#if russia was allowed into 2022s contest
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
the fact that the ebu is taking more time than usual to release the participants list for eurovision this year gives me hope they're at least reconsidering allowing israel (and maybe azerbaijan, for that matter) to participate
#tho since they had to have 10 whole broadcasters publicly threaten to withdraw#if russia was allowed into 2022s contest#it unfortunately isnt super likely#unless the broadcasters are doing it behind closed doors for some reason#either way hopefully they dont platform genocidal governments#but time will tell#eurovision#eurovision 2024
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
I'm gonna put it as simply and blatantly as possible.

Russia in 2022 attacked another Eurovision participant and made a whole bunch of other contestant countries scared of being attacked next, after already having attacked a fellow competitor in 2008 -> Russia got banned from Eurovision
Ukraine in 2022 got attacked, had its civilians targeted intentionally, did not choose to start the war, has no record of past attacks against ESC contestants, and is not currently posing a threat to any other Eurovision participating country -> Ukraine did not get banned
Israel in 2023 got attacked, had its civilians targeted intentionally, did not choose to start the war, has no record of past attacks against ESC contestants, and is not currently posing a threat to any other Eurovision participating country -> Israel did not get banned
There isn't a double standard, except for people who insist on not following the geopolitical logic. Same ones who didn't use Ukraine's retaliation activities against Russia as justification to get Ukraine banned, but are doing that to Israel, usually with a side dish of false, hyperbolic accusations that have nothing to do with reality.
Also...
The only flags allowed are of participating countries and the pride flag. The American flag is therefore banned. The Mexican flag. The Japanese, the Korean, the Nigerian flags. The world doesn't actually revolve around Palestinians, they're not actually the ultimate victims, and honestly, it's offensive they're cast that way when there are conflicts far worse and bloodier than the current war in Gaza, not to mention it takes away attention and help from them, to make everything constantly about the Palestinians.

Meanwhile, this is supposed to be the rule. Outside the performance hall, but within the borders of the Eurovision village, a visiting Israeli comedian called Guy Hochman was assaulted for walking around with the Israeli flag. Swedish police intervened, but they didn't act against the anti-Israel protesters who attacked and spat on Guy, they stopped him from openly carrying the Israeli flag. He asked why are they not allowing it, even though the flag is of a participating country, in accordance with the rules. He was told it's too dangerous. He then asked why are Palestinian flags not being removed, if they're banned according to contest rules, and was told that in Sweden, freedom of speech is above anything else. He was also grilled about whether he's Jewish by the Swedish policemen. Why was his flag denied, then? Why was his freedom of speech not protected, why was his Jewish identity a matter for questioning?
Another thing, the Swedish singer who ended up in third place in 2011 Eric Khaled Saade went on a childish rant crying over the Palestinian flag being banned (again, as if it's the only one), and as he was invited to perform this year, he got on stage live with a kaffiyeh tied to his left hand, even though he knew that was considered political, and therefore not allowed. Once more, he whined about it as if this is specifically against Palestinians, but you know what? The dress designers wanted to have a Star of David on the dress of the Israeli singer. She's a Jewish woman, that's a Jewish symbol, so why not represent her identity? But they were told that's "political." And you know what the Israeli delegation did? Followed the rules. You won't see the Star of David on Eden's dress. When they were told not to wear the hostage pin, because that's "political"? They followed the rules. When the Israeli song writers were told that their song, expressing Israeli pain, is "too political," what did they do? Followed the rules, they changed the lyrics. And you don't hear them crying about it all over social media and the news.
Not to mention, Eric Saade had no problem kissing the ass of Israeli fans back in 2011, when he competed and needed their votes. Was his dad less Palestinian back then? By the way, Israeli fans didn't hold his identity against him, they didn't demand he be questioned about Palestinian terrorists, or what his stance is on Hamas, they didn't drag politics into it, they focused on music and culture connecting people across borders and identities (as the ESC is supposed to do), and Israel gave its 12 points in both the semi and the final to Eric Saade that year. How did he repay those fans? Campaigning to ban Israel (and therefore them) from the contest, because he's incapable of seeing them as people first, and political rivals second, or maybe even (God forbid!) not at all...
It all smells like hypocrisy to me. But we all know this post won't get anywhere near the exposure (through likes and reblogs) that the lying, self-centered, hypocritical anti-Israel posts do. Doesn't matter. I'll still be here, speaking the truth.
(for all of my updates and ask replies regarding Israel, click here)
#israel#eurovision#esc#esc 2024#esc 24#antisemitism#israeli#israel news#israel under attack#israel under fire#anti terrorism#antisemitic#antisemites#jews#jew#judaism#jumblr#frumblr#jewish#eurovision 2024
829 notes
·
View notes
Text
btw, just quietly boycotting eurovision / saying you "don't watch anyway" won't accomplish anything. i know eurovision is cringe. i know its included israel uncritically until now (and that wasn't okay before the current genocide either). i know israel has used eurovision as a pinkwashing opportunity / marketing stunt for years. i know the eurovision overall claim of being "non-political" is bullshit.
but any boycott is only effective when its coupled with protest. if you already don't watch eurovision, and your reaction to israel's inclusion is just to roll your eyes and move on, your boycott is literally meaningless.
we need people to protest. be loud. be annoying, be ever-present. make sure the EBU sees that they won't quietly get away with this. make sure the EBU hears that this is not okay. make sure that the hypocrisy of banning russia in 2022 for invading ukraine, yet allowing israel to continue participating amid an ongoing genocide, is disgusting and reveals the contest as being much more political than it likes to admit.
this thread of how to contact every single broadcaster taking part in eurovision 2024 is a good start. for my own country of norway (which was one of the first to protest russia's inclusion in 2022), i would also recommend throwing a message stig karlsen's way, who is the head of the norwegian eurovision delegation.
when contacting any of these broadcasters or representatives, please be respectful to the best of your ability. argue not just from the horrors of war and genocide, as important as that is, but argue about how it will harm the contest itself.
that's like, the one thing eurovision / the EBU actually cares about. how banning russia but allowing israel is an inherently political move, which goes against the contest's spirit. or how the ferocity of protest will harm the actual live contest in malmo, which will undoubtably be a target of widespread protest.
#eurovision#eurovision 2024#free palestine#palestine#israel palestine conflict#world politics#politics
417 notes
·
View notes
Text
if you're a boycott Eurovision person just block or unfollow me, I'd like to be able to follow the tags I follow without it being clogged with moralfags trying to guilt trip people into getting on their bandwagon.
See, at Eurovision when a country does a thing you don't like, you let them join and then boo them until they leave themselves. Which is probably what's going to happen to Israel this year, not for the first time, and certainly not exclusively to Israel.
Russia invaded Georgia in 2008, have since been occupying a third of their territory, and hosted the next year. Even Georgia didn't boycott that year, but trolled the Russians into banning them that year by sending a song called "We Don't Wanna Put In".
Russia invaded Crimea in 2013, and in 2014 passed the foreign agents law and gay propaganda law, in-between occupying more bits of Ukraine. In 2014 the hair-conjoined twins that got memed by John Oliver that one time got booed so hard the EBU had to invent boo-dampening technology the next year. Of course Conchita Wurst won in 2014, which the Russian broadcaster had to show in full or they would lose broadcasting rights, despite Conchita Wurst *existing* probably counting as "gay propaganda".
For that matter, Ukraine won in 2016 and hosted the next year. Russia didn't even boycott, they sent fascist Tiny Tim as their entry, knowing she had entered Crimea from Russia which would force the Ukrainians to ban her from entering Ukraine to compete while looking like lunatics for doing so.
The ESC wasn't even going to ban the Russian broadcaster from competing in 2022. Initially they were like nah it's non political so it's chill (not to mention it had been 8 years), until about 6 countries including Sweden wrote to the EBU saying "if Russia's in, we're out", and then hours later the EBU decided you could have a contest without Russia but not without Sweden. Not because there's some rule in a song contest that says "you're not allowed to kill people or we won't let you sing".
There is a *WAY* these things are done.
I am perfectly fine with people looking at the way things are and going you know what, I'd rather give it a miss this year. Nobody is forcing you at gunpoint to watch a song contest, block the tag and see you in a month.
But brigading the eurovision tag with this moralizing bullshit about how nobody is allowed to enjoy a show that includes 42 entries that aren't Israel or else we're all genocidal (((zionists))), while turning off notes to your posts so nobody can respond to you, is toddler behaviour.
209 notes
·
View notes
Text


Absolutely!
Back in 2022 the EBU was originally gonna allow Russia to participate on the basis that the Eurovision "Is not a political contest" even though it very much is.
Ukraine initially protested this but they, still, didn't budge.
Only after Finland, Estonia and Iceland threatened to withdraw (I think it was these three) and only then did the EBU decide to suspend Russia on the basis that their broadcaster was spreading misinformation and propaganda regarding the Russian invasion of Ukraine.
The official statement given was not that they had an issue with one of the contestants actively invading another, rather that they weren't being honest about it.
It's worth noting that each country has to pay a participation fee based on their population. In other words, a country like Poland is not paying the same amount of money as a country like San Marino. You can therefore see why the EBU did not want to lose Russia. If one country with large population leaves that means the participation cost for the remaining ones will rise. In fact, Russia's expulsion has inadvertently caused Bulgaria's, North Macedonia's and Montenegro's withdrawal as they could no longer afford the participation fee. This year, Romania, a country with a large population but facing financial difficulties is possibly also withdrawing. Their participation is still up in the air, well after the period to announce their participation has ended, and Australia also took quite a well to finalize negotiations for their participation.
Just like they did with Russia, the EBU has already announced that they do not intend to ban Israel and unless no other countries complain about it and threaten to withdraw, like Estonia, Finland and Iceland did before for Russia, they're gonna keep Israel around.
I'm not here to discuss who should be allowed in and who not, because if we start with Israel then we should also take Azerbaijan, Serbia and every single northwestern European country that retains colonies around the world out too, but my point is, if the EBU's official reasoning for expelling Belarus was that they were trying to send a propaganda song and for Russia was that their broadcaster was spreading propaganda, I don't see how Israel's broadcaster isn't doing the exact same thing about the ongoing situation in Palestine.
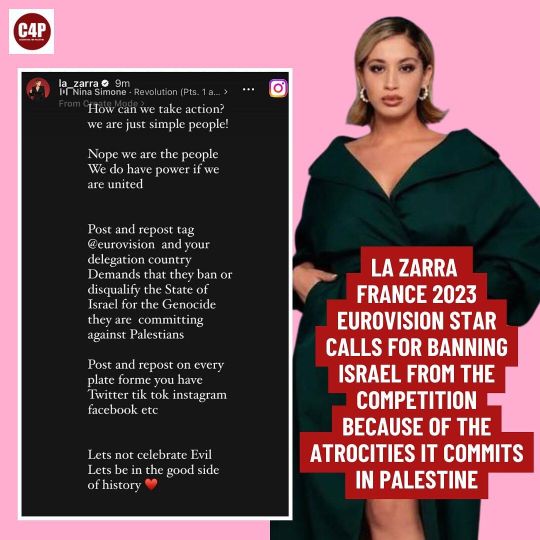
#Eurovision#Eurovision Song Contest#ESC#Eurovision 2024#Eurovision Song Contest 2024#ESC 2024#Ιsrael#Ρalestine#La Zarra#France#RUSSΙA#UΚRAINE
328 notes
·
View notes
Text
Some myth busting about Israel's Eurovision participation
Do note that I use countries here when referring to participation. The term broadcasters would be more accurate since a national broadcaster chooses the entrant and the broadcaster is a member of the European Broadcasting Union, the organization behind Eurovision. But a lot of people use the term countries instead of broadcasters, hence why I'm using that word as well.
Myth 1. "Israel isn't even in Europe"
Well, any country that's part of the European Broadcasting Union (EBU), which Israel, Azerbaijan, Armenia, and Georgia are members of, can participate. Same goes for associate members like Australia, hence why Australia is allowed to participate. Lebanon and Morocco could also participate but choose not to because of Israel. In fact, Morocco's only participation was when Israel wasn't participating in the contest, and Lebanon planned to participate but didn't because of Israel's participation. There are rumours going around that this is also the case for Tunisia and Qatar.
Myth 2. "Eurovision banned Russia but not Israel."
Not completely true. Russia was initially going to participate in the 2022 contest, but several countries protested against Russia's participation and threatened to withdraw if Russia was allowed to participate, thus leading to them being kicked out. We will come back to this point about several countries threatening to leave.
Myth 3. "A lot of the artists speaking out about Israel could actually just withdraw from the contest to make a real statement."
You do realize the EBU actually will fine countries if they withdraw too late without good reason? I'm pretty sure a lot of these countries have contracts in place for their contestants, and since the contest is set to take place in mid May, withdrawing would mean possibly being blacklisted from the music industry and losing out on more opportunities. Not for being pro Palestine, but because they backed out on a contract they signed and left the many, many people who work behind the scenes high and dry on really short notice.
Technically not a myth but worth mentioning: 4. "Israel should be kicked out because her presence is a security risk."
Where do we even begin with this? If a country like Sweden, where the contest is being hosted, isn't able to protect its contestants from terrorist attacks, they shouldn't be hosting. It's that simple. I doubt anyone would've said this if Russia was allowed to participate in 2022.
Myth 5. "Eurovision lets Israel pinkwash its crimes."
@pauvrecamille really summed up how a lot of the discourse around pinkwashing can be boiled down to "country I hate gives their gays more rights than one I like." We could talk about how the only transgender winner is from Israel herself.
And if there is a case to be made for pinkwashing in Eurovision, I would argue that it applies more to Russia and Azerbaijan than it does to Israel. At least Israelis can criticize their government and not fear being arrested.
Speaking of Azerbaijan:
Myth 6. "If even one country withdraws from the contest, then that will send a statement to the contest."
Not true. Armenia withdrew from the 2021 contest because of the war with Azerbaijan, while Azerbaijan was allowed to participate in the contest. This is even after we already know they've cheated twice in the contest, on top of the human rights violations. And we could talk about how so many were forcibly displaced because of Azerbaijan hosting the competition in 2012.
We can also talk about how Ukraine withdrew from the contest in 2015 because of Russia's invasion. Russia was still allowed to participate and went on to place second that year.
In 2008, Russia invaded Georgia and in 2009, the Georgian entry was called "We Don't Wanna Put In" which contained veiled references to Putin's invasion. Because Russia was hosting the contest that year, the EBU tried to get Georgia to change their song. Georgia refused and ended up withdrawing.
Remember what I said about several countries threatening to withdraw if Russia was allowed to participate in 2022? It took a total of 10 countries expressing their concerns about Russia's participation and three or four threatening to withdraw if Russia was allowed to actually get the EBU to reverse course on their decision. So there's that.
EDIT: Myth 7: "People wouldn't be bullying the artists for participating in the contest if the EBU kicked Israel out."
Why am I even surprised this is a talking point?

Edit: Myth 8: "Eurovision is treating Israel differently because of the whole lyrics change situation."
I've seen this on both sides, and this is not true. I've mentioned Georgia earlier, but I also want to mention Armenia's 2015 entry, originally called Don't Deny. It was changed to Face the Shadow and allowed to compete. It's reportedly about the Armenian genocide. The point is, stuff like this happens all the time. In 2021, in the midst of protests and lack of freedom, Belarus sent a pro government band with a song containing veiled lyrics threatening to subjugate the protestors. The EBU allowed them to submit another song but ultimately, Belarus was kicked out after they still failed to follow the rules.
So no, this is not out of the norm. At least from what I know. I'm more than happy to edit this section out if I have been proven wrong. God knows I've edited this post many, many times.
Final thoughts:
A lot of the people who are all high and mighty about boycotting Eurovision would absolutely not be doing that if it was Russia participating. They certainly didn't when Azerbaijan did in 2021.
A lot of the misinformation around Eurovision this year can be chalked up to antisemitism and not understanding how contracts work. I think it's also really performative and virtue signaling at best. Yes, it's true that the postcards(clips for the broadcast while preparing for the next performer) for the 2019 contest, held in Israel, where filmed in disputed territories.
Actually, let's talk about the postcards.
You see, KAN, the Israeli broadcaster, chose not to film the postcards in territories like the West Bank. And they were criticized for it by the right wing Israeli government. So there is a true fact about something bad the Israeli government did that you can criticize them for.
Now back to the topic at hand.
Yes, it's true that Israel's lyrics were changed so they could go ahead and participate this year. It's just that now, it's really difficult to have a sane conversation about Israel in general. It's difficult to have a sane conversation about antisemitism with some people. Take this post here trying to combat antisemitism only to end up having to fight Islamophobia. Put a big F in the chat for the OP of that post, yikes.
If no one got called anti LGBT when the World Cup was held in Qatar and people still watched, I don't see why people who choose to watch Eurovision this year should be called pro genocide.
Last but not least, I want to end this on a more positive note, so this year's contest is looking really good. No one's completely sure who will take the win this year, but right now the song with the most bets to win the contest is Switzerland. It's not like 2023, where we all knew who was going to win weeks before the actual contest. So I'm interested in the outcome this year. You guys are more than welcome to throw in your own opinions on this year's caliber of songs if you want.
#a lot of my fellow anti#tankies#will probably appreciate this post because of how much misinformation is going around about Eurovision and Israel this year#hence why I've tagged it as such#eurovision song contest#palestine#stop making the left look bad you donkeys#most of you don't know what you're talking about#israel#misinformation
129 notes
·
View notes
Text
Vladimir Putin & The Anti-Trans Cult
So lets just sum this up, shall we?
The UK, USA and all of Europe is at war with Russia, because we think Vladimir Putin is an evil bastard who is trying to take over Ukraine. We think he is one of the most evil men in the world, and anyone who is associated with him is also an evil bastard who can’t be trusted.
Very few people disagree with this, and it is the primary reason that Russia are not allowed to take part in The Olympics.
Are you all with me so far?
Good.
There is an organisation called The International Boxing Association.
It is run by a man named Umar Kremlev. A man who is widely criticised for having very close ties with Vladimir Putin (you remember him, right?), for being associated with a Russian state owned oil company and for there being “irregularities” during the elections of 2021 and 2022. He is, in short, a very suspicious character and did I mention him being very close to Putin (the guy who is the reason Russia aren’t allowed in polite company or The Olympics).
He is also the reason why The IBA aren’t permitted to oversee boxing at The Olympics — the first time an international authority was ever expelled from The Olympics.
And — if this wasn’t enough — he was the man in charge when a woman named Imane Khelif was disqualified from the World Championships for “undisclosed reasons” just after she defeated the previously undefeated Azalia Amineva — the previously unbeaten Russian contender.
The IBA — under the direction of a Russian man who is close friends with Putin, and who disqualified someone who beat a previously unbeaten Russian contender — claimed she had “high testosterone levels” but then said “they had not undergone testosterone testing” (so quite how they knew how high her testosterone levels were is curious — did they just look at her and go “No — too high”?), then they said DNA testing proved she “had XY chromosomes” except there is no evidence that she has XY chromosomes, and the only evidence that The Russian lead IBA is willing to provide is “confidential” and shows “a competitive advantage”
So — to sum up — The IBA, which is run by a Russian who is close friends with someone most of the known world hates, and who the UK, USA and Europe is at war with, and who is suspected of being incredibly corrupt, banned a woman from The World Championship for no apparent reason other than she beat a Russian contender who was going to go for the gold medal.
Are you still with me? Because all of this is merely prologue. Now we get to the good stuff.
The woman at the centre of all this — Imane Khelif — is about to go for The Olympic Gold in Paris.
Now given everything I have just told you — that she was banned from The World Championship by a corrupt organisation run by a man with ties to the Russian regime because she beat a Russian contender who was going to fight for the gold and so far there has been no evidence whatsoever to back up the reason she was banned — where do you think the press in the UK, USA and Europe would be on her performance in The Olympics?
Yes. That’s right. They want her kicked out of the contest.
The anti-trans cult is so fucking dedicated to the bigotry that they are willing to side with a man who runs a corrupt organisation, who is in bed with Putin, who has absolutely no proof to back up any of his claims and who banned someone because they dared to beat a Russian fighter just so they can continue to target a woman who has always been a woman and who can punch harder than another woman.
It’s fucking ridiculous.
#imane khelif#vladimir putin#paris 2024#olympics#olympic games#paris olympics#umar kremlev#iba#international boxing association
52 notes
·
View notes
Text
In a statement published the same week as the first Melodifestivalen semi-final, more than 1000 Swedish artists ask the EBU to exclude Israel from this year's Eurovision Song Contest, including 2 acts participating in this year's edition of melfest: Jacqline, and both members of Medina. Also among the signatures are former melfest participants Johan Hirvi (Panetoz) and Alvaro Estrella, as well as former winners Eric Saade and Malena Ernman.
Some other notable signatures belong to Robyn, First Aid Kit, Eagle-Eye Cherry, Petra Marklund (also known as September), The Wannadies, Thomas Stenström, Miriam Bryant, Sabina Ddumba, Daniel Adams-Ray, Timbuktu, Kaliffa and many others whose names I recognise but I'm too unfamiliar with the contemporary music scene to know their work.
Below is my translation of some parts of their statement, as well as sources:
Note: The bold parts are also bold in the original statement. I have tried to use the same terminology as the statement, but I'm no expert, so be aware that there can be some mistakes.
The first link includes the full statement in Swedish as well as a list of all the signatures:
[...] What is happening in Gaza is a humanitarian disaster and the International Court of Justice in The Hague has recently decided to continue the case where Israel is accused of crimes against the Genocide Convention. Despite this the European radio- and TV-union the EBU intends to allow Israel's participation in the Eurovision Song Contest 2024. The EBU grounds its position on Eurovision being a competition between public service companies rather than states. But in 2022 the EBU chose to exclude Russia by reason of the invasion of Ukraine, and in 2021 the participating broadcaster from Belarus was denied participation because the country broke the EBU's rules for the freedom of the press. In barely four months about 100 Palestinian journalists have been killed, and foreign press has been denied access to Gaza. It is one of the greatest attacks on journalistic freedom in modern times. We are of the opinion that the EBU by allowing Israel's participation displays a remarkable double-standard that undermines the credibility of the organisation. [...] We expect both the EBU and this year's host broadcaster SVT to be consistent in their approach towards participating countries that infringe on democratic values and human rights.
[...] We who sign this are 1000 artists who believe in music as a unifying force. The Eurovision Song Contest began as a peace project to unite countries and citizens through music. To allow Israel's participation undermines not just the competition's spiritual intent but the entire public service mission. It also sends the signal that governments can commit war crimes without facing consequences. That is why we ask the EBU: Exclude Israel from the Eurovision Song Contest 2024.
58 notes
·
View notes
Text
As Japan’s newly elected prime minister, Shigeru Ishiba, composes his cabinet, one position remains conspicuously vacant: Minister for Economic Cooperation with Russia. Moscow has noticed, with Russia Ministry of Foreign Affairs spokeswoman Maria Zakharova saying plainly, “If Japan closes ties, we will look for other partners.” Ishiba’s move signals a continued, and potentially more assertive, departure from the brief period of improvement of relations that Tokyo and Moscow enjoyed under Prime Minister Shinzo Abe in the late 2010s. This has since been interrupted by Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. The fact that Ishiba has been sanctioned by Moscow since 2022 does not help matters.
Created in 2016 under Abe, the Minister for Economic Cooperation with Russia has traditionally been held by Japan’s Minister of Economy, Trade, and Industry. It was occupied through Prime Minister Kishida’s tenure, despite calls from lawmakers in both Japan’s ruling Liberal Democratic Party (LDP) and opposition parties to abolish the title. Although largely symbolic, the position’s inception rests in the broader eight-point plan of economic cooperation presented by Abe to Vladimir Putin during the 2016 Russia-Japan Summit in Sochi. The plan was a notable step toward improving relations that had been inflamed following Russia’s invasion of Crimea and eastern Ukraine. This triggered a slew of retaliatory measures by Japan, including the freezing of agreements on investment, visas, and security.
Beyond moving to improve economic relations, the summit eased tensions surrounding Japan’s Northern Territories, the contested Kuril Islands claimed by Japan but administered by Russia since the Soviet occupation during World War II. The Russian program allowing visa-free access to the islands by its former Japanese residents was expanded, and more Japanese citizens were allowed access to visit the graves of their family members, a point of domestic political contention in Tokyo that Ishiba highlighted during his campaign.
The progress on the issue of the Northern Territories supported efforts for the establishment of a peace treaty between Moscow and Tokyo, which would formally end post-World War II hostilities and settle the issue of the sovereignty of the islands. Although no treaty was signed as a result of Abe’s efforts, Russia-Japan trade and visits to the Northern Territories continued mostly unimpeded until Russia’s invasion of Ukraine in 2022, despite several minor diplomatic rows.
Under Prime Minister Kishida, Japan joined the West’s sanctions regime against Russia, triggering a major diplomatic fallout between Moscow and Tokyo. Within a month of the invasion, Russia suspended all talks relating to a peace treaty with Japan. It halted visa-free access for former Japanese residents of the Northern Territories, alongside disruptions to trade due to sanctions and Japan’s downgrading of Russia’s ‘most favored nation’ status.
Although not wholly indicative of Russia’s diplomatic posture, former Russian president turned deputy chairman of Russia’s National Security Council Dmitry Medvedev proclaimed that the issue of the Northern Territories was “closed once and for all” and that those upset in Japan should “end their life in the traditional Japanese way, by committing seppuku.”
The growing division in Russia-Japan relations was accompanied by stronger bilateral relations between the United States and Japan, as the two countries pledged several new points of cooperation during Kishida’s state visit in April. Notably, both countries enhanced their defense partnership by agreeing to upgrade and modernize their Command and Control systems, including the long-awaited establishment of the Japan Self-Defense Forces Joint Operations Command. This new command structure aims to unify and oversee all SDF joint operations, complementing the restructured Joint Force Headquarters with US Forces Japan. The two countries also recently established the Defense Industrial Cooperation, Acquisition, and Sustainment Forum, which enables U.S. and Japanese officials and business leaders to discuss areas for closer industrial cooperation.
In addition to stronger bilateral defense ties, Japan has also increased its multilateral engagement with NATO. Since the 2022 NATO summit in Madrid, Kishida has participated in every successive NATO summit to identify areas of mutual security interests. Most recently, following the 2024 NATO Summit in Washington, DC, NATO and Japan agreed to enhance cooperation in cyber defense, emerging technologies, maritime security, and resilience under the Individually Tailored Partnership Programme.
Ishiba took an aggressive posture toward Moscow during his campaign to become the leader of the LDP in September. He articulated his foreign policy vision in comments to the Hudson Institute, recognizing a growing partnership between Pyongyang and Moscow and emphasizing the need for new methods of deterrence against Russia, China, and North Korea. Additionally, in response to several incursions by Russian aircraft last week, Ishiba proposed amending Japanese law to allow Japan’s Self-Defense Forces to fire on aircraft violating Japanese airspace.
During his security-heavy inaugural policy speech to the Japanese Diet this week, Ishiba referenced Russia’s airspace violation, calling it a “serious violation” of Japanese sovereignty. He also committed to continuing Japan’s sanctions regime against Russia over its invasion of Ukraine, echoing earlier statements made by his newly appointed foreign minister.
While recognizing that Japan-Russia relations are tense, Ishiba pledged to continue aiming for a Russia-Japan peace treaty and to resolve the issue of the sovereignty of the Northern Territories. However, as Zakharova’s comments highlight, continued negotiations are unlikely to occur as long as Japan maintains sanctions.
With all indicators pointing to, at minimum, a continuation of the tense diplomatic status quo between Russia and Japan, Ishiba is unlikely to reverse the Kishida administration’s course as long as the Russian invasion of Ukraine continues. His aspirations for a stronger Japanese defense, including the implication of greater deterrence against Russia, indicate further agitation in Moscow as Japanese cooperation with the United States and NATO continues to grow.
Just days into his administration, Ishiba has already drawn the ire of the Russian Ministry of Foreign Affairs—and it likely will not be the last time.
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
I have never particularly cared about Eurovision but I do like politics and Eurovision has become a thermometer for Europe's (and guests)'s political climate.
Like, I remember when whatever entity controlling Eurovision banned a performance in which two young women kissed. t.A.t.U. was their name. It was deemed too provocative. They were allowed to sing but not to kiss. That was 2011 and in 2014 Conchita Wurst won in all their gender-ambiguous glory.
(Ironically, t.A.t.U. is a Russian band. How things have changed).
In 2019 the contest took place in Tel-Aviv (... yeah) and Iceland was fined for their signs in support of Palestine. The contest is supposed to be neutral and performers can't make political statements. But in 2022 Russia was banned from participating and everybody showed support for Ukraine.
So I have been waiting to see what will happen this year. Will they ban Israel from participating? It doesn't look like it, but more and more participants are opposing Israel and showing support for Palestine. It's little, but it is more support than what we have seen in the last decades.
The contest has always been 40% insanity and 30% showing dislike to the UK (and only 10% music, the remaining 20% is a sacrifice to the old gods). But this year it looks like 50% insanity and 50% making political statements of any kind. With great pleasure, I share with you:
Finland. Finland is sending a pantless man emerging from a denim egg. Truly pantless. Nudity is forbidden in the contest but they are getting around it. I... I think it's an answer to some ridiculous rule lawyering on Eurovision's part. I don't know, you have to see it. It will be 3 minutes well spent.
Spain. Spain has gone "oh, are we getting political?" and, Tumblr, Tumblr, listen:
The performer is 56.
She looks 56.
When do we see women in their 50s singing and dancing? Does Madonna count? I mean women like the ones in the videoclip. I'm adding a picture.

Ma'am, I love you.
The main video differs from the performance for the contest. Sadly, there will be no women in their 50s dancing in the stage for Eurovision. They went with professional dancers.
Feminism 101. Let's have the male dancers perform like they expect women to perform in this kind of show.

The youtube comments have a not inconsiderable amount of lesbians thirsting after the drummer.
I wish them the best.
#eurovision#songs and politics#finland#spain#norules#zorra#nebulossa#windows95man#zorra is an earworm
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
Regarding the Eurovision I have seen a few posts where people are confused why Isreal is even participating.
Since 1956 the Grand Prix de la Chanson de L'Eurovision is held by the EBU.
The EBU has not really something to do with Europe as a Continent and especially not as a political Union.
It is a union of broadcasting stations. In this case Radio.
And 68 Nations from Europe, Asia and Northern Africa are part of it.
So everyone being part of the EBU is allowed to participate.
Some states dropped out because of costs and lack of interest like Andorra.
Others dropped out of different reasons.
But mostly financial.
From all European Countries only Liechtenstein and the Vatican never participated.
Others like the Färöer Islands want to But aren't part of the EBU.
From the African Countries only Marokko participated once in 1980 but due to poor placing and as a protest of Israel participating they dropped out.
Since 2016 Australia is an honorary participant because they love it so much.
It is very important to know that it's not the State that participates. It's the radio/TV station that is part of the EBU.
So. Israel is part of the EBU and participates since 1973.
It has been protested that it's part of the Esc but the Esc is in itself an apolitical event.
There have been instances where it was used for protest or influence over the contest was politically motivated.
Like the Spanish decision to change the singer and language in 1968 to not have a Catalan singer singing in Catala. It is still rumored that their win was initiated by Franco that year.
Why Israel but not Russia and Belarus?
Voices have been loud again to ban Israel from the Esc like it happened in 2022 with Russia and Belarus (for the first time in the history of the EBU) due to the attack on Ukraine.
The argument is simple: I Russia and Belarus there is no way to differentiate between the state and the media (who has to be a member of the EBU)
The argument does not work for the case of Israel.
The country has free media which can also be critical towards its government.
And Israel had its own problems with participants showing the Palestinian flag during their performance. 2000
2009 and 2020 their song was also in Arabic Hebrew and English.
Tldr: why is Isreal in Eurovision? They can broadcast radio throughout Europe north Africa and Asia.
Not the State participates but the radio station.
Why aren't they banned? Not a dictatorship like Russia.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Link without paywall:
And a copypaste for good measure:
Last October, Colin Kahl, then the Under-Secretary of Defense for Policy at the Pentagon, sat in a hotel in Paris and prepared to make a call to avert disaster in Ukraine. A staffer handed him an iPhone—in part to avoid inviting an onslaught of late-night texts and colorful emojis on Kahl’s own phone. Kahl had returned to his room, with its heavy drapery and distant view of the Eiffel Tower, after a day of meetings with officials from the United Kingdom, France, and Germany. A senior defense official told me that Kahl was surprised by whom he was about to contact: “He was, like, ‘Why am I calling Elon Musk?’ ”
The reason soon became apparent. “Even though Musk is not technically a diplomat or statesman, I felt it was important to treat him as such, given the influence he had on this issue,” Kahl told me. SpaceX, Musk’s space-exploration company, had for months been providing Internet access across Ukraine, allowing the country’s forces to plan attacks and to defend themselves. But, in recent days, the forces had found their connectivity severed as they entered territory contested by Russia. More alarmingly, SpaceX had recently given the Pentagon an ultimatum: if it didn’t assume the cost of providing service in Ukraine, which the company calculated at some four hundred million dollars annually, it would cut off access. “We started to get a little panicked,” the senior defense official, one of four who described the standoff to me, recalled. Musk “could turn it off at any given moment. And that would have real operational impact for the Ukrainians.”
Musk had become involved in the war in Ukraine soon after Russia invaded, in February, 2022. Along with conventional assaults, the Kremlin was conducting cyberattacks against Ukraine’s digital infrastructure. Ukrainian officials and a loose coalition of expatriates in the tech sector, brainstorming in group chats on WhatsApp and Signal, found a potential solution: SpaceX, which manufactures a line of mobile Internet terminals called Starlink. The tripod-mounted dishes, each about the size of a computer display and clad in white plastic reminiscent of the sleek design sensibility of Musk’s Tesla electric cars, connect with a network of satellites. The units have limited range, but in this situation that was an advantage: although a nationwide network of dishes was required, it would be difficult for Russia to completely dismantle Ukrainian connectivity. Of course, Musk could do so. Three people involved in bringing Starlink to Ukraine, all of whom spoke on the condition of anonymity because they worried that Musk, if upset, could withdraw his services, told me that they originally overlooked the significance of his personal control. “Nobody thought about it back then,” one of them, a Ukrainian tech executive, told me. “It was all about ‘Let’s fucking go, people are dying.’ ”
In the ensuing months, fund-raising in Silicon Valley’s Ukrainian community, contracts with the U.S. Agency for International Development and with European governments, and pro-bono contributions from SpaceX facilitated the transfer of thousands of Starlink units to Ukraine. A soldier in Ukraine’s signal corps who was responsible for maintaining Starlink access on the front lines, and who asked to be identified only by his first name, Mykola, told me, “It’s the essential backbone of communication on the battlefield.”
Initially, Musk showed unreserved support for the Ukrainian cause, responding encouragingly as Mykhailo Fedorov, the Ukrainian minister for digital transformation, tweeted pictures of equipment in the field. But, as the war ground on, SpaceX began to balk at the cost. “We are not in a position to further donate terminals to Ukraine, or fund the existing terminals for an indefinite period of time,” SpaceX’s director of government sales told the Pentagon in a letter, last September. (CNBC recently valued SpaceX at nearly a hundred and fifty billion dollars. Forbes estimated Musk’s personal net worth at two hundred and twenty billion dollars, making him the world’s richest man.)
Musk was also growing increasingly uneasy with the fact that his technology was being used for warfare. That month, at a conference in Aspen attended by business and political figures, Musk even appeared to express support for Vladimir Putin. “He was onstage, and he said, ‘We should be negotiating. Putin wants peace—we should be negotiating peace with Putin,’ ” Reid Hoffman, who helped start PayPal with Musk, recalled. Musk seemed, he said, to have “bought what Putin was selling, hook, line, and sinker.” A week later, Musk tweeted a proposal for his own peace plan, which called for new referendums to redraw the borders of Ukraine, and granted Russia control of Crimea, the semi-autonomous peninsula recognized by most nations, including the United States, as Ukrainian territory. In later tweets, Musk portrayed as inevitable an outcome favoring Russia and attached maps highlighting eastern Ukrainian territories, some of which, he argued, “prefer Russia.” Musk also polled his Twitter followers about the plan. Millions responded, with about sixty per cent rejecting the proposal. (Volodymyr Zelensky, Ukraine’s President, tweeted his own poll, asking users whether they preferred the Elon Musk who supported Ukraine or the one who now seemed to back Russia. The former won, though Zelensky’s poll had a smaller turnout: Musk has more than twenty times as many followers.)
By then, Musk’s sympathies appeared to be manifesting on the battlefield. One day, Ukrainian forces advancing into contested areas in the south found themselves suddenly unable to communicate. “We were very close to the front line,” Mykola, the signal-corps soldier, told me. “We crossed this border and the Starlink stopped working.” The consequences were immediate. “Communications became dead, units were isolated. When you’re on offense, especially for commanders, you need a constant stream of information from battalions. Commanders had to drive to the battlefield to be in radio range, risking themselves,” Mykola said. “It was chaos.” Ukrainian expats who had raised funds for the Starlink units began receiving frantic calls. The tech executive recalls a Ukrainian military official telling him, “We need Elon now.” “How now?” he replied. “Like fucking now,” the official said. “People are dying.” Another Ukrainian involved told me that he was “awoken by a dozen calls saying they’d lost connectivity and had to retreat.” The Financial Times reported that outages affected units in Kherson, Zaporizhzhia, Kharkiv, Donetsk, and Luhansk. American and Ukrainian officials told me they believed that SpaceX had cut the connectivity via geofencing, cordoning off areas of access.
The senior defense official said, “We had a whole series of meetings internal to the department to try to figure out what we could do about this.” Musk’s singular role presented unfamiliar challenges, as did the government’s role as intermediary. “It wasn’t like we could hold him in breach of contract or something,” the official continued. The Pentagon would need to reach a contractual arrangement with SpaceX so that, at the very least, Musk “couldn’t wake up one morning and just decide, like, he didn’t want to do this anymore.” Kahl added, “It was kind of a way for us to lock in services across Ukraine. It could at least prevent Musk from turning off the switch altogether.”
Typically, such a negotiation would be handled by the Pentagon’s acquisitions department. But Musk had become more than just a vender like Boeing, Lockheed, or other defense-industry behemoths. On the phone with Musk from Paris, Kahl was deferential. According to unclassified talking points for the call, he thanked Musk for his efforts in Ukraine, acknowledged the steep costs he’d incurred, and pleaded for even a few weeks to devise a contract. “If you cut this off, it doesn’t end the war,” Kahl recalled telling Musk.
Musk wasn’t immediately convinced. “My inference was that he was getting nervous that Starlink’s involvement was increasingly seen in Russia as enabling the Ukrainian war effort, and was looking for a way to placate Russian concerns,” Kahl told me. To the dismay of Pentagon officials, Musk volunteered that he had spoken with Putin personally. Another individual told me that Musk had made the same assertion in the weeks before he tweeted his pro-Russia peace plan, and had said that his consultations with the Kremlin were regular. (Musk later denied having spoken with Putin about Ukraine.) On the phone, Musk said that he was looking at his laptop and could see “the entire war unfolding” through a map of Starlink activity. “This was, like, three minutes before he said, ‘Well, I had this great conversation with Putin,’ ” the senior defense official told me. “And we were, like, ‘Oh, dear, this is not good.’ ” Musk told Kahl that the vivid illustration of how technology he had designed for peaceful ends was being used to wage war gave him pause.
After a fifteen-minute call, Musk agreed to give the Pentagon more time. He also, after public blowback and with evident annoyance, walked back his threats to cut off service. “The hell with it,” he tweeted. “Even though Starlink is still losing money & other companies are getting billions of taxpayer $, we’ll just keep funding Ukraine govt for free.” This June, the Department of Defense announced that it had reached a deal with SpaceX.
The meddling of oligarchs and other monied interests in the fate of nations is not new. During the First World War, J. P. Morgan lent vast sums to the Allied powers; afterward, John D. Rockefeller, Jr., poured money into the fledgling League of Nations. The investor George Soros’s Open Society Foundations underwrote civil-society reform in post-Soviet Europe, and the casino mogul Sheldon Adelson funded right-wing media in Israel, as part of his support of Benjamin Netanyahu.
But Musk’s influence is more brazen and expansive. There is little precedent for a civilian’s becoming the arbiter of a war between nations in such a granular way, or for the degree of dependency that the U.S. now has on Musk in a variety of fields, from the future of energy and transportation to the exploration of space. SpaceX is currently the sole means by which NASA transports crew from U.S. soil into space, a situation that will persist for at least another year. The government’s plan to move the auto industry toward electric cars requires increasing access to charging stations along America’s highways. But this rests on the actions of another Musk enterprise, Tesla. The automaker has seeded so much of the country with its proprietary charging stations that the Biden Administration relaxed an early push for a universal charging standard disliked by Musk. His stations are eligible for billions of dollars in subsidies, so long as Tesla makes them compatible with the other charging standard.
In the past twenty years, against a backdrop of crumbling infrastructure and declining trust in institutions, Musk has sought out business opportunities in crucial areas where, after decades of privatization, the state has receded. The government is now reliant on him, but struggles to respond to his risk-taking, brinkmanship, and caprice. Current and former officials from NASA, the Department of Defense, the Department of Transportation, the Federal Aviation Administration, and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration told me that Musk’s influence had become inescapable in their work, and several of them said that they now treat him like a sort of unelected official. One Pentagon spokesman said that he was keeping Musk apprised of my inquiries about his role in Ukraine and would grant an interview with an official about the matter only with Musk’s permission. “We’ll talk to you if Elon wants us to,” he told me. In a podcast interview last year, Musk was asked whether he has more influence than the American government. He replied immediately, “In some ways.” Reid Hoffman told me that Musk’s attitude is “like Louis XIV: ‘L’état, c’est moi.’ ”
Musk’s power continues to grow. His takeover of Twitter, which he has rebranded “X,” gives him a critical forum for political discourse ahead of the next Presidential election. He recently launched an artificial-intelligence company, a move that follows years of involvement in the technology. Musk has become a hyper-exposed pop-culture figure, and his sharp turns from altruistic to vainglorious, strategic to impulsive, have been the subject of innumerable articles and at least seven major books, including a forthcoming biography by Walter Isaacson. But the nature and the scope of his power are less widely understood.
More than thirty of Musk’s current and former colleagues in various industries and a dozen individuals in his personal life spoke to me about their experiences with him. Sam Altman, the C.E.O. of OpenAI, with whom Musk has both worked and sparred, told me, “Elon desperately wants the world to be saved. But only if he can be the one to save it.”
The terms of the Starlink deal have not been made public. Ukrainian officials say that they have not faced further service interruptions. But Musk has continued to express ambivalence about how the technology is being used, and where it can be deployed. In February, he tweeted, “We will not enable escalation of conflict that may lead to WW3.” He said, as he had told Kahl, that he was sincerely attempting to navigate the moral dilemmas of his role: “We’re trying hard to do the right thing, where the ‘right thing’ is an extremely difficult moral question.”
Musk’s hesitation aligns with his pragmatic interests. A facility in Shanghai produces half of all Tesla cars, and Musk depends on the good will of officials in China, which has lent support to Russia in the conflict. Musk recently acknowledged to the Financial Times that Beijing disapproves of his decision to provide Internet service to Ukraine and has sought assurances that he would not deploy similar technology in China. In the same interview, he responded to questions about China’s efforts to assert control over Taiwan by floating another peace plan. Taiwan, he suggested, could become a jointly controlled administrative zone, an outcome that Taiwanese leaders see as ending the country’s independence. During a trip to Beijing this spring, Musk was welcomed with what Reuters summarized as “flattery and feasts.” He met with senior officials, including China’s foreign minister, and posed for the kinds of awkwardly smiling formal photos that are more typical of world leaders.
National-security officials I spoke with had a range of views on the government’s balance of power with Musk. He maintains good relationships with some of them, including General Mark Milley, the chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff. Since the two men met, several years ago, when Milley was the chief of staff of the Army, they have discussed “technology applications to warfare—artificial intelligence, electric vehicles, and autonomous machines,” Milley told me. “He has insight that helped shape my thoughts on the fundamental change in the character of war and the modernization of the U.S. military.” During the Starlink controversy, Musk called him for advice. But other officials expressed profound misgivings. “Living in the world we live in, in which Elon runs this company and it is a private business under his control, we are living off his good graces,” a Pentagon official told me. “That sucks.”
One summer evening in the mid-nineteen-eighties, Musk and his friend Theo Taoushiani took Taoushiani’s father’s car for an illicit drive. Musk and Taoushiani were both in their mid-teens, and lived about a mile apart in a suburb of Johannesburg, South Africa. Neither had a driver’s license, or permission from Taoushiani’s father. But they were passionate Dungeons & Dragons fans, and a new module—a fresh scenario in the game—had just been released. Taoushiani took the wheel for the twenty-minute drive to the Sandton City mall. “Elon was my co-pilot,” Taoushiani told me. “We went under the cover of darkness.” At the mall, they found that they didn’t have enough money. But Musk promised a salesperson that they would return the next day with the rest, and dropped the name of a well-known Greek restaurant owned by Taoushiani’s family. “Elon had the gift of the gab,” Taoushiani said. “He’s very persuasive, and he’s quite dogged in his determination.” The two went home with the module.
Musk was born in 1971 in Pretoria, the country’s administrative capital, and he and his younger brother, Kimbal, and his younger sister, Tosca, grew up under apartheid. Musk’s mother, Maye, a Canadian model and dietitian, and his father, Errol, an engineer, divorced when he was young, and the children initially stayed with Maye. She has said that Errol was physically abusive toward her. “He would hit me when the kids were around,” she wrote in her memoir. “I remember that Tosca and Kimbal, who were two and four, respectively, would cry in the corner, and Elon, who was five, would hit him on the backs of his knees to try to stop him.” By the mid-eighties, Musk had moved in with his father—a decision that he has said was motivated by concern for his father’s loneliness, and which he came to regret. Musk, usually impassive in interviews, cried openly when he told Rolling Stone about the years that followed, in which, he said, his father psychologically tortured him, in ways that he declined to specify. “You have no idea about how bad,” he said. “Almost every crime you can possibly think of, he has done. Almost every evil thing you could possibly think of, he has done.” Taoushiani recalled witnessing Errol “chastise Elon a lot. Maybe belittle him.” (Errol Musk has denied allegations that he was abusive to Maye or to his children.) Musk has also said that he was violently bullied at school. Though he is now six feet one, with a broad-shouldered build, he was “much, much smaller back in school,” Taoushiani told me. “He wasn’t very social.”
Musk has said that he has Asperger’s syndrome, a form of what is now known as autism-spectrum disorder, which is characterized by difficulty with social interactions. As a child, he would sometimes fall into trancelike states of deep thought, during which he was so unresponsive that his mother eventually took him to a doctor to check his hearing. Musk’s quiet side persists—in my own interactions with him, I have found him to be thoughtful and measured. (Musk declined to answer questions for this story.) He can also be, as he joked during a stilted “Saturday Night Live” monologue, “pretty good at running human, in emulation mode.”
Musk escaped into science fiction and video games. “One of the reasons I got into technology, maybe the reason, was video games,” he said at a gaming-industry convention several years ago. In his early teens, Musk coded an eight-bit shooter game in the style of Space Invaders called Blastar, whose title screen, in a novelistic flourish, credits him as “E. R. Musk.” The premise was basic: “MISSION: DESTROY ALIEN FREIGHTER CARRYING DEADLY HYDROGEN BOMBS AND STATUS BEAM MACHINES.” But it won recognition from a South African trade magazine, which published the game’s hundred and sixty-seven lines of code and paid Musk a small sum.
Musk often talks about his science-fiction influences. Some have manifested in straightforward ways: he has connected his love of Isaac Asimov’s “Foundation” novels, whose characters grapple with a mathematically precise prediction of their civilization’s collapse, to his obsession with insuring human survival beyond Earth. But some of Musk’s touchstones present ironies. He has said that his hero is Douglas Adams, the writer who skewered both the hyper-rich and the progress-at-any-cost ethos that Musk has come to embody. In the “Hitchhiker’s Guide to the Galaxy” novels and radio plays, the latter of which were broadcast in South Africa during Musk’s childhood, a narcissistic playboy becomes the president of the galaxy, and Earth is demolished to make way for a space transit route. Musk is also an avowed fan of Deus Ex, a role-playing first-person-shooter video game that he has brought up when discussing his company Neuralink, which aspires to invent ability-enhancing body modifications like those featured in the game. During the pandemic, Musk seemed to embrace Covid denialism, and for a while he changed his Twitter profile picture to an image of the protagonist of the game, which turns on a manufactured plague designed to control the masses. But Deus Ex, like “The Hitchhiker’s Guide to the Galaxy,” is a fundamentally anti-capitalist text, in which the plague is the culmination of unrestrained corporate power, and the villain is the world’s richest man, a media-darling tech entrepreneur with global aspirations and political leaders under his control.
In 1999, Musk stood outside his Bay Area home to accept the delivery of a million-dollar McLaren F1 sports car. He was in his late twenties, and wearing an oversized brown blazer. “Some could interpret purchasing this car as behavior characteristic of an imperialist brat,” he told a CNN news crew. Then he beamed, saying that there were only about sixty such cars in the world. “My values may have changed,” he added, “but I’m not consciously aware of my values having changed.” Musk’s fiancée, a Canadian writer named Justine Wilson, seemed more aware. “It’s a million-dollar car. It’s decadent,” she said. “My fear is that we become spoiled brats. That we lose a sense of appreciation and perspective.” The McLaren, she observed, was “the perfect car for Silicon Valley.”
Musk had moved to Canada when he was in his late teens, and met Wilson when they both attended Queen’s University, in Ontario. He later transferred to the University of Pennsylvania, graduating with degrees in economics and physics. In 1995, the early days of the World Wide Web, he and Kimbal founded a company that came to be called Zip2, an online city directory that they sold to newspapers. Musk has often described the company’s humble origins, saying that he and his brother lived and worked in a small studio apartment, showering at a nearby Y.M.C.A. and eating at Jack in the Box. (Errol at one point gave his sons twenty-eight thousand dollars. Musk, who has a tendency to fuss over questions of credit, has stated that his father’s contribution came “much later,” in a round of funding that “would’ve happened anyway.”) At Zip2, Musk developed what he describes as his “hard-core” work style; even after he had his own apartment, he often slept on a beanbag at the office. But, in the end, the company’s investors stripped him of his leadership role and installed a more experienced chief executive. Musk believed that the startup should have been targeting not just newspapers but consumers. Investors pursued a more modest vision instead. In 1999, Zip2 was sold to Compaq for three hundred and seven million dollars, earning Musk more than twenty million dollars.
Justine and Musk married the following year. After their first child died at ten weeks, from sudden infant death syndrome, the couple dealt with the tragedy in very different ways. Justine, by her account, grieved openly; Musk later told one of his biographers, Ashlee Vance, that “wallowing in sadness does no good for anyone around you.” After pursuing I.V.F. treatment, the couple had twins, then triplets. (Musk now has at least nine children with three different women, and has said that he is doing his part to address one of his pet issues, the risk of population collapse; demographers are skeptical about the matter.) Justine wrote in an essay for Marie Claire that their relationship eventually buckled under the weight of Musk’s obsession with work and his controlling tendencies, which began with him insisting, as they danced at their wedding, “I am the alpha in this relationship.” A messy divorce ensued, leading to a legal dispute over their postnuptial financial agreement, which was settled years later. “He had grown up in the male-dominated culture of South Africa,” Justine wrote. “The will to compete and dominate that made him so successful in business did not magically shut off when he came home.” (Musk wrote a response to Justine’s account in Business Insider, discussing the financial dispute, but he did not address Justine’s characterizations of his behavior.)
After Musk left Zip2, he poured some twelve million dollars, a majority of his wealth, into another startup, an online bank called X.com. It was the first instance of his obsession with the letter “X,” which has now appeared in the names of his companies, his products, and his son with the artist Grimes: X Æ A-12. The bank also marked the beginning of a long and so far unfulfilled quest—recently revived in his effort to reinvent Twitter—to create an “everything app,” incorporating a payment system. In 2000, X.com merged with a competing online-payments startup, Confinity, co-founded by the entrepreneur Peter Thiel. In events that have since become Silicon Valley lore, Musk and Thiel battled for control of the company. Various accounts apportion blame differently. Hoffman told me, citing the story as an example of Musk’s disingenuousness, that Musk had pushed for the merger by highlighting the leadership of his company’s seasoned executive, only to force out the executive and place himself in the top role. “A merger like this, you’re doing a marriage,” Hoffman said. “And it’s, like, ‘I was lying to you intensely while we were dating. Now that we’re married, let me tell you about the herpes.’ ” People who have worked with Musk often describe him as controlling. One said, “In the areas he wants to compete in, he has a very hard time sharing the spotlight, or not being the center of attention.” In the fall of 2000, another coup, executed while Musk was on a long-delayed honeymoon with Justine, overthrew Musk and installed Thiel as the company’s head. Two years later, eBay acquired the company, by then called PayPal, for $1.5 billion, making Musk, who remained the largest shareholder, fabulously wealthy.
Perhaps the most revealing moment in the PayPal saga happened at its outset. In March, 2000, as the merger was under way, Musk was driving his new McLaren, with Thiel in the passenger seat. The two were on Sand Hill Road, an artery that cuts through Silicon Valley. Thiel asked Musk, “So what can this do?” Musk replied, “Watch this,” then floored the gas pedal, hit an embankment, and sent the car airborne and spinning before it slammed back onto the pavement, blowing out its suspension and its windows. “This isn’t insured,” Musk told Thiel. Musk’s critics have used the story to illustrate his reckless showboating, but it also underscores how often Musk has been rewarded for that behavior: he repaired the McLaren, drove it for several more years, then reportedly sold it at a profit. Musk delights in telling the story, lingering on the risk to his life. In one interview, asked whether there were parallels with his approach to building companies, Musk said, “I hope not.” Appearing to consider the idea, he added, “Watch this. Yeah, that could be awkward with a rocket launch.”
Of all Musk’s enterprises, SpaceX may be the one that most fundamentally reflects his appetite for risk. Staff at SpaceX’s Starship facility, in Boca Chica, Texas, spent December of 2020 preparing for the launch of a rocket known as SN8, then the newest prototype in the company’s Starship program, which it hopes will eventually transport humans to orbit, to the moon, and, in the mission Musk speaks about with the most passion, to Mars. The F.A.A. had approved an initial launch date for the rocket. But an engine issue forced SpaceX to delay by a day. By then, the weather had shifted. On the new day, the F.A.A. told SpaceX that, according to its model of the wind’s speed and direction, if the rocket exploded it could create a blast wave that risked damaging the windows of nearby houses. A series of tense meetings followed, with SpaceX presenting its own modelling to establish that the launch was safe, and the F.A.A. refusing to grant permission. Wayne Monteith, then the head of the agency’s space division, was leaving an event at the Cape Canaveral Space Force Station when he received a frustrated call from Musk. “Look, you cannot launch,” Monteith told him. “You’re not cleared to launch.” Musk acknowledged the order.
Musk was on site in Boca Chica when SpaceX launched anyway. The rocket achieved liftoff and successfully performed several maneuvers intended to rehearse those of an eventual manned Starship. But, on landing, the SN8 came in too fast, and exploded on impact. (No windows were damaged.) The next day, Musk visited the crash site. In a picture taken that day, Musk stands next to the twisted steel of the rocket, dressed in a black T-shirt and jeans, looking determined, his arms crossed and his eyes narrowed. His tweets about the explosion were celebratory, not apologetic. “He has a long history of launching and blowing up rockets. And then he puts out videos of all the rockets that he’s blown up. And like half of America thinks it’s really cool,” the former NASA administrator Jim Bridenstine told me. “He has a different set of rules.”
Hans Koenigsmann, then SpaceX’s vice-president for flight reliability, started working on a customary report to the F.A.A. about the launch. Koenigsmann told me that he felt pressure to minimize focus on the launch process and Musk’s role in it. “I sensed that he wanted it taken out,” Koenigsmann said. “I disagreed, and in the end we wound up with a very different version from what was originally intended.” Eventually, Koenigsmann was told not to write a report at all, and a letter was sent to the F.A.A. instead. The agency, meanwhile, opened its own investigation. Monteith told me that he agreed with Musk that the F.A.A. had been conservative about a situation that presented little statistical risk of casualties, but he was nevertheless troubled. “We had safety folks who were very upset about it,” Monteith recalled. In a series of letters to SpaceX, Monteith accused the company of relying on data “hastily developed to meet a launch window,” launching “based on ‘impressions’ and ‘assumptions,’ ” and exhibiting “a concerning lack of operational control and process discipline that is inconsistent with a strong safety culture.” In its responses, SpaceX proposed various safety reforms, but also pushed back, complaining that the F.A.A.’s weather model was unreliable and suggesting that the agency had been resistant to discussions about improving it. (SpaceX did not respond to requests for comment.)
The following March, Steve Dickson, then the F.A.A.’s administrator, called Musk. The two men spoke for thirty minutes. Like Kahl, Dickson was deferential, thanking Musk for his role in transforming the commercial space sector and acknowledging that SpaceX was taking steps to make its launches less risky. But Dickson, an F.A.A. spokesperson said in a statement, “made it clear that the FAA expects SpaceX to develop and foster a robust safety culture that stresses adherence to FAA rules.” Dickson had navigated such conversations before, including with Boeing after two 737 max aircraft crashed. But this situation presented a thornier challenge. “It’s not every day that the F.A.A. administrator releases a statement about a phone call that they have with the C.E.O. or the head of an aerospace company,” an official at the agency told me. “That kind of gets into the soft pressure, public pressure that you don’t do unless you are trying to change the incentive structure.”
The F.A.A. issued no fine, though it grounded SpaceX for two months. “I didn’t see that a fine would make any difference,” Monteith told me. “He could pull that out of his pocket. However, not allowing launches, that would get the attention of a company that prides itself on being able to iterate and go fast.” Musk has continued to complain about the agency. After it postponed another launch, he tweeted, “The FAA space division has a fundamentally broken regulatory structure.” He added, “Under those rules, humanity will never get to Mars.”
Musk has been fixated on space since his childhood. The idea for SpaceX came about after his exile from PayPal. “I went to the NASA website so I could see the schedule of when we’re supposed to go” to Mars, Musk told Wired, in 2012. “At first I thought, jeez, maybe I’m just looking in the wrong place! Why was there no plan, no schedule? There was nothing.” In 2001, he connected with space-exploration enthusiasts, and even travelled to Russia in an unsuccessful bid to buy missiles to use as rockets. The next year, he moved to Los Angeles, closer to California’s aerospace industry, and ultimately he pulled together a team of engineers and entrepreneurs and founded SpaceX, to make his own rockets. Private rocket launches date back to the eighties, but no one had attempted anything on the scale that Musk envisioned, and it proved to be more difficult and expensive than he had anticipated. Musk has said that, by 2008, the company was nearly bankrupt, and that, after putting much of his wealth into SpaceX and Tesla, he wasn’t far behind. “That was definitely the worst year of my life,” he said in an interview on “60 Minutes.” SpaceX’s first three launches had failed, and there was no budget for another. “I had no more money left,” Musk told Bridenstine, the NASA administrator, years later. “We managed to put together enough spare parts to do a fourth launch.” Had that failed, he added, “SpaceX would have died.” The launch was successful, and NASA soon awarded SpaceX a $1.6-billion contract to resupply the International Space Station. In 2020, the company flew its first manned mission there—ending nearly a decade of American reliance on Russian craft for the task. SpaceX now launches more satellites than any other private company, with four thousand five hundred and nineteen in orbit as of July, occupying many of Earth’s orbital routes. “Once the carrying capacity of an orbit is maxed out, you’ve basically blocked everyone from trying to compete in that market,” Bridenstine told me.
There are competitors in the field, including Jeff Bezos’s Blue Origin and Richard Branson’s Virgin Galactic, but none yet rival SpaceX. The new space race has the potential to shape the global balance of power. Satellites enable the navigation of drones and missiles and generate imagery used for intelligence, and they are mostly under the control of private companies. “The U.S. government is in massive catch-up to build a more resilient space architecture,” Kahl, the former Pentagon Under-Secretary, told me. “And that only works if you can leverage the explosion of commercial space.” Several officials told me that they were alarmed by NASA’s reliance on SpaceX for essential services. “There is only one thing worse than a government monopoly. And that is a private monopoly that the government is dependent on,” Bridenstine said. “I do worry that we have put all of our eggs into one basket, and it’s the SpaceX basket.”
Even Musk’s critics concede that his tendency to push against constraints has helped catalyze SpaceX’s success. A number of officials suggested to me that, despite the tensions related to the company, it has made government bureaucracies nimbler. “When SpaceX and NASA work together, we work closer to optimal speed,” Kenneth Bowersox, NASA’s associate administrator for space operations, told me. Still, some figures in the aerospace world, even ones who think that Musk’s rockets are basically safe, fear that concentrating so much power in private companies, with so few restraints, invites tragedy. “At some point, with new competitors emerging, progress will be thwarted when there’s an accident, and people won’t be confident in the capabilities commercial companies have,” Bridenstine said. “I mean, we just saw this submersible going down to visit the Titanic implode. I think we have to think about the non-regulatory environment as sometimes hurting the industry more than the regulatory environment.”
In early 2022, Steven Cliff, then the deputy administrator of the Department of Transportation’s National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, learned that potentially tens of thousands of Tesla vehicles had a feature that he found concerning. For years, Tesla has been working to create a totally self-driving car, a long-standing ambition of Musk’s. Now Cliff was told that a version of Tesla’s Full Self-Driving software, an experimental feature that lets the cars navigate with little intervention from a driver, permitted cars to roll through stop signs, at up to about six miles an hour. This was clearly illegal. Cliff’s enforcement team contacted Tesla, and, in several meetings, a surprising conversation about safety and artificial intelligence played out. Representatives for Tesla seemed confused. Their response, as Cliff recalled, was “That’s what humans do all the time. Show us the data, why it’s unsafe.” N.H.T.S.A. officials told Tesla that, regardless of human compliance, “you should not be able to program a computer to break the law for you.” They demanded that Tesla update all the affected cars, removing the feature—a recall, in industry terms, albeit a digital one. “There was a lot of back-and-forth,” Cliff told me. “Like, at midnight on the very last day, they blinked and ended up recalling the rolling-stop feature.” (Tesla did not respond to requests for comment.)
Musk joined Tesla as an investor in 2004, a year after it was incorporated. (He has spent years defending the formative nature of his role and was eventually, in a legal settlement, one of several people granted permission to use the term “co-founder.”) Musk was again entering a market bound by entrenched private interests and stringent regulation, which opened him up to more clashes with regulators. Some of the skirmishes were trivial. Tesla for a time included in its vehicles the ability to replace the humming noises that electric cars must emit—since their engines make little sound—with goat bleats, farting, or a sound of the owner’s choice. “We’re, like, ‘No, that’s not compliant with the regulations, don’t be stupid,’ ” Cliff told me. Tesla argued with regulators for more than a year, according to an N.H.T.S.A. safety report. Nine days after the rolling-stop recall, the company pulled the noises, too. On Twitter, Musk wrote, “The fun police made us do it (sigh).”
“It’s a little like Mom and Dad and children. Like, How far can I push Mom and Dad until they push back?” Cliff said. “And that’s not a recipe for a strong safety culture.”
The fart debate had low stakes; the over-all safety of the cars is a far greater matter. Tesla has repeatedly said that Autopilot, a more limited technology than Full Self-Driving, is safer than a human driver. Last year, Musk added that he would be “shocked” if Full Self-Driving didn’t become safer than human drivers by the end of the year. But he has never made public the data needed to fully corroborate those claims. In recent months, new crash numbers from the N.H.T.S.A., which were first reported by the Washington Post, have shown an uptick in accidents—and fatalities—involving Autopilot and Full Self-Driving. Tesla has been secretive about the specifics. A person at the N.H.T.S.A. told me that the company instructed the agency to redact specifics about whether driver-assistance software was in use during crashes. (By law, regulators must abide by such requests for confidentiality, unless they decide to contest them in court.) Pete Buttigieg, the Secretary of Transportation, recently said that there were “concerns” about the marketing of Autopilot. Cliff told me he had seen data that showed Teslas were involved in “a disproportionate number of crashes involving emergency vehicles,” though he said that the agency had not yet determined whether the technology or the human drivers was the cause. In a statement, a spokesperson for the agency said, “Multiple investigations remain open.”
Officials who have worked at OSHA and at an equivalent California agency told me that Musk’s influence, and his attitude about regulation, had made their jobs difficult. The Biden Administration, which is urgently trying to reduce reliance on fossil fuels, has concluded that it needs to work with Musk, because of his dominant position in the electric-car market. And Musk’s personal wealth dwarfs the entire budget of OSHA, which is tasked with monitoring the conditions in his workplaces. “You add on the fact that he considers himself to be a master of the universe and these rules just don’t apply to people like him,” Jordan Barab, a former Deputy Assistant Secretary of Labor at OSHA, told me. “There’s a lot of underreporting in industry in general. And Elon Musk kind of seems to raise that to an art form.” Garrett Brown, a former field-compliance inspector at California’s Division of Occupational Safety and Health, added, “We have a bad health-and-safety situation throughout the country. And it’s worse in companies run by people like Elon Musk, who was ideologically opposed to the idea of government enforcement of public-health regulations.”
In March, 2020, as pandemic lockdowns began, Musk e-mailed Tesla employees, telling them that he intended to violate orders and show up at work, and downplaying the significance of COVID-19. Soon after, he lost an initial fight to keep a factory in Alameda County—Tesla’s most productive in the U.S.—open. That April, after county officials extended shelter-in-place orders, Musk was on a conference call with outside financial analysts. His rhetoric became nakedly political, to an extent that would have been uncharacteristic just a few years earlier. “I would call it forcibly imprisoning people in their homes against all of their constitutional rights,” he told the analysts, speaking of the lockdowns. “What the fuck?” he added. “It’s an outrage. An outrage. . . . This is fascist. This is not democratic. This is not freedom. Give people back their goddam freedom.” The pandemic seems to have sparked a pronounced shift in Musk. The lockdowns represented an example of what Hoffman told me Musk considered to be a cardinal sin: “getting in the way of the mission.”
The following month, Musk sent a series of vitriolic tweets, threatening to file suit against Alameda County, to move Tesla’s headquarters, and to flout the rules and reopen his factory, all of which he eventually did. The county essentially rubber-stamped the reopening soon afterward—a far cry from what Musk had invited. “I will be on the line with everyone else,” he had tweeted, at the height of his frustration. “If anyone is arrested, I ask that it only be me.”
Musk has, for much of his public life, presented himself as a centrist. “I’m socially very liberal,” he told the technology reporter Kara Swisher in 2020. “And then economically right of center, maybe, or center.” He has said that he donated to Hillary Clinton, and voted for both her and Joe Biden. But, in recent years, the more radical perspective that characterized his diatribes about Covid has come to the fore. In March, 2022, Twitter restricted the account of the satirical Web site the Babylon Bee, after the site misgendered a government official. The next day, in texts later disclosed during the Twitter-acquisition process, Musk’s contact “TJ” (identified by Bloomberg as his ex-wife Talulah Riley) expressed frustration with the development and urged him to purchase Twitter to “fight woke-ism.” The following week, Musk polled his followers about whether Twitter respected free speech and, in a phone call to the Babylon Bee’s C.E.O., joked about buying the platform. Finally, in April, 2022, he offered forty-four billion dollars for the company. Almost immediately, he tried to back out of the deal, prompting Twitter to sue. After months of legal proceedings, Musk resumed the acquisition process, and in October he assumed control of the company.
“Given unprovoked attacks by leading Democrats against me & a very cold shoulder to Tesla & SpaceX, I intend to vote Republican in November,” he tweeted last year. By the time he bought Twitter, he was urging his followers to vote along similar lines, and appearing to back Ron DeSantis, whose candidacy he helped launch in a technically disastrous Twitter live event. Although Musk’s teen-age daughter, Vivian, has come out as trans, he has embraced anti-trans sentiment, saying that he would lobby to criminalize “irreversible” gender-affirming care for children. (Vivian recently changed her last name, saying in a legal filing, “I no longer live with or wish to be related to my biological father in any way, shape or form.”) Musk started spreading misinformation on the platform: he shared theories that the physical attack on Paul Pelosi, the husband of the former Speaker of the House, had followed a meeting with a male prostitute, and retweeted suggestions that reports accurately identifying a mass shooter as a white supremacist were a “psyop.” Some people who know Musk well still struggle to make sense of his political shift. “There was nothing political about him ever,” a close associate told me. “I’ve been around him for a long time, and had lots of deep conversations with the man, at all hours of the day—never heard a fucking word about this.”
When Musk arrived at Twitter, he immediately gutted the company’s staff, reducing the number of employees by about fifty per cent. One person who kept his job was Yoel Roth, the company’s head of trust and safety. Roth, who is in his mid-thirties, is gay, Jewish, and liberal. His department was responsible for determining Twitter’s rules; during the Trump Administration, he became embroiled in the culture wars. After the company began rolling out a new fact-checking policy that labelled two of Trump’s tweets as misinformation, Kellyanne Conway, President Trump’s aide, went on “Fox & Friends” and read out Roth’s full name and spelled his username, adding, “He’s about to get more followers.” Trump then held up a New York Post cover mocking Roth, and Twitter users began recirculating tweets that Roth had written criticizing conservative candidates.
But when Musk took over he resisted calls to fire Roth. “We’ve all made some questionable tweets, me more than most, but I want to be clear that I support Yoel,” he tweeted in October, 2022. “My sense is that he has high integrity, and we are all entitled to our political beliefs.” That evening, Roth messaged Musk on Signal, thanking him. Musk responded, “You have my full support,” and, the next day, he followed up with a screenshot of a tweet from Roth that described Mitch McConnell as “a bag of farts.” Musk added, “Haha, I totally agree.”
But the cuts that Musk had instituted quickly took a toll on the company. Employees had been informed of their termination via brusque, impersonal e-mails—Musk is now being sued for hundreds of millions of dollars by employees who say that they are owed additional severance pay—and the remaining staffers were abruptly ordered to return to work in person. Twitter’s business model was also in question, since Musk had alienated advertisers and invited a flood of fake accounts by reinventing the platform’s verification process. On November 10th, Roth sent a brief resignation e-mail. When his departure became public, Musk texted, asking to talk. “I[t] would mean a lot if you would consider remaining at Twitter,” he wrote. The two spoke that night, and Roth declined to return. Days later, he published an Op-Ed in the Times, questioning the future of user safety on the platform. (Twitter did not respond to requests for comment.)
Soon afterward, Musk replied to a Twitter user surfacing a 2010 tweet from Roth, in which he’d shared a link to a Salon article about a teacher’s being charged with having sex with an eighteen-year-old student and asked, “Can high school students ever meaningfully consent to sex with their teachers?”
“That explains a lot,” Musk tweeted in reply. Minutes later, he posted an image showing a portion of Roth’s doctoral dissertation, which focussed on the gay-hookup app Grindr and its user data. In the excerpt, Roth argued that such platforms will inevitably be used by people under eighteen, so they should do more to keep those individuals safe. “Looks like Yoel is in favor of children being able to access adult internet services,” Musk wrote.
The attack fit a pattern: Musk’s trolling has increasingly taken on the vernacular of hard-right social media, in which grooming, pedophilia, and human trafficking are associated with liberalism. In 2018, when a Thai youth soccer team was trapped in a cave, Musk travelled to Thailand to offer a custom-made miniature submarine to rescuers. The head of the rescue operation declined, and Musk lashed out on Twitter, questioning the expertise of the rescuers. After one of them, Vernon Unsworth, referred to the offer as a “P.R. stunt,” Musk called him a “pedo guy.” (Unsworth sued Musk for defamation, characterizing the harassment he received from Musk’s followers as “a life sentence without parole.” A judge ruled in favor of Musk, who argued that he hadn’t been accusing Unsworth of actual pedophilia, just trying to insult him.)
Musk’s tweet about Roth got nearly seventeen thousand quote tweets and retweets. “The moment that it went from being a moderation conversation to being a Pizzagate conversation, the risk level changed,” Roth told me. “I spent my career looking at the absolute worst things that the Internet could do to people. Certainly, worse things have happened to people. But this is probably up there.” Roth and his husband were forced to flee their house, a two-bedroom in El Cerrito, California, that they’d purchased just two years earlier. “And then as we are, like, packing our stuff and leaving and getting the dog loaded into the car and whatever, like, the Daily Mail publishes an article that gives people more or less a map to my house,” Roth said. “At that point, we’re, like, ‘Oh, we’re leaving this house potentially for the last time.’ ”
This summer, Twitter’s cheerful blue bird logo came down from the roof of the company’s headquarters, in San Francisco, and was replaced with a strobing “X.” The new entity is a marriage between two parts of Musk. There’s his career-long quest to create an everything app—integrating services ranging from communication to banking and shopping, and emulating products, like WeChat, that are popular in Asia. Sitting alongside that pragmatic goal is a newer, more confusing side of Musk, embodied by his desire to take back the town square from what he sees as woke discourse. Twitter has become a private company, so it’s difficult to assess its finances, but numerous prominent advertisers have departed, and Meta recently launched Threads, a competitor that shamelessly emulates the old Twitter, and broke records for downloads. Musk threatened to sue, then challenged Mark Zuckerberg, Meta’s founder and C.E.O., to a cage match, pledging to live-stream it and donate the proceeds to charity. (Zuckerberg has accepted. Musk has delayed committing to a date, citing a back injury.) The illuminated sign atop X’s headquarters, after complaints to the Department of Building Inspection, came down as quickly as it had gone up.
Some of Musk’s associates connected his erratic behavior to efforts to self-medicate. Musk, who says he now spends much of his time in a modest house in the wetlands of South Texas, near a SpaceX facility, confessed, in an interview last year, “I feel quite lonely.” He has said that his career consists of “great highs, terrible lows and unrelenting stress.” One close colleague told me, “His life just sucks. It’s so stressful. He’s just so dedicated to these companies. He goes to sleep and wakes up answering e-mails. Ninety-nine per cent of people will never know someone that obsessed, and with that high a tolerance for sacrifice in their personal life.”
In 2018, the Times reported that members of the Tesla board had grown concerned about Musk’s use of the prescription sleep aid Ambien, which can cause hallucinations. The Wall Street Journal reported earlier this year that he uses ketamine, which has gained popularity both as a depression treatment and as a party drug, and several people familiar with his habits have confirmed this. Musk, who smoked pot on Joe Rogan’s podcast, prompting a NASA safety review of SpaceX, has, perhaps understandably, declined to comment on the reporting that he uses ketamine, but he has not disputed it. “Zombifying people with SSRIs for sure happens way too much,” he tweeted, referring to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, another category of depression treatment. “From what I’ve seen with friends, ketamine taken occasionally is a better option.” Associates suggested that Musk’s use has escalated in recent years, and that the drug, alongside his isolation and his increasingly embattled relationship with the press, might contribute to his tendency to make chaotic and impulsive statements and decisions. Amit Anand, a leading ketamine researcher, told me that it can contribute to unpredictable behavior. “A little bit of ketamine has an effect similar to alcohol. It can cause disinhibition, where you do and say things you otherwise would not,” he said. “At higher doses, it has another effect, which is dissociation: you feel detached from your body and surroundings.” He added, “You can feel grandiose and like you have special powers or special talents. People do impulsive things, they could do inadvisable things at work. The impact depends on the kind of work. For a librarian, there’s less risk. If you’re a pilot, it can cause big problems.”
On July 12th, Musk announced xAI, his entry into a field that promises to alter much about life as we know it. He tweeted an image of the new company’s Web site, featuring a characteristically theatrical mission statement: the firm’s goal, he said, was “to understand the true nature of the universe.” In the image, Musk highlighted the date and explained its significance. “7 + 12 + 23 = 42,” the text read. “42 is the answer to the Ultimate Question of Life, the Universe, and Everything.” It was a reference to “The Hitchhiker’s Guide to the Galaxy.” In the series, an immensely complex artificial intelligence is asked to answer that question and, after computing for millions of years, answers with Adams’s most famous punch line: 42. “I think the problem, to be quite honest with you, is that you’ve never actually known what the question is,” the computer says. Earth itself, and all the organisms on it, are ultimately revealed to be a still larger computer, built to clarify the question. Adams does not portray this satirical vision as positive. Musk’s announcement suggested more optimism: “Once you know the right question to ask, the answer is often the easy part.”
Musk has been involved in artificial intelligence for years. In 2015, he was one of a handful of tech leaders, including Hoffman and Thiel, who funded OpenAI, then a nonprofit initiative. (It now has a for-profit subsidiary.) OpenAI had a less grandiose and more cautious mission statement than xAI’s: to “advance digital intelligence in the way that is most likely to benefit humanity.” In the first few years of OpenAI, Musk grew unhappy with the company. He said that his efforts at Tesla to incorporate A.I. created a conflict of interest, and several people involved told me that this was true. However, they also said that Musk was frustrated by his lack of control and, as Semafor reported earlier this year, that he had attempted to take over OpenAI. Musk still defends his centrality to the company’s origins, stressing his financial contributions in its fledgling days. (The exact figures are unclear: Musk has given estimates that range from fifty million to a hundred million dollars.) Throughout his involvement, Musk seemed preoccupied with control, credit, and rivalries. He made incendiary remarks about Demis Hassabis, the head of Google’s DeepMind A.I. initiative, and, later, about Microsoft’s competing effort. He thought that OpenAI wasn’t sufficiently competitive, at one point telling colleagues that it had a “0%” chance of “being relevant.” Musk left the company in 2018, reneging on a commitment to further fund OpenAI, one of the individuals involved told me. “Basically, he goes, ‘You’re all a bunch of jackasses,’ and he leaves,” Hoffman said. The withdrawal was devastating. “It was very tough,” Altman, the head of OpenAI, said. “I had to reorient a lot of my life and time to make sure we had enough funding.” OpenAI went on to become a leader in the field, introducing ChatGPT last year. Musk has made a habit of trashing the company, wondering repeatedly, in public interviews, why he hasn’t received a return on his investment, given the company’s for-profit arm. “If this is legal, why doesn’t everyone do it?” he tweeted recently.
It is difficult to say whether Musk’s interest in A.I. is driven by scientific wonder and altruism or by a desire to dominate a new and potentially powerful industry. Several entrepreneurs who have co-founded businesses with Musk suggested that the arrival of Google and Microsoft in the field had made it a new brass ring, as space and electric vehicles had been earlier. Musk has maintained that he is motivated by his fear of the technology’s destructive potential. In a podcast earlier this year, Ari Emanuel, the head of the Hollywood agency W.M.E., recalled Musk joking about an A.I.-dominated future. “Ari, do you have dogs?” Musk asked him. “Well, here’s what A.I. is to you. You’re the dog.” In March, Musk, along with dozens of tech leaders, signed an open letter calling for a six-month pause in the development of advanced A.I. technology. “Contemporary AI systems are now becoming human-competitive at general tasks, and we must ask ourselves: Should we let machines flood our information channels with propaganda and untruth?” the letter said. “Should we automate away all the jobs, including the fulfilling ones? Should we develop nonhuman minds that might eventually outnumber, outsmart, obsolete and replace us?”
Yet in the period during which Musk endorsed a pause, he was working to build xAI, recruiting from major competitors, including OpenAI, and even, according to someone with knowledge of the conversation, contacting leadership at Nvidia, the dominant maker of chips used in A.I. The month the letter was distributed, Musk completed the registrations for xAI. He has said little about how the company will differ from preëxisting A.I. initiatives, but generally has framed it in terms of competition. “I will create a third option, although starting very late in the game of course,” he told the Washington Post. “That third option hopefully does more good than harm.” Through A.I. research and development already under way at Tesla, and the trove of data he now commands through Twitter (which he recently barred OpenAI from scraping in order to train its chatbots), he may have some advantage, as he applies his sensibilities and his world view to that race. Hoffman told me, “His whole approach to A.I. is: A.I. can only be saved if I deliver, if I build it.” As humanity creates A.I. in its own image, Hoffman argued, the principles and priorities of the leaders in the field will matter: “We want the construction of this to be not people with Messiah complexes.”
At one point in “The Hitchhiker’s Guide,” Adams introduces the architects of the Earth supercomputer. They’re powerful beings who have been living among us, disguised as mice. At first, they were motivated by simple curiosity. But seeking the question made them famous, and they began considering talk-show and lecture deals. In the end, Earth is demolished in the name of commerce, and their path to existential clarity along with it. The mice greet this with a shrug, mouth vague platitudes, and go on the talk-show circuit anyway. Musk isn’t peddling pabulum. His initiatives have real substance. But he also wants to be on the show—or, better yet, to be the show himself.
In the open letter, alongside questions about the apocalyptic potential of artificial intelligence was one that reflects on the sectors of government and industry that Musk has come to shape. “Should we risk loss of control of our civilization?” he and his fellow-entrepreneurs wrote. “Such decisions must not be delegated to unelected tech leaders.” Published in the print edition of the August 28, 2023, issue.
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
The competition's motto is "united by music," and the EBU, a group of public media organizations, sees itself as an "apolitical" entity putting on an "apolitical" event. (Israel, alongside other non-European nations like Australia, Azerbaijan, and Georgia, is allowed to participate through membership in the EBU.) But in Feb. 2022, one day after Russia invaded Ukraine, the EBU announced the country was banned from participating in the song contest. “The decision reflects concern that, in light of the unprecedented crisis in Ukraine, the inclusion of a Russian entry in this year’s Contest would bring the competition into disrepute," the statement read. Yet this year, the EBU ignored calls from artists, politicians, and fans to remove Israel from the contest after the IDF launched its ongoing, brutal counter-attack on the Gaza strip following the Hamas-led attack on Oct. 7. In the months since, 1,139 Israelis and more than 35,000 Palestinians have been killed in the conflict. This might seem hypocritical, and it is. But the comms specialists have their own explanation. According to a Eurovision FAQ page created to defend the organization's decision to allow Israel to compete, the EBU clarified that Russia was suspended because of the Russian broadcasters' "persistent breaches of membership obligations and the violation of public service values." The issue, it seems, was never the invasion, could never be the genocide. "When 10,000 civilians are killed in more than two years in Ukraine, Eurovision is political. When 40,000 are killed in Gaza in just 7 months, most of whom women and children, the competition is non-political," wrote Fianna Coleman in a piece for Tribune Mag. Like anywhere else, being "apolitical" at Eurovision is a political act. In 2019, when Eurovision was held at Tel Aviv, Iceland was fined after their entry, the band Hatari, held up scarves decorated with Palestinian flags as the results were announced. The EBU issued the fine, it said, because Hatari's action violated the competition's rules banning political messages during the competition. The only flags that are allowed at Eurovision are the flags of competing countries, as well as pride flags. So while fans and performers were banned from carrying Palestinian flags, the Israeli flag remained, by Eurovision's rules, perfectly allowed.
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
look, as far as im concerned, eurovision lost their right to call themselves ‘non-political’ once they banned russia from competing in 2022. if they can ban russia for the invasion of ukraine, it is their DUTY to ban israel for its continued genocide in gaza. they keep trying to remove palestinian symbols and as far as ive heard hav also actively made some contestants remove ‘ceasefire now’ quotes and imagery from their performances. you do not get to make the ‘non-political’ argument anymore because it no longer holds any water. allowing israel to compete while actively censoring palestinian support IS political. you’ve chosen your side. and we will not forget what choice that was.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
EBU authorises Israel’s participation in Eurovision
The European Broadcasting Union (EBU) has announced that it does not intend to ban Israel’s participation in this year’s Eurovision Song Contest.
The EBU also stated that it wanted to maintain the competition’s status as a non-political event that united listeners around the world through music.
The decision not to ban Israel faced opposition: more than 1,400 Finnish musicians signed a petition demanding that Israel not be allowed to participate in the competition, accusing the country of crimes in Gaza. Lukas Korpelainen, the initiator of the petition, stated:
Israel violates human rights. We don’t think it’s okay for the country to be part of the (Eurovision) to polish its image.
The EBU, which banned Russia from competing in 2022 due to the war in Ukraine, rejected calls back in December to ban Israel, which has been carrying out bombardments in the Gaza Strip with more than 25,000 deaths, from the contest.
Read more HERE

#world news#world politics#news#europe#european news#european union#eu politics#eu news#eurovision#eurovision 2024#eurovision song contest#esc 2024#esc#israel#israel palestine conflict#israel hamas war#middle east#gaza#middle east news#middle east conflict#middle east war#middle east crisis#current events#human rights#international law#human rights violations#esc 2022#eurovision 2022#russia#russia news
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
I know everyone is angry at the seeming double standards between the treatment of Israel compared to how swiftly Russia was expelled after they invaded Ukraine, but you need to remember that Russia was going to be allowed to compete in 2022 until other participating countries threatened to boycott and the EBU reversed their decision within 24 hours.
I've seen a lot of people saying they'll boycott the contest but right now that's honestly the wrong approach because it's 6 months out and action needs to be taken NOW.
The best thing you can do if you're angry at Israel's inclusion is to lobby your participating broadcaster to take a stand because at this point in the process they are the ones who hold the cards to make the EBU listen. The list of this years broadcasters is HERE
iceland is threatening to pull out of eurovision unless israel is removed... please g-d let them blacklist israel that would be so huge
#I've seen loads of people talking about viewer boycotts and frankly it's pointless#Some broadcasters will undoubtedly be more sympathetic based on their national governments messaging#But what is the point in waiting to send a message 6 months down the line? It's too late by then#If other broadcasters are making noises and there's enough viewer discontent it could spur the EBU into taking action sooner#There are other complexities that make this slightly different to 22#But jeez if your pissed do NOT wait until May to take action#Being kicked out of eurovision didn't stop Russia and it won't stop Israel but it will send a message
51K notes
·
View notes