the dystopia happened; it just had to be there for the fiction to make a comment upon the author's present.
Dystopia is never a future prediction. see above: it's always a comment on the present in which it's written
That is massively fucking insulting to women who have actually lived with systemic oppression. They don't have to take away your name or your ability to read and write or put you in a color-coded costume. That's not what violent systemic misogyny looks like, because we KNOW what it looks like.
Sarah Emerson (1762-1784) could absolutely read. Based on what was expected of wealthy girls in her era, she probably spoke at least two languages- English and some French -as well as having knowledge of household accounting, basic first aid, history, literature, drawing, music, etc. She was still married to a man in his twenties when she was fourteen, because he wanted the inheritance her parents had left her (property she owned because, yes, women COULD own property back then). His family disapproved- they called her "the child bride" -but it still happened.
Women in the 19th century who couldn't vote, were discouraged strongly from public speaking (as in, speeches, not conversation), who sometimes had no control over that property they could in fact own, if they married, did normal things. They laughed and cried and petted cute animals. They spoke their minds. They wore what they wanted, albeit with societal constraints. They had names and voices and they still had so few rights under the law.
Women who died from backalley abortions as late as the 1960s could read and write. They had jobs. They dressed in ways we wouldn't consider remarkable today. They voted. They had access to the fucking pill, for gods' sakes. And yet that still happened to them. And yet they still died because the government didn't care about their lives as much as clumps of cells inside them.
Shirley Jackson (1916-1965) was a popular author with a rapier wit that she wasn't above using freely, living once again in a time we'd recognize many features of today. she married a Jewish man over the objections of...well, most of society back then, really. the nurse still wrote "housewife" for her career when she said "writer," during hospital admission to deliver her daughter Sarah
and that's all without getting into the double-damnations of women who aren't white, who aren't Christian, who aren't straight or cisgender. women in non-western countries where some of those things- like clothing laws or movement restrictions -have come to pass, but still not all and not in that way precisely
It doesn't have to be The Handmaid's Tale. In fact, it usually isn't, historically speaking. It's Call the Midwife. It's Harlots. It's Hidden Figures. it's Carol. It's astonishingly normal, among normal women living relatively normal- even happy lives, many of them.
Don't insult their memories by implying that it has to be speculative fiction to be real.
#long post#misogyny#systemic misogyny#abortion#and I even LIKE The Handmaid's Tale! I've been watching it a lot lately precisely because it's so fantastical that#it doesn't scare me#it's less realistic than something like (again) Call the Midwife which I have been avoiding like the plague
259 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hi love ya blog! I’ve been wondering how effective were the coir rain jackets?
Hi! Thanks for loving my blog, and sorry for taking ages to reply! (image via)

Chinese rain capes/raincoats are called 蓑衣/suoyi, and they are mainly made from local materials - in southern China, straw and coir grass are mostly used, as well as brown hair and brown leaves; in the north, thatch and cattail grass are mostly used. It takes about two to three days to make a suoyi by hand. They are typically worn with bamboo hats called 斗笠/douli.
Below - Ming dynasty illustration of a suoyi and douli (x):

Suoyi has a long history, originating before the Qin dynasty (221–206 BC). Although I haven't worn one myself, sources state that they were very effective. Compared with umbrellas, suoyi was not only better at keeping out the rain, but also freed up the two hands to work. Farmers liked to wear it on rainy days, and fishermen often wore it when fishing during rainy and snowy days. During the Ming and Qing dynasties, people travelling during the rainy season usually brought along suoyi (source).
Below - 19th-century late Qing dynasty suoyi made of palm and straw fiber, plus bamboo douli and basket (1, 2):
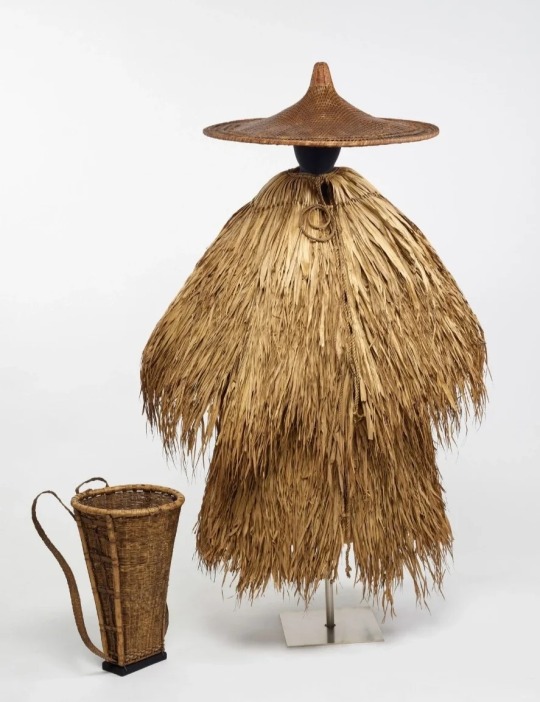


The tradition of working in the wind and rain wearing suoyi and douli continued until the late 1960s in China, after which they were gradually replaced with modern rain gear. Today, suoyi has become more of a tourist souvenir and decorative object than a practical item. Nevertheless, it can still be seen being worn by some elderly farmers and fisherman.
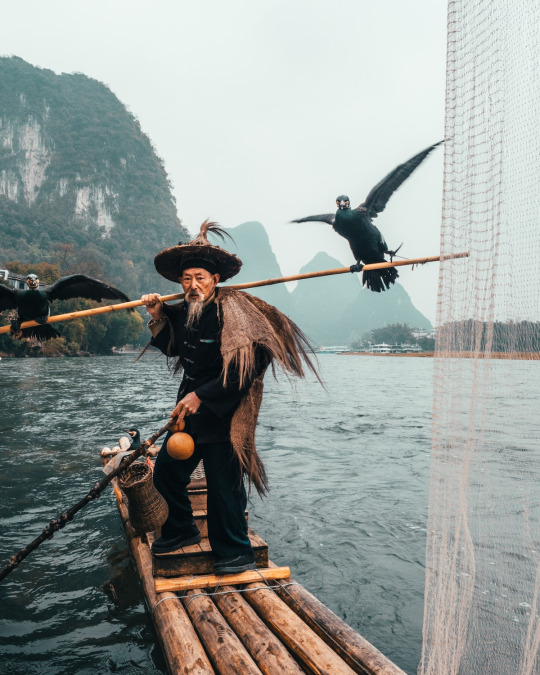
Below - a cormorant fisherman wearing suoyi and douli in Yangshuo, Guilin, Guangxi (x):

I highly recommend reading the following article for more information on suoyi's history, craftsmanship, and current status: Suoyi: RuCai Lyu’s rain cape and its ongoing tradition of protection.
For additional references, please see my suoyi tag.
If anyone has more info, please share! ^^
Hope this helps!
#hanfu#suoyi#rain cape#douli#commoners hanfu#hanfu accessories#crafts#art#artifact#history#>100#ask#reply#reference#chinese clothing#chinese fashion#chinese culture#china
214 notes
·
View notes
Text
Apparently unpopular opinion, but what I can judge from the screenshots we got today, the Capital is not just St. Petersburg, it’s more of a melange between St. Petersburg and Moscow. (Tbh, we got just one shot of the capital, so any opinion here is not really objective, but whatever)
Okay, so there is this:

My first thought was “wow is that inspired by Nevsky or by Tverskaya?”. (i. e. Nevsky Prospect in St. Petersburg and Tverskaya Street in Moscow). Consensus on Twitter is that this photo stinks of Nevsky vibes, however, I would like to point out several things, e. g. there are no sunny days in St Petersburg from architecture of the two Russian capitals to game design decisions made to create an atmosphere of a certain time period.
1) Architecture
I recall some people seeing the picture above and instantly suggesting Nevsky as an inspiration behind. I would like to point out, especially to the people who’d never been to either of the cities, that Moscow and St. Petersburg partly resemble each other (dear people of St. Petersburg - I know, sacrilegious of me to compare you with greedy Muscovites, no I’m not sorry).
Moscow is not only the Seven Sisters and modern skyscrapers. Petersburg is not only 200-300 y.o. buildings. Both cities underwent major changes during 19th and 20th centuries, both cities eventually adopted a somewhat similar style, a mix of late empire (1910s) and early soviet rule (1920s-1930s). Moreover, in many cases, these are even the same buildings, with a ground level from say 1913 and other floors from e.g. 1927. I’ll do you one better, if you compare historical districts of major cities of former Russian empire (e.g. Kyiv or Minsk), you’ll see the same thing. Yes, they’re not identical, but you can clearly see this specific architectural style of 1910-1920s.
Coming back to our screenshot above, I definitely can see Nevsky Prospect influence. However, when I saw those little decorative towers, they immediately reminded me of Tverskaya. I did some digging, and hey, there is actually something similar there:

Yes, not identical, but again, imo design of the Capital is done with goal to remind you of something you saw, not a copy, but close enough to understand the influence, to get the atmosphere of the city.
2) Historical aspect
Okay, from now on it’s my deluded gibberish, but hear me out. Considering the technologies presented in Pathologic (antibiotics, that massive ass artillery gun from P1 which honestly suspiciously looks like Schwerer Gustav), the game can be placed somewhere vaguely in 1920s-1930s. Taking into account what kind of language characters speak (for instance, Dankovsky speaks in a very specific manner, such Russian is more found in literature, than in actual spoken language. The same applies for most of the Utopians), lack of soviet-specific abbreviations and vocabulary, we can say that apparently October Revolution never happened. To be honest, Daniil wouldn’t survive the Revolution or early Soviet rule (read about repressions against intellectuals or the infamous Philosopher’s steamer)
You can argue: “but hey, isn’t Pathologic just a theatre play where such details don’t matter?”. Yes and no. Because it’s a theatre play, many otherwise important details are omitted. However, developers drop hints here and there, to set the tone and visually convey what kind of country and society they’re talking about. No offence to non-russian-speaking fans, but I’m still convinced that IPL still considers russian-speaking countries their primary audience. This leads to certain design choices, including architecture of the Capital.
In my opinion, IPL had to mix visuals of Moscow and St. Petersburg in order to convey a certain vibe. You see, since it’s somewhat suggested that revolution didn’t happen, developers have to utilise aesthetics of 1910s culture to show that we are talking about “Russia” from works of Gorky, Chekhov, and Bunin. At the same time, IPL have to add elements of early soviet culture, so the game world doesn’t look like weird 1910s with antibiotics and far too much advanced technologies.
How’s that connected to the Capital? Russian capital in late empire was St. Petersburg. In later years - Moscow. Moreover, if we are talking about Dankovsky as a character, his design (among other things) is heavily influenced by works of Bulgakov. But in Russian mindset Bulgakov is tightly associated with 1920s Moscow, you just can’t escape it. So, consequently, IPL decide not to sacrifice one for another, and just mix the two capitals, stylistically, in order to create the desired impression on the player.
We’ll see if all that is at least partially true from P3. Hopefully, even from the upcoming demo.
#also note the pre-reform orthography!!#and the electrotheatre right there#do you know what’s also on Tverskaya?#you guessed it! Stanislavsky Electrotheatre!#pathologic#pathologic 3#daniil dankovsky#даниил данковский#мор утопия
91 notes
·
View notes