#i LOVE conlangs
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
oh no no no i'm screwed
i realised that since tamar is an average uneducated commoner from cyrodiil, she probably doesn't speak/understand nordic, or at least not well
then i was like, okay but maybe if she lived close to the border she might?
well anyways fast forward a bit and now i'm knee deep in researching the linguistic anthropology of tamriel, and decided that tamar canonically knows at least 5 different varients of Cyrodilic, has lived in at least 4 different regions, and can partially understand Nordic but it's with guesswork involved, like with speakers of modern romance languages trying to communicate with one another
i'm just like

LINGUISTICS
#i was a linguistics and creative writing major in college#almost went into cultural anthropology too#so yeah i'm very thoroughly fucked#i just KNOW im gonna spend way too much time getting into tamriel's languages and shit#and if there's any official conlangs for em?? bye#i LOVE conlangs#i literally used to be able to speak conversational sindarin#and i can speak a little bit of mando'a as well#i fuckin love conlangs man don't try me#is any of this even coherent?? idk whatever#yaz yaks
0 notes
Text
As much as I adore conlangs, I really like how the Imperial Radch books handle language. The book is entirely in English but you're constantly aware that you're reading a "translation," both of the Radchaai language Breq speaks as default, and also the various other languages she encounters. We don't hear the words but we hear her fretting about terms of address (the beloathed gendering on Nilt) and concepts that do or don't translate (Awn switching out of Radchaai when she needs a language where "citizen," "civilized," and "Radchaai person" aren't all the same word) and noting people's registers and accents. The snatches of lyrics we hear don't scan or rhyme--even, and this is what sells it to me, the real-world songs with English lyrics, which get the same "literal translation" style as everything else--because we aren't hearing the actual words, we're hearing Breq's understanding of what they mean. I think it's a cool way to acknowledge linguistic complexity and some of the difficulties of multilingual/multicultural communication, which of course becomes a larger theme when we get to the plot with the Presgar Translators.
#imperial radch#also a great example of the 'you don't have to be Tolkien' phenomenon#if you want to think about linguistic differences by building all the languages in your setting#and being able to explain what those differences are through actual texts in the language in question#that's AWESOME#but it's not the only way to do it#it's also interesting because of course this style only works in book form#everyone's speaking different languages but in a written account they're all 'translated' for you#but of course if it was a TV series they would all have to be speaking a language the audience understands#(or you *would* have to go wild with conlangs)#and i think that's really cool as well--#how for a series where song is so central we don't actually hear any of the actual in-universe words or any of the music#it's all been filtered#and again you know this is happening but seeing the examples of how real songs--the shape hymns and 'L'homme Arme'--are presented#makes you a lot more viscerally aware of how limited your perspective is#it's good#ann leckie i love you
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
speaking of codes and music, in the 1800s someone made a language encoded not in spoken words, but in musical notes. its not english encoded in music either, it has a unique grammatical structure.
Thinking about the piano in the Creel house and knowing someone played piano. Henry doesn't sing or dance, and we don't have any hints that he's musical, but...Both eyes on Lucas's quip about playing a secret chord on the piano right after that shot of the chess set. Thinking abut how that connects to Henry having made ciphers/codes in other ways...Henry, did you ever play piano/take lessons?
I know it definitely would have been more popular for it to have been Alice, since she's a girl, but...if Virginia was so focused on Henry being kept isolated, piano is a perfect way to fill up after-school hours before dinner.
27 notes
·
View notes
Text
WAIT okay I don't know how to word this at all but basically the way we perceive speech sounds is through like. different frequencies are amplified or dampened by the ways we shape our vocal tract and we hear those differences in like which frequencies are louder and which frequencies are quieter and that's how we recognize different phonemes. or something. so if like aliens have a different hearing range and/or differently shaped vocal tracts they could have an entirely different phonemic inventory than human languages??? like shrimp colors but it's alien phonemes???? this might seem like a really obvious realization but like those guys could be distinguishing vowels based on formants we can't even perceive!! their hearing range could start above 5000 hz and they wouldn't be able to hear the difference between any of our vowels!! enough with giving klingon uvular plosives or whatever to make it sound ""exotic"" that shit should be UNPRODUCIBLE with a human vocal tract and UNPERCEIVABLE with human ears!! no wonder they need universal translators when your ears could be physically unable to distinguish between alien phonemes??? sorry I'm realizing that this really is an incredibly obvious thought just couched in overly technical language but I'm excited about it nonetheless. spock's surname is unpronounceable bc it's got a bunch of consonant clusters? NO it actually has secret vulcan phonemes distinguished by differences in frequencies above the human range of hearing so u can't even perceive it correctly let alone pronounce it. cardassians have a hearing range significantly smaller than humans so they physically cannot understand most human languages...
#shrimp colors alien phonemes.........#I. understand why we conlang within our physical limits as humans but it's a fun thought experiment idk#I love u phonetics 2 class.#narcissus's echoes#lingposting
155 notes
·
View notes
Text
okay SO. it took longer than I expected for various life reasons but here is the massive conlang masterpost, featuring all the languages and prominent dialects that I imagine would exist within the grishaverse. under a cut bc it got really long!
RAVKA
"standard" Ravkan. this is the language spoken in Os Alta, as well as most other places in East Ravka. used on any official documents within Ravka. spoken by most nobility, including those in West Ravka
West Ravkan. this dialect formed only after the creation of the Fold - because the two sides of the country were separated from each other, linguistic drift occurred. over the 400 years that the Fold existed, the two languages diverged from each other significantly, but are still mutually intelligible - they're still very clearly dialects of the same language, not separate languages altogether. most West Ravkan nobility don't use this dialect, although those who are in favour of West Ravka becoming an independent country WILL use this dialect to promote independence. many West Ravkans also speak "standard" Ravkan, because of military service; they would have to communicate with people from across the country - however, many of them would still speak West Ravkan at home, with family, etc. most East Ravkans, especially nobility, wouldn't speak West Ravkan and would probably look down on those who do; I imagine Nikolai speaks at least some because it's the kind of thing he'd do (and the place he's Grand Duke of, Udova, is in West Ravka)
Suli. definitely a completely separate language from Ravkan; they don't have much in common. spoken predominantly by travelling Suli, and very rarely by non-Suli - although in canon, it is taught at the Little Palace, and some Grisha will learn the language. diplomats who often have dealings with Suli communities, and soldiers who serve in areas with high Suli populations, will often learn some (though probably not enough to become fluent) - canon states that it's useful for travelling in the west and northwest of Ravka.
Suli/Ravkan dialect. in areas with high Suli populations (predominantly in the west and northwest), locals may have adopted parts of the Suli language, and vice versa, to create a pidgin language that can be understood by both groups. probably NOT spoken by soldiers/diplomats/etc, who prefer to learn the original Suli language
various other dialects! while the most significant difference is between "standard" and West Ravkan, small towns and communities across the country will speak slightly different versions of the language, just because of how big Ravka is
ancient Ravkan. this is briefly mentioned in canon - I imagine it bears a similar relationship to modern Ravkan as that between Old English and modern English; ie, it's a completely different language! very old books that were printed in ancient Ravkan probably still exist; I imagine it's spoken by some members of the clergy, similar to how the Catholic Church uses Latin in our world. often studied by historians or other scholars. iirc Mal's tattoo is also written in ancient Ravkan, which means that either he or somebody around him must have spoken it fairly well. I would guess that Tamar and Tolya probably speak at least some ancient Ravkan because they grew up in the church
FJERDA
"standard" Fjerdan. again, spoken in Djerholm, by the military and by the government. fun canon facts I found while researching for this: all nouns are both plural and singular (similar to English words like "fish") and the language has three grammatical genders, but they are called wolf class, hare class, and tooth class!
Hedjut. the Hedjut, in canon, are an indigenous group living on Kenst Hjerte, a pair of islands off the coast of Fjerda. though some have come to live on the mainland (I believe Ylva, Jarl Brum's wife, is Hedjut?) most still live on the islands and speak their own language, separate from Fjerdan
liturgical Fjerdan. religion plays a huge part in Fjerdan culture, and imo their holy texts would have been written in this liturgical version of the language, many centuries before canon takes place. drüskelle are probably taught liturgical Fjerdan. some people might also prefer to pray to Djel in liturgical Fjerdan? speakers of modern Fjerdan can probably understand it, but with some effort
again, multiple other dialects. Fjerda has a lot of peninsulas; the language would have developed differently in different places. when Nina is in the Elling peninsula in KoS, she probably has to speak the local dialect rather than the "standard" Fjerdan which she probably learnt in training
other indigenous languages. now, this is purely conjecture, but the grishaverse map shows other small islands off the coast of Fjerda, which don't seem to be part of Kenst Hjerte. it's entirely possible that there's other indigenous groups, like the Hedjut, living there, with their own separate languages. on the other hand, in an age of sea travel, it's likely that Fjerda would have colonised those islands and brought them into the larger country, meaning that the groups living there would be classed as Fjerdans and encouraged to speak Fjerdan
KERCH
"standard" Kerch. this one is so interesting because Kerch is canonically the language used for international trade, so diplomats and politicians across the grishaverse would likely be able to speak Kerch. knowing the language is probably also a sign of status in other countries, including Ravka. it's spoken by most people within Kerch, as well as being the language used for any kind of international relations. for example, I imagine that at the summit at the end of Rule of Wolves, both the Ravkan and Fjerdan delegations spoke Kerch
Barrel Kerch. has a similar relationship to "standard" Kerch as Cockney does to "standard" English - they're recognisably the same language, though spoken with very different accents, but Barrel Kerch has created so much new vocabulary that doesn't exist in "standard" Kerch. I also think that this is why Wylan didn't recognise the word "mark" in Six of Crows - it simply didn't exist in the version of Kerch he's used to speaking!
other dialects. Kerch is much smaller than Ravka or Fjerda, so I imagine there's fewer separate dialects, but people living in the Kerch countryside probably speak a slightly non-"standard" version of Kerch. Kaz probably grew up speaking a country dialect, and had to adjust when he started living in Ketterdam
SHU HAN
official Shu. probably? we know very, very little about the language(s) within Shu Han, but it's a fair bet that there's an official version of the language used by the government etc. this is probably the dialect that's taught to students studying Shu, particularly noble children or diplomats. its main difference from common Shu is that it has a smaller, simpler vocabulary and is easier to communicate effectively in
"common" Shu. in canon, we get a lot of references to words or phrases in Shu that are untranslatable - often in poetry or literature. that would probably be really impractical for a language used in business, so imo the dialect used by most people would be slightly different from the dialect used in government. this dialect has a lot of flowery, poetic language.
other dialects. while Shu Han is smaller than Ravka, it's still pretty big, so I imagine that again, there would be slightly differing variants of the language spoken in different places
THE WANDERING ISLE
there is no standard version of Kaelish. in my personal headcanon, the Wandering Isle is based on a mix of multiple different Celtic cultures and so has multiple different languages. honestly I could make a whole other masterpost based on my headcanons for the Wandering Isle, but I'll stick to the languages for now
Central Kaelish. this is what I imagine Colm and Jesper speak; it's loosely based on Welsh, given that Jesper's middle name is Welsh. it's probably Colm's first language, but he taught Jesper to speak it so he wouldn't lose touch with his Kaelish heritage
North Kaelish. this is what I think Pekka Rollins's dialect is; loosely based on Scottish Gaelic
basically, there's dozens of dialects across the country; some of them overlap somewhat with others, while some are more distinct
NOVYI ZEM
okay SO. once again there's like, zero canon material to work with here, but it's fine. canonically the language spoken is Zemeni. like with most of these countries, there's probably a "standard" version which is used for official purposes, spoken in and around the capital city, Shriftport
Northern Zemeni. the capital city is in the south of the country, so the dialect which differs most from "standard" Zemeni is probably spoken mostly in the north
other dialects. if I had to guess, I'd say that the other big separation of dialects is between coastal areas and inland areas - coastal cities which see a lot of trade would probably use "standard" Zemeni, so they can communicate with people who've learnt Zemeni (who would likely have studied the "standard" dialect), while inland areas would have developed their own dialects
OTHER AREAS
the Southern Colonies: is canonically a colony of Kerch, so their official language is probably "standard" Kerch. it's also canonically a place where criminals from Kerch are exiled (and the former King and Queen of Ravka, but that's almost certainly a rare exception) so there's probably also a lot of Barrel Kerch being spoken, that the criminals have brought over
there's almost certainly at least one indigenous language spoken there as well, though. whatever culture it used to have before being colonised by Kerch probably hasn't been entirely erased. the closest real-world comparison is probably Australia, where English criminals used to be sent? so I do think that there are indigenous groups living there, with their own culture and languages
a dialect has probably formed that mixes parts of Kerch with parts of the indigenous language, forming a new pidgin so that locals and new arrivals can communicate
if the Southern Colonies ever gets independence, I imagine that the original indigenous language would become its official language - the pidgin is probably used more day-to-day, though
it's also possible that the Southern Colonies used to be a part of Novyi Zem before being colonised; in which case, the indigenous people might speak Zemeni? I personally think it's separate, though
the Bone Road: a set of islands, near the Wandering Isle. apparently there are dozens but only two have names - the names they've been given sound vaguely Ravkan. I imagine that those two, Jelka and Vilki, have been "discovered" by Ravkan explorers (though probably not colonised? I think if they were Ravkan territories that would've been mentioned when Nikolai takes Alina to the Bone Road in S&S) and given Ravkan names
however, all of the islands have their own cultures and languages. they're pretty small islands so I don't think that there would be many different dialects within each island. on the other hand, I wouldn't be surprised if the languages spoken on each island were all quite similar to each other, though recognisably distinct. they're probably all at least from the same language family
#holy shit this took ages lmao#but I'm really proud of it!!#if anybody has any questions about any of this DEFINITELY send them my way - I'd love to chat about linguistics/conlangs/etc#I might actually make that Wandering Isle masterpost sometime tbh bc I have soooo many thoughts#mayhem.txt#grishaverse#mayhem grishaverse originals#I really hope I haven't forgotten anything here lmao#shadow and bone#six of crows#king of scars
94 notes
·
View notes
Text
OH PHIL BEING FULL ON INFODUMPING ABOUT LINGUISTICS THIS IS EVERYHING TO MEEEEEEE
#I LOVE THIS SHIT#I LEARNED LIKE A TINY AMOUNT I KNOW ABOUT LINGUISTICS BC I GOT OBSESSED WITH CONLANGS A WHILE BACK#YEAH CALL ME A LABIODENTAL FRICATIVE#dan and phil#phan
255 notes
·
View notes
Text
every youtuber ever: Always start your conlang with the phonetic inventory! always start here! you can't do anything without it! let's make one together: slap some vowels here, some consonants there, and you're done!
me: But what if I want my conlang's phonology and phonotactics to be complex, both for phonaesthetic purposes and to accurately reflect the natlangs I'm basing it on? What if this task becomes an insurmountable roadblock that prevents me from making any further progress?
youtuber: sucks for you then ig
#I'm making broad generalizations because I'm salty#RHGJFKJGHFDGKJN#CAN ANYONE HELP ME#IM SO FED UP WITH THIS STUPID LANG#that's a lie I love conlanging#but please#conlang#language creation#constructed language#language construction#my posts#phonology#phonetics
44 notes
·
View notes
Text
Me, an hour into explaining the plot of the first third of CoH: and then he goes with this elf guy to this other elf guy, his name is Thingol-
My sibling, only paying a little attention: wait isn't that the guy who banned quinoa
#i'm crying about it gang its so funny#ah yes#my favorite conlang#quinoa#i love them theyre so funny sometimes#don't worry they ranted back at me#song being loud
223 notes
·
View notes
Text

ntaalapraraasat sakunni kuvirutlip'ia. The feelings of the dead weigh less than a feather.
#conlang#constructed language#translation#conscript#constructed script#artlang#anni#arhanngi#conlanging#I love forcing art when I dont want to draw#definitely not my best drawing
83 notes
·
View notes
Text
i highly doubt Slugterra's human residents speak Surface language, given they've been separated from the Burning World for thousands of years. not to mention the fact that they've been surrounded by many non-human species, one of which canonically has their own language (the Shadow Clan). they also have their own unique written language, so it wouldn't be far-fetched to say their verbal language is different, too.
Eli automatically understands everyone the moment he comes through The Drop though, so ignoring the fact that this is a kid's show with surface-level (hah) worldbuilding, i like to think that during Will's visits he'd teach Eli the Terran language. Tad was probably in the same boat, with his mom probably teaching the language to him? maybe? given she was in some way affiliated with Dr. Blakk. somehow. although Tad's whole....situation....is a bit of a logistical nightmare.
anyway "floppers" as a canonical curse word is funny, and Will probably didn't teach that to Eli (although i love the idea of him probably accidentally letting it slip one time and had to pull the "you'll understand when you're older" card). so Eli being the first person in A While to say the English word "fuck" in the caverns with no one else knowing what it means until Tad comes along is peak comedy to me.
#.txt#slugterra#eli after messing up a shot: fucking goddammit#the shane gang: ????#if i were smarter i'd love to come up w a slugterran conlang. and by extension a slugterran biological taxonomy#love this kinda shit. love making things overly complex for a show maybe 15 other ppl care about
58 notes
·
View notes
Text
concept i've been thinking about lately: feanor writes all his notes in conlangs. so no one else can understand them, of course. except sometimes, he can't understand them either. this is the real reason why the silmarils were a one time thing.
#imagine: ñolo tries to sneak into feanaro's office and get his notes to figure out what hes working on and he just#cant understand any of it#iconic#tell me feanor wouldnt do his#and he would keep a journal where he talked shit about his brothers and indis also in conlangs#and eventually ñolo finds the key/notes for one of them and learns it#and just casually greets 'naro in it one day#and feanor's just like 👁️👄👁️#i love them your honor#feanor#feanaro#sons of finwe#nolofinwe#arafinwe#fingolfin#finarfin#indis#miriel#finwe#silm#silmarillion#tolkien#valinor#silmarils
275 notes
·
View notes
Text

god can no longer help me ive written prose. conlang prose
edit: this is more like poetry than prose i dont know my language arts
#conlang#constructed language#conlang writing#writing#prose#feel free to ask for translations i would love to get into more detail on this#ferise#herise#ferise/herise
50 notes
·
View notes
Text
hungarian words are so funny sometimes. calculator? that's the counting machine. airplane? you mean the flying machine. rain? the thing that falls. river? oh yeah, that's the thing that flows. deer? the animal with horns.
#i'm amusing myself by making up conlang words#& i have decided i'm stealing “the thing that falls” and “the thing that flows”#they are hysterical words. i love them.#eső & folyó my besties
295 notes
·
View notes
Text
Guys I like kinda need to be good at the deciphering system in Homicipher because I am straight a linguistics major; like if the monster dating simulator game defeats me through its use of intermixing SOV and SVO then I am COOKED for my syntax exam
#homicipher#ramblings#my syntax exam is in like 36 hours#Homicipher can be counted as syntax practice right?? right???#gurl if I get an A- in that class I’m like dropping my major idc#I love syntax and thinking of words and whatever#but unfortunately the East Asian language I’m learning is heavily case-based#y’know the monster language is basically a conlang I wonder if the creator did any linguistic research??#maybe the translation messed some of it up or maybe it’s just very similar to Japanese I mean it’s more SOV imo
29 notes
·
View notes
Note
My dearest, tell me about your conlang scripts, please❣
Yeassss thank you beloved I will now kill for you <3 Ask me to kill for you.
I truly do not know how long this is going to end up but I'm just gonna go for it.
Montaran
Montaran is fauns' native language: it is alphasyllabic (rather than alphabetic), made up of character 'blocks' that are themselves composed of syllabic components. It's based off a mix of Korean and Sanskrit (mostly Brahmi script).

⬆️ "This is an example sentence" written in Montaran. Pronounced "Bavna mōskadatōk nin."
Components are arranged in blocks of three max, with spaces between words. It's written and read top to bottom, left to right. In three-component characters (called full blocks or complete characters), the arrangement of the components tells you where the syllabic emphasis is.

Here's the same sentence but with the components split up. The first word bavna has it's emphasis on the syllable na, and you can tell by reading because it's alone, as opposed to the other two components, which share space on the top of the block. The second word, Mōskadatōk, has its emphasis on the first and fourth syllables mō and da- the ones that are alone in their vertical placement. For partial blocks, like the last word nin, you can't tell emphasis by reading it.
Montaran is an abugida, which means its alphasyllabary is made up of consonant letters and small, diacritic-like additions that determine vowel sounds. Consonants can exist alone, but vowels must be connected to a consonant.

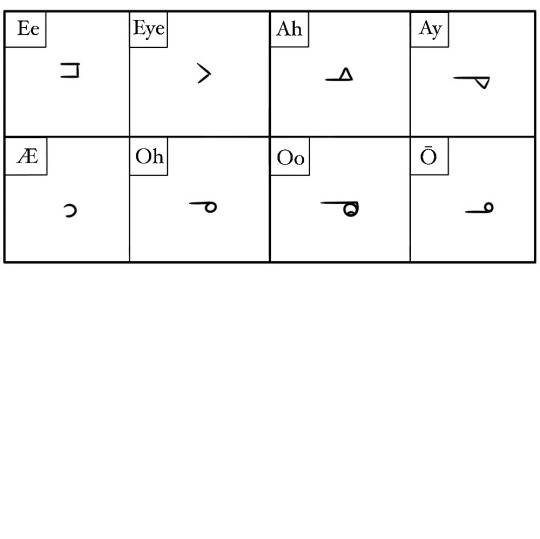
Where vowels are connected to a consonant can vary- usually there is a standardized method, but handwriting can alter it.
Montaran doesn't use any articles or particles, is written subject-verb-object (though the verb to be is considered an implied verb and therefore not actually written or spoken in sentences which would need it in other languages). Adjectives and adverbs are placed before what they alter.
Homonic
Homonic is humans' native language. It's alphabetic, made up mostly of vowels. The consonants are just 6 'base' ones, the sound of which changes with the inclusion of diacritics. It's based off of mostly English and Japanese.

⬆️ "This is an example sentence" written in Homonic. Pronounced "Goa ja ikaruth zonosh hfow."
Likewise I had more explanation for those weird phonetics but once again I am going to joker out so what the fuck ever. The r is a tapped r though.

Consonants base form is considered the default, while the diacritics change what sound it makes. The handakuten indicates a harder sound (P to B, F to V, L to tapped R), the tilde indicates a softer sound (hard G to Y, L to R, F to a sort of harder H that's not quite an english H), and the dakuten indicates a much softer, sometimes voiceless sound (P to W, F to H, T to Th). I should say now that I wrote out the phonetics of these in a way they make sense to me, so they might seem like nonsense to you. Because I don't understand international phonetic alphabet. But I digress. Vowels are never given diacritics.
Homonic uses both articles and particles, but particles are mostly used for action and subject indication. It's written subject-object-verb: Adjectives go after the noun they alter, but adverbs go before the verb. It's written left to right.
Paitarō
Paitarō is ipotanes' native language. It's an abugida, but unlike Montaran, consonants cannot exist alone. Instead, letters in their 'default' state are assigned the inherent vowel a, and all alterations from that indicate different vowel sounds. It's based mostly on Ge'ez and Eastern Cree.

⬆️ "This is an example sentence" written in Paitarō . Pronounced "Roujih myudae ba raisakō louhayka".
Paitarō has a bunch of different versions of verbs depending on context. They have general vs current forms, constant vs transient, beginning vs ending, and some verbs have a gladly vs reluctantly form. I gave examples, but this is my third time trying to edit this and I can't be assed to write it all out again without becoming the joker.

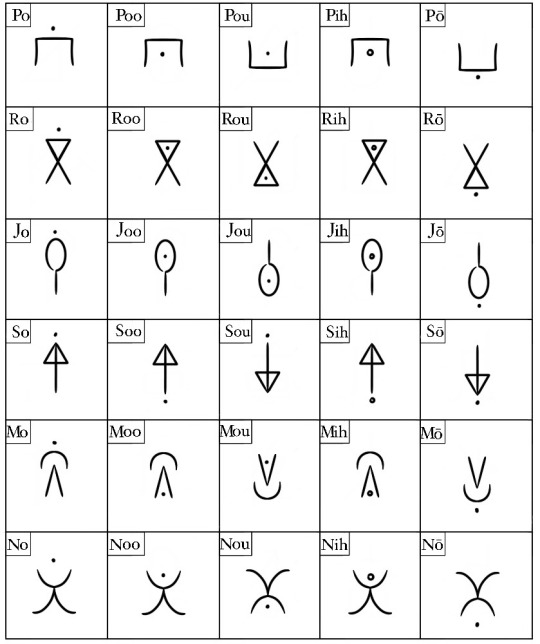

Rotation and diacritics determine the vowel sound of a letter. It's very consistent, so while it looks like there are 8 million letters, really there's just 12 that are altered slightly for different forms. A clockwise rotation 90 degrees will always result in the vowel ay, an macron will always result in the vowel i, etc.
It's written left to right, subject-verb-object, and uses no particles (but does use articles). It's also one of the harder languages to learn from an outside perspective, because many of the vowels (particularly o, oo, ou, and ō) sound similar to the untrained ear.
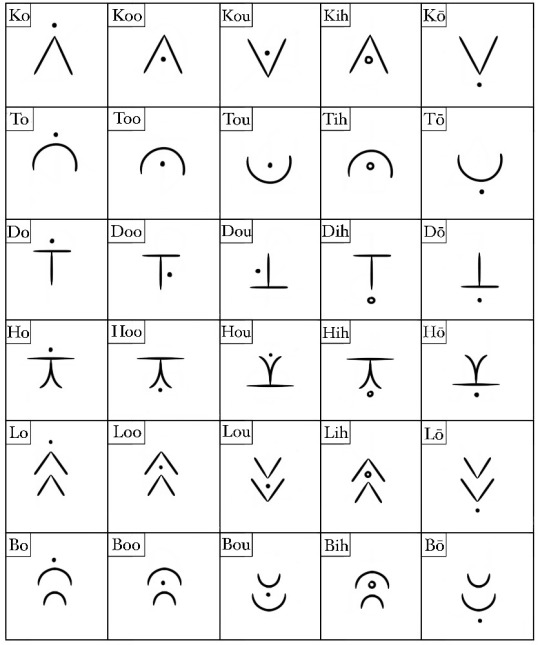
Arbor
Arbor is satyrs' native language. It's alphabetic, and has the largest alphabet of any language, with 42 letters (Paitarō beats it only if you consider all rotations and diacritics separate letters, which I don't). It's based mostly on Russian and Japanese.

⬆️ "This is an example sentence" written in Arbor. Pronounced "Shleya bouk dzyañen aotal voh."
It's written right to left, verb-subject-object. It doesn't use articles, but does use particles, which make up far more of the grammatical structure than of any other language. Particles indicate time, possession, location, direction, vocatives, pragmatics, formality, connectives, and conjunctions. For example, in the above sentence, the particle voh indicates certainty- what is being said is fact- not up for debate.
Formality particles are something that is mostly unique to Arbor: Homonic uses some, but they are loanwords from Arbor, and not used near as often. The only circumstance in which a satyr would not use formality particles is when speaking to children (or if the speaker is a child). Because of this, for an adult to speak without these particles is perceived as immature or patronizing or both. There are generally four 'levels' of respectful particles: familiar (for friends and family), peers (for acquaintances and strangers), respect (for superiors or elders), and higher status (for governmental or religious leaders). There are also degrading particles that are only used explicitly as insults, but are naturally not used in everyday life.

There are no true diacritics in Arbor, similar letters (like eh, ih, and uh, or v and fh) are considered distinct, not the same letter but altered).
Shotali
Shotali is nightlings' native language. It's syllabic, written calligraphically from top to bottom. It's made up of common humanoid phonemes as well as a clicking sound that is unique to their physiology. It's mostly based off of Khoisan and Vulcan.
⬆️ "This is an example sentence" written in Shotali. Pronounced "Sikosha taori niloth zhoi."


Here's the same sentence twice, one with the letters and other aspects of the sentence pointed out. The letters are designed to run into one another, where one letter ends another begins. Words are separated by a small open circle at the beginning and end to make clear the joint between the two.


It uses only two diacritics: a handakuten and a macron. In natural Shotali, they are used sparingly, but their usage has since expanded to allow for other sounds to be transcribed into Shotali. The macron traditionally changes just a few letters from an i vowel sound to an e (ri->re, ni->ne, li->le), but now can also be found to alter any letter with an i to an e, even if it was not originally allowed. The handakuten, in natural Shotali, indicates a click, made as part of the syllable alongside the voiced pronunciation, and is not actually considered a diacritic in this form. It's present only on hard consonants (k, v, d). These consonants can be written/spoken without the click and therefore without the handakuten, but only in very specific words or it is incorrect. Some words only define meaning by the presence or absence of this click- this makes things tricky for any other species trying to learn/speak Shotali.
Now, though, the handakuten is also placed as a diacritic on some other letters- not to indicate a click, but to harden the sound (Th to T, P to B, Zh to Z, J to hard G). These characters are not included in the base alphabet as they are considered adopted characters, meant to transcribe sounds from other languages- Shotali has a lot of technically allowed ways to write/speak that arent included in the 'official' alphabet.
Only d, j and th (or t with a handakuten) can exist as a consonantal sound without a vowel, considered a whole syllable by themselves in Shotali. It's written verb-object-subject, and uses no articles or particles. Adverbs and adjectives go before the noun or verb they alter.
Bonus: Chimerae's sign-morse
The chimerae, which live in the depths of the ocean and thus do not interact with any other humanoid species, converse with a form of sign language that utilizes their bioluminescent abilities. It is untranscribable, and so doesn't have a proper name. It's made up of similar signs as that of shallower merfolk: large, slow movements of the hands and caudal fin, but is additionally altered by light. Light carries meaning in: where on the body it is located, how quick the flash is, and what physical sign it accompanies.
Chimeraes have two distinct dialects of this language: a distant and close dialect, both used in conjunction with each other depending on context. Because detail gets much harder to see at distance, and the deep sea is big, the type of sign-morse used when far away from your conversation partner is different than that which is used when you are right next to each other. The former is vaguer, but more obvious, while the latter is more intricate and specific.
#ask#conlang#writing#<- trying to keep this so i can find it later teehee#THANKS BELOVED i sat with this for a bit but i shall now release her to the world. i am normal about fake languages and worldbuilding#also there is an ancient version of montaran that is not spoken but is used in tattoos and art. because it is aesthetic over function#also iarans (species of merfolk that can talk) have a language unique to them that is mostly used in song but it doesnt really...#..have a written alphabet or anything its very labile. likewise aesthetic (this time aural vs visual) over function#bcause they usually just sign to communicate with each other#AUGHC. i love making shit up. these were so fun to research for and put together#and they make the world feel a bit more fleshed out to know what their speaking sounds like?????#OH also the names for the diacritics are just what the closest analogue is called in the real world#they arent calling things macrons and tildes and dakutens. but thats basicslly what they are so thats what im calling them 👍#stupid as website broken ass website. post you asshole I'll kill you#.
21 notes
·
View notes
