#also there is an ancient version of montaran that is not spoken but is used in tattoos and art. because it is aesthetic over function
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Note
My dearest, tell me about your conlang scripts, please❣
Yeassss thank you beloved I will now kill for you <3 Ask me to kill for you.
I truly do not know how long this is going to end up but I'm just gonna go for it.
Montaran
Montaran is fauns' native language: it is alphasyllabic (rather than alphabetic), made up of character 'blocks' that are themselves composed of syllabic components. It's based off a mix of Korean and Sanskrit (mostly Brahmi script).

⬆️ "This is an example sentence" written in Montaran. Pronounced "Bavna mōskadatōk nin."
Components are arranged in blocks of three max, with spaces between words. It's written and read top to bottom, left to right. In three-component characters (called full blocks or complete characters), the arrangement of the components tells you where the syllabic emphasis is.

Here's the same sentence but with the components split up. The first word bavna has it's emphasis on the syllable na, and you can tell by reading because it's alone, as opposed to the other two components, which share space on the top of the block. The second word, Mōskadatōk, has its emphasis on the first and fourth syllables mō and da- the ones that are alone in their vertical placement. For partial blocks, like the last word nin, you can't tell emphasis by reading it.
Montaran is an abugida, which means its alphasyllabary is made up of consonant letters and small, diacritic-like additions that determine vowel sounds. Consonants can exist alone, but vowels must be connected to a consonant.

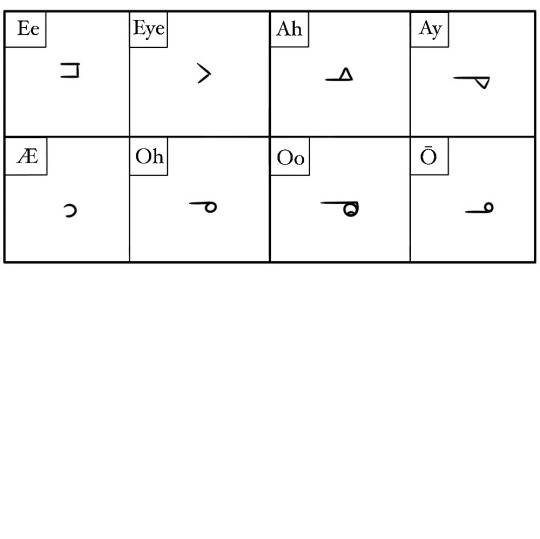
Where vowels are connected to a consonant can vary- usually there is a standardized method, but handwriting can alter it.
Montaran doesn't use any articles or particles, is written subject-verb-object (though the verb to be is considered an implied verb and therefore not actually written or spoken in sentences which would need it in other languages). Adjectives and adverbs are placed before what they alter.
Homonic
Homonic is humans' native language. It's alphabetic, made up mostly of vowels. The consonants are just 6 'base' ones, the sound of which changes with the inclusion of diacritics. It's based off of mostly English and Japanese.

⬆️ "This is an example sentence" written in Homonic. Pronounced "Goa ja ikaruth zonosh hfow."
If you compare the spelling above to the phonetics below you'll find a mismatch. That's because I simplified in in sentence form to make sense and be easier to read for an English reader. Directly, it would be "Goah jah ihkah/r/uhth zohnosh hfow" and you can see why i changed it now.
/R/ is a tapped r, kind of like the quick sound you make when you say the word kitty, but closer to the front of the mouth. Æ is a long A at the back of the throat, like in the word bat. Æ with the macron is just like saying the letter A. O is a shorter sound at the back of the mouth, as opposed to Oh, which is fronter and less O-shaped. Hf is a harder sound than H, but not quite an F.

Consonants base form is considered the default, while the diacritics change what sound it makes. The handakuten indicates a harder sound (P to B, F to V, L to /R/), the tilde indicates a softer sound (hard G to Y, L to R, F to Hf), and the dakuten indicates a much softer, sometimes voiceless sound (P to W, F to H, T to Th). I should say now that I wrote out the phonetics of these in a way they make sense to me, so they might seem like nonsense to you. Because I don't understand international phonetic alphabet. But I digress. Vowels are never given diacritics.
Homonic uses both articles and particles, but particles are mostly used for action and subject indication. It's written subject-object-verb: Adjectives go after the noun they alter, but adverbs go before the verb. It's written left to right.
Paitarō
Paitarō is ipotanes' native language. It's an abugida, but unlike Montaran, consonants cannot exist alone. Instead, letters in their 'default' state are assigned the inherent vowel a, and all alterations from that indicate different vowel sounds. It's based mostly on Ge'ez and Eastern Cree.

⬆️ "This is an example sentence" written in Paitarō . Pronounced "Roujih myudae ba raisakō louhayka".
Paitarō has a bunch of different versions of verbs depending on context. They have general vs current forms, constant vs transient, beginning vs ending, and some verbs have a gladly vs reluctantly form.
For example, the verb to bark (Harou). In Paitarō, the word Haroudō would be used to say dogs bark. Generally, it's something they do. Harouda would be used in the instance a dog is currently barking, right now. This is a good simple, ideal example, but more complex verbs get more complicated, and conjugations can also stack.

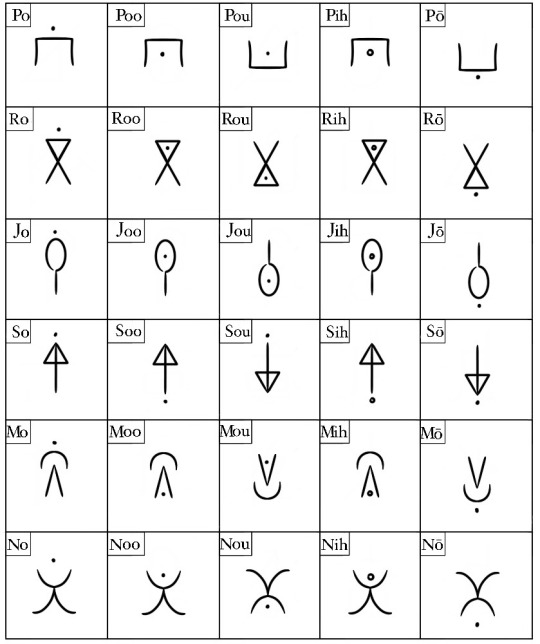

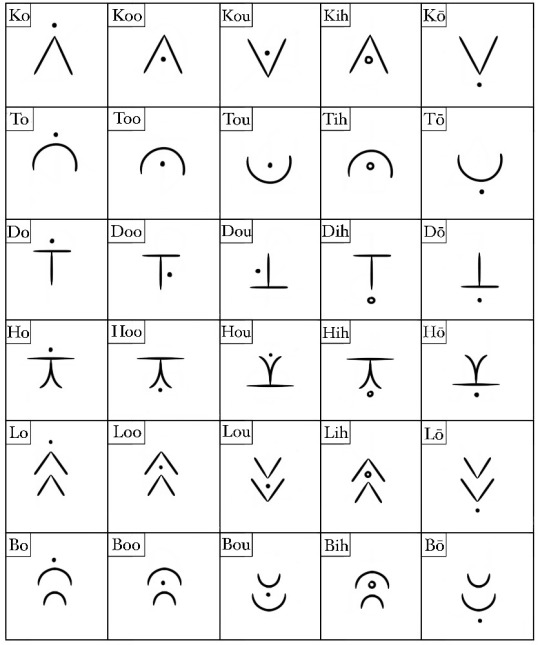
Rotation and diacritics determine the vowel sound of a letter. It's very consistent, so while it looks like there are 8 million letters, really there's just 12 that are altered slightly for different forms. A clockwise rotation 90 degrees will always result in the vowel ay, an macron will always result in the vowel i, etc.
It's written left to right, subject-verb-object, and uses no particles (but does use articles). It's also one of the harder languages to learn from an outside perspective, because many of the vowels (particularly o, oo, ou, and ō) sound similar to the untrained ear.
Arbur
Arbur is satyrs' native language. It's alphabetic, and has the largest alphabet of any language, with 42 letters (Paitarō beats it only if you consider all rotations and diacritics separate letters, which I don't). It's based mostly on Russian and Japanese.

⬆️ "This is an example sentence" written in Arbur. Pronounced "Shleya bouk dzyañen aotal voh."
It's written right to left, verb-subject-object. It doesn't use articles, but does use particles, which make up far more of the grammatical structure than of any other language. Particles indicate time, possession, location, direction, vocatives, pragmatics, formality, connectives, and conjunctions. For example, in the above sentence, the particle voh indicates certainty- what is being said is fact- not up for debate.
Formality particles are something that is mostly unique to Arbur: Homonic uses some, but they are loanwords from Arbur, and not used near as often. The only circumstance in which a satyr would not use formality particles is when speaking to children (or if the speaker is a child). Because of this, for an adult to speak without these particles is perceived as immature or patronizing or both. There are generally four 'levels' of respectful particles: familiar (for friends and family), peers (for acquaintances and strangers), respect (for superiors or elders), and higher status (for governmental or religious leaders). There are also degrading particles that are only used explicitly as insults, but are naturally not used in everyday life.

There are no true diacritics in Arbur, similar letters (like eh, ih, and uh, or v and fh) are considered distinct, not the same letter but altered).
Shotali
Shotali is nightlings' native language. It's syllabic, written calligraphically from top to bottom. It's made up of common humanoid phonemes as well as a clicking sound that is unique to their physiology. It's mostly based off of Khoisan and Vulcan.
⬆️ "This is an example sentence" written in Shotali. Pronounced "Sikosha taori niloth zhoi."


Here's the same sentence twice, one with the letters and other aspects of the sentence pointed out. The letters are designed to run into one another, where one letter ends another begins. Words are separated by a small open circle at the beginning and end to make clear the joint between the two.


It uses only two diacritics: a handakuten and a macron. In natural Shotali, they are used sparingly, but their usage has since expanded to allow for other sounds to be transcribed into Shotali. The macron traditionally changes just a few letters from an i vowel sound to an e (ri->re, ni->ne, li->le), but now can also be found to alter any letter with an i to an e, even if it was not originally allowed. The handakuten, in natural Shotali, indicates a click, made as part of the syllable alongside the voiced pronunciation, and is not actually considered a diacritic in this form. It's present only on hard consonants (k, v, d). These consonants can be written/spoken without the click and therefore without the handakuten, but only in very specific words or it is incorrect. Some words only define meaning by the presence or absence of this click- this makes things tricky for any other species trying to learn/speak Shotali.
Now, though, the handakuten is also placed as a diacritic on some other letters- not to indicate a click, but to harden the sound (Th to T, P to B, Zh to Z, J to hard G). These characters are not included in the base alphabet as they are considered adopted characters, meant to transcribe sounds from other languages- Shotali has a lot of technically allowed ways to write/speak that arent included in the 'official' alphabet.
Only d, j and th (or t with a handakuten) can exist as a consonantal sound without a vowel, considered a whole syllable by themselves in Shotali. It's written verb-object-subject, and uses no articles or particles. Adverbs and adjectives go before the noun or verb they alter.
Bonus: Chimerae's sign-morse
The chimerae, which live in the depths of the ocean and thus do not interact with any other humanoid species, converse with a form of sign language that utilizes their bioluminescent abilities. It is untranscribable, and so doesn't have a proper name. It's made up of similar signs as that of shallower merfolk: large, slow movements of the hands and caudal fin, but is additionally altered by light. Light carries meaning in: where on the body it is located, how quick the flash is, and what physical sign it accompanies.
Chimeraes have two distinct dialects of this language: a distant and close dialect, both used in conjunction with each other depending on context. Because detail gets much harder to see at distance, and the deep sea is big, the type of sign-morse used when far away from your conversation partner is different than that which is used when you are right next to each other. The former is vaguer, but more obvious, while the latter is more intricate and specific.
#ask#conlang#writing#<- trying to keep this so i can find it later teehee#THANKS BELOVED i sat with this for a bit but i shall now release her to the world. i am normal about fake languages and worldbuilding#also there is an ancient version of montaran that is not spoken but is used in tattoos and art. because it is aesthetic over function#also iarans (species of merfolk that can talk) have a language unique to them that is mostly used in song but it doesnt really...#..have a written alphabet or anything its very labile. likewise aesthetic (this time aural vs visual) over function#bcause they usually just sign to communicate with each other#AUGHC. i love making shit up. these were so fun to research for and put together#and they make the world feel a bit more fleshed out to know what their speaking sounds like?????#OH also the names for the diacritics are just what the closest analogue is called in the real world#they arent calling things macrons and tildes and dakutens. but thats basicslly what they are so thats what im calling them 👍#stupid as website broken ass website. post you asshole I'll kill you#.
22 notes
·
View notes