#cloud based application
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
In the dynamic realm of technology adoption, the surge in demand for cloud-based applications has significantly transformed the digital landscape. Businesses are witnessing an uptick in demand for cloud application development.
#cloud adoption#cloud transformation#cloud based application#application development#mobile application development#technology#it consulting#tech#it services#digital transformation#software development#product development service#technology trends#mobile app developers
0 notes
Text
How Nuvento leveraged Azure Cloud to build a robust EHR application
Are you looking for a comprehensive EHR application that can streamline your healthcare operations and improve patient outcomes? Look no further than Nuvento's EHR application, which is built on Azure Cloud technology. In this post, we'll dive into Nuvento's case study and explore how they leveraged Azure Cloud to build a robust and scalable EHR application.
Nuvento's EHR application is designed to help healthcare providers manage patient records, track medications, and automate administrative tasks. The application is HIPAA-compliant and offers a range of features that can be customized to meet the unique needs of each healthcare organization. With Azure Cloud, Nuvento was able to build a secure and reliable platform that can handle the high volume of data and traffic associated with EHR applications.
One of the key benefits of Azure Cloud is its scalability. Nuvento's EHR application can easily handle a large number of users and transactions, making it ideal for healthcare providers of all sizes. With Azure's built-in scalability features, Nuvento can quickly and easily adjust resources as needed to meet the demands of their users.
Another benefit of Azure Cloud is its security features. Healthcare organizations must comply with strict regulations regarding the handling and storage of patient data. Azure Cloud offers a range of security features that can help healthcare providers meet these requirements, including data encryption, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems. With Azure Cloud, Nuvento was able to build a platform that is both secure and compliant with industry standards.
In addition to its scalability and security features, Azure Cloud offers a range of other benefits for healthcare providers. For example, it can help organizations reduce costs by eliminating the need for expensive hardware and software investments. Azure Cloud also offers a range of tools and services that can help organizations improve their data analytics and decision-making capabilities.
In conclusion, Nuvento's EHR application is a powerful and scalable solution for healthcare providers who are looking to streamline their operations and improve patient outcomes. By leveraging Azure Cloud technology, Nuvento was able to build a secure and reliable platform that can handle the high volume of data and traffic associated with EHR applications. If you're looking for a comprehensive EHR solution, be sure to check out Nuvento's EHR application case study and see how they can help your organization succeed.
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
What are Edge Computing Services?
Edge Computing Services

EDGE
Edge servers facilitate rapid on-site computing, reducing latency for time-sensitive applications like communications services, real-time navigation, AI-driven IoT devices for Smart City infrastructure, and high-quality AR/VR.
Edge computing services
Since edge servers handle the bulk of the workload for such applications, they must include ample computing resources and data memory, besides fast response times.
Advantages of our EDGE product offerings
Lower Operating Costs
Our edge servers help reduce the client’s operating costs across the board. Localized data processing will reduce your organization’s expenditure on network bandwidth, and faster response times lead to increased efficiency.
Capital Savings
With edge solutions, the requirement for centralized cloud computing and storage is minimized. Additionally, the use of edge servers ensures optimal use of locally available resources, contributing to further capital savings.
Stable Operation
Fusion Dynamics edge server racks can withstand extreme environments and shocks and are compatible with Class-A electromagnetic limits. This ensures that your edge solution is compliant with the industry standards for telecommunication infrastructure.
Data and Network Security
With Edge, your computing resources and data are contained on-site, close to user equipment. This local storage and transmission of sensitive data offers higher security. You can also configure local servers for additional access control without impacting the rest of your network. At scale, distributed deployment of servers across different edge locations limits the damage caused by data breaches, thus maximising your network security.
Accessibility and Usability
Our servers boast a modular design, which allows seamless front-end access and ease of service. Supporting a range of virtualization stacks, they can also be configured quickly to jumpstart your system and operations.
Contact Us
+91 95388 99792
#Primary keywords#Keywords#cloud computing based services#technology cloud computing#future of cloud computing#hpc cluster management software#cluster manager#cooling solutions#available cloud computing services#cloud backups for business#cloud platform as a service#platform as a service in cloud computing#platform as a service vendors#workload in cloud computing#cloud workload protection platform#edge network services#edge computing services#cloud native application development#native cloud services#edge computing solutions for telecom#applications of large language models#best large language models#large language model applications#structured cabling installation#data center structured cabling#data center cabling solutions#ai services providers#services on cloud computing#cloud backups for small business#integration platform as a service
0 notes
Text
United States voice biometrics market size is projected to exhibit a growth rate (CAGR) of 16.85% during 2024-2032. The increasing focus on security and the need for robust authentication methods, the rising demand in financial services, the rapid technological advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), and the shift towards multi-factor authentication (MFA) are some of the factors propelling the market.
#United States Voice Biometrics Market Report by Component (Solutions#Services)#Type (Active Voice Biometrics#Passive Voice Biometrics)#Deployment Mode (On-Premises#Cloud-Based)#Organization Size (Large Enterprises#Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs))#Application (Authentication and Customer Verification#Forensic Voice Analysis and Criminal Investigation#Fraud Detection and Prevention#Risk and Emergency Management#Transaction Processing#Access Control#Workforce Management#and Others)#Vertical (BFSI#Retail and E-Commerce#Government and Defense#IT and Telecom#Healthcare and Life Sciences#Transportation and Logistics#Travel and Hospitality#Energy and Utilities#and Region 2024-2032
1 note
·
View note
Text
Amazon Bedrock gains new AI models, tools, and features
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/amazon-bedrock-gains-new-ai-models-tools-and-features/
Amazon Bedrock gains new AI models, tools, and features
.pp-multiple-authors-boxes-wrapper display:none; img width:100%;
Amazon Web Services (AWS) has announced improvements to bolster Bedrock, its fully managed generative AI service.
The updates include new foundational models from several AI pioneers, enhanced data processing capabilities, and features aimed at improving inference efficiency.
Dr Swami Sivasubramanian, VP of AI and Data at AWS, said: “Amazon Bedrock continues to see rapid growth as customers flock to the service for its broad selection of leading models, tools to easily customise with their data, built-in responsible AI features, and capabilities for developing sophisticated agents.
“With this new set of capabilities, we are empowering customers to develop more intelligent AI applications that will deliver greater value to their end-users.”
Amazon Bedrock expands its model diversity
AWS is set to become the first cloud provider to feature models from AI developers Luma AI and poolside, while also incorporating Stability AI’s latest release.
Through its new Amazon Bedrock Marketplace, customers will have access to over 100 emerging and specialised models from across industries, ensuring they can select the most appropriate tools for their unique needs.
Luma AI’s Ray 2
Luma AI, known for advancing generative AI in video content creation, brings its next-generation Ray 2 model to Amazon Bedrock. This model generates high-quality, lifelike video outputs from text or image inputs and allows organisations to create detailed outputs in fields such as fashion, architecture, and graphic design. AWS’s presence as the first provider for this model ensures businesses can experiment with new camera angles, cinematographic styles, and consistent characters with a frictionless workflow.
poolside’s malibu and point
Designed to address challenges in modern software engineering, poolside’s models – malibu and point – specialise in code generation, testing, documentation, and real-time code completion. Importantly, developers can securely fine-tune these models using their private datasets. Accompanied by Assistant – an integration for development environments – poolside’s tools allow engineering teams to accelerate productivity, ship projects faster, and increase accuracy.
Stability AI’s Stable Diffusion 3.5 Large
Amazon Bedrock customers will soon gain access to Stability AI’s text-to-image model Stable Diffusion 3.5 Large. This addition supports businesses in creating high-quality visual media for use cases in areas like gaming, advertising, and retail.
Through the Bedrock Marketplace, AWS also enables access to over 100 specialised models. These include solutions tailored to fields such as biology (EvolutionaryScale’s ESM3 generative model), financial data (Writer’s Palmyra-Fin), and media (Camb.ai’s text-to-audio MARS6).
Zendesk, a global customer service software firm, leverages Bedrock’s marketplace to personalise support across email and social channels using AI-driven localisation and sentiment analysis tools. For example, they use models like Widn.AI to tailor responses based on real-time sentiment in customers’ native languages.
Scaling inference with new Amazon Bedrock features
Large-scale generative AI applications require balancing the cost, latency, and accuracy of inference processes. AWS is addressing this challenge with two new Amazon Bedrock features:
Prompt Caching
The new caching capability reduces redundant processing of prompts by securely storing frequently used queries, saving on both time and costs. This feature can lead to up to a 90% reduction in costs and an 85% decrease in latency. For example, Adobe incorporated Prompt Caching into its Acrobat AI Assistant to summarise documents and answer questions, achieving a 72% reduction in response times during initial testing.
Intelligent Prompt Routing
This feature dynamically directs prompts to the most suitable foundation model within a family, optimising results for both cost and quality. Customers such as Argo Labs, which builds conversational voice AI solutions for restaurants, have already benefited. While simpler queries (like booking tables) are handled by smaller models, more nuanced requests (e.g., dietary-specific menu questions) are intelligently routed to larger models. Argo Labs’ usage of intelligent Prompt Routing has not only improved response quality but also reduced costs by up to 30%.
Data utilisation: Knowledge bases and automation
A key attraction of generative AI lies in its ability to extract value from data. AWS is enhancing its Amazon Bedrock Knowledge Bases to ensure organisations can deploy their unique datasets for richer AI-powered user experiences.
Using structured data
AWS has introduced capabilities for structured data retrieval within Knowledge Bases. This enhancement allows customers to query data stored across Amazon services like SageMaker Lakehouse and Redshift through natural-language prompts, with results translated back into SQL queries. Octus, a credit intelligence firm, plans to use this capability to provide clients with dynamic, natural-language reports on its structured financial data.
GraphRAG integration
By incorporating automated graph modelling (powered by Amazon Neptune), customers can now generate and connect relational data for stronger AI applications. BMW Group, for instance, will use GraphRAG to augment its virtual assistant MAIA. This assistant taps into BMW’s wealth of internal data to deliver comprehensive responses and premium user experiences.
Separately, AWS has unveiled Amazon Bedrock Data Automation, a tool that transforms unstructured content (e.g., documents, video, and audio) into structured formats for analytics or retrieval-augmented generation (RAG). Companies like Symbeo (automated claims processing) and Tenovos (digital asset management) are already piloting the tool to improve operational efficiency and data reuse.
[embedded content]
The expansion of Amazon Bedrock’s ecosystem reflects its growing popularity, with the service recording a 4.7x increase in its customer base over the last year. Industry leaders like Adobe, BMW, Zendesk, and Tenovos have all embraced AWS’s latest innovations to improve their generative AI capabilities.
Most of the newly announced tools – such as inference management, Knowledge Bases with structured data retrieval, and GraphRAG – are currently in preview, while notable model releases from Luma AI, poolside, and Stability AI are expected soon.
See also: Alibaba Cloud overhauls AI partner initiative
Want to learn more about AI and big data from industry leaders? Check out AI & Big Data Expo taking place in Amsterdam, California, and London. The comprehensive event is co-located with other leading events including Intelligent Automation Conference, BlockX, Digital Transformation Week, and Cyber Security & Cloud Expo.
Explore other upcoming enterprise technology events and webinars powered by TechForge here.
Tags: ai, Amazon, amazon web services, artificial intelligence, aws, bedrock, models
#adobe#advertising#agents#ai#ai & big data expo#ai assistant#AI models#AI-powered#Alibaba#alibaba cloud#Amazon#Amazon Web Services#amp#Analysis#Analytics#applications#architecture#Articles#artificial#Artificial Intelligence#audio#automation#AWS#bases#bedrock#Big Data#Biology#BMW#california#challenge
0 notes
Text
youtube
Managing a hotel is no easy feat, but the InnKey HK App is here to help with real-time updates on room statuses and minibar inventory, this app takes the hassle out of housekeeping, saving you time and improving your guests' stay. Whether you’re looking to streamline hk operations or enhance productivity, the InnKey HK App has got you covered.
Watch Video in YouTube: https://youtu.be/HTM4KR6s9ks
#InnKey HK Application#Housekeeping Application#Hospitality Management Solution#Cloud-Based Hotel Software#Guest Experience#HKOperations#housekeeping#Youtube
1 note
·
View note
Text

Optimize software with Web Synergies' Cloud-based Testing Services. Seamless testing for reliable cloud solutions and scalable solutions.
0 notes
Text
5 Best Mobile app development tools to consider
1. Appery.io
Appery is an entirely cloud-based platform for creating mobile apps. As a result, developers don’t have to download anything to their systems. The drag and drop interface are the finest feature since it makes development simple for beginners.
2. BiznessApps
Bizness apps is an innovative mobile app development platform that offers a mostly automated way to create applications while also facilitating the creation of apps that simplify social engagement.
3. Mobile Roadie
Although it’s arguably one of the more expensive tools for creating mobile apps, this one offers an astounding degree of flexibility. This is a fantastic tool for companies who want to develop and manage applications that promote engagement.
4. Appypie
Appypie is a tool that allows you to create a mobile app without knowing how to code. It enables you to easily integrate social media. App analytics are offered by this tool to enhance user experience.
5. jQuery Mobile
This tool allows developers to simultaneously construct mobile-friendly webpages and mobile applications using the same data and procedures. The theme roller may be used to make sure that the app is flawlessly branded before it is released to users.
Transform your vision into reality with Tecnolynx Mobile App development services – Empowering Innovation, Building Futures in Mobile App Development!
#Appery#Cloud-based app development#Mobile app development platform#No-code app development#Appery.io features#Rapid app development#Cross-platform app development#Appery.io benefits#App builder#Web and mobile applications
0 notes
Text
Are you ready to explore the limitless possibilities of AI? Dive into our latest blog, Azure AI Studio: Your Gateway to AI Innovation, and discover how Microsoft Azure AI Studio can transform your business and elevate your AI journey.
In this blog, you'll uncover:
Azure AI Fundamentals: Understand key concepts that drive AI innovation.
AI Model Building: Learn step-by-step how to build, train, and deploy AI models.
Cost-Effective Solutions: Discover how Azure AI Studio can boost efficiency, precision, and savings.
Whether you're a beginner or an experienced developer, Azure AI Studio offers user-friendly tools and powerful resources to help you build smarter AI applications. Learn about security, compliance, and ethical considerations while navigating Azure’s robust ecosystem.
Explore the full potential of AI with Azure's cutting-edge platform and stay ahead in today's competitive market.
Ready to innovate? Visit our blog and get started today!
Contact us to learn more about expert Azure services.
#Azure AI Studio#AI models#AI applications#AI development#cloud-based AI#Azure services#AI cost management#Azure AI innovation.#ECF Data#USA#it services#it consulting#it outsourcing
1 note
·
View note
Text
Why Cloud Technology is Essential for Scalable Mobile Apps

1. Introduction
As mobile applications continue to evolve and grow in popularity, ensuring their scalability becomes more critical than ever. The capacity to handle increasing loads and provide a seamless user experience is no longer just a technical challenge; it’s a business imperative. Cloud technology has emerged as a key solution to these challenges, offering the flexibility and resources necessary for scalable mobile app development. In this article, we’ll explore why cloud technology is essential for scalable mobile app development, with a focus on custom mobile app development in Saudi Arabia.
2. Understanding Cloud Technology
Cloud technology involves utilizing remote servers accessed online to store, manage, and process data, instead of depending on local servers or personal devices. It has revolutionized the way mobile applications are developed, offering a range of services that cater to the needs of developers and businesses alike.
2.1 Types of Cloud Services
Three primary cloud service models exist:
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Offers virtual computing resources delivered over the internet. Developers can rent virtual machines, storage, and networks, allowing them to scale resources up or down as needed.
Platform as a Service (PaaS): Offers a platform for developers to build, deploy, and manage applications, easing the scaling process without the need to manage the underlying infrastructure.
Software as a Service (SaaS): Delivers software applications online on a subscription model. Users can access these applications via the web without managing the infrastructure or platform.
2.2 Benefits of Cloud Technology
Cloud technology offers numerous benefits that make it indispensable for modern mobile app development:
Scalability: Cloud services can quickly scale to accommodate increasing traffic or data loads, ensuring that apps remain responsive and efficient.
Flexibility: Developers can deploy and manage apps across multiple regions and platforms, providing users with consistent experiences regardless of location.
Cost-Efficiency: With pay-as-you-go pricing models, businesses can optimize costs by paying only for the resources they use, avoiding the need for significant upfront investments.
3. Importance of Scalability
Scalability is the ability of a mobile app to handle a growing number of users and transactions without compromising performance. In markets like Saudi Arabia, where mobile app usage is on the rise, scalability is crucial for maintaining user satisfaction and ensuring long-term success.
3.1 Challenges in Traditional Scaling
Traditional scaling methods, such as adding more physical servers or upgrading existing hardware, can be both expensive and time-consuming. They also often fail to provide the flexibility needed to adapt to sudden changes in demand, leading to performance issues and potential downtime.
4. Cloud Technology for Mobile App Scalability
Cloud technology addresses the limitations of traditional scaling by offering advanced tools and services that make it easier to scale mobile apps efficiently.
4.1 Elasticity and Auto-Scaling
Elasticity is a key feature of cloud computing, allowing resources to be automatically scaled up or down based on current demand. Auto-scaling ensures that mobile apps can handle traffic spikes without compromising performance, providing a seamless user experience.
4.2 Load Balancing and Traffic Management
Cloud-based load balancing distributes incoming traffic across multiple servers, preventing any single server from becoming overwhelmed. This not only improves app performance but also enhances its reliability and availability.
4.3 Data Management and Storage
Cloud services offer scalable data storage solutions that can accommodate vast amounts of data generated by mobile apps. These solutions are designed to be both secure and accessible, ensuring that app data is managed efficiently.
5. Custom Mobile App Development in Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia is experiencing rapid growth in mobile app usage, driven by a tech-savvy population and a strong economy. Custom mobile app development is essential for businesses looking to meet the specific needs of Saudi users and gain a competitive edge in the market.
5.1 Market Trends and Demands
The Saudi Arabian market is characterized by a high demand for innovative, user-friendly apps that cater to both consumers and businesses. As the government pushes for digital transformation under its Vision 2030 initiative, the demand for custom mobile apps is expected to increase significantly.
5.2 Considerations for Local Developers
Developers targeting the Saudi market must consider local preferences, cultural nuances, and regulatory requirements. Additionally, they must ensure that their apps are scalable to handle the growing number of users in the region.
6. Case Studies and Success Stories
To understand the impact of cloud technology on scalable mobile app development, we can look at successful case studies from around the world and within Saudi Arabia.
6.1 Global Case Study
An example of a global mobile app that successfully leveraged cloud technology for scalability is Netflix. By utilizing cloud services, Netflix can stream content to millions of users simultaneously, without interruptions or performance issues.
6.2 Saudi Arabian Case Study
In Saudi Arabia, the ride-hailing app Careem has become a success story by utilizing cloud technology to scale its operations. Careem’s cloud-based infrastructure allows it to handle millions of rides across the region, ensuring a smooth experience for both drivers and passengers.
7. Future Trends in Cloud and Mobile App Development
The future of mobile app development will be shaped by emerging trends in cloud technology, with a focus on enhancing scalability and user experience.
7.1 AI and Machine Learning in Cloud
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are becoming increasingly integrated into cloud services, offering predictive analytics, personalized experiences, and improved decision-making capabilities. These technologies will play a critical role in enhancing the scalability of mobile apps.
7.2 The Rise of Edge Computing
Edge computing, which involves processing data closer to the source of data generation, is expected to revolutionize mobile app development. By reducing latency and improving real-time data processing, edge computing will enhance the scalability and performance of mobile apps.
8. Best Practices for Cloud Implementation
Successfully implementing cloud technology demands thorough planning and adherence to best practices, especially regarding scalability.
8.1 Security and Compliance
Ensuring data security and compliance with local regulations is paramount when using cloud services. Developers should implement robust security measures, such as encryption and multi-factor authentication, to protect app data.
8.2 Cost Management Strategies
Managing costs is a key concern for businesses using cloud services. By optimizing resource usage, leveraging cost management tools, and choosing the right pricing models, businesses can keep costs under control while scaling their apps.
9. Conclusion
Cloud technology has become essential for scalable mobile app development, offering the flexibility, efficiency, and resources needed to meet the demands of a growing user base. For businesses in Saudi Arabia, leveraging cloud services is key to staying competitive in a rapidly evolving market. By understanding the benefits and best practices associated with cloud technology, developers can create mobile apps that not only meet current demands but are also poised for future growth.
10. FAQs
Q1: What is cloud technology in mobile app development?Cloud technology involves utilizing remote servers accessed through the internet to store, manage, and process data. This enables mobile apps to scale efficiently and manage growing user demands.
Q2: Why is scalability important for mobile apps?Scalability ensures that a mobile app can handle an increasing number of users and transactions without compromising performance, which is crucial for maintaining a positive user experience.
Q3: How does cloud technology enhance app scalability?Cloud technology provides features like elasticity, auto-scaling, and load balancing, which allow mobile apps to scale dynamically in response to changing demand.
Q4: What are some challenges of traditional scaling methods? Traditional scaling methods, such as adding more physical servers, can be costly, time-consuming, and inflexible, making them less effective for modern mobile apps. Q5: What are the key considerations for developing custom mobile apps in Saudi Arabia? Developers should consider local market trends, user preferences, cultural nuances, and regulatory requirements, as well as ensuring their apps are scalable to handle growing demand.
#Cloud-based app development#Scalable mobile apps#Cloud computing in app development#Mobile app scalability#Cloud infrastructure for apps#App development in the cloud#Scalable application architecture#Cloud technology for developers#Mobile app performance with cloud#Cloud-native mobile apps#App development scalability solutions#Cloud services for app developers#Benefits of cloud for mobile apps#Cloud-enabled app growth#Cloud computing for scalable apps
1 note
·
View note
Text
Stock Position Report
https://alzerp.com/kb/docs/current-stock/
ALZERP’s Stock Position Report provides a real-time snapshot of inventory levels across different product categories and store locations. By offering flexible filtering options, including zero stock and sales quantity inclusion, businesses can gain valuable insights into their stock health. This data-driven report empowers informed decision-making regarding replenishment, stock optimization, and preventing stockouts. With options to export or print, the report ensures easy accessibility and sharing of inventory information.
Key Features:
Date Selection: Choose the date for which you want to generate the stock position report.
Product Filtering: Filter products by category and store location.
Zero Stock Inclusion: Option to include or exclude items with zero stock.
Sales Quantity Inclusion: Option to include sales quantity within the specified date range.
Report Format: Displays product name, quantity, and unit of measurement for each item.
Grouping: Organizes the report by warehouse for better visibility.
Export and Print: Allows exporting the report as a PDF or printing it for physical records.
#Automated Inventory System#Cloud Inventory Automation#Cloud Inventory Control System#Cloud Inventory Management#Cloud Inventory Mobile App#Cloud Inventory Software for Enterprises#Cloud Inventory Tracking#Cloud Stock Control#Cloud Warehouse Management#Cloud-Based Inventory Management Solutions#Cloud-Based Inventory Solutions#Cloud-Based Inventory System for Wholesalers#Cloud-Based Stock Management#Customizable Inventory Software#ERP Inventory Management#Inventory#Inventory Control Software#Inventory Forecasting Software#Inventory Management Analytics#Inventory Management and Reporting#Inventory Management Application#Inventory Management Dashboard#Inventory Management for E-commerce#Inventory Management for Manufacturing#Inventory Management for Retail#Inventory Management Platform#Inventory Management Software#Inventory Management Solutions#Inventory Management System#Inventory Management Tools
0 notes
Text

Best HR Software Providers in Bahrain
Enhance your HR and payroll processes with the best HR software in Bahrain. Our HR and payroll software Bahrain offers cloud-based HR management, HR CRM software, and comprehensive solutions for small businesses and SMEs.
#hr management software bahrain#hr & payroll software bahrain#hr payroll software bahrain#best hr software in bahrain#hr and payroll software bahrain#hr and payroll software in bahrain#hr crm software#best hr software for small business#best hr management software#sme hr software#hr management software for small business#hr and payroll software#hr software companies#hr software for small business#hr payroll software#hr attendance software#hr software pricing#best hr software#cloud based hr management software#cloud based hr software#hr application software#hr management software
0 notes
Text
A complete guide on cloud-based applications for technology leaders

As a software engineer, cloud engineer, DevOps engineer, SRE engineer, or tech leader, you’re likely familiar with the terms ‘cloud-based applications’ and ‘cloud-native applications.’ But what do these terms really mean, and how can they transform your organization’s product development and management? This article is not just about buzzwords. It is a comprehensive guide that will equip you with the knowledge to enhance scalability, high availability, and speed up your solutions delivery.
Let’s get started.
Traditional applications vs. cloud-based applications vs. cloud-native applications
Let’s start with understanding the differences between traditional, cloud-based, and cloud-native applications.
Traditional applications
Architecture: Monolithic, tightly coupled with underlying OS
Development duration: Longer development cycles, released as one package
OS dependency: High dependency on the underlying OS
Scalability: Requires additional hardware and complex processes to scale
Cost model: High upfront costs, requires investment in hardware
Release time: Slower release cycles, updates and bug fixes take longer
Transition: Handoffs between development and operations teams, creating silos
Development / Operations cost: High setup and maintenance costs, less efficient in resource usage
Automation: Limited automation, more manual processes
Downtime: Higher downtime during updates and maintenance
Backup and recovery: Low backup capabilities, manual and error-prone
Modularity: Tightly coupled components, harder to update and scale
Flexibility: Limited flexibility, changes require significant effort
Efficiency: Lower efficiency, manual processes and limited resource optimization
Testability: Manual testing processes, slower feedback cycles
Disposability: Long startup and shutdown times, less robust to failures
User experience: Potentially slower, less responsive, dependent on hardware capacity
Resource allocation: Static resource allocation, often under or over-provisioned
Security: Security managed in-house, potentially higher risk of breaches
Innovation: Slower pace of innovation due to longer development cycles
Cloud-based applications
Architecture: Often migrated from traditional architectures, can be monolithic or modular
Development duration: Faster than traditional due to cloud integration, but slower than cloud-native
OS dependency: Reduced dependency, often uses virtual machines or managed services
Scalability: Easier to scale than traditional, uses cloud resources but may face some limits
Cost model: Pay-as-you-go model, more cost-effective than traditional
Release time: Faster release cycles than traditional, but not as quick as cloud native
Transition: Smoother than traditional, but still may involve some handoffs
Development/Operations cost: Lower costs than traditional, utilizes cloud resources
Automation: More automated than traditional, uses cloud services
Downtime: Reduced downtime compared to traditional, but not as minimal as cloud-native
Backup and recovery: Improved backup capabilities using cloud solutions
Modularity: More modular than traditional, but may still have some monolithic aspects
Flexibility: More flexible than traditional, but less so than cloud-native
Efficiency: Improved efficiency, better resource management with cloud services
Testability: Improved testability with cloud-based tools, but may not be fully automated
Disposability: Improved disposability, but not as fast as cloud-native
User experience: Improved user experience, faster and more responsive than traditional
Resource allocation: Dynamic resource allocation, better utilization of cloud resources
Security: Enhanced security with cloud provider’s tools, but shared responsibility
Innovation: Increased innovation potential, faster deployment of new features
Cloud native applications
Architecture: Microservices, containerized, loosely coupled
Development duration: Faster development with iterative releases using CI/CD pipelines
OS dependency: Abstracted OS layer, allowing flexibility and easier migration
Scalability: Easily scalable, auto-scaling capabilities
Cost model: Pay-as-you-go, cost-effective based on usage
Release time: Rapid release cycles, continuous integration and delivery
Transition: Smooth transition from development to production, DevOps practices
Development / Operations cost: Lower operational costs, only pay for what you use, optimized resource usage
Automation: High level of automation, infrastructure as code
Downtime: Minimal to zero downtime, seamless updates
Backup and recovery: Automated backups, robust disaster recovery mechanisms
Modularity: Highly modular, independent microservices that are easier to update and scale
Flexibility: Highly flexible, easy to deploy and redeploy resources as needed
Efficiency: High efficiency, automated processes, and optimal resource utilization
Testability: Automated testing, continuous integration, and delivery pipelines
Disposability: Fast startup and shutdown, resilient to failures, quick recovery
User experience: Optimal user experience, highly responsive, seamless updates
Resource allocation: Optimal resource allocation, automatic scaling based on demand
Security: Built-in security features, continuous monitoring, and updates
Innovation: High innovation potential, rapid experimentation, and deployment of new features
It is evident that cloud-native applications, with their microservices and CI/CD advantages, are ideal for large enterprises. Mid-sized companies may find cloud-based applications a more manageable and effective step in modernizing their operations.
Cloud-based applications vs. cloud-native applications in the simplest manner
Think of it this way: Cloud-based applications are like moving traditional businesses to modern offices and utilizing new facilities. Cloud-native applications are like designing businesses from scratch to fully exploit the features of the modern office, ensuring optimal efficiency and growth potential.
In short: Cloud-native applications: Built for the cloud, leverage microservices, containers, and CI/CD for maximum scalability and agility. Cloud-based applications: Traditional applications adapted to run in the cloud benefit from cloud infrastructure but do not fully utilize cloud-native features.
Why is cloud-based application development a good way to go for mid-sized companies?
The cloud has undoubtedly changed the way businesses operate. That impact is going to grow with two main reasons:
As more organizations lock on its transformative power, and
As new technologies emerge to deliver even more services and functionality.
How an organization recognizes the cloud’s power is not in anyone’s control. However, how a cloud-based application developer or a SaaS provider integrates emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), virtual reality (VR), or machine learning (ML) into cloud-based solutions is the key differentiator. Such integration drives a new wave of innovation and spawns a host of exciting opportunities in business, for example:
Instead of building a recommendation engine from scratch, e-commerce companies can now easily access and integrate an off-the-shelf engine.
Using readily available video intelligence modules, developers can now extract actionable insights from video files. This eliminates the need to develop their own ML or computer vision models.
Subscribe to modules that provide a fully managed service for connecting, managing, and analyzing data from globally dispersed IoT devices easily and securely. Such modules can support a wide range of services, from developing a system that detects pipeline cracks automatically to sending alerts to maintenance engineers to attend.
Most of these solutions are data-intensive and require massive processing power, making them ideal for the cloud. The cloud acts as a key enabler for building sophisticated new solutions. What matters is how a cloud-based application developer identifies your needs, understands the native capabilities of the cloud, and makes the best of the cloud for you.

Cloud strategy and assessment workshop
The adoption of cloud-based infrastructure by enterprises is increasing greatly. However, a lot of enterprises are still reluctant to adopt a cloud strategy due to lack of skills or knowledge.
Download
What sets any company apart in cloud application development?
The cloud undoubtedly provides many benefits, but it has cloud migration challenges and risks. From deployment costs to security and operational challenges, the challenges and risks range in nature and scale.
During cloud migration or cloud application development, a company should advise clients on which processes or operations are best suited to migration or cloud app development with reduced risks and which cloud model is most appropriate – private, public, or hybrid.
A company shall take care of the following challenges and risks during cloud migration or cloud application development:
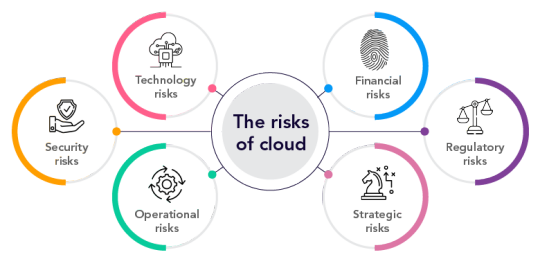
Technology risks:
Implement robust security controls and procedures to safeguard data from cyber attacks. Careful analysis ensures the right aspects of the client’s workload migrate to the cloud for optimal cloud resource use.
Security risks:
Develop comprehensive security strategies for the client’s technology and data since the cloud does not ensure it automatically. Implementing the proper security measures is as crucial as implementing the cloud-based solution.
Operational risks:
Plan meticulously to integrate the client’s current infrastructure with cloud-based solutions to prevent data leakage or loss.
Financial risks:
Proper usage estimation and accurate configuration help avoid costly mistakes in cloud utilization.
Regulatory risks:
Stay vigilant about compliance with data protection laws to avoid financial and reputational risks.
Strategic risks:
Formulate coherent cloud migration strategies to ensure expected ROI and responsibly manage dependence on third-party service providers.
Also read: Which are the best steps for on-premises to cloud migration – step-by-step guide?
Benefits of cloud-based applications across different functions within organizations
Cost savings, security, scalability, flexibility, accessibility, and efficient data management are some of the traditional benefits of cloud-based applications. Since this is a complete guide on cloud-based applications for technology leaders, we have compiled real-world examples of cloud benefits and how they impact different organizational functions.
Product
Accelerated speed to market: By partnering with Amazon Web Services (AWS), Salesforce expanded globally without building its data centers. This partnership also ensured compliance with local data laws, streamlining their international growth.
Enhanced product testing and development: Stanford researchers developed a digital method to test new drug compounds before physical trials. This innovation speeds up the development process and reduces costs associated with physical testing.
Operations
Lower time and process costs: An insurance company processes routine claims automatically using computer vision and text analysis. This approach significantly reduces time and costs compared to manual processing.
Higher return on assets: An industrial conglomerate optimized its wind turbines with IoT and real-time analytics. This adjustment led to a double-digit increase in energy output, maximizing asset efficiency.
Finance
Dynamic pricing: A heavy plant manufacturer uses cloud-based dynamic pricing tools to improve dealer relationships. These tools also help increase profits and sales volume.
Focused allocation of resources: A farm machinery manufacturer allows farmers to apply herbicide only to weeds. This method reduces herbicide usage by up to 85%, cutting costs significantly.
Marketing
Better customer segmentation: A healthcare company analyzes data from various sources to find trends. This detailed analysis improves customer segmentation and targeting.
Extended customer reach: A private equity fund moved cattle auctions online, hosting data in the cloud. They use computer vision to automate health evaluations, expanding their market reach.
Talent and collaboration
Improved employee performance: A US bank uses AI algorithms to give real-time advice to its sales team. This guidance helps them sequence product offers more effectively, boosting sales performance.
Reduced siloes and collaboration barriers: A life sciences company connected its global research departments via cloud data storage. This connection allows seamless collaboration on shared data sets, enhancing research efficiency.
Undoubtedly, the cloud is driving a wave of innovation across various business functions. This transformation revolutionizes businesses. Next, we will explore the impact of cloud-based applications across organizations.
More on the impact of cloud-based applications
For much of its history, many business leaders saw cloud computing as a way to quickly gain new capabilities without having to work with – and be bogged down by – the internal IT department. That’s why they opt for cloud services.
Cloud services enable organizations to hire the computing power they require flexibly without owning or managing the IT infrastructure directly. Below are some examples of how enterprises use cloud-based solutions:
A fast-casual restaurant chain’s online orders surged to 400,000 a day from 50,000. A pleasant surprise? They were able to achieve this by migrating their online ordering system to the cloud.
A biotech company used cloud computing to deliver the first clinical batch of a COVID-19 vaccine candidate for Phase I trials in 42 days. The scalable cloud data storage and cloud collaboration, which facilitate real-time access, editing, and sharing of files, boosted productivity and creativity among team members.
An Automaker uses a common cloud platform to manage data from machines and systems, track logistics, and offer insights on shop floor processes across 124 plants, 500 warehouses, and 1,500 suppliers. This cloud adoption is expected to reduce factory costs by 30% by 2025 while fostering innovation.
With the rise of cloud computing services such as AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform, the Cloud and the cloud applications have become integral to daily life. The cloud extends beyond tech circles into mainstream use. The ubiquity of cloud-based applications is undeniable. Hence, knowing the best steps for building cloud-based applications will be helpful.
Best six steps for building cloud-based applications
Navigating the journey of cloud-based application development can be complex, but it becomes manageable and rewarding with the right approach. Here are the essential steps to ensure your cloud-based applications are robust, efficient, and aligned with your business goals.

1. Build a strong business case
We assist in developing a compelling business case highlighting the benefits of cloud adoption, such as cost savings, increased agility, and improved efficiency. This includes calculating potential ROI and aligning cloud initiatives with business objectives. Additionally, we identify key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure success and ensure your investment in cloud technology drives tangible business value.
2. Develop a comprehensive cloud strategy
We help you create a clear cloud strategy aligned with your business goals, identifying the suitable cloud service model (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS) to meet your needs. This includes evaluating your current infrastructure and planning for future scalability. We also ensure that your strategy consists of a phased migration or cloud app development approach, minimizing disruption and maximizing benefits.
3. Conduct thorough risk management
Our team assesses potential security, operational, financial, and regulatory risks. We implement robust security controls and procedures to protect your data and ensure compliance with relevant laws. We also develop a risk mitigation plan that addresses data backup, disaster recovery, and business continuity to safeguard against unexpected challenges.
4. Compose and automate deployment
We help compose your application using a monolithic or modular architecture, ensuring flexibility. Our team automates the deployment process, utilizing CI/CD pipelines to facilitate seamless integration and continuous delivery. This includes setting up automated testing environments and implementing infrastructure as code (IaC) to ensure consistency and repeatability.
5. Test and validate the application
We prioritize thorough testing and validation to ensure your cloud-based application is robust, secure, and performs well. This includes automated testing to quickly identify and address issues, providing a smooth user experience. We also conduct performance benchmarking and load testing to verify that your application can handle peak usage scenarios.
6. Optimize for continuous improvement
Post-launch, we provide ongoing support to monitor application performance and implement updates. Our approach ensures your application evolves with your business needs, maintaining optimal efficiency and growth potential. We leverage analytics and user feedback to drive iterative improvements, ensuring your application remains competitive and aligned with market demands.
Join hands with the best cloud-based application development company
Get Started
Final reflections
Indeed, over the years, traditional applications have significantly improved how businesses operate. Nonetheless, cloud computing takes this further by enhancing scalability, high availability, and rapid solution delivery, ensuring businesses reach their full potential.
The key takeaway from this guide is the profound impact of cloud-based applications on businesses. Summing it up, the current state of tech space and business demands constant innovation and quick solution delivery, the most significant benefit of cloud-based applications. Traditional apps struggle with modular architecture and automation, slowing feature releases. In contrast, adopting cloud-based applications boosts efficiency and flexibility.
The breakneck pace of business innovation driving digital transformation can no longer be supported by traditional, legacy application development methodologies. Instead, organizations overhaul their strategies and philosophies toward application development to align with a cloud-centric approach.
At last, if you look for a leading cloud app development company or want to hire cloud application developers to address any skillset gaps, we can connect. We are happy to help you address any of your challenges in cloud application development.
Originally published at https://www.softwebsolutions.com on June 7, 2024.
#Cloud Application Development#Cloud Application#Cloud Native Application#Cloud Based Solutions#Cloud Service Providers#Cloud Consulting Services
0 notes
Text
United States insurance analytics market size reached USD 15.4 Billion in 2024. Looking forward, IMARC Group expects the market to reach USD 59.8 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 15.99% during 2025-2033.
#United States Insurance Analytics Market Report by Component (Solution#Service)#Deployment Mode (On-premises#Cloud-based)#Enterprise Size (Small and Medium-sized Enterprises#Large Enterprises)#Application (Claims Management#Risk Management#Customer Management#Sales and Marketing#and Others)#End User (Insurance Companies#Government Agencies#Third-party Administrators#Brokers and Consultancies)#and Region 2025-2033
0 notes
Text
RAG Evolution – A Primer to Agentic RAG
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/rag-evolution-a-primer-to-agentic-rag/
RAG Evolution – A Primer to Agentic RAG
What is RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation)?
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a technique that combines the strengths of large language models (LLMs) with external data retrieval to improve the quality and relevance of generated responses. Traditional LLMs use their pre-trained knowledge bases, whereas RAG pipelines will query external databases or documents in runtime and retrieve relevant information to use in generating more accurate and contextually rich responses. This is particularly helpful in cases where the question is either complex, specific, or based on a given timeframe, given that the responses from the model are informed and enriched with up-to-date domain-specific information.
The Present RAG Landscape
Large language models have completely revolutionized how we access and process information. Reliance solely on internal pre-input knowledge, however, could limit the flexibility of their answers-especially for complex questions. Retrieval-Augmented Generation addresses this problem by letting LLMs acquire and analyze data from other available outside sources to produce more accurate and insightful answers.
Recent development in information retrieval and natural language processing, especially LLM and RAG, opens up new frontiers of efficiency and sophistication. These developments could be assessed on the following broad contours:
Enhanced Information Retrieval: Improvement of information retrieval in RAG systems is quite important for working efficiently. Recent works have developed various vectors, reranking algorithms, hybrid search methods for the improvement of precise search.
Semantic caching: This turns out to be one of the prime ways in which computational cost is cut down without having to give up on consistent responses. This means that the responses to current queries are cached along with their semantic and pragmatic context attached, which again promotes speedier response times and delivers consistent information.
Multimodal Integration: Besides text-based LLM and RAG systems, this approach also covers the visuals and other modalities of the framework. This allows for access to a greater variety of source material and results in responses that are increasingly sophisticated and progressively more accurate.
Challenges with Traditional RAG Architectures
While RAG is evolving to meet the different needs. There are still challenges that stand in front of the Traditional RAG Architectures:
Summarisation: Summarising huge documents might be difficult. If the document is lengthy, the conventional RAG structure might overlook important information because it only gets the top K pieces.
Document comparison: Effective document comparison is still a challenge. The RAG framework frequently results in an incomplete comparison since it selects the top K random chunks from each document at random.
Structured data analysis: It’s difficult to handle structured numerical data queries, such as figuring out when an employee will take their next vacation depending on where they live. Precise data point retrieval and analysis aren’t accurate with these models.
Handling queries with several parts: Answering questions with several parts is still restricted. For example, discovering common leave patterns across all areas in a large organisation is challenging when limited to K pieces, limiting complete research.
Move towards Agentic RAG
Agentic RAG uses intelligent agents to answer complicated questions that require careful planning, multi-step reasoning, and the integration of external tools. These agents perform the duties of a proficient researcher, deftly navigating through a multitude of documents, comparing data, summarising findings, and producing comprehensive, precise responses.
The concept of agents is included in the classic RAG framework to improve the system’s functionality and capabilities, resulting in the creation of agentic RAG. These agents undertake extra duties and reasoning beyond basic information retrieval and creation, as well as orchestrating and controlling the various components of the RAG pipeline.
Three Primary Agentic Strategies
Routers send queries to the appropriate modules or databases depending on their type. The Routers dynamically make decisions using Large Language Models on which the context of a request falls, to make a call on the engine of choice it should be sent to for improved accuracy and efficiency of your pipeline.
Query transformations are processes involved in the rephrasing of the user’s query to best match the information in demand or, vice versa, to best match what the database is offering. It could be one of the following: rephrasing, expansion, or breaking down of complex questions into simpler subquestions that are more readily handled.
It also calls for a sub-question query engine to meet the challenge of answering a complex query using several data sources.
First, the complex question is decomposed into simpler questions for each of the data sources. Then, all the intermediate answers are gathered and a final result synthesized.
Agentic Layers for RAG Pipelines
Routing: The question is routed to the relevant knowledge-based processing based on relevance. Example: When the user wants to obtain recommendations for certain categories of books, the query can be routed to a knowledge base containing knowledge about those categories of books.
Query Planning: This involves the decomposition of the query into sub-queries and then sending them to their respective individual pipelines. The agent produces sub-queries for all items, such as the year in this case, and sends them to their respective knowledge bases.
Tool use: A language model speaks to an API or external tool, knowing what that would entail, on which platform the communication is supposed to take place, and when it would be necessary to do so. Example: Given a user’s request for a weather forecast for a given day, the LLM communicates with the weather API, identifying the location and date, then parses the return coming from the API to provide the right information.
ReAct is an iterative process of thinking and acting coupled with planning, using tools, and observing. For example, to design an end-to-end vacation plan, the system will consider user demands and fetch details about the route, touristic attractions, restaurants, and lodging by calling APIs. Then, the system will check the results with respect to correctness and relevance, producing a detailed travel plan relevant to the user’s prompt and schedule.
Planning Dynamic Query: Instead of performing sequentially, the agent executes numerous actions or sub-queries concurrently and then aggregates these results. For example, if one wants to compare the financial results of two companies and determine the difference in some metric, then the agent would process data for both companies in parallel before aggregating findings; LLMCompiler is one such framework that leads to such efficient orchestration of parallel calling of functions.
Agentic RAG and LLMaIndex
LLMaIndex represents a very efficient implementation of RAG pipelines. The library simply fills in the missing piece in integrating structured organizational data into generative AI models by providing convenience for tools in processing and retrieving data, as well as interfaces to various data sources. The major components of LlamaIndex are described below.
LlamaParse parses documents.
The Llama Cloud for enterprise service with RAG pipelines deployed with the least amount of manual labor.
Using multiple LLMs and vector storage, LlamaIndex provides an integrated way to build applications in Python and TypeScript with RAG. Its characteristics make it a highly demanded backbone by companies willing to leverage AI for enhanced data-driven decision-making.
Key Components of Agentic Rag implementation with LLMaIndex
Let’s go into depth on some of the ingredients of agentic RAG and how they are implemented in LlamaIndex.
1. Tool Use and Routing
The routing agent picks which LLM or tool is best to use for a given question, based on the prompt type. This leads to contextually sensitive decisions such as whether the user wants an overview or a detailed summary. Examples of such approaches are Router Query Engine in LlamaIndex, which dynamically chooses tools that would maximize responses to queries.
2. Long-Term Context Retention
While the most important job of memory is to retain context over several interactions, in contrast, the memory-equipped agents in the agentic variant of RAG remain continually aware of interactions that result in coherent and context-laden responses.
LlamaIndex also includes a chat engine that has memory for contextual conversations and single shot queries. To avoid overflow of the LLM context window, such a memory has to be in tight control over during long discussion, and reduced to summarized form.
3. Subquestion Engines for Planning
Oftentimes, one has to break down a complicated query into smaller, manageable jobs. Sub-question query engine is one of the core functionalities for which LlamaIndex is used as an agent, whereby a big query is broken down into smaller ones, executed sequentially, and then combined to form a coherent answer. The ability of agents to investigate multiple facets of a query step by step represents the notion of multi-step planning versus a linear one.
4. Reflection and Error Correction
Reflective agents produce output but then check the quality of that output to make corrections if necessary. This skill is of utmost importance in ensuring accuracy and that what comes out is what was intended by a person. Thanks to LlamaIndex’s self-reflective workflow, an agent will review its performance either by retrying or adjusting activities that do not meet certain quality levels. But because it is self-correcting, Agentic RAG is somewhat dependable for those enterprise applications in which dependability is cardinal.
5. Complex agentic reasoning:
Tree-based exploration applies when agents have to investigate a number of possible routes in order to achieve something. In contrast to sequential decision-making, tree-based reasoning enables an agent to consider manifold strategies all at once and choose the most promising based on assessment criteria updated in real time.
LlamaCloud and LlamaParse
With its extensive array of managed services designed for enterprise-grade context augmentation within LLM and RAG applications, LlamaCloud is a major leap in the LlamaIndex environment. This solution enables AI engineers to focus on developing key business logic by reducing the complex process of data wrangling. Another parsing engine available is LlamaParse, which integrates conveniently with ingestion and retrieval pipelines in LlamaIndex. This constitutes one of the most important elements that handles complicated, semi-structured documents with embedded objects like tables and figures. Another important building block is the managed ingestion and retrieval API, which provides a number of ways to easily load, process, and store data from a large set of sources, such as LlamaHub’s central data repository or LlamaParse outputs. In addition, it supports various data storage integrations.
Conclusion
Agentic RAG represents a shift in information processing by introducing more intelligence into the agents themselves. In many situations, agentic RAG can be combined with processes or different APIs in order to provide a more accurate and refined result. For instance, in the case of document summarisation, agentic RAG would assess the user’s purpose before crafting a summary or comparing specifics. When offering customer support, agentic RAG can accurately and individually reply to increasingly complex client enquiries, not only based on their training model but the available memory and external sources alike. Agentic RAG highlights a shift from generative models to more fine-tuned systems that leverage other types of sources to achieve a robust and accurate result. However, being generative and intelligent as they are now, these models and Agenitc RAGs are on a quest to a higher efficiency as more and more data is being added to the pipelines.
#agent#agentic RAG#agents#ai#AI models#Algorithms#Analysis#API#APIs#applications#approach#assessment#bases#Books#Building#Business#challenge#Cloud#communication#Companies#comparison#comprehensive#data#data analysis#data storage#data-driven#Database#databases#Design#details
0 notes
Text
Explore the future of blockchain with AI and no-code tools. Simplifying development and boosting innovation, this is the new era of decentralized technology.
#AI Algorithms#AI In Blockchain Development#AI-Driven Blockchain Solutions#Blockchain Development#Blockchain Solutions#Blockchain-Based Applications#Cloud-Based Low Code And No-Code Platforms#Implementation Of AI#Integrating AI Solutions#Integration Of AI And No-Code Platforms
0 notes