#crumpled dark
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Sometimes you get very attached to a gaggle of antagonists from a book you read when you were twelve and they live in your brain for the next decade and change. So you Just Keep Drawing Them
Art from baby ernie under the cut bc I’ve been drawing these fellas for A While



#i had a fucking awful day please reblog my art and say nice things#i don’t even have anything funny to say#it was just a genuinely god awful day and I am upset#but you can look at my boys if you want and that would be nice#how the fuck to. tag them#firefox inkheart#the piper inkheart#basta inkheart#inkheart#inkspell#inkdeath#inkheart book#tintenherz#crumpled dark
40 notes
·
View notes
Text

i had no clue what to replace with “and the diamonds” so i went w her knife collection

#i wanted to make her lashes more crumpled and decimated but idk how to do that pls imagine it tho#i tried to make it look like the cover more#but then the pink took over#yeah sorry tevy likes pink to the point i washed this shit w pink#btw i scower the internet for the exact font type for these albums LMAO#🪐evren art#oc: tevy melaku#marina#world of darkness#vtm#vampire the masquerade#vtm oc#vtm art#vampire the masquerade oc#salubri#salubri antitribu#electra heart
53 notes
·
View notes
Text

new jjk was great and normal and smiles were had all around
#scribbles#jjk#jujutsu kaisen#kento nanami#yuji itadori#i sent this and dark went 'yuji doodled this before setting out to shibuya' and it made me want to crumple
171 notes
·
View notes
Text



#natsume sakasaki#leo tsukinaga#enstars#ensemble stars#post by galaxy#Story: Next Door#How is Natsume both so good and so bad at making friends#I had been wondering how the roommate dynamics play out I'm obsessed with them#Even their dorm room is so funny#Natsume's side is dark and classy and elegant#And Leo's side is just an unmade bed with crumpled up papers and musical notes scribbled on the walls 😭😭💀#And poor Nazuna is in the middle of them💀💀#Post by galaxy
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
"You with the dark curls, you with the watercolour eyes."
KleinphyKleinphyKleinphy
#kleinphy#jared kleinman#connor murphy#connor got the dark curls#jared got the watercolour eyes#i mean so does connor but we're not gonna talk about that#dear evan hansen#conman#i drew something for this but it got all crumpled
40 notes
·
View notes
Text
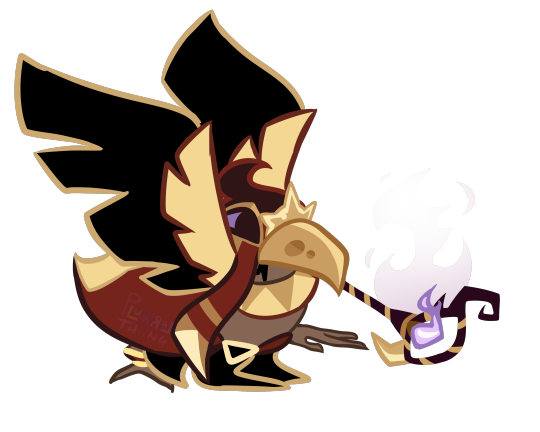

baby need smoko cheese
reference under cut
[ commissions | patreon (18+) | store ]

#cookie run#cookie run kingdom#digital art#crk#smoked cheese cookie#hi! im not crumpling from illness anymore so comms are open again#also our store is still there! please look at it and maybe buy something if you want we're working on adding more things :]#next in line is a smilk glow inthe dark keychain! design will probably be done by the end of this month or the beginning of next month#when they'll ship though eeehhhh well. they take a bit to ship out#anyways!#baby need smoko
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
that....... episode 3............... 😨
#sth#sonic x shadow dark beginnings#im literally...... DNT. DONT LOOK AT ME I HAURCE...... AUGH........I .......... *crumples into a wet heap* AUUUWWHHHH...😟
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

What a privilege it is, to see your hair go grey.
I’m LATE but happy birthday @solittles my lovely partner in. well. solittle!!!! Finally drew our versions of the boys from our “rescuing each other” au !!!
#HAPPY BIRTHDAY ELLIOT ILYYYY SORRY THIS IS LATE LOL#i simply love our au SO SO MUCH#our boys!!! our sole survivors!!!!! finding comfort in each other once they’re home!!!!!!#rescuing each other from everything that comes after!!!!!!!#AAAA I love them so much ur honour!!!!!!#the terror#amc the terror#solomon tozer#edward little#solittle#rescuing each other au#crumpled dark
120 notes
·
View notes
Text
.
#saw some interesting characters today#I’m in my car with my coffee#and I look up and see a couple leaving a bookstore#the girl is tall with her hair piled on her head with pretty dark strands framing her face and sunglasses perched on her head#she’s wearing a cute black tshirt and boyfriend jeans with horizontal tips on them and some sandals with some cute bracelets jingling#the guy she’s with is wearing jeans that hang lower on his hips with a black belt holding them up#some sneakers and a white tank top#he’s bald and wearing sunglasses with tattoos up and down his arms#they smile at each other#and say bye#perhaps a coffee date? they both had coffees in their hands#her smile is genuine shes been looking forward to this all morning#he’s smirky and trying to play it off like he’s not sweating#they say their goodbyes and he climbs on his motorcycle as she walks off to her car#as he’s pulling out to leave another woman walks by and his gaze lingers on her just a little longer#and my heart crumples
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
//A Happy birthday to Riversal, who, in true middle child fashion had his birthday forgotten last year so hopefully by shouting him out here I can get rid of the guilt that's been burdening me ever since ;w; Again, happy birthday to our little boy!! Asks ofc are open (Of all the siblings, I'm sure he'd appreciate them the most lmao) though I'm currently trying to focus on some older asks as well (When i'm not caught up in college and bighttown), so if it takes a second just know I'll get to you eventually!! Thank you~ :3
#||OOC||#{/been playing dark souls lately and man....}#{/blighttown is KICKING my ass though i kinda prefer it from a frustration point compared to the sewers??? just because I don't have to}#{/deal with getting cursed; poison IS annoying tho not a fucking nightmare like getting cursed dghdfbk}#{/i DO find myself wanting out a lot more; though}#{/like... the sewers were annoying and felt so STIFLING compared to the undead burg and firelink but this is just downright... ufffnngn}#{/just swamp}#{/nothing but blighttown}#{/nowhere to go}#{/nowhere to THINK about going}#{/and this ENTIRE time I can only think about getting out and ringing that bell and coming back so the crestfallen warrior will be proud of#{/me :')}#{/i'm not even kidding when i say im doing it solely for him at this point he made me happy when he actually seemed to brighten up a bit at#{/the first bell being rung and so I GOTTA DO IT}#{/HES ROOTING FOR ME}#{/im just rolling through here like 'MAN firelink is gonna be so refreshing after this' skgsdjfhkd}#{/that aside; ive also been playing parasite eve!! which i'll have to ramble about once i finish but chinatown... *crumples* either I need}#{/a guide or some grinding because GODDAMN}#{/I'm getting my ass beat!!}#{/also have been thinking about leonards Lord of Vermillion card and how it listed his defining character trait as just 'gay'}#{/no mention of kids. hes just gay lmao}#{/a HORRIBLE move but also kinda funny at the same time dgkhsdgh}
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
also wwe all agree that that submersible exploded like 2 days ago and everyone is just fucking pretending it didn't and there's still hope right
#C'mon#Those people died the minute they missed the first check in lmfao#Crumpled like a tin fucking can#And honestly? It's better if they did#Can you imagine being stuck in a minivan in the dark on the ocean floor#having to shit in a Ziploc bag in front of a failed reagan-era astronaut turned ceo named Stockton Rush#And a rich 1800s British factory owner who murders endangered species for fun who time traveled#Just so he could choose to dress and act like your weird uncle who tried to get you to buy mlm protein drinks on Facebook#Named Hamish fucking Harding#☠️#titan submersible
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
I feel bad for Gale getting stuck with Joyce. Imagine planing out and preparing this whole night, just to woo this man you’ve been into for a decent amount of time, on what you think is probably one of your last nights alive. And it’s all going well! He loves like you love him, he’s a pretty decent kisser, and you’re pumped! …only to find out that you can’t connect your souls and have this experience you cherish, because he sorta maybe kinda a little bit neglected to even consider mentioning the fact that he sorta kinda maybe doesn’t have a soul…
#‘anything else you’ve neglected to mention?’ ‘I’m 137.’#so sorry Gale#so so sorry Gale#you can explode him if you want#gale x tav#it’s not that Joyce is malicious about hiding it#he just doesn’t think 90% of things about him are of any consequence or any interest to anyone#the soul thing is more traumatizing for him than other things that he doesn’t bring up#but he doesn’t consider it some deep dark secret he has to hide#Joyce Actaeon#it’s weird to talk about Joyce or label Joyce as a Tav since he’s just my dnd main#my most beloved and adored dnd character#the only thing he’ll go out of his way to hide the best he can is that he has a thing for wizards#if Gale found out about that (which he does) Joyce would simply perish and crumple up onto the ground
0 notes
Text

Lets see if tumblr snipes this or not but. Wanted to draw something tender with Edgar and Markus. Also I wanted to show off all of Edgar’s burns. Old man tender embrace be upon ye
#can Tumblr handle bare old man ass#can tumblr APPRECIATE bare old man ass#anyway. i love them so so SO much#markus absolutely adores his husband it’s not even funny#he thinks Edgar is the most beautiful man in the whole world#oc: edgar#oc: markus#edgar tremaine#markus hearst#crumpled dark
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
Master Chief on Hug Duty

#no but actually he's the only one of the three who's still in chain of command#obviously military bad im NOT saying him being in the UNSC is what makes him a Good Person or that he even IS a good person but#Doomguy has been out of the Marine Corps for so long (and been in hell for so many years) that he's pretty much become addicted to death#he exists to kill maim harm and destroy.#he is a ballistic cannon pointed at (luckily) The Baddest of Bad Guys#he's the ultimate “He's only the hero because his world has a big evil face to punch” of superheroes (although i believe in a vacuum#he's a good guy)#(like. if daisy hadn't been killed. if his comrades weren't eviscerated. he'd still be a really chill dude.)#(and outside of battle he's probably pretty cool. just when he's demon slaying he sees red and just killkillkills.)#and samus is a fucking bounty hunter#she's awesome and a nintendo hero so she usually makes the compassionate and morally sound choice but that bitch is a bounty hunter#and i support woman's wrongs. she should be allowed to kill and also do whatever she wants#but master chief - the only one of them who's had a companion or a community throughout his trials -#the one that isn't most comfortable on desolate destroyed wasteland planets -#it makes sense that he'd understand isaac.#he's been in the system since birth but more than enough marines have crumpled under the pressure for him to see the signs of PTSD#intense severe PTSD#imo isaac's attitudes towards the necromorphs would be similar to survivors of The Flood and MC would be equipped to help#him process the really. really dark stuff he's seen.#ANYWAY#MASTER CHIEF GIVES GOOD HUGS. IS WHAT IM TRYING TO SAY.
95K notes
·
View notes
Text


"......!?" Similar to the Grotesqueries, Leonard is feeling more than a little overwhelmed and distressed at the question of why they're coming back.
#||dash commentary||#{/*UPSET WAILING* WE GOT RID OF THEM FOR A FEW WEEKS. TUMBLRRRRR}#{/sigh.... Well; at any rate; I'll be playing Drakengard today (and probably watch some of the Dark Crystal too) and then HOPEFULLY get one#{/of my asks done. After that.... Well. The other lmao}#{/THEN i hope to try some stuffs since I'm hoping I can get my computer in by then; if not soon. *Crumples* I'm really praying... 😭}
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Anatomy of Passing Out: When, Why, and How to Write It

Passing out, or syncope, is a loss of consciousness that can play a pivotal role in storytelling, adding drama, suspense, or emotional weight to a scene. Whether it’s due to injury, fear, or exhaustion, the act of fainting can instantly shift the stakes in your story.
But how do you write it convincingly? How do you ensure it’s not overly dramatic or medically inaccurate? In this guide, I’ll walk you through the causes, stages, and aftermath of passing out. By the end, you’ll be able to craft a vivid, realistic fainting scene that enhances your narrative without feeling clichéd or contrived.
2. Common Causes of Passing Out
Characters faint for a variety of reasons, and understanding the common causes can help you decide when and why your character might lose consciousness. Below are the major categories that can lead to fainting, each with their own narrative implications.
Physical Causes
Blood Loss: A sudden drop in blood volume from a wound can cause fainting as the body struggles to maintain circulation and oxygen delivery to the brain.
Dehydration: When the body doesn’t have enough fluids, blood pressure can plummet, leading to dizziness and fainting.
Low Blood Pressure (Hypotension): Characters with chronic low blood pressure may faint after standing up too quickly, due to insufficient blood reaching the brain.
Intense Pain: The body can shut down in response to severe pain, leading to fainting as a protective mechanism.
Heatstroke: Extreme heat can cause the body to overheat, resulting in dehydration and loss of consciousness.
Psychological Causes
Emotional Trauma or Shock: Intense fear, grief, or surprise can trigger a fainting episode, as the brain becomes overwhelmed.
Panic Attacks: The hyperventilation and increased heart rate associated with anxiety attacks can deprive the brain of oxygen, causing a character to faint.
Fear-Induced Fainting (Vasovagal Syncope): This occurs when a character is so afraid that their body’s fight-or-flight response leads to fainting.
Environmental Causes
Lack of Oxygen: Situations like suffocation, high altitudes, or enclosed spaces with poor ventilation can deprive the brain of oxygen and cause fainting.
Poisoning or Toxins: Certain chemicals or gasses (e.g., carbon monoxide) can interfere with the body’s ability to transport oxygen, leading to unconsciousness.
3. The Stages of Passing Out
To write a realistic fainting scene, it’s important to understand the stages of syncope. Fainting is usually a process, and characters will likely experience several key warning signs before they fully lose consciousness.
Pre-Syncope (The Warning Signs)
Before losing consciousness, a character will typically go through a pre-syncope phase. This period can last anywhere from a few seconds to a couple of minutes, and it’s full of physical indicators that something is wrong.
Light-Headedness and Dizziness: A feeling that the world is spinning, which can be exacerbated by movement.
Blurred or Tunnel Vision: The character may notice their vision narrowing or going dark at the edges.
Ringing in the Ears: Often accompanied by a feeling of pressure or muffled hearing.
Weakness in Limbs: The character may feel unsteady, like their legs can’t support them.
Sweating and Nausea: A sudden onset of cold sweats, clamminess, and nausea is common.
Rapid Heartbeat (Tachycardia): The heart races as it tries to maintain blood flow to the brain.
Syncope (The Loss of Consciousness)
When the character faints, the actual loss of consciousness happens quickly, often within seconds of the pre-syncope signs.
The Body Going Limp: The character will crumple to the ground, usually without the ability to break their fall.
Breathing: Breathing continues, but it may be shallow and rapid.
Pulse: While fainting, the heart rate can either slow down dramatically or remain rapid, depending on the cause.
Duration: Most fainting episodes last from a few seconds to a minute or two. Prolonged unconsciousness may indicate a more serious issue.
Post-Syncope (The Recovery)
After a character regains consciousness, they’ll typically feel groggy and disoriented. This phase can last several minutes.
Disorientation: The character may not immediately remember where they are or what happened.
Lingering Dizziness: Standing up too quickly after fainting can trigger another fainting spell.
Nausea and Headache: After waking up, the character might feel sick or develop a headache.
Weakness: Even after regaining consciousness, the body might feel weak or shaky for several hours.
4. The Physical Effects of Fainting
Fainting isn’t just about losing consciousness—there are physical consequences too. Depending on the circumstances, your character may suffer additional injuries from falling, especially if they hit something on the way down.
Impact on the Body
Falling Injuries: When someone faints, they usually drop straight to the ground, often hitting their head or body in the process. Characters may suffer cuts, bruises, or even broken bones.
Head Injuries: Falling and hitting their head on the floor or a nearby object can lead to concussions or more severe trauma.
Scrapes and Bruises: If your character faints on a rough surface or near furniture, they may sustain scrapes, bruises, or other minor injuries.
Physical Vulnerability
Uncontrolled Fall: The character’s body crumples or falls in a heap. Without the ability to brace themselves, they are at risk for further injuries.
Exposed While Unconscious: While fainted, the character is vulnerable to their surroundings. This could lead to danger in the form of attackers, environmental hazards, or secondary injuries from their immediate environment.
Signs to Look For While Unconscious
Shallow Breathing: The character's breathing will typically become shallow or irregular while they’re unconscious.
Pale or Flushed Skin: Depending on the cause of fainting, a character’s skin may become very pale or flushed.
Twitching or Muscle Spasms: In some cases, fainting can be accompanied by brief muscle spasms or jerking movements.
5. Writing Different Types of Fainting
There are different types of fainting, and each can serve a distinct narrative purpose. The way a character faints can help enhance the scene's tension or emotion.
Sudden Collapse
In this case, the character blacks out without any warning. This type of fainting is often caused by sudden physical trauma or exhaustion.
No Warning: The character simply drops, startling both themselves and those around them.
Used in High-Tension Scenes: For example, a character fighting in a battle may suddenly collapse from blood loss, raising the stakes instantly.
Slow and Gradual Fainting
This happens when a character feels themselves fading, usually due to emotional stress or exhaustion.
Internal Monologue: The character might have time to realize something is wrong and reflect on what’s happening before they lose consciousness.
Adds Suspense: The reader is aware that the character is fading but may not know when they’ll drop.
Dramatic Fainting
Some stories call for a more theatrical faint, especially in genres like historical fiction or period dramas.
Exaggerated Swooning: A character might faint from shock or fear, clutching their chest or forehead before collapsing.
Evokes a Specific Tone: This type of fainting works well for dramatic, soap-opera-like scenes where the fainting is part of the tension.
6. Aftermath: How Characters Feel After Waking Up
When your character wakes up from fainting, they’re not going to bounce back immediately. There are often lingering effects that last for minutes—or even hours.
Physical Recovery
Dizziness and Nausea: Characters might feel off-balance or sick to their stomach when they first come around.
Headaches: A headache is a common symptom post-fainting, especially if the character hits their head.
Body Aches: Muscle weakness or stiffness may persist, especially if the character fainted for a long period or in an awkward position.
Emotional and Mental Impact
Confusion: The character may not remember why they fainted or what happened leading up to the event.
Embarrassment: Depending on the situation, fainting can be humiliating, especially if it happened in front of others.
Fear: Characters who faint from emotional shock might be afraid of fainting again or of the situation that caused it.
7. Writing Tips: Making It Believable
Writing a fainting scene can be tricky. If not handled properly, it can come across as melodramatic or unrealistic. Here are some key tips to ensure your fainting scenes are both believable and impactful.
Understand the Cause
First and foremost, ensure that the cause of fainting makes sense in the context of your story. Characters shouldn’t pass out randomly—there should always be a logical reason for it.
Foreshadow the Fainting: If your character is losing blood, suffering from dehydration, or undergoing extreme emotional stress, give subtle clues that they might pass out. Show their discomfort building before they collapse.
Avoid Overuse: Fainting should be reserved for moments of high stakes or significant plot shifts. Using it too often diminishes its impact.
Balance Realism with Drama
While you want your fainting scene to be dramatic, don’t overdo it. Excessively long or theatrical collapses can feel unrealistic.
Keep It Short: Fainting typically happens fast. Avoid dragging the loss of consciousness out for too long, as it can slow down the pacing of your story.
Don’t Always Save the Character in Time: In some cases, let the character hit the ground. This adds realism, especially if they’re fainting due to an injury or traumatic event.
Consider the Aftermath
Make sure to give attention to what happens after the character faints. This part is often overlooked, but it’s important for maintaining realism and continuity.
Lingering Effects: Mention the character’s disorientation, dizziness, or confusion upon waking up. It’s rare for someone to bounce back immediately after fainting.
Reactions of Others: If other characters are present, how do they react? Are they alarmed? Do they rush to help, or are they unsure how to respond?
Avoid Overly Romanticized Fainting
In some genres, fainting is used as a dramatic or romantic plot device, but this can feel outdated and unrealistic. Try to focus on the genuine physical or emotional toll fainting takes on a character.
Stay Away from Clichés: Avoid having your character faint simply to be saved by a love interest. If there’s a romantic element, make sure it’s woven naturally into the plot rather than feeling forced.
8. Common Misconceptions About Fainting
Fainting is often misrepresented in fiction, with exaggerated symptoms or unrealistic recoveries. Here are some common myths about fainting, and the truth behind them.
Myth 1: Fainting Always Comes Without Warning
While some fainting episodes are sudden, most people experience warning signs (lightheadedness, blurred vision) before passing out. This gives the character a chance to notice something is wrong before losing consciousness.
Myth 2: Fainting Is Dramatic and Slow
In reality, fainting happens quickly—usually within a few seconds of the first warning signs. Characters won’t have time for long speeches or dramatic gestures before collapsing.
Myth 3: Characters Instantly Bounce Back
Many stories show characters waking up and being perfectly fine after fainting, but this is rarely the case. Fainting usually leaves people disoriented, weak, or even nauseous for several minutes afterward.
Myth 4: Fainting Is Harmless
In some cases, fainting can indicate a serious medical issue, like heart problems or severe dehydration. If your character is fainting frequently, it should be addressed in the story as a sign of something more severe.
Looking For More Writing Tips And Tricks?
Are you an author looking for writing tips and tricks to better your manuscript? Or do you want to learn about how to get a literary agent, get published and properly market your book? Consider checking out the rest of Quillology with Haya Sameer; a blog dedicated to writing and publishing tips for authors! While you’re at it, don’t forget to head over to my TikTok and Instagram profiles @hayatheauthor to learn more about my WIP and writing journey!
#hayatheauthor#haya's book blog#haya blogs#writing community#quillology with haya#writing tools#writer things#writing advice#writer community#writing techniques#writing prompt#writing stuff#creative writing#ya writing advice#writing tips and tricks#writer tools#writers of tumblr#writer blog#writers block#quillology with haya sameer#writers on tumblr#writerscommunity#writer stuff#author help#author advice#author#writing inspiration#writeblr#novel writing#on writing
6K notes
·
View notes