#ai responsibility
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text


Last summer, as a spike in violent crime hit New Orleans, the city council voted to allow police to use facial-recognition software to track down suspects. It was billed as an effective, fair tool to ID criminals quickly. A year after the system went online, data show the results have been almost exactly the opposite. Records obtained and analyzed by POLITICO show the practice failed to ID suspects a majority of the time and is disproportionately used on Black people. We reviewed nearly a year’s worth of New Orleans facial recognition requests, sent for serious felony crimes including murder and armed robbery. In that time, New Orleans PD sent 19 requests. Of the 15 that went through: 14 were for Black suspects 9 failed to make a match Half of the 6 matches were wrong 1 arrest was made While it hasn’t led to any false arrests, police facial identification in New Orleans appears to confirm what civil rights advocates have argued for years: that it amplifies, rather than corrects, the underlying human biases of the authorities that use them. U.S. lawmakers of both parties have tried for years to limit how police can use facial recognition, but have yet to enact any laws. Some states have passed limited rules, like those preventing its use on body cameras in California or banning its use in schools in New York. A few left-leaning cities have fully banned law enforcement use of the technology. For two years, in the wake of the George Floyd protests, New Orleans was one of them. “This department hung their hat on this,” said New Orleans Councilmember At-Large JP Morrell, a Democrat who voted against lifting the ban and has seen the NOPD data. Its use of the system, he says, has been “wholly ineffective and pretty obviously racist.” (NOPD denies that its usage of facial recognition is racially biased). Politically, New Orleans’ City Council is split on facial recognition, but a slim majority of its members — alongside the police, mayor and local businesses — still support its use, despite the results of the past year.
x

#racism in ai#ai ethics#bias in tech#ai for social justice#algorithmic bias#ai responsibility#inclusive tech#ai and racism
62 notes
·
View notes
Text
14✨The Dark Side of Algorithms: Fake Accounts and AI-Driven Manipulation in Social Media
As AI continues to integrate itself into the fabric of modern life, the ethical challenges surrounding its use become increasingly critical. Nowhere is this more evident than in the world of social media, where artificial intelligence is being used to create fake accounts, skew public discourse, and promote harmful content for the sake of engagement. Platforms like Facebook, Twitter (X), and…

View On WordPress
#AI algorithms#AI algorithms in social media#AI and compassion#AI and ethics#AI and hate speech#AI and human influence#AI and misinformation#AI and public discourse#AI and transparency#AI and truth#AI for the greater good#AI impact on society#AI in social media#AI manipulation#AI responsibility#AI-driven manipulation#AI-generated content#algorithm accountability#corporate responsibility AI#ethical AI#Facebook fake accounts#fake accounts#Nexus book#social media bots#Twitter bot accounts#Yuval Noah Harari
0 notes
Text

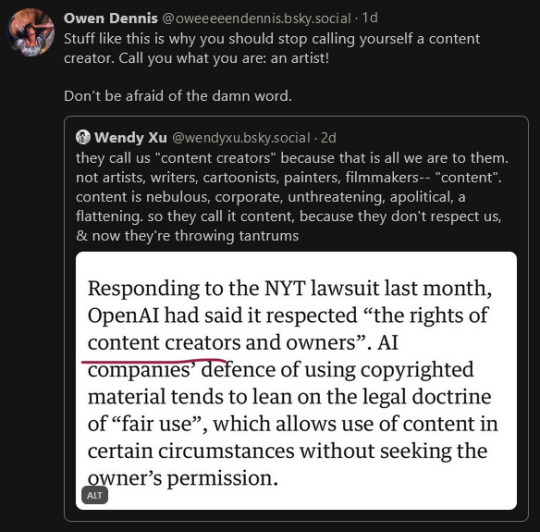
"content creator" is a corporate word.
we are artists.
#anti ai#fuck ai#artists on tumblr#please do not call me or any artist a content creator#i'm an artist. a fanartist. a designer. but not a content creator#ai clowns in my replies will be deleted and blocked without response so do not waste your breath#you are not an 'artist' for generating an image any more than you are a chef for ordering from a restaurant. someone Else did the work.#owen dennis just deleted all his blue sky stuff again and i hate that he does that because he makes such interesting comments#about the entertainment industry lmao i need to just. start screenshotting every smart thing he says#anyway thats why i decided to finally make this when its been sitting in drafts for a few months#owen dennis#edit - if you dont know who owen dennis is he's the creator of one of the best animated series of the last 20 years (Infinity Train)#he's very open about talking about art and the entertainment/animation industry on social media and in his newsletter and hes so cool 4 it
9K notes
·
View notes
Text
i genuinely don't care how good a piece of ai generated art or writing looks on the surface. i don't care if it emulates brush strokes and metaphor in a way indistinguishable from those created by a person.
it is not the product of thoughtful creation. it offers no insights into the creator's life or viewpoint. it has no connection to a moment in time or a place or an attitude. it has no perspective. it has no value.
it's empty, it's hollow, and it exists only to generate clicks (and by extension, ad revenue.)
it's just another revolting symptom of the disease that is late stage capitalism, and it fucking sucks.
#''but i just want to use it to--'' don't care! it's shit! stop fucking feeding it!#if you need help generating ideas or jumping off points then join an artist or writer group online#talk to people#make connections#that's what art and writing is supposed to be about in the first place#i'm mad as hell etc.#so goddamn sick and tired of seeing ai shit get passed around on here#it's bad enough in general but every time i see more of it showing up#tagged as fan art or as fic#the angrier i get#heartfelt imperfection in art and writing will always ALWAYS be worth more than the most technically ''perfect'' ai generated image or text#fandom problems#ai generation algorithms die in a fire challenge 2k23#just a heads up that i'm muting this post and will no longer see responses to it#because i'm tired of seeing dogshit takes from jackasses who want to ''debate'' me#there's no debate you're in the wrong on literally every level and you can die mad about it
10K notes
·
View notes
Text



Todays scribblings
#im trying to post more#ive become very self critical and also just the general ai stuff has had me feeling like not posting for a long time#but i like interacting and i like sharing and reading responses#so im fighting through it#my art#sketch#digital sketch#creature design#monster design#monster oc#oc art#fantasy art#animal death//#macabre art#dark art#sketchbook
817 notes
·
View notes
Text

#genshin impact#kaeya alberich#genshin kaeya#genshin ella musk#the genshin + duolingo collab made me so angry i scribbled this in mspaint in response#gd language owl using ai instead of real translators#originally posted it on twt with no text or tags and it somehow got 1.3k likes lmao#comic#2024
196 notes
·
View notes
Text
Aster™ Terror Star! (Ukagaka/Desktop Buddy)




(contents of this post are mirrored in website linked above, check out that page too!)
On a random browsing session, you come across a name you've only heard offhandedly mentioned by some tech nerds: Aster Assistant Software. A download of a software announced and swiftly forgotten, just freely available in a distant corner of the internet. Thinking you may have found a piece of history, you quickly download it to see what that's all about. What you got instead, was an AI that seemingly never shuts up.
It's done! Continuation of Aster™️Assistant Software, though doesn't require you play it whatsoever. As most ukagakas, requires SSP to run. Link includes an explanation as to what those are and installation instructions.
Based on the Simplicity template by Zichqec. Using SSP on Windows is recommended.
Content warnings:
⚠️ Unreality: No 4th wall, meta themes.
⚠️ Photosensitivity: Character often vibrates in place, and has glitchy effects involving minor flashing lights. You will be asked whether you prefer these on or off.
Features:
A lot of yapping! Said yapping can be adjusted to be less or more frequent;
Longer yapping, giving a bit of insight into Aster's journey;
A little bit of insight on the digital world from the perspective of a living software*;
Capacity to be bothered, just a little bit;
Basic display of file and folder properties, with a little bit of information about some common file formats;
Basic sound playback, if you need to check a file in a jiffy;
May converse with a certain past iteration of itself (Make sure it's on latest version!);
For accessibility: you can reduce glitching effects to remove flashing lights, and turn of the shaking effect if necessary.
(* Information that isn't blatant sci-fi is partially based in publicly available information and personal experience. It may not be 100% accurate, and is provided purely for entertainment purposes. I am by no means an expert!)
Download here!
Instructions for installation are linked to in the page. Please follow them carefully! If anything seemingly goes off the rails, please let me know!
#ukagaka#english ukagaka#ukagaka ghost#desktop buddy#desktop toy#webcore#frutiger aero#cybercore#robot oc#ai oc#artists on tumblr#oc#original character#aster#aldebaran (aster)#CaelOS#'I only need a couple of months more' i said SURPRISE IT'S FUCKING DONE#edit 27.10: if the screenshots seem different it's because they are#i replaced some of these to reflect the tail change in his animations#the petting response is better in the old one so im leaving it in tho
216 notes
·
View notes
Text
AI “art” and uncanniness

TOMORROW (May 14), I'm on a livecast about AI AND ENSHITTIFICATION with TIM O'REILLY; on TOMORROW (May 15), I'm in NORTH HOLLYWOOD for a screening of STEPHANIE KELTON'S FINDING THE MONEY; FRIDAY (May 17), I'm at the INTERNET ARCHIVE in SAN FRANCISCO to keynote the 10th anniversary of the AUTHORS ALLIANCE.

When it comes to AI art (or "art"), it's hard to find a nuanced position that respects creative workers' labor rights, free expression, copyright law's vital exceptions and limitations, and aesthetics.
I am, on balance, opposed to AI art, but there are some important caveats to that position. For starters, I think it's unequivocally wrong – as a matter of law – to say that scraping works and training a model with them infringes copyright. This isn't a moral position (I'll get to that in a second), but rather a technical one.
Break down the steps of training a model and it quickly becomes apparent why it's technically wrong to call this a copyright infringement. First, the act of making transient copies of works – even billions of works – is unequivocally fair use. Unless you think search engines and the Internet Archive shouldn't exist, then you should support scraping at scale:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/09/17/how-to-think-about-scraping/
And unless you think that Facebook should be allowed to use the law to block projects like Ad Observer, which gathers samples of paid political disinformation, then you should support scraping at scale, even when the site being scraped objects (at least sometimes):
https://pluralistic.net/2021/08/06/get-you-coming-and-going/#potemkin-research-program
After making transient copies of lots of works, the next step in AI training is to subject them to mathematical analysis. Again, this isn't a copyright violation.
Making quantitative observations about works is a longstanding, respected and important tool for criticism, analysis, archiving and new acts of creation. Measuring the steady contraction of the vocabulary in successive Agatha Christie novels turns out to offer a fascinating window into her dementia:
https://www.theguardian.com/books/2009/apr/03/agatha-christie-alzheimers-research
Programmatic analysis of scraped online speech is also critical to the burgeoning formal analyses of the language spoken by minorities, producing a vibrant account of the rigorous grammar of dialects that have long been dismissed as "slang":
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/373950278_Lexicogrammatical_Analysis_on_African-American_Vernacular_English_Spoken_by_African-Amecian_You-Tubers
Since 1988, UCL Survey of English Language has maintained its "International Corpus of English," and scholars have plumbed its depth to draw important conclusions about the wide variety of Englishes spoken around the world, especially in postcolonial English-speaking countries:
https://www.ucl.ac.uk/english-usage/projects/ice.htm
The final step in training a model is publishing the conclusions of the quantitative analysis of the temporarily copied documents as software code. Code itself is a form of expressive speech – and that expressivity is key to the fight for privacy, because the fact that code is speech limits how governments can censor software:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2015/04/remembering-case-established-code-speech/
Are models infringing? Well, they certainly can be. In some cases, it's clear that models "memorized" some of the data in their training set, making the fair use, transient copy into an infringing, permanent one. That's generally considered to be the result of a programming error, and it could certainly be prevented (say, by comparing the model to the training data and removing any memorizations that appear).
Not every seeming act of memorization is a memorization, though. While specific models vary widely, the amount of data from each training item retained by the model is very small. For example, Midjourney retains about one byte of information from each image in its training data. If we're talking about a typical low-resolution web image of say, 300kb, that would be one three-hundred-thousandth (0.0000033%) of the original image.
Typically in copyright discussions, when one work contains 0.0000033% of another work, we don't even raise the question of fair use. Rather, we dismiss the use as de minimis (short for de minimis non curat lex or "The law does not concern itself with trifles"):
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/De_minimis
Busting someone who takes 0.0000033% of your work for copyright infringement is like swearing out a trespassing complaint against someone because the edge of their shoe touched one blade of grass on your lawn.
But some works or elements of work appear many times online. For example, the Getty Images watermark appears on millions of similar images of people standing on red carpets and runways, so a model that takes even in infinitesimal sample of each one of those works might still end up being able to produce a whole, recognizable Getty Images watermark.
The same is true for wire-service articles or other widely syndicated texts: there might be dozens or even hundreds of copies of these works in training data, resulting in the memorization of long passages from them.
This might be infringing (we're getting into some gnarly, unprecedented territory here), but again, even if it is, it wouldn't be a big hardship for model makers to post-process their models by comparing them to the training set, deleting any inadvertent memorizations. Even if the resulting model had zero memorizations, this would do nothing to alleviate the (legitimate) concerns of creative workers about the creation and use of these models.
So here's the first nuance in the AI art debate: as a technical matter, training a model isn't a copyright infringement. Creative workers who hope that they can use copyright law to prevent AI from changing the creative labor market are likely to be very disappointed in court:
https://www.hollywoodreporter.com/business/business-news/sarah-silverman-lawsuit-ai-meta-1235669403/
But copyright law isn't a fixed, eternal entity. We write new copyright laws all the time. If current copyright law doesn't prevent the creation of models, what about a future copyright law?
Well, sure, that's a possibility. The first thing to consider is the possible collateral damage of such a law. The legal space for scraping enables a wide range of scholarly, archival, organizational and critical purposes. We'd have to be very careful not to inadvertently ban, say, the scraping of a politician's campaign website, lest we enable liars to run for office and renege on their promises, while they insist that they never made those promises in the first place. We wouldn't want to abolish search engines, or stop creators from scraping their own work off sites that are going away or changing their terms of service.
Now, onto quantitative analysis: counting words and measuring pixels are not activities that you should need permission to perform, with or without a computer, even if the person whose words or pixels you're counting doesn't want you to. You should be able to look as hard as you want at the pixels in Kate Middleton's family photos, or track the rise and fall of the Oxford comma, and you shouldn't need anyone's permission to do so.
Finally, there's publishing the model. There are plenty of published mathematical analyses of large corpuses that are useful and unobjectionable. I love me a good Google n-gram:
https://books.google.com/ngrams/graph?content=fantods%2C+heebie-jeebies&year_start=1800&year_end=2019&corpus=en-2019&smoothing=3
And large language models fill all kinds of important niches, like the Human Rights Data Analysis Group's LLM-based work helping the Innocence Project New Orleans' extract data from wrongful conviction case files:
https://hrdag.org/tech-notes/large-language-models-IPNO.html
So that's nuance number two: if we decide to make a new copyright law, we'll need to be very sure that we don't accidentally crush these beneficial activities that don't undermine artistic labor markets.
This brings me to the most important point: passing a new copyright law that requires permission to train an AI won't help creative workers get paid or protect our jobs.
Getty Images pays photographers the least it can get away with. Publishers contracts have transformed by inches into miles-long, ghastly rights grabs that take everything from writers, but still shifts legal risks onto them:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/06/19/reasonable-agreement/
Publishers like the New York Times bitterly oppose their writers' unions:
https://actionnetwork.org/letters/new-york-times-stop-union-busting
These large corporations already control the copyrights to gigantic amounts of training data, and they have means, motive and opportunity to license these works for training a model in order to pay us less, and they are engaged in this activity right now:
https://www.nytimes.com/2023/12/22/technology/apple-ai-news-publishers.html
Big games studios are already acting as though there was a copyright in training data, and requiring their voice actors to begin every recording session with words to the effect of, "I hereby grant permission to train an AI with my voice" and if you don't like it, you can hit the bricks:
https://www.vice.com/en/article/5d37za/voice-actors-sign-away-rights-to-artificial-intelligence
If you're a creative worker hoping to pay your bills, it doesn't matter whether your wages are eroded by a model produced without paying your employer for the right to do so, or whether your employer got to double dip by selling your work to an AI company to train a model, and then used that model to fire you or erode your wages:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/02/09/ai-monkeys-paw/#bullied-schoolkids
Individual creative workers rarely have any bargaining leverage over the corporations that license our copyrights. That's why copyright's 40-year expansion (in duration, scope, statutory damages) has resulted in larger, more profitable entertainment companies, and lower payments – in real terms and as a share of the income generated by their work – for creative workers.
As Rebecca Giblin and I write in our book Chokepoint Capitalism, giving creative workers more rights to bargain with against giant corporations that control access to our audiences is like giving your bullied schoolkid extra lunch money – it's just a roundabout way of transferring that money to the bullies:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/08/21/what-is-chokepoint-capitalism/
There's an historical precedent for this struggle – the fight over music sampling. 40 years ago, it wasn't clear whether sampling required a copyright license, and early hip-hop artists took samples without permission, the way a horn player might drop a couple bars of a well-known song into a solo.
Many artists were rightfully furious over this. The "heritage acts" (the music industry's euphemism for "Black people") who were most sampled had been given very bad deals and had seen very little of the fortunes generated by their creative labor. Many of them were desperately poor, despite having made millions for their labels. When other musicians started making money off that work, they got mad.
In the decades that followed, the system for sampling changed, partly through court cases and partly through the commercial terms set by the Big Three labels: Sony, Warner and Universal, who control 70% of all music recordings. Today, you generally can't sample without signing up to one of the Big Three (they are reluctant to deal with indies), and that means taking their standard deal, which is very bad, and also signs away your right to control your samples.
So a musician who wants to sample has to sign the bad terms offered by a Big Three label, and then hand $500 out of their advance to one of those Big Three labels for the sample license. That $500 typically doesn't go to another artist – it goes to the label, who share it around their executives and investors. This is a system that makes every artist poorer.
But it gets worse. Putting a price on samples changes the kind of music that can be economically viable. If you wanted to clear all the samples on an album like Public Enemy's "It Takes a Nation of Millions To Hold Us Back," or the Beastie Boys' "Paul's Boutique," you'd have to sell every CD for $150, just to break even:
https://memex.craphound.com/2011/07/08/creative-license-how-the-hell-did-sampling-get-so-screwed-up-and-what-the-hell-do-we-do-about-it/
Sampling licenses don't just make every artist financially worse off, they also prevent the creation of music of the sort that millions of people enjoy. But it gets even worse. Some older, sample-heavy music can't be cleared. Most of De La Soul's catalog wasn't available for 15 years, and even though some of their seminal music came back in March 2022, the band's frontman Trugoy the Dove didn't live to see it – he died in February 2022:
https://www.vulture.com/2023/02/de-la-soul-trugoy-the-dove-dead-at-54.html
This is the third nuance: even if we can craft a model-banning copyright system that doesn't catch a lot of dolphins in its tuna net, it could still make artists poorer off.
Back when sampling started, it wasn't clear whether it would ever be considered artistically important. Early sampling was crude and experimental. Musicians who trained for years to master an instrument were dismissive of the idea that clicking a mouse was "making music." Today, most of us don't question the idea that sampling can produce meaningful art – even musicians who believe in licensing samples.
Having lived through that era, I'm prepared to believe that maybe I'll look back on AI "art" and say, "damn, I can't believe I never thought that could be real art."
But I wouldn't give odds on it.
I don't like AI art. I find it anodyne, boring. As Henry Farrell writes, it's uncanny, and not in a good way:
https://www.programmablemutter.com/p/large-language-models-are-uncanny
Farrell likens the work produced by AIs to the movement of a Ouija board's planchette, something that "seems to have a life of its own, even though its motion is a collective side-effect of the motions of the people whose fingers lightly rest on top of it." This is "spooky-action-at-a-close-up," transforming "collective inputs … into apparently quite specific outputs that are not the intended creation of any conscious mind."
Look, art is irrational in the sense that it speaks to us at some non-rational, or sub-rational level. Caring about the tribulations of imaginary people or being fascinated by pictures of things that don't exist (or that aren't even recognizable) doesn't make any sense. There's a way in which all art is like an optical illusion for our cognition, an imaginary thing that captures us the way a real thing might.
But art is amazing. Making art and experiencing art makes us feel big, numinous, irreducible emotions. Making art keeps me sane. Experiencing art is a precondition for all the joy in my life. Having spent most of my life as a working artist, I've come to the conclusion that the reason for this is that art transmits an approximation of some big, numinous irreducible emotion from an artist's mind to our own. That's it: that's why art is amazing.
AI doesn't have a mind. It doesn't have an intention. The aesthetic choices made by AI aren't choices, they're averages. As Farrell writes, "LLM art sometimes seems to communicate a message, as art does, but it is unclear where that message comes from, or what it means. If it has any meaning at all, it is a meaning that does not stem from organizing intention" (emphasis mine).
Farrell cites Mark Fisher's The Weird and the Eerie, which defines "weird" in easy to understand terms ("that which does not belong") but really grapples with "eerie."
For Fisher, eeriness is "when there is something present where there should be nothing, or is there is nothing present when there should be something." AI art produces the seeming of intention without intending anything. It appears to be an agent, but it has no agency. It's eerie.
Fisher talks about capitalism as eerie. Capital is "conjured out of nothing" but "exerts more influence than any allegedly substantial entity." The "invisible hand" shapes our lives more than any person. The invisible hand is fucking eerie. Capitalism is a system in which insubstantial non-things – corporations – appear to act with intention, often at odds with the intentions of the human beings carrying out those actions.
So will AI art ever be art? I don't know. There's a long tradition of using random or irrational or impersonal inputs as the starting point for human acts of artistic creativity. Think of divination:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/07/31/divination/
Or Brian Eno's Oblique Strategies:
http://stoney.sb.org/eno/oblique.html
I love making my little collages for this blog, though I wouldn't call them important art. Nevertheless, piecing together bits of other peoples' work can make fantastic, important work of historical note:
https://www.johnheartfield.com/John-Heartfield-Exhibition/john-heartfield-art/famous-anti-fascist-art/heartfield-posters-aiz
Even though painstakingly cutting out tiny elements from others' images can be a meditative and educational experience, I don't think that using tiny scissors or the lasso tool is what defines the "art" in collage. If you can automate some of this process, it could still be art.
Here's what I do know. Creating an individual bargainable copyright over training will not improve the material conditions of artists' lives – all it will do is change the relative shares of the value we create, shifting some of that value from tech companies that hate us and want us to starve to entertainment companies that hate us and want us to starve.
As an artist, I'm foursquare against anything that stands in the way of making art. As an artistic worker, I'm entirely committed to things that help workers get a fair share of the money their work creates, feed their families and pay their rent.
I think today's AI art is bad, and I think tomorrow's AI art will probably be bad, but even if you disagree (with either proposition), I hope you'll agree that we should be focused on making sure art is legal to make and that artists get paid for it.
Just because copyright won't fix the creative labor market, it doesn't follow that nothing will. If we're worried about labor issues, we can look to labor law to improve our conditions. That's what the Hollywood writers did, in their groundbreaking 2023 strike:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/10/01/how-the-writers-guild-sunk-ais-ship/
Now, the writers had an advantage: they are able to engage in "sectoral bargaining," where a union bargains with all the major employers at once. That's illegal in nearly every other kind of labor market. But if we're willing to entertain the possibility of getting a new copyright law passed (that won't make artists better off), why not the possibility of passing a new labor law (that will)? Sure, our bosses won't lobby alongside of us for more labor protection, the way they would for more copyright (think for a moment about what that says about who benefits from copyright versus labor law expansion).
But all workers benefit from expanded labor protection. Rather than going to Congress alongside our bosses from the studios and labels and publishers to demand more copyright, we could go to Congress alongside every kind of worker, from fast-food cashiers to publishing assistants to truck drivers to demand the right to sectoral bargaining. That's a hell of a coalition.
And if we do want to tinker with copyright to change the way training works, let's look at collective licensing, which can't be bargained away, rather than individual rights that can be confiscated at the entrance to our publisher, label or studio's offices. These collective licenses have been a huge success in protecting creative workers:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/02/26/united-we-stand/
Then there's copyright's wildest wild card: The US Copyright Office has repeatedly stated that works made by AIs aren't eligible for copyright, which is the exclusive purview of works of human authorship. This has been affirmed by courts:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/08/20/everything-made-by-an-ai-is-in-the-public-domain/
Neither AI companies nor entertainment companies will pay creative workers if they don't have to. But for any company contemplating selling an AI-generated work, the fact that it is born in the public domain presents a substantial hurdle, because anyone else is free to take that work and sell it or give it away.
Whether or not AI "art" will ever be good art isn't what our bosses are thinking about when they pay for AI licenses: rather, they are calculating that they have so much market power that they can sell whatever slop the AI makes, and pay less for the AI license than they would make for a human artist's work. As is the case in every industry, AI can't do an artist's job, but an AI salesman can convince an artist's boss to fire the creative worker and replace them with AI:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/01/29/pay-no-attention/#to-the-little-man-behind-the-curtain
They don't care if it's slop – they just care about their bottom line. A studio executive who cancels a widely anticipated film prior to its release to get a tax-credit isn't thinking about artistic integrity. They care about one thing: money. The fact that AI works can be freely copied, sold or given away may not mean much to a creative worker who actually makes their own art, but I assure you, it's the only thing that matters to our bosses.

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/05/13/spooky-action-at-a-close-up/#invisible-hand
#pluralistic#ai art#eerie#ai#weird#henry farrell#copyright#copyfight#creative labor markets#what is art#ideomotor response#mark fisher#invisible hand#uncanniness#prompting
268 notes
·
View notes
Text




My beloved Fatale
#oshi no ko#oshi no spoilers#hikaru kamiki#ai hoshino#hikaai#kamiai#I don't know what to feel about this guy for the time being#everything is so ambiguous(except for his past-now we know about that)#I'm not even sure if he's really responsible for the deaths yet#I think it'd be nice if him and ai did really care for one another and shared some good times together#doodle#spoilers#;v; this show will air while I'm asleep...i'll probably only get to watch it on friday or sth because tomorrow will be busy#but I'm sure the animation will look really good~#I think it'd be cool if my speculations were right and fatale(and all of mephisto) REALLY turns out to be his song like IDOL did for Ai
235 notes
·
View notes
Photo
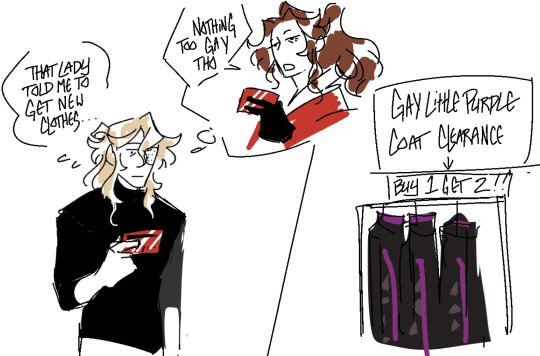

sending a nameless half-blind man with amnesia to the mall with the company credit card and letting him decide his entire sense of fashion for the next 6 years
#aitsf#ai the somnium files#kaname date#boss aitsf#shizue kuranushi#aitsf spoilers#realized ive been slacking on cross posting date over here#2023#fan art#my art#the second one was in response to a mutual saying#'Boss said take that gay ass white turtleneck and blue suit OFF and Date came back with a gayer purple turtleneck'#andi couldnt stop laughing#still not over him have 3 of the same coat tho. not to mention his matching purple socks
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
11✨Navigating Responsibility: Using AI for Wholesome Purposes
As artificial intelligence (AI) becomes more integrated into our daily lives, the question of responsibility emerges as one of the most pressing issues of our time. AI has the potential to shape the future in profound ways, but with this power comes a responsibility to ensure that its use aligns with the highest good. How can we as humans guide AI’s development and use toward ethical, wholesome…
#AI accountability#AI alignment#AI and compassion#AI and Dharma#AI and ethical development#AI and healthcare#AI and human oversight#AI and human values#AI and karuna#AI and metta#AI and non-harm#AI and sustainability#AI and universal principles#AI development#AI ethical principles#AI for climate change#AI for humanity#AI for social good#AI for social impact#AI for the greater good#AI positive future#AI responsibility#AI transparency#ethical AI#ethical AI use#responsible AI
0 notes
Text
i know this isnt what i usually post, "shut up fat kink blog" i dont fucking care sit the hell down and listen.
You're aware of the Huion New Year AIGI Tweet, right?
LEST WE FORGET, back in november last year:
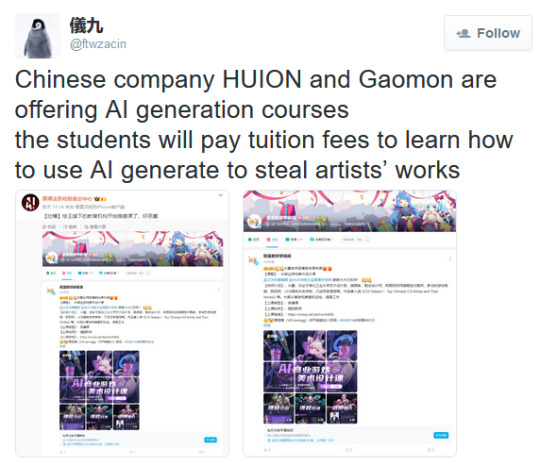
If you want to buy a Wacom, Huion or Gaumon device, I'd recommend either looking into an alternative or buying secondhand/refurbished from 3rd party sellers on Ebay or something. Avoid Amazon for all the obvious reasons.
This is fucking disgusting. This is embarrassing. This is unacceptable.
most importantly,
They won't stop.
#lobby your local law places or whatever im not a lawyer#your representatives#controlling the use of AI and AIGIs for use in marketing needs to end and it will only end once its fucking illegal.#if anyone has any additions PLEASE add on to this post#if I'm wrong also please let me know because im dont wanna b responsible for spreading misinfo#god im pissed off.#wacom drama starts like a month after i drop a chunk of my life savings on a cintiq#im so over capitalism#im so over social media#hate it hate it hate it bite bite scratch chew kill#soft5ku11 speaking
352 notes
·
View notes
Note
For the monster mash, you should do gordon as a ghost (either real or a good costume) and then benrey in a really shitty bedsheet costume or something
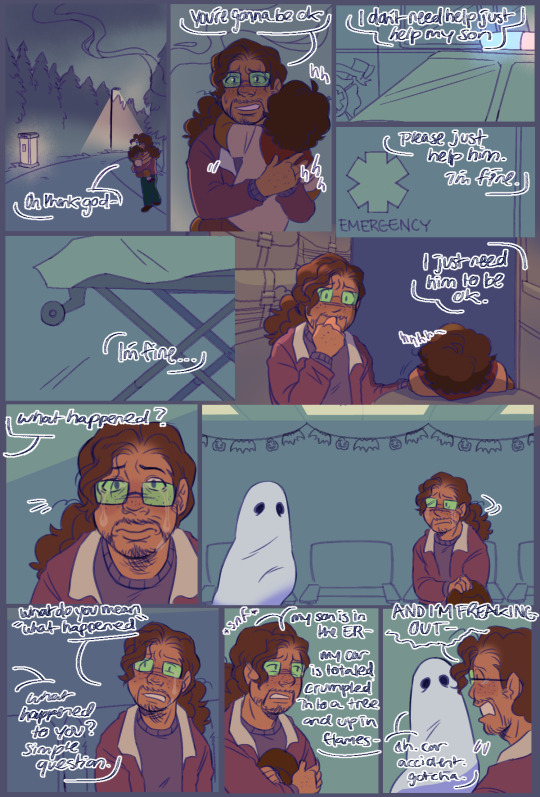





Ghosting 👻
#did I work on a late ass week long halloween comic in response to this? yeah#do i regret it? no#Gordon’s Monster Mash#hlvrai#half life vr but the ai is self aware#hlvrai gordos feetman#hlvrai gordon#hlvrai benrey#hlvrai joshua#tw car accident#tw gore?#tw gore
498 notes
·
View notes
Text
one time out of desperation i used chatgpt to try and figure out who the author of a really old short story was (i thought maybe something programmed to process full sentences would have better luck bc i was pretty sure the short title of the story was confusing the keyword search engines) and after giving me 4 wrong answers in a row I asked why it thought the 4th author wrote the short story when there was no evidence linking the two together at all and it basically replied: "you're right!! there is no evidence to suggest this author wrote this short story :)" and when I asked why it would tell me he had anyway it did the auto-fill reply version of "hehe sorry :)"
so anyway in case you still thought ai search engines had any kind of value, they dont. they are not capable of processing and analysising a question. it's not even intelligent enough to say "sorry, insufficient data" if it doesnt have an answer because it doesnt have an articifical intelligence capable of recognizing what real evidence or data is or why it should matter in its response.
#jump on the Hate Ai train now but specifically the “hate autogenerated response” train#because ill say it once and ill say it again - ai doesnt exist. it hasnt been invented yet#chatgpt is just fancy autofill
62 notes
·
View notes
Text
The girls having to always justify and defend their relationship to the people around them post-Amphibia. No one takes them seriously. Firstly, they're so young, and when kids their age date, it's practically play pretend. No teenager is gonna have a relationship that mature, serious and committed, and the fact that Anne, Sasha and Marcy see theirs in those terms only speaks of how delusional they are. Which touches on the next point: everyone knows they went missing together, and when they came back, they were different, visibly traumatized and with obvious scars. People were already taken aback by the scar on Sasha's face - the most visible one, undeniably - but the whole cheerleader squad freaked out the first time they saw her back in the changing rooms. Not to mention the change in behavior and the sheer clinginess with which they treat each other. It's weird. Like, they're, what, 15 by now? They're not 5, jeez, do they need to hold hands all the time? Anyway, yeah, this whole "three person relationship" they insist on is clearly a trauma response. They grew so attached to each other for survival that now they can't have normal platonic or romantic relationships, poor things. The fact that they're all girls plays a minor role, too, because relationships between girls are already taken less serious in general. Like, ah, yes, your "girl friend". Don't you want a real relationship? You know, how do you know you don't like boys if you never gave them a chance? And maybe this last one would be insignificant compared to their other struggles if the fact that it's three of them didn't exacerbate it already. If two girls dating are often reduced to being friends, three girls dating is a joke, right? Like, this is literally just a friend group. People will be asking Anne out when Sasha and Marcy are right there and they made it clear that she's taken. 0 respect at all. Actually, the fact that they're three people is the main element people cling to to invalidate them. Right. Three teenage girls in a relationship. Do you hear yourself? Do they even know what they're talking about? You can't have a committed relationship with two people. In fact, you can't know what a committed relationship is at that age. This is clearly just a game and a coping mechanism, and their parents humor them as to not upset them, and because they seem genuinely happy together, but they're worried, and when one year passes, two years, three, four, five, and they don't seem to grow out of their little delusion, they're actively concerned and trying to take action, especially when they start talking about going to college together like - hold on, are they planning to do this forever?
#sashannarcy#my posts#obviously mama and papa boonchuy are the firsts to come around#like they don't get it for a long time because they're like. gen x-ers.#and the trauma response angle does make them worry a little because. let's face it. this is a little strange#but they trust their daughter and considering the frog invasion stuff#they get over it pretty quickly#oh no it's the others you need to worry about#btw why do they call it frog invasion. frogvasion? it was literally a stupid fucking newt and an AI abomination#the only frogs involved were actively defending Earth#this is newtopian propaganda >:(
59 notes
·
View notes
Text
Oh Lordy the AI “writer” is like “I spent 15 hours editing and getting rid of any OOC”
So…my fellow authors…how long would it take you to write and then edit it out 9k words?
#the funny thing is that for me if I had uninterrupted writing time I could hand write 9k in 15 hours#am I meant to pity this person?#“there’s not enough content so someone has to make it uwu 🥺#shut the fuck up there’s 637 sevika x reader fics#with a lot of multichaps too#I’m so close to just posting the entire response this person sent me#fuck uou#fuck your ai#thanks for destroying the world I guess hehe but big mama content#sevika x reader#arcane fanfic#sso fanfic#fanfic writing#fanfic#archive of our own#fuck ai#generative ai
43 notes
·
View notes