#United American Indians of New England
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
was thinking about this

To be in "public", you must be a consumer or a laborer.
About control of peoples' movement in space/place. Since the beginning.
"Vagrancy" of 1830s-onward Britain, people criminalized for being outside without being a laborer.
Breaking laws resulted in being sentenced to coerced debtor/convict labor. Coinciding with the 1830-ish climax of the Industrial Revolution and the land enclosure acts (factory labor, poverty, etc., increase), the Metropolitan Police Act of 1829 establishes full-time police institution(s) in London. The "Workhouse Act" aka "Poor Law Amendment Act of 1834" forced poor people to work for a minimum number of hours every day. The Irish Constabulary of 1837 sets up a national policing force and the County Police Act of 1839 allows justices of the peace across England to establish policing institutions in their counties (New York City gets a police department in 1844). The major expansion of the "Vagrancy Act" of 1838 made "joblessness" a crime and enhanced its punishment. (Coincidentally, the law's date of royal assent was 27 July 1838, just 5 days before the British government was scheduled to allow fuller emancipation of its technical legal abolition of slavery in the British Caribbean on 1 August 1838.)
---
"Vagrancy" of 1860s-onward United States, people criminalized for being outside while Black.
Widespread emancipation after slavery abolition in 1865 rapidly followed by the outlawing of loitering which de facto outlawed existing as Black in public. Inability to afford fines results in being sentenced to forced labor by working on chain gangs or prisons farms, some built atop plantations.
---
"Vagrancy" of 1870s-onward across empires, people criminalized for being outside while being "foreign" and also being poor generally.
Especially from 1880-ish to 1918-ish, this was an age of widespread mass movement of peoples due to the land dispossession, poverty, and famine induced by global colonial extraction and "market expansion" (Scramble for Africa, US "American West", nation-building, conquering "frontiers"), as agricultural "revolutions" of imperial monoculture cash crop extraction resulted in ecological degradation, and as major imperial infrastructure building projects required a lot of vulnerable "mobile" labor. This coincides with and is facilitated by new railroad networks and telegraphs, leading to imperial implementation or expansion of identity documents, strict work contracts, passports, immigration surveillance, and border checkpoints.
All of this in just a few short years: In 1877, British administrators in India develop what would become the Henry Classification System of taking and keeping fingerprints for use in binding colonial Indians to legal contracts. That same year during the 1877 Great Railroad Strike, and in response to white anxiety about Black residents coming to the city during Great Migration, Chicago's policing institutions exponentially expand surveillance and pioneer "intelligence card" registers for tracking labor union organizing and Black movement, as Chicago's experiments become adopted by US military and expanded nationwide, later used by US forces monitoring dissent in colonial Philippines and Cuba. Japan based its 1880 Penal Code anti-vagrancy statutes on French models, and introduced "koseki" register to track poor/vagrant domestic citizens as Tokyo's Governor Matsuda segregates classes, and the nation introduces "modern police forces". In 1882, the United States passes the Chinese Exclusion Act. In 1884, the Ottoman government enacts major "Passport Nizamnamesi" legislation requiring passports. In 1885, the racist expulsion of the "Tacoma riot".
Punished for being Algerian in France. Punished for being Chinese in San Francisco. Punished for being Korean in Japan. Punished for crossing Ottoman borders without correct paperwork. Arrested for whatever, then sent to do convict labor. A poor person in the Punjab, starving during a catastrophic famine, might be coerced into a work contract by British authorities. They will have to travel, shipped off to build a railroad. But now they have to work. Now they are bound. They will be punished for being Punjabi and trying to walk away from Britain's tea plantations in Assam or Britain's rubber plantations in Malaya.
Mobility and confinement, the empire manipulates each.
---
"Vagrancy" amidst all of this, people also criminalized for being outside while "unsightly" and merely even superficially appearing to be poor. San Francisco introduced the notorious "ugly law" in 1867, making it illegal for "any person, who is diseased, maimed, mutilated or deformed in any way, so as to be an unsightly or disgusting object, to expose himself or herself to public view". Today, if you walk into a building looking a little "weird" (poor, Black, ill, disabled, etc.), you are given seething spiteful glares and asked to leave. De facto criminalized for simply going for a stroll without downloading the coffee shop's exclusive menu app.
Too ill, too poor, too exhausted, too indebted to move, you are trapped. Physical barriers (borders), legal barriers (identity documents), financial barriers (debt). "Vagrancy" everywhere in the United States, a combination of all of the above. "Vagrancy" since at least early nineteenth century Europe. About the control of movement through and access to space/place. Concretizing and weaponizing caste, corralling people, anchoring them in place, extracting their wealth and labor.
You are permitted to exist only as a paying customer or an employee.
#get to work or else you will be put to work#sorry#intimacies of four continents#tidalectics#abolition
3K notes
·
View notes
Text

Via United American Indians of New England
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
At the outset of H. G. Wells’s The War of the Worlds (1898), Wells asks his English readers to compare the Martian invasion of Earth with the Europeans’ genocidal invasion of the Tasmanians, thus demanding that the colonizers imagine themselves as the colonized, or the about-to-be-colonized. But in Wells this reversal of perspective entails something more, because the analogy rests on the logic prevalent in contemporary anthropology that the indigenous, primitive other’s present is the colonizer’s own past. Wells’s Martians invading England are like Europeans in Tasmania not just because they are arrogant colonialists invading a technologically inferior civilization, but also because, with their hypertrophied brains and prosthetic machines, they are a version of the human race’s own future.
The confrontation of humans and Martians is thus a kind of anachronism, an incongruous co-habitation of the same moment by people and artifacts from different times. But this anachronism is the mark of anthropological difference, that is, the way late-nineteenth-century anthropology conceptualized the play of identity and difference between the scientific observer and the anthropological subject-both human, but inhabiting different moments in the history of civilization. As George Stocking puts it in his intellectual history of Victorian anthropology, Victorian anthropologists, while expressing shock at the devastating effects of European contact on the Tasmanians, were able to adopt an apologetic tone about it because they understood the Tasmanians as “living representatives of the early Stone Age,” and thus their “extinction was simply a matter of … placing the Tasmanians back into the dead prehistoric world where they belonged” (282-83). The trope of the savage as a remnant of the past unites such authoritative and influential works as Lewis Henry Morgan’s Ancient Society (1877), where the kinship structures of contemporaneous American Indians and Polynesian islanders are read as evidence of “our” past, with Sigmund Freud’s Totem and Taboo (1913), where the sexual practices of “primitive” societies are interpreted as developmental stages leading to the mature sexuality of the West. Johannes Fabian has argued that the repression or denial of the real contemporaneity of so-called savage cultures with that of Western explorers, colonizers, and settlers is one of the pervasive, foundational assumptions of modern anthropology in general. The way colonialism made space into time gave the globe a geography not just of climates and cultures but of stages of human development that could confront and evaluate one another.
The anachronistic structure of anthropological difference is one of the key features that links emergent science fiction to colonialism. The crucial point is the way it sets into motion a vacillation between fantastic desires and critical estrangement that corresponds to the double-edged effects of the exotic. Robert Stafford, in an excellent essay on “Scientific Exploration and Empire” in the Oxford History of the British Empire, writes that, by the last decades of the century, “absorption in overseas wilderness represented a form of time travel” for the British explorer and, more to the point, for the reading public who seized upon the primitive, abundant, unzoned spaces described in the narratives of exploration as a veritable “fiefdom, calling new worlds into being to redress the balance of the old” (313, 315). Thus when Verne, Wells, and others wrote of voyages underground, under the sea, and into the heavens for the readers of the age of imperialism, the otherworldliness of the colonies provided a new kind of legibility and significance to an ancient plot. Colonial commerce and imperial politics often turned the marvelous voyage into a fantasy of appropriation alluding to real objects and real effects that pervaded and transformed life in the homelands. At the same time, the strange destinations of such voyages now also referred to a centuries-old project of cognitive appropriation, a reading of the exotic other that made possible, and perhaps even necessary, a rereading of oneself.
John Rieder, Colonialism and the Emergence of Science Fiction
#words#hg wells#fiction#science fiction#colonialism and the emergence of science fiction#john rieder
471 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Best News of Last Week - June 20, 2023
🐕 - Meet Sheep Farm's Newest Employee: Collie Hired After Ejection from Car!
1. Border Collie ejected from car during Sunday crash found on sheep farm, herding sheep

Tilly, the 2-year-old Border Collie who was ejected from a car Sunday during a crash, has been found. He was found on a sheep farm, where he had apparently taken up the role of sheep herder.
According to Tilly's owner, he has lost some weight since Sunday's crash and is now drinking lots of water but is otherwise healthy.
2. After 17-Year Absence, White Rhinos Return to the Democratic Republic of the Congo

The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) recently welcomed the reintroduction of 16 southern white rhinoceroses to Garamba National Park, according to officials. The last wild northern white rhino was poached there in 2006.
The white rhinos were transported to Garamba, which lies in the northeastern part of the country, from a South African private reserve. In the late 19th century, the southern white rhino subspecies was believed to be extinct due to poaching until a population of fewer than 100 was discovered in South Africa in 1895, according to WWF.
3. UK to wipe women’s historic convictions for homosexuality

Women with convictions for some same-sex activity in the United Kingdom can apply for a pardon for the first time, the Home Office has announced.
The Home Office is widening its scheme to wipe historic convictions for homosexual activity more than a decade after the government allowed applications for same-sex activity offences to be disregarded.
It means anyone can apply for a pardon if they have been convicted or cautioned for any same-sex activity offences that have been repealed or abolished.
4. Study shows human tendency to help others is universal

A new study on the human capacity for cooperation suggests that, deep down, people of diverse cultures are more similar than you might expect. The study, published in Scientific Reports, shows that from the towns of England, Italy, Poland, and Russia to the villages of rural Ecuador, Ghana, Laos, and Aboriginal Australia, at the micro scale of our daily interaction, people everywhere tend to help others when needed.
5. In a First, Wind and Solar Generated More Power Than Coal in U.S.

Wind and solar generated more electricity than coal through May, an E&E News review of federal data shows, marking the first time renewables have outpaced the former king of American power over a five-month period.
The milestone illustrates the ongoing transformation of the U.S. power sector as the nation races to install cleaner forms of energy to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from fossil fuels.
6. Iceland becomes latest country to ban conversion therapy

Lawmakers in Iceland on June 9 approved a bill that will ban so-called conversion therapy in the country.
Media reports note 53 members of the Icelandic Parliament voted for the measure, while three MPs abstained. Hanna Katrín Friðriksson, an MP who is a member of the Liberal Reform Party, introduced the bill.
7. The temple feeding 100,000 people a day

Amritsar, the north Indian city known for its Golden Temple and delicious cuisine, is also renowned for its spirit of generosity and selfless service. The city, founded by a Sikh guru, embodies the Sikh tradition of seva, performing voluntary acts of service without expecting anything in return.
This spirit of giving extends beyond the temple walls, as the Sikh community has shown immense compassion during crises, such as delivering oxygen cylinders during the COVID-19 pandemic. At the heart of Amritsar's generosity is the Golden Temple's langar, the world's largest free communal kitchen, serving 100,000 people daily without discrimination. Despite a history marred by tragic events, Amritsar continues to radiate kindness, love, and generosity.
----
That's it for this week :)
This newsletter will always be free. If you liked this post you can support me with a small kofi donation:
BUY ME A COFFEE ❤️
Also don’t forget to reblog.
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
At the outset of H. G. Wells's The War of the Worlds (1898), Wells asks his English readers to compare the Martian invasion of Earth with the Europeans' genocidal invasion of the Tasmanians, thus demanding that the colonizers imagine themselves as the colonized, or the about-to-be-colonized. But in Wells this reversal of perspective entails something more, because the analogy rests on the logic prevalent in contemporary anthropology that the indigenous, primitive other's present is the colonizer's own past. Wells's Martians invading England are like Europeans in Tasmania not just because they are arrogant colonialists invading a technologically inferior civilization, but also because, with their hypertrophied brains and prosthetic machines, they are a version of the human race's own future.
The confrontation of humans and Martians is thus a kind of anachronism, an incongruous co-habitation of the same moment by people and artifacts from different times. But this anachronism is the mark of anthropological difference, that is, the way late-nineteenth-century anthropology conceptualized the play of identity and difference between the scientific observer and the anthropological subject-both human, but inhabiting different moments in the history of civilization. As George Stocking puts it in his intellectual history of Victorian anthropology, Victorian anthropologists, while expressing shock at the devastating effects of European contact on the Tasmanians, were able to adopt an apologetic tone about it because they understood the Tasmanians as "living representatives of the early Stone Age," and thus their "extinction was simply a matter of … placing the Tasmanians back into the dead prehistoric world where they belonged" (282-83). The trope of the savage as a remnant of the past unites such authoritative and influential works as Lewis Henry Morgan's Ancient Society (1877), where the kinship structures of contemporaneous American Indians and Polynesian islanders are read as evidence of "our" past, with Sigmund Freud's Totem and Taboo (1913), where the sexual practices of "primitive" societies are interpreted as developmental stages leading to the mature sexuality of the West. Johannes Fabian has argued that the repression or denial of the real contemporaneity of so-called savage cultures with that of Western explorers, colonizers, and settlers is one of the pervasive, foundational assumptions of modern anthropology in general. The way colonialism made space into time gave the globe a geography not just of climates and cultures but of stages of human development that could confront and evaluate one another.
The anachronistic structure of anthropological difference is one of the key features that links emergent science fiction to colonialism. The crucial point is the way it sets into motion a vacillation between fantastic desires and critical estrangement that corresponds to the double-edged effects of the exotic. Robert Stafford, in an excellent essay on "Scientific Exploration and Empire" in the Oxford History of the British Empire, writes that, by the last decades of the century, "absorption in overseas wilderness represented a form of time travel" for the British explorer and, more to the point, for the reading public who seized upon the primitive, abundant, unzoned spaces described in the narratives of exploration as a veritable "fiefdom, calling new worlds into being to redress the balance of the old" (313, 315). Thus when Verne, Wells, and others wrote of voyages underground, under the sea, and into the heavens for the readers of the age of imperialism, the otherworldliness of the colonies provided a new kind of legibility and significance to an ancient plot. Colonial commerce and imperial politics often turned the marvelous voyage into a fantasy of appropriation alluding to real objects and real effects that pervaded and transformed life in the homelands. At the same time, the strange destinations of such voyages now also referred to a centuries-old project of cognitive appropriation, a reading of the exotic other that made possible, and perhaps even necessary, a rereading of oneself.
John Rieder, Colonialism and the Emergence of Science Fiction
682 notes
·
View notes
Photo
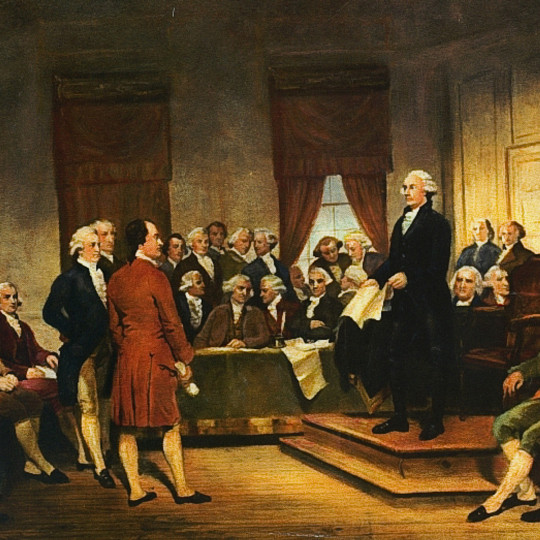

American Revolution
The American Revolution (1765-1789) was a period of political upheaval in the Thirteen Colonies of British North America. Initially a protest over parliamentary taxes, it blossomed into a rebellion and led, ultimately, to the birth of the United States. Rooted in the ideas of the Enlightenment, the Revolution played an important role in the emergence of modern Western democracies.
Origins: Parliament & the American Identity
In February 1763, the Seven Years' War – or the French and Indian War as the North American theater was called – came to an end. As part of the peace agreement, the vanquished Kingdom of France ceded its colony of New France (Canada) as well as all its colonial territory east of the Mississippi River to its victorious rival, Great Britain. While this left Britain as the dominant colonial power in North America, this newfound supremacy came at a cost, namely a massive war debt. To offset the debt, the British Parliament decided to levy new taxes on the Thirteen Colonies along the eastern seaboard of North America. Much of the war had been fought defending these colonies, after all, and Parliament decided that the colonists should help shoulder the empire's financial burden.
Prior to this decision, Parliament had adhered to an unofficial policy of 'salutary neglect' when dealing with the American colonies. This meant that, despite their royal governors, the colonies were largely left to manage their own affairs, with colonial legislatures overseeing governance and taxation. The influence of these legislatures often equaled if not eclipsed the power of the colony's royally appointed governor. Due to differing foundational and developmental circumstances, each colony maintained its own identity – the Puritan society of New England, the Dutch origins of New York, and the tobacco economy of Virginia, for example, all influenced the formation of their colonial identities. Despite viewing themselves as separate from one another, the colonies were loosely bound by their shared ties to Britain and had united in common defense multiple times during the last century of colonial wars.
At the same time, the American colonists considered themselves Britons, and proudly so. After the Glorious Revolution of 1689, and the constitutional reforms that went with it, the British were viewed as the freest people in the world; they were guaranteed a right to representative government (Parliament) as well as the right to self-taxation. The colonists believed that these 'rights of Englishmen' extended to them, as befitting of their English blood and allegiance to the English king; indeed, many of these rights were echoed in the colonies' own charters. The idea that Parliament could directly tax the colonies, therefore, went against this notion; since no Americans were represented in Parliament, Parliament had no constitutional authority to tax them (i.e. taxation without representation). Parliament, of course, disagreed, arguing that the Americans were virtually represented, as was the case with the thousands of Englishmen who owned no property and could not vote. It was this fundamental disagreement over the Americans' rights and liberties – expressed in the guise of taxation – that lay at the heart of the American Revolution and the birth of the United States.
Continue reading...
28 notes
·
View notes
Note
i know people talk a lot about the us and UK special relationship but it kind of fell after the Suez and France kind of sneakily stole it didn't he? I mean did the same before the wars
thanks for the ask! ngl, as a londoner, i've always personally felt the representation of the "Special Relationship" as this mega-close and affectionate dynamic is kind of...an un-holistic understanding of the UK or England, as well as of the United States. don't get me wrong, it's one of their most important relationships and there's a lot of deep history there—my issue is mostly with rose-tinted interpretations underpinning it and what biases they showcase. these were heavily biased by Churchill's (imperialist) gaze of envisioning Anglo-American affinity and leadership on the world stage. this interpretation quite significantly downplayed the rivalry, power struggles, conflicts and differences that historians existed between the US and the British Empire, or how US presidents tended to see it in far less majestic terms. like, Churchill rather downplays FDR's vehement disagreements with him over the issue of Indian independence lol or decolonisation (because the US was eyeing the world as a chessboard, re: new markets and also whether or not support for the old colonial power would be a bulwark against or risk soviet or other communist influence).
so, while you're right that Suez was a pretty low moment in US-Britain relations due to the US being pissed at Britain and France jeopardising its ostensible goal of swaying Egypt away from the Soviet sphere of influence (sidenote: Egypt itself was trying to navigate the mess of the Cold War rivalry to secure its interests), i don't really see it as "falling" after Suez or stolen by France simply because that dynamic Churchill painted a picture of never really existed in that way. plus, Europe (France included) and the ex-colonies of the British Empire (like the dominions and India) weighed heavily on British foreign policy/its national outlook too; i tend to find an overemphasis on a rose-tinted view of the "Special Relationship" leads to a lot of US-centrism that shuts out this understanding. to me, Arthur and Alfred's relationship is most interesting when we situate them properly amidst all these other imperial and geopolitical cross-currents. of which Francis is an important one, from the time he helped Alfred during the Revolutionary War, to the Entente Cordial, WWI and the post-WWII world of NATO, the EU and so on.
in hetalia-verse, it's one of the reasons I personally headcanon Arthur and Alfred as father and son. their bond is lasting, forged by the blood, steel and saltwater of empire, and all the familial, deep and troubling implications that implies. they are "stuck" with each other in some ways, because post 1945, it's a familial dynamic of the old king and the young, ambitious crown prince who thinks his father is out of time—and out of line. francis never really "steals" anything because he and arthur's relationship is on a very different axes: francis is the neighbour who has been by arthur's side as his enemy, friend, lover, rival in imperial douchebaggery, ally (for better and also for worse, like in suez...)—and everything in between. whereas arthur and alfred have some real patricidal/regicidal, titanomachy-level father-son power struggles going on, mixed in with this dysfunctional level of understanding and them also colluding together shadily (you are different from him in many ways, there are many things he'll never understand about you—but you are your father's son, alfred; to be powerful is to be tainted).
so in conclusion, i see alfred-arthur and arthur-francis as both very important foundational dynamics crucial to arthur's character, but conceptualised differently from that understanding of the "special relationship" because they're two different kinds of relationships, even if there is the overlapping dynamic of power, rivalry and empire. ✌🏼
83 notes
·
View notes
Text
Today's the 250th anniversary of the Boston Tea Party so here's some information on the Sons of Liberty, the lead up to the Boston Tea Party and what happened after!
apologies for any inaccuracies, I wrote this pretty late
The conflict between the American colonies and New England started after the French and Indian war ended with the Treaty of Paris on the 10th of February, 1763. The French and Indian war started because of conflicting territory claims in North America between the British and the French. Originally it was fought between only the British Americans and the French colonists with Native Americans helping on either side (especially with the French because they were severely outnumbered). However two years into the war the United Kingdom - except for ireland - decided enough was enough and officially declared a war with France which started a large world-wide conflict over many territories. In the end, the war was won by the Colonial Americans and British, the French lost all of their North American territory and what used to be their territory was split somewhat evenly between the Spanish and the British but that was only sorted out after the British fought in a war against the Spanish called the Anglo-Spanish war (the first one). So a victory, that sounds good for America right? Wrong. Wars are expensive, maintaining an army is expensive and the British were dealing with many other wars in all different territories at around the same time so England had a national debt of nearly 177.645 MILLION modern day USD.
England had a HUGE poverty crisis. They had to come up with a way to get money and quickly so on April the 5th 1764 the British parliament amended their pre-existing Sugar and Molasses Act. A tax on the importation of wine, molasses, indigo and sugar from places that weren't part of Britain, mainly the non-British Caribbean. This act also banned all foreign rum. Then on March the 22nd, 1765 the British parliament passed the stamp act. A tax on playing cards, newspapers, legal documents. The main problem with this tax was that it couldn't be paid in the paper money used in the 13 colonies, it had to be paid off using the British Sterling which wasn't easy to obtain in America. That and paper was possibly the most important resource in the 18th century. Later in October 1765, a Stamp Act Congress was held in Philadelphia to discuss all of the problems with this act. Then on March the 24th the British passed the Quartering Act which stated that if British troops want to stay at your house you have to provide them with food and let them inside of your house. This was a clear invasion of two very basic rights of Englishmen, private property and personal security.
The Americans fought back against these acts like with Boston's non-importation agreement where merchants from Boston agreed not to buy or sell anything from/to Britain and the Golden Hill riot in New York and the Gaspée Affair which was when a group burned a British ship while the soldiers were off looking for smugglers in Rhode Island, the group was then accused of treason. The most notable of all of these protests though was the later Boston Tea Party.
The Boston Tea Party happened because of a group called the Sons of Liberty which was created in 1765 out of a strong hatred of the Stamp Act. They believed that it was ridiculous that the British could tax the Americans when the Americans didn't even have a representative in parliament, their phrase was 'no taxation without representation'. There's a lot of dispute over what kind of organisation the Sons of Liberty actually was. I might go into all of the theories in another post but for the moment if you want to come up with your own idea on it I suggest looking into them yourself, for this post I'm just going to call them a group or organisation because it's pretty ambiguous. Anyway, the Sons of Liberty usually met at liberty poles/liberty trees which are believed to have been marked as meeting places using the Sons of Liberty's flag. The group was founded in Boston in the Massachusetts Bay colony and it's leader was Samuel 'Sam' Adams.
The Sons of Liberty's first big really move was to burn an effigy of the local Stamp Act enforcer, Andrew Oliver and then burn his office and destroyed the house of his associate. The group's protests were more often then not violent but they got their points across. It didn't help when the Boston Massacre happened in 1770, which only further outraged the colonists, expect the Boston Massacre to get it's own in depth post one day because the court trial was super interesting. Then on the 10th of May, 1773 the British made another act called the Tea Act which made it so that the colonists had to pay more for tea that wasn't legally imported. The Tea Act was meant to help the British East India Tea Company because they were making most of Britains money and they'd gone into a huge debt which caused 20-30 English banks to collapse and started the British Credit Crisis of 1772-1773. The problem was that because the imported tea from Britain was really cheap people didn't buy from local businesses which caused farmers to go completely bankrupt. The Tea Act was the final straw for the Sons of Liberty and many Americans.
Britain sent a shipment of East India Company Tea to America and all of the American colonies that the tea was going to be sent to convinced the people on the ship to resign except for Massachusetts. So the Dartmouth, a ship full of tea arrived in Boston Harbour, Samuel Adams called for a meeting at Fanueuil Hall and thousands of people turned up so they had to move meeting places. During the meeting the Colonists discussed possible resolutions, they decided to have a medium group of men watching the tea to make sure it wouldn't be unloaded and pleaded for the ship to leave. The governor of Massachusetts refused to let the ship leave and two more ships arrived. On December the 16th, 1773, Samuel Adams met with the people of Massachusetts again to tell them about the governors refusal, the meeting caused total fury amongst all of the colonists.
In protest of the Tea Act and all of the other taxes the British had put on the Americans, the people ran out of the meeting room, some of them put on Native American costumes both in an attempt to conceal their identity because what they were about to do was illegal and as a symbolic choice to show that America's their country, not Britain. They then ran onto the 3 tea ships while Samuel Adams was telling everyone to calm down and stay for the end of the meeting. And spent 3 hours hurling all of the chests of tea into the water.
The British did not respond well, they believed that the Colonists needed to be punished so they passed the infamous Intolerable Acts which consisted of the Boston Port Act, meant to force Boston to pay for the tea by closing the port until the people of Boston paid for the tea which the Colonists argued was unfair because it was punishing the whole population for something only about half of them did, the Massachusetts Government Act which changed the way that the government of Massachusetts worked by giving people appointed by the British Parliament/King far more power, this made it easier for the British government to manage the Massachusetts Bay colony from England, the Administration of Justice Acts which state that any accused Royal officials can get a trial in England if they don't believe that they would be judged fairly in Massachusetts - which seems like a strange thing to add given how the Boston Massacre trial with John Adams went? - And I've already talked about the last intolerable act, the Quartering act which states that you have to let British troops stay in your house if they want to and you have to give them food.
#amrev#american revolution#american revolutionary war#american history#history#revolutionary war#sons of liberty#boston#boston tea party#massachusetts#world history#military history#on this day#on this date
58 notes
·
View notes
Text

Queer Ecologies: Sex, Nature, Politics, Desire Chapter 2 : Enemy of the Species by Ladelle McWhorter (part 3)
Species Troubled Past
1830s, USA—the abolitionists movement was growing. “it was simply wrong to enslave fellow human beings, no matter what benefits to society might result and no matter what racial differences might exist in intelligence, strength, health or ability” and old justifications for slavery no longer carried weight so slavery defenders turned to science—“Negroes and Caucasians were in fact distinct species” (79)
‘Important’ Names: John Bachman- naturalist, South Carolina Josiah Nott- physician, Alabama, “the most vocal of slavery’s scientific proponents” Samuel G. Morton- world-renowned anatomist and professor medicine, Philadelphia James Cowles Prichard- biologist, England
Nott used Prichard’s definition of species, “separate origin and distinctness of races, evinced by a constant transmission of some character peculiarity of organization” and referenced Morton’s study that found “significant racial differences in cranial capacity” to claim that Caucasians, Negroes, American Indians were separate species (79)=polygeny
Monogeny =the theory that humanity is one unitary species; Bachman offered this definition of species: “those individuals resembling each other in dentition and general structure. In wild animals […] they must approach the same size; but in both wild and domesticated animals they must have the same duration of life, the same period of utro-gestation, the same average number of progeny, the same habits and instincts, in a word, they belong to one stock that produce fertile offspring by association” (2005, 220) (80)
Racial diversity already existed in the USA, so Nott argued that ‘Mulattoes’ (crosses between Negroes and Caucasians) were sterile hybrids like mules and thus met Buffon’s requirement and qualified as two distinct species (80)-- he used his ‘observations’ as a physician who had treated many enslaved people to support this.
“Between 1846 and 1850 most respected scientists in the United States converted to polygeny”. Types of Mankind (1854)-published by what is now known as the American School of Anthropology.
Returning to Foucault’s words the author states, “concepts […] are for cutting. They are never merely benign representations of a natural arrangement.” (81) “Species could be made to function oppressively to separate white from blacks because […] it was already a tool for marking separations in natures heterogenous continuities in the interest of prevailing human practices” (81).

The Origin of Species (1859) Charles Darwin, who like many others maintained that the concept of species was practically meaningless, given the inevitability of evolution. “There are not eternally fixed types, nor are there eternally distinct lines of descent. All life on earth, no matter how morphologically or functionally distinct at present, conceivably could be traced back to a single germ line” (81) To me this concept is also what Mitakuye Oyasin means—we are all related. I believe my ancestors knew this ‘scientific’ truth long before Charles Darwin was alive. Charles Darwin never answered the question on the origin of species—species must change over time but not when change amount to a new species (82).
The theory of natural selection was remarkable, proponents agreed but it was incomplete—clearly certain groups like Africans, Pacific Islanders, and indigenous people from North and South America had not evolved sufficiently to produce ‘civilization’ (82) (Between indigenous peoples and those who supposedly created ‘civilization’, only one group has nearly destroyed their very environment at almost every turn—making them remarkably unfit and poorly adapted to the planet--and it isn’t indigenous peoples). But even those in the ‘higher races’ could fail to adapt—criminals, idiots, the mad, the degenerate, the chronically ill…like the ‘lower races’ these weaklings should be eliminated by natural selection. BUT, the Caucasian elite grew increasingly anxious…was humanity still evolving? Or was civilization circumventing the evolutionary process? Could it even reverse itself?—devolution. Modern technology and medicine= saving more people who might have once not survived, “allowing those with inferior traits to mature and reproduce” (82).
Madison Grant, was one of the many theorists who was concerned about devolution. He was a New York attorney and a conservationist who co-founded the Save-the-Redwoods League and the Bronx Zoo and helped establish Glacier and Denali National Parks. (83) Grant believed humans had evolved under harsh environmental conditions. Anglo Saxon history and the rising tide of inferiority that was everyone else…”Mistaken regard for what are believed to be divine laws and a sentimental belief in the sanctity of human life, tend to prevent both the elimination of defect in infants and the sterilization of such adults as are themselves of no value to the community. The laws of nature require the obliteration of the unfit” (Grant 1916,44-45) (83). (When in fact it is humans caring for one another that built humanity and underlies the entire point and purpose of civilization). Grant advocated for the sterilization of the criminal, diseased, insane and other weaklings and those he termed ‘worthless race types’ like Jews, blacks and indigenous peoples. Immigration, they believed, should also be curtailed to prevent undesirables from entering the USA. “Immigration is thus, from the racial standpoint a form of procreation and like the more immediate form of procreation it may be either the greatest blessing or the greatest curse” (Stoddard 1925, 252) (84).
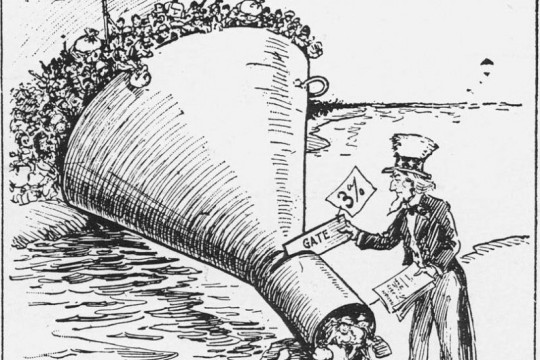
So elite influential men and their allies created organizations such as the Immigration Restriction League (full of Harvard alumni), the American Breeders’ Association (later renamed the American Genetics Association), and what later became the American Psychiatric Association-- and they won passage of an immigration restriction bill (1917)—it instituted literacy tests, put caps on the number of immigrants, national quotas and denial of entry basis on the condition called ‘constitutional psychopathy’. This effectively screened out anyone who did not conform to gender norms or anyone who admitted to homosexual desire. “Further, any immigrant who, during the first give years of residence in the United States, committed a crime or showed signs of any allegedly hereditary physical or mental defect, including sexual inversion, could be deported” (84). Congress also barred people who were ‘feebleminded, morally degenerate, or sexually suspect’. Then in 1924, they reduced the number of people who could immigrate to the US by an annual total of 150,000, making it the exclusive country in the world. These provisions stayed in effect well past the middle of the twentieth century (85).
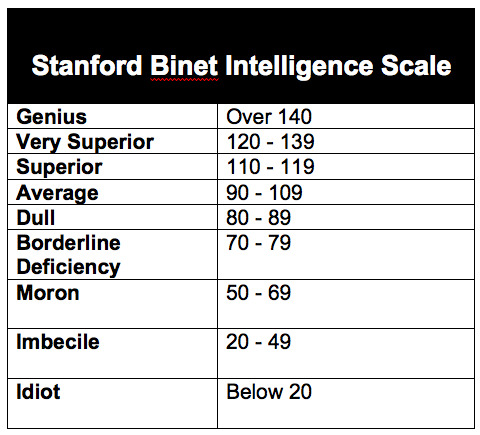
The introduction of the Simon-Binet IQ test in 1912 made identifying those were ‘intellectually unfit’ quick and easy (85)—public schools became screening grounds. Certain children would be segregated from their classmates until they could be institutionalized. The test was modified by eugenicist psychologist Henry Goddard to include a grade of ‘feeblemindedness beyond the imbecile. Individuals with a test measured mental age of eight to twelve years were classified as morons.’ (85) “Women who had children out of wedlock were automatically classified as such but any deviation from heterosexuality and prescribed gender roles could earn a person the label of moral imbecile in addition to the label of degenerate, lunatic or psychopath” (85-86). Hundreds of thousands were locked up for life as a result of these efforts to forestall a perceived threat to natural selection and evolution of humanity.
Quietly, eugenicist physicians had been sterilizing ‘defectives’ in prison, hospitals and asylums since the 1880s. In 1927, the Supreme Court endorsed these eugenic practices in Buck v Bell (86). By 1927, the number of Americans legally sterilized without their consent would reach 65,000~ (86).
“Adolf Hitler learned a great deal from American eugenicists, particularly about involuntary sterilization” –1934 Nazi involuntary sterilization law was based on the Model of Eugenical Sterilization Law drafted by American biologist Harry Laughlin (1922). He advocated for the sterilization of about 10% of the U.S population, those deemed ‘socially inadequate’ such as the (1) feeble-minded; (2) Insane, (including the Psychopathic); (3) Criminalistic (including the delinquent and wayward);(4) Epileptic; (5) Inebriate (including drug habites); (6) Diseased (including the tuberculosis, the syphilitic, the leprous, and others with chronic infections and legally segregable diseases); (7) Blind (including those with seriously impaired vision); (8) Deaf (including those with seriously impaired hearing); (9) Deformed (including the crippled); and (10) Dependent (including orphans, ne-er-do-wells, the homeless, tramps and paupers) (Laughlin) (86-87).
By 1934, nearly thirty US states had enacted such laws, though few were as drastic as Lauglin’s suggestion. Some provinces in Canada and in Europe also followed. “The Nazis […] has some serious eugenic catching up to do” (87).
By 1937, the Nazis had sterilized approx. 250,000 Germans before they began to eliminate defectives through eugenic ‘euthanasia’ (87)—genocide.

Though such things were never enacted in the US, proponents of eugenics considered it and continued to push their sterilization agenda (Partlow and his three-man committee designed to sterilize any sexual perverts, Sadists, homosexualists, Masochist, Sodomists or two-time convicted rapists. They would have no right to judicial review. The bill passed state legislature when it was vetoed twice by Governor Bibb Graves) (88).
As the details of the Nazi regime became more widely understood in the US, the eugenics movement lowered its profile and changed tactics. “Eugenics should therefor operate on a basis of individual selection” and “Eugenics, in asserting the uniqueness of the individual, supplements the American ideal of respect for the individual” (89)
#queer ecologies: sex nature politics desire#eugenics#genetics#critical ecology#queer ecology#ecofeminism#queer theory#environmental politics#colonialism#racism#ableism#erotophobia#heteronormativity#queer history#nazis#ww2#immigration#immigrants#ecology#long post
25 notes
·
View notes
Text
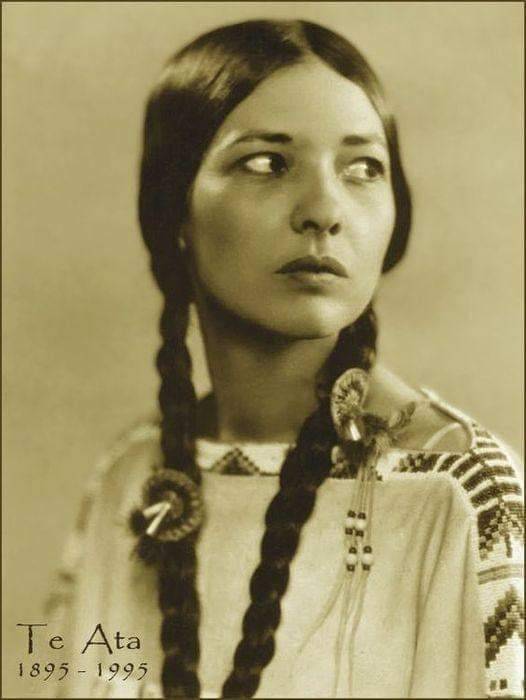

Mary "Te Ata" Thompson Fisher
1895 - 1995 Lived to be 100 yrs old ...
Te Ata Thompson Fisher, whose name means “Bearer of the Morning,” was born Dec. 3, 1895, near Emet, Oklahoma. A citizen of the Chickasaw Nation, Te Ata was an accomplished actor and teller of Native American stories ... She received her early education in Tishomingo, and eventually went to the Oklahoma College for Women. While there, it was evident Te Ata had a natural talent for drama ... Her career as an actor and storyteller spanned more than 60 years. She worked as a storyteller to finance her acting career. She would tell Chickasaw legends, myths and chants, including performing rituals in native regalia ... Te Ata attended the Carnegie Institute of Technology in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, for one year. From there, she moved to New York City, where she met and married Clyde Fisher. During the 1930s she performed at summer camps in New York and New England ... In the prime of her career, she performed in England and Scandinavia, at the White House for President Franklin Roosevelt, for the King and Queen of Great Britain, and on stages across the United States ... Although Te Ata worked as an actor and drama instructor, she is best known for her artistic interpretations of Indian folklore, and for her children's book she co-authored on the subject ... Her world-renown talent has won her several honors including induction into the Oklahoma Hall of Fame in 1957, being named The Ladies’ Home Journal Woman of the Year in 1976, being named Oklahoma's Official State Treasure in 1987, and having a lake near Bear Mountain in New York named in her honor ... She is also the subject of a video, God's Drum, the proceeds of which have supported the Te Ata Scholarship Fund for Indian students at her alma mater, the University of Science and Arts of Oklahoma in Chickasha, Oklahoma.
Te Ata died Oct. 26, 1995, in Oklahoma City, though her legacy and influence on the Native American storytelling traditions continues to this day.
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
Livestream of the National Day of Mourning by United American Indians of New England is around 12 today.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Lately I have been thinking a lot about how the northwestern frontier of the War of 1812 is ultimately part of the Sixty Years' War for control of the Great Lakes region.
Settler colonial powers clashed with each other (with other overlapping conflicts like the Seven Years' War); and numerous First Nations/Indigenous people joined one side or another in a fight against genocidal removal and the loss of their culture. The frontier was already militarised before the War of 1812.
When he turned his attention to politics, General Harrison specifically emphasised his 1811 win over Tecumseh's confederacy ("Tippecanoe and Tyler too") where he destroyed the Indigenous community of Prophetstown—not his impressive role in the War of 1812 against the British at Fort Meigs.
In the introduction to his 1985 book Men of Patriotism, Courage & Enterprise! Fort Meigs in the War of 1812, Larry L. Nelson discusses his reliance on primary sources in the form of letters, diaries, and journals from the (settler) participants, and how this affects the interpretation of a complicated history:
The use of these primary sources, however, often serves to accentuate the underlying and widely held prejudices of the times. The unsympathetic treatment of the Native American is a case in point. Scorn for the Indian runs as a common thread throughout much of the writing of the period, and is inescapably found in some of the excerpts quoted in this work. For much of white North America during the period, the American Indian was the object of fear and hatred held in equal portion.
The United States already looks pretty Not Great in the long view of the War of 1812—all of our enslaved people constantly fleeing to the British, the bungled invasion of Upper Canada and the burning of York—and there's another dark legacy in the frontier warfare. No wonder the western parts of the United States were so eager for a war with Britain: because it was mainly a war for the expansion of settlement, and there was propaganda depicting the Indigenous population as allies of the British. The New England states wanted to avoid war and almost seceded from the US.
I feel sympathy for many of the defenders of Fort Meigs, particularly the ordinary enlisted men. I don't think they were monsters, even if they were fighting for their nation in a long campaign to break old treaties and expand settlement at the expense of violently displacing native people. The Fort Meigs museum did a nice job with the different perspectives on the conflict, although it's mostly the voices of the US military because they have all of the diaries and letters and other primary sources.
I only just learned that Tecumseh's verbal sketch of Henry Proctor as "a fat animal with its tail between its legs" was in Shawnee, not in English. Tecumseh was revered as an orator, but so few of his words seem to have been written down (that was one of my takeaways from Tecumseh and the Prophet: The Shawnee Brothers Who Defied a Nation, by Peter Cozzens).
There are many challenges for me as a historian, but I am increasingly fascinated by the northwestern theatre of the War of 1812. (And now living there, getting to personally visit these military history sites).
#war of 1812#fort meigs#tecumseh#military history#us history#indigenous#settler colonialism#ohio#sixty years war#tecumseh's confederacy#old northwest#the war of 1812 ties into the napoleonic wars but also this violent settler conflict!#and i want to be careful how i am approaching it and whose voices are informing me
20 notes
·
View notes
Text

2024 National Day of Mourning
Thursday, November 28 - 12:00 p.m. to 3:00 p.m. EST
Cole’s Hill, Plymouth, MA
Join us as we continue to create a true awareness of Native peoples and history. Help shatter the untrue image of the Pilgrims, and the unjust system based on white supremacy, settler colonialism, sexism, homophobia and the profit-driven destruction of the Earth that they and other European settlers introduced to these shores.
Solidarity with Indigenous struggles throughout the world! From Turtle Island to Palestine, Colonialism is a Crime! Free Leonard Peltier! www.freeleonardpeltiernow.org
While many supporters will attend in person, we will also livestream the event from Plymouth.
United American Indians of New England (decolonizing since 1970) [email protected] * UAINE website * UAINE Facebook Group
#NDOM#LandBack#Indigenous#Native American#solidarity#protest#Plymouth#Massachusetts#white supremacy#colonialism#imperialism#FreePalestine#Leonard Peltier#UAINE#Struggle La Lucha
31 notes
·
View notes
Text
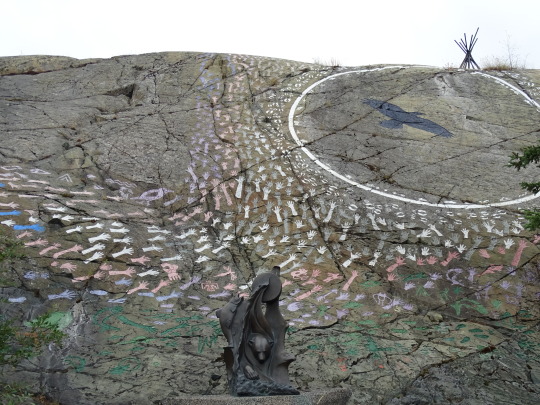
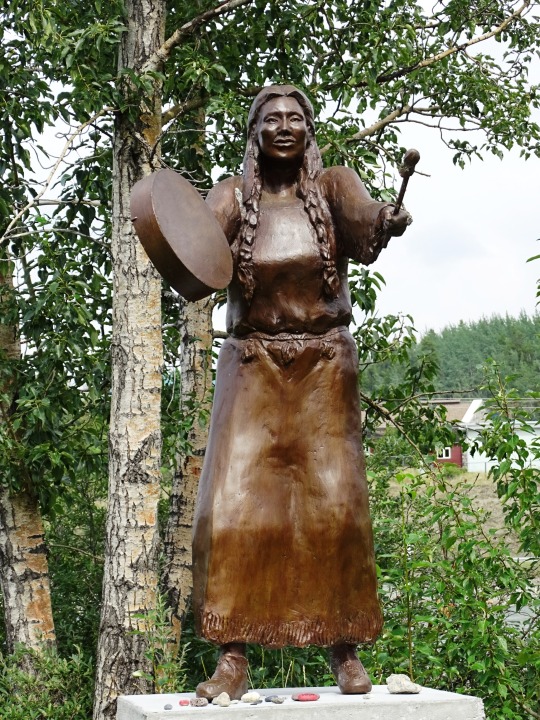
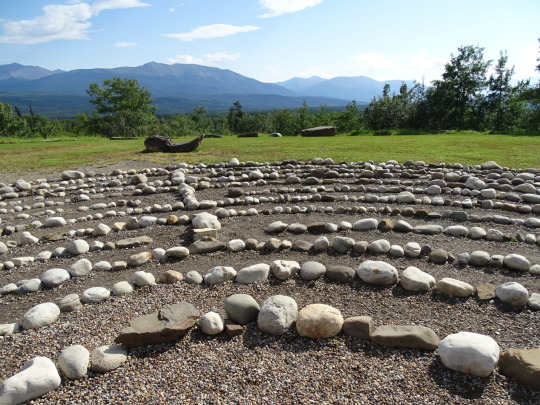
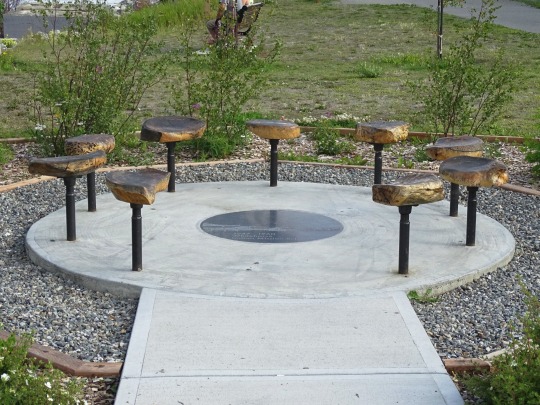
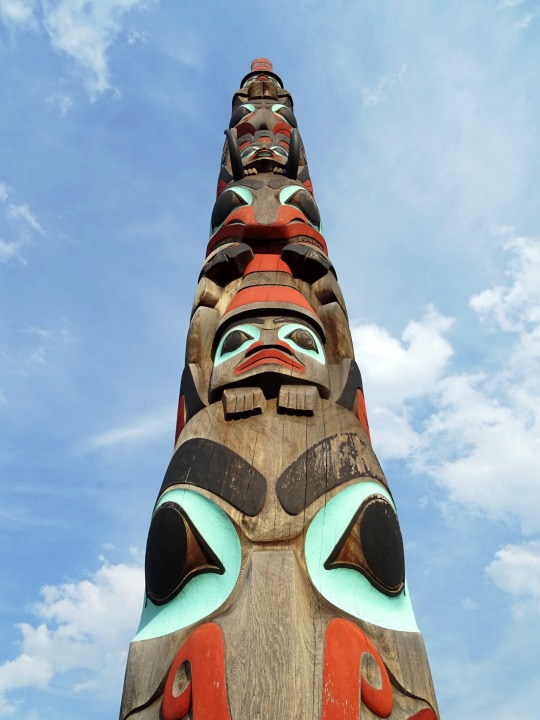
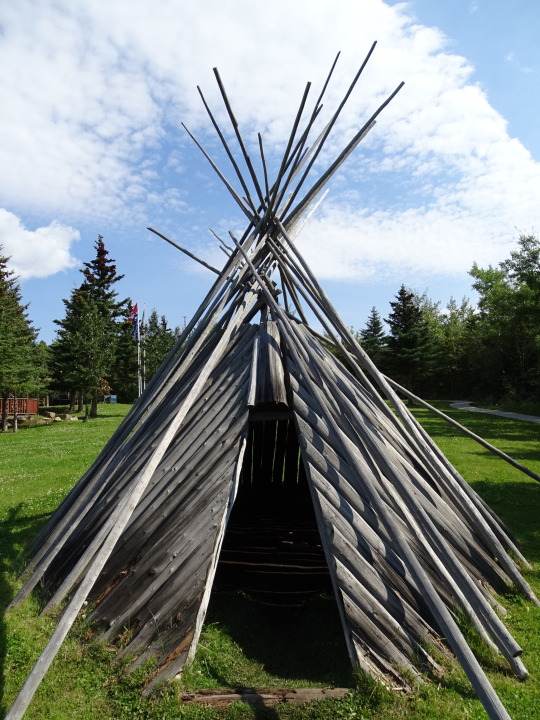
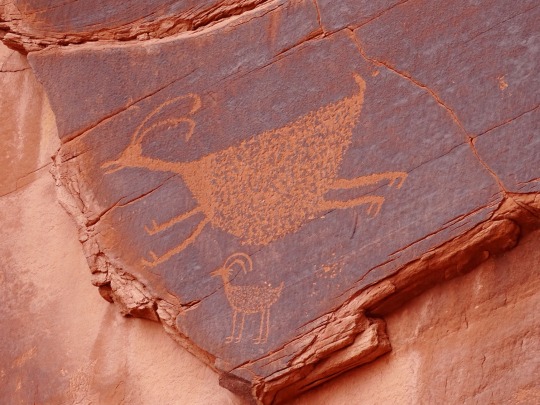
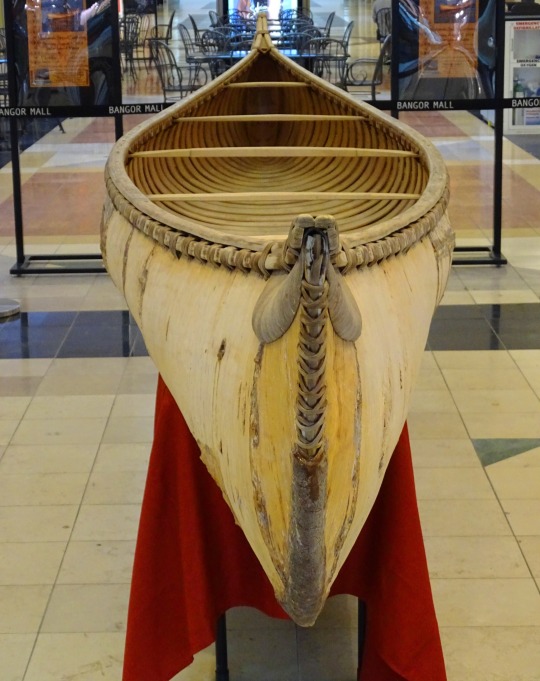
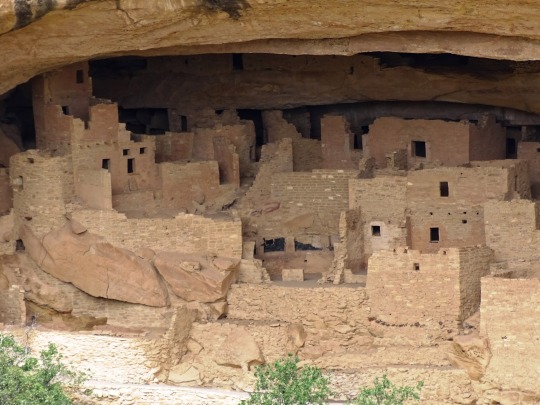
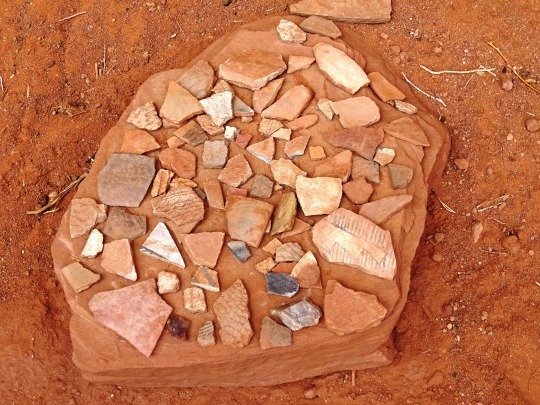
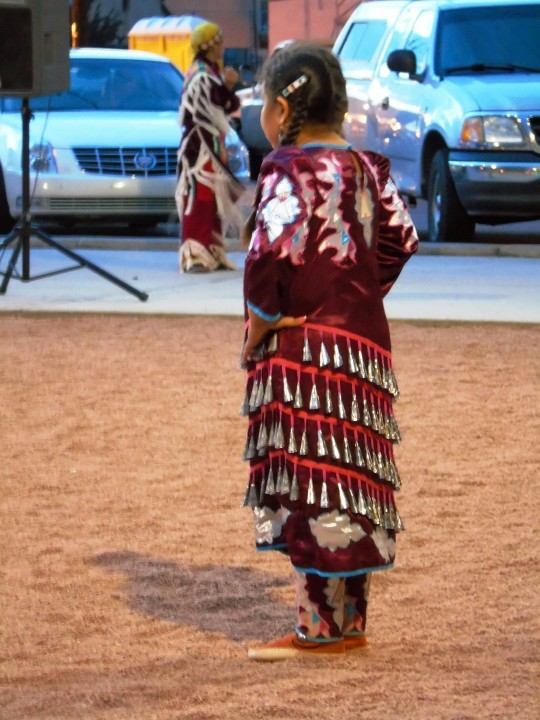
























National Day of Mourning
The National Day of Mourning takes place on the fourth Thursday of November, this year it’s on November 28. If this date sounds familiar to you, it’s because the fourth Thursday of November also coincides with Thanksgiving in the U.S. Every year on the National Day of Mourning, Native American people in New England gather together to protest. To them, Thanksgiving serves as a reminder of the unjust treatment that Native Americans have received since the 1620 Plymouth landing.
History of National Day of Mourning
The National Day of Mourning reminds us all that Thanksgiving is only part of the story. Native Americans, since 1970, have gathered at noon on Cole’s Hill in Plymouth, Massachusetts, to commemorate a National Day of Mourning on Thanksgiving Day.
Pilgrims landed in Plymouth and established the first colony in 1620. As such, it’s the oldest municipality in New England. Many Native Americans, however, don’t celebrate the arrival of the Pilgrims and other European settlers. Thanksgiving, to them, is a brutal reminder of “the genocide of millions of Native people, the theft of Native lands, and the relentless assault on Native culture.”
They participate as a way to honor Native ancestors and the struggles of Native peoples to survive today. “It is a day of remembrance and spiritual connection as well as a protest of the racism and oppression which Native Americans continue to experience.”
The United American Indians of New England (UAINE) sponsors this event. They maintain that the Pilgrims arrived in North America and claimed tribal land for their own, as opposed to establishing a mutually beneficial relationship with the local inhabitants. UAINE members believe that these settlers “introduced sexism, racism, anti-homosexual bigotry, jails, and the class system.”
The National Day of Mourning generally begins at noon and includes a march through the historic district of Plymouth. While the UAINE encourages people of all backgrounds to attend the protests, only Native speakers are invited to give these speeches about the past, as well as current obstacles their people have overcome. Guests are asked to bring non-alcoholic beverages, desserts, fresh fruits and vegetables, or pre-cooked items. The protest is open to anyone, and has attracted other minority activists.
National Day of Mourning timeline
1998
No permit needed
UAINE receives permission from local authorities to march in protest without having to obtain a permit.
1997
Protests got violent
State troopers use force against protesters who gathered together to observe the 28th annual National Day of Mourning.
1970
National Day of Mourning began
The first annual protest for the National Day of Mourning takes place.
1620
Pilgrims arrived
English separatist Puritans, who had broken away from the Church of England, land at Plymouth Rock. Today we refer to them as Pilgrims.
National Day of Mourning FAQs
What really happened in 1621?
The Pilgrims celebrated their first successful harvest by firing guns and cannons in Plymouth. The noise alarmed ancestors of the Wampanoag Nation who went to investigate. That is how native people came to be present at the first Thanksgiving
Are federal offices closed on a national day of mourning?
U.S. government offices are closed on the National Day of Mourning due to the Thanksgiving holiday.
What happens on the National Day of Mourning?
Native Americans and supporters gather in Plymouth to “mourn our ancestors and the genocide of our peoples and the theft of our lands.”
How to Observe National Day of Mourning
Brush up on your history: Do you know much about the first Thanksgiving? Do some research online, stop by your local library, or watch a documentary that will help give you a better understanding of what Native Americans actually went through.
Learn more about the United American Indians of New England (UAINE): UAINE is responsible for helping the National Day of Mourning protest take shape. To observe this important day, take some time to learn about about the UAINE. It's a fascinating organization that has done a great deal to promote better treatment for the Native American people.
Attend a protest: Protesters gather on Cole's Hill, a location overlooking Plymouth Rock, in Massachusetts. Everyone is welcome to observe these gatherings, and recently, other minority groups have started to become involved in the events of this day.
4 Reasons To Thank Native Americans
They've been here a while: Native Americans have existed in what is now known as the United States since 12,000 BC.
Thank you for your service: Although they were not considered American citizens, over 8,000 Native Americans served in the military in World War I.
Your great-grandma is who?: Many of the first families who settled in Virginia trace their roots directly back to Pocahontas.
An important vocabulary lesson: A bunch of Native American words have made their way into the English language; for example, coyote, tomato, poncho, potato, and chia.
Why National Day of Mourning is Important
It serves as an important history lesson: Textbooks often glaze over the unjust treatment of Native Americans. The National Day of Mourning, however, is a reminder that the people native to the Americas have been the recipients of a great deal of unfair treatment. It's important to discuss.
It's a time to come together: For protesters, the National Day of Mourning serves as a time to rally together to advocate for what they believe in. UAINE has worked to improve relations between the government and native people.
It shifts our attention away from turkey: Yes, Thanksgiving can be a great day filled with tons of good food and time spent with loving family and friends. However, the mission behind the National Day of Mourning is to highlight that the Thanksgiving holiday is actually quite painful for some people. For quite a few Native Americans in New England, Thanksgiving marks a time when their ancestors were treated poorly.
Source
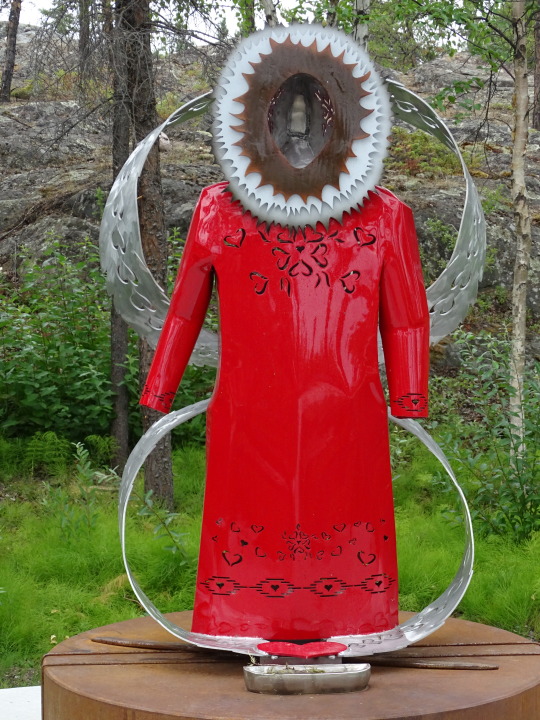
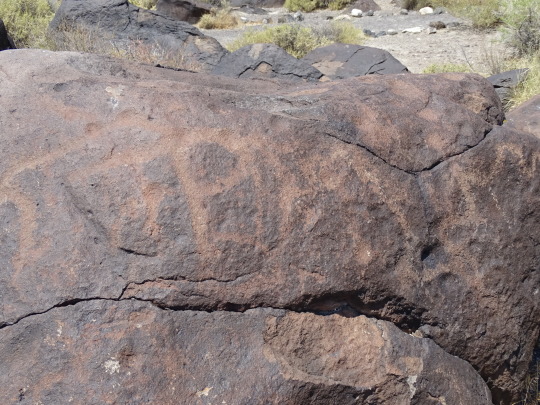
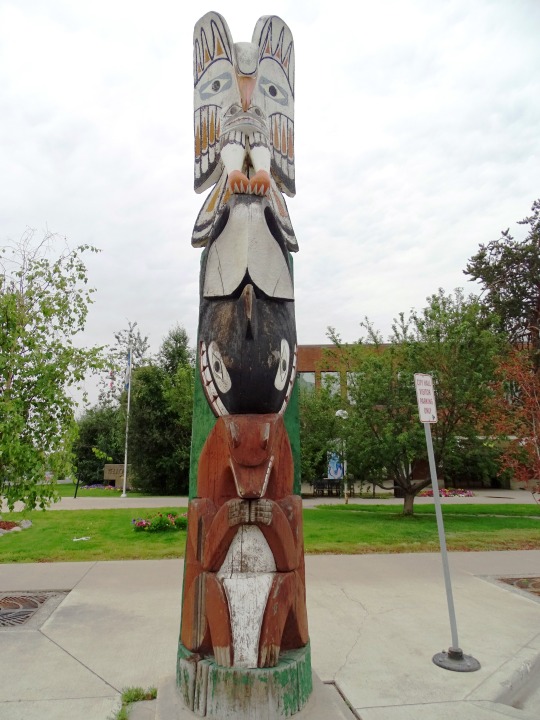
#MMIWG monument by Myrna Pokiak#Yellowknife#White Bird Battlefield Historical Landmark#The Gather-Ring by Manuel Báez and Charlynne Lafontaine#National Day of Mourning#28 November 20243#NationalDayofMourning#native american#Wabanki Canoe#Founding Fathers by Dale Faulstich#Jamestown S'Klallam Tribe#fourth Thursday in November#Unthanksgiving Day#travel#original photography#vacation#tourist attraction#Canada#USA#First Nations#Labyrinth Park#Monument Valley Navajo Tribal Park#Dinosaur National Monument#Mesa Verde National Park#Finding Peace Monument by Halain De Repentigny#Survivors of Whitehorse Indian Mission School by Ken Anderson#Two Brothers Totem Pole by Jaalen and Gwaai Edenshaw#Jasper National Park
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Wikipedia Featured Article Poll, Biographies Edition. Summaries and links below the cut
Margaret Ives Abbott (June 15, 1878 – June 10, 1955) was an American amateur golfer. She was the first American woman to win an Olympic event: the women's golf tournament at the 1900 Summer Olympics.
Lilias Eveline Armstrong (29 September 1882 – 9 December 1937) was an English phonetician. She worked at University College London, where she attained the rank of reader. Armstrong is most known for her work on English intonation as well as the phonetics and tone of Somali and Kikuyu. Her book on English intonation, written with Ida C. Ward, was in print for 50 years. Armstrong also provided some of the first detailed descriptions of tone in Somali and Kikuyu.
Morris Berg (March 2, 1902 – May 29, 1972) was an American catcher and coach in Major League Baseball, who later served as a spy for the Office of Strategic Services during World War II. Although he played 15 seasons in the major leagues, almost entirely for four American League teams, Berg was never more than an average player and was better known for being "the brainiest guy in baseball." Casey Stengel once described Berg as "the strangest man ever to play baseball".
Edward Dando (c. 1803 – 28 August 1832) was a thief who came to public notice in Britain because of his unusual habit of overeating at food stalls and inns, and then revealing that he had no money to pay. Although the fare he consumed was varied, he was particularly fond of oysters, having once eaten 25 dozen of them with a loaf and a half of bread with butter.
Harold Francis Davidson (14 July 1875 – 30 July 1937), generally known as the Rector of Stiffkey, was a Church of England priest who in 1932, after a public scandal, was convicted of immorality by a church court and defrocked. Davidson strongly protested his innocence and to raise funds for his reinstatement campaign he exhibited himself in a barrel on the Blackpool seafront. He performed in other sideshows of a similar nature, and died after being attacked by a lion in whose cage he was appearing in a seaside spectacular.
Marjory Stoneman Douglas (April 7, 1890 – May 14, 1998) was an American journalist, author, women's suffrage advocate, and conservationist known for her staunch defense of the Everglades against efforts to drain it and reclaim land for development. Moving to Miami as a young woman to work for The Miami Herald, she became a freelance writer, producing over one hundred short stories that were published in popular magazines. Her most influential work was the book The Everglades: River of Grass (1947), which redefined the popular conception of the Everglades as a treasured river instead of a worthless swamp. Its impact has been compared to that of Rachel Carson's influential book Silent Spring (1962). Her books, stories, and journalism career brought her influence in Miami, enabling her to advance her causes.
George Went Hensley (May 2, 1881 – July 25, 1955) was an American Pentecostal minister best known for popularizing the practice of snake handling. A native of rural Appalachia, Hensley experienced a religious conversion around 1910: on the basis of his interpretation of scripture, he came to believe that the New Testament commanded all Christians to handle venomous snakes.
Margaret Alice Murray FSA Scot FRAI (13 July 1863 – 13 November 1963) was a British-Indian Egyptologist, archaeologist, anthropologist, historian, and folklorist who was born in India. The first woman to be appointed as a lecturer in archaeology in the United Kingdom, she worked at University College London (UCL) from 1898 to 1935. She served as president of the Folklore Society from 1953 to 1955, and published widely over the course of her career.
Dom Pedro Afonso (19 July 1848 – 10 January 1850) was the Prince Imperial and heir apparent to the throne of the Empire of Brazil. Born at the Palace of São Cristóvão in Rio de Janeiro, he was the second son and youngest child of Emperor Dom Pedro II and Dona Teresa Cristina of the Two Sicilies, and thus a member of the Brazilian branch of the House of Braganza. Pedro Afonso was seen as vital to the future viability of the monarchy, which had been put in jeopardy by the death of his older brother Dom Afonso almost three years earlier.
Elias Abraham Rosenberg (Hebrew: אליאס אברהם רוזנברג; Hawaiian: Eliaka Apelahama Loselabeka; c. 1810 – July 10, 1887) was a Jewish immigrant to the United States who, despite a questionable past, became a trusted friend and adviser of King Kalākaua of Hawaii. Regarded as eccentric, he lived in San Francisco in the 1880s and worked as a peddler selling illegal lottery tickets. In 1886, he traveled to Hawaii and performed as a fortune-teller. He came to Kalākaua's attention, and endeared himself to the king with favorable predictions about the future of Hawaii. Rosenberg received royal appointments to several positions: kahuna-kilokilo (royal soothsayer), customs appraiser, and guard. He was given lavish gifts by the king, but was mistrusted by other royal advisers and satirized in the Hawaiian press.
#i expanded the summaries from the first sentence of the article to the first paragraph#cause with some of these people you don't get the full effect from just the first sentence#and also cause it's my poll.#Wikipedia polls
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
12. why the 1880s?
something about this decade really sings to me. I find in particular, nearing the end of the nineteenth century, so much was happening on around the world in terms of arts, politics, technology, colonization. world events and global news don’t personally reach the day-to-day lives of the everyday folk, but they are an important part in gauging what life, thought, and society was about—what things were important then and now?
basically for myself, reminding me of notable things that occured during the 1880s—some thematic, some of relevance to context and characters, and the rest just ?? interesting and/or wild?
cocaine is a hot new cure for everything and anything. perscribed, sold in foods and more. heroine introduced as a lesser-addictive substitute for morphine…
lots of developments in fields of psychology; many experiments and happenings; Freud starts his work 1886.
1880-1914 had +twenty million immigrants to the United States: Germany, Ireland, England, China had the most arrivals.
William Dorsey Swann, the first self-proclaimed drag queen, organizes a series of drag balls in Washington, D.C. 1880-1890s.
Jack the Ripper claims his “first” victim in 1888 White Chapel, London. big scare.
Sherlock Holmes first appears in Arthur Conan Doyle’s A Study In Scarlet as part of the British magazine’s Beeton’s Christmas Annual in 1887.
Strange Case of Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hyde by Robert Louis Stevenson is published in 1886. Gothic fiction, drawing from emerging fields of science and psychology. & Treasure Island was published earlier in 1883 by him too!
Mark Twain drops The Prince and the Pauper (1881), Adventures of Huckleberry Finn (1884), A Connecticut Yankee in King Arthur’s Court (1889).
Bel-Ami, Guy de Maupassant’s second novel is published in 1885. about a man who seduces and manipulates high society French women in the French colonies for power and wealth. MOVIE WAS ADAPTED IN 2012 STARTING ROBERT PATTINSON LOL
western European art movements very romantic and swirly and pretty: Monet, Debussy xoxo.
meanwhile, African American ragtime music becomes the “pop” music across the pond here.
North Dakota (1889), South Dakota (1889), Montana (1889), Washington (1889) become states.
train segregation laws flag beginning of Jim Crow; Civil Rights Movement of 1875 voided, making discrimination in private is not illegal, and prohibiting state intervention to personal or commercial segregation. l*nching continues throughout the south. slavery may be over on paper, but indentured labour is legal.
1882 infamous O.K Corral gunfight.
Gold Rush continues, all over the world—South Africa, to British Columbia, to California, to Argentina, to Russia-China borders.
centuries of American “Indian” wars continue.
American Dawes Act of 1887 granted American government authorization to regulate indigenous lands, including creating and assigning and enforcing reservations.
Sitting Bull’s 1883 speech of the atrocities experienced at the hands of white American settler colonists.
Canadian Pacific Railway 1881-1885. foreign labourers were hired to do a lot of heavy, dangerous, unwanted work. in America, more than 100,000km of tracks were laid by majority Chinese, Irish, Scandinavian workers.
America’s Chinese Exclusion Act of 1882 and Canada’s Chinese Immigration Act of 1885 was officiated, enforcing law of a Head Tax to be paid for every Chinese person entering North America. over the course of the next couple of decades, the fee of $1,500 was doubled to $5,000 was increased 500% to $25,000 in today’s currency—per person. this had devastating and lasting impacts on generations and societies of Chinese living both overseas and already in North America. propaganda at this time created many racist myths that persist today: there are too many Asians, they are taking our jobs, (the men) are gross and effeminate and a threat to (white) women, they shady and scheming people. these were the first and only major federal legislation to explicitly suspend immigration for a specific nationality in American and Canadian history. (I study Asian Canadian history, I can go on about this all day)
Tong Wars (1883-1913) had Chinatown gangs and factions in violent street wars across America, San Fransisco to New York.
large, targeted, and repeated anti-Jewish rioting (pogorm) and antisemitism rampant throughout Imperial Russia, 1881-1882 had more than two hundred anti-Jewish events alone. Jews continue to be racialized and othered.
fuck ton of colonization happening in Africa and the Middle East, Southeast Asia. Berlin conference 1884-1885 literally chopped up Africa to distribute to European powers.
Irish nationalist efforts to push forth Home Rule bill of sovereignty is defeated in British Parliament. Irish are not “white”, they are “othered” in Europe and in Americas.
use of photographic film pioneered by George Eastman, who started manufacturing film. his first camera (Kodak) was ready for sale in 1888.
Thomas Edison gets lit in New York 1883 with first electrical power station. next several year sees major cities being lit up with street lamps and public lighting with the science and works of a Nikolas Tesla (1886-1893).
hell of a lot more inventions in the works and patents being claimed. Hertz and radiowaves, Bell for telephone services.
“Between the years of 1850–1900, women were placed in mental institutions for behaving in ways the male society did not agree with”
way too much history to cram, obviously. here are some keywords for further research oki
prison industry / spiritualism / opium epidemic / irregular and uneven “modernizations” in rural vs. urban areas / class and poverty gaps / morality scares, checks, comparisons, gaps / new businesses and gadgets, products, tech to help with anything / fascination of the (colonial) Other; side shows, “freak shows” and other human zoos
#update#victorian era#1880s#1800s#1880s history#update: research#writing research#drugs cw#lynching cw#inventions#technology#gold rush#ref: poc history#ref: indigenous history#ref: black history#ref: queer history#ref: womxn history#ref: research#american history
11 notes
·
View notes