#high fat dies caused heart attack
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
3 Terrifying Mistakes that can cause Heart Attack
Heart attacks are caused by the blood supply to the heart being suddenly interrupted. Without treatment, the heart muscles will experience irreversible damage. Without this supply, heart muscles may be damaged and begin to die. If a large portion of the heart is damaged in this way, the heart stops beating (known as a cardiac arrest), resulting in death. Before a heart attack, one of the plaques…

View On WordPress
#can heart attack caused by high fat diet#Coronary heart disease#Coronary heart disease effects#Coronary heart diseases#does Coronary heart disease caused by smoking#does smoking causes heart attack#empty stomach causes heart attack#heart attack#heart attack caused by empty stomach#heart attack caused by overweight#heart attack prevention#high fat dies caused heart attack#natural ways to prevent heart attack#overweight causes heart attack#remedies for heart attack#smoking caused by heart attack#smoking causes Coronary heart disease#smoking causes heart attack#what causes Coronary heart disease#what causes heart attack
0 notes
Text
HALF LIFE VRAI (+gorgeous & og gordon) HEADCANONS IF YOU EVEN CARE!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
BENREY WOOO
during. the end, he had 2 extra eyes, one above his left eye one below his right eye, now he has scars where they laid, they’re faint but he. is autistic im sorry he’s too me to not be he had a tail during the end too faint freckles ^_^ he REALLY likes red meat he likes blue flavor, not blueberries, not blue raspberry, blue stubble YAYY specifically in end, benreys feet to knees and hands to elbows fade into rlly dark blue/black looks like he’s dying of illness but like. has never been sick disassociates very often very touch very very touchy polyamorous, exes with forzen & is now crushing on both Tommy & gordon orphaned, kinda lived on his own since he isn’t human, picked his own name doesn’t actually have brothers, he’s a loser breaths through his mouth esp when he’s comfortable weird but like imagine he’s cuddled up to someone and he just yeah
COOMER YAYYY
fat, idc i’m right
gender-fluid, transmasc & gay ^_^ old man yaoi with bubby YAYYY
cool little funky punching enhancement thingies
big ol’ doe brown eyes
brunette hair before he started graying
after the resonance cascade he retired, they deserve it
has nightmares over clones. a lot, a big lot
autistic, everyone knows the science team kinda is autistic,
going off the autistic thing, one of his vocal stims is hello gordon
loves talking, loves it so much, he loves just talking to people she likes
has a high score on punch out & that one punching game where you punch the punching bag to get evaluated on
the reason is divorced because he realized he was gay
hawaiian shirts FTW!!
(most of these are somewhat canon, holly (his va) headcanons him as transmasc, short and stocky, and 5’4!)
Bubbster
Intersex & bisexual (idc if gir hcs him as straight it’s my world now/pf)
if he didn’t live with Coomer after the resonance cascade, he’d probably just be a basement dweller and just sit in the corner and cry
Bionic legs :3
canonically test tube baby, he’s probably really freaked the fuck out over it & has had genuine panic attacks over being artificially made, only in front of coomer
literally always has epi-pens for coomer
naturally(?) ginger idk what you wanna consider it, he’s canonically like 6 but in my head he’s like 67, he’s been locked in black mesa for 67 years
blue eyes
has a leather jacket with a tiger on it he will wear just to do so
has made the science team watch scrubs.. twice
picks at skin as a stress tick
has tourettes
near blind
when he got his bionic heart he died so he will sometimes just be like “hey guys i’ve died before”
being put back in the tube after betraying gordon was one of the worst things he’s been through, it was terrifying
GORDON FEETMAN!!!
also fat
joshua exists but he was an accidental pregnancy (gordon seahorse father yayy)
ftm based off last hc, that’s just canon cuz i said so
joshua is like, 9 in my head so gordon had him at like 18
bisexual
has a crush on benrey (canon but yk)
mexican and african
curly ass hair, takes really good care of it, always smells nice
bilingual
blind in left eye, 25% prescription in right eye
feels guilty as fuck even when everyone would joke about him being the cause of the RC
also autistic
wayne did not dk him justice when he lost his hand, he was screaming so gutturally loud it was painful, he strained his voice so bad, the pain was so excruciatingly terrible
tommy genuinely was the only one he could trust after benrey & bubby turned their backs on him, and that sucked because his feelings for benrey before that point were getting to him
only was adamant about not being friends with benrey at the end because of the betrayal, he wanted to hate benrey
tommy is like his. comfort friend, he doesn’t have to worry about him.. he does but he always feels comfy around him
Tommy cool man
Autistic, ADHD, PTSD and OCD
G man species, half human
strawberry enthusiasts:3 (me too)
every flavor tic tac enthusiast, always give the science team tic tacs like all the time
not very good at games enjoys playing them though
very touchy for multiple reasons
Sunkist service dog for multiple things as well, helps with panic attacks, PTSD symptoms, anxiety attacks etc
Tommy doesn’t know how Sunkist was trained to do all this, he made her sk he just kinda accepts it for how she is, and loves her
compression hugs, likes being laid on top of, it’s comforting
looks scrawny but can like. genuinely pick up all the science team & benrey with ease
started collecting propeller hats after the RC
the reason he can read sweet voice is cuz g-man species
thinking about getting a cat, maine coon or norwegian forest cat, he likes big ass animals
Sunkist is LARGE like large as fuck for a golden Tommy made sure she was huge
milk enjoyer :3 drinks it with most of his meals
wears readers
ANGEL KISSES!! (moles or beauty marks whatever you wanna call them)
tooth gap :3
walks on tiptoes
Gorgeous
6’7
cuts his hair into a fringe, lets it grow out to shoulder length, then cuts it fringe, never ending cycle
beauty marks man
freckles too
nobody fucking knows his trauma
doesn’t understand why he can understand cicero?? he just.. can??
learned ASL as a kid
clearly has some form of mommy issues he will not touch on
wears solid colors, he doesn’t wear shirts with decals, or anything, a. he doesn’t like them. b. for ASL purpose, it’s recommended to wear light/dark clothes (light in his case) depending on your skin tone to MAKE it easier to read sign, usually in light pink
prefers skirts cuz.. they’re comfy, usually knee & ankle length.. sometimes he will wear mini skirts……. cuz he’s gross
actually hates head crabs.
would be a nudist if it was sociably acceptable
actually really enjoys video games! he doesn’t talk about it, he’s good at them too
he’s a dog person, he wants a saint bernard
freeman YAYY
6’
beauty marks
patchy beard
dark hazel eyes
starting to grey, short pony tail
has scars from his HEV suit
actually lost his hearing DUE to the RC, his mother was deaf so that’s why he knows ASL, it completely shot out his hearing
has always dressed nice
cat person
Alyx is like his daughter to him
i can’t decide if he’s trans or not
same situation with gorgeous, he wears solid colors for ASL purpose
him and cicero have yet to find a way to communicate
when he found out alyx learned ASL for her boyfriend (this is canon, was planned for episode 3) he was over the moon
enjoys IASIP (it’s always sunny in philadelphia)
scary when he’s pissed off
G-Manual samual
major RBF
scottish
moles kuz hes kawaii
wears readers
hes autistic
going on with him being autistic, the fabric his suits are a comfort fabric to him
enjoys sitcoms
drinks his coffee straight black
he is trans masc to me
praises his employers like god tbh
if he were to drink, which he doesnt, his go to drink would be rum on ice
some form of alien, not from xen though, no one knows where hes from
some type of holy creature??? he cant die?? hes weird
you'll never see it but he doesnt bleed red, his blood is black
enjoys fishing
goes to bed at 11pm, wakes up at 4am hes weird
hes also the best father ever???
songs that remind me of science team members + benrey the 6th
Benrey the 6th
I Will - Mitski
Kiss Me, Son Of God - They Might Be Giants
I’m Gonna Win - Rob Cantor
Mad World - Tears for Fears
We Will Commit Wolf Murder - Of Montreal
Gallery Piece - Of Montreal
Everybody Wants to Rule the World - Tears for Fears
The Party's Crashing Us - Of Montreal
Tommy Coolman
Living Island - POGO
Fireflies - Owlcity
Teenage Dirtbag - Weetus
rises the moon - liana flores
Good Old-Fashioned Lover Boy - Queen
Head Over Heels - Tears for Fears
#half live vr but the ai is self aware#hlvrai#dr bubby#dr coomer#gordon freeman#hlvrai dr bubby#hlvrai dr coomer#gordon freemind#gorgeous freeman#benrey#tommy coolatta#benry#benrey hlvrai#bubby#half life#half life au#headcanonsd#headcanons#i like men#gay???#gay pride#gay
35 notes
·
View notes
Note
Is the trolls practicing fattening up their wives into immobility thing still canon? Cause it’s not on the article anymore? I’d still like to figure out more about this feedism practice though like where it originated and what it symbolizes in troll culture?
This is still canon, I just removed it from the main troll article because it's not really a species-specific thing, it's more of a cultural thing. Not all trolls practice this.
All of today's trolls descend from just two ancient groups: the Skadgrik (of Halostira) and the Hukus (of Wokina). This fattening practice originated with the Skadgrik.
As the Skadgrik travelled away from their native land, they brought their culture to new lands and introduced it to other trolls. The Skadgrik immigrants kept their ancient traditions alive over many generations, and so these traditions spread throughout different trollish societies on Looming Gaia. Their strange wife-fattening practice left a big impression on all who witnessed it, so it became a stereotype of all trolls, even though many troll societies have never done this.
So, why did the Skadgrik fatten their wives in the first place? To answer this, I have to talk about their native homeland first. The Skadgrik come from a frozen island off the coast of Halostira. There is very little food in this region except during migration season, when thousands of walruses use the island as a breeding ground. This season is a time of feasting and abundance for the Skadgrik, who hunt the walruses and preserve their leftover meat in the ice to carry them through the rest of the year.
Hunting and preparing these animals is hard, dangerous work, which is done exclusively by male Skadgrik. In this culture, males are valued by how hard they work and females are valued by how hard they don't work. The Skadgrik believe that for every meal a male eats, he should feed his wife at least double that amount. If he can do this, then he's considered a good provider by his tribe. If he can feed her more than this, then he is exceptional.
So, Skadgrik husbands scramble to feed their wives as much as possible, because the fatter she gets, the more respected he is. Fat, lazy wives are a status symbol in this culture. Many of these trollesses get so fat that they become immobile, and then it becomes her children's duty to care for her while her husband is out huntiung more food.
This tradition may seem strange and cruel to outsiders, but the Skadgrik trollesses are proud to be this big. It's a status symbol for them as much as it is for their husbands. If a trolless is too thin, it gives other Skadgrik a bad impression of her and her family. They think her husband must be a lazy bum, or she's a difficult woman and not worth the hard work, or that she has somehow alienated her children and they refuse to care for her.
Of course, being this big does lead to extra challenges in life. These trollesses don't live very long, usually dying from obesity-related causes like high blood pressure, heart attacks, and diabetes. It also makes them sitting ducks in emergency situations, as they're unable to escape disasters fast enough. They're also prone to devastating falls, bone breaks, and even suffocating under their own weight.
In "Flopper and the Whopper", a Halostiran troll named Xydoz explains what kind of tragedies can happen when their wives get too big. Check out this excerpt:
--
One of the yaks tried to stop and graze. With a whip of the reins, Xydoz urged it back on the trail. Once the laughter died down, Glenvar asked, “Come on, how did ya really get here?”
“Real answer not interesting,” the troll admitted. “Trolls wait until winter when water freeze into bridge, then walk across.” He paused. “Only one time interesting. Heavy troll make ice break. Then swallowed by whopper, gone forever.”
“Is that a joke?”
“Not joke.” Xydoz’ grin faded. “Was Xydoz’ wife, Iiab. Xydoz bad troll, not save Iiab fast enough.”
Glenvar’s grin faded too, curving into a frown. “Oh. I’m sorry,” he said quietly.
The troll lowered his horned head with a small nod. “Iiab was fat, sweaty troll. Smell like a thousand dead fish. Collect most flies in Toraag.”
A slight smile returned to his craggy lips, doleful eyes above. “Iiab so beautiful, Xydoz kill all Iiab’s brothers and father to have wedding.”
“You killed ‘em? Why?” Glenvar flipped over on his belly, resting his chin on his fists.
Xydoz replied, “They not give permission to marry. Say Xydoz not have enough pigs!” His nostrils crinkled. “Xydoz come to Halostira for fortune. One day buy pigs, return to Toraag and marry again. But no troll replace Iiab, lumpiest, foulest, meanest of trolls.”
--
This snippet also gives some insight into trollish beauty standards. Trollish men like their women fat, lumpy-skinned, mean, and smelly! The Skadgrik and their descendants just happen to value weight above other things because food was such a scarce resource for their ancestors. Food didn't come around often, and when it did, they had to risk their lives battling a horde of rutting walruses on a godforsaken chunk of ice to get it.
*
Questions/Comments?
Lore Masterpost
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Sudden Heart Attacks in Young People: A Growing Concern
In recent years, India has seen a worrying rise in heart attacks among young people. Daily news of sudden cardiac arrests among young Indians has turned the spotlight on this issue. Television icon Sidharth Shukla passed away suddenly due to a heart attack. Andhra Pradesh’s Minister of Information Technology and Industries, Mekapati Goutham Reddy, died of a heart attack at the age of 50. Famous singer KK also passed away at 53 after falling ill during a show. These sudden deaths have left millions shocked—how can individuals who appear fit, eat well, and regularly visit the gym die so unexpectedly? Recently, many other tragic cases have also highlighted this alarming trend.
BUY BEST SUPPLEMENTS FOR HEART HEALTH
"The increasing number of heart disease-related deaths among the youth has raised serious concerns about heart health and preventive measures."
Also Read: शरीर के 5 अंगों में दर्द होना नहीं है सामान्य, ये हो सकता है दिल की बीमारी का संकेत
The figures say it all
According to many doctors and health experts, the heart problems among Indians have doubled in the last decade. "Heart health" has become one of the most searched terms on google and there is growing concern about the rise in cardiac arrest cases, especially among young people, after the COVID-19 pandemic.
Here are some key facts:
The World Health Organization states that India accounts for one-fifth of the 17.9 million global deaths from cardiovascular diseases, particularly among the younger generation.
The Indian Heart Association reports that 50% of all heart attacks in Indian men occur under the age of 50, and 25% occur under 40.
Heart attacks in people under 40, once rare, now affect 1 in every 5 patients.
Between 2000 and 2016, the rate of heart attacks in young people (20s and early 30s) increased by 2% every year.
"These facts highlight the alarming rise in heart attacks among the young generation."
How Common Are Sudden Heart Attacks?
Heart attacks are becoming more common among young people in India, especially those aged 25-44.
Studies show a 30% increase in heart attacks in this age group during the first two years of the COVID-19 pandemic.
This alarming trend highlights the need for increased awareness and preventive measures for heart health in young adults.
Causes of Sudden Heart Attacks in Young People
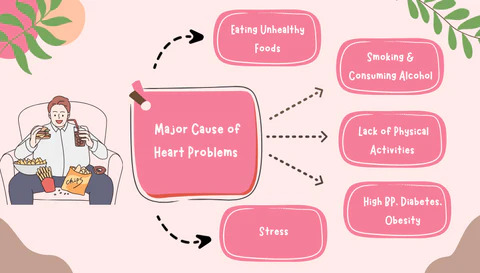
Genetics
Family History: If your close relatives (like parents or siblings) have had heart disease, your risk is higher because you might inherit the same genes.
Inherited Conditions: Conditions like high cholesterol or high blood pressure can be passed down, increasing your risk of heart disease.
Lifestyle
Unhealthy Foods: Eating too much fast food, sugary drinks, and processed foods can increase the risk of heart disease. These foods are high in fat, sugar, and salt, which can block arteries.
Lack of Physical Activity: Not being active enough can weaken your heart. Regular exercise is essential to keep heart healthy.
Smoking and Alcohol: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption are major risk factors for heart disease. They damage blood vessels and heart.
Rise of Fast Food in India: The rise in fast food and sugary drink consumption in India has contributed to more heart disease cases.
Also Read: 8 Steps for Preventing Heart Disease
Health Conditions
High Blood Pressure: This means heart has to work harder to pump blood. Over time, this can damage heart and lead to a heart attack.
Diabetes: High sugar levels in blood can harm blood vessels and heart.
Obesity: Being overweight puts extra strain on heart.
Stress
High Stress Levels: Constant stress can raise blood pressure and harm heart.
COVID-19 and Heart Problems
COVID-19 can cause inflammation in the heart muscle, known as myocarditis. This inflammation can lead to complications like irregular heartbeats, heart failure, and even sudden cardiac arrest. The virus can also affect the lining of blood vessels, leading to blood clots, which can cause heart attacks or strokes.
Diabetes and Heart Disease
Diabetes is a major risk factor for heart disease. High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and the nerves that control the heart. Over time, this damage can lead to atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries), which increases the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
"In India, the number of people with diabetes is rising rapidly, making it a significant health concern."
Signs of a Sudden Heart Attack

Knowing the signs of a heart attack can save lives. Common symptoms include:
Chest pain or discomfort: Feels like pressure, squeezing, fullness, or pain.
Shortness of breath: Can happen with or without chest pain.
Nausea or vomiting: Some people feel sick to their stomach.
Lightheadedness or dizziness: Feeling faint or dizzy.
Pain in the arms, neck, jaw, or back: This pain can be in one or both arms, the neck, jaw, or back.
How to Lower Risk of Heart Attacks
Regular Exercise: Activities like walking, jogging, or yoga can keep heart strong.
Balanced Diet: Eating a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins helps maintain heart health.
Avoid Smoking and Alcohol: Smoking and drinking too much alcohol can damage heart and blood vessels, so it’s best to quit or limit these habits.
Manage Stress: Techniques like meditation, deep breathing, and spending time with loved ones can help reduce stress.
Regular Health Check-ups: These can help detect and manage risk factors like high blood pressure and diabetes early on.
Conclusion
The increase in sudden heart attacks among young people is worrying and needs attention. By living a healthy lifestyle, managing stress, and staying informed about heart health, you can lower your risk of heart disease. Awareness and proactive measures are key to fighting this growing heart health issue
BEST SUPPLEMENTS FOR HEART HEALTH
"The increasing number of heart disease-related deaths among the youth has raised serious concerns about heart health and preventive measures."
Also Read: शरीर के 5 अंगों में दर्द होना नहीं है सामान्य, ये हो सकता है दिल की बीमारी का संकेत
The figures say it all
According to many doctors and health experts, the heart problems among Indians have doubled in the last decade. "Heart health" has become one of the most searched terms on google and there is growing concern about the rise in cardiac arrest cases, especially among young people, after the COVID-19 pandemic.
Here are some key facts:
"These facts highlight the alarming rise in heart attacks among the young generation."
How Common Are Sudden Heart Attacks?
This alarming trend highlights the need for increased awareness and preventive measures for heart health in young adults.
Causes of Sudden Heart Attacks in Young People
Genetics
Lifestyle
Also Read: 8 Steps for Preventing Heart Disease
Health Conditions
Stress
COVID-19 and Heart Problems
COVID-19 can cause inflammation in the heart muscle, known as myocarditis. This inflammation can lead to complications like irregular heartbeats, heart failure, and even sudden cardiac arrest. The virus can also affect the lining of blood vessels, leading to blood clots, which can cause heart attacks or strokes.
Diabetes and Heart Disease
Diabetes is a major risk factor for heart disease. High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and the nerves that control the heart. Over time, this damage can lead to atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries), which increases the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
"In India, the number of people with diabetes is rising rapidly, making it a significant health concern."
Signs of a Sudden Heart Attack
Knowing the signs of a heart attack can save lives. Common symptoms include:
How to Lower Risk of Heart Attacks
Conclusion
The increase in sudden heart attacks among young people is worrying and needs attention. By living a healthy lifestyle, managing stress, and staying informed about heart health, you can lower your risk of heart disease. Awareness and proactive measures are key to fighting this growing heart health issue
0 notes
Text
What Are 3 Warning Signs Of A Heart Attack?

Heart attacks may come with no prior warnings. But if they do, it is important to recognize them and take immediate action.
Did you know that heart attacks are one of the leading causes of death worldwide? According to the World Health Organization (WHO), an estimated 1.79 crore people died from Cardiovascular Diseases (CVDs) in 2019, of which 85% were due to heart attacks and strokes.
The most concerning characteristic of a heart attack is its unpredictability. It is often referred to as a ‘silent killer’ because it usually does not show any noticeable signs, or if it does, it is mistaken for benign conditions. Researchers continue to look for ways to identify any form of warning sign associated with the life-threatening disease. A recent study conducted by researchers at Uppsala University in Sweden was somewhat successful in identifying blood biomarkers that could prove useful in predicting a heart attack risk within 6 months. However, research is still ongoing, and there is currently no sure-shot way to predict a cardiac event. Meanwhile, what people can do is address the common risk factors and pay attention to these three warning signs of heart attack that are often overlooked, as shared by Dr Vikrant Khese, Consultant Cardiologist, Apollo Clinic, Kharadi.
Chest Pain Or Discomfort
Chest pain or discomfort, also known as angina, typically occurs when there's a reduction in blood flow to the heart muscle due to narrowing of the coronary arteries,” explains Dr Khese.
He adds, “This narrowing is often caused by the buildup of plaque, a combination of fat, cholesterol, and other substances, on the arterial walls. When the blood flow to the heart is restricted, it can result in chest pain or discomfort. According to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), most heart attacks involve pain and discomfort in the center or left side of the chest that lasts for more than a few minutes or that goes away and comes back.
Dr. Khese says that this type of unease becomes more severe and prolonged during a heart attack as the blood flow to a part of the heart muscle is completely blocked.
Shortness Of Breath
When it comes to a heart attack, shortness of breath is a common symptom. This is also a sign of your heart’s inability to effectively pump oxygen-containing blood around the body.
Dr Khese says, “When the heart muscle is deprived of oxygen due to a blocked artery, it struggles to function properly. This can lead to a backup of fluid in the lungs, causing difficulty breathing.”
Additionally, the body's response to stress, pain, and decreased oxygen levels can also contribute to shortness of breath during a heart attack, he adds.
Discomfort In Other Areas Of The Upper Body
Many people may not experience any symptoms before a heart attack—however, those who do often ignore the signs or mistake them for other health problems.
This often includes discomfort in areas such as the arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach, referred to as pain.
It occurs because the nerves that transmit pain signals from the heart also connect to other parts of the body, says Dr Khese. He further notes that when the heart muscle is deprived of oxygen, these nerves can become activated, causing pain or discomfort in these other areas.
“The brain may interpret this pain as originating from the arm, back, neck, jaw, or stomach, rather than the heart itself,” he shares.
Who Is At Risk?
There is no way to know if you're going to have a heart attack. However, some factors can tell you whether you're at risk or not. These include:
Age: Men aged 45 and older and women aged 55 and older are more at risk of having a heart attack.
Family history of early heart disease
Having pre-existing conditions, like high blood cholesterol, high blood pressure, or diabetes
Being overweight and obese
An unhealthy diet includes eating too many foods high in saturated fat or sodium.
Lack of regular physical activity
Smoking
Alcohol consumption
Conclusion
Assessing your risk factors and addressing them on time can minimize your risk of developing heart disease. While it does not guarantee heart attack prevention, it sure does reduce the risk. Eating healthy, doing regular exercise, managing stress levels, quitting smoking, and cutting down on alcohol can help tremendously. Moreover, do not overlook even the slightest indication of a heart attack. Consult a doctor if you have chest pain, shortness of breath, or discomforting sensations in your upper body, particularly if you have any of the risk factors mentioned above.
#Best Cardiologist in Pune#Best Cardiologist in Dhanori#Sonography Test in Dhanori#Cardiologist in Dhanori#Heart Specialist in Dhanori#2 D Echo in Dhanori#Stress Test in Dhanori#ECG in Dhanori#Cardiologist in Lohegoan#Coronary Angiography in Dhanori#Coronary Angioplasty in Dhanori
0 notes
Text

All About Cholesterol! The Latest Science on How Blood Levels of HDL, LDL and More Relate to Cardiovascular Health
— By Amber Dance | February 14, 2024
When C. Michael Gibson of Boston saw his doctor in the spring of 2023, the blood test results were confusing. His cholesterol levels were decent — he was already taking statins to keep the “bad” cholesterol low — but the arteries delivering blood to his heart were nonetheless crammed with dangerous plaque. “It didn’t make sense,” says Gibson, himself a cardiologist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center.
So Gibson asked his physician to check his blood for a specific kind of cholesterol called lipoprotein(a). And there was the explanation: He had more than double the normal amount of that cholesterol. Gibson turned out to be one of the unlucky people who has inherited a predisposition toward high lipoprotein(a) levels; he suspects that his grandfather, who died of a heart attack at age 45, had it too.
About one in five people have this unfortunate heritage, and there’s nothing they can do to combat it — but soon that might change. Scientists are researching medications that can lower lipoprotein(a), as well as other approaches that could slash the risk of cardiovascular disease more than drugs like statins can.
Statins, approved in the late 1980s to lower levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, have been a lifesaving tool: They cut risk of heart attack and stroke by up to 50 percent for the more than 200 million people globally who take the medications. Yet even statin takers still get heart disease, and some still die. Cardiovascular disease remains the leading cause of death in the United States and across the world. Clearly, something’s been missing from the cholesterol picture.
The picture coming into focus today incorporates not just bad, LDL cholesterol and good, high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, but also lipoprotein(a) and a poorly understood substance called “remnant cholesterol.” Medical researchers aim to minimize all of these except HDL. And HDL cholesterol itself, though it’s still understood to be beneficial, has turned out to be more complex than anticipated. Various attempts to raise HDL levels haven’t improved people’s health beyond what statins already achieve.
Yet despite this and other disappointments in which medicines haven’t panned out as expected, many researchers feel optimistic about treatments currently in clinical trials. “It’s really an exciting time,” says Stephen Nicholls, a cardiologist at Monash Health in Melbourne, Australia.
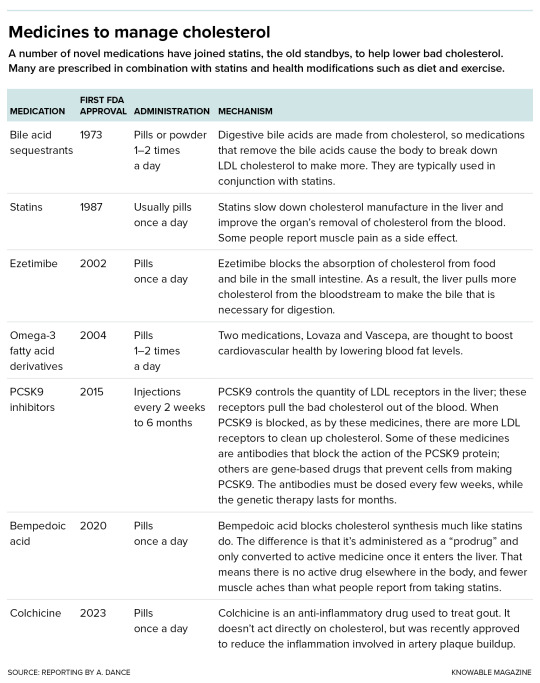
The list of drugs used to address high LDL cholesterol is growing.
LDL Cholesterol
Though it gets a bad rap among the health-conscious, cholesterol plays important roles in our body: It helps to control the stability and fluidity of cell membranes and is an important starting ingredient for making hormones such as testosterone and estrogen. What matters for our health is the company that the cholesterol molecule keeps when it travels.
Its waxy nature means it can’t mix well with water, so it can’t pass through the bloodstream on its own: Lone cholesterol molecules would separate out, like oil does in water. Cholesterol’s solution is to join up with complexes of proteins and fats, called lipoproteins, that carry it around. These lipoprotein carriers include LDL, HDL and other types. Cholesterol, in addition to being cargo, is a structural part of these carriers, too.
Lipoproteins are made in the gut and liver, and they deliver cholesterol and fat to body tissues. Fat goes to muscles, to be used for energy, or to fat tissue for storage. Cholesterol is dropped off in tissues to be incorporated into cell membranes or made into hormones. Cholesterol can also be returned to the liver where it can be stored, incorporated into new lipoproteins, turned into bile acids used by the digestive system to break down fats, or sent to be excreted.
When the delivery particles from the liver have dropped off most of their fats, they become LDL particles, which are still jam-packed with cholesterol. The problem happens when these LDL particles, instead of returning to the liver to be recycled, squeeze into blood vessel walls and get chemically modified. There, they incite or exacerbate an immune reaction called inflammation. In response, immune cells come in to eat LDL particles — but if they eat too much, they can get stuck in the blood vessel wall. This forms the beginnings of an atherosclerotic plaque.
Over time, that plaque accumulates more cholesterol, more fat and more immune cells, reducing the space through which blood can flow and deliver oxygen to tissues. If a plaque limits blood supply to the heart, it might cause chest pain called angina. A plaque might also lead to formation of a blood clot, which may break off and clog vessels elsewhere. The clot might cause a stroke in the brain, for example, or a heart attack.
Today, it’s clear that the less LDL cholesterol in the bloodstream, the better. Statins are good at achieving this, cutting LDL cholesterol levels by up to about half. And for those who need a bigger effect, or who can’t tolerate statins (muscle pain or weakness is an occasional side effect), there are newer medicines. “We now have the ability to get almost anyone’s LDL cholesterol down into the range that we would consider appropriate,” says Steven Nissen, a cardiologist at the Cleveland Clinic in Ohio.
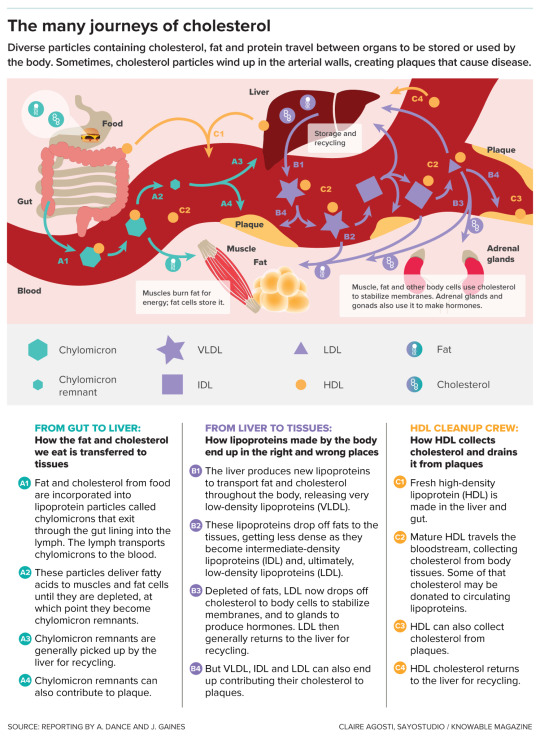
As cholesterol moves around the body within various protein- and fat-containing particles, it aids in important functions but also has the potential to create health risks.
Lipoprotein(a)
But these LDL-cholesterol treatments generally don’t do much against levels of lipoprotein(a), pronounced “lipoprotein-little-a.” This substance, composed of LDL cholesterol particles plus an extra protein, apolipoprotein(a), is mysterious: Scientists don’t know what its natural job is, though since apolipoprotein(a) has some similarity to a protein involved in blood clotting, it might have a role in wound healing. But it can’t be all that important to animal survival: Weirdly, the gene that carries instructions for making apolipoprotein(a) is found only in certain primates. (A similar gene evolved in hedgehogs.)
It’s also unclear why lipoprotein(a) is such a bad version of cholesterol, but it’s clearly up to no good much of the time. It delivers cholesterol to the blood vessel walls like LDL does, promotes blood clotting that blocks arteries and can cause inflammation and increase the risk of clots. And if your lipoprotein(a) is high — too bad. “Statins won’t get it down,” laments Gibson. “Exercise doesn’t get it down. Diet doesn’t get it down.”
Some of the newer LDL cholesterol-lowering drugs can reduce lipoprotein(a) cholesterol a bit, but probably not enough to significantly reduce cardiovascular risk, says Anand Rohatgi, a cardiologist at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas. The only thing physicians can do, in extreme cases, is to regularly administer a blood-cleaning procedure called apheresis to remove lipoprotein(a).
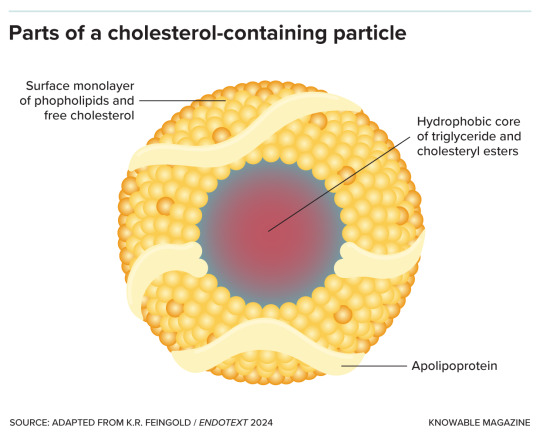
Lipoprotein particles are made up of a core containing fat in the form of triglycerides and cholesterol in the form of cholesteryl esters, surrounded by phospholipids, free cholesterol molecules and apolipoprotein.
For a long time, doctors ignored lipoprotein(a). “Nobody measured it, because you could not do anything about it,” says Prakriti Gaba, a cardiologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. That may be about to change now that several groups are testing medicines that target the substance. (Gaba got her own levels checked at a cardiology conference, where booths offering free tests have sprung up recently.)
Many of these experimental medications use genetic technology to silence the apolipoprotein(a) gene. In a handful of small studies, involving dozens to a few hundred subjects each, different apolipoprotein(a)-silencing therapies cut lipoprotein(a) levels by varying levels, from no change up to 92 percent. But it isn’t yet known whether cutting lipoprotein(a) will actually reduce cardiovascular problems. “We won’t know for a while,” says Leslie Cho, a cardiologist at the Cleveland Clinic who’s coleading one of the trials.
Cho’s HORIZON study, the farthest along, is testing a lipoprotein(a)-gene-silencing treatment compared to a placebo in more than 8,300 people with high lipoprotein(a) and a history of heart problems such as heart attack or stroke. The hope is that reducing lipoprotein(a) will decrease the rate of heart attacks, strokes, need for a medical procedure to improve blood flow, and death, but HORIZON isn’t expected to have results until 2025. Another trial that Gaba is involved in, called OCEAN(a)-Outcomes, is testing a similar approach in about 6,000 people, but is not expected to be completed until the end of 2026.
HDL Cholesterol
Just as lipoprotein(a) and LDL cholesterol are known as the baddies, HDL cholesterol has long been considered a good guy. HDL particles are thought to help by sucking cholesterol out of plaques. The HDL then takes this cholesterol to the liver for recycling or disposal. It’s the cardiovascular system’s cholesterol “garbage truck,” says Bob Eckel, a retired cardiometabolic physician and professor emeritus at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus.
If high levels of HDL cholesterol are good, scientists reasoned, then more of this cleanup crew should be even better. Exercising and weight loss can both raise HDL cholesterol. Scientists have tried to do the same with medications — but with disappointing results. The drugs did raise HDL cholesterol levels, yes, but they didn’t save lives in people already on statins, and they were weaker than statins at stopping heart attacks and strokes. “To sum it up very simplistically, approaches to raise HDL failed. Nothing really worked,” says Anatol Kontush, a lipid biochemist at the Sorbonne University in Paris.
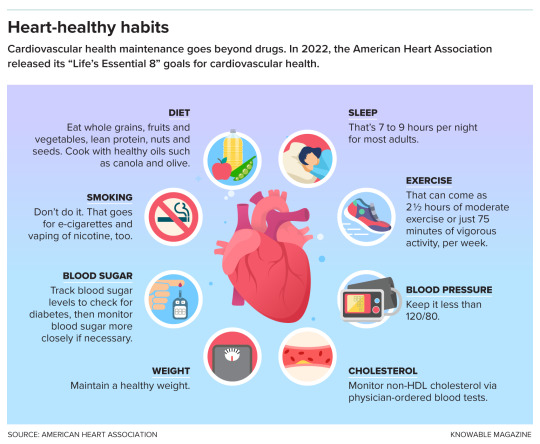
Lifestyle changes can help to reduce the risk of heart disease.
It’s not entirely clear why raising HDL cholesterol in statin-takers bombed. It might be that the idea of boosting HDL cholesterol was simply wrong. High HDL cholesterol might be a marker for good cardiovascular health, rather than a direct cause of it, says Rohatgi. If so, artificially amplifying its levels wouldn’t help.
But the problem also might have been an overly simplistic understanding of HDL cholesterol. Scientists now know that HDL comes in many types and can do many jobs. In addition to hoovering up cholesterol from plaques, it can fight inflammation — that’s good. But sometimes, HDL can turn bad and promote inflammation instead, Cho says, though it’s not clear how. And, she adds, people who are genetically wired to make too much HDL cholesterol can have an enhanced risk for heart disease.
The problem, then, may be that various drugs meant to amplify HDL cholesterol focused on quantity over quality, and increased the wrong kind of HDL. For example, one promising category of drugs raised HDL levels by inhibiting an enzyme that transfers cholesterol away from HDL particles, giving it to LDL particles. Several studies found these inhibitors failed to improve heart health. It might be that stopping the transfer of cholesterol away from HDL particles means the particles had less capacity to pick up new cholesterol from plaques, leaving the cholesterol to languish there. In other words, these garbage trucks were already full.
So the new plan, a last-ditch effort to save lives with HDL, is to help HDL do its cholesterol-removal job better, rather than to just make more of it. Gibson, for example, is chairing a clinical trial of a medicine called CSL112. It’s made of the key protein component of HDL particles — that is, it’s the starting material for HDL particles but still empty of cholesterol. These CSL112 molecules seem to work by creating new HDL molecules primed to pack in as much cholesterol as they can possibly hold. In a preliminary study of more than 1,200 people, two-thirds of whom received CSL112 infusions, the treatment was safe. And when the scientists took blood samples for lab tests, they found that the higher the dose of CSL112 participants received, the more their blood was able to suck up cholesterol.

Depending on their composition, lipoprotein particles can be of different sizes and densities, from small and dense like HDL to large and less dense like chylomicrons and VLDL.
In another study called AEGIS-II, the researchers tested CSL112 infusions in a larger group of people who had just suffered a heart attack and could be most likely to benefit from treatment. Following 18,200 people for a year, it asked whether CSL112 prevents second heart attacks, strokes and death in this population. “That’s a really big, definitive study, and if that doesn’t work, then I suspect the field will completely abandon HDL,” said Nicholls some months back.
In mid-February, CSL of King of Prussia, Pennsylvania — CSL112’s makers — announced that the study did not achieve its main goal of reducing major cardiac events such as stroke, heart attack or death. The researchers are still analyzing the data and will present results in more depth at the American College of Cardiology conference in April.
Triglycerides
If the HDL waters seem murky, the situation with triglycerides, the fatty component of blood that’s carried around in lipoprotein particles, is muddier still. The amount a person has depends on lifestyle: diet, exercise and so on. High triglycerides are linked to a greater risk for cardiovascular disease, and very high levels can lead to inflammation of the pancreas, known as pancreatitis. Thus, it made sense to posit that getting rid of triglycerides would be a healthy thing to do, and many studies have attempted just that — with boggling results.
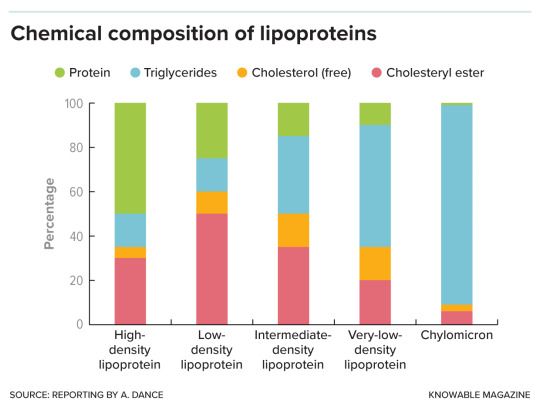
Lipoproteins are made up of protein, fat in the form of triglycerides, and cholesterol — both free cholesterol and a chemically modified, cholesteryl ester, form. The proportion of each varies with lipoprotein type.
One top candidate to reduce triglycerides is based on fish oil, which is high in the omega-3 fatty acids eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). Diets rich in fatty fish or omega-3s have long been linked to lower rates of cardiovascular problems. The fish or fish oil supplements are thought to work by cutting down on fat production by the liver.
So, in a study called REDUCE-IT, researchers tested a highly purified derivative of EPA in more than 4,000 people with cardiovascular disease or diabetes. They compared these patients to a similar number of people who received inert mineral oil as a placebo.
At first glance, the results reported in 2019 looked “really spectacular,” says Nicholls, who wasn’t involved in the trial. In the group that had taken the EPA for about five years, risk of major cardiovascular problems or death dropped by 25 percent or more compared to those getting a placebo. But oddly, this benefit came without a big reduction in the triglycerides themselves.
In other words, “if EPA is working, it’s doing something other than lowering triglycerides,” says Kenneth Feingold, an endocrinologist and emeritus professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco. EPA might counter inflammation, for example, or stabilize the membranes of heart cells.
Based on the REDUCE-IT results, the US Food and Drug Administration approved the purified EPA derivative in 2019 as a medicine for people with high triglycerides and other cardiovascular risk factors. But things got more confusing in 2020, when Nicholls, Nissen and colleagues published another trial, called STRENGTH. This study also aimed to lower triglycerides in high-risk patients, about 6,500 of them, using EPA plus DHA. The researchers compared these patients to people who received a corn oil placebo. But the team halted their study early because, although triglyceride levels did fall, EPA plus DHA didn’t seem to have any beneficial effect on the rate of heart attack, stroke, hospitalization for heart problems, or death.
Researchers are still debating why REDUCE-IT hit paydirt but STRENGTH faltered. Looking back at REDUCE-IT, some experts see a problem with the mineral oil placebo that was used. LDL cholesterol levels and signs of inflammation went up in that group — and if the control participants were worse off than if they’d received nothing at all, then their data would make the experimental treatment look better than it really is.
But Gibson, who was part of the REDUCE-IT team, argues for a different explanation: that pure EPA is better than the EPA/DHA combo. And supporting REDUCE-IT’s conclusions, he points to an older, 1990s study that compared people taking EPA plus statins with people taking statins alone and also found fewer major coronary events in the EPA group.
Then, in 2022, came the latest blow to the once-promising idea of lowering triglycerides: the PROMINENT trial, in which Eckel and colleagues tested a drug called pemafibrate that reduces blood triglycerides. The 10,000-plus study participants had type 2 diabetes, high triglycerides and low HDL, and were at risk for cardiovascular events. But even though triglyceride levels fell by about 26 percent, on average, in the group receiving the drug, this made no difference to the rate of cardiovascular events.
Taken together, the results suggest that triglycerides indicate poor cardiovascular health without being the reason behind the problem. “Triglycerides were just innocent bystanders,” concludes Eckel. The exception, he adds, might be people with very high triglycerides who are at risk of pancreatitis and might still benefit from triglyceride-lowering treatment.
Remnant Cholesterol
This is a loosely used term, with science still to be settled. In the doctor’s office, physicians assume that any cholesterol that isn’t HDL or LDL is a leftover or “remnant” fraction. From a molecular point of view, remnant cholesterol is a fat-delivering lipoprotein in an intermediate state: It left the liver, loaded with fat and cholesterol, and has dropped off some of its triglycerides in the body’s tissues, but not so much of its cargo that it’s become an LDL lipoprotein. Chylomicrons from the gut, once depleted of fats, also become remnant particles.
In people with healthy metabolisms, the body quickly disposes of remnant particles. But if a person has a problem such as diabetes or obesity, these fatty remnants might stick around. Remnant cholesterol may accumulate in atherosclerotic plaques, potentially making it as dangerous as the classic bad LDL cholesterol. Indeed, high levels of remnant cholesterol have been linked to cardiovascular disease in some studies, quite independently of patients’ LDL cholesterol measurements. That suggests that getting rid of those remnants could be beneficial.
The substances remain a bit of a black box, though. “We still don’t know precisely how to define them, we don’t know precisely how to measure them, so it’s kind of difficult to be precise about remnants,” says Feingold. Nonetheless, some researchers are interested in treatments that might target remnants in addition to, or instead of, triglycerides. For example, Nicholas Marston, a cardiologist at Brigham and Women’s, and colleagues are testing a medication called olezarsen that, he says, appears to promote clearance of the cholesterol-carrying particles. But it will take more study to learn if that translates into fewer cardiovascular problems.
Remnant cholesterol is “probably important,” says Nissen — so even though the science is still nascent, he says he feels hopeful about the potential of treatments targeting it.
In sum, the emerging picture is one in which certain forms of HDL cholesterol are good and all the other lipoproteins are bad. The best approach, experts suggest, may be to reduce all the non-HDL cholesterol — whether by diet and exercise or some of these new medicines, should they prove effective.
“If it’s not HDL, we should minimize it,” says Feingold. “The lower, the better.”
— Editor’s Note: This article was amended February 15, 2024, to add the preliminary results of the AEGIS-II trial aimed at raising levels of HDL and to remove a speculative quote about the ramifications of a positive result from the trial.

#Source: KnowledgeMagazine.Org#Cholesterol#Latest Science#Blood Levels of HDL | LDL#Cardiovascular 🫀 Health#Medicines to Manage#Lipoprotein#Triglycerides#Remnant Cholesterol
0 notes
Text
Could the ‘central dogma’ of biology be misleading bioengineers? - Technology Org
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/could-the-central-dogma-of-biology-be-misleading-bioengineers-technology-org/
Could the ‘central dogma’ of biology be misleading bioengineers? - Technology Org
Today, medicines based on antibodies — proteins that fight infection and disease — are prescribed for everything from cancer to COVID-19 to high cholesterol. The antibody drugs are supplied by genetically engineered cells that function as tiny protein-producing factories in the laboratory.
Confocal microscopic image shows mesenchymal stem cells (green) captured within nanovials (pink). The nanovial technology was developed by UCLA’s Dino Di Carlo and colleagues. Image credit: Shreya Udani/UCLA
Meanwhile, researchers have been targeting cancer, injuries to internal organs and a host of other ailments with new strategies in which similarly engineered cells are implanted directly into patients.
These biotechnology applications rely on the principle that altering a cell’s DNA to produce more of the genetic instructions for making a given protein will cause the cell to release more of that protein.
A new UCLA study suggests that — at least in one type of stem cell — the principle doesn’t necessarily hold true.
The researchers examined mesenchymal stem cells, which reside in bone marrow and can self-renew or develop into bone, fat or muscle cells. Mesenchymal cells secrete a protein growth factor called VEGF-A, which plays a role in regenerating blood vessels and which scientists believe may have the potential to repair damage from heart attacks, kidney injuries, arterial disease in limbs and other conditions.
When the researchers compared the amount of VEGF-A that each mesenchymal cell released with the expression of genes in the same cell that code for VEGF-A, the results were surprising: Gene expression correlated only weakly with the actual secretion of the growth factor.
The scientists identified other genes better correlating with growth factor secretion, including one that codes for a protein found on the surface of some stem cells. Isolating stem cells with that protein on their surface, the team cultivated a population that secreted VEGF-A prolifically and kept doing so days later.
The findings, published today in Nature Nanotechnology, suggest that a fundamental assumption in biology and biotechnology may be up for reconsideration, said co-corresponding author Dino Di Carlo, the Armond and Elena Hairapetian Professor of Engineering and Medicine at the UCLA Samueli School of Engineering.
“The central dogma has been, you have instructions in the DNA, they’re transcribed to RNA, and then the RNA is translated into protein,” said Di Carlo, who is also a member of UCLA’s California NanoSystems Institute and Eli and Edythe Broad Center of Regenerative Medicine and Stem Cell Research. “Based on this, many scientists assumed that if you had more RNA, you’d have more protein, and then more protein released from the cell. We questioned that assumption.
“It seems we can’t assume that if a gene is expressed at higher levels, there will be higher secretion of the corresponding protein. We found a clear example where that doesn’t happen, and it opens up a lot of new questions.”
The results could help make the manufacturing of antibody-based treatments more efficient and define new cellular treatments that would be more effective. Knowing the right genetic switches to flip could enable the engineering or selection of extraordinarily productive cells for making or delivering therapies.
The UCLA study was conducted using standard lab equipment augmented with a technology invented by Di Carlo and his colleagues: nanovials, microscopic bowl-shaped hydrogel containers, each of which captures a single cell and its secretions. Leveraging a new nanovial-enabled analytic method, the scientists were able to connect the amount of VEGF-A released by each one of 10,000 mesenchymal stem cells to an atlas mapping tens of thousands of genes expressed by that same cell.
youtube
“The ability to link protein secretion to gene expression on the single-cell level holds great promise for the fields of life science research and therapeutic development,” said Kathrin Plath, a UCLA professor of biological chemistry, a member of the Broad Stem Cell Research Center and a co-corresponding author of the study. “Without it, we couldn’t have arrived at the unexpected results we found in this study. Now we have an exciting opportunity to learn new things about the mechanisms underpinning the basic processes of life and use what we learn to advance human health.”
While activation of the genetic instructions for VEGF-A displayed little correlation with release of the protein, the researchers identified a cluster of 153 genes with strong links to VEGF-A secretion. Many of them are known for their function in blood vessel development and wound healing; for others, their function is currently unknown.
One of the top matches encodes a cell-surface protein, IL13RA2, whose purpose is poorly understood. Its exterior location made it simpler for the scientists to use it as a marker and separate those cells from the others. Cells with IL13RA2 showed 30% more VEGF-A secretion than cells that lacked the marker.
In a similar experiment, the researchers kept the separated cells in culture for six days. At the end of that time, cells with the marker secreted 60% more VEGF-A compared to cells without it.
Although therapies based on mesenchymal stem cells have shown promise in laboratory studies, clinical trials with human participants have shown many of these new options to be safe but not effective. The ability to sort for high VEGF-A secreters using IL13RA2 may help turn that tide.
“Identifying a subpopulation that produces more, and markers associated with that population, means you can separate them out very easily,” Di Carlo said. “A very pure population of cells that’s going to produce high levels of your therapeutic protein should make a better therapy.”
Nanovials are available commercially from Partillion Bioscience, a company co-founded by Di Carlo that started up at the CNSI’s on-campus incubator, Magnify.
The first author of the study is Shreya Udani, who earned a doctorate from UCLA in 2023. Other co-authors, all affiliated with UCLA, are staff scientist Justin Langerman; Doyeon Koo, who earned a doctorate in 2023; graduate students Sevana Baghdasarian and Citradewi Soemardy; undergraduate Brian Cheng; Simran Kang, who earned a bachelor’s degree in 2023; and Joseph de Rutte, who earned a doctorate in 2020 and is a co-founder and CEO of Partillion.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health and a Stem Cell Nanomedicine Planning Award funded jointly by the CNSI and the Broad Stem Cell Research Center.
Source: UCLA
You can offer your link to a page which is relevant to the topic of this post.
#000#2023#antibodies#applications#Biology#biotechnology#Biotechnology news#blood#blood vessels#bone marrow#Cancer#cell#cell therapy#Cells#CEO#chemistry#cluster#code#Containers#covid#development#Disease#DNA#drugs#engineering#equipment#factor#Factories#Featured life sciences news#Fight
0 notes
Text
Diet After Stent Implant- What to Consume and What Not?
Heart disease has cast its shadow over India in the last few decades. As per research, one out of four Indians dies in CVD(cardiovascular disorder). While stent placement is not the only solution, it’s time that we take care of our heart after surgery.
Experts suggest heart disease is preventable and, in many circumstances, reversible if dietary modifications are made. Simple lifestyle changes and healthy eating habits can go a long way to fighting against heart disease. Here we will discuss which diet you should plan after heart treatment and what to avoid after stent. Continue reading to learn more.
Understanding angioplasty- How diet can affect the treatment outcome after angioplasty?
The arteries of your heart might get clogged or restricted as a result of an accumulation of cholesterol, cells, or fatty plaques.
As a result, the flow of blood to your heart may be reduced, causing chest tightness or blood clots, and finally leading to a heart attack.
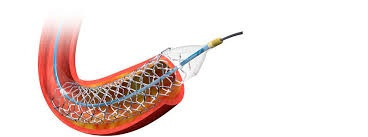
The angioplasty procedure can be life-saving to open up the clogged arteries by placing a stent inside the artery. But can not cure atherosclerosis or narrowing of blood vessels.
With minimal dietary changes, you can reduce the risk of developing heart diseases by severalfold.
Diet after stent implant- What to consume?
A well-balanced diet enriched with heart-protective nutrients can help your heart to score a long run. Vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, dietary fibers are necessary to improve your overall cardiovascular health, lower the cholesterol level and prevent any recurrent plaque build-up after angioplasty or stent placement.
Here is a list of foods that you can depend on -
Fresh fruits and vegetables- Yes, you read it right! 3-4 servings of fresh fruit and veggies are a rich source of vitamins, minerals, and fibers. While these low-calorie foods can help you to stay active throughout the day and take good care of your health too.
Do not add those toppings loaded with cheese, butter, or high sauce.
Avoid having canned juice with added sugar or salt.
Nuts- It is beneficial to consume these on a daily basis. Cashews are high in zinc, iron, and magnesium, whereas almonds are high in calcium and Vitamin E. Walnuts are highly recommended since they are abundant in omega 3 and are known antioxidants. They also play an important role in reducing LDL.
Sprouts and legumes- Sprouts and legumes (beans, peas, and lentils) are another wonderful source of critical nutrients and low-fat protein, providing fiber and protein to keep your stomach full for extended periods of time. They also lower the chances of heart disease. Sprouts should be consumed in two portions each day.
Healthy oils-Not all fats are unhealthy, in fact, a few are necessary for the body's vital functioning and for lubricating joints. Olive oil and peanut oil are two examples. Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) are preferred.
Freshly brewed tea-When you're in the need of something relaxing and peaceful, opt for freshly made tea rather than packaged one. Tea high in flavonoids may reduce the risk of developing heart issues.
Whole grains- choose whole grains instead of processed flour. Rich in fibers and helps to reduce the cholesterol content from your blood.
Stay hydrated- There is no better way to compensate for fluid loss than to drink more water. When you're sick, your body needs a lot of water to function, fight viruses, eliminate toxins, and replace lost fluids.
Caffeinated beverages should be avoided since they increase water loss through the kidneys and increase heart palpitation as well.
Poultry and fish- Not all protein sources are good for your health. Because they contain less saturated fat than red meat, fish and poultry are considered ideal choices.
Just remember to cook them in a healthy method, such as broiling, baking, or poaching, and stay away from high-fat sauces and gravies.
Fatty fish, such as salmon, trout are high in beneficial fats known as omega-3 fatty acids.
What should you avoid after stent placement?
Avoid having fatty foods, foods with added preservatives or sugars.
Limit coffee intake.
Restrict your salt intake too. This will help to lower your blood pressure and reduce the overall workload of your heart.
Processed fish or meats are not good for your heart. Stay away from red meat as well.
Apart from this, while COVID-19 has affected India’s health care system, our panel of cardiologists has recommended the negative impact of this virus on one’s heart. So to stay hale and hearty, start following the diet regimen.
Why should you consider getting a stent implant in India?
India is the most favored place for heart treatment operations for a few major reasons. And if you are searching for the best heart hospital in India, we will help you out to find the same.
India's cutting-edge reproductive techniques,
medical skills
Multidisciplinary approach
Personalized diet chart for faster healing for post-surgery recovery
Heart treatment costs in India are among the best in the world, as our patients need affordable and quality outcomes.
All these have significantly increased the success rate of stent implant treatment in India.
Conclusion-By simply packing their medical journey to India, heart treatment can substantially benefit the patient. We also offer a comprehensive range of counseling for coping with emotional changes to our international patients.
How can we help in the treatment?
If you are in search of a cancer treatment hospital in India, we will serve as your guide throughout your treatment and will be physically present with you even before your treatment begins. The following will be provided to you:
Opinions of expert physicians and surgeons
Transparent communication
Coordinated care
Prior appointment with specialists
Assistance in hospital formalities
24*7 availability
Arrangement for travel
Assistance for accommodation and healthy recovery
Assistance in emergencies
We are dedicated to offering the highest quality health care to our patients. We have a team of highly qualified and devoted health professionals that will be by your side from the beginning of your journey.
0 notes
Text
‘Keto-like’ diet may be linked to higher risk of heart disease

The ketogenic or “keto” diet, which involves consuming very low amounts of carbohydrates and high amounts of fats, has been gaining popularity. However, a new study presented at the American College of Cardiology’s Annual Scientific Session suggests that a “keto-like” diet may be associated with higher blood levels of “bad” cholesterol and a twofold heightened risk of cardiovascular events such as chest pain (angina), blocked arteries requiring stenting, heart attacks and strokes. Previous studies have shown that a low-carbohydrate, low-fat diet (LCHF) can lead to elevated levels of LDL cholesterol in some people. While elevated LDL cholesterol is a known risk factor for heart disease (caused by atherosclerosis, a buildup of cholesterol in the coronary arteries), the effects of such a diet on risk for heart disease and stroke have not been well studied.
About the new study
The study was conducted by researchers from the Healthy Heart Program Prevention Clinic, St. Paul’s Hospital and the University of British Columbia’s Centre for Heart Lung Innovation in Vancouver, Canada. A LCHF diet was defined as consisting of no more than 25% of total daily calories from carbohydrates and more than 45% of total daily calories from fat. A “standard diet” was defined as ones as a diet that did not meet these criteria and were more balanced in carbohydrates and fat. Proponents of a ketogenic diet generally recommend limiting carbohydrates to 10% of total daily calories, protein to 20% to 30% and consuming 60% to 80% of daily calories from fat. The research team analyzed data from the UK Biobank, a large-scale database with health information from over half a million people living in the United Kingdom who were followed for at least 10 years. Upon enrollment in the biobank, 70,684 participants completed a one-time self-reported 24-hour diet questionnaire and, at the same time, had blood drawn to check their levels of cholesterol. The researchers identified 305 participants whose questionnaire responses indicated that their diet during the 24-hour reporting period met the study’s definition of an LCHF. These participants were matched by age and sex with 1,220 individuals who reported eating a standard diet.
The findings
Compared with participants eating a standard diet, those who followed a LCHF diet had significantly higher levels of both LDL cholesterol and apolipoprotein B (ApoB), the main protein found in LDL cholesterol, also known as "bad" cholesterol because high levels of it can damage the arteries. Previous studies have shown that elevated ApoB may be a better predictor than elevated LDL cholesterol for risk of cardiovascular disease. After an average of 11.8 years of follow-up—and after adjustment for other risk factors for heart disease, such as diabetes, high blood pressure, obesity and smoking—people on an LCHF diet had more than two-times higher risk of having several major cardiovascular events, such as blockages in the arteries that needed to be opened with stenting procedures, heart attack, stroke and peripheral arterial disease. In all, 9.8% of participants on an LCHF diet experienced a new cardiac event, compared with 4.3% of those on a standard diet, a doubling of risk for those on an LCHF diet. The findings suggest that people who are considering going on an LCHF diet should be aware that doing so could lead to an increase in their levels of LDL cholesterol. “Before starting this dietary pattern, they should consult a health care provider”, the researchers said. “While on the diet, it is recommended they have their cholesterol levels monitored and should try to address other risk factors for heart disease or stroke, such as diabetes, high blood pressure, physical inactivity and smoking.”
Individual variation found
The study’s findings also suggest that not everyone responds to an LCHF diet in the same way. “On average, cholesterol levels tend to rise on this diet, but some people’s cholesterol concentrations can stay the same or go down, depending on several underlying factors,” the lead researcher said. “There are inter-individual differences in how people respond to this dietary pattern that we don’t fully understand yet. One of our next steps will be to try to identify specific characteristics or genetic markers that can predict how someone will respond to this type of diet.”
Study limitations
Participants provided dietary information at only one point in time. Moreover, self-reports of food consumption can be inaccurate. Because the study was observational, it can only show an association between the diet and an increased risk for major cardiac events, not a causal relationship. However, the researchers said the findings merit further research, especially considering that approximately 1 in 5 Americans report being on a low-carb, keto-like or full keto diet. Source: American College of Cardiology Annual Scientific Session, 2023. All research on this web site is the property of Leslie Beck Nutrition Consulting Inc. and is protected by copyright. Keep in mind that research on these matters continues daily and is subject to change. The information presented is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. It is intended to provide ongoing support of your healthy lifestyle practices. Source link Read the full article
0 notes
Text
How to Develop Daily Heart-Healthy Habits
How to Develop Daily Heart-Healthy Habits
Worldwide, heart disease is the number one cause of death in both men and women. Heart disease is the leading cause of death for men and women worldwide. We've compiled a list of healthy habits that you can adopt into your daily routine to help prevent heart disease. Heart Care Consultants is the top cardiologist philadelphia. Visit us for philadelphia heart surgery or best consultation.
How to keep your heart healthy
Did you know one American dies from heart disease every 36 seconds? The disease is preventable, but it costs more than $360 billion a year in health care services and medicines. It also causes productivity loss due to deaths. What can you do to avoid heart disease? Here are some heart-healthy tips!
Get regular exercise
The heart is a muscular organ, and it too needs to be exercised to remain strong. Experts suggest moving around at least one hour per day to maintain blood circulation. For heart health, aerobic exercises such as walking, swimming or running are recommended for 30 minutes most days.
Balance your diet

You are what your eat! Heart-healthy food can provide the nutrients your body needs to thrive. Eat a healthy diet that includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains and legumes. Also, include lean meats, fish, and dairy products with low fat. When possible, limit saturated fats, sodium, sugars processed and trans fats. Drink plenty of water and other fluids. You can also enjoy coffee or green tea with no added sugar. Supplements like vitamin D, fish oil and fiber can help fill in nutritional gaps.
Keep a healthy body weight
Extra weight can be harmful to your heart. According to new studies by the American Heart Association, excess belly fat may increase your risk of heart disease. Create a realistic weight loss plan and follow it. You can maintain a healthy body weight by reading food labels, keeping track of your calorie intake, and paying attention to portion sizes.
Stress management: Reduce it
Stress management can be achieved by using simple breathing exercises or meditation techniques. Exercises like yoga, walking outdoors and tai-chi can reduce stress.
Maintain a healthy blood pressure and cholesterol
Heart disease is a major cause of high cholesterol and high blood pressure. High blood pressure can cause cardiovascular complications, which can weaken your heart and place strain on it. High cholesterol can make it harder for your blood to flow into your heart. Healthy eating and exercise can help to keep these levels low.
Stop smoking
Stop smoking. Secondhand smoke can damage the blood vessels and heart. Quitting smoking can reduce the risk of heart attacks and premature deaths and reverse the damage.
.
Why choose Heart Care Consultants to Improve Your Heart Health
Heart Care Consultants is committed to providing our patients with comprehensive cardiovascular care. We can assist you with our cutting-edge cardiac imaging services, or a plan to prevent heart disease through healthy habits. Call us at 215-747-4512 to schedule a cardiologist's checkup.
#top cardiologist philadelphia#heart specialist philadelphia#cardiologist philadelphia#philadelphia heart surgery#Heart Care Consultants in Philadelphia#heart center philadelphia#heart care consultant usa#best cardiologist philadelphia#cardiology center philadelphia
0 notes
Text
I agreed to go and now I am freaking out.
My therapist told me it's my family who needs to make it up me and not the other way around. And that I do not need to put up with their disrespect anymore. I can just walk away if they start any of their bullshit. But I'm still so scared. I feel like the sad little girl who was mistreated all those years and spent nights crying in her room alone.
I agreed to go bc I want to show support for my cousin and his future wife. He's been nothing but nice to me my whole life. I've never had any issues with him. The issues are with most of my aunts and uncles and my older cousins. I want him to know I'm happy for him. And I want his future wife to know I'm on her side. My dad's side of the family can be summed up as "we're better than you because we're Catholic and we will look down on you because of this." I'm worried how the rest of the family will treat her. My mom made sure my sister and I weren't raised that way. But all my other family was raised believing this garbage. Also, for some reason, my dad's side of the family HATES fat ppl. More than the gays. Which says a lot bc Catholics. And my cousin's future wife is "heavy" according to my cousin's mom. Who has expressed her dislike of her (cousin's future wife) to my mom because for that reason. She (my aunt - cousin's mom) never said anything bad about my cousin's future wife other than her weight. As one of the few fat members of the family I want her to know she's not alone. Bc my family will comment on her weight to her. I want to tell her how pretty she looks. I want to make her feel confident bc she deserves to feel that way on her special day.
She's marrying a great man. I want my cousin and his future wife to have a wonderful day. I've never met her but she can't be anything but amazing if she caused my cousin to fall in love with her.
My cousin even reached out to my sister to say he hopes I can come. I never thought any of them would miss me. One of the issues I've had with my dad's side of the family was the constant comparison to my cousin who is 6 months older than me (not the cousin getting married). I was always second best. Never the center of attention. Everyone would pay attention to her and not me. And her parents had to make it so she was better at everything than me. I remember when my Grandpa was in the hospital and my uncle made a big deal about my cousin being in advanced classes and having a 2.5 GPA. I just mentioned I was also in advanced classes and had a 3.8 GPA. We went to different high schools. (My choice. I could have gone to the same school as her but I didn't want too). My uncle had to ask my older cousin (not the one getting married) who is a teacher which school had "the better" advanced classes.
I haven't been to a family gathering on my dad's side of the family in like 7/8 years maybe longer. I've seen a few family members throughout the years but not many and never all of them at once. My dad's side of the family is v large. My dad is 1 of 9. All but 2 had at least 1 child. Most had more. And I'm one of the youngest. So my older cousin's have been having kids. There's an insane amount of us. I'm worried about seeing all of them again. What will I tell them? The truth? That most of you and their parents caused me an insane amount of childhood trauma? That you caused me to have eating disorders? That you caused me to start self harming? That I think some of you hid the fact my dad was cheating on my mom from her? That I hate you bc you encouraged my dad to drink and just pretended my mom no longer existed after my dad left her 6 months after she had a massive heart attack and died 6 times on the operating table? She was still recovering! She had to relearn how to walk! It's a mircale she survived let alone didn't have any brain damage! How do you think I'm not mad at you for telling my dad to put her in a nursing home while she was having her first surgery? You guys had no idea what was going on! And were already planning on getting rid of her! How can I not hate you for not even asking my sister and I if we were doing okat after my dad moved out? We would have told you our mom spent all her time crying and threating to kill herself! We had no money! Our mom was only working part time at the time my dad left! You discarded us like you discarded our mom! I can't tell them all that. Not at my cousin's wedding at least. It's a happy event. Idk what to do.
I’m being guilt tripped into going to a wedding.
14 notes
·
View notes
Note
Okay then for the ask game, let me think... We both know I was gonna give ya Kallus. Go!
Yeah I did know you were gonna ask me about him, that fine I'm happy to anyways!
First impression: well I was about 12 when I frist watched rebels and I kinda thought he was a big fat jerk. I thought his muttonchops were stupid.
Impression now: he's just a sad sleepy baby and I love him. He's a real bad ass and a /snarky son of a bitch/tm. All he ever really wanted to do was help people and it blew up spectacularly in his face and he didn't even realize. Also he's an excellent actor but has atrocious people skills. And his muttonchops are glorious.
Favorite moment: in "the Honorable ones" (*cough cough broke back mountain*) you can actually pin point the second he realizes he's in love with Zeb. It's just after the spectors leave and he leans against the wall to keep out of sight. You can actually see the gay panic on his face.
Story idea: Zeb meets the Lasat mercenary but he's so excited that there's another Lasat that he doesn't realize who he is. Kallus doesn't want to take away the opertunity to connect with another member of his species from Zeb so he just sits quietly in the back of the ghost definitely not having a panic attack until Ezra and Sabine find him. He doesn't want to worry them so they build a blanket fort together and get Kannan to go check on Zeb because even if he is with a lasat they're not going to just leave him alone with a dangerous murderer. Eventually Kallus is more scared for Zeb than he is for himself and he runs out to find him but he confronts the merc instead who eventually does recognize him. I'll eventually write the whole thing but that's it for now.
Unpopular opinion: Okay you're gonna hate me. He dies semi young, around early to mid 70s. Cause of death is heart failure due to decades of constant chronic stress.
Favorite relationship: Kalluzeb for life baby! Also love him being family with the spectors, him and Kannan bonding over growing up on Coruscant around the same time. I bet they both have *dad energy* when they hang out. They would both wear Hawaiian shirts and socks with sandels and rock out to Queen music. Of course Sabine would be super protective of Zeb and really not like Kallus hanging around him at first, but she warms up to him after she sees how much Zeb likes him. Then she starts to like him more than Zeb (but she only says that to tease him) Kallus calls her "his favorite" right infront of Zeb. He doesn't really get along with Rex at first. Every civilian on Coruscant during the war has a "complicated" opinion on the clones. Actually I'll just make a separate post for all of them.
Favorite headcannon: OH man how could I narrow it down to just one!? I can't, here's 3:
1. He has scars from the lasat merc that he's extremely self conscious about. He was terrified to show them to Zeb because he thought he would be seen as "damaged goods" or Zeb would think he got them on lasan and be reminded of what a terrible person he is.
2. When he was a teenager he was very good in school, always ambitious but also had a manageable but harmful substance abuse problem. He used to blackout drinking and get into bar fights almost every night, and got high every other night.
Someone: you know your future self is gonna hate you.
Young Kallus: jokes on that asshole, I'm gonna ruin his life.
3. He is a massive dork. He would love murder mystery novels, sings to himself as he cooks and talks to his pet tooka. One time he got a concussion because he sneezed and smacked his face against a wall.
#star wars#alexsandr kallus#sw rebels#hot kallus#garazeb orrelios#kalluzeb#star wars rebels#incorrect star wars rebels quotes#ezra bridger#sabine wren#star wars rebels headcanons#ask game#writing
43 notes
·
View notes
Note
"i know she doesnt have a body any real person can have but you shouldnt bodyshame it!!" ok so does how someone treat a doll show how they feel about real peoples bodies or not??? @ that person not you
I don't know how to answer this because it's not directed at me.
But I'm gonna do it anyways.
I love Monster High with all of my cold black heart, HOWEVER one thing I have always had contempt for was how super thin the characters were.
On one hand, as an artist myself I get it! they aren't supposed to look like real people, they are stylistic skinny! but on the other hand - any style that does not allow for bigger characters is a garbage art style and whoever endorses it is a hack artist whom I refuse to respect.
That being said: the G1 doll bodies set an unrealistic standard for actual people to try and replicate and you all KNOW they did. I comb the MH tag pretty regularly and I have seen the most depressing eating disorder posts, pro-ana/mia propaganda, calorie counters to look like cartoon characters. it's not right, As someone who had an eating disorder in High school I refuse to let that social sickness ruin my happy place and I report these posts with extreme prejudice because I don't want that brainwashing that infected me to hurt anyone else, I didn't deserve that, NO ONE deserves that! I will shield this fandom from that poison with every fiber of my being.
The G1 bodies looked good while dressed but the nude dolls looked so awkward, there is only one person I can think of who looks like that, a French Model named Isabelle Caro, Should I perhaps message Ms. Caro to ask how she feels about having this one in a million body that she shares with a popular doll line?.... oh wait! I can't! Because she's fucking dead.

She was only 28 when she died. The cause? immunodeficiency due to anorexia. This poor woman needlessly died because of an obsession with being thin. Her death was not in vain though, 4 years after she died France (her home) put a ban on super thin models and in her later years Ms. Caro used her platform to denounce super thin models and warn others to not be like her. a beautiful person taken from us too soon.
I also have personal reasons for not wanting people to get the wrong ideal about super skinny bodies. When I was in High school I had a boyfriend with Anorexia, I loved him with all I had I told him he was beautiful and that I will love him, thin, fat, buff, whatever makes him happy... but my words fell upon deaf ears as the disorder was a lot louder than I was, he was so painfully skinny. 3 years later he had a heart attack and died. I'm not a doctor or nothing but maybe if he was sturdier he would have survived the attack and still be here with me... I don't know. But I would not wish this pain upon my worst enemy.
Now that you know -why- I am so highly motivated to protect others from this blight I hope you'll understand me a little better when I say that Mattel making their dolls thicker is good for everybody involved, there is literally no downside. People who are naturally skinny still get dolls to relate too but now so do other types of people! it's an absolute win! except for Muscular girls y'all kinda got the shaft - but fingers crossed Abbey brings us a new buff body! (which we need, we also need an even chubbier body too but I'm not going to hold my breath) We need every BODY to make our world work. G2 gave us a weak and pathetic attempt at meatier doll bodies, it was too little too late but an attempt was made!
Now... if you read all of this and your a thin person with hurt feelings (Like whoever sent this anon clearly is) you need to get over yourself buttercup. I'm a busy bitch and I don't have time to coddle thin people. Similar to how Black people should not have to tip toe around White folks because their precious white feelings get hurt when they're told they have privilege, I am not going to coddle the thin who make it sound like being told to "eat a sandwich" once in a GREAT while somehow compares to what People of Size face daily, I don't play in the Pain Olympics, there are no winners in the Pain Olympics only losers.
I just won't do it, it's exhausting and I'm already exhausted from navigating a world that doesn't want me to exist.
If your thin and normal I'm confident you can see where I'm going with this and won't wrongfully misinterpret my words as some thinly veiled skinny shaming (which isn't real) Unless you are a Bride in Uganda I don't want to hear a word about how hard life is being thin, that's it! that's the only group of people who I'll give a pass too. everyone else can get a grip and do some research yourself, I don't get paid enough to pander to curious but cowardly thin folks.
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
Kevin Samuels’ Death Caused By Hypertension + Twitter Reacts
Xaviera BryantJuly 18, 2022

Kevin Samuels, the controversial self-proclaimed relationship guru, died as a result of hypertension.
Samuels passed away suddenly on May 5, 2022, at his apartment in Atlanta.
He was 57.
The news of his sudden passing left both his fans and his critics in disbelief. It also caused many to raise an eyebrow about the circumstances surrounding his death.
The Fulton County Medical Examiner’s Office released their findings on Monday (July 18) that Kevin died due to high blood pressure.
“Evidence of hypertension includes a heart whose chambers are thicker than normal,” the medical examiner said.
Kevin Samuels was taking Atenolol, which is a medication used to treat hypertension.
His death is classified as due to natural causes.
According to WedMD, “High rates of high blood pressure in Black people may be due to the genetic makeup of people of African descent.”
The site also reports, “Researchers have uncovered some facts: In the U.S., Black people respond differently to high blood pressure drugs than do other groups of people. African Americans also seem to be more sensitive to salt, which increases the risk of having high blood pressure.”
Even in death, the impact of Kevin’s beliefs, words, and teachings still garner strong reactions.
He is currently trending on social media as people react to the news of his cause of death.
One person commented, “You mean to tell me Kevin Samuels died from hypertension after building his platform attacking fat women and saying their health was failing? hm.”
“I’ll never understand why so many people were mad at Kevin Samuels for telling the truth. I still enjoy watching all of his videos, he speaks nothing but facts,” another person wrote.
Read more Twitter reactions below.
Kevin Samuels: **drinks 10 Red Bulls a day**
Hypertension:
pic.twitter.com/ByKyjlEktt
— ? (@dirtywhiteups) July 18, 2022
TMZ: “Kevin Samuels’ cause of death was hypertension.”
Black women: “I guess he wasn’t a high value man after all.” pic.twitter.com/6b6kA8NMkW
— ? (@dirtywhiteups) July 18, 2022
Kevin Samuels died of hypertension. Lesson: focus on your diet, not black women's lacefronts.
— Byewig (@Hazel_ieye) July 18, 2022
People REALLY propped up Kevin Samuels and he ain’t push for a single law, ain’t give away a single meal, ain’t get a single person out of jail. If correlation was cornbread the chili would die single! https://t.co/bARjwFzRKJ
— Northwest Cee (@CeeHawk) July 18, 2022
If a black man ever celebrated the death of a black woman like how y’all did Kevin samuels we would never hear the end of it. He had waaaay too much control over y’all emotions he’s been dead for more than a month now and y’all still bringing him up https://t.co/NdTj2X26vD
— ? (@DonteMarvin) July 18, 2022
Red Bulls and viagra don’t mix
— lil duval (@lilduval) July 18, 2022
So I watched a few Kevin Samuels interviews and the verdict is a lot of things he said was facts a lot of y’all just be goin off of snippets and don’t know the context…
— RamBo (@tharealflexgod) July 18, 2022
Despite how controversial he may have been, Kevin Samuels was still a human being with a family who loves and misses him dearly.
My condolences and prayers to his loved ones.
Sent from my iPhone
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Natural Way - How to Reduce High Cholesterol
Cholesterol is a wax-like substance present in the cell membranes of body tissues and is carried in the blood plasma. It is a sterol (alcohol and steroid combination), also called atherosclerotic plaque. The body requires cholesterol to form and sustain the plasma membrane, help with bile production, and aid the metabolism of fat-soluble vitamins. However, having high blood cholesterol levels is not always good and can even cause an increased risk of cardiovascular health problems such as a heart attack or stroke.
Over time cholesterol builds up on the artery walls, a condition called atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis was thought to be an affliction of the elderly until the 1950s. When American pathologists were sent to Korea by the Pentagon to study the bodies of soldiers who died during the conflict, they autopsied around 2000 soldiers and found that approximately 75% had waxy, yellow deposits on the walls of their arteries; a shocking statistic considering the average age of the soldiers was 21. Their findings astonished the scientific community by highlighting the onset of heart disease in the very young. That’s why our focus here is to help you know a natural way to lower high cholesterol. https://unbelievablehealth.com/the-natural-way-how-to-reduce-high-cholesterol
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
Fear Toxin
@bonebrokebuddy
Alright! As promised, here is my breakdown of my theory on how the fear toxin works. I’ll add a few images in of how I organized some of this thought process, and once I’ve done the toxins I can, I’ll link a google doc with it all combined.
Please remember to take everything I share with a grain of salt. I’m a high school student who did this in the total time of roughly 1.5 hours (not including my required watching of the Gotham episode titled “Scarecrow,” which is helpful if you want background on the versions I researched. Below is also a comic strip exploring some of the other versions (year one, Batman/scarecrow 001))


Alright! Without further ado; lets explain fear gas! History:
When Jonathan Crane was eight years old, his mom died in a house fire, which prompted his father to essentially get rid of fear. The why doesn’t really matter.
What matters is the how.
During Jim Gordon’s first year as a detective in Gotham, he ran into Gerald Crane’s case. What Mr. Crane was doing was killing Phobics (people with extreme phobias) while they faced their worst fears, and turned their adrenaline glands into what was essentially “liquid fear.” This was trial run 1 of fear toxin.
He also injected his sixteen year old kid with it.
What it is:
Fear toxin is a hallucinogenic drug that is designed to target phobias or fears of someone.
What’s in it:
As mentioned before, the fear toxin started out made from solely the adrenaline glands, however liquified.
I don’t know the exact science behind how, but the adrenaline glands produce both aldosterone and cortisol. Both of these are steroid drugs (remember that video of a mom lifting a bus? That).
Aldosterone is a steroid hormone that is normally and regularly produced in your body and used for sodium conservation, regulation of blood pressure, water retention, blood volume, etc.
Cortisol is a steroid hormone that is released in response to stress, and normally increases blood sugar, and metabolites fat, protein, and carbs by suppressing the immune system that would usually fight those off.
There was also, in one version, wildfowl pheromones, which I didn’t research too deeply, but the general idea is that it makes birds attack you.
It also contains some form of hallucinogenic drug that would probably just be trippy as hell, but generally fine, normally.
How it works:
So, how this fear toxin works, is by increasing the aldosterone and cortisol in your body, which can result in, for aldosterone, too much sodium, above average water retention, elevated blood pressure, kidney disease, and cardiovascular disease. For Cortisol, it can result in fucked up bone formation, an under-responsive immune system, and high blood sugar.
The general adrenaline glands are also where most of our fear response comes from, which means that your body is already experiencing paranoia, hyper vigilance, anxiety, and an incredibly extreme paralysis as your body tries to decide between fight or flight.
Not to mention the wildfowl pheromones, which means you are currently getting attacked by every bird nearby.
Now, while all of these things are happening simultaneously (which are all causes of Heart attacks, strokes, seizures, etc.), the hallucinogenic part is targeting your amygdala, specifically the memories.
To make sense of all of this, your body would essentially just throw all of these things together in order to make it make sense, which is where the fear would conjure up the memories that the hallucinogenic would make real, made worse by the birds attacking you, which then triggers your adrenaline glands, and that then increases the issues with Aldosterone and Cortisol, and all of this comes full circle.
And, now that your body is in an extremely stressed scenario and currently being pumped with enough steroid hormones to kill someone, does exactly that.
The blood pressure and sodium, as well as the excess carbs, fat, and protein, the high blood sugar, and the increased risk of cardiovascular disease gives you a heart attack.
If you manage to survive that, there is now an excess of water in your body, as well as an increased blood pressure, and the amount of blood in your body just Keeps Increasing. Which can cause you to literally implode or explode with the pressure that is putting on you physically, and can cause internal bleeding, coughing up blood, blood leaking from eyes, noses, ears, (if you have an Aunt Flo. Down there too), etc. because that blood has to go somewhere.
And if, by some miracle, you survive all of that? Have fun with the immune system of a poor person in the 18th century, as well as underdeveloped bones and an increased risk of like, every medical condition Ever.
If I missed anything, or you want to know more, please let me know! And if you notice any mistakes, please politely correct me. My primary info source is Wiki, and I’m a high school student.
5 notes
·
View notes