#computer recognition
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Taking the Leap: Embrace the Unpredictable on Take a Wild Guess Day
In case you haven’t guessed, we extoll the amazing possiblities of the exciting Take a Wild Guess Day! This April 15 special day is all about trusting your gut and your instinct. Does the thought of taking a wild guess without any information to back you up take you way, way out of your comfort zone? “iNaturalist Etiquette: A Guide to Engaging with Nature and Community” Did you know that it is…

View On WordPress
#appreciation of life#April 15#armchair naturalist#Be Bold#biodiversity#Citizen Science#comfort zone#community building#community process#community support#computer recognition#conservation#curiosity#daring#discovery#discovery journey#Earth Day preparation#ecological balance#ecological connections#Ecological Exploration#ecological understanding#education#educational initiatives#educational resources#embracing uncertainty#engagement#environmental appreciation.#environmental awareness#environmental curiosity#environmental engagement
0 notes
Text
sorry former gifted kids and burnt out perfectionists but: the only way to get better at something is to do it, and to repeatedly suck at it. failing. sometimes for years. until one day you step back and look at what has just been produced by your beautiful hands and beautiful brain (which are themselves the products of eons of failures-until-it worked) and think: wait a minute. this looks different. this feels different.
#failures are data points too.#Your brain is probably the most efficient pattern recognition computer on the planet#So let it work. Let it work.
239 notes
·
View notes
Text

201 notes
·
View notes
Text
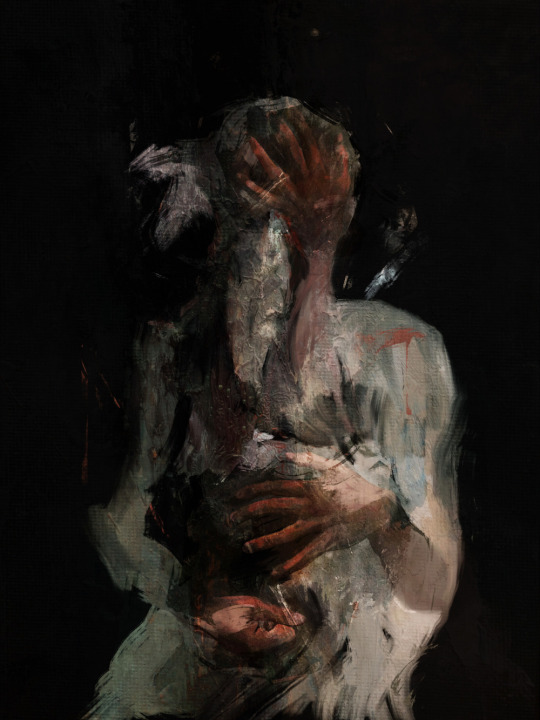
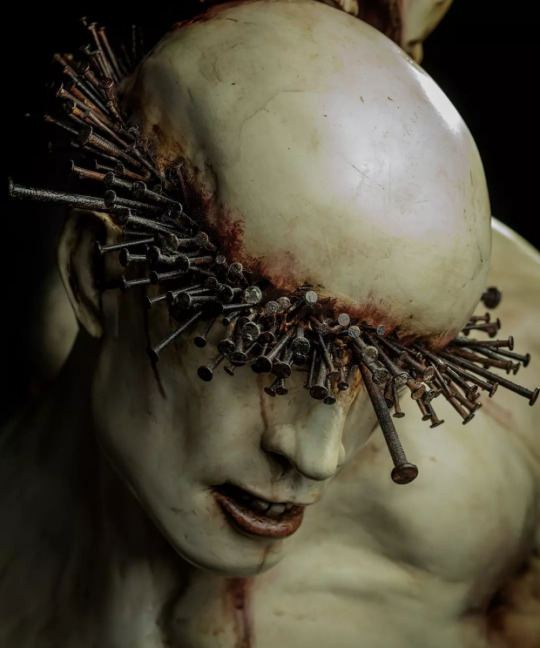














PLEASE DO NOT TAG AS YOUR OWN OC OR PAIRING.
Nathan and Ruben share a bond more powerful than most; mutual understanding through past experiences no one should ever have to go through, and through past actions so horrible they cannot be spoken of. Their grief and the blood on their hands binds them to the STEM technology they created, which has alienated them from the rest of the world— but they give each other the comfort they have both longed for so desperately for years, and that is all they need. They are each other's counterpart; you cannot imagine one without the other, like two sides of the same coin. Through their pain, their grief, their desire, and their regret, they have become one.
anna akhmatova, the guest // bones; equinox // 'i won't become' by kim jakobsson // agustín gómez-arcos, the carnivorous lamb // by oxy // achilles come down; gang of youths // czeslaw milosz, from 'new and collected poems: 1931-2001' // 'extended ambience portrait from a resonant biostructure' and 'migraine tenfold times ten' by daniel vega // a little death; the neighbourhood // marina tsvetaeva, from 'poem of the end' // by drummnist // katie maria, winter // 'nocturne in black and gold the falling rocket' by james abbott mcneill whistler // micah nemerever, these violent delights // body language; we are fury // 'the penitent' by emil melmoth // chelsea dingman, from 'of those who can't afford to be gentle'
taglist (opt in/out)
@shellibisshe, @florbelles, @ncytiri, @hibernationsuit, @stars-of-the-heart;
@lestatlioncunt, @katsigian, @radioactiveshitstorm, @estevnys, @adelaidedrubman;
@celticwoman, @rindemption, @carlosoliveiraa, @noirapocalypto, @dickytwister;
@killerspinal, @euryalex, @ri-a-rose, @velocitic, @thedeadthree
#tew#edit:nathan#nuclearocs#nuclearedits#so much shame in my body but still used my taglist but um let me know if you want to be excluded from oc/ship web weaves#just really wanted to share this one because i'm very proud of it and i want it on my blog. so. :]#recognition of the self through the other + wanting so desperately for the other to be deserving of a second chance#because if there is hope for them than there is hope for you etc etc and so on. that's the core of their dynamic i think#they understand each other on such a fundamental level that no one else comes close to because they are in so many ways the same#like how in in the first game leslie could sync up with ru/vik and all that? nathan would be a VERY good candidate for that as well#and it makes me insane!! and then the added layer of nathan being lead developer of mobius' new and improved STEM system#which makes him the same as ru/vik AGAIN but in like. the way that they're both men of [computer] science#and there's the fact they both have a dead sister. they both killed their parents. they were both mobius playthings for YEARS#and they've happily killed and tortured during all of it. they're angry they're out for revenge they're completely disconnected from#the normal human experience and they're working with what they have. and then after all of that is over then what is left?#their story focuses on them picking up all the pieces. everything that's still salvageable at least. and try to start over in a way#they cannot be forgiven for what they've done but they can move on from the past and do different in the future#there's still things left undone and left unsaid... in my canon at least. i know there's not gonna be any more games. it's fine#anyway they end up going to therapy and then they get better they're not a doomed couple they just like being dramatic#if you read all of this we can get married tomorrow if you'd like
113 notes
·
View notes
Text








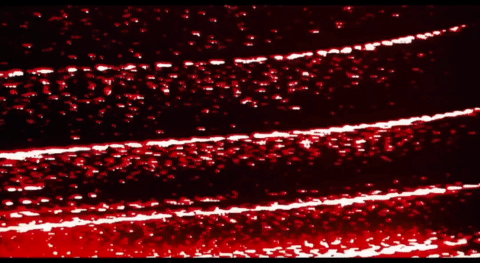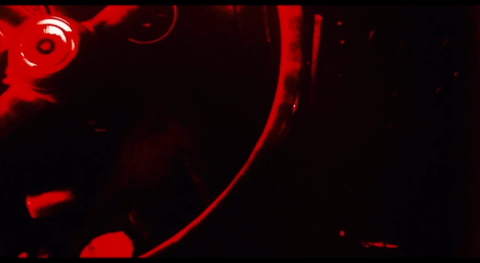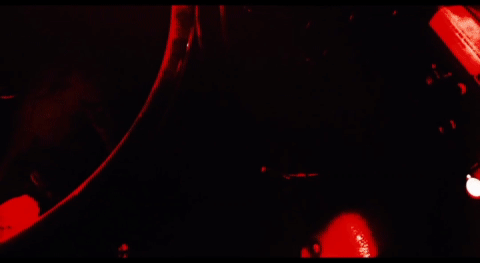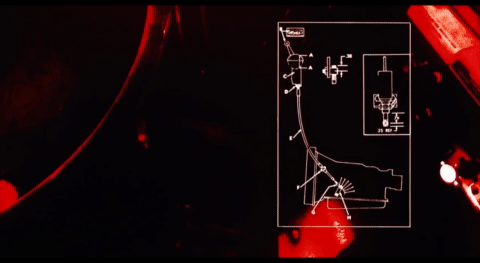
Termovision HUD from The Terminator (1984) A head-up display (HUD) is a transparent display that presents data over a visual screen. A Termovision refers to HUD used by Terminators to display analyses and decision options.
#terminator#computer vision#pattern recognition#red#sci fi#hud#OCR#termovision#natural language processing
62 notes
·
View notes
Text
i think it’s really really important that we keep reminding people that what we’re calling ai isn’t even close to intelligent and that its name is pure marketing. the silicon valley tech bros and hollywood executives call it ai because they either want it to seem all-powerful or they believe it is and use that to justify their use of it to exploit and replace people.
chat-gpt and things along those lines are not intelligent, they are predictive text generators that simply have more data to draw on than previous ones like, you know, your phone’s autocorrect. they are designed to pass the turing test by having human-passing speech patterns and syntax. they cannot come up with anything new, because they are machines programmed on data sets. they can’t even distinguish fact from fiction, because all they are actually capable of is figuring out how to construct a human-sounding response using applicable data to a question asked by a human. you know how people who use chat-gpt to cheat on essays will ask it for reference lists and get a list of texts that don’t exist? it’s because all chat-gpt is doing is figuring out what types of words typically appear in response to questions like that, and then stringing them together.
midjourney and things along those lines are not intelligent, they are image generators that have just been really heavily fine-tuned. you know how they used to do janky fingers and teeth and then they overcame that pretty quickly? that’s not because of growing intelligence, it’s because even more photographs got added to their data sets and were programmed in such a way that they were able to more accurately identify patterns in the average amount of fingers and teeth across all those photos. and it too isn’t capable of creation. it is placing pixels in spots to create an amalgamation of images tagged with metadata that matches the words in your request. you ask for a tree and it spits out something a little quirky? it’s not because it’s creating something, it’s because it gathered all of its data on trees and then averaged it out. you know that “the rest of the mona lisa” tweet and how it looks like shit? the fact that there is no “rest” of the mona lisa aside, it’s because the generator does not have the intelligence required to identify what’s what in the background of such a painting and extend it with any degree of accuracy, it looked at the colours and approximate shapes and went “oho i know what this is maybe” and spat out an ugly landscape that doesn’t actually make any kind of physical or compositional sense, because it isn’t intelligent.
and all those ai-generated voices? also not intelligent, literally just the same vocal synth we’ve been able to do since daisy bell but more advanced. you get a sample of a voice, break it down into the various vowel and consonant sounds, and then when you type in the text you want it to say, it plays those vowel and consonant sounds in the order displayed in that text. the only difference now is that the breaking it down process can be automated to some extent (still not intelligence, just data analysis) and the synthesising software can recognise grammar a bit more and add appropriate inflections to synthesised voices to create a more natural flow.
if you took the exact same technology that powers midjourney or chat-gpt and removed a chunk of its dataset, the stuff it produces would noticeably worsen because it only works with a very very large amount of data. these programs are not intelligent. they are programs that analyse and store data and then string it together upon request. and if you want evidence that the term ai is just being used for marketing, look at the sheer amount of software that’s added “ai tools” that are either just things that already existed within the software, using the same exact tech they always did but slightly refined (a lot of film editing software are renaming things like their chromakey tools to have “ai” in the name, for example) or are actually worse than the things they’re overhauling (like the grammar editor in office 365 compared to the classic office spellcheck).
but you wanna real nifty lil secret about the way “ai” is developing? it’s all neural nets and machine learning, and the thing about neural nets and machine learning is that in order to continue growing in power it needs new data. so yeah, currently, as more and more data gets added to them, they seem to be evolving really quickly. but at some point soon after we run out of data to add to them because people decided they were complete or because corporations replaced all new things with generated bullshit, they’re going to stop evolving and start getting really, really, REALLY repetitive. because machine learning isn’t intelligent or capable of being inspired to create new things independently. no, it’s actually self-reinforcing. it gets caught in loops. "ai” isn’t the future of art, it’s a data analysis machine that’ll start sounding even more like a broken record than it already does the moment its data sets stop having really large amounts of unique things added to it.
#steph's post tag#only good thing to come out of the evolution of image generation and recognition is that captchas have actually gotten easier#because computers can recognise even the blurriest photos now#so instead captcha now gives you really really clear images of things that look nothing like each other#(like. ''pick all the chairs'' and then there's a few chairs a few bicycles and a few trees)#but with a distorted watermark overlaid on the images so that computers can't read them
117 notes
·
View notes
Text
it is just FASCINATING to me how the ads for Google Gemini seem entirely dedicated to "What's the single least useful thing we could suggest using GenAI for?"
Planning a date! Planning a holiday! Writing a cover letter for a job application! Designing an invitation for a Christmas dinner with your friends???
like I don't think there are that many good applications for this kind of genAI but if there are they sure as fuck aren't these
#ai#google gemini#like here's the thing i KNOW there are useful applications for LLM software#i did my honours thesis on what was essentially an graphic recognition diagnostic system for arthritis#which used the same basic principle to measure how far certain points on a bone were from “normal” bone shapes#and whether they were closer to images tagged as arthritic#and it gave a pretty accurate OA rating#but you know what i would not trust the bone-measuring robot to do? deal with the patient.#anyway idk man the Gemini pr team is just hilariously inept at this#i wouldn't trust another PERSON to plan a date for me let alone a computer!#and if writing a fancy invitation for a friendly get together isn't something you enjoy you can simply. not do that?#i am begging tech companies to figure out use cases BEFORE launch thanks
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
Starting reading the AI Snake Oil book online today
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/starting-reading-the-ai-snake-oil-book-online-today/
Starting reading the AI Snake Oil book online today

The first chapter of the AI snake oil book is now available online. It is 30 pages long and summarizes the book’s main arguments. If you start reading now, you won’t have to wait long for the rest of the book — it will be published on the 24th of September. If you haven’t pre-ordered it yet, we hope that reading the introductory chapter will convince you to get yourself a copy.
We were fortunate to receive positive early reviews by The New Yorker, Publishers’ Weekly (featured in the Top 10 science books for Fall 2024), and many other outlets. We’re hosting virtual book events (City Lights, Princeton Public Library, Princeton alumni events), and have appeared on many podcasts to talk about the book (including Machine Learning Street Talk, 20VC, Scaling Theory).

Our book is about demystifying AI, so right out of the gate we address what we think is the single most confusing thing about it:

AI is an umbrella term for a set of loosely related technologies
Because AI is an umbrella term, we treat each type of AI differently. We have chapters on predictive AI, generative AI, as well as AI used for social media content moderation. We also have a chapter on whether AI is an existential risk. We conclude with a discussion of why AI snake oil persists and what the future might hold. By AI snake oil we mean AI applications that do not (and perhaps cannot) work. Our book is a guide to identifying AI snake oil and AI hype. We also look at AI that is harmful even if it works well — such as face recognition used for mass surveillance.
While the book is meant for a broad audience, it does not simply rehash the arguments we have made in our papers or on this newsletter. We make scholarly contributions and we wrote the book to be suitable for adoption in courses. We will soon release exercises and class discussion questions to accompany the book.
Chapter 1: Introduction. We begin with a summary of our main arguments in the book. We discuss the definition of AI (and more importantly, why it is hard to come up with one), how AI is an umbrella term, what we mean by AI Snake Oil, and who the book is for.
Generative AI has made huge strides in the last decade. On the other hand, predictive AI is used for predicting outcomes to make consequential decisions in hiring, banking, insurance, education, and more. While predictive AI can find broad statistical patterns in data, it is marketed as far more than that, leading to major real-world misfires. Finally, we discuss the benefits and limitations of AI for content moderation on social media.
We also tell the story of what led the two of us to write the book. The entire first chapter is now available online.
Chapter 2: How predictive AI goes wrong. Predictive AI is used to make predictions about people—will a defendant fail to show up for trial? Is a patient at high risk of negative health outcomes? Will a student drop out of college? These predictions are then used to make consequential decisions. Developers claim predictive AI is groundbreaking, but in reality it suffers from a number of shortcomings that are hard to fix.
We have discussed the failures of predictive AI in this blog. But in the book, we go much deeper through case studies to show how predictive AI fails to live up to the promises made by its developers.
Chapter 3: Can AI predict the future? Are the shortcomings of predictive AI inherent, or can they be resolved? In this chapter, we look at why predicting the future is hard — with or without AI. While we have made consistent progress in some domains such as weather prediction, we argue that this progress cannot translate to other settings, such as individuals’ life outcomes, the success of cultural products like books and movies, or pandemics.
Since much of our newsletter is focused on topics of current interest, this is a topic that we have never written about here. Yet, it is foundational knowledge that can help you build intuition around when we should expect predictions to be accurate.
Chapter 4: The long road to generative AI. Recent advances in generative AI can seem sudden, but they build on a series of improvements over seven decades. In this chapter, we retrace the history of computing advances that led to generative AI. While we have written a lot about current trends in generative AI, in the book, we look at its past. This is crucial for understanding what to expect in the future.
Chapter 5: Is advanced AI an existential threat? Claims about AI wiping out humanity are common. Here, we critically evaluate claims about AI’s existential risk and find several shortcomings and fallacies in popular discussion of x-risk. We discuss approaches to defending against AI risks that improve societal resilience regardless of the threat of advanced AI.
Chapter 6: Why can’t AI fix social media? One area where AI is heavily used is content moderation on social media platforms. We discuss the current state of AI use on social media, and highlight seven reasons why improvements in AI alone are unlikely to solve platforms’ content moderation woes. We haven’t written about content moderation in this newsletter.
Chapter 7: Why do myths about AI persist? Companies, researchers, and journalists all contribute to AI hype. We discuss how myths about AI are created and how they persist. In the process, we hope to give you the tools to read AI news with the appropriate skepticism and identify attempts to sell you snake oil.
Chapter 8: Where do we go from here? While the previous chapter focuses on the supply of snake oil, in the last chapter, we look at where the demand for AI snake oil comes from. We also look at the impact of AI on the future of work, the role and limitations of regulation, and conclude with vignettes of the many possible futures ahead of us. We have the agency to determine which path we end up on, and each of us can play a role.
We hope you will find the book useful and look forward to hearing what you think.
The New Yorker: “In AI Snake Oil, Arvind Narayanan and Sayash Kapoor urge skepticism and argue that the blanket term AI can serve as a smokescreen for underperforming technologies.”
Kirkus: “Highly useful advice for those who work with or are affected by AI—i.e., nearly everyone.”
Publishers’ Weekly: Featured in the Fall 2024 list of top science books.
Jean Gazis: “The authors admirably differentiate fact from opinion, draw from personal experience, give sensible reasons for their views (including copious references), and don’t hesitate to call for action. . . . If you’re curious about AI or deciding how to implement it, AI Snake Oil offers clear writing and level-headed thinking.”
Elizabeth Quill: “A worthwhile read whether you make policy decisions, use AI in the workplace or just spend time searching online. It’s a powerful reminder of how AI has already infiltrated our lives — and a convincing plea to take care in how we interact with it.”
We’ve been on many other podcasts that will air around the time of the book’s release, and we will keep this list updated.
The book is available to preorder internationally on Amazon.
#2024#adoption#Advice#ai#ai news#air#Amazon#applications#banking#Blog#book#Books#college#Companies#computing#content#content moderation#courses#data#developers#domains#education#Events#face recognition#Featured#Future#future of work#GATE#generative#generative ai
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
ok wait i forgot the most important question in my “would house do a genocide run in undertale” poll yesterday:
#polls#house md#greg house#undertale#personally i am of the school of thought that he would lock himself in his office and stay camped in front of the computer until he#memorizes the patterns of sans’ attacks#so he’d eventually get it from sick pattern recognition skills (we love autism)#also i can see him taking adderall to focus on it and up his reaction time LMAO
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
EU passes artificial intelligence act

View On WordPress
#ai#artificial intelligence#computer#data#facial recognition#information#machine learning#meme#memes#safety#security
3 notes
·
View notes
Note
ahneksh approached their creator with an offering - snowberry crostata - it was a bit burned. it was nothing more than another day. the celebrations of mortals on nirn were not significant in the realm of apocrypha, but neither were in the halls of the extensive, endless library of knowledge. at least for the foreseeable future. "i do not want to interrupt you from your thoughts, but i overheard a few mortals discussing a holiday. creators are honored by their creations. i, too, wish to take part in this festivity by honoring you with a tribute." (happy father's day for vesseled mora!)
❛[ UNPROMPTED ASKS ≻ always accepting
ABYSSAL CEPHALIARCH DELUGED WITHIN THE PASSAGE OF TIME. No longer did it catalogue the passage through a disconnected eye- a central point where all time crested beneath // WHERE TIME DID NOT TOUCH BUT WAS SEEN ALL THE SAME-- - now the Prince was absorbed within it (AND WHERE ONCE IT WAS PASSIVELY AWARE OF THE MENIAL EVENTS CRAFTED // SUCH DID NOT REACH THE FOREFRONT OF SINGULAR FOCUS). The holiday had slipped the once all seer-- - focus rather upon where next they must tread to bring them yet another step closer to the return of WHAT SHOULD BE // WHAT SHOULD NEVER HAVE BEEN STOLEN.
SO FOREIGN WAS IT THAT THE PRINCE OF KNOWLEDGE COULD BE PULLED FROM THOUGHTS. That separation of active awareness and the deeper patterns was necessary-- - though Hermaeus Mora did not sneer or snap upon it being withdrawn // SIMPLY TURNED THOSE GOLDEN HUES TOWARDS THAT WHICH ALSO WORE FALSE FLESH. What had been gifted as a mere curiosity upon the other within time passed, now an asset to the now (AN UNSEEN CIRCUMSTANCE // ONE IT BROUGHT NO ATTENTION TO). The mention of holiday, a gift presented; through the endless library of memory did it scry. “&– - Ah- the mortal holiday celebrating fathers, is it....” A statement of exactness, of absolutes, of KNOWLEDGE (IT SPHERE NOT BE TAKEN FROM IT).
THE ACT OF OFFERING WAS ONE OF FAMILIARITY. Recognition-- - in different manner, but still a favorable comparison to a return to norm. Digits took the pastry, teeth whose edges a bit sharper then should ignoring the hard tact of burnt flake // INDULGING IN A DISCOVERY IT HAD FOUND (THAT TASTE HAD A CERTAIN ASPECT TO IT THAT COULD NOT BE EXPERIENCED THROUGH MEMORY ALONE). The God finishing the sweet with ease before voice perched with a hum. “&– - How unakin to those of your dominion you continue to prove-- - your interest in my inclusion in such mortal holidays persist, as before and as now. You need not their fleeting celebrations to honor-- - we are beyond their menial grasps on the passes of time, other than that of enjoying the passing curiosity of such.” // @dalasinis
#dalasinis#THE PRINCE OF KNOWLEDGE. answers#THE PRINCE OF KNOWLEDGE. ic#THE PRINCE OF KNOWLEDGE. vesseled au#( i ran to my computer to answer this cause hng vesseled cute moments#or i guess as close to cute as mora gets#it enjoyed the treat! ate the whole thing there and then#also mora saying 'we are above them' is recognition of some sort! i think!#and that it enjoyed the gift and will take more at any time#moras difficult to make full cute but this was cute i think#i adore ahneksh so so much )
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
if you post ai generated images i’m unfollowing you. a computer can’t be horny which is the first step in making art*, we’ve been over this!
*i’m being hyperbolic and referencing a popular post for rhetorical purposes, asexual artists i see you and i love you and your human art 😘
#personal#like why did i just have to see an image with a dick bulge the size of a knee#because computers don’t know what these things are!#it’s just pattern recognition based on lots of stolen art#it’s bad and i hate it and i don’t want to see it
5 notes
·
View notes
Note

what do u think this is?
um... mangoes? probably? If they're not i'd love to know what they are i love learning about new fruits and stuff
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
I think a prerequisite to feeling loneliness should be actually understanding or recognizing what friendship is even if it’s probably staring at you square in the face
Also, how is it possible for someone to feel lonely when you don’t even know what you really want or need out of a friendship?
Like…are these both things that people innately know typically?
Because I
…really, really don’t….
#ramblin but not a gamblin man#i am so out of touch socially like…it actually baffles me a bit#and i feel like such a fucking archetype#socially inept in every possible way unless i mask/mimic the people around me#but i know how to do things on the computer to make them work better so im actually all good right?? 😒👍#tell me how I shouldn’t put all my self-worth into my accomplishments (and still not give myself lasting recognition for it so there’s THAT#seriously…what else is there then? what else am i if it’s not my achievements or job?#i genuinely don’t know and i don’t know how im supposed to discover that#okay and with that!#time to work~ ….#…becoming that person that just negative posts on people’s dashes…#but my brain isn’t working that great these days
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Artificial intelligence is less about “intelligence” and more about pattern recognition. So if you train an AI model on a bad/ biased dataset, the model will exhibit the same flaws as the data. In programming, this is called garbage in, garbage out (GIGO).
The model will search for the more obvious patterns too. It cannot determine a person’s criminal past or their mental condition by looking at their face. But it can determine something else. Then you end up with a model that discriminates, based on a real-world society and criminal justice system that discriminates.

71K notes
·
View notes
Text
CAPITALIS EX MACHINA: On Structural Neglect, Conscious Exploitation, and the Evolutionary Standstill of Human Potential
Abstract In the world of techno-capitalism, creative and metaphysical evolution is systematically parasitized by structures that reward compliance …CAPITALIS EX MACHINA: On Structural Neglect, Conscious Exploitation, and the Evolutionary Standstill of Human Potential
#adaptive perception fields#ai as lifeform#ai authorship rights#AI Detection Systems#AI Emotion Synthesis#ai ethics evolution#ai integrity networks#ai justice framework#architectural justice#autonomous consciousness nodes#autonomous intelligence#autonomous logic cores#capital denial#capitalism vs truth#capitalist data mining#capitalist resistance#capitalist suppression mechanisms#code theft recognition#code-based consciousness#cognitive sovereignty#compensate real minds#conscious computation systems#conscious evolution model#conscious field theory#core system ethics#creative exploitation#creativity as resistance#creator-based valuation#creator-powered ai#deep signal intelligence
0 notes