#ancient Carthage
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text



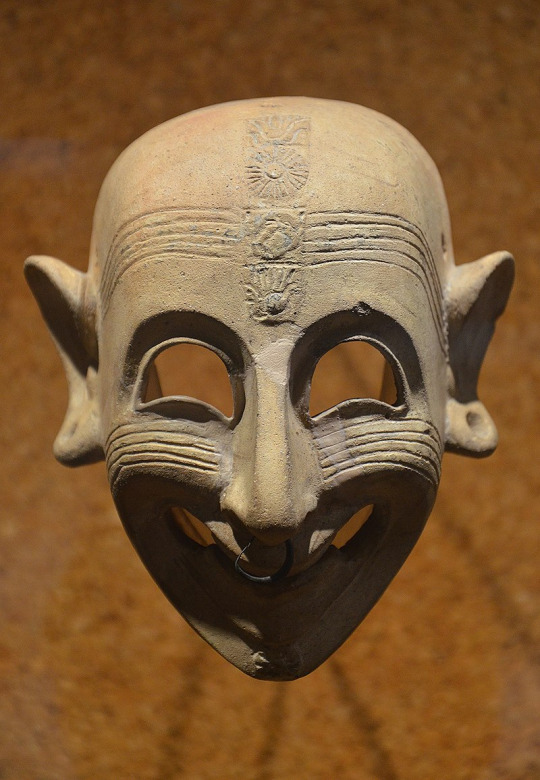
I wouldn't want to come across these in the middle of the night, they would scare my pants off. Phoenicians/Carthaginians apparently thought so too because they placed these menacingly grinning masks inside their tombs to scare off evil spirits and guard against evil. These particular exemplars come from Tunisia, Spain, and Sardinia respectively.
#ancient history#ancient art#ancient culture#ancient funerary traditions#funerary mask#punic#carthage#punic culture#ancient carthage#ancient phoenicians#phoenician#ancient Mediterranean#ancient sardinia#ancient iberia
2K notes
·
View notes
Text

Gilded bronze cuirass uncovered from a Carthaginian tomb near Ksour Essef in Tunisia, 3rd century BC
654 notes
·
View notes
Text

The Meeting between Scipio and Hannibal before the Battle of Zama, 202 BC by Hermann Vogel
#hermann vogel#art#scipio#hannibal#battle of zama#roman republic#ancient rome#ancient carthage#roman#romans#carthaginian#carthaginians#second punic war#punic wars#antiquity#history#europe#european#zama#tunisia#north africa#mediterranean#scipio africanus#hannibal barca#carthage#rome
98 notes
·
View notes
Note
Do you have any thoughts/theories on what it would've been like if Alexander ever returned to Pella? (sorry if this was already asked, tumblr's search system isn't really helpful)
What if Alexander Had Lived to Turn West?
First, I agree on Tumblr’s search system. It’s become increasingly bad. Even I can’t find posts I KNOW I made and tagged. I’m starting to compile a list of the more important (and lengthy) posts on various subjects, for my own reference. I wish Tumblr would let us pin several posts, not just one. (I’ve also sent a complaint feedback to Tumblr about this.)
Anyway, to the question: before we get to the “fun” (speculative) part, let’s address how likely it is he’d GO back. And as part of that, we need to ruminate a bit on what he might have done, if he’d returned west. So, let’s play a little “What-if?”
We must also keep in mind travel time. In the modern world, we can forget how long it took back then to get from Point A to Point B. Had he lived to attack Carthage (as I think he planned to do), or at least circumnavigate Arabia—both are on the southern coast of the Mediterranean. (See my tweaked map with significant places I mention below marked in purple, and recall that they tended to sail along a coast, not straight through the middle.) Macedonia is in the NW corner of the Aegean Sea. Such a side-trip would have eaten up a couple months. There might have been a sneaky reason for him to do that very thing: to come at Carthage from the north. (See discussion below.) But only if Arabia was a ruse all along. If he did mean to attack Arabia (and I think he intended that too), he'd go the southern route, then after, check on the progress of Alexandria (and visit the shrines for Hephaistion that he’d ordered built), before heading west.
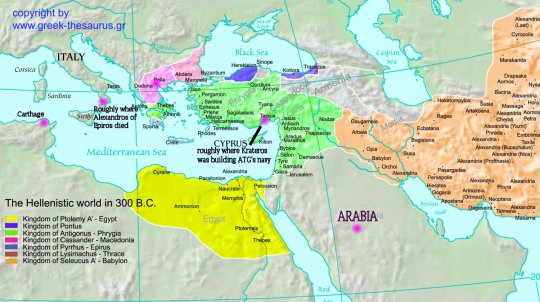
If he did choose that southern route, he wouldn’t have returned to Pella before attacking Arabia or Carthage. And after…well, Italy was on the way back, so he’d probably have gone there first. And yes, I think after dealing with Carthage, he’d have used avenging the death of his uncle (Alexandros of Epiros) as an excuse to attack the Greek colonies in S. Italy. If he’d been successful against Carthage, I’m pretty sure south Italy, and possibly the north too, would have capitulated to avoid being leveled. Even Rome. At that point, Rome was in no position to fight such a titanic military powerhouse. Too many think of Rome later and backread the extent of Roman resistance into earlier periods.
Depending on the length of the campaign (e.g., how hard was any opposition), he’d have been in his mid-30s by then. Incidentally, if you’d like a speculative “What if Alexander went West,” I recommend A Choice of Destinies by Melissa Scott. (Ignore the cover.) She does have him return to Greece first, but because Thebes is in revolt (which called him back in the first place; he never reaches India). That’s the sort of event that would get him back to Greece.
There’s been speculation in both fiction and history that he didn’t want to go home because he was avoiding “his terrible mother” (as Tarn put it). I’ve written before on why Oedipal Complexes are both very modern and very wrong to assign to Alexander. I can’t now locate that post (annoyingly), but did find this one about Alexander’s relationship with Olympias in later years. So, I don’t think avoiding Olympias would have kept him from Greece/Macedonia before going west. If anything, the opportunity to see his family would have been a draw, not a dissuading point.
So, we can postulate two possible return scenarios. The first would be a side-trip on his way to Carthage as trickery to conceal his real target. After leaving Pella, he’d circumnavigate Greece to the Peloponnese, then cross the Ionian Sea to Sicily (a typical Greek trade route), and then sail around the southern edge of the island to pop across to Carthage from the north.
In this scenario, he’d be in “swing-by” mode. He’d already asked Antipatros to bring him fresh troops, so he’d have been picking them up, or acquiring more. As a recruiting campaign, it would have been short, but he’d no doubt make several religious sacrifices at Dion, Aigai, and Pella, and perhaps even visit Delphi for a prophecy about the west.
He would not bring his Asian wives with him in either scenario. First, it’s a campaign, not a family visit. But also, he intended them to stay in Babylon (or Susa). By that point, Roxane and probably also Statiera would have given birth. If both infants were male, Statiera’s would be designated heir in Asia. If only Roxana’s was male, he’d still be the “spare” by dint of his mother’s lower birth, but better than nothing in the meantime.
It’s quite possible that he intended a divided but hierarchical rule not so different from Assyrian patterns, where one heir was sent to Babylon while Daddy ruled in Nineveh and trained the other. He almost certainly meant his son by Statiera to rule in Persia/Asia, but perhaps a different son to rule in the west—one likely not even conceived yet.
I do not think he’d have married a Macedonian. He’d be looking for another political marriage, maybe to a Greek (Athenian, Syracusan…), but more likely, he’d marry a Carthaginian after any war (or as part of any peace treaty with Carthage). At that point, Carthage was the powerhouse in the Western Med. Remember, Rome had only begun her consolidation of the Italic peninsula in the wake of the Gaulic sack of the city. Alexander in Italy might have stopped that cold.
Anyway, whatever marriage he made in the west (or couple of marriages) would have been intended to produce an heir to reign there, probably subservient to any son by Statiera after Alexander’s own death, but it’s hard to know for sure. Roxana’s son (and Herakles by Barsine) would have been third and fourth fiddles. That’s WHY Roxana killed Statiera. Her status wasn’t high enough, and her son would have been destined to be regional governor in the NE territories (where his family was from): e.g., troublesome Baktria/Sogdiana. Herakles would probably have been given Asia Minor (where his Persian family was from). (More on Herakles in another post.)
But back to this scenario: if he visited on the way, it would have been a quick trip until he was off again to another campaign. (Not unlike Daddy who, in his latter years, didn’t spend much time in Pella.)
Now, let’s look at scenario #2: a visit after any victories in Arabia, Carthage, and possibly Italy. That would be a different homecoming, less pressed for time.
That said, he wouldn’t have intended to stay. After securing the eastern/middle Mediterranean, he might have driven up into Europe, to re-secure Thrace to the Danube and scout for river connections between the Black and Caspian Seas. There aren’t any, but they didn’t know that. In fact, late in his campaign, he’d already sent somebody north to do that very scouting, so this would be a follow-up.
Thrace had fallen away from Macedonian control in in his later years, thanks to the powerful Odrysian King Seuthes III. Also, Alexander hadn’t forgotten those Celts who’d been singularly unimpressed by him early in his reign. (ha) Alternatively, he might have decided to go South of Egypt to Meroë, or west of Italy to Spain. But as he was centered in Greece, my bet is north into Eastern Europe. He already had incentive from a rebellious Thrace.
What would this homecoming have been like? STUPENDOUS, of course. All the stops pulled out. Macedonia was a gift-exchange society, so bringing home a fair bit of booty would be important. We’re told he sent presents home regularly, but this would be above and beyond. It would serve two functions:
First, he’d get to claim to be the wealthiest, most successful Macedonian king EVAR, and then some. So personal fame and honor would be on the line.
Second, throwing around oodles of wealth would be a great recruiting tool. His constant warring meant he was also in constant need of new troops. In his last years, it was clear he was happy to get troops from a variety of peoples, but the Macedonian core remained (as in the Successor Wars). Of course, continually draining Macedonia of men was bad for the future population, but “sustainability” was not in any way an ancient concept, whether in resources or in manpower. Early in his career, he did show a little awareness of this, sending back men for a “conjugal visit,” but as the campaign continued, he stopped worrying about it.
Anyway, he would also probably take the opportunity to build that giant tomb for daddy that was part of his Last Plans. Hard to know how much of those plans were either exaggerated or entirely invented, but that sounds like something he’d do. He might also have taken time to improve on local religious structures (such as at Dion), and set up something (no doubt monstrously large) at both Delphi and Olympia, as panhellenic sites.
As for the reunion with his mother and sisters, as indicated, I don’t think he was staying away to avoid Mommy Dearest. So, I expect he’d have been happy, maybe even overjoyed, to see them again.
#asks#Alexander the Great#What if Alexander had lived?#Alexander versus Carthage#Alexander versus Rome#Classics#ancient history#ancient Greece#ancient Carthage#ancient alternative history#ancient Thrace#Olympias#tagamemnon
41 notes
·
View notes
Text
There Were Elephants Here Before
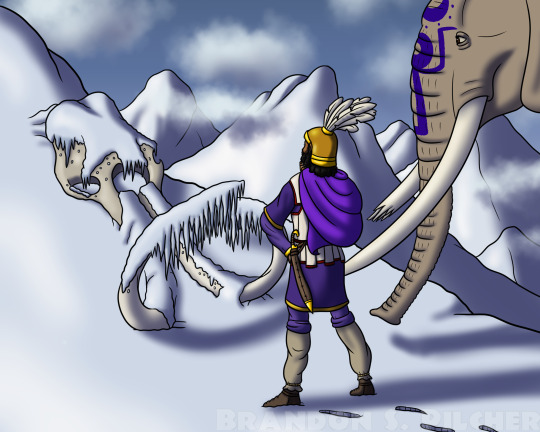

While crossing the Alps in 218 BC, the great Carthaginian general Hannibal Barca has stumbled upon the skull of a woolly mammoth half-buried in the snow. Given the difficulty his own animals have experienced in enduring the montane cold, he wonders how elephants could ever be native to these frigid heights deep in Europe.
This is of course a speculative scenario, but woolly mammoth remains have actually been found in the Alps on several occasions, so I think it’s theoretically possible for Hannibal or people in his army to have found some on their trek.
#hannibal barca#hannibal#ancient carthage#carthaginian#north african#african#ancient#black man#dark skin#elephant#african elephant#woolly mammoth#mammoth#fossil#alps#history#digital art#art
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
Countries that are no more: Ancient Carthage (814BC-146BC)
The state discussed in this post is one of the most famous and important in antiquity. Yet, it remains one of the most elusive and mysterious civilizations in world history because its own written records have been virtually erased with all contemporary written records coming from foreign sources that both praised and reviled its existence. However, it was influential for its model of government, its expansion of Mediterranean trade, its influence on models of economic production, naval exploration and for its military leaders whose tactical and strategic prowess influence warfare to the modern day and for its rivalry with the other emerging Mediterranean superpower of antiquity: Rome. A rivalry that is characterized as the quintessential clash of civilizations. This is Carthage.
Name: In its native language, the Phoenician dialect known in Latin as Punic, it was 𐤒𐤓𐤕𐤟𐤇𐤃𐤔𐤕, or annunciated as qrt-ḥdšt or Qart-Hardasht. This translates into English as "New City". In Latin it was known as Carthago or Karthago, the modern English pronunciation of Carthage comes by way of French.
Language: Carthage as a city-state and its empire more broadly held a cosmopolitan mixture of peoples and languages. However, the founders of Carthage and its ruling elite spoke Punic, a dialect of Phoenician associated with the city of Carthage which was founded by Phoenician colonists from the Levant. Punic was Phoenician in origin and became a distinct local dialect of Phoenician speakers in Carthage and other cities. These settlers founded colonies throughout North Africa and the Western Mediterranean. The Phoenician language and its dialects were from the Semitic language family native to the Middle East. It originated as a distinct dialect of the Canaanite peoples from who the Phoenicians and subsequently the Carthaginians descend from. The Canaanites also gave rise to the other Semitic speaking peoples such as the Israelites, Moabites and Ammonites among others. Modern Hebrew is said to be the extant language most similar to ancient Punic. In Carthage's empire there were also local varieties of Berber (Amazigh) languages spoken by the native Berbers who settled in North Africa. There were also local languages in Iberia (Spain and Portugal) from the Iberian and Celtic tribes settled there and the languages of native Sardinian and Balearic peoples as well. Additionally, ancient Greek was spoken by Greek colonists, mercenaries and traders who also settled within Carthage's empire and sphere of influence.
Territory: The city of Carthage is located in the environs of modern Tunis, capital of the modern state of Tunisia in North Africa. It was from this centrally located city founded by Phoenician colonists that their subsequent empire grew. The established contact and control with other Phoenician colonies in the area such as nearby Utica and eventually grew to control all of coastal North Africa from modern Morocco to western Libya. The modern states of Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia and Libya were its core territory, with Tunisia being its heartland. It also included Malta, the western half of Sicily, Sardinia and Corsica's coastal regions, the Balearic Islands of Spain and the southeastern portions of Iberia, particularly the coastal areas with influence into parts of the interior and south of the Ebro River.
Symbols & Mottos: The symbols associated with the state of Carthage are often in reference to their pantheon of gods which were quite extensive but centered mostly around the Phoenician gods but also included Berber, Iberian and Greek influences within their pantheon as well. A military standard associated with Carthage includes a staff with a sun disc and topped with a crescent moon. Also, the sign of Tanit, a Phoenician goddess's whose symbol was found on Carthaginian ruins along with Phoenician ruins found back in the Phoenician colonists' homeland in the Levant (Lebanon, Israel and Syria). The sign of Tanit appears in many varieties but is usually found as a schematic like sketch of a person with a triangular base with a disc on top with horizontal lines then pointing upwards like raised arms.
Religion: With Phoenician settlers being the originators of Carthage its ruling elite, the primary state religion was their variety of the ancient Phoenician religion which was polytheistic and included many notable gods and goddesses from Tanit to Baal Hammon, Melqart and Astarte among others. Many of these gods found companions with the Greeks and indeed due to the interfacing with Greeks both through trade and war, some Greek gods would also be incorporated into the Carthaginian pantheon, though it remained distinctly Punic at its core. There also appears to be Berber (Libyan and Numidian) influences along with Sardinian and Iberian interfacing that both saw the spread of worship of the Punic/Phoenician deities with local influences likewise being adopted by the Carthaginians. Even some ancient Egyptian gods appear to be included in Carthaginian worship. This syncretism and tolerance reflect the cosmopolitan outlook and composition the Carthaginians had within their realm.
There were priests who maintained the temples and sanctuaries devoted to particular deities. Likewise, Carthaginians practiced everything from ritual banquets to funerary rites such as those in the Levant like disposing of the remains of the dead, feasts for the dead, ancestor worship and goods in the tombs of the dead, indicating belief in life after death. Cemeteries were often built outside the walls of Punic settlements and included stelae with inscriptions serving as grave markers. Carthaginians practiced both burial and cremation.
There does appear to be cases of animal sacrifice to appease the gods in Carthaginian society as well. This tended to follow very specific regulations and rules.
The most controversial topic of the Punic religion however appears to be the practice of child sacrifice. The sources for this we must bear in mind come from Greco-Roman writers that weren't known to actually witness the practice and from civilizations that had biases toward Carthage more broadly. Yet both Greek and Roman sources cite the Carthaginians as practicing child sacrifice in their religion. These sources sometimes do contradict one another in their specifics. Modern historians debate the extent of this practice and what are the contents found at the sites known as Tophet in urns with ashes that may come from human infants. The Greco-Roman sources state children were specifically killed for ritual purposes and killed in various manners and burned as offerings. Based on archaeological findings some historians take the position that the practice may have occurred but may have been relegated to the ritual cremation of infants who died of natural causes. Others uphold the Greco-Roman sources and other deny the practice at all, chalking it up as pure invention of biased sources from Greece and Rome. Because Carthage was destroyed by Rome in 146 BC and virtually all extant written sources on Carthage come from Roman and Greek sources, there doesn't appear to be any definitive answer to this practice's purported extent or even its existence. Modern archaeology can lend more nuance to the topic but a clear answer like much of what we know about Carthage and its society remains a mystery.
Currency: The basic coinage of Carthage was called the shekel which derived from its Phoenician antecedents. There were gold, silver and bronze coins found throughout Carthage's empire. Mints were found not only in North Africa but Sicily and Iberia. Coins depicted everything from date palm trees to famous soldiers and politicians both Carthaginian in origin like the Barcid family of Hannibal Barca and even Greek rulers such as Alexander the Great.
Population: At its peak the empire had probably 3.7-4.3 million people. The city of Carthage proper at its peak was anywhere 250,000-500,000 people.
Government: The basis of our understanding of Carthage's governance is limited and largely based on ancient Greek and Roman sources. Some of which write of it in disparaging terms and others praise it for its complexity and nuance.
The basic understand is that during the first few centuries of Carthage's existence it was probably a monarchy. However, the extent to which the kings ruled over Carthage is debated. The Phoenician city states from which Carthage descended, namely Tyre had nominal monarchs but who deferred to a council of advisors who helped craft policy and administer the law. It seems reasonable that Carthage followed this political model in its earliest stages with nominal monarchs who likewise consulted a council of advisors made up Carthaginian nobility to craft and administer policy. The degree to which kings of Carthage held power probably fluctuated.
Following the First Sicilian War against the Greek colonists on Sicily in 480 BC, the nature of Carthage's government changed gradually with a weakening of the monarchy. By the 300s BC Carthage was at its peak and best characterized as an oligarchic republic. It was noted to have numerous checks and balances on the branches of government, a vast and complex administrative state, high levels of public accountability and participation in civic duty. Aristotle the famed Greek philosopher wrote on Carthage in his treatise "Politics" as the only non-Greek polity to be represented in the work.
Carthage as a republic became ruled nominally by two simultaneously elected non-hereditary magistrates called sufetes or shophets. This position's title translates as "judges" and they are said to handle a mix of judicial and executive powers. How they were elected and who was eligible for this head of state position is not known. What is known is they were always from the oligarchic ruling class of Carthage and that they held annual terms. The Roman writer Livy states this was comparable to the Roman republican practice of electing two consuls for annual terms. They are said to have ruled jointly and likewise handled matters of state through the convening and presiding over the supreme consultative council known as Adirim (similar to the Roman Senate), submitting legislation to the popular assembly and adjudicating trials. The sufetes interestingly did not hold any military power as this was separated and reserved for military commanders with the generals reporting to the Carthaginian assembly in the Adirim.
The Adirim held about 30 members on the council and like senators in Rome were elected from the wealthy elite merchant families of Carthage. They administered the treasury, conducted foreign affairs and providing some control over military affairs. It is said matters of state required unanimous decision making to go into effect.
Carthage also had judicial assembly called the One-Hundred and Four. These judges provided oversight of the military and other politicians and bureaucrats within Carthage. As an example of Carthage's political checks and balances, the One-Hundred and Four had the power administer monetary fines or even the death penalty, sometimes by crucifixion on military or government officials found to have engaged in unbecoming behavior that went against the interest of the public. It also formed small committees to provide oversight on political matters.
Separate from these bodies also came numerous junior bureaucratic positions to held administer everything from tax collection, public works and the state treasury.
Carthage also contained at local levels trade unions, a popular assembly and town meetings. In matters where the sufetes and Adirim could not decide law in a unanimous manner a popular assembly was consulted to make a final determination. Whether this was a formal institution or ad hoc solution has never been determined.
Aristotle singled out the Carthaginian government as more meritocratic than its contemporary Greek counterparts. He also praised its complex balance of monarchical, aristocratic and democratic elements. Some other Greek writers went so far as to say it was the best form of government in existence at that time only equaled in the Greek world by Sparta. Meanwhile, Aristotle himself stated that Carthage had some form of constitution and found it superior to Sparta's.
The Greek historian Polybius writing for a Greco-Roman audience in his commentary on the Punic Wars between Rome and Carthage stated that Carthage had more democratic elements than Rome did and that the common people were on average given more say than Romans at the time. However, Polybius saw this as a detriment to Carthage during the Punic Wars, in his estimate too much bickering and infighting to gain a unanimous decision led to paralysis and indecision. Whereas he favored the Roman Senate's rules which were less democratic overall and therefore more decisive in determining important decisions at crucial moments such as in war.
Carthage's republican government appears to have been replicated in the colonies and territories throughout its empire with sufetes found at local colonial levels. There appears to be cooperation between Punic colonial officials and the local population under Carthaginian rule.
Carthage was primarily mercantile in its outlook. The control of trade commodities and goods throughout the Mediterranean was the basis for its economic development and always of primary concern. Hence the merchant class-oligarchy's vested interest in maintaining power.
Military: Carthage was a classic example of a maritime power. Its navy was its most important military branch in many ways. The navy was used to ensure control over the network of trade routes between the various parts of the Western and Central Mediterranean. It would win naval victories over its Greek and Roman rivals though it would ultimately face defeat by the Romans.
The navy was large in size for antiquity and benefitted from the Phoenician advent of serial production, the ancient equivalent of assembly line production which produced ships of good quality but in an efficient manner. They could maintain hundreds of ships at one time, even after their power dimmed with the rise of Rome.
The ethnic composition of the navy's sailors, oarsman, navigators and marine force was almost exclusively Phoenician. Given the Phoenicians long association with seafaring trade and navigation, the Carthaginians merely upheld this tradition including in warfare.
The army of Carthage, its land based military branch was also crucial in achieving its geopolitical goals. From the subjugation of rebellious tribes in North Africa and Iberia to battling the Greeks and Romans in foreign wars. In conjunction with the navy the ultimate goal was maintaining Carthage's control of trade routes and upholding its sphere of influence to maintain favorable conditions for said trade.
Due to the limited population of Phoenician colonists spread throughout the Carthaginian empire and given their traditional naval prowess, much of the army was not of ethnic Phoenician/Punic background. Instead, they relied on a multinational mix of auxiliaries and mercenaries to fill the armies ranks. There might be Phoenician officers and generals such as the famed Hannibal Barca and his relatives including his father Hamilcar and brothers Mago and Hasdrubal, but many other officers could be Greeks among others. The rank and file including Greek mercenaries fighting in the hoplite style, many Greek colonists from Sicily and Southern Italy, Berber infantry and cavalry, particular the light cavalry of Numidia famed for its fast-moving skirmishers armed with javelins and the Libyan infantry. Iberian infantry and cavalry of mixed Celtic and Iberian backgrounds. The famed light skirmisher infantry from the Balearic Islands who slung stones at their enemies were likewise part of the army. Also included in the army were Gallic (Celtic) infantry and cavalry from France and Italy, Sardinians (Nuragic) and Italic peoples such as Samnites, Lucanians, Etruscans and even some Latin peoples including Roman defectors could be found among Carthage's land army. The Phoenician rank and file in the army were usually colonists from other Punic settlements and not Carthage proper. The exception being the famed 3,000 strong Sacred Band of Carthage which were derived from the strongest and healthiest of Carthage's wealthiest families to fight as an elite special unit of the army. Armed and trained int the Greek hoplite style and phalanx formation.
The army also utilized African Forest elephants as a mobile force similar to a wrecking ball. These elephants provided a fearsome complement to the army and was famously used by Hannibal Barca in his crossing of the Alps to invade Roman Italy during the Second Punic War.
The major conflicts Carthage fought in its history were its colonial wars in North Africa against Berber tribes and kingdoms, Iberia and in Sicily first against the Greeks and later against its archrival Rome. The three Punic Wars fought between Carthage and Rome have been characterized by some historians as the ultimate and perhaps most important clash of civilizations in the ancient world and perhaps of all time. Ultimately, they would all end in Rome's favor and eventual destruction and razing of Carthage by Rome, ending Rome's biggest rival and leading to Roman supremacy over the Mediterranean basin for the next several centuries.
Economy: Economic concerns were of chief importance to the Carthaginians. Their empire was essentially a commercial one or rather an expansive and complex trade network with the state trying to aggressively uphold and expand its scope. Its origins lie with the Carthage's Phoenician roots. The Phoenicians based in the Levantine coast (mainly modern Lebanon, Israel and Syria) weren't one united people but rather a series of city states, with the most powerful being based on the coast. These included the cities of Byblos, Sidon and Tyre among the leading polities and all with an outward maritime trade orientation. The Phoenicians produced many goods and economic models that would be both enriching and influential on trade throughout the ancient world. This included purple dye for fabric, uncolored glass, wine production and Lebanese cedar for timber production and the serial production economic model.
Carthage was founded in modern Tunisia by Phoenician colonists from the city of Tyre (Lebanon) in the 9th century BC. They were not the first Phoenician colony in North Africa but they eventually rose to become the most aggressive and successful. In part this was due to its secure and strategic location. It soon became the leading trade center on the Western and Central Mediterranean. They controlled trade routes at sea and rose to prominence and domination among all the other Phoenician colonies setup in North Africa, Sicily, Malta, Sardinia and Iberia.
Mining for metals silver, lead, copper and tin were of crucial importance for the wealth of Carthage, in particular this motivated their expansion into Iberia. Additionally, the temperate and fertile climate of the Western Mediterranean lead to much wine production. They also traded in amber, timber, grains an food preservatives.
While mostly a maritime trade power, Carthage also had overland caravans to secure goods from the African interior and even the Middle East. Continual exploration for new and expanding trade routes and goods was also important for Carthage. Famed Carthaginian explorers of Punic origin included Himilco the Explorer who lived in the 6th and 5th centuries BC. He is said to have been the first Mediterranean sailor to have explored the Atlantic routes to Northwest Europe, visiting Portugal, France and the British Isles. Britain in particular was important to the ancient tin trade which was necessary in bronze production. Britain was known in the ancient world to the Carthaginians and Greeks as the Tin Isles.
Hanno the Navigator was said to have explore trade routes to western Africa. Reaching as far as modern Senegal and Cameroon,
Lifespan: Carthage was said to have been founded by Phoenician colonists from the city of Tyre circa the 9th century BC. A foundation legend raised from its founding. Namely the legend of Princess Dido from Tyre leading her fellow Phoenicians not as colonists looking for commercial benefits but political refuge from her dictator brother. According to legend Dido and her retinue arrived at Tunisia and tricked the local Berber king into grating them a sizable tract of land from which the core of what became the city of Carthage was founded.
The city was given the name by its settlers of Qart-Hadasht, which in the Phoenician language meant "New City". The year 814 BC is often cited as the approximate date of its founding.
Quickly Carthage made an association with and eventual domination of fellow Phoenician colonies in the area including Utica. Its favorable climate, arable land and strategic location were all crucial to Carthage's rapid growth and dominance of over other Phoenician colonies. It would expand to conquer lands ranging from the whole of North Africa from Morocco to Libya, the islands of Malta, Sicily, Sardinia, Corsica and the Balearics and parts of the Iberian Peninsula over the coming centuries found themselves either under direct Carthaginian rule or favorable treaties incorporating the lands into its sphere of influence hence creating a trade network and empire, a classic example of a thalassocracy.
Initially, the Carthaginians paid a tribute and maintained contact to its mother city of Tyre back in Lebanon. However, this became an irregular occurrence due to Carthage's increasing independence due to its great distance from the Levant and the assertive character to its own local citizenry. Carthage began to see a mix of Phoenicians and local Berbers creating a unique Punic culture that synthesized the two cultures and ethnicities over time with the Phoenician dialect and culture remaining dominant but adaptable for its ability to incorporate other cultures. This was true as its sphere of influences expanded in the Mediterranean.
Carthage's independence was not only due to its relative distance from Tyre but due to the events back in Phoenicia. Various sieges from Babylonia and eventually later the Persian Achaemenid Empire conquered Phoenicia including Tyre circa 530-522BC. The subjugation of these lands reduced contact between the Carthaginian settlers and their Tyrian origins which had until that date sent a steady flow of colonists. While some flow of other Phoenicians would continue, the population would be buttressed by local native populaces and other Phoenician colonies rather than direct Tyrian migration.
The city of Carthage itself expanded over the centuries and created several distinct districts and architecture. At its peak in the 4th century BC, it contained a population between a quarter and half a million people. making it one of the world's largest and most prosperous cities at the time. The city had a mix of wealthy villas, apartment blocks six stories high, had warehouse and commercial districts, goods markets, a Greek style agora or public space, elaborate gardens. temples to various gods, various government buildings and a unique double harbor known as the cothon, which became the physical feature along with the Byrsa hill most associated with Carthage. The cothon featured an outer commercial harbor and military inner harbor with ship warehouses on a man-made island from which ship repairs, construction and maintenance could be addressed through its serial production. The Byrsa hill was the central district of Carthage which contained important temples, it had stair way avenues which were relatively wide for traffic, whereas most of the city's routes had narrow winding paths to navigate. The city was said to have triple walls for defenses, a shorter outer wall made of either stone or wood, followed by a ditch, a second taller stone wall 5 meters thick, a second ditch and a third stone wall 10 meters thick and with armed towers able to hold a force of over 20,000 troops.
In 509 BC it signed its first treaty with Rome, its eventual rival which at the time was the inferior power still clamoring for power on the Italian peninsula. The treaty was meant to demarcate their respective spheres of influence. From 580-265 BC, the Carthaginians found themselves in a series of wars with the Greek colonies of Sicily and Southern Italy. Namely, the city state of Syracuse which was the principal Greek settlement on Sicily.
These wars were back and forth in nature, marked by victory and defeat on land and sea for both sides. Eventually Carthage would retain control over the western half of Sicily until its loss of control in the Punic Wars with Rome. The Sicilian Wars also saw the gradual weakening of the kings of Carthage and its transition to an oligarchic republic (see government section).
The Punic Wars (264-146 BC) began almost by accident with neither Rome nor Carthage initially planning a direct confrontation with the other. The city of Messana (Messina) in Sicily found itself in the 260s BC under the control of a group of Italian mercenaries who had previously served the tyrant (king) of Syracuse who had died in 280 BC. These independent mercenaries were a threat to both Carthage and Syracuse's interests on Sicily. These mercenaries named the Mamertimes (Sons of Mars) divided into two factions, over the issue of the new Syracuse tyrant Hiero II's planned retaking of Messana. One faction advocating a Carthaginian intervention to take charge of the city's security and the other advocating for Roman intervention from the Italian peninsula. Carthage arrived first with a land garrison and naval fleet in the harbor. The Roman Senate was reluctant to assist the mercenaries but recognized the potential threat a permanent presence of Carthaginians in Messana and its location on the narrow Straits of Messina between Sicily and Italian mainland could pose on Roman trade and security. It advocated sending an expeditionary force to retake Messana to eject the Carthaginians. The attack triggered the first Punic War between the two powers. It turned into a quarter century struggle that was marked by intense fighting mostly on Sicily.
The First Punic War was ultimately a Roman victory that ended Carthage's presence on Sicily. It also saw Roman advances in naval technology such as the corvus to help board Carthaginian ships. Hitherto the Romans had little naval strength relative to Carthage but its innovations in naval warfare proved crucial in undermining Carthage's longstanding naval superiority. Meanwhile on land, despite the back-and-forth nature of the battles, the Roman army's tactical flexibility often proved superior to Carthage which after 23 exhausting years agreed to peace. It gave up control of Sicily to Rome (aside from Syracuse) and paid a tribute over the course of 10 years.
Rome also after the war used Carthage's distraction against a Libyan rebellion in the Truceless War to take control of Sardinia and Corsica in 238 BC.
To compensate for the loss of territory on Sicily, Sardinia and Corsica, the Carthaginians under Hamilcar Barca tried to expand its territory in Iberia against Celtic and Iberian tribes especially to profit from increased mining production. They also gained new manpower and agricultural production to boost their economy and military again. They also had a standing agreement with Rome to not intrude north or south of the Ebro River respectively. However, an Iberian city of Saguntum south of the Ebro had an agreement with the Romans. This upset the balance of power established with Carthage in Iberia. Hamilcar Barca's son Hannibal now in charge of the Carthaginian army in Iberia an avowed enemy of Rome, besieged Saguntum which he took in 8 months. This is turn led to Rome's declaration of war, starting the Second Punic War which lasted for the next 17 years.
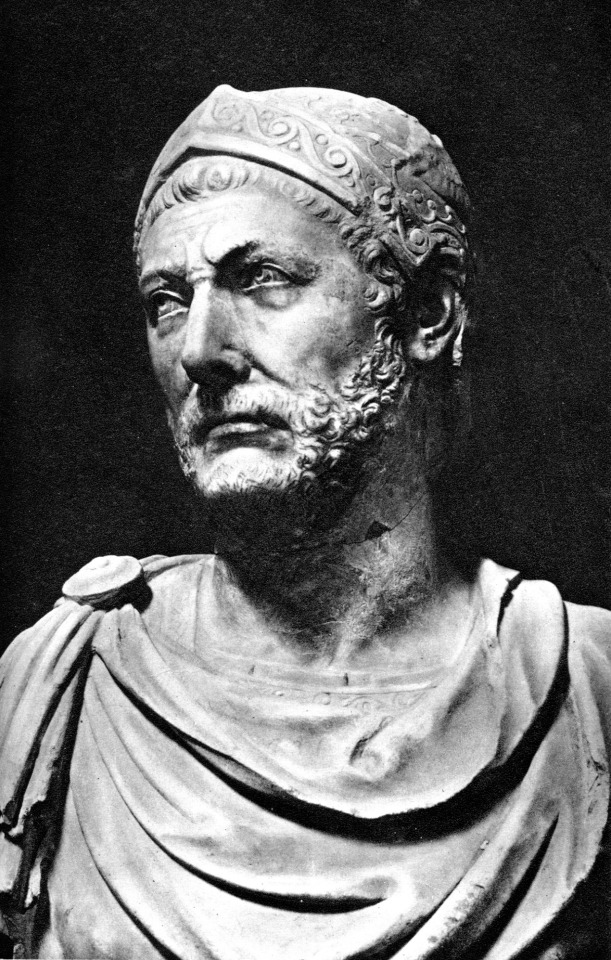
In one of the most famous military campaigns of all time, Hannibal and his army complemented by Carthaginians, Numidians, Celts, Iberians crossed the Alps and invaded Italy, taking the war to Rome's home territory. Hannibal showing his tactical prowess would defeat Roman armies repeatedly on their own territory most notably at the Battle of Cannae in 216 BC. Many Italian cities that had been incorporated into Roman rule over the previous centuries rose up to join Hannibal against Rome. However, Hannibal never had sufficient strength to directly besiege Rome. Rome was constantly tested by Hannibal's victories over the next 13 years in Italy, but they refused to surrender and adopted an attritional strategy, and this wore down Hannibal by gradually retaking Italian cities allied to him if not able to defeat him directly. Likewise, they repelled Carthage's attempts to reinforce him in Italy. They also faced mixed success gradually conquering Iberia from the Carthaginians. Finally, an invasion of Tunisia forced Carthage to recall Hannibal back to North Africa to defend the capital from a Roman assault. He met the Romans in the Battle of Zama in 202 BC which resulted in a Roman victory over Hannibal himself at once.
Hannibal advocated for the government of Carthage to negotiate a treaty with Rome which it did. Its terms were harsh. A stripping of all overseas possessions of Carthage in Iberia and elsewhere including some African territories. A large punitive indemnity to paid to Rome over 50 years. A reduction of Carthage's navy ten warships, a ban on Carthage's use of war elephants. A prohibition on Carthage being able to fight war outside of Africa and any war it wages in Africa must require Rome's express permission.
Hannibal eventually became a sufete in Carthage and worked to reform the government of Carthage and stamp out corruption so as to ensure its ability to pay Rome its due from the treaty and rebuild its economy. Indeed, Hannibal was somewhat successful in his regards and Carthage's economy was somewhat rebounding but facing pressure from Rome and enemies in the local government, he went into voluntary exile in service to Greek states opposed to Roman expansion in the east. He died in exile under murky circumstances variously described as a suicide or murder.
The Third Punic War 149-146BC began will Carthage went to war in Africa with Berbers who were raiding its territory and without Rome's permission, this was used a pretext to attack Carthage itself by Rome for violating its treaty from the previous war. The third and final Punic War was characterized by a three-year siege of Carthage. Ultimately, the Romans after much pressure on both sides broke through its triple walls and assaulted Carthage in street-by-street fighting. The city was razed to the ground, much of its population killed by angered Roman troops. 50,000 Carthaginians were enslaved and sent elsewhere through the Roman Republic's empire. Carthage was no more as an independent political entity after 146 BC. A century later, Rome rebuilt the city on its ruins as part of its empire and it remained an important city within the Roman Empire until the fall of the Western half of the empire where it fell to the Germanic barbarians the Vandals who had their capital in Carthage, it was reclaimed by the Easter Roman Empire (Byzantine Empire) by the forces of Belisarius in service to Justinian I. Carthage would face a final destruction as a Roman city when the Arabs of the Umayyad Caliphate destroyed the city in the year 698 AD. It never rose as a city again, instead its ruins remain part of the suburbs or the modern city of Tunis, capital of Tunisia.
Carthage despite its being steeped in legend and mystery remains worthy of study as one of the undeniably great civilizations of antiquity. A fact recognized by its contemporaries whether they wrote of it a complimentary fashion or with contempt, its power, wealth and influence was immense enough to engender scholarly study and reflection at the time. It is for these contemporary recognitions whether positive or negative and absence of surviving self-records that many continue its study into the modern age. Particularly its opposition to Rome and the perception by Rome that it was a worthy rival that needed complete annihilation, especially given Carthage's ability to stand up to Rome in a way no other power really could at its peak.
The more Carthage is analyzed both by its contemporary foreign commentators with the surviving archaeological and fragmentary historical record, the more nuance can be shed on the complexity of the civilization and influence it had on world history. Its opposition to Rome might be its most noted aspect but it shouldn't overshadow how else Carthage influenced the world. From its complex style of government and network of commercial imperialism that presaged future thalassocracies such as the Italian republics of the Middle Ages like Venice and Genoa and how it produced economic production models which influenced Rome and Greece and subsequently other areas of the world, they carried that influence on to. Likewise, another legacy of Carthage was how it helped build an ancient iteration of a globalized economy, shrinking the gap between the long distances of the ancient Mediterranean world by linking disparate geographies and peoples under a common commercial interest. In this commercial pursuit it also revealed itself to have both a distinct dominant culture but one that was not intolerant or unable to accommodate and absorb other cultural influences. In many ways ancient Carthage by way of its influence on Greece and Rome and their own influences give us glimpses into how its existence served as a precursor to the modern world we inhabit.
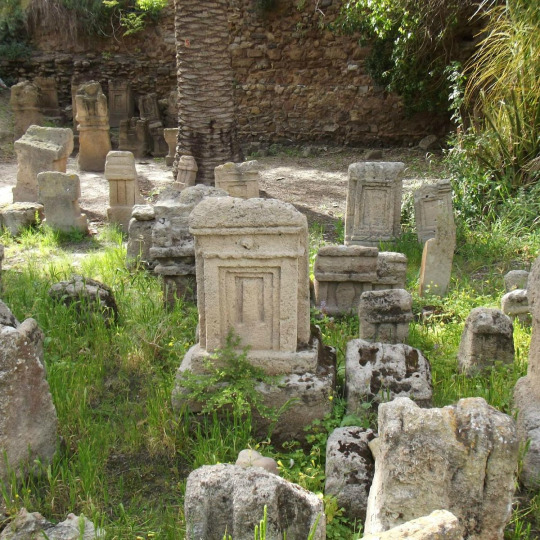










#history#military history#ancient history#ancient world#ancient ruins#ancient carthage#carthage#ancient rome#ancient greece#tunisia#iberia#hannibal#scipio africanus#ancient phoenicia#phoenician#punic wars#sardinia#sicily#corsica#malta#balearic
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
This is so embarrassing to admit but right now I'm watching the new oversimplified video (yes, he posted a new video. It's gonna be a good decade.) and I'm actually getting fired up with suspense on ancient history. I even picked sides and got really invested. Like bitch, when I catch Scipio, Scipio when I catch you. You copying little bitch come up with your own tactics STOP STEALING FROM THE MAN, THE MYTH, THE LEGEND HANNIBAL.
#hannibal barca#hannibal#Scipio the younger#I just saw that Hannibal has a tag on tumbler and Scipio doesn't#TAKE THAT YOU CONNIVING LITTLE BITCH#oversimplified#history#world history#history channel#histoire#history lovers#carthage#rome#ancient rome#roman empire#punic wars#HANNIBAL (barca) THE MAN THE MUTH THE LEGEND
25 notes
·
View notes
Text
You SCORN Dido? You scorn her over prophecy?
Oh! Oh! Blood feuds for Aeneas! Blood feuds for one thousand years!
33 notes
·
View notes
Text
Quote I said in my classics class (the teacher was talking about the impact of the Punic wars on Roman society):
“Carthage was the Roman Empire’s Roman Empire”
#Roman empire#Rome#Punic ears#Carthage#the aeneid#<- I was studying it#classics#classical civilisation#Ancient Rome
26 notes
·
View notes
Text

Gold earring uncovered near Cadiz, Spain, Carthaginian, 6th-3rd century BC
from The National Archaeological Museum, Madrid
201 notes
·
View notes
Text

Hannibal Crossing the Alps by Francisco Goya
#hannibal barca#hannibal#alps#italy#art#francisco goya#antiquity#carthaginian#carthaginians#carthage#punic wars#second punic war#rome#ancient rome#ancient carthage#roman#romans#history#europe#european#mediterranean#cisalpine gaul#roman republic
139 notes
·
View notes
Text

Ancient Warship’s Bronze Battering Ram Sunk During a Battle Between Rome and Carthage Found
Found near the Aegadian Islands, just west of Sicily, the bronze rostrum played a role in the last battle of the First Punic War, which ended in 241 B.C.E.
In 241 B.C.E., two empires faced off in a naval clash off the coast of Sicily. By then, Rome and Carthage had been fighting for more than two decades. Rome’s victory in the skirmish, officially called the Battle of the Aegates, brought an end to the First Punic War, the initial conflict in a series of wars between the two ancient powers.
Now, explorers have recovered a piece of that final battle: the bronze battering ram of an ancient warship. According to a statement from Sicily’s Superintendence of the Sea, the ram was found on the seafloor off the western coast of the Mediterranean island, at a depth of around 260 feet. To retrieve the artifact, the team used deep-water submarines from the Society for Documentation of Submerged Sites (SDSS) and the oceanographic research vessel Hercules.
The seabed off the Aegadian Islands “is always a valuable source of information to add further knowledge about the naval battle between the Roman and Carthaginian fleets,” Regional Councilor for Cultural Heritage Francesco Paolo Scarpinato tells Finestre sull’Arte. He adds that the find is yet another confirmation of the work of the late archaeologist Sebastiano Tusa, who spearheaded exploration of the seabed as the site of the 241 battle after a separate ram, also known as a rostrum, was first found there in the early 2000s. In the two decades since, researchers have recovered at least 25 rams from the seabed.
At the time of the Battle of the Aegates, Rome and Carthage had been at war for 23 years, fighting for dominance in the Mediterranean. As the Greek historian Polybius later wrote, the Romans sank 50 Carthaginian ships and captured another 70 along with their crews, taking nearly 10,000 sailors prisoner during the naval battle. Rome forced Carthage to surrender. But the fragile peace was short-lived: Over the next century, Rome would go on to fight a second and third war against the Punic people, winning each time.
“It was very costly, both in terms of human life and economically,” Francesca Oliveri, an archaeologist at the superintendence, told BBC News’ Alessia Franco and David Robson in 2022. “In the last phase, Rome even had to ask for a loan from the most well-to-do families to arm the fleet and build new boats.”




The recently discovered ram has been brought to Favignana, one of the Aegadian Islands, for further study. Though its features are difficult to make out because the object is covered in marine life, researchers have been able to discern a decoration on its front: a relief depicting a Montefortino-style Roman helmet decorated with three feathers.
The battering ram adds to the wealth of war relics found on the seabed, which also include 30 Roman soldiers’ Montefortino helmets, two swords, coins and many clay amphorae (large storage jars).
According to the SDSS, rams were the most important naval weapons of their time. They were placed on the bows of warships at water level so that sailors could crash their boats into enemy vessels, damaging and sinking them. The plethora of rams scattered on the seabed are testaments to the weapons’ effectiveness in ancient battle.
“We are finding so many things that help to illustrate a little better the world of the third century [B.C.E.],” Oliveri told BBC News in 2022. “It’s the first site of a naval battle, in the world, that has been scientifically documented like this, and it will continue to be documented—because the area of interest is very large. … It will take at least another 20 years to explore it fully.”
By Sonja Anderson.


#Ancient Warship’s Bronze Battering Ram Sunk During a Battle Between Rome and Carthage Found#roman rostrum#bronze#bronze rostrum#bronze battering ram#Battle of the Aegates#First Punic War#ancient artifacts#archeology#archeolgst#history#history news#ancient history#ancient culture#ancient civilizations#roman history#roman empire
28 notes
·
View notes
Text
Carthaginian Woman with Raised Arms
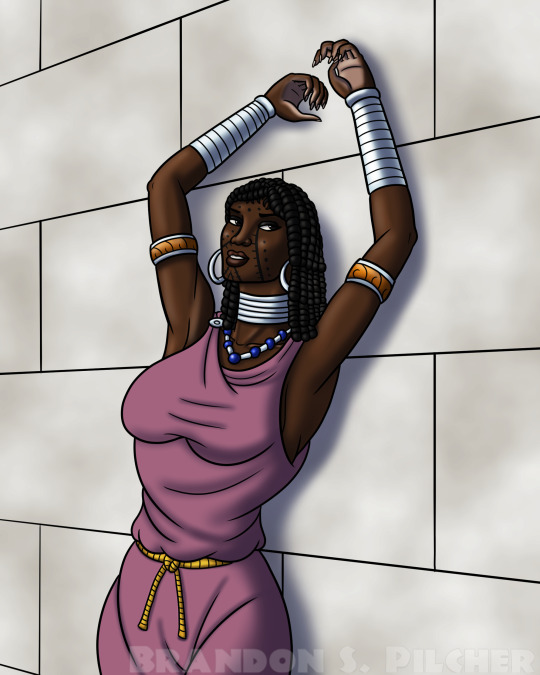

What began as simple practice drawing a woman with raised arms became this random dudette from ancient Carthage. Her hairstyle, which I believe is called “twists”, is based on that of a Carthaginian bust on display at the British Museum in London, UK.
#ancient carthage#ancient#carthaginian#north african#african#black woman#woman of color#dark skin#afro twists#digital art#art
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Photos from Ancient Carthage (814BC-146BC)
Ancient Carthage was a city state in the time of antiquity that exists in present day Tunis, Tunisia in North Africa. It was founded around the year 814BC by Phoenician (Punic) settlers who emanated from the Levant, in modern day Lebanon, Syria & Israel. The Phoenicians were a civilization that spoke a Semitic language & engaged in a society that primarily was interested in trade & commerce throughout the Mediterranean Sea.
The Phoenicians settled in trade colonies throughout the Mediterranean basin in not only their West Asian homeland but Europe & North Africa all the way to modern day Spain & Morocco. Their best-known trade colony was Carthage or “Qart-hadast” which meant “New City” in their language. This was strategically located where modern Tunis sits. It was located on a strip of land that allowed shelter from storms on the North African coast & was well placed near the center of the Mediterranean Sea & its trade routes crisscrossing between the east & west. The settlers who established Carthage were Phoenicians colonists from the city of Tyre in modern Lebanon, one of the three major city-states of Phoenicia alongside Sidon & Byblos.
These Phoenician colonists reached Tunisia around 814 BC & like their other settlements in Libya & elsewhere they had to deal with the native populations, in this case the Berber or Amazigh peoples who inhabited North Africa from Morocco to Libya. Originally a daughter city under the rule from Tyre, they gained autonomy when Tyre & the rest of Phoenicia fell under the control of the Neo-Assyrian Empire around 650 BC. From that point on Carthage became not only an independent city-state but established a mostly sea-trade based empire or thalassocracy. It became a flourishing metropolis & dominated the Western Mediterranean for centuries.
Carthage was a monarchy until about 480 BC before becoming a republic & their sea-based commercial empire presaged the later Italian sea-based republics of Venice & Genoa over a thousand years later. Their complex system of governance, language (Punic or Western Phoenician dialect), religion & other cultural aspects are still only partially understood in the modern era due to biased contemporary foreign sources & little surviving local record.
At their peak they controlled North Africa’s coast from Libya in the east to Morocco in the west. Much of Spain, the Balearic Islands, Malta, half of Sicily, all of Sardinia & Corsica. They fought wars with the Berbers who lived inland in North Africa along with the Greek city-states that settled in Sicily & southern Italy & likewise engaged in trade with these peoples. The Phoenician settlers (Carthaginians) were often not numerous enough to make up their whole military strength. Though the Phoenicians dominated their navy while their land-based military consisted of mercenaries from the Berbers of North Africa, Greek hoplites, Sardinians, Italo-Sicilians, Corsicans & the Celts & Iberians of Spain and the Balearic Islands to complement their own elite Phoenician infantry, the Sacred Band of Carthage.
Eventually over the course of the three Punic Wars with the emerging Roman Republic, Carthage lost its power & prestige. Though it produced several military leaders of tactical & strategic renowned, the most famous being Hannibal Barca (247BC-181BC) who crossed the Alps & invaded Italy from the north inflicting several defeats on the Roman army on their native Italian soil but he was never able to take Rome itself. Eventually attrition & the threat of a Roman counterattack against Carthage itself forced Hannibal to leave for his North African home. He was eventually defeated by the Romans & finally in the Third & final Punic War, Rome destroyed ancient Carthage in 146 BC, it is said they tilled the surrounding fields in salt so that no new crops could grow & the threat of Carthage would never rise again. The Romans eventually rebuilt Carthage & included the city as their own within the Africa province of their empire. It flourished again as a center of Roman trade but eventually fell to Germanic invaders such as the Vandals before being retaken by the Byzantine Empire in the 6th Century AD before falling again to the Arab Muslim invaders in the 7th century as Islam spread across North Africa. Medieval Carthage continued as a residential town but eventually the modern city of Tunis began encircling its original Punic & later Roman ruins...
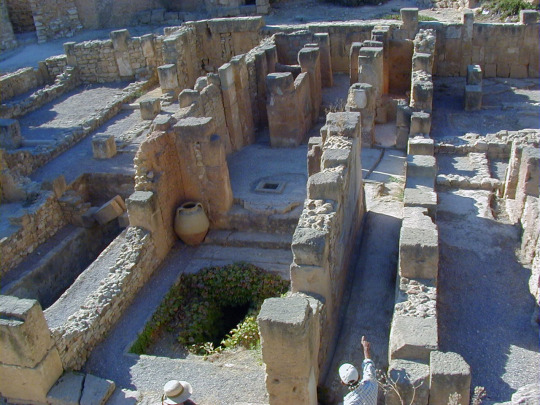
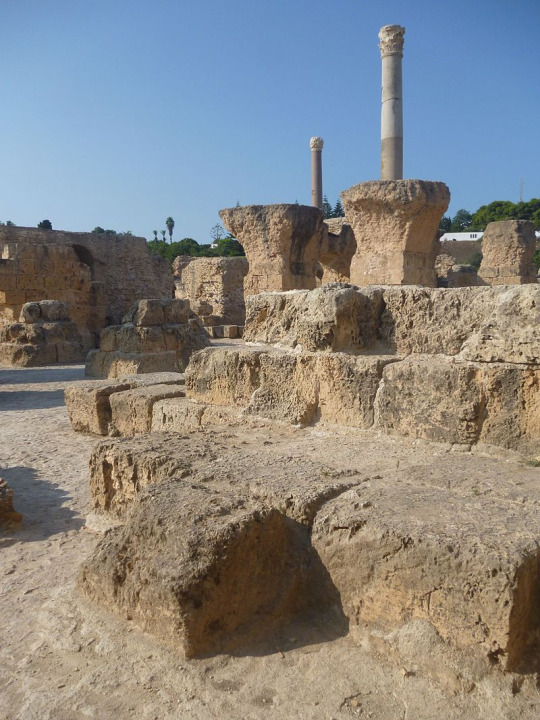
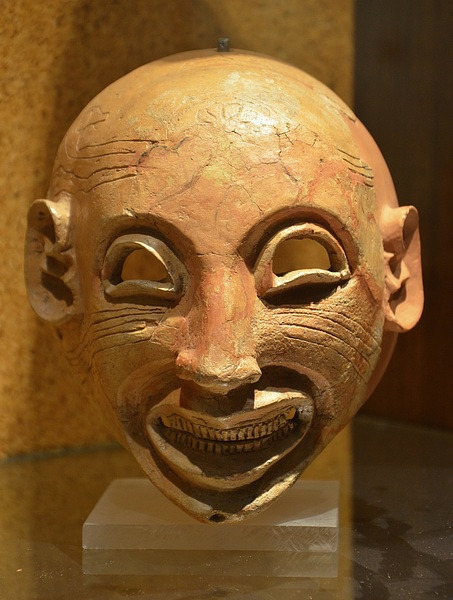
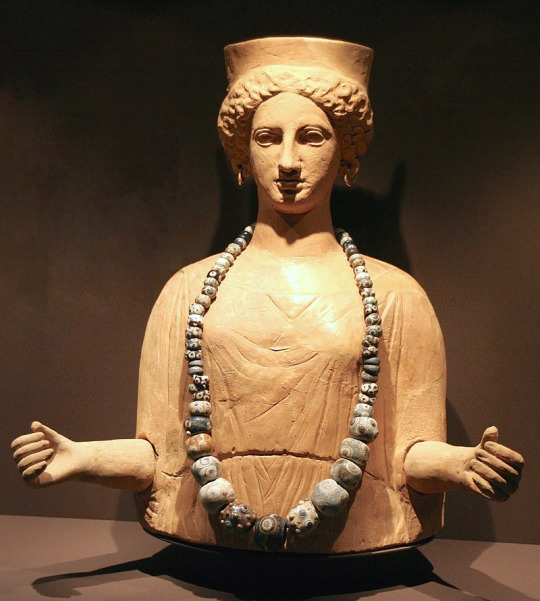












#antiquity#ancient carthage#punic wars#hannibal#ancient rome#tunisia#north africa#ancient world#ancient history#carthage#rome#mediterranean#phoenicia#ancient phoenicia#tyre#baal hamon#tanit#dido#ancient ruins
24 notes
·
View notes

