#as are camille and charles
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Note
This is a little out of nowhere but perhaps it'd be amusing to know that I've passively wondered about this whenever you tag auralysis, is that the name of one of your OCs or like, some combination of their name and analysis like you're tagging analysis type stuff for them? Also uh, what do they kind of look like because I assume they're some sort of robot or something but that could range from anything
i was holding this ask hostage until i finished my work but now that it's done i'm sitting down to answer :D
all my oc-related tags are for characters i share with @checkers-dance (except #engraved, which i have yet to formulate a pitch for and which probably won't be a thing for months if not years yet, we have a whole Process™ for creating characters and fleshing them out). some of the tags are fic related as well, and those are my own reference.
okay! onto auralysis. the name, firstly, comes from aura (the android's name) + hydrolysis, which lavender told me is a chemistry/biology term meaning "to split with water" = so to split with aura, or to split aura; implications of prisms & migraines as well
(all our oc verses are named by some combination of my brain free-associating concepts like this: citycomet, winterknights)
auralysis features 4 characters at the moment: aura itself, an android with a mysterious (and as yet unrevealed to the other characters) past; morgan, a werewolf and enforcer (think the blade runners from blade runner 2049, same concept in a different font); camille, an erstwhile artist who is now the full-time model & muse of his abusive husband; charles, said husband, artist and photographer.
aura itself is a fascinating little creature. its story starts when morgan finds it in a high-rise hotel building after a party during which every single human inhabitant of the building was brutally murdered. his team encounters it sitting in a pool of blood, drawing spirals, and examines it for evidence of what happened by going through its memory storage, only to find that its been completely wiped clean. in the process of poking in its memory, the android shuts down, and morgan decides to take it home to see if he can fix it.
the android is a beautiful piece of work, fancy and delicate, made of painted porcelain but damaged and cracking. it's very impractical, so morgan focuses at first on fixing up the obvious issues (frayed wiring, broken pieces) before trying to poke around in its software. but the android refuses to start up at all, so he gives up eventually and puts it in a corner of his workshop and forgets it.
he forgets it for 6 whole months, and then aura wakes up again. it's spent all that time quietly sorting through its memories, discarding some and keeping others, attempting to make sense of its own actions and terrified that those actions will be revealed and it will be discarded again, as it has been by countless prior owners. because aura was the one who killed all those people
and nobody knows why it did that, including us :)
i can't wait to find out
#auralysis#aura and morgan (aurgan) are some of the Most Characters Ever#as are camille and charles#i love them#uyecaq#asks#i love talking about our ocs
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Survey: Who is your favorite feminist revolutionary of the frev (or at least someone who contributed to women's rights)?
In this survey, I have deliberately chosen a representative from each different faction.
On the Girondist side: Marquis de Condorcet The revolutionary who campaigned for gender equality, one of the few in his era. He is impossible not to mention in this discussion.

On the Dantonist side: Camille Desmoulins He advocated for the rights of married women to administer their property in 1793. In issue 14 of his journal Révolutions de France et de Brabant, he speaks highly of Théroigne de Méricourt and writes the following passage: "At the request of Mademoiselle Théroigne to be admitted to the district with a vote of consent, the assembly followed the president’s conclusions, thanking this excellent citizen for her motion; a canon from the Council of Mâcon having formally recognized that women have a soul and reason like men, they cannot be forbidden from making as good use of them as the speaker did; he will always make Mademoiselle Théroigne, and all women of her sex, free to propose what they believe to be advantageous to the homeland."

For the Maratist group: Jean-Paul Marat The journalist from L’Ami du Peuple often defended women who were victims of domestic violence, encouraging them to flee their homes and denounce those who abused them. Here is an excerpt from his writings found in the excellent book Madame Marat: A Heroic Life in the Turmoil of the French Revolution by Stefania di Pasquale: "Women are more inclined to tenderness than men. During their childhood, children are expected to oppose themselves to shame, but as soon as they come to the age in which women start listening to us, we hurry to conquer them and to excite their imagination; we focus all of our thoughts to unleash their senses. Hasn’t the time come to create a sweet bond with them? Men have always chosen while women have always accepted! How many foolish parents sacrifice the happiness of their daughters? Forced to yield the object of their heart forever, they become unable to love again, seeing only misfortune in their future." He also defended prostitutes.

For the Cretois group: Charles-Gilbert Romme The revolutionary mathematician, founder of the revolutionary calendar, also worked for certain women's rights. He founded a mixed club with Théroigne de Méricourt, and in a report on public education dated December 20, 1792, he advocated for girls to have access to republican schools. He made the following remark: "They should not be strangers to social virtues, since, in addition to needing them for themselves, they can develop or strengthen them in the hearts of men. If, in the natural and social order, man is called to execute and act, woman, by an imperious and necessary influence, is called to give the will a stronger and more vehement impulse." Although Romme’s feminism had limits, as seen in his statement: "The secondary schools in question are not for both sexes."

For the Robespierristes group: Georges Couthon One of the best-known members of the CPS in Year II, also spoke in favor of women's rights to share property administration in August 1793, as seen here: source. Additionally, he allowed his wife to give a speech at the Federation Festival in Clermont-Ferrand in 1790, before he gave his own speech, as seen here: source.

For the Enragés group: Jacques Roux Here is an excerpt from Markov Walter on this Enragés leader: "All the revolutionary parties tried to involve women, while, with the exception of the Enragés, they sought to exclude them from any real political activity. Jacques Roux considered them the decisive reserve of the Revolution. 'Victory was indisputable as soon as women joined the sans-culottes.'"

For the Hébertist group: Jean-Nicolas Pache This former Girondin minister of the War , who became an Hébertist and later Mayor of Paris, founded the Société patriotique du Luxembourg club, which, according to Louis Devance, "admitted women from the age of fourteen, with the same formalities as men, but their numbers could not exceed one-fifth of the total members; they were eligible for the same positions in the society, excluding the office roles."

For the Babouvist group: Gracchus Babeuf Babeuf wrote a letter in favor of gender equality to Dubois de Fosseux in 1786, as seen here: source. He supported the full participation of women in political clubs and paid tribute to the women of the French Revolution in his journal article: "Women dedicate their entire days to prevent us from starving," and said of them, "But beware, women, whom we have degraded, without whom, however, and without their courage on the 5th and 6th of October, we might not have had freedom!" He even remarked to one of his colleagues: "The advice you give us regarding the role women can play is sensible and judicious; we will take advantage of it. We know the influence that this fascinating sex can have, who, like us, cannot endure the yoke of tyranny and who are no less courageous when it comes to breaking it." He believed that the homeland had everything to gain from exploiting women’s talents in politics.

For the Thermidorian group: Armand Benoît Joseph Guffroy When he is not making false accusations against Élisabeth Le Bas or showing appalling behavior by kicking his former collaborator Marie-Anne Babeuf out after a violent argument, or writing poorly about Lucile Desmoulins and Marie-Françoise Hébert(euphemism) , one can find some quality in Guffroy's progressive views on women's rights. He wrote: "I had proposed to admit women to the primary assemblies, to deliberate on the choice of municipalities, and I still believe that my two separate ballots and my posted ballots would disturb all the conspiracies. If one is wise, one will come back to it; and I predict that we will never have a public spirit, public morals, if women do not participate in the administration as I have proposed. The National Assembly admitted to swearing the constitution, those who were in the tribune on the 4th of this month. Why would we separate them from the public good? The queen promised to raise her son in the principles of constitutional liberty; all French mothers must publicly swear this civic oath: without that, I repeat, no morals, no morals, no fatherland. Frenchmen, prove that you are men, by giving back to your wives all their dignity; French women, prove that you are worthy of giving birth to a race of free men."
Sources:
Antoine Resche
Louis Devance Le féminisme pendant la révolution française
Walter Markov
Stefania di Pasquale
Jean-Marc Schiappa
Charles-Gilbert Romme, "Rapport sur l’instruction publique, considéré dans son ensemble, suivi d’un projet de décret sur les principales bases du plan général, prononcé devant la Convention le 20 décembre 1792"
Thank you @anotherhumaninthisworld without whom I would not have been able to see the writings of Couthon, Guffroy, and Desmoulins in favor of women's rights.
#frev#french revolution#condorcet#camille desmoulins#jean paul marat#charles gilbert romme#Jacques Roux#Jean-Nicolas Pache#gracchus babeuf#Guffroy#It was difficult to find a somewhat more reasonable figure for the Hébertists in terms of women's rights#as the focus on women's rights was so limited.#Even more for the Thermidorians as we know what happen to the womens who were driven from the assembly with whips#but we can at least give this quality to Guffroy#My goal was at least one representative from each faction#It seemed more fair and “fun” to me.
103 notes
·
View notes
Text
Frev appearance descriptions masterpost



Jean-Paul Marat — In Histoire de la Révolution française: 1789-1796 (1851) Nicolas Villiaumé pins down Marat’s height to four pieds and eight pouces (around 157 cm). This is a somewhat dubious claim considering Villiaumé was born 26 years after Marat’s death and therefore hardly could have measured him himself, but we do know he had had contacts with Marat’s sister Albertine, so maybe there’s still something to this. That Marat was short is however not something Villaumé is alone in claiming. Brissot wrote in his memoirs that he was ”the size of a sapajou,” the pamphlet Bordel patriotique (1791) claimed that he had ”such a sad face, such an unattractive height,” while John Moore in A Journal During a Residence in France, From the Beginning of August, to the Middle of December, 1792 (1793) documented that ”Marat is little man, of a cadaverous complexion, and a countenance exceedingly expressive of his disposition. […] The only artifice he uses in favour of his looks is that of wearing a round hat, so far pulled down before as to hide a great part of his countenance.” In Portrait de Marat (1793) Fabre d’Eglantine left the following very detailed description: ”Marat was short of stature, scarcely five feet high. He was nevertheless of a firm, thick-set figure, without being stout. His shoulders and chest were broad, the lower part of his body thin, thigh short and thick, legs bowed, and strong arms, which he employed with great vigor and grace. Upon a rather short neck he carried a head of a very pronounced character. He had a large and bony face, aquiline nose, flat and slightly depressed, the under part of the nose prominent; the mouth medium-sized and curled at one corner by a frequent contraction; the lips were thin, the forehead large, the eyes of a yellowish grey color, spirited, animated, piercing, clear, naturally soft and ever gracious and with a confident look; the eyebrows thin, the complexion thick and skin withered, chin unshaven, hair brown and neglected. He was accustomed to walk with head erect, straight and thrown back, with a measured stride that kept time with the movement of his hips. His ordinary carriage was with his two arms firmly crossed upon his chest. In speaking in society he always appeared much agitated, and almost invariably ended the expression of a sentiment by a movement of the foot, which he thrust rapidly forward, stamping it at the same time on the ground, and then rising on tiptoe, as though to lift his short stature to the height of his opinion. The tone of his voice was thin, sonorous, slightly hoarse, and of a ringing quality. A defect of the tongue rendered it difficult for him to pronounce clearly the letters c and l, to which he was accustomed to give the sound g. There was no other perceptible peculiarity except a rather heavy manner of utterance; but the beauty of his thought, the fullness of his eloquence, the simplicity of his elocution, and the point of his speeches absolutely effaced the maxillary heaviness. At the tribune, if he rose without obstacle or excitement, he stood with assurance and dignity, his right hand upon his hip, his left arm extended upon the desk in front of him, his head thrown back, turned toward his audience at three-quarters, and a little inclined toward his right shoulder. If on the contrary he had to vanquish at the tribune the shrieking of chicanery and bad faith or the despotism of the president, he awaited the reéstablishment of order in silence and resuming his speech with firmness, he adopted a bold attitude, his arms crossed diagonally upon his chest, his figure bent forward toward the left. His face and his look at such times acquired an almost sardonic character, which was not belied by the cynicism of his speech. He dressed in a careless manner: indeed, his negligence in this respect announced a complete neglect of the conventions of custom and of taste and, one might almost say, gave him an air of ressemblance.”
Albertine Marat — both Alphonse Ésquiros and François-Vincent Raspail who each interviewed Albertine in her old age, as well as Albertine’s obituary (1841) noted a striking similarity in apperance between her and her older brother. Esquiros added that she had ”two black and piercing eyes.” A neighbor of Albertine claimed in 1847 that she had ”the face of a man,” and that she had told her that ”my comrades were never jealous of me, I was too ugly for that” (cited in Marat et ses calomniateurs ou Réfutation de l’Histoire des Girondins de Lamartine (1847) by Constant Hilbe)
Simonne Evrard — An official minute from July 1792, written shortly after Marat’s death, affirmed the following: “Height: 1m, 62, brown hair and eyebrows, ordinary forehead, aquiline nose, brown eyes, large mouth, oval face.” The minute for her interrogation instead says: “grey eyes, average mouth.”Cited in this article by marat-jean-paul.org. When a neighbor was asked whether Simonne was pretty or not around two decades after her death in 1824, she responded that she was ”très-bien” and possessed ”an angelic sweetness” (cited in Marat et ses calomniateurs ou Réfutation de l’Histoire des Girondins de Lamartine (1847) by Constant Hilbe) while Joseph Souberbielle instead claimed that ”she was extremely plain and could never have had any good looks.”
Maximilien Robespierre — The hostile pampleth Vie secrette, politique et curieuse de M. J Maximilien Robespierre… released shortly after thermidor by L. Duperron, specifies Robespierre’s hight to have been ”five pieds and two or three pouces” (between 165 and 170 cm). He gets described as being ”of mediocre hight” by his former teacher Liévin-Bonaventure Proyart in 1795, ”a little below average height” by journalist Galart de Montjoie in 1795, ”of medium hight” by the former Convention deputy Antoine-Claire Thibaudeau in 1830 and ”of middling form” by his sister in 1834, but ”of small size” by John Moore in 1792 and Claude François Beaulieu in 1824. The 1792 pampleth Le véritable portrait de nos législateurs… wrote that Robespierre lacked ”an imposing physique, a body à la Danton,”supported by Joseph Fiévée who described him as ”small and frail” in 1836, and Louis Marie de La Révellière who said he was ”a physically puny man” in his memoirs published 1895. For his face, both François Guérin (on a note written below a sketch in 1791), Buzot in his Mémoires sur la Révolution française (written 1794), Germaine de Staël in her Considerations on the Principal Events of the French Revolution (1818), a foreign visitor by the name of Reichardt in 1792 (cited in Robespierre by J.M Thompson), Beaulieu and La Révellière-Lépeaux all agreed that he had a ”pale complexion.” Charlotte does instead describe it as ”delicate” and writes that Maximilien’s face ”breathed sweetness and goodwill, but it was not as regularly handsome as that of his brother,” while Proyart claims his apperance was ”entirely commonplace.” The foreigner Reichardt wrote Robespierre had ”flattened, almost crushed in, features,” something which Proyart agrees with, writing that his ”very flat features” consisted of ”a rather small head born on broad shoulders, a round face, an indifferent pock-marked complexion, a livid hue [and] a small round nose.” Thibaudeau writes Robespierre had a ”thin face and cold physiognomy, bilious complexion and false look,” Duperron that ”his colouring was livid, bilious; his eyes gloomy and dull,” something which Stanislas Fréron in Notes sur Robespierre (1794) also agrees with, claiming that ”Robespierre was choked with bile. His yellow eyes and complexion showed it.” His eyes were however green according to Merlin de Thionville and Guérin while Proyart insists they were ”pale blue and slightly sunken.” Etienne Dumont, who claimed to have talked to Robespierre twice, wrote in his Souvernirs sur Mirabeau et sur les deux premières assemblées législatives (1832) that ”he had a sinister appearance; he would not look people in the face, and blinked continually and painfully,” and Duperron too insists on ”a frequent flickering of the eyelids.” Both Fréron, Buzot, Merlin de Thionville, La Révellière, Louis Sébastien Mercier in his Le Nouveau Paris (1797) and Beffroy de Reigny in Dictionnaire néologique des hommes et des choses ou notice alphabétique des hommes de la Révolution, qui ont paru à l’Auteur les plus dignes d’attention… (1799) made the peculiar claim that Robespierre’s face was similar to that of a cat. Proyart, Beaulieu and Millingen all wrote that it was marked by smallpox scars, ”mediocretly” according to Proyart, ”deeply” according to the other two. Proyart also writes that Robespierre’s hair was light brown (châtain-blond). He is the only one to have described his hair color as far as I’m aware.
For his clothes, both Montjoie, Louis-Sébastien Mercier in 1801, Helen Maria Williams in 1795, Duperron, Millingen and Fiévée recall the fact that Robespierre wore glasses, the first two claiming he never appeared in public without them, Duperron that he ”almost always” wore them, and Millingen that they were green. Pierre Villiers, who claimed to have served as Robespierre’s secretary in 1790, recalled in Souvenirs d'un deporté (1802) that Robespierre ”was very frugal, fastidiously clean in his clothes, I could almost say in his one coat, which was was of a dark olive colour,” but also that ”He was very poor and had not even proper clothes,” and even had to borrow a suit from a friend at one point. Duperron records that ”[Robespierre’s] clothes were elegant, his hair always neat,” Millingen that ”his dress was careful, and I recollect that he wore a frill and ruffles, that seemed to me of valuable lace,”Charlotte that ”his dress was of an extreme cleanliness without fastidiousness,” Williams that he ”always appeared not only dressed with neatness, but with some degree of elegance, and while he called himself the leader of the sans-culottes, never adopted the costume of his band. His hideous countenance […] was decorated with hair carefully arranged and nicely powdered,” Fiévée that Robespierre in 1793 was ”almost alone in having retained the costume and hairstyle in use before the Revolution,” something which made him ressemble ”a tailor from the Ancien régime,” Thibadeau that ”he was neat in his clothes, and he had kept the powder when no one wore it anymore,” Germaine de Staël that ”he was the only person who wore powder in his hair; his clothes were neat, and his countenance nothing familiar,” Révellière writes that Robespierre’s voice was ”toneless, monotonous and harsh,” Beaulieu that it ”was sharp and shrill, almost always in tune with violence,” and Thinadeau that his ”tone” was ”dogmatic and imperious.”
Augustin Robespierre — described as ”big, well formed, and [with a] face full of nobility and beauty” in the memoirs of his sister Charlotte. Charles Nodier did in Souvenirs, épisodes et portraits pour servir à l'histoire de la Révolution et de l'Empire (1831) recall that Augustin had a ”pale and macerated physiognomy” and a quite monotonous voice.
Charlotte Robespierre — an anonymous doctor who claimed to have run into Charlotte in 1833, the year before her death, described her as ”very thin.” Jules Simon, who reported to have met her the following year, did him too describe her as ”a very thin woman, very upright in her small frame, dressed in the antique style with very puritanical cleanliness.”
Camille Desmoulins — described as ”quite tall, with good shoulders” in number 16 of the hostile journal Chronique du Manège (1790). Described as ugly by both said journal, the journal Journal Général de la Cour et de la Ville in 1791, his friend François Suleau in 1791, former teacher Proyart in 1795, Galart de Montjoie in 1796, Georges Duval in 1841, Amandine Rolland in 1864 (she does however add that it was ”with that witty and animated ugliness that pleases”) and even himself in 1793. Proyart describes his complexion as ”black,” Duval as ”bilious.” Both of them agree in calling his eyes ”sinister.” Duval also claims that Desmoulins’ physiognomy was similar to that of an ospray. Montjoie writes that Desmoulins had ”a difficult pronunciation, a hard voice, no oratorical talent,” Proyart that ”he spoke very heavily and stammered in speech” and Camille himself that he has ”difficulty in pronunciation” in a letter dated March 1787, and confesses ”the feebleness of my voice and my slight oratorical powers” in number 4 of the Vieux Cordelier. In his very last letter to his wife, dated April 1 1794, Desmoulins reveals that he wears glasses.
Lucile Desmoulins — The concierge at the Sainte-Pélagie prison documented the following when Lucille was brought before him on April 4 1794: ”height of five pieds and one and a half pouce (166 cm). Brown hair, eyebrows and eyes. Middle sized nose and mouth. Round face and chin. Ordinary front. A mark above the chin on the right.” Cited in Camille et Lucile Desmoulins: un rêve de république (2018). Described as beautiful by the journal Journal Général de la Cour et de la Ville in 1791 (it specifies her to be ”as pretty as her husband is ugly”), former Convention deputy Pierre Paganel in 1815, Louis Marie Prudhomme in 1830, Amandine Rolland in 1864 and Théodore de Lameth (memoirs published 1913).
Georges Danton — Described as having an ugly face by both Manon Roland in 1793, Vadier in 1794, the anonymous pamphlet Histoire, caractère de Maximilien Robespierre et anecdotes sur ses successeurs in 1794, Louis-Sébastien Mercier in 1797, Antoine Fantin-Desodoards in 1807, John Gideon Millingen in 1848, Élisabeth Duplay Lebas in the 1840s, the memoirs (1860) of François-René Chateaubriand (he specifies that Danton had ”the face of a gendarme mixed with that of a lustful and cruel prosecutor”) as well as the Mémoires de la Societé d’agriculture, commerce, sciences et arts du department de la Marse, Chalons-sur-Marne (1862). As reason for this ugliness, Millingen lifts his ”course, shaggy hair” (that apparently gave him the apperance of a ”wild beast”), the fact he was deeply marked with small-poxes, and that his eyes were unusually small (”and sparkling in surrounding darkness”), while Chateaubriand instead underlines that he was ”snub-nosed,” with ”windy nostrils [and] seamed flats.” Mercier writes that Danton’s face was ”hideously crushed.” The former Convention deputy Alexandre Rousselin (1774-1847) reported in his Danton — Fragment Historique that Danton developed a lip deformity after getting gored by a bull as a baby, had his nose crushed by another bull, got trampled in the face by a group of pigs and finally survived ”a very serious case of smallpoxes, accompanied by purpura.” In 1792, John Moore reported that ”Danton is not so tall, but much broader than Roland; his form is coarse and uncommonly robust,” while Vadier claims that Danton possessed a ”robust form, colossal eloquence,” the anonymous pamphlet that ”he was very strong, he said himself that he had athletic forms,” Desodoards that he ”held the nature of athletic and colossal forms,” Chateaubriand that he was ”a vandal in the size of Goth” (don’t know who he’s referring to), Pierre Paganel (in Essai historique et critique sur la révolution française: ses causes, ses résultats, avec les portraits des hommes les plus célèbres (1815)) that he was of an ”enormous stature,” while the pamphlet described him as a ”gigantic orator” whose voice ”shook the vaults of the hall.” René Levasseur in 1829, John Moore, Millingen, Paganel and Desodoards all agreed with this, the first four writing that Danton possessed a ”stentorian voice,” the latter that he had ”a very strong voice, without being sonorous or flexible.” In her memoirs (1834) Charlotte Robespierre claims that ”[Danton] did not at all conserve the dignity suited to the representative of a great people in his manners; his toilette was in disorder.”
Louis Antoine Saint-Just — In Saint-Just (1985) Bernard Vinot writes that Saint-Just’s childhood friend Augustin Lejeune recalled his “honest physiognomy,” and that his sister Louise would evoke her brother’s ”great beauty” for her grandchildren (I unfortunately can’t find the original sources here). The elderly Élisabeth Le Bas too stated that ”he was handsome, Saint-Just, with his pensive face, on which one saw the greatest energy, tempered by an air of indefinable gentleness and candor” (testimony found in Les Carnets de David d’Angers (1838-1855) by Pierre-Jean David d’Angers, cited in Veuve de Thermidor: le rôle et l'influence d'Élisabeth Duplay-Le Bas (1772-1859) sur la mémoire et l'historiographie de la Révolution française (2023) by Jolène Audrey Bureau, page 127). In Souvenirs de la révolution et de l’empire, Charles Nodier (who was twelve years old when he met Saint-Just…) agrees in calling him ”handsome,” but adds that he ”was far from offering this graceful combination of cute features with which we have seen it endowed by the euphemistic pencil of a lithograph,” had an ”ample and rather disproportionate chin,” that ”the arc of his eyebrows, instead of rounding into smooth and regular semi-circles, was closer to a straight line, and its interior angles, which were bushy and severe, merged into one another at the slightest serious thought that one saw pass on his forehead” and finally that ”his soft and fleshy lips indicated an almost invincible inclination to laziness and voluptuousness.” How would you know what his lips were like, Nodier. In Essai historique et critique sur la révolution française (1815) Pierre Paganel writes that Saint-Just had ”regular features and austere physiognomy.” He describes his complexion as ”bilious” while Nodier calls it ”pale and grayish, like that of most of the active men of the revolution.” Similar to Élisabeth’s description, Nodier writes that Saint-Just’s eyes were big and ”usually thoughtful,” while Paganel instead writes they were ”small and lively.” Saint-Just was of ”average height” according to Paganel, but ”of small stature” according to Nodier. According to Paganel, Saint-Just had a ”healthy body [and] proportions which expressed strength,” while Saint-Just’s colleague Levasseur de la Sarthe instead wrote in his memoirs that he was ”weak in body, to the point of fearing the whistling of bullets.” Finally, Paganel also gives the following details: ”large head, thick hair, disdainful gaze, strong but veiled voice, a general tinge of anxiety, the dark accent of concern and distrust, an extreme coldness in tone and manners.” In Lettre de Camille Desmoulins, député de Paris à la Convention, August général Dillon en prison aux Madelonettes (1793) Desmoulins jokingly writes that ”one can see by [Saint-Just’s] gait and bearing that he looks upon his own head as the corner-stone of the Revolution, for he carries it upon his shoulders with as much respect and as if it was the Sacred Host.” In Histoire de la Révolution française(1878), Jules Michelet claims that Élisabeth Le Bas had told him that this portrait, depicting Saint-Just as having ”a very low forehead, [with] the top of his head flattened, so that his hair, without being long, almost touched his eyes,” was similar to what he had looked like.
Jacques-Pierre Brissot — The following was documented after Brissot had been arrested at Moulins on June 10 1793 — ”height of five pieds (162 cm), a small amount of flat dark brown hair, eyebrows of the same color, high forehead and receding hairline, gray-brown, quite large and covered eyes, long and not very large nose, average mouth, long chin with a dimple, black beard, oval face narrow at the bottom” (cited in J.-P. Brissot mémoires (1754-1793); [suivi de] correspondance et papiers (1912)). In Journal During a Residence in France, from the Beginning of August, to the Middle of December, 1792 John Moore described Brissot as ”a little man, of an intelligent countenance, but of a weakly frame of body” and claimed that a person had told him that Brissot had told him that he is ”of so feeble a constitution” that he won’t be able to put up any resistance was someone try to assassinate him.
Jérôme Pétion — described as ”big and fat” (grand et gros) by Louis-Philippe in 1850 (cited in The Croker Papers: the Correspondence and Diaries of the late right honourable John Wilson Croker… (1885) volume 3, page 209). Manon Roland wrote in her memoirs that Pétion ”had nothing to regret physically; his size, his face, his gentleness, his urbanity, speak in his favor” as well as that he ”spoke fairly well,” a descriptions which Louis Marie Prudhomme partly agreed with, himself recording that Pétion ”had a proud countenance, a fairly handsome face, an affable look, a gentle eloquence, movements of talent and address; but his manners were composed, his eyes were dull, and he had something glistening in his features which repelled confidence” in Paris pendant le révolution (1789-1798) ou le nouveau Paris (1798). In Quelques notices pour l’histoire, et le récit de mes périls depuis le 31 mai 1793 (1794) Jean-Baptiste Louvet reported that, while on the run from the authorities after the insurrection of May 31, the less than forty years old Pétion already had a white hair and beard. This is confirmed by Frédéric Vaultier, who in Souvenirs de l'insurrection Normande, dite du Fédéralisme, en 1793 (1858) described Pétion during the same period as ”a good-looking man, with a calm and open physiognomy and beautiful white hair,” as well as by the examination of his mangled courpse on June 26 1794, which states he had ”grayish hair” (cited in Charlotte de Corday et les Girondins: pièces classées et annotées (1872) by Charles Vatel, volume 2, page 154.
François Buzot — according to the memoirs (1793) of Manon Roland, he had ”a noble figure and elegant size.” In the examination made of Buzot’s body after the suicide there is to read that he had black hair (cited in Charlotte de Corday et les Girondins: pièces classées et annotées (1872) by Charles Vatel, volume 2, page 153)
Charles Barbaroux — his son wrote in Jeunesse de Barbaroux (1822) that ”nature had richly endowed Barbaroux; a robust and large body; a charming, fine and witty physiognomy.” In 1867, François Laprade, who had witnessed Barbaroux’ execution as a thirteen year old, recollected that ”he was a brown man - that is to say he had brownish skin, black hair and beard, reclining figure” (cited in Charlotte de Corday et les Girondins: pièces classées et annotées, volume 3, page 728). Valazé’s daughter did in her old age too describe Barbaroux as very dark, with black hair, black beard and large black eyes. According to her, he was ”excessively beautiful,” with well-defined lips, beautiful teeth and fine, delicate features, so much so in fact that colleagues would often joke about his beauty. Cited in Ibid, volume 3, page 728.
Marguerite-Élie Guadet — According to his passport (cited in Charlotte de Corday et les Girondins: pièces classées et annotées, volume 3, page 672): ”height of 5 pieds, 5 pouces (176 cm) middle sized mouth, black hair and eyebrows, ordinary chin, blue eyes, big forehead, thin face, upturned nose.” According to Frédéric Vaultier’s Souvenirs de l'insurrection Normande, dite du Fédéralisme, en 1793(1858), ”Guadet was a man of fine height, meagre, brown, bilious complexion, black beard, most expressive face.”
Joseph Le Bon — his passport description (cited in Louis Jacob, Joseph Le Bon, (1932) by Louis Jacob, volume 1, page 63) gives the following information: ”Height of five pieds six pouces (178 cm), light brown hair and eyebrows, high forehead, average nose, blue eyes, medium-sized mouth, smallpox scars.”
Claire Lacombe — the concierge of the Sainte Pélagie documented the following about the imprisoned Lacombe: ”height of 5 pieds, 2 pouces (168 cm). Brown hair, eyebrows and eyes, medium nose, large mouth, round face and chin, plain forehead” (cited in Trois femmes de la Révolution : Olymps de Gouges, Théroigne de Méricourt, Rose Lacombe (1900) by Léopold Lacour)
Charlotte Corday — according to her passport, ”height of five pieds one pouce (165 cm), brown hair and eyebrows, gray eyes, high forehead, long nose, medium mouth, round, forked (fourchu) chin, oval face.” (cited in Dossiers du procès criminel de Charlotte Corday, devant le Tribunal révolutionnaire(1861) by Charles-Joseph Vatel, page 55)
Prieur de la Marne — a passport dated October 1 1793 gives the following details: ”age of 37 years, height of 5 pieds 5 pouces (176 cm), blondish brown hair and eyebrows, receding hairline, long nose, grey eyes, large mouth.”
Maurice Duplay — ”height of 5 pieds 6 pouces (179 cm), blondish brown hair and eyebrows, receding hairline, grey eyes, long, open nose, large mouth, round, full chin and face.” Descriptions given in 1795 and cited in Les deniers montagnards (1874) by Jules Claretie.
Jean Lambert Tallien — Both a spy report written in 1794 found among Robespierre’s papers and Mme de la Tour du Pin, a noblewoman who met Tallien in late 1793, describe Tallien’s hair as blonde. Mme de la Tour du Pin adds that said hair was curly and that he had a pretty face.
#might eventually reblog a part 2 i ran out of links for the moment#frev#french revolution#robespierre#georges danton#jean paul marat#albertine marat#simonne évrard#maximilien robespierre#augustin robespierre#camille desmoulins#desmoulins#lucile desmoulins#charlotte robespierre#charlotte corday#brissot#pétion#prieur de la marne#maurice duplay#jean lambert tallien#joseph lebon#charles barbaroux#françois buzot#saint-just#louis antoine de saint just#yes robespierre was taller than brissot this is no drill#i like this beauty and the beast thing camille and lucile seemed to have going tho…
290 notes
·
View notes
Text

#f1#1904#lewis hamilton#charles leclerc#max verstappen#lando norris#oscar piastri#george russell#kimi antonelli#alexander albon#carlos sainz#fast cars#sports#paris france#europe#formula 1#Camille Jenatzy#charles jarrott#Achille Varzi
38 notes
·
View notes
Text
I think I cooked
#would you believe me if this is one of those animatics that I play in my head when I listen to Willwood?#ermmm what the scallop#artists on tumblr#silly drawing#art#digital illustration#frev community#frev media#camille desmoulins#marie antoinette#charles henri sanson#Louis XVI#maximillian robespierre#louis antoine de saint just#animatic#will wood
101 notes
·
View notes
Text






It’s Fine Press Friday!
Our fine press selection this week comes out of the summer “High Jinks” of The Bohemian Club – an elite and exclusive social club for men based in San Francisco. In the summer of 1940, surrounded by redwoods, a group of prominent white men put on an original play for other prominent white men. Saul was written by Benjamin Allen Purrington (1894-1960), and draws from the struggles between Samuel and Saul in the Old Testament – struggles, he suggests, “analogous to those of our own unhappy times.” The book contains notes on the music by composer Charles Hart, as well as several illustrations by Albert J. Camille (1904 - 1981). San Francisco’s Grabhorn Press printed and bound the book in a limited edition of 1,300 copies. The typeface is Lutetía and the text is printed in black with red marginal captions. The decorative board binding displays a pattern of male figure in blues and purples.
In his biography of the Grabhorn Press, Roby Wenz indicates the high honor it was when Edwin Grabhorn was elected to The Bohemian Club – and how this meant the Press was now part of The Club’s establishment. Printing each summer’s “High Jinks” was now a yearly responsibility, though it was “seen usually as a piece of annual drudgery, seldom if ever worthy of the Press’s best efforts” (102).
The Club was formed in 1872 by a small cadre of newspaper men, who, according to a 1980 profile in American Heritage, “imagined themselves, on no substantial evidence, to be the artistic elite of a provincial city.” Before long however, the organization “succumbed to an irresistible urge” to admit capitalists, and was soon “led by men who would never before have called themselves ‘bohemian,’ much less have fraternized with newspapermen.”
Saul contains an extensive list of credits, highlighting all the men who performed the play, danced or sang in the chorus, played for the orchestra, assisted in constructing sets or designing costumes, or contributed in numerous other ways. One woman also appears! A Miss Betty Horst is thanked for help with choreography, though it is unclear if she was welcomed at the production.
Occasionally select women are invited to attend or become “honorary members” of The Bohemian Club. After a lawsuit, the company was forced to allow women to work for The Club, along with all the other employees allegedly falling victim to wage theft.
Recent guests and members include Sam Altman and Harlan Crow.



Read more about The Bohemian Club and its significance through an extensive study by UC Santa Cruz Emeritus Professor G. William Domhoff.
View more posts on the Grabhorn Press.
View other Fine Press Friday posts.

-- Amanda, Special Collections Graduate Intern
#Fine Press Friday#Fine Press Fridays#finepressfriday#finepressfridays#Bohemian Club#Bohemian Grove#Saul#Benjamin Allen Purrington#Charles Hart#Albert J. Camille#Grabhorn Press#Lutetía#Inequality#capitalism#boys clubs#rich white creeps#fine press books
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
Doodle dump on my OC’s :D Including…. A new OC I made 👀….
I just realized yesterday that I made an ABCD line of my OC’s BRUH XD feels good man :D

And you may have noticed Camille over there hehehe! I wonder who he is? 👀

Camille was brought back to life from the late 1700’s by Benz doing a private government experiment hehehe!


What time period is Camille from you asked? 👀
Well imma tease some hints hehehe…. Camille is French and he needs his bow tie to keep his head from falling off since he was executed byyyyyyy *drumroll* ……the guillotine :)



His head falls off from time to time but he needs someone to tighten his bow tie to keep his head on lol >:)
#thsc#the henry stickmin collection#henry stickmin collection#captured!charles au#thsc camille desmoulins#danny felizima#benz rodriguez#mr. allwork
49 notes
·
View notes
Text







Some training camp vibes as gifs for you
#woso#chelsea fcw#chelsea women#sam kerr#millie bright#erin cuthbert#guro reiten#sonia bompastor#camille abily#maika hamano#niamh charles#hannah hampton
21 notes
·
View notes
Text










Blues in the sun ☀️
#fun in the sun#millie bright#aggie beever jones#hannah hampton#johanna rytting kaneryd#niamh charles#nathalie björn#sonia bompastor#guro reiten#erin cuthbert#sophie ingle#camille abily#zecira musovic#emily orman#julia bartel#alejandra abernabe#water fight#chelsea fcw#cfcw#football#footy#soccer#woso#woso community#woso soccer#wsl#womens super league#epl#womens football
32 notes
·
View notes
Text
Episode 127: Duncan Do Nots

This time Cody tells Garth all about Ectoplasm! What is it? Where does it come from? Should you eat it? etc. And along the way tells the story of the last woman to be "tried for witchcraft" in The United Kingdom!
As always, please come join the episode discussion on the Least Haunted Discord!
Enjoy the images and videos below!
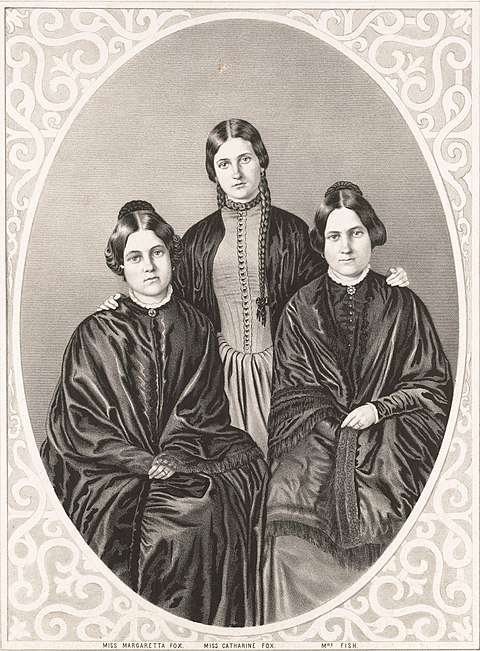
The Fox Sisters, "founders" of Spiritualism.

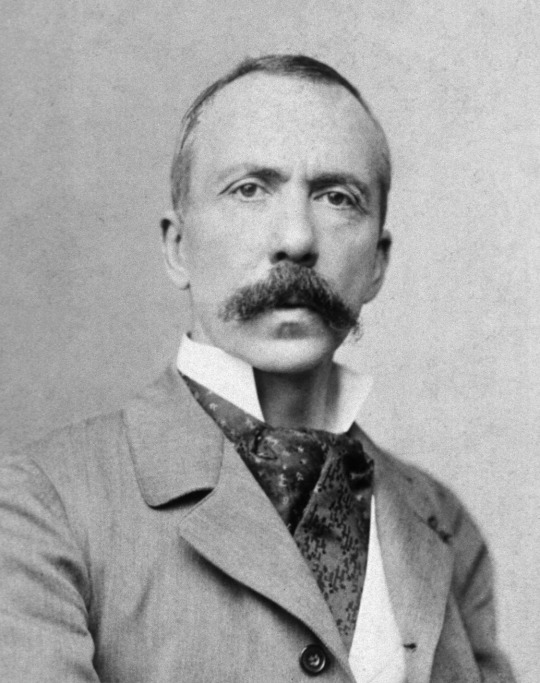
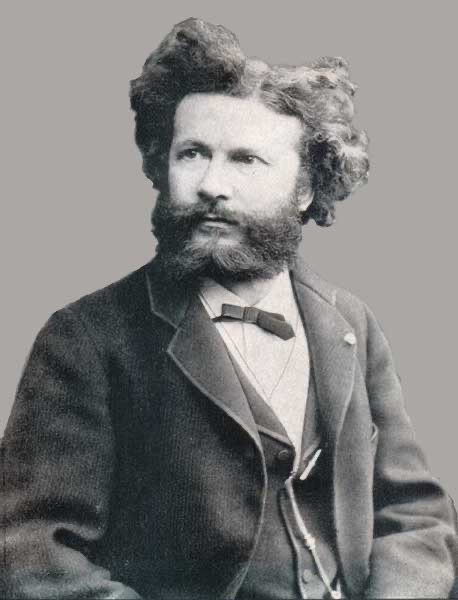
Charles Richet, Nobel Prize winning scientist and discoverer of anaphylaxis also a spiritualist who coined the term Ectoplasm, and the idea of "The Sixth Sense."

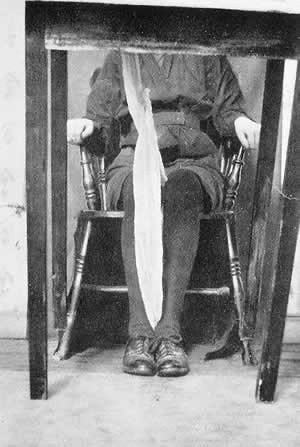
Medium Kathleen Goligher photographed with her ectoplasm "lever" that allowed her to move tables. Ectoplasm was said to come from the orifices and pores of psychic mediums.
Eva Carrier with ectoplasm face, 1912. The face was actually cut from a newspaper.

Unknown Male medium with ectoplasm.
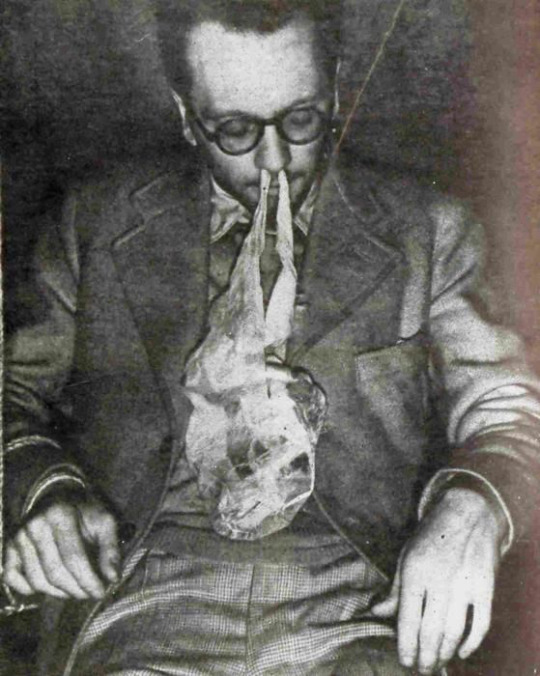
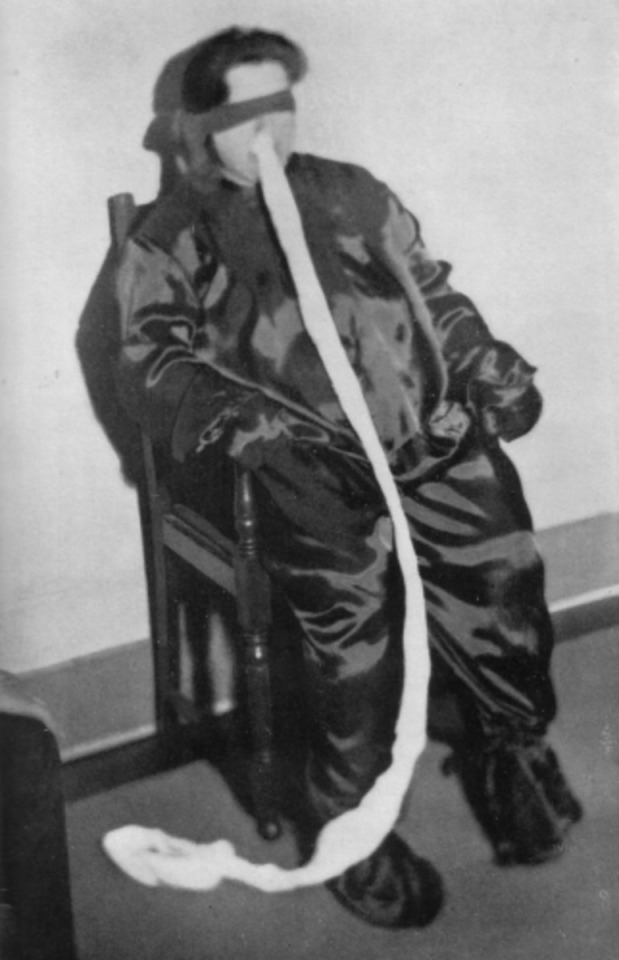
Psychical Researcher and fraud exposer Harry Price. Harry Price took an interest in Ectoplasm and medium Helen Duncan in particular. He obtained a sample of her ectoplasm and found it to be made of a combination of egg whites, lavatory paper, and cheese cloth that she swallowed and then regurgitated during seances, or hid in her sinus cavity.

Ectoplasm with "Spirit" face conjured by Cody for the Least Haunted Podcast. A mixture of egg whites and toilet paper with a face cut from a newspaper. Just how physical mediums made theirs 100 years ago!


Victoria Helen McCrae Duncan (1897-1956), Scottish physical medium famous for her ectoplasmic conjurings.

Helen with some of her "conjured spirits" made from paper mache. The ectoplasm coming from her nose is egg whites, toilet paper, and cheese cloth.
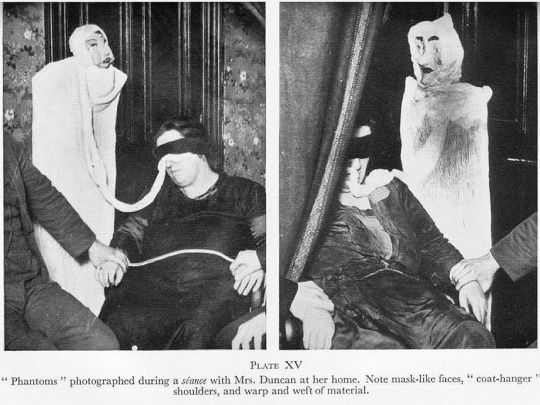
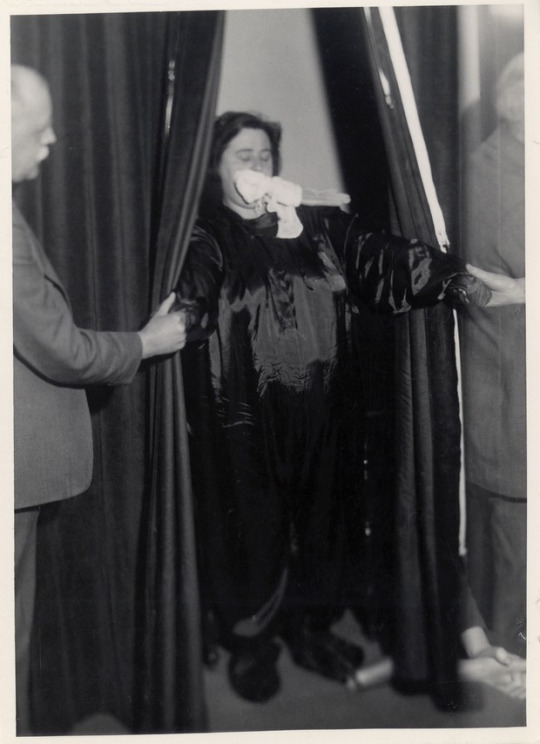
Helen in her black frock séance outfit expelling ectoplasm.


GARTH'S CORNER! GARTH'S CORNER! GARTH'S CORNER!
Camille Flammarion. Astronomer, and father of modern speculative fiction, and possibly, accidentally responsible for scientology.

Camille working as a computer at the Societé Astonomie Francais.

Wood cut depicting a person gaining access to outside knowledge. First published by Camille Flammarion, but the original artist is unknown.

#leasthaunted#podcast#funny#podcasts#paranormal#skeptics#ghosts#cryptids#ectoplasm#mediums#fake mediums#psychic mediums#spiritualism#fox sisters#seances#fake seances#charles richet#harry price#fake ghosts#garth's corner#camille flammarion
9 notes
·
View notes
Text




Coin de table, Henri Fantin-Latour, 1872
#musée d'orsay#coin de table#henri fantin latour#19th century#poets#Elzéar Bonnier#Emile Blémont#Jean Aicard#Paul Verlaine#Arthur Rimbaud#Léon Valade#Ernest d'Hervilly#Camille Pelletan#charles baudelaire#literature#Poète maudit#bohemian#art history#art#french art#painting#portrait#fashion history
26 notes
·
View notes
Text
Results of the first Survey: Who is your favorite feminist revolutionary of the French Revolution (or at least someone who contributed to women's rights)? Plus the second and final survey about this.
As seen in the previous survey [https://www.tumblr.com/nesiacha/779667028438138880/survey-who-is-your-favorite-feminist?source=share], due to an error on my part, I forgot to include Couthon as an option. Therefore, I am now putting him up against the winner of the first survey.
First, the results: the winner is Jean-Paul Marat ( Maratist), the Friend of the People, who fought against forced marriages, domestic violence, and defended prostitutes.
In second place, Camille Desmoulins(dantonist), one of the first republicans of 1789, as he advocated for the rights of married women to manage their property in 1793.
In third place, the man who, in a letter, expressed an egalitarian opinion on women and, during the French Revolution, publicly honored them while supporting their full participation in political clubs: Gracchus Babeuf (babouvist).
In fourth place, one of the leaders of the Enragés faction, which was one of the few not to want to exclude women from political activities: Jacques Roux. He even said, "Victory was indisputable as soon as women joined the sans-culottes."
In fifth place: Nicolas de Condorcet ( girondin ), who campaigned for gender equality during this period.
In sixth place: Charles-Gilbert Romme (crêtois), who founded a mixed club with Théroigne de Méricourt, and in a report on public education dated December 20, 1792, advocated for girls to have access to republican schools.
In seventh place, Guffroy (thermidorian) : He advocated for the inclusion of women in primary assemblies, particularly in deliberating on the selection of municipalities, and he emphasized the importance of their active participation in public administration. He wanted women to have the same rights as men in this regard.
The final position goes to Pache ( hébertist), the founder of the Société patriotique du Luxembourg, who admitted women on the same terms as men. Although they received few votes or none at all, they can take solace in the fact that they received votes despite such a large number of options in this survey and managed to secure a place in it.
"Now the face-off: Couthon vs. Marat."

For the Robespierristes group: Georges Couthon One of the best-known members of the CPS in Year II, also spoke in favor of women's rights to share property administration in August 1793, as seen here: source. Additionally, he allowed his wife to give a speech at the Federation Festival in Clermont-Ferrand in 1790, before he gave his own speech, as seen here: source.

For the Maratist group: Jean-Paul Marat The journalist from L’Ami du Peuple often defended women who were victims of domestic violence, encouraging them to flee their homes and denounce those who abused them. Here is an excerpt from his writings found in the excellent book Madame Marat: A Heroic Life in the Turmoil of the French Revolution by Stefania di Pasquale: "Women are more inclined to tenderness than men. During their childhood, children are expected to oppose themselves to shame, but as soon as they come to the age in which women start listening to us, we hurry to conquer them and to excite their imagination; we focus all of our thoughts to unleash their senses. Hasn’t the time come to create a sweet bond with them? Men have always chosen while women have always accepted! How many foolish parents sacrifice the happiness of their daughters? Forced to yield the object of their heart forever, they become unable to love again, seeing only misfortune in their future." He also defended prostitutes.
#frev#french revolution#georges couthon#jean paul marat#condorcet#camille desmoulins#gracchus babeuf#jacques roux#charles gilbert romme#guffroy#jean nicolas pache#history#france#survey
21 notes
·
View notes
Note
I'm honestly shocked that since Emotion/Representation aired I've yet to see anyone do anything at all with Felix and Mary Shelley's Frankenstein??? I think about it every day it's literally THE Felix piece of media. It's his entire character thesis. What are we doing guys
I KNOW I WAS JUST THINKING ABOUT IT THE OTHER DAY
To be fair I have seen a few people headcanoning it as one of Felix’s favourite books (Which yes. Absolutely. 1,000,000%) but there hasn’t been any fics/art/edits/etc. about it yet to my knowledge. My copy is at my parents’ and in French but I am tempted to find an English PDF since it’s been public domain for a good while now. The web weave potential is insane.
I have many thoughts about Felix and literature in general… I have him quote Cyrano de Bergerac all the time in my fics, for example. I was thinking of starting a list of works of art and literature he’d enjoy, so I’ll take this as a sign to get writing! I can get my fandom friends to make some suggestions as well! 📝
Edit: @bittersweetresilience got us covered, our honour is safe 💜🦚
#For now I really need to go to bed but here’s an overview:#Frankenstein and Cyrano of course#The portrait of Dorian Gray for Emilie#Ovid’s Metamorphoses (my sister and I actually wrote a fic about it!)#L’Albatros by Charles Baudelaire (see: web weave)#Psychopompe by Amélie Nothomb (see: other web weave)#J’aime l’araignée et j’aime l’ortie by Victor Hugo#She walks in beauty by Byron for Kagami#East of Eden (I’ve yet to read it but the movie is one of my favourites to this day)#Phantom of the Opera by Gaston Leroux#The Odyssey and EPIC#All of Magritte’s art but especially La Grande Famille & L’Empire des Lumières & La Trahison des Images#Stuart Semple’s entire vibe#I wonder what he’d think of Bauhaus art actually. The entire philosophy would create conflicting feelings I’m sure#Danse Macabre by Camille Saint-Saëns#Bach’s Toccata and Fugue in D minor#He’d also prefer Salieri to Mozart while also detailing how Salieri actually made a name for himself every time the topic comes up#OH and he has the biggest crush on Milady de Winter#And Zagreus from Hades#miraculous ladybug#felix graham de vanily#tumblr asks
20 notes
·
View notes
Text

















First Monday - CBS - January 15, 2002 - May 3, 2002
Legal Drama (13 Episodes)
Running Time: 60 minutes
Stars:
Joe Mantegna as Justice Joseph Novelli
James Garner as Chief Justice Thomas Brankin
Charles Durning as Justice Henry Hoskins
Randy Vasquez as Miguel Mora
Hedy Burress as Ellie Pearson
Christopher Wiehl as Jerry Klein
Joe Flanigan as Julian Lodge
Camille Saviola as Justice Esther Weisenberg
James McEachin as Justice Jerome Morris
James Karen as Justice Michael Bancroft
Gail Strickland as Justice Deborah Szwark
Stephen Markle as Justice Theodore Snow
Lyman Ward as Justice Brian Chandler
Linda Purl as Sarah Novelli
Brandon Davis as Andrew Novelli
Rachel Grate as Beth Novelli
Dean Stockwell as Senator Edward Sheffield
#First Monday#TV#CBS#2002#2000's#Legal Drama#Joe Mantegna#James Garner#Charles Durning#James Karen#Camile Saviola#James McEachin#Gail Strickland#Stephen Markle#Lyman Ward
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

"PERSEUS STAGGERS OUT WITH THE HEAD OF MEDUSA LIKE A SEX WAR WHERE THE MALE BARELY SURVIVES EXTINCTION IN HIS ENCOUNTER WITH THE FEMALE UNDERWORLD"
- CAMILLE PAGLIA
#camille paglia#greek mythology#perseus#medusa#andromeda#painting#the kraken#symbolism#Charles Napier Kennedy
20 notes
·
View notes
Note
imo c!dreambur letters would be like james joyce's letters to his wife (sidenote: don't read james joyce's letters).
please delete this fucking ask. this is seriously fucked up
#I’M AN ENGLISH MAJOR OKAY. I’VE READ HIS LETTERS. SO FUCKING UPSETTING#genuinely don’t look them up guys 😭😭😭😭#it’s like charles+camill but worse
14 notes
·
View notes