#cancer immunotherapy.
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
youtube
#Tislelizumab#advanced gastric cancer#first-line treatment#immunotherapy#anti-PD-1#monoclonal antibody#cancer treatment#progression-free survival#overall survival#oncology research#chemotherapy#tumor response#survival rate#gastric cancer care#clinical trials#safety profile#patient outcomes#immune checkpoint inhibitor#combination therapy#cancer immunotherapy.#Youtube
0 notes
Note
AM supporting pride month
Day 122






#am ihnmaims#i have no mouth and i must scream#ihnmaims#ihnmaims am#shittyamdaily#allied master computer#allied mastercomputer#men’s mental health#pride month#lgbt pride#queer pride#happy pride 🌈#mens mental health#cancer survivors month#alzheimers#alzheimers awareness month#cancer#gun violence#gun violence awareness month#immigrants#immigrant heritage month#psa#antiphospholipid antibody syndrome#antiphospholipid antibody syndrome awareness month#audiobooks#audiobook appreciation month#cancer immunotherapy awareness month#immunotherapy#ptsd#june
120 notes
·
View notes
Text
Im addicted to hot sauce now. I couldn’t have anything the least bit spicy on chemo and now that I’m off it all I crave is spicy food
#never really liked spicy food before cancer#rec your favourite hot sauce or spicy thing#also did i mention I’m off chemo? still on immunotherapy infusions tho
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
How cool is this!
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Power of Immunotherapy: A Deep Dive into Cancer Treatment
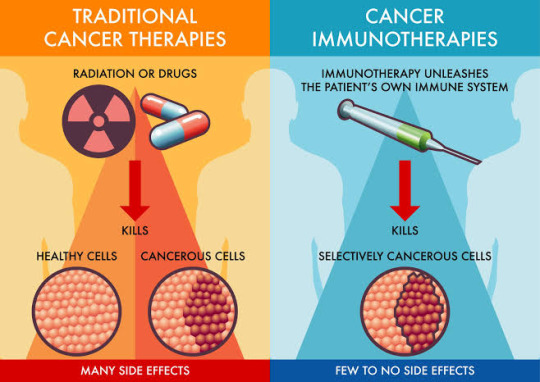
Immunotherapy, a groundbreaking approach in cancer treatment, has been making waves in the medical world. 🌟 But what exactly is it, and how does it work? Let's delve into the intricacies of this cutting-edge therapy. 💉
Immunotherapy at a Glance: 🔬 Immunotherapy, or immuno-oncology, is a therapeutic strategy that harnesses the body's immune system to combat cancer cells. Unlike traditional treatments like chemotherapy, which target both healthy and cancerous cells, immunotherapy is highly targeted, making it a game-changer in the fight against cancer.
Key Players in Immunotherapy: 🦠
Tumor Antigens are molecules found on cancer cells that act as red flags, signaling the immune system to attack. 👥
T Cells: The immune system's soldiers. They are trained to recognize and destroy threats, including cancer cells.
💡 Checkpoint Inhibitors: Proteins that, when blocked, enhance the immune response against cancer. 🧬
CAR-T Cell Therapy: Genetic engineering to supercharge T cells for precision attacks on tumors.
How Does Immunotherapy Work? Immunotherapy comes in various forms, but they all aim to accomplish one goal: boost the immune system's ability to recognize and eradicate cancer cells. Whether through checkpoint inhibitors, vaccines, or CAR-T cell therapy, the goal remains: empower the immune system's fighters!
Immunotherapy is a testament to the power of science and innovation, offering new hope to cancer patients worldwide. 🌍
Let's continue to explore, research, and advance this remarkable field to improve the lives of those affected by cancer.
References:
Postow, M. A., Callahan, M. K., & Wolchok, J. D. (2015). Immune Checkpoint Blockade in Cancer Therapy. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 33(17), 1974–1982. doi:10.1200/jco.2014.59.4358
Rosenberg, S. A., Yang, J. C., & Restifo, N. P. (2004). Cancer immunotherapy: moving beyond current vaccines. Nature Medicine, 10(9), 909–915. doi:10.1038/nm1100
June, C. H., & Sadelain, M. (2018). Chimeric Antigen Receptor Therapy. New England Journal of Medicine, 379(1), 64–73. doi:10.1056/nejmra1706164
#immunotherapy#science#biology#college#education#school#student#medicine#doctors#health#healthcare#immune system#cancer#disease#immune health#immune response
58 notes
·
View notes
Text
Scientists uncover how cancer cells hijack T-cells, making it harder for the body to fight back
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
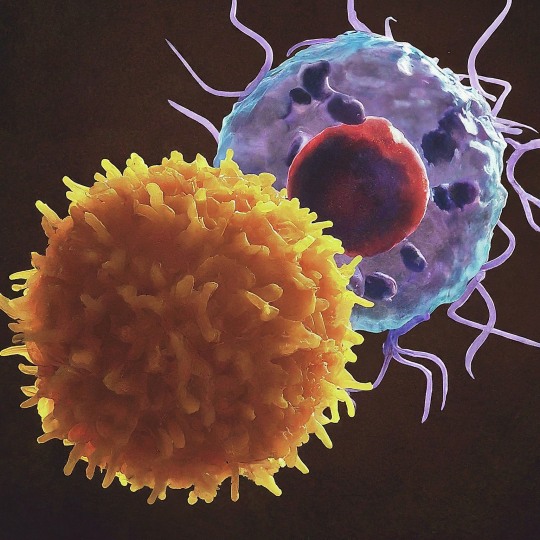
The T Cell Landscape
T cells, a critical component of the adaptive immune system, stand as the body's elite force in combatting infections and diseases. These specialized lymphocytes boast remarkable diversity, each type playing a distinct role in orchestrating a targeted and effective immune response.
T cells, like all blood cells, originate from hematopoietic stem cells residing in the bone marrow. However, their training ground lies within the thymus, a specialized organ located in the chest. Here, they undergo a rigorous selection process known as thymocyte education. During this process, immature T cells, called thymocytes, are presented with self-antigens (molecules unique to the body) by special cells. Thymocytes that bind too strongly to these self-antigens are eliminated, preventing them from attacking healthy tissues later. Only thymocytes that demonstrate the ability to recognize foreign invaders while exhibiting tolerance to self are released into the bloodstream as mature T cells.
Following this rigorous training, mature T cells exit the thymus and embark on their patrol, circulating throughout the bloodstream and lymphatic system. They remain vigilant, constantly scanning for their specific targets – antigens. Antigens are foreign molecules, such as fragments of viruses, bacteria, or even cancerous cells, that trigger the immune response.
The hallmark of a T cell is its T cell receptor (TCR), a highly specialized protein complex embedded on its surface. This receptor acts like a lock, uniquely shaped to fit a specific antigen, the "key." Each T cell develops a unique TCR capable of recognizing only a single antigen, enabling a highly specific immune response.
But how do T cells encounter these hidden antigens lurking within infected or cancerous cells? This critical role is played by antigen-presenting cells (APCs). APCs, such as macrophages and dendritic cells, engulf pathogens or abnormal cells, break them down into smaller fragments (peptides), and present them on their surface complexed with major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules. MHC molecules act as identification tags, allowing T cells to distinguish between "self" and "non-self." When a T cell's TCR encounters its specific antigen bound to an MHC molecule on an APC, a dance of activation begins. The T cell becomes stimulated, and a cascade of signaling events is triggered. This leads to the T cell's proliferation, producing an army of clones specifically tailored to combat the recognized threat.
T cells are not a single, monolithic entity. They comprise a diverse population, each type with a specialized function:
Helper T Cells (Th Cells):
Helper T cells, often abbreviated as Th cells, play a central role in coordinating immune responses. They express the CD4 surface marker and can recognize antigens presented by major histocompatibility complex class II (MHC-II) molecules. Subtypes of helper T cells include Th1, Th2, Th17, and regulatory T cells (Tregs), each with distinct functions and cytokine profiles.
Th1 cells mediate cellular immunity by activating macrophages and cytotoxic T cells, crucial for defense against intracellular pathogens.
Th2 cells are involved in humoral immunity, promoting B cell activation and antibody production, thus aiding in defense against extracellular parasites.
Th17 cells contribute to the immune response against extracellular bacteria and fungi, producing pro-inflammatory cytokines. Regulatory T cells (Tregs) maintain immune tolerance and prevent autoimmunity by suppressing excessive immune responses.
Cytotoxic T Cells (Tc Cells):
Cytotoxic T cells, also known as Tc cells or CD8+ T cells, are effector cells responsible for directly killing infected or aberrant cells. They recognize antigens presented by MHC class I molecules on the surface of target cells. Upon activation, cytotoxic T cells release perforin and granzymes, inducing apoptosis in target cells and eliminating the threat.
Memory T Cells:
Memory T cells are a long-lived subset of T cells that persist after the clearance of an infection. They provide rapid and enhanced immune responses upon re-exposure to the same antigen, conferring immunological memory. Memory T cells can be either central memory T cells (TCM), residing in lymphoid organs, or effector memory T cells (TEM), circulating in peripheral tissues.
γδ T Cells:
Unlike conventional αβ T cells, γδ T cells express a distinct T cell receptor (TCR) composed of γ and δ chains. They recognize non-peptide antigens, such as lipids and metabolites, and are involved in immune surveillance at epithelial barriers and responses to stress signals.
Beyond the Battlefield: The Expanding Roles of T Cells: The remarkable capabilities of T cells have opened doors for several groundbreaking applications in medicine:
Vaccines: By presenting weakened or inactivated forms of pathogens, vaccines "train" the immune system to generate memory T cells. This prepares the body to recognize and rapidly eliminate the real pathogen upon future exposure, preventing disease.
Cancer immunotherapy: CAR T-cell therapy, a revolutionary approach, genetically engineers a patient's own T cells to express chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) that recognize and target specific cancer cells. These "supercharged" T cells are then reintroduced into the patient, unleashing a potent attack against the tumor.
Autoimmune disease treatment: Researchers are exploring ways to manipulate T cells to suppress harmful immune responses that underlie autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis.
The diverse array of T cells underscores the immune system's complexity and adaptability in mounting tailored responses against a myriad of threats. From orchestrating immune reactions to maintaining tolerance and establishing long-term immunity, T cells play multifaceted roles in safeguarding the body's health. Understanding the intricacies of T cell biology not only sheds light on immune-mediated diseases but also paves the way for developing novel therapeutic strategies harnessing the power of the immune system.
T cells represent a fascinating aspect of immunology, with their diversity and specificity driving the complexity of immune responses. As research advances, further insights into T cell biology promise to revolutionize immunotherapy and enhance our ability to combat diseases ranging from infections to cancer. By understanding and harnessing their power, we can unlock new avenues for protecting and improving human health.
#science sculpt#life science#science#molecular biology#biology#biotechnology#artists on tumblr#t cells#T helper cells#autoimmune#autoimmunity#helathcare#immunology#immunotherapy#medical care#cancer#human health#research#scientific research#the glass scientists#scientific illustration#research scientist
11 notes
·
View notes
Text

Tumour Environment Effects
Combined immunotherapy (GVAX + anti-PD1) and targeted radiotherapy for pancreatic cancer not only promotes anti-cancer T cells but also immunosuppressive macrophages – insight for skewing therapy towards greater anti-tumour effects
Read the published research article here
Image from work by Junke Wang and Jessica Gai, and colleagues
Department of Oncology, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD, USA
Image originally published with a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0)
Published in Science Advances, February 2024
You can also follow BPoD on Instagram, Twitter and Facebook
#science#biomedicine#immunofluorescence#cancer#pancreatic cancer#immunotherapy#radiotherapy#macrophages#T cells#oncology
15 notes
·
View notes
Link
A recent publication in Nature Journal has presented the TNBC (Triple Negative Breast Cancer) ICI (Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors) response predictive classifier (TNBC-ICI) integrating gene expression profiles of TNBC specimens and artificial intelligence, which has demonstrated a significant performance in identifying TNBC patients who would potentially achieve pCR (Pathological Complete Response) to the chemotherapy treatment supplemented with ICI, opening an avenue to improve the decision making and disease management of patients diagnosed with primary TNBC.
Researchers from the Health Research Institute of the Balearic Islands (IdISBa), Spain, have implemented a random forest machine learning algorithm to construct and evaluate gene expression-based signatures to efficiently predict Pathological Complete Response (pCR) to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors (ICI) therapy assisted with chemotherapy in patients with primary TNBC treated in the phase II/III I-SPY2 clinical trial that includes clinical and gene expression data. This study involved 188 ICI-naïve and 721 specimens treated with ICI plus chemotherapy.
Here, patients who achieved a pCR or absence of invasive cancer in the breast and regional nodes at the time of surgery were classified as ‘responders,’ whereas those who had residual disease were considered ‘non-responders’ during the classifier construction. The algorithm is applied to select the most informative gene combinations to predict response to ICI in primary TNBC tumors.
Continue Reading
43 notes
·
View notes
Text
Please please help if you can,
Anything will be greatly appreciated!! ❤️
Please share as well, thank you for your kindness in this tough time
#cancer#loss#memorial#in memoriam#loss of a parent#loss of a loved one#chemotherapy#immunotherapy#ukraine#ukrainian tumblr#gofundme#vichnaya pamyat#kidney health#kidney cancer#health#medicine#oncology#grief
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
#Natural products with anti-tumorigenic potential#macrophage modulation#tumor-associated macrophages#TAMs#immune response in cancer#M1 macrophages#M2 macrophages#tumor microenvironment#curcumin#resveratrol#epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG)#inflammation suppression#phagocytosis enhancement#cancer immunotherapy#angiogenesis inhibition#tumor progression#metastasis prevention#anti-inflammatory compounds#natural anticancer agents#integrative oncology.#Youtube
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Researchers create AI tool to forecast cancer patients' responses to immunotherapy

- By InnoNurse Staff -
NIH scientists have developed an AI tool that uses routine clinical data to predict cancer patients' responses to immunotherapy, potentially aiding in treatment decisions.
Read more at National Institutes of Health (NIH)
///
Other recent news and insights
New analytical tool enhances comprehension of heritable human traits and diseases (University of Oslo/Medical Xpress)
#health informatics#ai#cancer#oncology#immunotherapy#data science#health tech#medtech#analytics#genetics#health it
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
i’m bleaching and dying my hair green this weekend omg i’m so excited!!! it’s like taking back something cancer took away when this chemo made me lose so much of my hair
#this chemo wasn’t supposed to make me lose any hair#and it had been growing for a year while i was on immunotherapy#but then i started this one and im not bald but its so thin and short and i hate how i look#so im hoping this will make me look edgy and cool in the way i used to feel#when i would do my hair crazy colors#cancer post
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
A Dive into CAR-T Cell Therapy
Imagine training your own soldiers to fight cancer. Not just any soldiers, but elite warriors genetically modified to recognize and demolish the enemy with laser-like precision. That's the essence of CAR-T cell therapy, a revolutionary approach turning heads in the medical world. In the fight against cancer, CAR-T cell therapy embodies this very concept, harnessing the body's own immune system to wage war against malignant cells. T cells are the special forces of your immune system, constantly scanning for and eliminating threats. But sometimes, cancer cells outsmart them, hiding in plain sight. CAR-T cell therapy steps in, equipping these T-cells with a unique weapon: a Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR). Think of it as a GPS that locks onto a specific protein on cancer cells, guiding the T-cells straight to their target.
How does it work? Here's the simplified version:
Recruitment: First, T cells are extracted from your blood. Modification Station: In the lab, scientists use a virus or other tools to insert the CAR gene into the T cells' DNA. This equips them with the cancer-targeting GPS. Bootcamp Boost: The modified T cells are grown in a special environment, multiplying into a powerful army. Redeployment: The CAR-T cell troops are infused back into your bloodstream, ready to seek and destroy.
Sounds amazing, right? But like any powerful technology, CAR-T comes with its own set of challenges. The treatment process is complex and expensive, and there can be serious side effects like cytokine release syndrome, where the immune system goes into overdrive. So, is CAR-T a miracle cure? Not yet. But for some patients with aggressive blood cancers like leukemia and lymphoma, it has shown remarkable results, offering hope where other treatments have failed. Researchers are constantly working to improve the safety and efficacy of CAR-T, making it a potential game-changer for even more cancers in the future. CAR-T cell therapy has demonstrated remarkable efficacy in the treatment of certain types of hematologic malignancies, including acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and certain subtypes of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Clinical trials have shown unprecedented response rates and durable remissions in patients who have exhausted all other treatment options. Furthermore, ongoing research is exploring the potential of CAR-T cell therapy in treating solid tumors, extending its therapeutic reach to a broader spectrum of cancers. The future is bright for CAR-T. It's a testament to the power of human ingenuity and our ongoing quest to conquer one of humanity's greatest foes. While there's still a way to go, this groundbreaking therapy is a beacon of hope, reminding us that even the seemingly impossible can become reality.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

Killer Particles
Nanoparticles engineered to induce death of cancer cells by activating an immune response
Read the published article here
Image from work by Zhanzhan Zhang and Zheng Pan, and colleagues
College of Chemistry, Key Laboratory of Functional Polymer Materials (Ministry of Education), Nankai University, Tianjin, China
Image originally published with a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0)
Published in Science Advances, February 2024
You can also follow BPoD on Instagram, Twitter and Facebook
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
Understanding Immunotherapy for Autoimmune Diseases
Introduction
Immunotherapy, a groundbreaking approach primarily recognized for cancer therapy immunotherapy, is now making significant strides in treating autoimmune diseases. This article delves into how immunotherapy is applied beyond cancer immunology immunotherapy to manage and treat autoimmune conditions.
The Mechanism of Immunotherapy in Autoimmune Diseases
Immunotherapy works by modulating the immune system, enhancing its ability to fight diseases. Unlike in immunotherapy cancer treatment, where the goal is to target and destroy cancer cells, in autoimmune diseases, the therapy aims to recalibrate the immune system to stop attacking the body's tissues.
Types of Immunotherapy for Autoimmune Diseases
There are various types of immunotherapy used to treat autoimmune diseases. These include monoclonal antibodies, cytokine inhibitors, and immune checkpoint inhibitors, each designed to alter specific immune system pathways. While some of these therapies overlap with those used in cancer treatment, their application in autoimmune diseases focuses on immune regulation and suppression of overactive immune responses.
Immunotherapy Medications and Treatments
Immunotherapy medications for autoimmune diseases are tailored to reduce inflammation and curb the immune system's erroneous attacks on healthy cells. The precise medication or combination of therapies depends on the specific autoimmune condition being treated, highlighting the personalized nature of immunotherapy.
The Role of Immunotherapy and Vaccines
Exploring the intersection of immunotherapy and vaccines reveals potential for preventative strategies in autoimmune diseases. Vaccines designed to induce tolerance in the immune system are under research, potentially preventing autoimmune diseases from developing or worsening.
Managing Side Effects and Costs
While immunotherapy offers new hope, it's crucial to consider immunotherapy side effects and immunotherapy cost. Side effects vary widely, from mild to severe, and must be carefully managed under medical supervision. The cost can also be significant, necessitating a discussion about healthcare resources and insurance coverage.
Conclusion
Immunotherapy for autoimmune diseases represents a promising frontier in medical treatment, offering hope for millions suffering from these conditions. As research progresses, it could redefine the therapeutic landscape for autoimmune diseases, much like it has for cancer.
Discovering Excellence in Cancer and Autoimmune Disease Treatment at CBCC India
At the forefront of medical innovation and care, CBCC India stands as one of the leading Cancer Hospital in India, dedicated to eliminating cancer and advancing treatment for autoimmune diseases. Our commitment to innovative research and exceptional care ensures that every patient receives personalized, state-of-the-art treatment. Discover the pinnacle of healthcare excellence at CBCC India, where we strive to conquer cancer and improve the lives of those with autoimmune diseases through cutting-edge immunotherapy and comprehensive care.
#Immunotherapy#Autoimmune diseases#Cancer therapy#Immune system modulation#Monoclonal antibodies#Immune checkpoint inhibitors#Inflammation reduction#Personalized treatment#Vaccines
1 note
·
View note