#florida state university system
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
This is Florida House Bill 999 (2023).
It was was filed on 2/21/2023 3:37 PM
Since most of the elected officials in the state government of FL are fascits this will pass and will be signed and will go into effect on July 1, 2023. and will IMIDIATELY cause problems, because that's the middle of summer semesters in the Florida State Universty System, who will, under House Bill 999, be in chaos trying to meet the demands of this bill, which are numerous and dangerous.
According to it's summary this bill is:
An act relating to public postsecondary educational institutions; amending s. 1001.706, F.S.; requiring the Board of Governors to periodically review specified information relating to state universities and provide certain direction to such universities; revising the contents of the Board of Governor's strategic plan; authorizing state universities to initiate post-tenure reviews at any time for cause; amending s. 1001.7065, F.S.; revising the academic and research excellence standards for preeminent state research universities; creating s. 1001.725, F.S.; providing requirements for hiring state university faculty; authorizing state university boards of trustees to review the tenure status of faculty members; requiring such boards to confirm the selection and reappointment of specified personnel; providing requirements for certain employment contracts and responsibilities; requiring state university presidents to annually present specified information to such boards; amending s. 1004.06, F.S.; providing that certain entities may not expend funds for certain purposes relating to activities that violate a specified law; providing exceptions; amending s. 1004.6496, F.S.; conforming a provision to changes made by the act; amending s. 1004.6499, F.S.; renaming the "Florida Institute of Politics" as the "Florida Institute for Governance and Civics"; revising the goals of the institute; amending s. 1004.64991, F.S.; authorizing the Adam Smith Center for the Study of Economic Freedom within Florida International University to take specified actions; amending s. 1007.25, F.S.; revising the duties and responsibilities of specified faculty committees relating to general education core courses; deleting a provision authorizing certain course maximums to be exceeded; revising requirements for general education core courses; requiring public postsecondary educational institutions to offer and accept certain credits for certain general education core courses; creating s. 1007.55, F.S.; providing legislative findings; requiring the Articulation Coordinating Committee to submit certain courses to the State Board of Education and the Board of Governors; providing requirements for general education courses; providing requirements for public postsecondary educational institutions and their presidents and boards of trustees relating to general education courses; providing an effective date.
As it is written in the text of the actuall bill, the above is a single 2 page long sentence. I have adjusted the formating by adding paragraph breaks after each semicolon because I can't read it clearly as written in the bill.
It is February 24, 2023. This bill, as I said earlier, most likely going to pass. This is a problem both because of it's deadline and because of it's content. Just one of the many things not explicitly made clear in the summary is that it will require universities to report on its highest and lowest performing degrees with regards to job placement to the board of governors.
It also will efectively end tenure and make professors volunerable to the whims of both the board of governors and the individual university presidents.
It redefines "preeminent research institution," a thing with an industry standard definition, and will hand that title out to Universities that meet the new state definition (this will trick potential students into applying to schools that are NOT in fact preeminent research institutions)
Everyone should just go read page 13 where they kill the DEI programs, and tenure, and contracts for administrators.
There's this paragraph starting at the bottom of page 19 that does the exact opposite of what it's commanding and will lead to accrediting issues (a thing the institutions are already concerned about because the governor is already requiring a change in accrediting body)
General education core courses may not suppress or distort significant historical events or include a curriculum that teaches identity politics, such as Critical Race Theory, or defines American history as contrary to the creation of a new nation based on universal principles stated in the Declaration of Independence.
This paragraph exists on page 22
The Legislature finds it necessary that every undergraduate student of a public postsecondary educational institution in the state graduates as an informed citizen through participation in rigorous general education courses that promote the values necessary to preserve the constitutional republic through traditional, historically accurate, and high quality coursework. Courses with a curriculum based on unproven, theoretical, or exploratory content are best suited to fulfill elective or specific program prerequisite credit requirements, rather than general education credit requirements.
This is not education this is indoctronation. This is using edicational institutions as a politial weapon. This is facism. This is not JUST Ron DeSantis, and what Ron DeSantis is doing is not JUST putting on a show for voters.
#Florida poltics#florida state university system#education#politics#flroida house bill#fascism#us politics#florida#HB 999
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
25 Years of Exploring the Universe with NASA's Chandra Xray Observatory

Illustration of the Chandra telescope in orbit around Earth. Credit: NASA/CXC & J. Vaughan
On July 23, 1999, the space shuttle Columbia launched into orbit carrying NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory. August 26 marked 25 years since Chandra released its first images.
These were the first of more than 25,000 observations Chandra has taken. This year, as NASA celebrates the 25th anniversary of this telescope and the incredible data it has provided, we’re taking a peek at some of its most memorable moments.
About the Spacecraft
The Chandra telescope system uses four specialized mirrors to observe X-ray emissions across the universe. X-rays that strike a “regular” mirror head on will be absorbed, so Chandra’s mirrors are shaped like barrels and precisely constructed. The rest of the spacecraft system provides the support structure and environment necessary for the telescope and the science instruments to work as an observatory. To provide motion to the observatory, Chandra has two different sets of thrusters. To control the temperatures of critical components, Chandra's thermal control system consists of a cooling radiator, insulators, heaters, and thermostats. Chandra's electrical power comes from its solar arrays.
Learn more about the spacecraft's components that were developed and tested at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Fun fact: If the state of Colorado were as smooth as the surface of the Chandra X-ray Observatory mirrors, Pike's Peak would be less than an inch tall.

Engineers in the X-ray Calibration Facility at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, integrating the Chandra X-ray Observatory’s High-Resolution Camera with the mirror assembly, in this photo taken March 16, 1997. Credit: NASA
Launch
When space shuttle Columbia launched on July 23, 1999, Chandra was the heaviest and largest payload ever launched by the shuttle. Under the command of Col. Eileen Collins, Columbia lifted off the launch pad at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Chandra was deployed on the mission’s first day.

Reflected in the waters, space shuttle Columbia rockets into the night sky from Launch Pad 39-B on mission STS-93 from Kennedy Space Center. Credit: NASA
First Light Images
Just 34 days after launch, extraordinary first images from our Chandra X-ray Observatory were released. The image of supernova remnant Cassiopeia A traces the aftermath of a gigantic stellar explosion in such captivating detail that scientists can see evidence of what is likely the neutron star.
“We see the collision of the debris from the exploded star with the matter around it, we see shock waves rushing into interstellar space at millions of miles per hour,” said Harvey Tananbaum, founding Director of the Chandra X-ray Center at the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory.
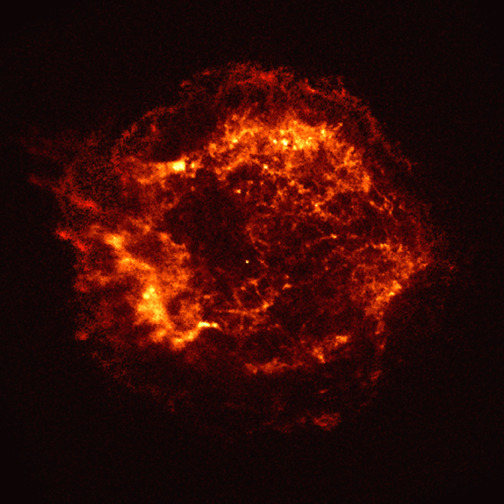
Cassiopeia A is the remnant of a star that exploded about 300 years ago. The X-ray image shows an expanding shell of hot gas produced by the explosion colored in bright orange and yellows. Credit: NASA/CXC/SAO
A New Look at the Universe
NASA released 25 never-before-seen views to celebrate the telescopes 25th anniversary. This collection contains different types of objects in space and includes a new look at Cassiopeia A. Here the supernova remnant is seen with a quarter-century worth of Chandra observations (blue) plus recent views from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (grey and gold).

This image features deep data of the Cassiopeia A supernova, an expanding ball of matter and energy ejected from an exploding star in blues, greys and golds. The Cassiopeia A supernova remnant has been observed for over 2 million seconds since the start of Chandra’s mission in 1999 and has also recently been viewed by the James Webb Space Telescope. Credit: NASA/CXC/SAO
Can You Hear Me Now?
In 2020, experts at the Chandra X-ray Center/Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory (SAO) and SYSTEM Sounds began the first ongoing, sustained effort at NASA to “sonify” (turn into sound) astronomical data. Data from NASA observatories such as Chandra, the Hubble Space Telescope, and the James Webb Space Telescope, has been translated into frequencies that can be heard by the human ear.
SAO Research shows that sonifications help many types of learners – especially those who are low-vision or blind -- engage with and enjoy astronomical data more.
Click to watch the “Listen to the Universe” documentary on NASA+ that explores our sonification work: Listen to the Universe | NASA+

An image of the striking croissant-shaped planetary nebula called the Cat’s Eye, with data from the Chandra X-ray Observatory and Hubble Space Telescope. NASA’s Data sonification from Chandra, Hubble and/or Webb telecopes allows us to hear data of cosmic objects. Credit: NASA/CXO/SAO
Celebrate With Us!
Dedicated teams of engineers, designers, test technicians, and analysts at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are celebrating with partners at the Chandra X-ray Center and elsewhere outside and across the agency for the 25th anniversary of the Chandra X-ray Observatory. Their hard work keeps the spacecraft flying, enabling Chandra’s ongoing studies of black holes, supernovae, dark matter, and more.
Chandra will continue its mission to deepen our understanding of the origin and evolution of the cosmos, helping all of us explore the Universe.
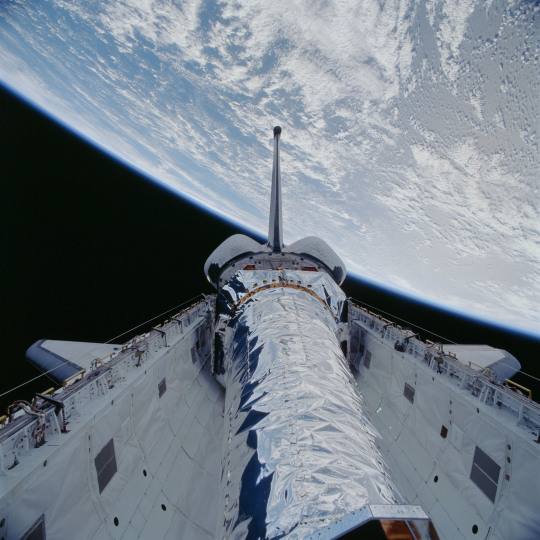

The Chandra Xray Observatory, the longest cargo ever carried to space aboard the space shuttle, is shown in Columbia’s payload bay. This photo of the payload bay with its doors open was taken just before Chandra was tilted upward for release and deployed on July 23, 1999. Credit: NASA
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
2K notes
·
View notes
Video
n240_w1150 by Biodiversity Heritage Library Via Flickr: The North American sylva;. Philadelphia,Rice, Rutter & co.,1865.. biodiversitylibrary.org/page/29146650
#North America#Trees#University of Pittsburgh Library System (archive.org)#bhl:page=29146650#dc:identifier=http://biodiversitylibrary.org/page/29146650#taxonomy:binomial=Ficus citrifolia#Leaves#Fruit#taxonomy:binomial=Ficus brevifolia#taxonomy:family=Moraceae#taxonomy:common=#taxonomy:common=Shortleaf Fig#taxonomy:common=Wild Banyantree#geo:continent=North America#geo:continent=South America#geo:locality=West Indies#geo:locality=Central America#geo:country=United States#geo:state=Florida#geo:country=Mexico#flickr#ficus#fig#ficus brevifolia#Ficus citrifolia#shortleaf fig#giant bearded fig#Jagüey#wild banyantree#Wimba tree
0 notes
Text
I would have bled out in the parking lot
Amber Nicole Thurman's death is on Trump's hands
Bess Kalb
Sep 17
In 2019, about six weeks after my first child was born, I found myself on the bathroom floor in a small, but nonetheless unsettling puddle of blood.
“Oh no,” I remember thinking. “I just did the laundry.”
I called out my husband’s name, but the sound caught in my throat. The pain I felt inhaling to get enough air out of my lungs to yell the two syllables in “Char-lie” jabbed my guts like a bicycle spoke to the abdomen.
So I was quiet, trying to keep breathing in a way that didn’t move anything inside me, and the pain pulsed a bit, then steadied, then dulled, then evaporated into whatever hell ether it came from.
Because there is no G-d (unless there is, in which case I abbreviated His name so as not to desecrate it, and also thank you, King of the Universe, for subscribing to this newsletter) this was the one time in my life I hadn’t brought my phone with me to the bathroom.
I decided to sort of slither-lumber to the door like a lame harbor seal, because I didn’t want to stand and loosen the spoke that had just stabbed me. I reached for the knob and let the door creak open.
The cat was there, looking at me right at eye level, keenly aware what was happening, and completely unmoved by it.
“You are dying,” he blinked, “Pity. Have a nice time.” He sashayed away.
Fortunately, our house in Los Angeles was small enough that from the bathroom door one could see everything. My husband was sitting on the couch with our infant, and I knocked on the open door to summon him. Within one one thousandth of a second, he set the baby on the (since-recalled) donut pillow and was holding my head.
I sat up. I breathed. No pain. I took a picture of the bloody mess on my husband’s phone, texted it to myself, he found my phone, then I texted the picture to my OBGYN.
Apologies for being graphic, but within the puddle there was something roughly the size and shape and color of a fig.
“Is this ok?” I said to my doctor, the bicycle spoke scraping lightly at my insides again from all the lumbering.
“Come in,” she replied.
Within two hours, I was in the waiting room of her office, accompanied by my terrified but SMILING mother, who was still, as is the Jewish custom, in town for “a few days or so” after the birth.
An ultrasound which felt like the finger of Satan himself revealed there was retained placenta in my uterus. If I hadn’t come in, there would have been more hemorrhaging, then sepsis, then whatever the cat foretold.
The next day, I was in surgery getting a Dilation and Curettage.
I went home, pumped the anesthesia milk, then fell asleep perfectly fine, my sweet newborn cooing merrily in the bassinet next to his alive mother.
Amber Nicole Thurman’s story was the same as mine, but it happened to her in Georgia in 2024, not California in 2019. She was a Black woman in a healthcare system that disproportionately kills Black women, especially postpartum. In 2021, the Black maternal mortality rate was nearly three times the rate it is for white women. Post-Roe, the toll is and will continue to be staggering.
Because post-Roe, the procedure that saved my life, the D&C, is something doctors cannot perform in states where matters of life and death have been left up to non-medical Christian-supremacist superstitions.
I know the pain Amber Thurman felt when that placenta dislodged and carved its tiny, treacherous hole in her uterine wall. I know the terror she felt when she saw the blood, and the rush of dread when she thought of what her child would do without her.
And when I vote in November for Kamala Harris and every progressive down-ballot candidate, I will do it because she can’t. And I will do it so that women in Georgia and Idaho and Texas and North Dakota and South Dakota and Utah, Arizona, Nebraska Iowa, Missouri, Arkansas, Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama, Tennessee, Kentucky, Indiana, Florida, South Carolina, and West Virginia won’t have to meet the same completely preventable doom.
This election isn’t just about Amber Thurman. Every day of my lucky, breathing life is about Amber Thurman. Because the only thing that separates us, is one of us bled out under the right Supreme Court.
Let’s raise absolute federal hell about it.
-- From Bess Kalb's newsletter The Grudge Report. I pay for this substack -- though it's free-- and think this is a message worth sharing far beyond her newsletter.
#bess kalb#the grudge report#abortion#abortion rights#abortion is healthcare#kamala harris#amber thurman
345 notes
·
View notes
Text
Dandelion News - October 8-14
Like these weekly compilations? Tip me at $kaybarr1735 or check out my Dandelion Doodles on Patreon!
1. All 160 dogs at Florida shelter found homes ahead of Hurricane Milton

“[The shelter] offered crates, food and anything else the dogs would need in exchange for the animals to spend just five days with the foster parents if the human didn't want to keep them for longer. […A]fter about a day of receiving around 100 messages every 30 minutes, Bada said, all 160 were gone from the shelter and in safe and warm homes.”
2. Restoring Ecosystems and Rejuvenating Native Hawaiian Traditions in Maui

“[Volunteers] are restoring water flow to the refuge, removing invasive species, and restoring a loko iʻa kalo using ʻike kūpuna, ancestral knowledge. […] This human-made ecosystem will provide food for community members and habitat for wildlife while protecting coral reefs offshore.”
3. Solar-powered desalination system requires no extra batteries

“In contrast to other solar-driven desalination designs, the MIT system requires no extra batteries for energy storage, nor a supplemental power supply, such as from the grid. […] The system harnessed on average over 94 percent of the electrical energy generated from the system’s solar panels to produce up to 5,000 liters of water per day[….]”
4. Threatened pink sea fan coral breeds in UK aquarium for first time

“The spawning is part of University of Exeter Ph.D. student Kaila Wheatley Kornblum's research into the reproduction, larval dispersal and population connectivity of Eunicella verrucosa. […] Pink sea fans are believed to have been successfully bred by only one other institution, Lisbon Oceanarium, in 2023.”
5. Tiny 'backpacks' are being strapped to baby turtles[….]

““We analysed the data and found that hatchlings show amazingly consistent head-up orientation – despite being in the complete dark, surrounded by sand [… and] they move as if they were swimming rather than digging[…. This new observation method is] answering questions about best conservation practices,” says Dor.”
6. New California Law Protects Wildlife Connectivity

“A new state law in California will instruct counties and municipalities to conserve wildlife corridors when planning new development. […] This could entail everything from creating wildlife crossings at roads or highways, employing wildlife-safe fencing, or not developing on certain land.”
7. ‘I think, boy, I’m a part of all this’: how local heroes reforested Rio’s green heart

“By 2019, [the program] had transformed the city’s landscape, having trained 15,000 local workers like Leleco, who have planted 10m seedlings across […] roughly 10 times the area of New York’s Central Park. Reforested sites include mangroves and vegetation-covered sandbars called restinga, as well as wooded mountainsides around favelas.”
8. Alabama Town Plans to Drop Criminal Charges Over Unpaid Garbage Bills

““Suspending garbage pickup, imposing harsh late penalties and prosecuting people who through no fault of their own are unable to pay their garbage and sewage bills does not make payment suddenly forthcoming,” West said. [… The city] has agreed to drop pending criminal charges against its residents over unpaid garbage bills.”
9. New Hampshire’s low-income community solar program finally moves forward

“The state energy department is reviewing seven proposals for community solar arrays that will allocate a portion of their bill credits to low-income households. […] New Hampshire’s strategy of working with utilities to automatically enroll households that have already been identified streamlines the process.”
10. The Future Looks Bright for Electric School Buses

“EPA has awarded about $3 billion in grants from the infrastructure law, which paid to replace about 8,700 buses. Of those, about 95 percent are electric. [… Electric buses are] cheaper to operate and require less maintenance than diesel buses and will soon be at cost parity when looking at the lifetime cost of ownership[….]”
October 1-7 news here | (all credit for images and written material can be found at the source linked; I don’t claim credit for anything but curating.)
#hopepunk#good news#dogs#hurricane milton#florida#animal shelters#foster dog#hawaii#hawaiʻi#maui#solar#water#solar energy#coral#endangered species#coral reef#turtles#sea turtle#technology#wildlife#habitat#nature#california#rio#south america#reforestation#poverty#anti capitalism#solar panels#electric vehicles
194 notes
·
View notes
Text
Palmetto Tortoise Beetle: the larvae of this species produce long, thin strands of feces that are gradually woven together to form protective "fecal shields" around their bodies
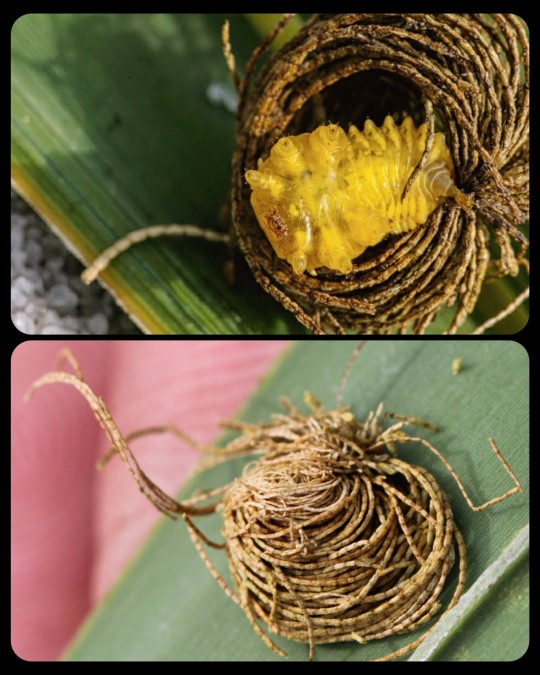

During its larval stage, the Palmetto tortoise beetle (Hemisphaerota cyanea) uses its own feces to create a defensive layer known as a "fecal shield" or "fecal thatch."
As this article explains:
Most remarkable, perhaps, is the fecal “thatch” of Hemisphaerota cyanea. In the larva of this beetle, the feces are emitted in strands, which, as they build up over the course of larval life, form a loose assemblage that totally hides the larva from view.
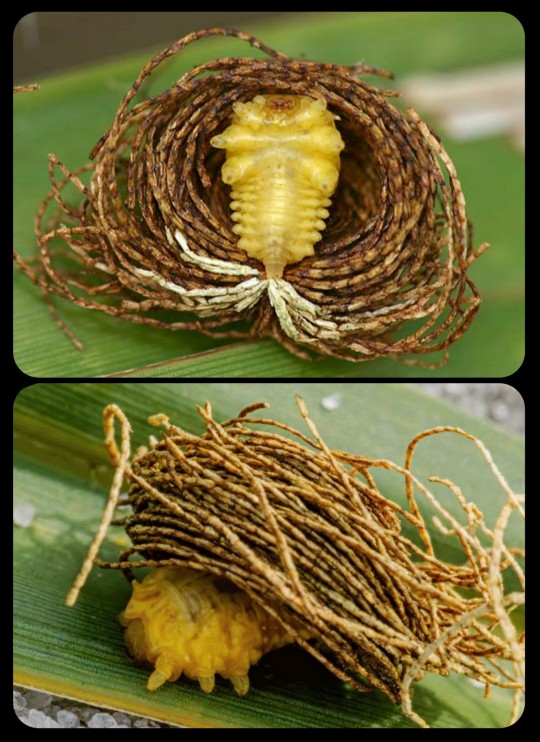

The construction of the "fecal thatch" begins almost immediately after the larva hatches. Each larva begins to feed within minutes of hatching, and the very first fecal strands emerge from its anal turret just a few minutes later. Subsequent strands are then produced in quick succession, and they begin to accumulate around the larva's body; as each strand emerges, it is made to curve around the larva's left or right side depending on whether the anal turret is flexed to the left or right. The direction of the curve usually alternates from one strand to the next, ensuring that a nest-like structure is formed around the larva's body.
As they emerge, the fecal strands are gathered together and then cemented into place with the help of an anatomical feature known as a caudal fork. Once an individual strand has been extruded to its full length, the anal turret is rotated upward until it comes into contact with the caudal fork, and the larva then pinches off the strand while secreting a droplet of "glue," which effectively cements each fecal strand into place against the caudal fork.
It generally takes about 12 hours for the larva to finish building its very own "fecal shield."
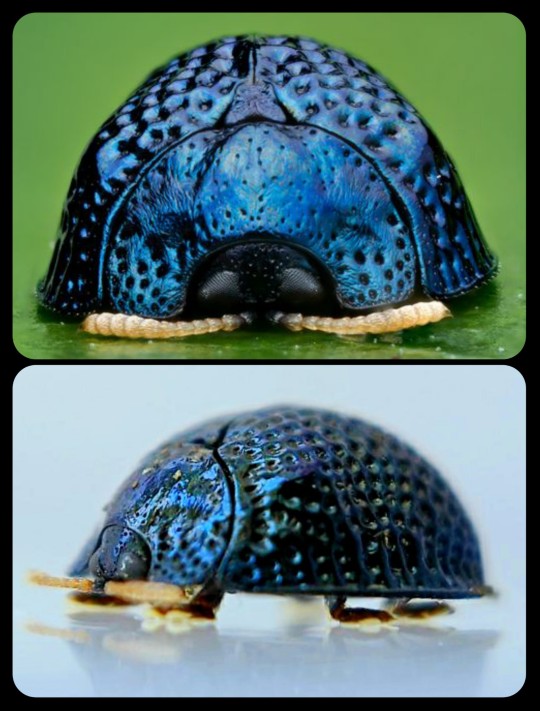

As an adult, the Palmetto tortoise beetle has another unusual defense mechanism: its tarsi (i.e. feet) are each lined with 10,000 tiny adhesive bristles, and when the beetle is attacked, it can press its feet flat against the surface of a leaf and secrete an oil that allows it to adhere to that surface with an enormous amount of strength. The adhesive mechanism is strong enough to resist pulling forces that are up to 60 times greater than the beetle's own weight for a full 2 minutes; it can resist even greater forces (up to 230 times greater than the beetle's own weight) for shorter periods of time.
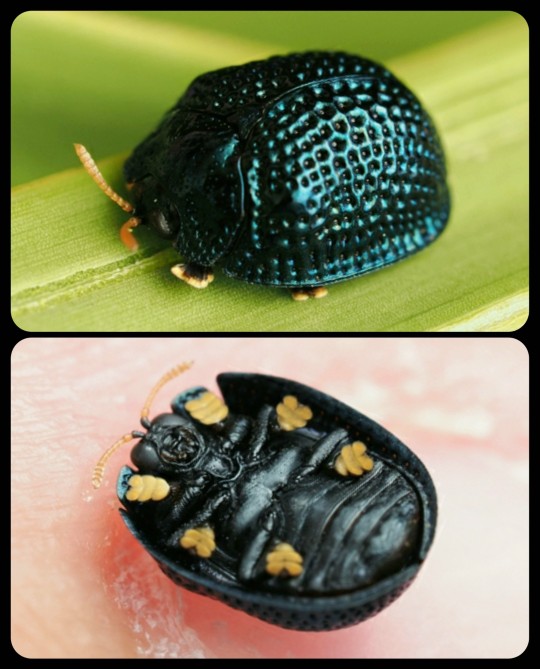

According to this article from the University of Florida:
Each of the greatly enlarged tarsi is equipped with approximately 10,000 adhesive bristles. Each bristle has two terminal pads. When walking, only a few of the bristles touch the leaf surface. However, when attacked by a predator, the beetle puts all or nearly all of the bristles in contact with the surface and secretes oil onto the pads. With the adhesive force created by the oil between the leaf surface and tarsi, the beetle is able to clamp its hemispherical shell down tightly against the leaf and has been demonstrated to withstand pulling forces of approximately 60 times its own weight for up to two minutes. This time period is sufficient to thwart the efforts of predatory ants attempting to pry the beetle from the leaf.
Palmetto tortoise beetles are native to the southeastern United States, and they're especially common in Florida (which is why they're also known as Florida tortoise beetles).
Sources & More Info:
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences: Defensive Use of a Fecal Thatch by a Beetle Larva (Hemisphaerota cyanea)
Earth Touch News Network: By the Power of the Poop-Shield: Beetle Defenses of the Faecal Kind
Cornell Chronicle: Fecal Defense: This Beetle Uses 'Overhead Sewer System' to Ward off (most) Predators, Cornell Biologists Discover
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences: Defense by Foot Adhesion in a Beetle (Hemisphaerota cyanea)
University of Florida: Palmetto Tortoise Beetle
Bug Guide: Hemisphaerota cyanea
#entomology#arthropods#coleoptera#palmetto tortoise beetle#hemisphaerota cyanea#insects#beetles#bugs#animal facts#tortoise beetles#larvae#fecal shield#evolution#defense mechanisms#nature is weird
67 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Perfect Match

Every third week in March, fourth year medical students find out where they'll be going for their residency. A quick 2.2K word one-shot of Jake's girlfriend going through that process.
-----------------------------------------------------------
The nervous energy in the auditorium was almost overwhelming as the clock ticked closer to 11:50AM. All across the US, fourth-year medical students gathered in ceremonies like this, ready to find out where they would be headed in just a few months to begin their residency. It had been a long week - on Monday, everyone received an email letting them know if a residency program had selected them. For those who got one, it was a waiting game to see where they would be moving. Those who hadn't been selected went through the nerve-wracking SOAP process, hoping to secure a job after graduation. With the number of medical graduates increasing faster than residency positions, it wasn't always a guarantee.
You, however, already knew where you were going and what specialty you would be practicing. For months last year, you'd flown across the country, interviewing with residency programs at different installations and civilian hospitals—backups in case you didn’t match with a base hospital and had to compete for a civilian spot. And a perk of matching through the military was getting notified of your posting in mid-December, while civilians had to wait until the third week of March.
On December 15th, you received that wonderful email alerting you that you had matched into Emergency Medicine at Naval Medical Center San Diego. Not only was Emergency Medicine a competitive specialty, but the location meant that you would finally be able to be close to your long-distance boyfriend, Jake, after seven long years.
A chance encounter over Spring Break freshman year led to late-night calls when he returned to Annapolis and you to College Park. For four years, you lived 35 minutes apart in Maryland, stealing as much time as possible together over the weekends. And after graduation, you had a long conversation about your future.
Jake had been clear from the beginning that he wanted to be a pilot, just as you had been firm about attending medical school. He supported you as you struggled through Organic and Biochemistry and tutored you in Physics. He would try not to laugh as you traced his skin, naming the muscles, bones, and systems as you reviewed for anatomy. Care packages showed up at your apartment when you spent as much time as you could getting clinical hours, volunteering in a research lab, and studying for the MCAT. Jake knew how important getting your CV ready was and tried not to complain too much when your weekends spent together were mainly catching up on chores or sleep.
Senior year, you were offered a spot at Florida State University College of Medicine. Jake had been notified in his junior year that he had been accepted into the flight program.
After graduation, you and Jake packed up your things and drove to Florida together. He had a few weeks until he had to report to Pensacola, just a 3-hour drive down I-10 from where you would be in Tallahassee. The apartment you got was right across the street from the med school, a small one-bedroom, but you knew you wouldn’t spend much time there anyway. It would be a place to eat and sleep, but most of your time would be spent on campus or driving to Jake’s in Pensacola. He would only be there for a few months until transitioning to the next base, and you wanted to spend as much time together as possible.
Unlike other medical schools, FSU required students to start in the summer to complete the Anatomy course. Over the short term, students would complete a full-body dissection. The smell of formaldehyde became commonplace, and the TAs warned you to wear shoes and scrubs you wouldn’t hate to throw away in August.
They were right.
It was a rough transition to med school, but it was manageable. And you loved it. Your professors ensured you treated the cadavers with the utmost respect while gently encouraging competition by announcing a dissection team winning each week. The faculty brought you to a rural community to learn about rural medicine, sharing food and stories with those less fortunate. The physician assistant students joined on the trip, and you learned about an inter-professional day that you’d be expected to participate in later - role-playing a case with MD, PA, pharmacy, and social work students.
And while you were working toward your dream, Jake was getting closer to his. Nights were spent catching up, and he was so excited to tell you about his flight training. He promised to get his civilian pilot license as soon as possible and rent a plane to take you up in the air. On the rare weekend you didn’t need to spend in the anatomy lab cramming for an exam, you drove to his place late Friday night and headed back to Tally on Sunday morning.
In August, Jake requested time off to come and see you celebrate finishing your first semester. Seated in the audience, he watched as your faculty member helped you don your first white coat, and you recited the Hippocratic oath. The one-week vacation before Fall term started wasn’t long enough, but you enjoyed waking up in Jake’s bed and going to the beach.
Joining the military had never been in your future, but the longer you spent around Jake and his friends, the more commissioning in the Navy seemed attractive. A medical officer recruiter spoke at the college, and you signed your paperwork. After spending a few weeks working in a clinic during the summer after the first year, you headed to Rhode Island to complete Officer Training. Jake called you as soon as you graduated, welcoming you into the service with only some light teasing about outranking you. As an Ensign, you would be forced to salute your Lieutenant boyfriend when you saw him.
It was harder to see each other when he graduated from flight school and was stationed in California, but you managed to get by with phone calls and vacations. Toward the end of your second year, Jake was sent on deployment as you studied for the Step 1 exam - testing your foundational knowledge and one of the most intimidating exams you faced. The school gave you dedicated study time, and you took advantage of his offer to study at his apartment in Lemoore. His buddy, Coyote, met you at the airport and drove you to Jake’s apartment. A bouquet of flowers was sitting on the counter, and you stared at them as you mentally ran through Anki decks to quiz yourself.
Jake came home the last week you were there. Fully recovered from the 8-hour exam, you greeted him with all the other family members on the flight line. It was the first time you saw him in his jet, and you made sure he knew how much you appreciated the sight. But too soon, you had to return to Florida and pack up your apartment in Tally to move to Pensacola for your last two years of medical school. On your last night in Lemoore, Jake took you out dancing and promised he would request leave to visit soon.
Between your rotations and his shitty schedule as a junior officer, it was hard to see one another. At the end of your third year, you hit a rocky spot and talked about breaking up. But cooler heads prevailed, and you promised to do your best to match into a residency near him. He agreed to try and get orders to be closer to you once you graduated.
Jake had been your first call on December 15th. Sobbing, you told him you’d join him in San Diego, where he’d been stationed for the last four months.
The last-minute plane tickets had been expensive, but it had been so worth it to spend Christmas with him, making plans to move your stuff across the country, and finally be together. He’d held your hand as you pulled your name from the NBME Match Database, officially alerting the civilian hospitals you’d interviewed at that you were no longer hoping to match with them.
So, while your friends waited anxiously to open their envelopes, you felt a sense of calm. In nine short weeks, you would be back in this auditorium wearing your dress whites under your cap and gown. After getting your diploma, your new orders would be published, and you would be promoted to Lieutenant. And after? Jake was scheduled to return from a deployment in a month and requested leave to help you pack up your apartment and start the cross-country road trip.
Eight years of hard work would culminate in moving in with the man you loved. Who could support you in person as you went through the hell of residency and got used to being a full-time Naval officer.
The Dean crossed the stage and welcomed everyone. As the clock struck noon, she encouraged everyone to open their envelopes.
Tearing it open, you stared at the words confirming your future - Emergency Medicine, Naval Medical Center San Diego.
Jake.
Cheers broke out, and you turned to hug your friends as they screamed with happiness or smiled to hide disappointment on not getting their top choice.
The ceremony began with each regional campus called up to allow the students to announce their match.
You hadn’t planned on going on stage. The trip back to Tally had only been to see your favorite staff members and to support your friends as they found out where they would be moving. They had brought their family members, partners, and kids to share in the moment. You had come alone, preferring your family to go to graduation instead. But your friends dragged you into the line and handed your name card to the smiling staff.
“Hi,” you said, leaning into the microphone after the Regional Campus Dean introduced you. “I just wanted to say thank you to all of my friends and family. Without you, I wouldn’t have made it through all of this. I matched in Emergency Medicine and will be moving across country to be with my boyfriend, who kept me sane throughout all of this. And I’ll be at Naval Medical Center San Diego
The crowd cheered louder than they had for any of your classmates. Blushing, you lifted your hand and waved, stepping back and quickly walking toward the Campus Dean to shake his hand. But as you neared, he smiled and took a step back.
You froze.
Jake grinned.
Wearing his dress whites, he quickly strode toward you, pulling you into his arms. “What are you doing here?” you demanded, blinking away tears.
“Wasn’t gonna miss your Match Day, darlin’,” he replied.
“You’re supposed to be on the carrier!”
“Might have lied about that.” There wasn’t a trace of regret on his face. “You worked so hard for this, and I wanted to surprise you. My beautiful, smart, adrenaline junky doctor girlfriend.”
“Not yet - won’t be a doctor for another few weeks.”
“You’ve got it in the bag. But I figured since you’re already trading in a couple of ranks - med student and Ensign…” Taking your left hand, he reached into his pocket and lowered himself to one knee.
Vaguely, you heard the crowd get louder, but you couldn’t tear your gaze away from Jake as he held out a diamond ring.
“I thought maybe we could change girlfriend to wife. Will you marry me?”
Unable to speak, you nodded quickly. Jake leapt to his feet and kissed you, smiling against your mouth.
The next few minutes were a blur. You hugged the Deans while Jake shook their hands, and your parents met you off stage - Jake had called to let them in on his plan. His parents texted him after watching the proposal on the school’s livestream. After promising to meet up after the ceremony, Jake joined you in the student section while your parents returned to their seats. Your friends hugged you, whispering excitedly as you showed them your engagement ring.
And later, after a celebratory dinner with your family and drinks at the beer garden with your classmates, you tumbled into bed with Jake. You could taste the beer on his tongue as he licked into your mouth, and you grinned when your ring caught the light and shimmered.
“Lieutenant and Lieutenant Seresin,” Jake chuckled, catching your hand and kissing your ring. “Sounds kinda nice.”
“Mmmm,” you hummed. “My diploma will be issued in two months, Seresin. Then I’m applying for my medical license and getting all my onboarding paperwork done for NMCSD. I might have to go by my last name for a bit… but I kinda like how it sounds with Lieutenant…”
“It does sound nice,” he agreed. “You sayin’ I’ve got 2 months to get it official, or are you telling me you wanna keep your last name?”
“Dunno,” you shrugged. “I’ve spent the last four years thinking I’d practice under my own name.”
“How do you feel about hyphenating?”
Your eyebrows shot up, “You’d be okay with that?”
“Darlin', you did the hard work, and it’s your name. As long as I can call you Doctor Seresin at home, I don’t care.”
In the middle of May, you stood at attention on stage in your whites, having quickly changed out of your cap and gown. The medical recruiter, a local chief petty officer, had been called onto the stage to publish your orders. Forcing yourself not to smile, you pressed your lips together as he read out your name — your new, hyphenated last name and all.
-----------------------------------------------------------
Notes: I used to work in a medical school, and went through three years of working on Match Day. It was one of my favorite events because of the level of excitement. (And yes, we did have a proposal one year.) But it can also be a really hard day - as state above, the number of residency spots is lower than the number of people who graduate. Every year, people go through the SOAP process and don't match. Which means they have to find something to do for a year, and then start the process over again.
Definitely didn't plan on writing this - I think in about an hour? - but I watched a class I worked with Match today and it kicked up a lot of feelings. I had the pleasure of watching young students grow into doctors, and play some small part in that.
As always, thank you to @mamachasesmayhem for encouraging me to write this, and for giving feedback.
#hangman fic#hangman x reader#jake seresin x reader#Jake Seresin#jake hangman seresin#top gun#top gun fanfiction#top gun x female reader
364 notes
·
View notes
Text
Tuition of state institutions is decided by a government body. I'm blaming the state governments for tuition prices not associate deans who run departments unrelated to financial decisions.
Also I'm blaming SCOTUS for deciding student loans are special for some reason so the lender (the department of education) isn't allowed to forgive them because it's unfair to people they didn't lend money to.
There is SOOO much blame to go around for so many different things.
Also I'm addicted to coffee and like baristas idk why they're getting attacked over student loans they most likely have the and are blaming not the associate deans but the governments bodies and politicians who put us in this situation


*Froggie has activated INFINITE BLAME*
421 notes
·
View notes
Text
Emmanuel the Emu: A Story of HPAI Mismanagement
Emmanuel, the TikTok-famous emu owned by Taylor Blake of Knuckle Bump Farms, made national news last month when Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza (HPAI) hit the farm. According to Blake’s initial Twitter thread, Knuckle Bump Farms lost 99% of their avian flock- over 50 individuals- in only three days. These deaths were attributed both to the disease itself and to a cull carried out by the Florida Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services, who did so with Blake’s permission. Emmanuel and a black swan named Rico were the only two survivors, with Emmanuel left unable to stand, unwilling to eat or drink, and quickly fading. Hundreds of thousands rallied behind Emmanuel on social media as Blake documented Emmanuel’s progress, reaching out to public figures like Dr. Pol of The Incredible Dr. Pol and Bindi Erwin of Crikey! It’s the Irwins for help when she failed to find any other sources for emu rehabilitation. But soon, controversy emerged.
Early on, avian influenza experts expressed concern that Blake was not wearing any PPE when interacting with a presumably HPAI-positive bird. Avian influenza is transmissible from bird to human which, combined with the virus’ ability to mix genes and rapidly change, means that PPE is universally recommended when dealing with a suspected or confirmed HPAI outbreak.

In response to concerns, Blake explained that “Emmanuel freaks out whenever we approach him wearing a mask” and that the farm is on a state-mandated quarantine for 150 days, which is the amount of time HPAI is estimated to survive in the environment under ideal conditions. This quarantine reportedly only allowed Blake, Blake’s girlfriend Kristian Haggerty, Blake’s family, and veterinary professionals to enter the property. “I have taken every precaution recommended by the FDA” Blake stated, referencing the Florida Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services (FDACS) rather than the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Many people, including HPAI experts, found this explanation unsatisfactory and instead decided to contact the FDACS and USDA directly. Both the FDACS and USDA work collaboratively to manage avian influenza outbreaks in Florida. Dr. Danielle Stanek of the Florida Department of Health clarified that the DOH can recommend that private individuals comply with CDC guidelines, which includes wearing full PPE when interacting with HPAI-infected birds, but they cannot mandate that they do so. Therefore, Blake’s decision to forgo PPE was hers to make, even if it wasn’t in accordance with the recommendations of the FDACS, CDC, USDA, and Florida DOH.
Just as discourse between experts and Emmanuel fans reached its peak, Blake announced that Emmanuel tested negative for HPAI. Instead, Emmanuel’s sudden decline was attributed to stress. “Emus are incredibly susceptible to stress. He was incredibly overwhelmed by the state coming in and euthanizing our flock . . . He stopped eating the day they depopulated.” His lingering issues- the inability to stand or walk independently, twisted neck (torticollis), continued inappetence and dehydration, and lethargy- were caused by a nighttime collapse that left Emmanuel “thrashing on the ground for hours, trying to get himself up”. “He never once had a single symptom of AI, other than not eating”, Blake stated.
HPAI symptoms in birds varies depending on the species and the individual. In chickens, HPAI often presents as respiratory and digestive distress, followed quickly by death. In other poultry species, symptoms may also include the nervous system, causing “tremors, twisted necks, paralyzed wings, laying down and pedaling”. Ratites- referring to the diverse group of keel-less birds that include emus, ostriches, rheas, kiwis, and cassowaries- also tend to develop neurological symptoms. Notably, emus can present with twisted necks (torticollis), ataxia (discoordination), leg and wing paralysis, inability to stand, decreased food and water consumption, purple discoloration or swelling of the legs and head, and lethargy. This corresponds with many of the symptoms Blake has documented in Emmanuel. And it should, considering that Emmanuel did test positive for HPAI.
Test results completed on October 27th, 2022 at the USDA’s National Veterinary Services Laboratories showed that Emmanuel’s serum sample, collected six days after the start of the outbreak, contained antibody levels that were consistent with recent infection.
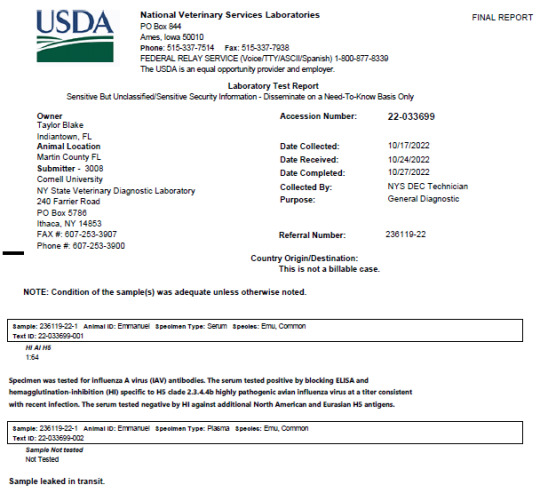
When Blake announced Emmanuel’s stress diagnosis, she was likely relying on information provided by a rapid test, which can provide results within 48 hours. These tests detect viral proteins that indicate active infection and virus shedding. Serology tests, on the other hand, look for the presence of antibodies produced in response to infection, not necessarily active infection. For an indeterminate number of days prior to the sample collection (October 17, 2022) Emmanuel had an active HPAI infection that, rather than stress, likely led to his rapid decline.
Why, then, was Emmanuel not included in the state’s cull on Knuckle Bump Farms? An email between Dr. Michael Short, the FDACS’ Animal Industry Director, and Kassandra Curiel of the FDACS’ Office of the Commissioner, answers this question. Dr. Short states that “USDA guidance is that ratites (emus and ostriches), black swans and exotic pet birds do not have to be euthanized due to lower risk”. Blake echoes this on her Twitter, when she says that “the state only focused on the “super spreaders” which are poultry species and ducks. Ratites aren’t included because they typically aren’t as susceptible.”.
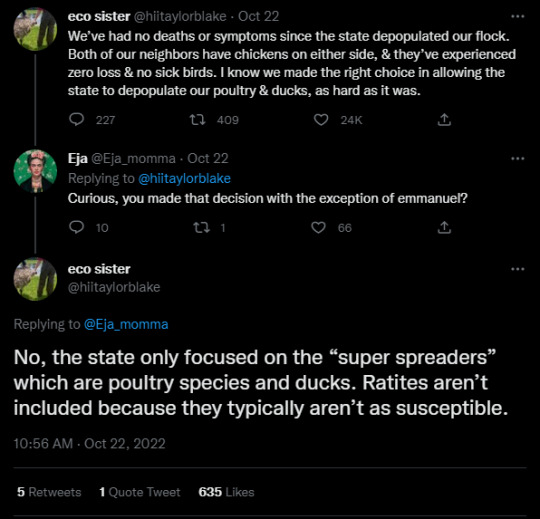
This allowed Knuckle Bump Farms’ four emus (Emily, Eliza, Elliot, and Emmanuel) and three black swans (two unnamed females and Rico), to be exempted from the cull. I cannot find any reference, either in USDA literature or anywhere else, that supports Dr. Short’s statement. In fact, all the literature that I reviewed and all the experts I talked to during my research only confirmed the devastating effects that HPAI can have on both ratites and black swans. This, coupled with the fact that three of Knuckle Bump Farms’ four emus and two of their three black swans died when “the virus hit them extremely hard and very quickly”, calls Dr. Short’s statement into question.
The USDA was also unable to substantiate Dr. Short’s statement. When asked how exemptions to culls were determined they explained that, rather than look at individual species, the USDA classifies HPAI-infected domestic birds as either commercial, backyard poultry, or backyard non-poultry. These definitions ascribe risk of potential HPAI spread by determining the level of contact a poultry premise has with other poultry premises. If a private farm or private household, where the poultry does not have any contact with poultry beyond the property, has an outbreak then they are classified as a non-poultry premises, even if they have chickens, turkeys, or other poultry birds. These non-poultry premises can thus be exempted from culling all their birds by being placed on quarantines by state officials, provided that they adhere to the quarantine and continue to not have contact with any poultry facilities. Knuckle Bump Farms does not sell poultry products; therefore, they were classified as backyard non-poultry and eligible for quarantine. The FDACS seems to have added their own interpretation onto this guidance when they specify ratites, black swans, and exotic pet birds as “lower risk”. I reached out to Dr. Short for comment but received no response.
This isn’t the only time Dr. Short and, by extension, the FDACS demonstrated faulty logic. In that same email between him and Curiel, Dr. Short used this comparison to explain why a citizen’s concern about Emmanuel’s exemption from the cull was unfounded.
“I have heard of only one report of a clinically ill human, over the past 1.5 years of a national response to the current avian flu outbreak. The risk of HPAI to the owner is much less than occurred with household pets that tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 (Covid). I am assuming no one would advocate to euthanize all pets testing positive for Covid (At least I have not heard of anyone asking us to euthanize pets).
The risk of avian influenza is constantly occurring with all the wild birds in South Florida. My understanding (not being a human health expert) is the risk to people, especially children and those immuno-compromised at public or private lakes, ponds and waterways from the AI being shed by water fowl is much greater than the sick emu at knuckle bump farm.”
Dr. Ben Golas, a VMD and postdoc with the USGS who is currently working on avian influenza research, weighed in. “It’s a bit like comparing apples and oranges to talk about risk of transmission of COVID vs. HPAI. With COVID, our primary concern is human-to-human contact. [. . .] With HPAI, farm animals are euthanized not only because the disease spreads within the farm flock like wildfire, but also to prevent spreading infection locally to other farms, because HPAI virus can be stable in the environment.”
The CDC agrees. “There is no evidence that animals play a significant role in spreading SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, to people. […] It’s important to remember that people are much more likely to get COVID-19 from other people than from animals. There is no need to euthanize or otherwise harm animals infected with SARS-CoV-2.” When it comes to HPAI, however, they emphasize that human-to-human spread is rare and often limited to only a few individuals. Bird-to-human transmission is the primary method of human infection, with each new infection increasing the risk that a new, more virulent strain will emerge. This, along with the potential for massive bird-to-bird outbreaks that could devastate both wildlife and industry, is why complete depopulation (euthanasia) is standard for HPAI and not COVID-19.
The FDACS seems to be operating on contradicting and unsubstantiated information when it comes to managing HPAI outbreaks. Unsurprisingly, the employees seem equally conflicted in their internal emails regarding Knuckle Bump Farms. One Florida USDA representative noted, while forwarding a citizen concern about Blake’s lack of PPE, that “her face is real close to a bird that has HPAI”. Another USDA employee responded “actually, in one of the pictures she appears to be kissing it on the head.”. Dr. Kendra Stauffer of the USDA wrote, “. . . part of the allowing the pet bird to live was that there were rules the owner was to follow from DOH, which clearly she is not”.
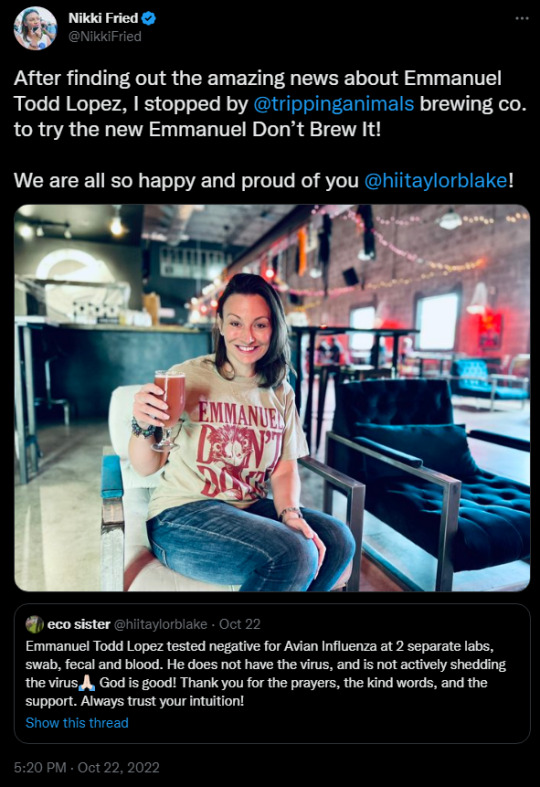
Other employees, however, were eager to show their support. Commissioner Nikki Fried of the FDACS posted a photo of her, Blake, and Haggerty, and later posted a photo of herself drinking Knuckle Bump Farms’ branded beer while wearing an Emmanuel t-shirt.

Fried’s support generated a lot of concern, particularly amongst local farmers. One Florida emu farmer stated, “my disappointment and concern is 100% with the actions of Nikki Fried as Agricultural Commissioner to allow some birds to be exempt from depopulation, including emus, for no quantifiable reason. Emus are susceptible to HPAI. Emus in other states have contracted HPAI in this current outbreak and they either died on their own or were put down. Research shows they are susceptible to HPAI, and can spread it to other birds and humans. The decision by Fried and FDACS makes no sense and it sets a dangerous precedent.”
Considering that Blake has over 847.4K followers on Twitter, 938K on Instagram, and 2.4 million on TikTok, the precedent the FDACS and USDA have set here is, indeed, dangerous. Many of Blake’s followers learned about avian influenza for the first time through her documentation of Emmanuel’s illness and the state’s response to the outbreak. “I watch for Emmanuel updates every day! This has also been a great lesson for many people in farming education.”, one follower said. Another echoed this sentiment, saying “Thank you for taking the time to let us know what’s going on, and answering questions. You truly are an educator”.
Herein lies the problem. Knuckle Bump Farms is a small, backyard operation. Through social media, however, they reach millions. This specific outbreak of HPAI and its subsequent (mis-)management by the FDACS and USDA has now set the standard for many, rather than the exception. Blake’s public failure to comply with PPE recommendations, the lack of transparency regarding Emmanuel’s true diagnosis, a similar lack of transparency within the FDACS and USDA regarding this outbreak, exemptions to cull protocols made with seemingly no supporting data, and a publicly-elected official openly (and financially) supporting Blake through this process, all pose a serious threat to public confidence in HPAI management and future public health. The concerns of farmers, virologists, public health workers and organizations, wildlife rehabilitators, and animal sanctuaries have been ignored, particularly when they asked whether Emmanuel’s fame and the risk of public backlash led to the FDACS’ decision to leave him and several other symptomatic birds alive. It seems, through this research, that there is more support for this theory than the narrative we’ve been provided until now. It is my hope that, with the publishing of this information, the very real concerns raised by people directly effected by HPAI will be given the weight they deserve.
Please take this opportunity to learn about avian influenza from reputable sources:
Protecting Birds from Avian Influenza
Avian influenza and PPE
CDC Avian Influenza
USDA HPAI Response Plan
Florida Avian Influenza Update (Oct 2022)
A huge thank you to the following experts who generously answered my questions: Dr. Ben Golas, Dr. Jim Wellehan, and Dr. Jennifer Riley.
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
On Tuesday morning, five days after Hurricane Helene ripped through Boone, North Carolina, David Marlett was on his way to the campus of Appalachian State University. The managing director of the university’s Brantley Risk & Insurance Center, Marlett was planning to spend the day working with his colleagues to help students and community members understand their insurance policies and file claims in the wake of the storm. He didn’t sound hopeful. “I’m dreading it,” he said. “So many people are just not going to have coverage.”
Helene made landfall southeast of Tallahassee, Florida, last week with winds up to 140 miles per hour, downing trees and bringing record-breaking storm surges to areas along the Gulf Coast before charging up through Georgia. But perhaps its most shocking impacts have been on inland North Carolina, where it first started raining while the storm was still over Mexico. At least 57 people are dead in Buncombe County in the west of the state alone. Communities like Boone received dozens of inches of rainfall despite being hundreds of miles from the coast. Waters rose in main streets, sinkholes and mudslides wreaked havoc, and major roads were blocked, flooded, or degraded by the storm.
Now, there’s a good chance that many homeowners in North Carolina won’t see any payouts from their insurance companies—even if they have policies they thought were comprehensive.
“The property insurance market for homes was already a patchwork system that really doesn’t make a lot of sense,” Marlett says. “Now you’re adding in the last couple of years of economic uncertainty, inflation, climate change, population migration—it’s just an unbelievably bad combination happening all at once.”
For North Carolinians, the issue right now has to do with what, exactly, private insurance is on the hook for when it comes to a storm. An average homeowner policy covers damage from wind, but private homeowners’ insurance plans in the US do not cover flooding. Instead, homeowners in areas at risk of flooding usually purchase plans from the National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP).
The way a hurricane wreaks havoc on a state is a crucial deciding factor for insurers’ wallets. Hurricane Ian, which hit Florida as a category 4 storm with some of the highest wind speeds on record, caused $63 billion in private insurance claims. In contrast, the bulk of the $17 billion in damage caused by 2018’s Hurricane Florence, which tore up the North Carolina coast, was water damage, not wind; as a result, private insurers largely avoided picking up the check for that disaster.
This breakout of flood insurance from home policies dates back to the 1940s, says Donald Hornstein, a law professor at the University of North Carolina and a member of the board of directors of the North Carolina Insurance Underwriting Association. Private insurance companies decided that they did not have enough data to be able to accurately predict flooding and therefore could not insure it. “In some ways, that calculation of 50 years ago is still the calculation insurers make today,” he says.
While the NFIP, which was created in the late 1960s, provides virtually the only backup against flood damage, the program is saddled with debt and has become a political hot potato. (Project 2025, for instance, recommends phasing out the program entirely and replacing it with private options.) Part of the problem with the NFIP is low uptake. Across the country, FEMA statistics show that just 4 percent of homeowners have flood insurance. Some areas hit by Helene in Appalachia, initial statistics show, have less than 2.5 percent of homeowners signed up for the federal program.
“Even in coastal areas, not many people buy that, much less here in the mountains,” Marlett says. “People have never seemed to fully understand that flood is a separate policy.”
Flooding is not unprecedented in the mountains of North Carolina: Hurricane Ivan swept through Appalachia in 2004, and flash floods from rivers are not unheard of. Purchasing flood insurance is mandatory with a government-backed mortgage in some areas of the country, based on flood zones set by FEMA. But the data is based on extremely outdated floodplain maps that have not taken the most recent climate science on record rainfall into account.
“The biggest non-secret in Washington for decades is how hopelessly out of date these flood maps are,” Hornstein says.
Even if water wasn’t the cause of destruction for some homeowners in North Carolina, the storm’s disastrous mudslides—another risk supercharged by climate change—may not be covered either. Many home insurance policies have carve-outs for what are known as “earth movements,” which includes landslides, sinkholes, and earthquakes. In some states, like California, insurers are mandated to offer additional earthquake insurance, and homeowners can purchase private additional policies that cover earth movements. But in a state like North Carolina, where earthquake risk is extremely low, homeowners may not even know that such policies exist.
It’s also been a tough few years for the insurance industry across the country. A New York Times analysis from May showed that homeowners’ insurers lost money in 18 states in 2023—up from eight states in 2013—largely thanks to expensive disasters like hurricanes and wildfires. Payouts are increasingly costing insurers more than they are getting in premiums. Homeowners are seeing their policies jump as a result: According to statistics compiled by insurance comparison shopping site Insurify, the average annual cost of home insurance climbed nearly 20 percent between 2021 and 2023. In Florida, which has the highest insurance costs in the country, the average homeowner paid over $10,000 a year in 2023—more than $8,600 above the national rate.
Florida has made headlines in recent months as ground zero for the climate-change insurance crisis. More than 30 insurance companies have either fully or partially pulled out of Florida over the past few years, including big names like Farmers’ and AAA, after mounting losses from repeated major hurricanes like 2022’s Ian, the most expensive natural disaster in the state’s history. Florida’s insurer of last resort, now saddled with risk from multiple homeowners, has proposed a rate increase of 14 percent, set to go into effect next year.
In comparison, North Carolina’s insurance market looks pretty good. No insurers have exited the state since 2008, while homeowners pay an average of $2,100 per year—high, but avoiding the sky-high rates of states like Florida, California, and Texas.
“What traditionally has happened is that there’s a rate increase every few years of 8 to 9 percent for homeowner’s insurance,” says Hornstein. “That has kept the market stable, especially when it comes to the coast.”
But as natural disasters of all kinds mount, it’s tough to see a way forward for insurance business as usual. The NFIP is undergoing a series of changes to update the way it calculates rates for flood insurance—but it faces political minefields in potentially expanding the number of homeowners mandated to buy policies. What’s more, many homeowners are seeing the prices for their flood insurance rise as the NFIP adjusts its rates for existing floodplains using new climate models.
Many experts agree that the private market needs to reflect in some way the true cost of living in a disaster-prone area: in other words, it should be more expensive for people to move to a city where it’s more likely your house will be wiped off the map by a storm. The cost of climate change does not seem to be a deterrent in Florida, one of the fastest-growing states in the country, where coastal regions like Panama City, Jacksonville, and Port St. Lucie are booming. (Some research suggests that the mere existence of the NFIP shielded policyholders from the true costs of living in flood-prone areas.)
Asheville, at the heart of Buncombe County, was once hailed as a climate haven safe from disasters; the city is now reeling in the wake of Helene. For many homeowners, small business owners, and renters in western North Carolina, the damage from Helene will be life-changing. FEMA payouts may bring, at best, only a fraction of what a home would be worth. Auto insurance generally covers all types of damage, including flooding—a small bright spot of relief, but not enough to offset the loss of a family’s main asset.
“People at the coast, at some point after the nth storm, they start to get the message,” Hornstein says. “But for people in the western part of the state, this is just Armageddon. And you can certainly forgive them for not having before appreciated the fine points of these impenetrable contracts.”
Marlett says that there are models for insurance that are designed to better withstand the challenges of climate change. New Zealand, for instance, offers policies that cover all types of damage that could happen to your house; while these policies are increasingly tailored price-wise to different types of risk, there’s no chance a homeowner would experience a climate disaster not covered by their existing policies. But it’s hard, he says, to see the US system getting the wholesale overhaul it needs, given how long the piecemeal system has been in place.
“I sound so pessimistic,” he said. “I’m normally an optimistic person.”
30 notes
·
View notes
Text
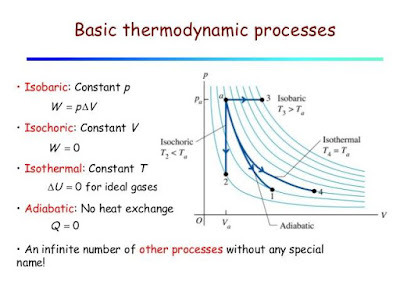
Thermodynamic Processes: Isobaric, Isochoric, Isothermal, and Adiabatic
A process in thermodynamics is the method by which the initial state of a system changes to the final state of a system. Technically speaking, there are countless types of thermodynamic processes to define each possible method in existence, most of which are unnamed. Of the specific named thermodynamic processes, there are four basic options.
Isobaric, isochoric, and isothermal (and, indeed, any other processes with the prefix iso-) are all processes in which a single variable is kept constant. For isobaric, pressure is constant, for isochoric, volume is constant, and for isothermal, temperature is constant. The fourth option, adiabatic processes, are processes in which there is no exchange of heat.
Sources/Further Reading: (Image source - Mechanics Tips blog) (University of Illinois lecture slides) (University of Central Florida) (Wikipedia) (Law of Thermodynamics Info)
51 notes
·
View notes
Text

https://www.miamiherald.com/news/local/education/article278582149.html
Tallahassee
When Florida rejected a new Advanced Placement course on African American Studies, state officials said they objected to the study of several concepts — like reparations, the Black Lives Matter movement and “queer theory.”
But the state did not say that in many instances, its reviewers also made objections in the state’s attempt to sanitize aspects of slavery and the plight of African Americans throughout history, according to a Miami Herald/Tampa Bay Times review of internal state comments.
For example, a lesson in the Advanced Placement course focused on how Europeans benefited from trading enslaved people and the materials enslaved laborers produced. The state objected to the content, saying the instructional approach “may lead to a viewpoint of an ‘oppressor vs. oppressed’ based solely on race or ethnicity.”
In another lesson about the beginnings of slavery, the course delved into how tens of thousands of enslaved Africans had been “removed from the continent to work on Portuguese-colonized Atlantic islands and in Europe” and how those “plantations became a model for slave-based economy in the Americans.”
READ MORE: DeSantis says AP African-American studies class was ‘pushing an agenda’
In response, the state raised concerns that the unit “may not address the internal slave trade/system within Africa” and that it “may only present one side of this issue and may not offer any opposing viewpoints or other perspectives on the subject.”
“There is no other perspective on slavery other than it was brutal,” said Mary Pattillo, a sociology professor and the department chair of Black Studies at Northwestern University. Pattillo is one of several scholars the Herald/Times interviewed during its review of the state’s comments about the AP African American Studies curriculum.
“It was exploitative, it dehumanized Black people, it expropriated their labor and wealth for generations to come. There is no other side to that in African American studies. If there’s another side, it may be in some other field. I don’t know what field that is because I would argue there is no other side to that in higher education,” Pattillo said.
Alexander Weheliye, African American studies professor at Brown University, said the evaluators’ comments on the units about slavery were a “complete distortion” and “whitewashing” of what happened historically.
“It’s really trying to go back to an earlier historical moment, where slavery was mainly depicted by white historians through a white perspective. So to say that the enslaved and the sister African nations and kingdoms and white colonizers and enslavers were the same really misrecognizes the fundamentals of the situation,” Weheliye said.
DeSantis’ efforts to transform education in Florida
The commentary is also an example of how Gov. Ron DeSantis has transformed the state’s education system in his quest to end what he calls “wokeism” and “liberal indoctrination” in schools — a fight that began in the aftermath of the pandemic and the Black Lives Matter movement that followed the high-profile murder of George Floyd at the hands of police in Minnesota.
“It’s not really about the course right? It’s kind of about putting down Black struggles for equality and freedom that have been going on for centuries at this point in time and making them into something that they are not through this kind of distorted rightist lens,” Weheliye said.
When asked about the findings of the previously unreported internal reviews, the Florida Department of Education said the course was rejected after state officials “found that several parts of the course were unsuitable for Florida students.”
Cailey Myers, a spokesperson for the agency, cited the work of many Black writers and scholars associated with the academic concepts of critical race theory, queerness and intersectionality — a term that she said “ranks people based on their race, wealth, gender and sexual orientation.” The term, however, refers to the way different social categorizations can interact with discrimination.
Brandi Waters, the executive director of the AP African American Studies course, said it is hard to understand the Florida Department of Education’s critiques on the content because state officials have not directly shared their internal reviews with the College Board. The state and the College Board, however, were in communication about the course for several months before it was rejected.
Waters maintains the coursework submitted to the state was the most holistic introduction to African American Studies.
A deeper look at Florida’s objections
The course materials provided by the College Board were reviewed by Florida Department of Education’s Bureau of Standards and Instructional Support and the decision to reject the course was made by “FDOE senior leadership,” records show.
John Duebel, the director of the state agency’s social studies department, and Kevin Hoeft, a former state agency official who now works at the New College of Florida in Sarasota, were identified as the two evaluators in the review. Hoeft is listed as an “expert consultant” to the Civics Alliance, a national conservative group that aims to focus social studies instruction in the Western canon and eliminate “woke” standards. His wife is a member of the conservative group Moms for Liberty.
Duebel declined to comment on the story and referred questions to the Department of Education, which did not respond. Hoeft did not respond to a request seeking comment. While the documents say that Duebel and Hoeft led the state reviews, much of the comments included in the state review are not attributed, making it hard to tell who said what.
The documents reviewed were provided to the Herald/Times by American Oversight, a left-leaning research organization that sued the state Department of Education for the records.
“We sued the Florida Department of Education to shed light on the DeSantis administration’s efforts to whitewash American history and turn classrooms into political battlegrounds,” American Oversight Deputy Executive Director Chioma Chukwu said in a statement. “The records obtained by American Oversight from Florida’s internal review of the AP African American Studies course expose the dangers of Gov. DeSantis’ sweeping changes to public education in Florida, including preventing students from learning history free from partisan spin.”
READ MORE: How a small, conservative Michigan college is helping DeSantis reshape education in Florida
The documents offer more detail into the state’s reasoning for rejecting the pilot course from being offered to high school students in Florida — and how topics related to racism, identity and gender were continually flagged out of concern that lessons were biased, misleading or “inappropriate” for students.
And, in cases where state officials did not find a violation of a state law or rule, concerns were often raised about how educators would teach the content, underscoring the growing distrust between state officials and educators as disputes over social issues engulf local school politics.
For example, the state worried educators teaching about how the 1960s Black is Beautiful movement helped lay a foundation for multicultural and ethnic studies movements, could “possibly teach that rejecting cultural assimilation, and promoting multiculturalism and ethnic studies are current worthy objectives for African Americans today.”
“This type of instruction tends to divide Americans rather than unify Americans around the universal principles in the Declaration of Independence,”the state officials wrote about a lesson in the course.
Records also show how some of the comments made by the state evaluators contained contradictions, such as advocating for primary sources and then later writing that certain primary sources contained “factual misrepresentations.” Many comments from the state pushed for the material to include perspectives from “the other side” but failed to elaborate whose perspective they wanted to be added.
Slavery
One of the lessons in the course, for example, set out to teach students how slavery set back Black people’s ability to build wealth.
“Enslaved African Americans had no wages to pass down to descendants, no legal right to accumulate property, and individual exceptions depended on their enslavers’ whims,” the College Board’s lesson plan said.
When reviewing the content, however, state reviewers said the lesson plan might violate state laws and rules because it “supposes that no slaves or their descendants accumulated any wealth.”
“This is not true and may be promoting the critical race theory idea of reparations,” state officials wrote in documents reviewed by the Herald/Times. “This topic presents one side of this issue and does not offer any opposing viewpoints or other perspectives on the subject.”
While there were scattered instances where enslaved people were given the chance to earn money to pay for their freedom, the wealth they accumulated still did not belong to them, said Paul Finkelman, the editor-in-chief of Oxford University Press’ “Encyclopedia of African American History 1619-1895.”
“Under the law of every slave state, including Florida, no slave could own anything. That is, slaves did not own the clothes on their back. They did not own the shoes on their feet,” said Finkelman. “So for the Florida Education Department to question whether slaves accumulated property is to not understand that slaves owned no property. In fact, they were property belonging to slave owners.”
Even in cases where slaves were allowed to make money, Finkelman argued, it would be a stretch to say they were able to accumulate wealth.
Black middle class
Evaluators also objected to a lesson plan that taught how Black Americans, even after slavery, continue to experience wealth disparities due to ongoing discrimination.
The coursework included the following statement: “Despite the growth of the Black middle class, substantial disparities in wealth along racial lines remain. Discrimination and racial disparities in housing and employment stemming from the early 20th century limited Black communities accumulation of generational wealth in the second half of the 20th century.”
State reviewers, however, said the unit could potentially violate state rules because it failed to offer other reasons outside of systemic racism and discrimination for the wealth disparity between Black Americans and other racial groups.
“The only required resource in this topic cites ‘systemic racism,’ ‘discrimination,’ ‘systemic barriers,’ ‘structural barriers,’ and ‘structural racism’ as a primary or significant causative factor explaining this disparity of wealth,” wrote one evaluator. “This topic appears to be one-sided as non-critical perspectives or competing opinions are cited to explain this wealth disparity.”
Pattillo said that while many of the comments made by the state in the review claimed that they wanted to see more balance of perspectives in the course materials, she felt state officials largely tried to minimize the topics of discrimination.
Abolitionist Movement
When it came to teaching students about the movement to end slavery, the College Board highlighted some of the prominent activists who led that abolitionist movement and the ways the government tried to stop those who resisted slavery.
“Due to the high number of African Americans who fled enslavement, Congress enacted the Fugitive Slave Acts of 1793 and 1850, authorizing local governments to legally kidnap and return escaped refugees to their enslavers,” the lesson plan stated.
Primary sources were scrutinized
When the College Board addressed the resistance to slavery, it wanted to teach students how to “describe the features of 19th-century radical resistance strategies promoted by Black activists to demand change.” In that unit, the state objected to two primary sources: “The Appeal” by David Walker and “An Address to the Slaves of the United States” by Henry Highland Garnet.
State reviewers said that “The Appeal” included “content prohibited under Florida law,” but does not offer more details; and that “An Address to the Slaves of the United States” contains “factual mis-representations” and potential violations of state rules.
“They complain that this primary source is not historically accurate. Well, of course it’s not historically accurate because it’s a political speech. It is not a piece of history, but it’s a perfectly historically accurate primary source to understand the anger of a Black abolitionist,” Finkelman said.
However, earlier in the review, the evaluators applauded the College Board for stating that “anchoring the AP course in primary sources fosters an evidence-based learning environment” and that the course will be focused on the works and documents of African American studies rather than “extraneous political opinions or perspectives.”
“This is exactly how all courses are to be taught in the state of Florida and we commend [the] College Board on this position,” wrote the state reviewer .
Scholars’ political leanings questioned
In one review, one of the state evaluators questioned the balance of the content because of the individuals the College Board picked to develop the coursework.
But one of the evaluators had a gripe: they claimed that there were no conservative Black scholars. This was a concern because, as the state evaluator put it, there may not be an “adequate level of intellectual balance.”
“Conservative and traditional liberal members may need to be added to the committees to bring balance and ensure compliance with Florida statutes, rules, and policies,” the state evaluator wrote.
Waters said the College Board is focused on having scholars on their committees who are the leaders in the field of African American studies and that their political background isn’t something they take into consideration.
“In terms of the scholars, we never really asked them ‘what is your political background?’,” Waters said. “I don’t assume that is a characteristic that remains static in a person’s life over time.”
“What we do is look for scholars who represent the expertise needed for the course. So who is leading the field in how we understand the origins of the African diaspora? Who is leading the field in cutting edge research on unearthing new perspectives of the civil rights movement? We look for their expertise and also the different backgrounds that they represent,” she added.
How did we get to this point?
While Florida law requires the study of African American history, the state reviews of the AP course show how the DeSantis administration and Republican policymakers are implementing changes to how schools can teach about race, slavery and other aspects of Black history.
In 2021, Florida barred lessons that deal with critical race theory, a 1980s legal concept that holds that racial disparities are systemic in the United States and not just a collection of individual prejudices. Critical race theory was not being taught in Florida schools. The state also barred lessons about “The 1619 Project,” a New York Times project that reexamines U.S. history by placing the consequences of slavery and contributions of Black Americans at the center.
A year later, the Republican-led Legislature approved a new law, known as the “Stop W.O.K.E. Act,” which prohibited instruction that could prompt students to feel discomfort about a historical event because of their race, ethnicity, sex or national origin.
To DeSantis, the restrictions are a necessary effort to protect students from what he sees as a cultural threat that, as he puts it, teaches “kids to hate this country.” But the policies have been widely criticized by Democrats, educators, historians and even a few Republican lawmakers who see the laws as an attempt to distort historic events.
State officials’ interpretation of these policies collided with many of the learning objectives outlined in the A.P. courses. This collision, some scholars say, is emblematic of the chilling effect the state’s vague laws can foster in academia.
“I think this is the point that many people have been saying,” Pattillo said. “That the misguided blanket use of this term critical race theory, and in the absence of some definition of what that means or what they think it means, makes any teaching of racism questionable per that vagueness...”
Based on the state reviews the Herald/Times provided to him, Finkelman said it appeared the state was “hunting for bias.”
“And if you hunt long enough, you can find bias anywhere,” Finkelman said, noting that “anyone can find faults, and even small mistakes with any scholarly enterprise.”
To do the job right, Finkelman said, the state should ensure the course is reviewed by historians, with expertise in the specific subject area — not political scientists or state bureaucrats. He questioned whether the state prioritized reviewers’ credentials after seeing the state’s comments on the topics of slavery, or subjects that took into account the issue of racism and identity.
Based on Finkelman’s review of the content, he said, the state reviewers were more interested in correcting content based on their reading of the material over “scholarly accuracy.”
Read more: Only 3 reviewers said Florida math textbooks violated CRT rules. Yet state rejected dozens
Since Florida rejected the pilot course in January, students in other parts of the country have been taking part in the pilot program. Education officials in only one other state — Arkansas — are disputing whether to make the AP course eligible for credit. The Arkansas Department of Education — led by Florida’s former K-12 Chancellor Jacob Oliva — recently removed the class from its course code listing.
In November, the College Board plans to submit the final version of the course’s curriculum for approval. But with Florida’s laws still in place, the fate of the course remains in limbo — and the outcome could potentially make Florida students in public high schools less likely to have access to the course. If approved, parents and students can choose to enroll in the course.
College Board officials are aware of this possibility, but remain hopeful.
“We certainly hope that Florida students will have the opportunity to take this course,” said Holly Stepp, a spokesperson with the College Board.
Myers, the Florida Department of Education spokesperson, said the College Board is welcome to resubmit the course for review in November.
But, Myers said, “at this point, it is inappropriate to comment on what the future could hold – it is just speculation.”
This story was originally published August 29, 2023, 5:30 AM.
#florida#white washing history#Black Lives Matter#Black History Matters#ron desatan#white lies#florida department of education#florida students
117 notes
·
View notes
Text
personal theory on how the wttt verse works in terms of states
hi gang
cw: i do mention some policy/politics as a referential thing because this is a satirical series about american politics so these issues appear within the series.
welcome to the table. gotta love it. so
i think states represent
their people
their policy
their environment
(there's more focus on the first two definitely however the last one is also relevant. i also like mentioning this because it allows for good fic content, frankly.)
and then the relevancy of this changes depending on whats going on. when a state reflects one of these very strongly and cannot represent another, then you get manifestations of that. alternatively, enough division within the state and you get things like new jersey (watch his intro episode) and texas (cmon gang we all know im talking about austin). you can also see regional differences if they're stark enough (nocal and socal).
because texas is, within canon, implied to have did and non healthy multiplicity ("i feel like i saw this on Moonknight"), my next point is that depending on how geniunely major a difference is and how poorly one of the things is being represented by the state, the more intrusive whatever is going on becomes. so while most of the gang is generally..... kind of... fine... texas, as a state that is a swing state but still making big discriminatory policy represents the policy well, and the rights and needs of the people less so, meaning that instead of the mostly functional/positive multiplicity seen throughout the series starts becoming less functional altogether.
the government also represents people, policy and a little bit of environment. it/he also represents the system and its needs/wants; such as explicitly benefitting from the industrial military complex over in america, or with the democratic party utilising big issues as part of a campaign (re, overturning roe v wade).
states also probably have some kind of magic to them; they're manifestations who are older than the states as they are part of the US, and we know that loui definitely got something going on there. mother nature tries to get florida and when she misses, both texas and louisiana are soaked from afar, again, representing environment, but also magic is an abstract property which is perfectly realistic in thsi universe. the government does the statehouse; which is a house which externally appears to be normal and holds over 50 rooms and somehow was not destroyed already. this is all to say, the idea of states being able to manifest shit is not beyond canon. go nuts. show nuts, even
yeah lol anyone got any agreeeing/disagreeing opinions
26 notes
·
View notes
Note
I’m writing a story that takes place in my home city of Atlanta. The main character is a student who is new to the environment as a university freshman from out of state. I want to make her interactions with the landscape feel natural and not “touristy” if that makes sense. I don’t want for her to just be like “oh wow, the traffic here is terrible; it must be because of all the [insert forced info/history dump here]”. How can I avoid this? Thanks for your help.
Out of Town College Student
Unless the character comes from a similarly area/city or has been to Atlanta on previous occasions, you probably want them to be a little touristy, at least at first. I wonder if it's less that you want them to appear "touristy" and more that you don't want to repeat the usual out-of-towner cliches? Which, in that case, I think you can think about some of the less cliche things that might stand out to your character on that level. Some things I noticed on my first visits: it was so green! So many trees! Beautiful parks, too. Quite a lot of diversity and cultural vibrancy. I didn't know until I visited that they had a rapid transit system. The proximity to other places is great, too... an hour and a half to Helen, two hours to Chattanooga, three hours to Asheville, four hours to Savannah and the Golden Isles, five hours to Charleston, six hours to the Florida panhandle... So, that said, I think you can avoid the cringey "tourist" aspect by just having her notice less cliche things.
I hope that helps!
•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••
I’ve been writing seriously for over 30 years and love to share what I’ve learned. Have a writing question? My inbox is always open!
♦ Questions that violate my ask policies will be deleted! ♦ Please see my master list of top posts before asking ♦ Learn more about WQA here
21 notes
·
View notes
Text
by Dion J. Pierre
The State University System of Florida has at least two institutions with active National SJP chapters, according to Rodrigues. Citing state law that deems the knowing provision of material support to a terrorist group as a felony, he said that the two chapters cannot continue operating.
“These chapters exist under the headship of the National Students for Justice in Palestine, who distributed a toolkit identifying themselves as part of the Operation Al-Aqsa Flood,” the memo stated. “Based on the National SJP’s support of terrorism, in consultation with Governor DeSantis, the student chapters must be deactivated. These two student chapters may form another organization that complies with Florida state statutes and university policies. The two institutions should grant these two chapters a waiver for the fall deadlines, should reapplication take place.”
The measure will affect SJP chapters at the University of North Florida, located in Jacksonville, and Florida State University, located in Tallahassee.
Support for terrorism against Israeli civilians among SJP chapters is not new. The Anti-Defamation League (ADL), for example, reported that SJP expressed on at least 10 occasions last year admiration for Leila Khaled, a member of the Popular Front for the Liberation of Palestine (PFLP), a US-designated terror group. She is known for previously hijacking two planes.
Other SJP chapters at the University of Texas, Dallas, New York University Law School, and the University of Massachusetts posted violent images containing PLFP’s logo and guns. In January, the University of Chicago’s SJP chapter honored Khairy Alqam — who murdered seven Israeli civilians exiting a synagogue in Jerusalem — in a collage titled “Honoring the Martyrs.”
DeSantis has taken previous steps to crack down on anti-Israel activity in Florida.
52 notes
·
View notes
Text
Excerpt from this story from Yale Environment 360:
Strong winds sweep over the Rhön, a vast region of rolling, forested hills and pastureland in central Germany. Undeterred, Stefan Zaenker, leading a group of four volunteers, runs through his checklist alongside a forest road. Are rubber boots disinfected to prevent introducing potentially harmful microorganisms into the wetland? Are the team app and GPS functioning correctly? Have enough flags been packed?
When all is in order, Zaenker, 56, leads the group into a soggy alder forest. Its mission for the day: to locate and map as-yet-undiscovered springs and document any species inhabiting them.
A senior conservation official for the state of Hesse, Zaenker considers springs so important for human life and biodiversity that he — along with volunteers from the Hesse Association for Cave and Karst Research — spends much of his spare time conducting large-scale searches for them in the Rhön, which includes the German states of Bavaria, Thuringia, and Hesse, and in a nearby national park.
Conservation strategies around the globe focus on rivers, bogs, forests, reefs, and many other habitat types. Springs rarely get any special attention. In the United States, for example, springs do “not appear to be a prominent feature on the conservation radar,” says Kirsten Work, a zoologist from Stetson University in DeLand, Florida.
But for the biosphere, these tiny spots dotted across Earth’s land surface play a powerful role: They connect reservoirs of groundwater to the outside, sunlit world. Only so-called “fossil” aquifers — ancient bodies of groundwater that do not recharge — lack a link with the surface. Without a continual connection to groundwater, which also feeds rivers, many landscapes would quickly dry up and become hotter. In addition, springs are home to a wide range of highly specialized species, some of which live outside by night and in the darkness of groundwater by day.
Far too little is known about where springs occur and what species they harbor, Zaenker says. In a country like Germany, which has no wilderness but a very efficient bureaucracy, most people assume that everything in nature has already been discovered and mapped. This is not true, he claims: “I can stand right next to an impressive spring with water flowing out, but the official topographical map shows nothing.” Official maps denote springs with a blue dot, indicating they are habitats protected by law. Yet many — if not most — springs remained undocumented. “How are we going to effectively protect these important habitats or know if they dry up,” asks Zaenker, “if we don’t even know they exist?”
Halfway around the globe, ecologist Larry Stevens is on a similar mission and is equally worried about the future of springs. In 2013, Stevens cofounded the Springs Stewardship Institute, a nonprofit science initiative linked with the Museum of Northern Arizona, and in 2023 he published Springs of the World: Distribution, Ecology, and Conservation. Stevens considers springs prime examples of “canaries in coal mines” because they act as early warning systems of water table decline and biodiversity loss.
Stevens is particularly fascinated by the large number of highly specialized and endemic species found in and around springs. He points out that with constant temperatures and high purity, spring water offers unique living conditions. Springs are often isolated from one another geographically and many have been in place for millennia, characteristics that make them hotspots for new species to arise and refuges for species that have lost their habitats elsewhere. “Although miniscule in habitat area compared to rivers, lakes, and oceans, springs support more than 10 percent of U.S. endangered species, as well as thousands of other rare and endemic biota,” he notes. For example, the so-called Comal Springs riffle beetle is limited to a few springs in Texas, while the endangered White River springfish lives only in isolated warm springs in eastern Nevada.
While there are many spectacular springs — like the white Pamukkale terraces of Turkey, Blue Spring in New Zealand, or the hot springs in Yellowstone National Park — most are rather inconspicuous. That doesn’t diminish their importance, though. Every creek, river, pond, and lake starts with at least one, and often many, springs.
13 notes
·
View notes