#industry guidelines
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Little P.Eng. Engineering For CIPP Liner Design As Per ASTM F1216 Using Finite Element Method
In the realm of civil engineering, the rehabilitation of pipelines is a critical task that ensures the longevity and safety of underground infrastructure. One of the most innovative and efficient methods for pipeline rehabilitation is Cured-in-Place Pipe (CIPP) lining. This technique not only offers a less intrusive alternative to traditional pipeline repair but also significantly reduces the environmental impact and cost associated with excavation. Little P.Eng. Engineering, a pioneering firm in the engineering consultancy landscape, has taken strides in optimizing CIPP liner design to comply with ASTM F1216 standards through the application of the Finite Element Method (FEM).
Understanding ASTM F1216 and its Significance
ASTM F1216 is a standard that outlines the procedures for rehabilitating existing pipelines using the CIPP method. This standard is critical as it provides guidelines for the design, installation, and testing of CIPP liners, ensuring that rehabilitated pipelines meet specific safety and performance criteria. Compliance with ASTM F1216 is essential for any project involving CIPP lining, as it not only guarantees the structural integrity of the rehabilitated pipeline but also its longevity.
Little P.Eng. Engineering's Approach to CIPP Liner Design
Little P.Eng. Engineering has embraced the challenges of CIPP liner design by leveraging the Finite Element Method (FEM), a sophisticated computational technique that simulates how materials behave under various conditions. FEM allows engineers to model the complex interactions between the CIPP liner and the host pipe, taking into account factors such as material properties, external loads, and environmental conditions. By using FEM, Little P.Eng. Engineering can predict the performance of CIPP liners with high accuracy, ensuring that designs are not only compliant with ASTM F1216 but also optimized for durability and efficiency.
The Role of Finite Element Method in Ensuring Compliance and Optimization
The Finite Element Method plays a pivotal role in Little P.Eng. Engineering's design process by providing a detailed analysis of stress distribution, deformation, and potential failure points within the CIPP liner. This detailed analysis is crucial for two main reasons:
Compliance with ASTM F1216: FEM analysis helps ensure that the designed CIPP liner can withstand the intended service life under varying conditions, as stipulated by ASTM F1216. This includes assessing the liner's ability to handle internal pressures, ground movement, and other environmental factors without compromising its structural integrity.
Optimization of Design: Beyond compliance, FEM enables Little P.Eng. Engineering to optimize the thickness, material composition, and installation parameters of CIPP liners. This optimization not only reduces material costs but also minimizes the risk of over-engineering, ensuring that resources are used efficiently without sacrificing performance.
Case Studies and Success Stories

Conclusion
The innovative approach of Little P.Eng. Engineering to CIPP liner design, grounded in the rigorous application of the Finite Element Method and adherence to ASTM F1216 standards, represents a significant advancement in pipeline rehabilitation technology. This method not only ensures the structural integrity and longevity of CIPP liners but also exemplifies how engineering innovation can lead to more sustainable and cost-effective infrastructure solutions. As the demand for efficient and environmentally friendly rehabilitation methods grows, the work of Little P.Eng. Engineering in this field is set to become increasingly important, paving the way for future advancements in civil engineering practices.
Read More:
Innovating Pipeline Rehabilitation: Pipe CIPP Lining Engineering Design Services as per ASTM F1216
Pipeline Rehabilitation Engineering Design Services as per ASTM F1216 Using CIPP and PVC
Little P.Eng. Engineering For CIPP Liner Design As Per ASTM F1216 Using Finite Element Method
Revolutionizing Pipe Rehabilitation: Little P.Eng. Engineering's Mastery of CIPP Liner Design via Finite Element Method in Accordance with ASTM F1216
Tags:
Little P.Eng. Engineering
ASTM F1216
structural integrity
design optimization
engineering innovation
material properties
Finite Element Method
underground infrastructure
performance prediction
industry guidelines
CIPP liner design
material optimization
infrastructure longevity
safety criteria
environmental impact
maintenance cost reduction
pipeline rehabilitation
simulation techniques
performance criteria
durability assessment
compliance standards
computational modeling
non-invasive repair methods
failure point identification
sustainable solutions
installation parameters
stress distribution analysis
external loads
civil engineering practices
cost reduction
Engineering Services
•
Pipe Rehabilitation
Located in Calgary, Alberta; Vancouver, BC; Toronto, Ontario; Edmonton, Alberta; Houston Texas; Torrance, California; El Segundo, CA; Manhattan Beach, CA; Concord, CA; We offer our engineering consultancy services across Canada and United States. Meena Rezkallah.
#Little P.Eng. Engineering#ASTM F1216#structural integrity#design optimization#engineering innovation#material properties#Finite Element Method#underground infrastructure#performance prediction#industry guidelines#CIPP liner design#material optimization#infrastructure longevity#safety criteria#environmental impact#maintenance cost reduction#pipeline rehabilitation#simulation techniques#performance criteria#durability assessment#compliance standards#computational modeling#non-invasive repair methods#failure point identification#sustainable solutions#installation parameters#stress distribution analysis#external loads#civil engineering practices#cost reduction
0 notes
Note
Crimes anon: 2 questions. Who's Woongi? And wanna do fictional payback crimes to HYBE with me for disrespecting Monsta X?
HEY CRIMES ANONNN🫶 sooo cha woongki is an idol who I first met as a member of TOO (later re-debuted as TO1 after contract issues with their companies) but then was removed from TO1 along with other members minsu and jerome, the three of whom were the most feminine of the group and helped the group get popular by covering gg songs and generally being very queer friendly... and they were replaced with more masculine members ... definitely just a coincidence there... not at all femmephobia... but anyway woongki has always had a solo following because of his personality and how queer friendly he is (and his following increased after joining boysplanet) but he's struggled to re-debut a lot (has just entered his third survival show) and struggled to get signed to a company that actually has his best interest. But he is extremely popular for an idol who hasn't been able to debut so lots of us are waiting for it to finally happen so he can finally get some stability 🫶 and here's hybe staff calling him a slur that means femme in an official document. Like hybe need to die anyway but it's truly just so disrespectful to call an individual that as a way to sum up their character. They call him slurs for having a feminine personality but then are like hmm 🤔 he is a super popular entertainment personality we could take notes🤔 and wakeone kicking him out of the group for being femme even tho he's the most popular member and FOR A REASON. He's So entertaining he is So talented, he has been able to stay relevant and get gigs without a company, he organised his own fanmeets without a company and sold them out .. he's respected by established idols as an equal in the industry.... he's just So So capable and has just been fucked over by homophobic/femmephobic companies left right and centre. So yeah I'm rly not cool with hybe throwing a slur at him like he couldn't take all of their jobs fr
Also YES let's murder them to avenge monsta x !!!
#he was a child actor too btw like he's been in entertainment his whole life he knows how it works#woongki is super super queer friendly and has been from the get go hes answered questions on his sexuality rly respectfully even tho -#- he had every right in my opinion to tell them to fuck off#he's been politically active since a teenager he's talked openly about dealing with bullying in school sooo impressively like ...#I wanna cry everytime I think about all the stuff he's done coz he's just so wonderful#he helped his members use more inclusive language when talking about anything related to gender or the fans#he acted in a bl recently as a side character and spoke so well about it ....#he spoke out in favour of social distancing guidelines in his college gc and was not afraid to stand by it#I could go on and on he's truly one of the best people in the industry#I love him soooooosososoo much I respect and admire him so wholely#anyway fndjjdjd sorry I will never be normal about him but I hope u enjoyed learning#woongki#anons#crimes anon#asks
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Lie That Made Food Conglomerates Rich (often the same conglomerates that own tobaco companies) ...And Is Slowly Poisoning Us
youtube
We live in an age of unmitigated greed.
#youtube#processed foods#processed foods industry#big tobacco#health#health guidance#health guidelines
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Chef WK, lead charcuterie specialist in Alberta Canada
Table of contents
1. Control Program Requirements for Fermented Meat Products
2. Facility and Equipment Requirements
3. Starter Culture
4. Chemical Acidification
5. Water Activity Critical Limits
6. Time and Temperature for Fermented Products
7. Fermentation Done at a Constant Temperature
8. Examples of Degree-hours at constant room temperatures
9. Fermentation Done at Different Temperatures
10. Fermentation done at Different temperatures
11. What happens if fermentation fails to hit critical limit?
12. E. coli and Salmonella Control in Fermented Sausages
13. Options for E. coli validation
14. Option1; Heating
15. Option 2; pH, heating, holding, diameter
16. Safety and consistency
Control Program Requirements for Fermented Meat Products
The producer must have a program in place to assess the incoming product. This program should outline specifications for the incoming ingredients. This may include criteria including receiving temperature, farm/ supplier, lot code or packed on date, species/cut etc.
2. Facility and Equipment Requirements
Equipment used in the fermentation process must be included in the operator's prerequisite control programs. These must include the following elements:
Temperature in the fermentation, drying and smoking chambers must be uniform and controlled to prevent any fluctuation that could impact on the safety of the final product.
Fermentation, drying and smoking chambers must be equipped with a shatter resistant indicating thermometer, (or equivalent), with graduations of 1°C or less. If mercury thermometers are used, their mercury columns must be free from separations. All thermometers must be located such that they can be easily read.
Fermentation and smoking chambers must be equipped with a recording thermometer for determining degree-hours calculations in a reliable manner. Recording thermometers are also preferable in drying and aging rooms but, in these rooms, it may be sufficient to read and record the temperatures 2 times a day.
Drying and aging rooms must be equipped with humidity recorders in order to prevent uncontrolled fluctuations of the relative humidity. The only alternative to an automatic humidity recorder in these rooms would be for the company to manually monitor and record ambient humidity twice a day (morning and afternoon) every day with a properly calibrated portable humidity recorder.
For routine monitoring, accurate measurement electronic pH meters (± 0.05 units) should be employed. It is important that the manufacturer's instructions for use, maintenance and calibration of the instrument as well as recommended sample preparation and testing be followed.
When the aw of a product is a critical limit set out in the HACCP plan for a meat product, accurate measurement devices must be employed. It is important that the manufacturer's instructions for use, maintenance and calibration of the instrument be followed.
3. Starter Culture
The operator must use a CFIA approved starter culture. This includes Freeze-dried commercially available culture as well as back-slopping (use of previously successful fermented meat used to inoculate a new batch). When performing back-slopping, the operator must have a control program in place to prevent the transmission of pathogens from when using the inoculum from a previous batch to initiate the fermentation process of a new batch. These must include:
The storage temperature must be maintained at 4°C or less and a pH of 5.3 or less.
Samples for microbiological analysis must be taken to ensure that the process is in line with the specifications.
The frequency of sampling is to be adjusted according to compliance to specifications.
Any batch of inoculum which has a pH greater than 5.3 must be analysed to detect at least Staphylococcus aureus. Only upon satisfactory results will this inoculum be permitted for use in back slopping.
This can be an expensive and a time exhaustive process and is generally avoided due to food safety concerns. AHS does not allow back-slopping.
[Chef WK was in communication with the U of A to get his method, a starter mix, studied.]
4. Chemical Acidification
If product is chemically acidified by addition of citric acid, glucono-delta-lactone or another chemical agent approved for this purpose, controls must be in place and records kept to ensure that a pH of 5.3 or lower is achieved by the end of the fermentation process. These acids are encapsulated in different coatings that melt at specific temperatures, which then release the powdered acids into the meat batter and directly chemically acidulate the protein.
Summer sausage is a very common chemically acidified product. The flavor profile tends to be monotone and lacking depth.
5. Water Activity Critical Limits
The aw may be reduced by adding solutes (salt, sugar) or removing moisture.
Approximate minimum levels of aw (if considered alone) for the growth of:
molds: 0.61 to 0.96
yeasts: 0.62 to 0.90
bacteria: 0.86 to 0.97
Clostridium botulinum: 0.95 to 0.97
Clostridium perfringens: 0.95
Enterobacteriaceae: 0.94 to 0.97
Pseudomonas fluorescens: 0.97
Salmonella: 0.92 - 0.95
Staphylococcus aureus: 0.86
parasites: Trichinella spiralis will survive at an aw of 0.93 but is destroyed at an aw of 0.85 or less.
The above levels are based on the absence of other inhibitory effects such as nitrite, competitive growth, sub-optimum temperatures, etc., which may be present in meat products. In normal conditions, Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins are not produced below aw 0.86, although in vacuum packed products this is unlikely below aw 0.89.
6. Time and Temperature for Fermented Products
Certain strains of the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus are capable of producing a highly heat stable toxin that causes illness in humans. Above a critical temperature of 15.6°C, Staphylococcus aureus multiplication and toxin production can take place. Once a pH of 5.3 is reached, Staphylococcus aureus multiplication and toxin production are stopped.
Degree-hours are the product of time as measured in hours at a particular temperature multiplied by the "degrees" measured in excess of 15.6°C (the critical temperature for growth of Staphylococcus aureus). Degree-hours are calculated for each temperature used in the process. The limitation of the number of degree-hours depends upon the highest temperature in the fermentation process prior to the time that a pH of 5.3 or less is attained.
The operator is encouraged to measure temperatures at the surface of the product. Where this is not possible, the operator should utilize fermentation room temperatures. The degree hour calculations are based on fermentation room temperatures. Temperature and humidity should be uniform throughout the fermentation room.
A process can be judged as acceptable provided the product consistently reaches a pH of 5.3 using:
fewer than 665 degree-hours when the highest fermentation temperature is less than 33°C;
fewer than 555 degree-hours when the highest fermentation temperature is between 33° and 37°C; and
fewer than 500 degree-hours when the highest fermentation temperature is greater than 37°C.
This means that as the temperature increases, the amount of time that you have available to reach 5.3 or under is shorter. The warmer the temperature, the sharper the log growth phase of bacteria, which equates to more overshoot in lactic acid production, faster.
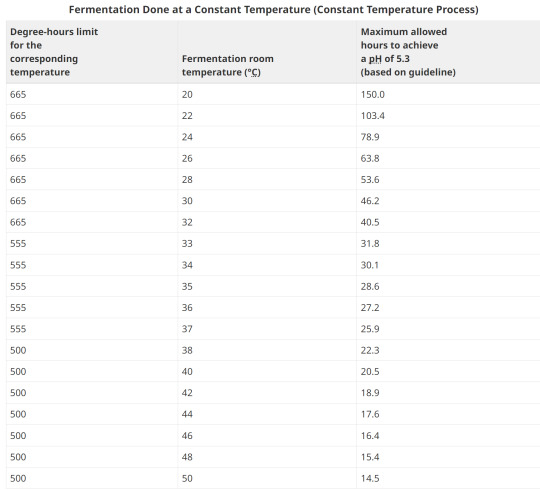
8. Examples of Degree-hours at constant room temperatures
Example 1:
Fermentation room temperature is a constant 26°C. It takes 55 hours for the pH to reach 5.3.
Degrees above 15.6°C: 26°C - 15.6°C = 10.4°C Hours to reach pH of 5.3: 55 Degree-hours calculation: (10.4°C) x (55) = 572 degree-hours
The corresponding degree-hours limit (less than 33°C) is 665 degree-hours.
Conclusion: Example 1 meets the guideline because its degree-hours are less than the limit.
Example 2:
Fermentation room temperature is a constant 35°C. It takes 40 hours for the pH to reach 5.3.
Degrees above 15.6°C: 35°C - 15.6°C = 19.4°C Hours to reach pH of 5.3: 40 Degree-hours calculation: (19.4°C) x (40) = 776 degree-hours
The corresponding degree-hours limit (between 33 and 37°C) is 555 degree-hours.
Conclusion: Example 2 does not meet the guideline because its degree-hours exceed the limit
9. Fermentation Done at Different Temperatures
When the fermentation takes place at various temperatures, each temperature step in the process is analyzed for the number of degree-hours it contributes. The degree-hours limit for the entire fermentation process is based on the highest temperature reached during fermentation.
Example 1:
It takes 35 hours for product to reach a pH of 5.3 or less. Fermentation room temperature is 24°C for the first 10 hours, 30°C for second 10 hours and 35°C for the final 15 hours.
Step 1
Degrees above 15.6°C: 24°C - 15.6°C = 8.4°C Hours to reach pH of 5.3: 10 Degree-hours calculation: (8.4°C) x (10) = 84 degree-hours
Step 2
Degrees above 15.6°C: 30°C - 15.6°C = 14.4°C Hours to reach pH of 5.3: 10 Degree-hours calculation: (14.4°C) x (10) = 144 degree-hours
Step 3
Degrees above 15.6°C: 35°C - 15.6°C = 19.4°C Hours to reach pH of 5.3: 15 Degree-hours calculation: (19.4°C) x (15) = 291 degree-hours
Degree-hours calculation for the entire fermentation process = 84 + 144 + 291 = 519
The highest temperature reached = 35°C
The corresponding degree-hour limit = 555 (between 33°C and 37°C)Conclusion: Example 1 meets the guideline because its degree-hours are less than the limit.
10. Fermentation done at Different temperatures
Example 2:
It takes 38 hours for product to reach a pH of 5.3 or less. Fermentation room temperature is 24°C for the first 10 hours, 30°C for the second 10 hours and 37°C for the final 18 hours.
Step 1
Degrees above 15.6°C: 24°C - 15.6°C = 8.4°C Hours to reach pH of 5.3: 10 Degree-hours calculation: (8.4°C) x (10) = 84 degree-hours
Step 2
Degrees above 15.6°C: 30°C - 15.6°C = 14.4°C Hours to reach pH of 5.3: 10 Degree-hours calculation: (14.4°C) x (10) = 144 degree-hours
Step 3
Degrees above 15.6°C: 37°C - 15.6°C = 21.4°C Hours to reach pH of 5.3: 18 Degree-hours calculation: (21.4°C) x (18) = 385.2 degree-hours
Degree-hours calculation for the entire fermentation process = 84 + 144 + 385.2 = 613.2
The highest temperature reached = 37°C
The corresponding degree-hour limit = 555 (between 33°C and 37°C)
Conclusion: Example 2 does not meet the guidelines because its degree-hours exceed the limit.
11. What happens if fermentation fails to hit critical limit?
What happens if the batch takes longer than degree-hours allows? For restaurant level production, it's always safer to discard the product. The toxin that Staph. Aureus produces is heat stable and cannot be cooked to deactivate. In large facilities that produce substantial batches, the operator must notify the CFIA of each case where degree-hours limits have been exceeded. Such lots must be held and samples of product submitted for microbiological laboratory examination after the drying period has been completed. Analyses should be done for Staphylococcus aureus and its enterotoxin, and for principal pathogens, such as E. coli O157:H7, Salmonella, and Clostridium botulinum and Listeria monocytogenes.
If the bacteriological evaluation proves that there are fewer than 104 Staphylococcus aureus per gram and that no enterotoxin or other pathogens are detected, then the product may be sold provided that it is labelled as requiring refrigeration.
In the case of a Staphylococcus aureus level higher than 104 per gram with no enterotoxin present the product may be used in the production of a cooked product but only if the heating process achieves full lethality applicable to the meat product.
In the case where Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin is detected in the product the product must be destroyed.
12. E. coli and Salmonella Control in Fermented Sausages
Business' that manufacture fermented sausages are required to control for verotoxinogenic E. coli including E. coli O157:H7 and Salmonella when they make this type of product. This includes:
establishments which use beef as an ingredient in a dry or semi-dry fermented meat sausage;
establishments which store or handle uncooked beef on site;
Establishments which do not use beef and do not obtain meat ingredients from establishments which handle beef are not currently required to use one of the five options for the control of E. coli O157:H7 in dry/semi-dry fermented sausages.
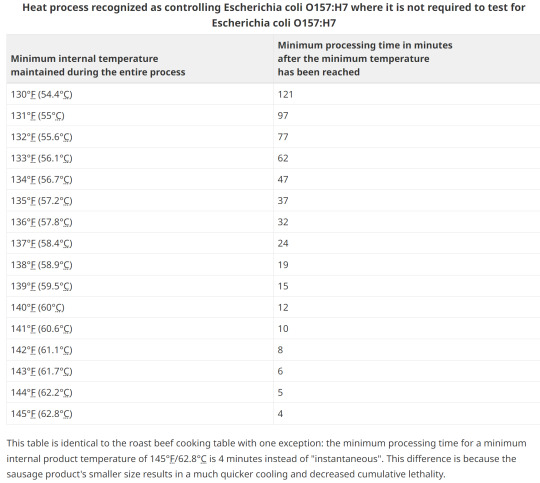
Any processed RTE product containing beef or processed in a facility that also processed beef, must be subjected to a heat treatment step to control E. coli O157:H7. Heating to an internal temperature of 71°C for 15 seconds or other treatment to achieve a 5D reduction is necessary. This is a CFIA requirement and is not negotiable.
Uncooked air dried products produced as RTE, must meet shelf stable requirements as detailed for Fermented-Dry products.
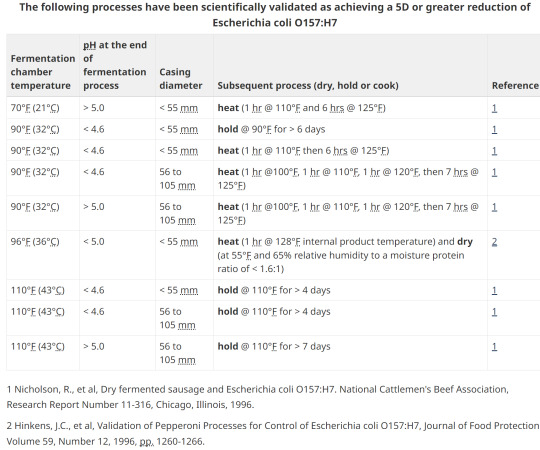
13. Options for E. coli validation
Without lab testing, the two main methods of validation are with heat treating by either low temp and a long duration, or various hotter processing temperatures for a shorter timeframe.
A challenge study to validate a process can take 1 year and over $100,000!
14. Option1; Heating
15. Option 2; pH, heating, holding, diameter
16. Safety and consistency
The aw and pH values are critical in the control of pathogens as well as to ensure shelf-stability in all semi-dry and dry fermented meat products. Each batch must be tested for aw and/or pH in order to verify that the critical limits are met.
Although aw measurement is mandatory only for shelf stable products, it is strongly recommended that the producer determine the aw values achieved for each product type they manufacture and for each product. Once this has been established, frequent regular checks should be made to ensure consistency. In the U.S., they rely on moisture to protein ratio and have set targets. This lab-tested value is a direct correlation of the % water to % meat protein and not aw. This gives more consistency to common names. For example, to legally call a product "jerky" it must have a MPR of 0.75:1 or lower. Remember your ABCs:
Always be compliant.
-AND-
Documentation or it didn't happen.
(tags)
Charcuterie,Fermented Meat,Food Safety,Starter Culture,Chemical Acidification,Water Activity,Fermentation Process,Degree-Hours Method,Foodborne Pathogens,Meat Processing Guidelines,Chef WK Alberta Canada,Food Industry Standards,pH Critical Limits,Thermal Processing,Food Preservation,Food Microbiology,Sausage Fermentation,Charcuterie Expertise,Fermented Meats ,Food Safety Standards,Food Processing Guidelines,Starter Cultures,Chemical Acidification,Water Activity (a_w),Critical Limits,Degree-Hours Method,Foodborne Pathogens,Meat Processing Equipment,Processing Facility Requirements,Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP),Food Preservation Techniques,Temperature Control,Pathogen Reduction,Food Industry Compliance,Documentation Practices,Heat Treatment,pH Control,Food Stability,Consistency in Production,Microbial Testing,Real-time Monitoring,Process Validation,Regulatory Requirements,Verotoxigenic E. coli,Lethality Standards,Product Labelling,Spoilage Prevention,Enterotoxin Detection,Shelf-Stable Products,Moisture to Protein Ratio (MPR)
#Charcuterie#Fermented Meat#Food Safety#Starter Culture#Chemical Acidification#Water Activity#Fermentation Process#Degree-Hours#Meat Processing Guidelines#Thermal Processing#Food Preservation#Food Microbiology#Sausage Fermentation#Starter Cultures#Critical Limits#Meat Processing#Food Preservation Techniques#Temperature Control#Pathogen Reduction#Food Industry#Heat Treatment#pH Control#Food Stability#Microbial Testing#Real-time Monitoring#Process Validation#Spoilage Prevention#Enterotoxin Detection#Shelf-Stable Products#Moisture to Protein Ratio (MPR)
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Exploring the Growth and Excellence of the Pharmaceutical Industry in India
Exploring the Growth and Excellence of the Pharmaceutical Industry in India
The pharmaceutical industry in India has emerged as a key global player, recognized for its cost-effective production, advanced pharmaceutical development and technology, and strong presence in international markets. With a growing focus on healthcare R&D, innovation in drug research and development, and robust pharmaceutical manufacturing, India continues to be a trusted supplier of pharmaceutical products and medicines across the globe.
The Rise of India's Pharmaceutical Sector
India holds a prominent position in the global pharmaceutical landscape, being among the largest pharmaceutical companies contributors to generic drug supply and vaccine production. The Indian government’s support, combined with private sector innovation, has made the country a leader in pharmaceutical manufacturing companies, with exports reaching over 200 countries.
This growth is driven by the country's commitment to high standards in quality control in pharmaceuticals, investment in pharma healthcare, and a vision to lead in global healthcare solutions.
Pharmaceutical Manufacturing and Innovation
India’s pharma manufacturing companies operate under stringent international regulations and practices, including GLP (Good Laboratory Practices), WHO-GMP certifications, and advanced automation systems. These companies are constantly innovating through strong R&D departments in pharmaceutical industry, focusing on developing new therapies, enhancing drug delivery methods, and ensuring quality throughout the supply chain.
Such innovation has fueled the creation of effective, accessible pharmaceutical drugs that have transformed public health outcomes both in India and abroad.

Key Attributes of Leading Pharma Companies
The top pharmaceutical manufacturing companies in India are recognized not just for their production volumes, but for their dedication to quality assurance, ethical standards, and technological advancement. Many of them rank among the top pharma companies worldwide thanks to their continuous delivery of new pharma products, global reach, and patient-focused approaches.
In this elite group, Zuventus Healthcare holds a distinguished place, known for its excellence in innovation, affordability, and trust.
About Zuventus Healthcare
Zuventus Healthcare Ltd. is a reputed name in the Indian pharmaceutical landscape. Based in Mumbai, Zuventus has steadily climbed the ranks to be recognized as a top pharmaceutical company in Mumbai and is counted among the top 10 pharmaceutical companies in India.
With a diverse portfolio of Zuventus healthcare products, the company serves multiple therapeutic areas, delivering effective and high-quality treatments. Its flagship brands, including Zuventus Gromaxx and Zuventus Odenea, highlight the company’s capability in creating targeted, result-driven medications that meet real-world healthcare demands.
Zuventus' Commitment to Quality and Ethics
What sets Zuventus Healthcare apart from other pharmaceutical companies in India is its unwavering focus on ethical practices, innovation, and operational excellence. The company follows robust quality management systems, with a strong emphasis on quality control methods to ensure that every product released meets stringent safety and efficacy benchmarks.
Its facilities are equipped to meet global manufacturing standards, making Zuventus a trusted name not only within India but also in the international health care market.
Driving Healthcare Through Vision and Values
Zuventus believes that a strong foundation lies in strong values. The company’s core corporate values—integrity, teamwork, innovation, and accountability—drive every aspect of its operations. Its organization's vision is to contribute meaningfully to healthcare by being a partner in wellness, committed to improving lives through quality and affordable medication.
With a clear teamwork vision, Zuventus cultivates a collaborative culture that encourages innovation, learning, and shared responsibility—making it not only a leading pharmaceutical company but also a great place to work and grow.
The Future of Indian Pharma: Opportunities and Challenges
The Indian pharmaceutical industry is poised for even greater expansion, driven by increasing global demand, a maturing domestic healthcare system, and rapid adoption of digital technologies. Challenges such as regulatory complexities and pricing pressures remain, but with continued investments in research and development in the pharmaceutical industry, the outlook remains highly optimistic.
Companies like Zuventus, with their blend of innovation, ethical focus, and manufacturing strength, are well-positioned to lead this next phase of growth. Their continuous contribution to drug research and development, focus on pharma manufacturing excellence, and strong market presence reflect the future of Indian pharma.
Final Thoughts
India’s pharma industry is a shining example of how science, innovation, and purpose can come together to serve humanity. From groundbreaking Zuventus medicines to world-class pharmaceutical manufacturers in India, the nation stands tall on the global healthcare stage.
Zuventus Healthcare, with its strong legacy, state-of-the-art infrastructure, and a values-driven mission, embodies the promise and potential of the Indian pharmaceutical sector. As the company continues to grow, launch new pharma products, and expand its impact, it remains a beacon of trust, quality, and healthcare advancement in both local and global markets.
#quality standards#top pharmaceutical manufacturing companies in india#quality control and quality assurance#quality control methods#quality management system#glp good lab practice#quality control in pharmaceuticals#pharmaceutical quality assurance#good manufacturing practices#pharmaceutical compliance#GMP certification#drug quality testing#pharmaceutical manufacturing process#regulatory standards in pharmaceuticals#pharmaceutical testing labs#pharmaceutical industry standards#medicine manufacturing companies in india#pharmaceutical product quality#pharma regulatory compliance#pharma quality guidelines#pharmaceutical quality control techniques#research and development#R&D#R&D pharma#pharma industry
0 notes
Text
Maintaining Conductive Flooring: Best Practices for Cleaning and Conductivity
Introduction: Maintaining the conductive properties of your flooring is essential to ensure safety and compliance with industry standards. Over time, surface contaminants can accumulate, potentially compromising the floor’s conductivity. This post explores effective cleaning practices to preserve your floor’s conductive performance. Understanding Conductive Flooring: Conductive flooring is…
#anti-static floor care#anti-static floor cleaning procedures#anti-static floor maintenance guidelines#best practices for ESD floor cleaning#choosing the right cleaner for anti-static floors#cleanroom cleaning protocols#cleanroom floor maintenance#commercial floor maintenance#conductive floor cleaning best practices#conductive flooring maintenance#electrostatic discharge floor care#ESD floor cleaning#ESD floor cleaning agents#ESD flooring maintenance tips#factory floor cleaning solutions#floor conductivity testing#how to maintain conductive flooring in cleanrooms#industrial floor cleaning services#industrial floor cleaning solutions#preventing conductivity loss in industrial flooring#static control flooring maintenance#static dissipative flooring upkeep#step-by-step guide to conductive floor maintenance#warehouse floor maintenance
0 notes
Text
Macadamia Farmers Beware: Kenya Steps Up Crackdown on Illegal Macadamia Exports, Traders Face Arrest
The Agriculture and Food Authority (AFA) warns macadamia industry players against harvesting, trading, or processing immature nuts, threatening legal action, license revocation, and prosecution to protect Kenya’s market integrity. Kenya’s macadamia industry faces strict regulations as AFA cracks down on illegal harvesting and smuggling. Violators risk hefty penalties, including revoked licenses…
#AFA regulations#Agriculture and Food Authority#immature macadamia harvesting#Kenya macadamia industry#Kenya nut industry#macadamia farming in kenya#macadamia farming regulations#macadamia licensing requirements#macadamia market integrity#macadamia nut export ban#macadamia processing guidelines#macadamia quality standards#macadamia smuggling crackdown#macadamia trading laws#value addition in macadamia
0 notes
Text
The Importance of Cosmetic Product Notifications in Canada: A Guide to Compliance
In Canada, cosmetic products must adhere to strict regulatory standards to guarantee consumer safety and product quality. Health Canada requires the submission of the Cosmetic Notification Form (CNF) for all cosmetic items prior to market entry. This guide highlights the significance of cosmetic product notifications and offers a detailed step-by-step approach to help brands remain compliant. The Importance of Cosmetic Notifications The CNF is Health Canada’s mechanism for ensuring the safety of cosmetic products and confirming that ingredients do not pose health risks. Through cosmetic notifications, Health Canada can monitor products and their ingredients, identify potential hazards, and conduct market surveillance as needed. Compliance with notification requirements is vital for brands to safeguard their reputation, avert legal issues, and sustain consumer trust. Essential Regulations for Cosmetic Compliance in Canada Canada’s Food and Drugs Act: Cosmetics are governed by this act, specifically through the Cosmetic Regulations it encompasses. It broadly defines cosmetics, including makeup, skincare, haircare, and dental hygiene products. Prohibited and Restricted Ingredients: Health Canada maintains a detailed list of substances that are prohibited or restricted in the Cosmetic Ingredient Hotlist. Manufacturers must ensure products exclude banned substances and comply with concentration limits for restricted ingredients. Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP): While not mandatory, following GMP standards is strongly advised to ensure product safety and quality. Compliance with GMP reflects a dedication to quality control, which benefits companies during Health Canada’s monitoring processes. Steps for Submitting a Cosmetic Notification Form (CNF) Fill Out the Cosmetic Notification Form (CNF): The CNF requires crucial details such as the product’s brand name, intended use, ingredient list, and whether it is a rinse-off or leave-on product. For each ingredient, the specific concentration and range of concentration must be indicated, enabling Health Canada to assess product safety effectively. Submission Timeline: The CNF must be submitted to Health Canada within 10 days of launching a product in Canada. This is applicable to all new launches, reformulations, or rebranded items. Electronic Submission: Health Canada mandates electronic submission of the CNF through the Cosmetics Notification System. Companies receive a confirmation upon successful submission, which serves as proof of regulatory compliance. Post-Submission Compliance and Monitoring After submitting the CNF, companies must uphold compliance with Health Canada’s standards and be ready for post-market evaluations. Health Canada performs inspections and may request documents such as safety data, product labels, or formulation re-evaluations to confirm compliance. Companies need to report any adverse effects linked to their products promptly and maintain records of complaints, which could be audited during inspections. Conclusion Submitting a Cosmetic Notification Form goes beyond a regulatory requirement; it signifies a commitment to consumer safety and brand integrity in Canada. By adhering to Health Canada’s regulations and fostering transparency, brands can confidently position themselves in Canada’s dynamic cosmetics market. Reach out to our regulatory specialists at Freyr for guidance on CNF submissions and regulatory assistance for a smooth entry into the Canadian
#Cosmetic Compliance#Health Canada Regulations#Cosmetic Notification Form (CNF)#Health Canada Cosmetic Guidelines#Cosmetics Industry Regulations#Cosmetic Ingredients Safety#Canadian Market Entry#Cosmetics Market Surveillance#Cosmetic Labeling Regulations
0 notes
Text
how tf did I not realise mackerel was no longer sustainably supplies to the UK...
j will now pine away like that pregnant woman with the lettuce in Rapunzel and I'll have to fucking sell my sister to some mackerel witch or some shit I actually can't do this....
#ive literally been thinking sbout eating mackerel for weeks its so so bad#i may actually die#yes i know this is a horrifically shallow problem to have but also really fucked up that the fishing industry refuses to adhere to#guidelines maintaining fish populations
1 note
·
View note
Text
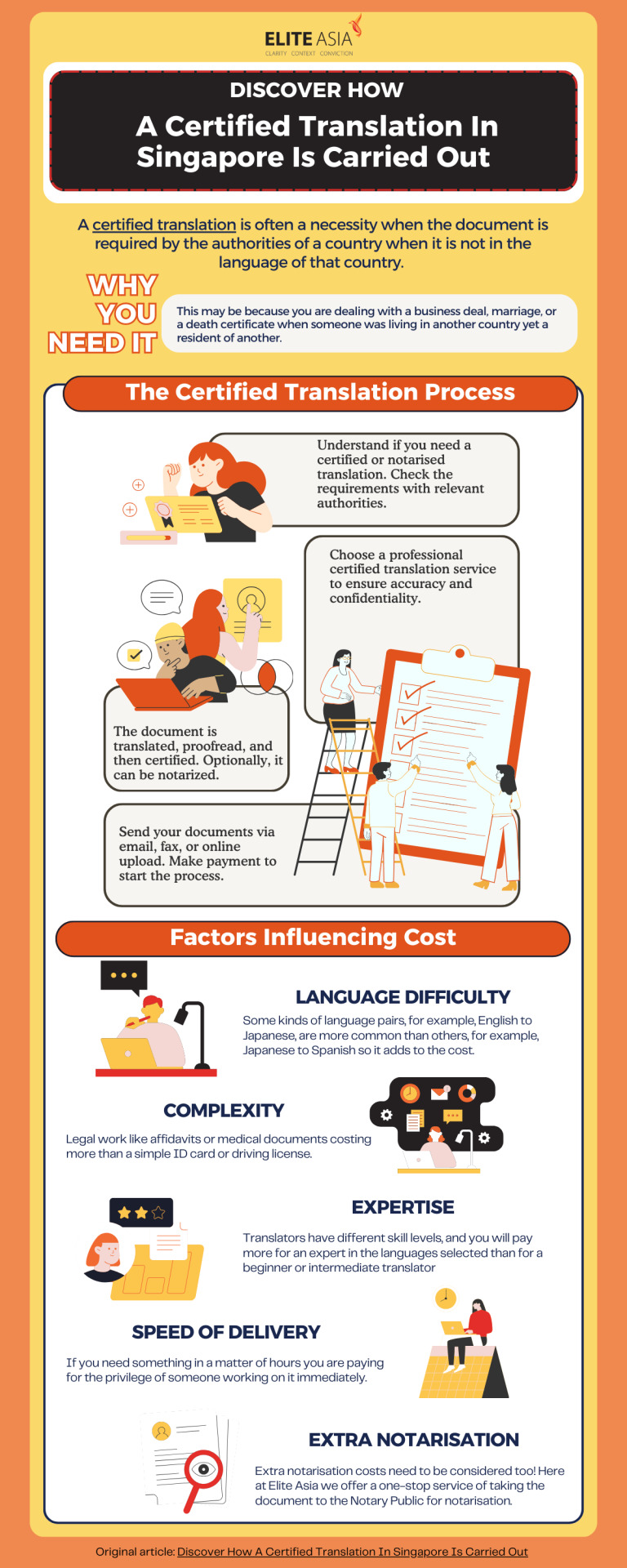
Ever wondered how a certified translation in Singapore works? This infographic breaks down the entire process—from understanding when you need a certified translation to the factors that influence its cost. Don't miss out on these key insights that can save you time and money!
#infographic#design#infographicdesign#vectordesign#infographicmarketing#Certified Translation#Singapore Translation Services#Document Certification#Translation Process#Legal Translation#Business Translation#Translation Costs#Notarisation#Translation Expertise#Language Translation#International Documents#Certified Translators#Translation Accuracy#Translation Guidelines#Translation Industry#Cross-border Documentation#Translation Requirements#Multilingual Translation#Professional Translation#Translation Tips#Translation Agencies#Official Translation#Translation Steps#Compliance Translation#Translation Certification
0 notes
Text
its beyond embarrassing how some of you act like this is love island lotto and youre putting in your bets to get picked by the guy whos likely going to spend his life behind bars. and for what. literally for what

Finally mailed my letter to Luigi today. As per my friend’s suggestion, I spritzed a little of my favorite perfume on it. :P
#your stamp will be ripped off and your letter will be rejected if it smells like perfume. you cant even respect him enough to read basic#guidelines on how to send prison snailmail yet you want to be romantically linked to him. rancid putrid awful offensive etc etc etc etc#cute font. were you hoping he picks yours out of the thousands he gets per week. go donate to his legal fund instead#get a grip!#britney spears criminal and its industrial consequences
113 notes
·
View notes
Text
Category of software hardware as per gamp guideline their validation.
Discover the essential insights into software and hardware categories according to GAMP (Good Automated Manufacturing Practice) guidelines, focusing on GAMP 5 in the pharmaceutical industry. Understand the critical validation processes to ensure compliance, enhance operational efficiency, and maintain quality control in pharmaceutical manufacturing. Explore comprehensive strategies for validating automated systems, ensuring they meet regulatory standards and deliver consistent, reliable results.
0 notes
Text
Ensuring Pharmaceutical Excellence Through Robust Quality Standards
Ensuring Pharmaceutical Excellence Through Robust Quality Standards
In the pharmaceutical industry, quality standards are not just benchmarks — they are lifelines. Ensuring the safety, efficacy, and consistency of medicinal products is critical for protecting public health and upholding trust in healthcare systems. From the development of new drugs to their final packaging and distribution, pharmaceutical companies must adhere to stringent processes governed by regulatory bodies across the globe.
With the growing complexity of medicines and increasing regulatory scrutiny, the implementation of effective quality control and quality assurance systems has become more crucial than ever. Pharmaceutical manufacturers are now investing heavily in advanced technologies, global certifications, and comprehensive training to ensure their products meet both national and international standards.
This article explores the significance of quality control in pharmaceuticals, the core principles that drive compliance, and how one of the top pharmaceutical manufacturing companies in India, Zuventus Healthcare Ltd., exemplifies these standards through their commitment to excellence.
The Role of Quality Standards in the Pharmaceutical Industry
In any healthcare setup, patient safety is paramount. This is why pharmaceutical companies must adhere to defined quality standards to minimize variability, ensure batch-to-batch consistency, and eliminate risks associated with substandard medications.
These standards are often guided by international frameworks such as:
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP)
Good Laboratory Practices (GLP)
ISO and WHO certification requirements
Such guidelines cover every aspect of production, including the sourcing of raw materials, equipment validation, packaging, labelling, and even logistics. Ensuring full compliance guarantees that medications are safe, effective, and free from contamination.
Understanding Quality Control and Quality Assurance
While both quality control and quality assurance play vital roles, they serve distinct purposes within pharmaceutical operations:
Quality Control (QC) focuses on the quality control methods used during and after the manufacturing process. This includes testing raw materials, in-process samples, and finished products using scientific tools and techniques to ensure they meet predetermined specifications.
Quality Assurance (QA) is a broader concept. It includes establishing and maintaining a quality management system that oversees all procedures, documentation, and systems to prevent errors and ensure continuous improvement.
A successful pharmaceutical company integrates both functions seamlessly, ensuring every product released to the market meets the highest standards.

The Importance of GLP (Good Lab Practice)
GLP (Good Lab Practice) is another critical component of pharmaceutical quality assurance. These are a set of principles intended to assure the quality and integrity of non-clinical laboratory studies. GLP ensures that studies conducted are scientifically sound, reproducible, and acceptable to regulatory authorities.
By adhering to GLP, pharmaceutical companies can maintain confidence in their testing results, supporting product safety and efficacy claims with validated data.
Common Quality Control Methods in Pharmaceuticals
The most common quality control methods used in the pharmaceutical industry include:
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
Gas Chromatography (GC)
Spectrophotometry (UV/IR)
Dissolution and Disintegration Testing
Stability Testing
These methods are vital for evaluating critical parameters such as purity, potency, dissolution, and shelf life, helping ensure consistent therapeutic outcomes.
How Zuventus Healthcare Embodies Pharmaceutical Quality
Among the many companies setting the bar in the pharmaceutical space, Zuventus Healthcare Ltd. stands out as one of the top pharmaceutical manufacturing companies in India, thanks to its unwavering commitment to quality.
Zuventus operates with a deep-rooted belief in the power of trust and transparency. Its operations are built on a world-class quality management system that governs every stage — from product development to distribution. Every unit of medicine manufactured undergoes rigorous testing and review, in line with international regulatory requirements.
Infrastructure and Compliance
Zuventus’s manufacturing facilities are WHO-GMP certified and comply with other leading quality standards, ensuring their products are globally accepted. The infrastructure supports high-volume production without compromising safety, thanks to integrated automation, controlled environments, and validated systems.
Quality Control and Assurance Practices
The company follows a structured quality control and quality assurance framework. Advanced labs equipped with HPLC, GC, UV spectrophotometers, and other validated instruments ensure robust quality control methods are consistently applied.
Meanwhile, the QA team manages documentation, SOP implementation, deviation tracking, and audits, aligning with best practices in quality control in pharmaceuticals.
Emphasis on GLP and R&D
Zuventus also ensures that GLP (Good Lab Practice) principles are followed rigorously in their research and development efforts. Their R&D division not only innovates new drug formulations but also ensures that lab data supporting these innovations are scientifically valid and reproducible.
Training and Continuous Improvement
An organization’s commitment to quality is only as strong as its people. Zuventus invests in continuous training and development programs to ensure employees stay updated on evolving regulations, technological advancements, and quality expectations.
Regular internal and external audits, CAPA systems, and real-time monitoring drive continuous quality enhancement and compliance.
Final Thoughts
As healthcare needs grow and evolve, so does the responsibility of pharmaceutical companies to maintain the highest quality standards. The integration of quality control and quality assurance, the application of effective quality control methods, and adherence to global best practices like GLP (Good Lab Practice) and GMP are non-negotiable elements for delivering safe and effective medications.
Companies like Zuventus Healthcare demonstrate how a focused approach to quality can lead not only to regulatory compliance but also to consumer trust, product excellence, and long-term success.
In a world where pharmaceutical integrity can mean the difference between health and harm, adopting a comprehensive, forward-thinking quality management system isn’t just an option — it’s a responsibility. And those who lead the way, like Zuventus, continue to set new standards for the industry.
#quality standards#top pharmaceutical manufacturing companies in india#quality control and quality assurance#quality control methods#quality management system#glp good lab practice#quality control in pharmaceuticals#pharmaceutical quality assurance#good manufacturing practices#pharmaceutical compliance#GMP certification#drug quality testing#pharmaceutical manufacturing process#regulatory standards in pharmaceuticals#pharmaceutical testing labs#pharmaceutical industry standards#medicine manufacturing companies in india#pharmaceutical product quality#pharma regulatory compliance#pharma quality guidelines#pharmaceutical quality control techniques#pharma industry#pharma company#zuventus healthcare#pharma companies in india
0 notes
Text
The book is not about environmental control – about detailed technologies for preventing or eliminating pollution, including important initiatives in 'green chemistry',¹ or about standards and laws that set guidelines and limits on levels of contaminants.
¹ Green chemistry is an important branch of chemistry and engineering that considers design of industrial chemical processes in the context of their environmental impacts. As such, it includes subjects like the use of benign materials in production, minimizing energy consumption, finding uses for by-products, and integrating processes, often in a cyclical manner. The goal of green chemistry is to carry out industrial activities in a way that reduces, even eliminates, adverse impacts of production on the environment.
"Environmental Chemistry: A Global Perspective", 4e - Gary W. VanLoon & Stephen J. Duffy
#book quotes#environmental chemistry#nonfiction#textbook#environmental control#technology#prevention#elimination#pollution#green chemistry#standards#laws#guidelines#contamination#contaminant#chemistry#engineering#design#industrial chemistry#environmental impact#energy consumption#production#byproducts#integration#cyclical process
0 notes
Text
#Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP)#GMP guidelines#cosmetic industry#cosmetic businesses in Philippines#Food and Drug Administration (FDA)#GMP principles
0 notes
Text
Navigating The MSME Loan Government Scheme: A Comprehensive Guide
Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) play a crucial role in the economic growth and development of countries around the world. In recognition of their importance, governments have introduced various schemes to support these enterprises, including the MSME loan government scheme. This comprehensive guide aims to help business owners understand the intricacies of this scheme, including eligibility criteria, application processes, and available subsidies.
Understanding the MSME Loan Government Scheme
The MSME loan government scheme is designed to provide financial support to small and medium enterprises. This support comes in various forms, including loans, grants, and subsidies for MSMEs. These initiatives help businesses overcome financial hurdles, expand operations, and achieve sustainable growth.
Key components of the MSME loan government scheme
1. MSME business loan eligibility
To qualify for an MSME loan, businesses must meet specific criteria. These include the size of the business, annual turnover, and the nature of the enterprise. Understanding the MSME business loan eligibility criteria is essential for applicants to ensure their application stands a good chance of approval. Typically, businesses must be registered under the MSME category and adhere to the defined limits for investment in plant and machinery or equipment.
2. Unsecured business loan for MSME
One of the significant advantages of the MSME loan government scheme is the provision for unsecured business loans. Unlike traditional loans that require collateral, unsecured business loans for MSMEs provide access to capital without the need to pledge assets. This is particularly beneficial for small businesses that may not have significant assets to offer as collateral.
3. MSME subsidies and grants
The government offers various subsidies and grants to MSMEs to reduce the financial burden and encourage business growth. These MSME subsidies can cover aspects such as technology upgrades, quality improvement, and market development. Applying for an MSME grant can provide businesses with the necessary funds to innovate and compete in the market.
4. Govt scheme for small scale industry
There are numerous government schemes tailored specifically for small scale industries. These schemes provide a mix of financial support, training, and advisory services to help small businesses thrive. By taking advantage of a govt scheme for small scale industry, business owners can access resources that might otherwise be out of reach.
5. MSME loan process
The MSME loan process involves several steps, from application to approval. Business owners need to prepare detailed documentation, including business plans, financial statements, and proof of business registration. Understanding the MSME loan process helps ensure that applications are complete and submitted correctly, increasing the likelihood of approval.
6. MSME guidelines for payment
MSME guidelines for payment are designed to ensure timely and fair transactions within the sector. These guidelines protect small businesses from delayed payments and ensure they have a steady cash flow to support operations. Adhering to these guidelines is crucial for maintaining financial health and building trust with partners and suppliers.
How to apply for an MSME loan government scheme
1. Prepare necessary documentation: Gather all required documents, such as business registration certificates, financial statements, and business plans. This preparation is essential for a smooth application process.
2. Choose the right scheme: Identify the most suitable MSME loan government scheme based on your business needs. Whether it's an unsecured business loan for MSME or a specific grant, choosing the right scheme can significantly impact your business's success.
3. Submit the application: Fill out the application form accurately and submit it along with the required documents. Ensure that all information is correct and complete to avoid delays.
4. Follow up: After submission, regularly follow up on the application status. This proactive approach can help address any issues promptly and keep the process moving.
Benefits of the MSME loan government scheme
1. Financial support: Access to necessary funds without the need for significant collateral, thanks to unsecured business loans for MSMEs.
2. Growth opportunities: Subsidies for MSMEs and grants enable businesses to invest in growth opportunities, such as technology upgrades and market expansion.
3. Enhanced competitiveness: Government schemes help small businesses improve their products and services, making them more competitive in the market.
4. Improved cash flow: MSME guidelines for payment ensure timely transactions, helping businesses maintain a healthy cash flow.
Conclusion
Navigating the MSME loan government scheme requires a thorough understanding of the eligibility criteria, application process, and available benefits. One noteworthy example is Klub, a platform that focuses on revenue-based financing, providing startups with growth capital without requiring equity.By leveraging these schemes, small and medium enterprises can access essential financial support, drive growth, and contribute significantly to the economy. Whether seeking an unsecured business loan for MSME or applying for an MSME grant, these government initiatives provide invaluable resources for business success.
#msme guidelines for payment#msme business loan eligibility#govt scheme for small scale industry#msme subsidies#subsidies for msme#msme loan process
0 notes