#U.S.-China summit
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
San Francisco's Homeless Cleanup Efforts Spark Controversy Ahead of U.S.-China Summit
https://headlinehorizon.com/Politics/House/1296
In preparation for the upcoming U.S.-China summit, San Francisco has faced criticism for its efforts to remove homeless camps from its streets. This article sheds light on the ongoing debate and the potential implications of the city's actions.
0 notes
Text
Russia Is Responsible for Havana Syndrome Attacks on U.S. Personnel
“The former head of the Pentagon’s investigation into the mysterious health incidents known as Havana Syndrome told the CBS investigation show 60 Minutes he believes Russia was behind them and was attacking U.S. officials abroad and at home.”[1] This television show, in partnership with The Insider (a Russian exile media outlet) and a German magazine (Der Spiegel), reported on new evidence…
View On WordPress
#"60 Minutes"#"Havana Syndrome"#Bogota#China#Cuba#Der Spiegel#Europe#Greg Edgreen#Hanoi#India#London#NATO Summit (Lithuania) 2023#Russia#U.S. Defense Intelligence Agency#United States of America#Vietnam
2 notes
·
View notes
Note
i've noticed you're Canadian, and as an incredibly terrified american, are you guys getting news that war is actually likely? our news and search engines are being heavily censored, i actually cannot find anything past 2024 about possible war. i'm reeling that it's possible, but i wouldn't put it past the orange fuck. i am so sincerely sorry for that cockalorum.
Hey! First of all, thanks for reaching out, and I'm sorry to hear you're terrified. We are also terrified to hear that your news is being censored. As I'm sure you can imagine, now more than ever, we want Americans to be aware of our situation and what's going on up north.
In terms of whether our news is saying war is likely... that's hard to answer. Truthfully, our news sources take a bit of a different tone than yours, for the most part. We're very avoidant of absolutes until things are certain, and our journalists (the respectable ones) tend to avoid alarmist rhetoric - at least compared to the kind of reporting and headlines we often see from many (still very respectable!) publications in the States.
So, what I'll say is this: in short, no. I have not seen any explicit reporting that war is imminent. However, there have been a lot of signals that a Big Bad is coming, and that's what a lot of us have been deducing from that. Here are some examples:
PM Justin Trudeau called a summit with most of our major industry leaders, informing them that Trump's annexation threats were very real and that we needed to start preparing.
Following that meeting, he flew to Europe to meet with several EU leaders to strengthen alliances and met with the Secretary-General of NATO for apparently similar discussions.
On a potentially related note, CSIS (our version of the CIA) released a foreign interference intelligence report to Parliament on Jan 28, most of which has not been made available to the public. However, I’ve seen some reporting that the United States was one of the countries mentioned as trying to interfere in our elections, and that the government’s response could be read as a silent invocation of NATO Article 4.
Perhaps most telling of something bad to come: our leaders are reaching across the aisle more than I've ever seen. Trudeau has been meeting with our premiers often, and outside of the numbnut in Alberta, they’ve unanimously come together to work on plans that prioritize Canada. We're hearing some of our most despicable, power-hungry conservatives advocate for Country Over Party and Country Over Province, willingly working with Trudeau—whom not even a month ago they treated like the most egregiously offensive man who ever lived—in supporting his plans to push back on Trump.
Our most conservative, openly pro-Trump candidate for the next election (Pierre Poilievre) is adding the establishment of a new military base and an Arctic defense strategy to his platform.
All candidates have been talking about increasing military spending.
Finally, all of our economic conversations have been focused on trade diversification and expanding internal manufacturing capabilities. We just signed a massive trade deal with China—something we had been refusing to do primarily because of our allegiance to the United States as our ally, which has now clearly been broken.
So yeah. Nothing overt, but it's not looking good.
On the ground, regular people (at least where I live) have been talking about war as if it's a real possibility and discussing what they'd do. Overwhelmingly, people are willing to stand up to this if it comes to it.
War aside, I've never seen anti-American sentiment run so high in this country. It's truly terrifying. People—on the right and left—are buying Canadian and boycotting American products. People are selling their American vacation homes, canceling travel to the U.S. (and those still taking their American vacations are being called traitors in some circles). Companies are ripping up American contracts. Stores are pulling American products off the shelves. And then, of course, there's the booing.
I know this seems grim, but I want to be honest with you. Our nations' relationship has been irrevocably harmed. There is no world where we go back to how it was before—whether or not Trump is gone—because we simply can't trust we won’t be put in this position again. And honestly—no offense to you, your ask was very polite, and I truly sympathize with every American who is as appalled by this as we are—I don’t think Canadians would feel this strongly about “never going back” if it weren’t for the response we’re seeing from American people online and American media.
Initial reactions to these threats were outright dismissal... of a threat to our sovereignty. Then, it was met with jokes and condescension, with late-night hosts chalking it up to picking a fight with your lapdog ally (literally, Jon Stewart called us golden retrievers), and people online treating it like just another crazy Trump-ism. Which is, again, a) not an appropriate reaction to a threat to a country’s sovereignty, and b) a complete dismissal of the real-time effects we're already feeling from this. The Canadian dollar dropped CONSIDERABLY in value the day the tariffs were announced. Just look at the USD:CAD forex charts and see how fucking stupid it looks since Trump took office.
And then, finally, we keep being met with either MAGA idiots who double down on the threat and tell us about how they can't wait to annex us/invade us and how we don't stand a chance against your military, or we're met by well-meaning but ultimately self-centered Americans who didn't vote for Trump and seem to be looking for us to absolve them and confirm we know they, in particular, didn’t do this. Which, like, okay, but how does that help anything? And really, should you be turning to us for comfort in this moment? This might sound dramatic, but literally go to the comment section of any Canadian creator, and you'll see this playing out there. It's aggressive and overwhelming, and you can’t blame Canadians for feeling like we can't count on you (again, en masse—not you specifically) to have our backs.
That said, the Canadian people and the Canadian government still truly sympathize with Americans—and immigrants in America (documented or not)—who did not choose this and are being impacted. We really, truly, and deeply appreciate Americans like you who are seeking out our voices, seeing through the noise, and trying to stay informed.
So, with that in mind, to help with the root of your question regarding news sources... first, I would recommend getting a VPN. I think your online experience would greatly improve. Second, there are a few Canadian sources you can go directly to, like our national broadcaster, the CBC.
Personally, I also enjoy following some left-leaning creators on TikTok, most of whom are journalists. I just try to be careful to keep their biases in mind and do my own follow-up research/think critically about what I hear. Here are a few of my favourites: Kat Arnett - she's a photographer but she used to be a political journalist. She's been pretty great at talking about how Canadians have experienced all of this.
KnittyKnits - she's a progressive (I'd say left but not far left) creator based in Alberta and she covers a lot of Canadian news.
Contra Tenore - He's a left-wing creator who I personally feel has a fairly pragmatic approach to analysis. He's VERY supportive of our left wing party (The New Democratic Party or 'NDP') and he's been talking a lot about this situation with the U.S. He doesn't mince words, though, and sometimes his videos are a little hard to take.
Cole.NotCole - He's probably my favourite starting point for a lot of my research right now. He gives short summaries of the day's news. He's sort of our Aaron Parnas but less problematic and less priviledged. He has a Liberal (center-left) leaning lens, but I don't personally feel he editorializes too much.
JB|Canadian Politics - Overtly progressive, but great political updates in my opinion - bias or no bias. He's been engaging Americans a lot during this whole thing in really interesting ways.
Unlearn16 - They're an extremely progressive high school history teacher (or maybe social studies?). I've really enjoyed their content covering all of this. They do a great job of breaking down the impact of political maneuvering and spelling out historical contexts.
Anyway... I hope this helps! And thank you again for asking. It really does mean a lot to see people seeking out Canadian perspectives at this time.
#made in canada#canada politics#canada#canadian#oh canada#us tariffs#trump tariffs#trump trade war#fuck trump#cdnpoli#canadian news#canadian politics#america#american politics#usa politics#justin trudeau#jasmeet singh#pierre poilievre#nato#canada us relations
474 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Dilemma Bulletin: Friday April 4th, 2025
Keeping you informed about the daily events of the Trump Administration
Donald Trump’s tariffs are already seeing a rippling effect on a global scale as he escalates a global trade war.
China announces a 34% retaliatory tariff on the United States. This tariffs are set to affect US soybean, corn and meat farmers the most.
Canada will impose a 25% tariff on all U.S. vehicle imports that do not comply with the USMCA free trade agreement negotiated previously by Donald Trump himself.
Nintendo announces pre order delays for the Nintendo Switch 2 due to Trump’s tariffs.
Target sees a continuous drop in sales after abandoning DEI initiatives.
Nike stock plummets after Trump’s tariff announcement.
Trump skipped the dignified transfer of American soldiers who died in Lithuania as he flew to Miami to attend the Saudi Arabian funded LIV golf tournament at his Doral golf course.
Kamala Harris gives speech at Leading Women Defined Summit where she discussed women empowerment and addressed the worsening conditions of the United States and how this was all warned during her campaign.
$2.8 trillion dollars and counting have been wiped out from the US stock market since Trump’s tariffs were announced.
Donald Trump fired several members of his National Security Team after meeting with MAGA social media influencer Laura Loomer
Republican Senator Chuck Grassley (R-IA) and Democrat Senator Maria Cantwell (D-WA) introduce bipartisan legislation to require congressional approval for all new tariffs






#donald trump#us politics#breaking news#potus#president trump#politics#news#president of the united states#tumblr#united states politics#us tariffs#thoughts and tariffs#trump tariffs#tariffs#usa news#usa#united states news#united states politics and government#president donald trump#the dialogue dilemma#nintendo switch 2#nintendo switch#nintendo
86 notes
·
View notes
Text

Remains of Andrew 'Sandy' Irvine Who Vanished in 1924 Found on Mount Everest
The foot, boot and sock thought to belong to Sandy Irvine, who disappeared during George Mallory's 1924 expedition to climb Mount Everest, have likely been found. They could be a vital clue in unraveling an even bigger mystery.
Remains believed to belong to a British explorer who vanished more than 100 years ago while climbing Mount Everest have finally been found.
Andrew Comyn "Sandy" Irvine, aged 22, disappeared along with the mountaineer George Mallory in June 1924. The pair were attempting to become the first people to scale the world's highest peak.
It's still a mystery whether they succeeded in their goal before they died. Mallory's remains were discovered in 1999, which were missing a photograph of his wife that the climber had planned to leave on the summit. Irving, who had been carrying a Kodak camera that may have recorded a possible historic summit, was never recovered. The summit was officially first reached 29 years later, when Edmund Hillary and Tenzing Norgay scaled Everest from its south side in 1953.
Now, a National Geographic documentary team, including the Oscar-winning director Jimmy Chin and the climbers and filmmakers Erich Roepke and Mark Fisher, have found what they believe is Irvine's foot.
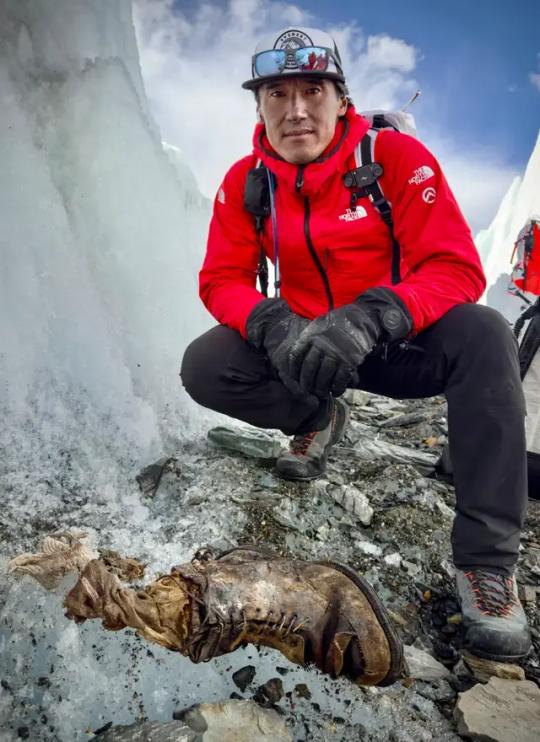

Encased in a boot and wearing a sock stitched with his name, the foot was discovered on Everest's Central Rongbuk Glacier, further down the mountain from Mallory's remains.
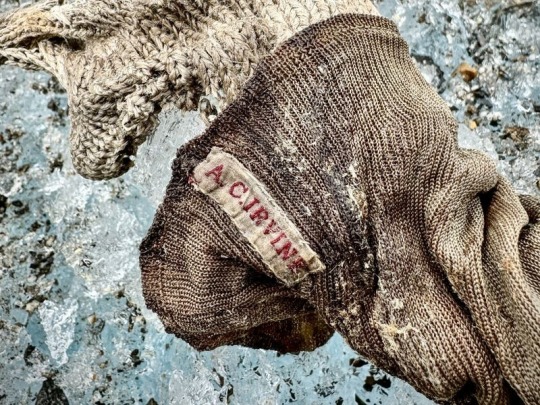
"I lifted up the sock," Chin told National Geographic, "and there's a red label that has A.C. IRVINE stitched into it."
Irvine and Mallory were last seen on June 8, 1924, as they set off to scale the summit. One of their expedition teammates, Noel Odell, reported spotting the two near the second of the mountain's three steps as two tiny black dots. One of the dots broke past the skyline during a brief parting of the clouds, then they disappeared.

Mallory's body was found less than 2,000 feet (600 meters) from the summit by the U.S. rock climber Conrad Anker. Mallory's remains were tied by a rope around the waist and had injuries suggesting that the pair had fallen while connected together.
By searching near these remains and scouring the glacier for clues, Chin and his team located the boot melting out of the ice.
"This was a monumental and emotional moment for us and our entire team on the ground, and we just hope this can finally bring peace of mind to his relatives and the climbing world at large," Chin said.




The team sent the remains to China Tibet Mountaineering Association, which is responsible for climbing permits on Everest's northern side. The find was also reported to the Royal Geographical Society, which organized Irvine and Mallory's expedition, and Irvine's great niece and biographer, Julie Summers.
"I have lived with this story since I was a 7-year-old when my father told us about the mystery of Uncle Sandy on Everest," Summers said, as reported by the Guardian. "When Jimmy told me that he saw the name AC Irvine on the label on the sock inside the boot, I found myself moved to tears. It was and will remain an extraordinary and poignant moment."
The Irvine family has volunteered to take a DNA test so that the identity of the remains can be conclusively determined. Meanwhile, Chin and his team will continue to search for more artifacts. If Irvine's camera is found and it can prove they scaled the peak, it could potentially rewrite history.
By Ben Turner.

#Mt. Everest#Mount Everest#Sandy Irvine#Remains of Andrew 'Sandy' Irvine Who Vanished in 1924 Found on Mount Everest#George Mallory#1924 British Mount Everest expedition#mountain climbing#archeology#archeolgst#history#history news
174 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Putin is isolated."

BRICS, 50% of the World population is telling a big "fuck off" to the arrogant, declining and decadent G7 amounting to 10% of the World's population.

🇺🇳🇷🇺 UN Secretary General Guterres respectfully bows and shakes the hand of Putin in Russia’s Kazan at the BRICS summit.
A lot of people start crying and scream hysterically when they see this picture, for some reason.

[BRICS Currency Looms Large: Could This Be the Beginning of the End for U.S. Dollar Dominance?
For decades, the U.S. dollar has been weaponized as a tool of global dominance, wielded by the American empire to enforce its geopolitical will.
Through sanctions, coercive financial practices, and the threat of exclusion from the dollar-based system, the U.S. has effectively terrorized nations across the world.
The pretense of a “free market” economy has long been shattered by Washington's aggressive use of the dollar as a weapon to cripple economies, isolate adversaries, and exert control over global trade.
But the world is growing tired—sick and tired—of this financial tyranny. And now, with the rise of BRICS, we may be witnessing the beginning of the end for U.S. dollar supremacy.
BRICS—Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa—represent a bloc of nations that together account for nearly half of the global population and a significant chunk of the world’s GDP.
For years, these nations have been quietly collaborating to counterbalance the West's stranglehold over international finance, and now, they are inching closer to launching their own currency.
The creation of a BRICS currency signals an outright challenge to the dollar-dominated global economy, and it is nothing short of a revolt against American financial imperialism.
Why is this happening? The answer is simple: countries are fed up with being bullied. The U.S. has used its currency like a sledgehammer, smashing nations that dare to defy its hegemony.
Whether through sanctions on Iran, Venezuela, or Russia, or by financially suffocating smaller nations into submission, the dollar has become a tool of coercion rather than commerce.
Nations who once played by the rules of the so-called “global order” have found themselves punished, their economies crippled, and their people starved—merely for refusing to kowtow to Washington's dictates.
But BRICS is offering an alternative. The creation of a BRICS currency, backed by the economic strength of its member nations, offers the world a way out of the suffocating grip of the dollar.
This is not just about financial autonomy—it’s about reclaiming sovereignty, independence, and the right to conduct trade without the constant threat of U.S. interference.
Russia and China have been leading the charge in this effort, driven in part by the U.S. sanctions imposed on Moscow following the Ukraine conflict and the ongoing trade war with Beijing.
Both countries have moved aggressively to reduce their reliance on the U.S. dollar, increasing trade with each other and with other BRICS members in their local currencies.
They are laying the groundwork for a currency that could be based on a basket of commodities, potentially gold-backed, further weakening the grip of the U.S. dollar on the global market.
The U.S. has long prided itself on its role as the issuer of the world’s reserve currency, but this dominance was never guaranteed to last forever.
The BRICS currency threatens to dismantle the global financial architecture that has allowed the U.S. to live far beyond its means.
For decades, the U.S. has run massive deficits, printing money at will, secure in the knowledge that the world would continue to rely on the dollar.
But as BRICS nations move to establish their own currency, that privilege could evaporate overnight.
The implications for the U.S. are dire. If the dollar loses its status as the world’s reserve currency, the U.S. economy could face a severe reckoning.
The artificial demand for dollars that has kept interest rates low and allowed the U.S. to run massive debt could vanish, leading to inflation, higher borrowing costs, and potentially a fiscal crisis.
The American empire, propped up for so long by its control of global finance, could find itself in rapid decline.
For the rest of the world, however, the rise of a BRICS currency represents hope—a chance to escape the iron grip of U.S. financial imperialism. No longer will countries have to fear the punitive measures of the U.S. Treasury.
No longer will they have to worry about being cut off from the global financial system for standing up to American bullying.
The creation of a new currency could usher in a multipolar world, where nations are free to trade without being subject to the whims of a single superpower.
Of course, the U.S. will not go quietly. Washington will likely pull out all the stops to crush the BRICS currency before it can gain traction. The playbook will be the same: propaganda, financial sabotage, and even the threat of military intervention.
But this time, the world may not be so easily intimidated. The BRICS nations, backed by their vast resources and burgeoning economies, are prepared to stand their ground.
In the end, the creation of a BRICS currency is not just an economic development—it’s a revolutionary act. It’s a declaration that the age of American financial dominance is coming to an end, and that a new world is on the horizon.
The U.S. dollar, once seen as the bedrock of global stability, has become a symbol of oppression, and the world is ready to move on.
The question now is not whether the U.S. dollar will fall, but when. And as BRICS moves closer to launching its own currency, that day may be sooner than anyone expects.
The empire, long propped up by its financial manipulation, is facing a reckoning—one that could change the course of history.]
IMF Growth Forecast: 2024
🇮🇳India: 7.0% (BRICS)
🇨🇳China: 4.8% (BRICS)
🇷🇺Russia: 3.6% (BRICS)
🇧🇷Brazil: 3.0% (BRICS)
🇺🇸US: 2.8% (G7)
🇸🇦KSA: 1.5% (invited to BRICS)
🇨🇦Canada: 1.3% (G7)
🇿🇦RSA: 1.1% (BRICS)
🇬🇧UK: 1.1% (G7)
🇫🇷France: 1.1% (G7)
🇮🇹Italy: 0.7% (G7)
🇯🇵Japan: 0.3% (G7)
🇩🇪Germany: 0.0% (G7)

‼️ 159 out of 193 countries have signed up to use the new BRICS settlement system.
US and European Union will no longer be able to use economic sanctions as a weapon.
This system allows countries to settle trades and payments in their own currencies, reducing reliance on the U.S. dollar, which has long been the dominant global currency.
61 notes
·
View notes
Text




Following latest news and developments, the American Coalition for Ukraine, issues statement on the U.S. Administration's Decision to Pause Military Aid to Ukraine Undermines U.S. Security.
For decades, the United States has championed peace through strength. Now, the current Administration’s pause on military aid and intelligence information to Ukraine undermines U.S. interests by signalling retreat to our adversaries. While the battlefield impact of this decision will take weeks to play out, the moral and diplomatic fallout is immediate, and the risk of civilian casualties increases immediately.
Additionally, lifting economic sanctions imposed on Russia would only serve to empower Putin and hand him additional resources to continue his invasion, while making the U.S. look weak and unreliable.
Supporting Ukraine is a smart defense investment. Less than 5% of the U.S. defense budget helped significantly degrade Russia’s military without American boots on the ground. If Ukraine falls, U.S. costs and risks will escalate.
Any pause or disruption of aid to Ukraine helps Putin, weakens NATO, and emboldens America’s adversaries. China may target Taiwan, while Iran and North Korea will test U.S. resolve. Ignoring Russia’s war crimes against Christians, children, and civilians does not represent America’s values of faith and freedom.
The American Coalition for Ukraine calls on the administration to immediately restore military and intelligence aid to Ukraine and pursue peace talks from a position of strength. We urge Congress to represent the will of their constituents, who overwhelmingly support Ukraine and distrust Putin; to act decisively to uphold American values in the face of autocratic aggression; and to continue bipartisan support for Ukraine through military, economic, and humanitarian assistance.
The situation is evolving rapidly, but one thing must continue to grow — the number of calls from Ukraine supporters to Congress.
We urge you to keep calling your representatives. To make this process easier, we have launched an automated tool that allows you to reach your elected officials in just a few clicks. Your voice matters — let’s make it heard!
visit http://americancoalitionforukraine.org for more details, or click the link below for quick access to our online tool.
JOIN RALLIES FOR UKRAINE
In recent days, many of our communities have come together for emergency rallies to demonstrate the broad support Ukraine has among the American people. We invite you to join our rally in Washington, D.C., this weekend or stand with your local community to voice your support for Ukraine.
visit event Facebook page for more details
CONTACT YOUR LOCAL MEDIA
Write a letter to the editor, an op-ed, or reach out to your local radio and TV stations to share your perspective on this critical moment for Ukraine. Your voice matters!
REGISTER FOR UKRAINE ACTION SUMMIT, SPRING 2025
Three years in, Ukraine still fights for its survival. The Ukraine Action Summit is an incredible opportunity to reinforce long-term support for Ukraine at a crucial moment.
Register today to take advantage of early bird pricing—prices increase tomorrow!
Our community of advocates has grown exponentially since the launch of the American Coalition for Ukraine. We are committed to delivering expert-driven advocacy coordination and reliable support for our community, ensuring that all our actions and engagements yield top results. But we need your help to make it happen!
Please donate to support our work for Ukraine!
Zelle email for donations: [email protected]
or use button below to donate via PayPal and CC
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
Trump treats Latinos as enemies, Lula says
Alongside Chile’s Boric, president warned that “cold war” between the U.S. and China is not in Latin American’s interest

President Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva accused American Donald Trump yesterday of treating Latinos as “enemies” even after the population of the region helped “build American wealth.” The criticism came during the state visit of Chilean President Gabriel Boric to Brazil. During the same ceremony, the Brazilian leader invited Mr. Boric to participate in the BRICS summit, a strategy aimed at strengthening regional integration.
"It is important for us to seriously discuss this issue of democracy and integration [in Latin America]. We need to leverage this [integration] to grow our countries. Why don’t we have any place like the Netherlands in South America?” Mr. Lula questioned. “We all remain poor, wanting to go to the U.S. for a better life. After helping build American wealth, a U.S. president comes along and treats Latin Americans as enemies,” he added.
Similarly, the Brazilian president argued that it is not in South America’s interest to enter a “Cold War” between Americans and Chinese.
“The United States has decided to establish a discussion favorable to a protectionist policy, contrary to everything that was told to us since the 1980s, [contrary] to globalization, [contrary] to free trade. In other words, everyone was talking about free trade and globalization, and suddenly, none of that is worthwhile, and what counts is protectionism,” Mr. Lula stated.
Continue reading.
#brazil#brazilian politics#politics#united states#geopolitics#luiz inacio lula da silva#image description in alt#mod nise da silveira
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
Trump is taking action to withhold military aid from Ukraine amid an ongoing public feud with Zelensky, according to multiple reports. Bloomberg is reporting that the U.S. is “pausing all current military aid to Ukraine until Trump determines the country’s leaders demonstrate a good-faith commitment to peace.”
This, after the Wall Street Journal reported on Monday that the Trump Administration “has stopped financing new weapons sales to Ukraine and is considering freezing weapons shipments from U.S. stockpiles.”
The U.S. seems to be on the path to transfer the responsibility of support for Ukraine over to Europe, amid efforts to begin the process of normalization with Russia… and wasn’t that exactly what U.S. Defense Secretary Pete Hegseth said the Trump Admin wanted when he addressed European leaders last month and said Washington’s goal was to focus on China?
SOURCE LINKS:
3 March 2025 - Trump Pauses Military Aid to Ukraine After Clash With Zelensky
3 March 2025 - U.S. Hitting Brakes on Flow of Arms to Ukraine
3 March 2025 - White House seeks plan for possible Russia sanctions relief, sources say
3 March 2025 - Ukraine’s Zelensky says end of war with Russia is ‘very, very far away’
3 March 2025 - Trump on Truth Social: “This is the worst statement that could have been made by Zelenskyy, and America will not put up with it for much longer!”
2 March 2025 - Zelensky on Sky News: “I am exchangeable for NATO”
2 March 2025 - Brian Berletic on X: “London Ukraine Summit ‘Comes Up With’ LITERALLY US Secretary of Defense Pete Hegseth's February Directive.”
12 Feb. 2025 - Opening Remarks by Secretary of Defense Pete Hegseth at Ukraine Defense Contact Group (As Delivered)
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
World: A Growing BRICS Bloc Shows U.S. Is Losing the Battle for the Global South
— BY Tom O'Connor | August 22, 2023

South African President Cyril Ramaphosa Delivers a Speech at the 15th BRICS Summit in Johannesburg, South Africa. © Sputnik/Grigory Sysoev/Go to the Mediabank
While Russian President Vladimir Putin's in-person absence due to international legal troubles looms over the BRICS conference attended by the leaders of fellow member states Brazil, India, China and South Africa, the growing interest in expanding the group to include additional countries from across the globe is likely to cement the bloc's future as a force in global geopolitics.
And with no seat at the table for the United States, the three-day summit that began Tuesday in Johannesburg demonstrates how Washington has struggled to project influence throughout the vast, developing Global South.
"The U.S. is trailing countries such as Russia, India and China in the Global South," Akhil Ramesh, a senior fellow at the Hawaii-based Pacific Forum, told Newsweek. "The Global South does not have this special solidarity it has with nations such as China and India. As victims of Western imperialism/colonialism and having faced similar challenges in reconstruction and development, they have a unique solidarity."
"The U.S. approach continues to be one where they use nations of the Global South as pawns in their future, larger cold/hot conflict with China or Russia," Ramesh added. "This understandably has not helped them win friends."
Such solidarity continues to extend to Putin, who has accelerated his country's outreach to developing nations, especially in Africa, in recent years.
Moscow's overtures have been met with ongoing interest, as evidenced by the recent Russia-Africa Summit in Saint Petersburg. The summit was attended by 16 African heads of state and representatives of 25 additional African countries, even as the West has accused Putin of war crimes, resulting in an International Criminal Court warrant, and of weaponizing food by bombing grain infrastructure and allowing a deal that safeguarded the continued export of Ukrainian grains via the Black Sea to collapse.
U.S. warnings about forging closer economic ties with China have been met with even stiffer resistance, as President Xi Jinping presses on with his ambitious Belt and Road Initiative extending across continents despite a slowing economy at home.
Ramesh argued that nations of the Global South simply "do not view Beijing and Moscow the same way the West does," and instead see new opportunities where traditional mechanisms have failed.
"So, when there was a group presenting an alternative to the Western-led world order/vision of the world," he added, "nations were quick to jump on the bandwagon."
Newsweek has reached out to the U.S. State Department for comment.
Still, obstacles to progress exist within a bloc whose core members already have little alignment in their broader geopolitical goals, while some, especially China and India, have active disputes between them. Such feuds have the potential to only grow as the coalition considers taking on new members, such as Iran and Saudi Arabia.
Others who have applied include Algeria 🇩🇿, Argentina 🇦🇷, Bahrain 🇧🇭, Bangladesh 🇧🇩, Belarus 🇧🇾, Bolivia 🇧🇴, Cuba 🇨🇺, Egypt 🇪🇬, Ethiopia 🇪🇹, Honduras 🇭🇳, Indonesia 🇮🇩, Kazakhstan 🇰🇿, Kuwait 🇰🇼, Morocco 🇲🇦, Nigeria 🇳🇬, the Palestinian National Authority 🇵🇸, Senegal 🇸🇳, Thailand 🇹🇭, the United Arab Emirates 🇦🇪, Venezuela 🇻🇪 and Vietnam 🇻🇳, according to the most recent count offered last week by South African Foreign Minister Naledi Pandor.

Brazil, Lula, arrives, BRICS, summit, South, Africa! Brazilian President Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva arrives in Johannesburg, South Africa ahead of the 15th BRICS summit. The leaders of 67 countries have been invited to join the forum led by Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa. Ricardo Stuckert/Presidency of The Federative Republic of Brazil
"Those who are there for the day-to-day negotiations, at least from the Brazilian government side, say it is already very hard to come to consensus when you have China, India and Russia at the table," Ana Elisa Saggioro Garcia, a professor at the Pontifical Catholic University of Rio de Janeiro's Institute of International Relations and general coordinator of the BRICS Policy Center, told Newsweek.
But "there's another side of the story," she said. That's the growing view, including from Brazilian President Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva, that "a strong BRICS" is necessary, and a "strong BRICS is also a big BRICS."
South Africa, the current chair, is the only nation to have been added to what began as an informal BRIC bloc, born out of a term coined by then-Goldman Sachs chief economist Jim O'Neill in 2001 to describe emerging economic powers. Russia led the initiative to bring Brazil, China and India together for the first summit in 2009, and South Africa was admitted the following year.
Initially, BRICS was focused on effecting reform within existing, primarily Western-led economic institutions, such as the International Monetary Fund (IMF), in the wake of the 2008 global financial crisis.
"The first common agenda that they had, despite their differences, was the reform of the international financial architecture," Garcia said. "So, international financial institutions, those grounded in the Bretton Woods Conference, in the post-war period, they do not represent the world anymore. Those huge economies don't have enough voice in those institutions, they need to be reformed. They need to reflect the new configuration of the world economic power."

© Russian Ministry of Foreign Affairs/Go to the Mediabank
Gradually, the group became more focused on creating alternative mechanisms, most notably in the establishment in 2014 of the Shanghai-based New Development Bank, which today also counts Bangladesh, Egypt and the United Arab Emirates as members. With this transformation, Garcia explained, "the geopolitical character of BRICS started to be more important and more relevant than only the economic one."
China, in particular, she argued, "has been very clever and very strategic to use this opportunity to advance and to expand another coalition where China is predominant, where China doesn't have to deal with negotiations with Western powers."
But as evidenced by Brazil's enthusiasm for a more active role for BRICS and the growing list of prospective members, it's not all about Beijing.
"BRICS has become this pole of attraction of all countries now who've seen that they can have more power if they ally with a coalition such as BRICS to face measures that the West has been doing for years now," Garcia said, "and also to face these sorts of constraints and repression in terms of worldview and values."
Ryan Berg, director of the Center for Strategic and International Studies' (CSIS) Americas Program in Washington, D.C., also discussed how countries like Brazil were becoming more interested in the geopolitical nature of BRICS as an exercise in "active nonalignment."
"It can heighten the relevance of a country like Brazil, which is sometimes overlooked and feels overlooked and neglected," Berg said in response to Newsweek's question during a CSIS call held in the leadup to the BRICS summit.
"By pursuing this strategy," he explained, "you can basically make it a competition for the affection or for the attention of major world powers or leading world powers that would otherwise overlook Brazil's position on a particular issue."

BRICS, Summit, South, Africa, 2018! (Left to right) Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi, Chinese President Xi Jinping, South African President Cyril Ramaphosa, Russian President Vladimir Putin and then-Brazilian President Michel Temer pose for a group picture during the 10th BRICS summit on July 26, 2018 at the Sandton Convention Centre in Johannesburg, South Africa. South Africa's most populous city against hosts the BRICS summit in 2023, after each of the other four members hosted gatherings, three of which were virtual due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Mike Hutchings/POOL/AFP/Getty Images
Speaking on the same call, CSIS Africa Program director Mvemba Phezo Dizolele highlighted the importance of the host nation itself, saying BRICS membership "strengthened the position of South Africa among non-aligned countries" at a polarizing time in global geopolitics.
"Non-aligned countries have absolutely been at odds at least with Western countries, particularly ideologically because they do not want to align either with the Russians or with the United States and allies," Dizolele said.
A key goal for the summit's participants "will be discussing their disillusionment with U.S. leadership or at least the U.S.-led coalition around the world and how that world order is affecting adversely the countries of the Global South," he said, noting that "this will be a time when they will be seeking an alternative to that power."
The phenomenon of a competition among major powers to court the Global South was also observed by Mrityunjay Tripathi, a research fellow at the New Delhi-based Public Policy Research Center who previously served as part of India's delegation to the 2018 BRICS Youth Summit in South Africa.
"U.S. attempts to engage the Global South will only benefit the region, as the U.S. will act as a balancing power in the region dominated by China," Tripathi told Newsweek. "This competition will only benefit the developing economies and the multipolarity of the BRICS will ensure that region remains free and open to all."
Here, he said that "the presence of India adds credibility to BRICS and assures the West that India will act as a balancing power in the alliance that consists of Russia and China."
While New Delhi and Washington have strengthened ties in recent years, this does not mean total alignment in their positions. Tripathi argued that the trends apparent in the summit and context surrounding it show that Washington was on the backfoot in this competition over developing nations.

BRICS, Business, Forum, meets, in, South, Africa! (From left to right) Shaogang Zhang, vice chair of China's Council for the Promotion of International Trade, Onkar Singh Kanwar, chair of the BRICS Business Council's India chapter, Sergei Katyrin, chair of the BRICS Business Council's Russia chapter, José Serrador, chair of the BRICS Business Council's Brazil chapter, Busi Mabuza, chair of the BRICS Business Council's South Africa chapter, and Nozipho Tshabalala, CEO of the Conversation Strategist, attend a panel discussion during the 2023 BRICS Business Forum in Sandton, north of Johannesburg, South Africa, on August 22. Gianluigi Guercia/AFP/Getty Images
"The growing interest in BRICS does suggest that the U.S.' attempts to assert influence, particularly across the Global South, have not always produced desired results," Tripathi said. "The rise of BRICS is indicative of a shift in power dynamics from the traditionally Western-dominated world order to a more multipolar global scenario."
A key part of this shift identified by Tripathi was not only expansion, but the vision of "instituting a common currency," something that "further solidifies the group's commitment to long-term sustainable progress of the Global South."
"A common currency will not only boost intra-BRICS trade," he added," but also eliminate the high dollar conversion costs of international transactions."
Shen Shiwei, a journalist and analyst with a background in Chinese business dealings in Africa and the Middle East, argued that "the only thing that can beat the U.S. dollar is the dollar itself, driven by weaponization from Washington."
"The global trend of increasing the use of multiple currencies, instead of fully relying on U.S. dollars, is not a new idea," Shen told Newsweek. "Three decades ago, the euro was created in part because the majority of the EU wanted to move away from its deep reliance on the U.S. dollar."
"The dollar is still essential to global investments and trade," he added, "but the process of de-dollarization is accelerating, mainly because its weaponization has caused an erosion of confidence and alerted emerging economies to take actions to safeguard economic security."

People walk past a banner outside the venue for the 2023 BRICS Summit at the Sandton Convention Centre in Sandton, Johannesburg, on August 20. The BRICS countries, an acronym of the five members Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa, meet for three days for a summit in Johannesburg from August 22-24. Gianluigi Guercia/AFP/Getty Images
The U.S. dollar continues to command a significant lead against competitors, comprising some 59 percent of the world's foreign exchange reserves. The euro constitutes around 20 percent, with other currencies such as the Japanese yen, the United Kingdom's pound sterling and the Chinese renminbi in the single digits.
Still, a number of countries, particularly members of BRICS, have called for conducting bilateral trade in their own national currencies, and the idea of a common currency has been increasingly put forth. In April, Lula delivered an impassioned speech at the New Development Bank headquarters in which he railed against the notion that "all countries are forced to do their trade backed by the dollar."
The message has continued to gain traction among existing and prospective BRICS members.
"But that doesn't mean BRICS is anti-West," Shen said.

Russian President Vladimir Putin addresses BRICS summit in South Africa, August 22, 2023. © Sputnik/Grigory Sysoev
He argued that "the zero-sum game narrative developed in the West that the BRICS was created as competition to the G7 or the Global North is very misleading."
The G7, officially the Group of Seven, is a bloc consisting of the world's largest developed economies, including Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the United States and the U.K., with participation from the European Union as well. The G7 existed as the G8 until 2014, when it was expelled due to its role in the first major outbreak of conflict in Ukraine.
"All BRICS members have important political and economic cooperation with the G7 countries," Shen said. "More importantly, BRICS doesn't want to copy the Western hegemony in mentality and reality, which has brought too many problems to the Global South."
As opposed to the G7, "the BRICS mechanism has met the demands of the Global South, especially marginalized countries, to advance a collective agenda and push the building of a more inclusive, representative, just and fair global architecture," Shen argued.
"BRICS is not an exclusive club or small circle," he added, "but a big family of good partners."
#World 🌎#BRICS#Global South#United States 🇺🇸#Vladimir Putin#Russia 🇷🇺 | Brazil 🇧🇷 | India 🇮🇳 | China 🇨🇳 | South Africa 🇿🇦#Western Imperialism/Colonialism#Russia-Africa Summit | Saint Petersburg | Russia 🇷🇺#Beijing | Moscow#President Xi Jinping#Akhil Ramesh | Hawaii-based Pacific Forum#Ana Elisa Saggioro Garcia | Professor | Pontifical Catholic University of Rio de Janeiro#Shanghai | New Development Bank#Ryan Berg | Center For Strategic and International Studies' (CSIS) | Americas Program in Washington D.C.#CSIS Africa Program | Mvemba Phezo Dizolele#Disillusionment with U.S. | Leadership | U.S.-led World’s Coalition#Mrityunjay Tripathi | New Delhi | Public Policy Research Center#European Union 🇪🇺#G7 | G8#UK 🇬🇧 | Ukraine 🇺🇦#Japanese Yen#US 🇺🇸 Dollar | United Kingdom 🇬🇧 Pound Sterling#Shen Shiwei | China | Africa | Middle East
0 notes
Text
Three imprisoned Americans have been released after years of detention in China, the White House said Wednesday.
Mark Swidan, Kai Li, and John Leung have been released, a spokesperson for the National Security Council said, and they will soon "return and be reunited with their families for the first time in many years."
The Biden administration has repeatedly raised the issue of wrongfully detained Americans with Chinese officials. President Biden spoke with Chinese President Xi Jinping about the issue on the sidelines of the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation summit in Lima, Peru earlier in November.
Secretary of State Antony Blinken and National Security Adviser Jake Sullivan spoke to foreign minister Wang Yi about the release of wrongfully detained Americans during multiple meetings in recent months.
"Thanks to this Administration's efforts and diplomacy with the PRC, all of the wrongfully detained Americans in the PRC are home," the National Security Council spokesperson said.
Swidan, a 48-year-old Texas businessman, was on death row in China. He had been behind bars since 2012 after being charged with narcotics trafficking. Swidan has denied the charges, which the U.S. says are trumped-up. The State Department categorized him as wrongly detained, and has previously raised concerns about his health. His family said earlier this year they feared Swidan might take his own life while detained.
Li, 60, has been held in a Chinese prison since September 2016. He had a stroke in prison, according to John Kamm, executive director of Dui Hua Foundation, a human rights group that pushes for the release of those detained in China.
Leung, 78, was arrested in 2021 and sentenced to life in prison for espionage in May 2023. Few details have been shared about the case.
In a statement addressing Li's release, Senate Majority Leader Chuck Schumer credited Mr. Biden's "personal engagement with President Xi" with securing the release of the three men.
"For the families of those Americans newly freed by the Chinese government, this Thanksgiving there is so much to be thankful for," Schumer said.
David Lin, a 68-year-old American pastor imprisoned on fraud charges for 18 years, was released by China in September.
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
The U.S.-commanded military alliance called NATO includes the armed forces of the U.S. and all other countries in the alliance, including Britain, Germany, and France.
NATO has undertaken eight military actions, all since 1990. The alliance did not undertake any military operations during the Cold War. Since 1990, NATO has engaged in two actions related to the first Gulf War, two in the former Yugoslavia, and military operations in Afghanistan, Iraq, Somalia, and Libya.
Stoltenberg then said that NATO’s primary focus now is targeting China, Russia, Iran, and North Korea. He called them threats to NATO’s dominance. He didn’t talk about the war threats that have come from NATO and the “Asian version of NATO.”
The specter of war will loom large over the NATO summit in Washington.
18 notes
·
View notes
Text

❗️Russia will not participate in the "Peace Summit" and will not monitor Zelensky's statements, said Russian Foreign Minister Lavrov.
Additional statements:
▫️Ukraine's non-aligned status remains a goal of the "special military operation." ▫️Russia will lift the moratorium on intermediate- and short-range missiles capable of carrying nuclear warheads. ▫️NATO is allegedly involved in long-range missile strikes on Russian territory. ▫️The U.S. is using the Ukrainian scenario to pressure China.
#ukraine#ukraine war#russian agression#war#war crimes#genocide#stop russia#stop war#stop putin#russian terrorism
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
2024 US Election Results Live Updates: President Joe Biden meets Trump at White House, both pledge smooth transition
Link Here : https://tinyurl.com/3u8b9tjr

Biden and Xi will meet in Peru as US-China relations tested again by Trump's return
President Joe Biden will hold talks Saturday with China's Xi Jinping on the sidelines of an international summit in Peru, a face-to-face meeting that comes as Beijing braces for Donald Trump's return to the White House. A senior Biden administration official, who briefed reporters on condition of anonymity ahead of the formal announcement, confirmed plans for the meeting to take place while the two leaders are in Lima for the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation summit. That will come just over two months before Trump's inauguration. The official declined to comment on how Biden and his advisers would address questions certain to be raised by Xi and Chinese officials about the incoming Trump administration or whether Biden would discuss the US-China relationship with Trump during the president-elect's visit to the White House on Wednesday. Washington and Beijing have long had deep differences on the support China has given to Russia during its war in Ukraine, human rights issues, technology and Taiwan, the self-ruled democracy that Beijing claims as its own. A second Trump administration is expected to test US-China relations even more than the Republican's first term, when the US imposed tariffs on more than $360 billion in Chinese products. That brought Beijing to the negotiating table, and in 2020, the two sides signed a trade deal in which China committed to improve intellectual property rights and buy an extra $200 billion of American goods. A couple of years later, a research group showed that China had bought essentially none of the goods it had promised. (AP)
00:18 (IST) Nov 14
Melania Trump boycotts tea invitation from Jill Biden while husbands meet
Melania Trump boycotted a meeting with Jill Biden, while their husbands held a traditional meeting at the White House on Wednesday. Two hours before US President-elect Donald Trump and President Joe Biden were to meet, the office of Melania Trump said in an X post, "Mrs Trump will not be attending today's meeting at the White House." "Her husband's return to the Oval Office to commence the transition process is encouraging, and she wishes him great success," it said. Her office did not give a reason for her not taking up First Lady Jill Biden's invitation for tea. But it added, "In this instance, several unnamed sources in the media continue to provide false, misleading, and inaccurate information. Be discerning with your source of news." It did not specifically deny any of the reports about her not meeting Jill Biden. (IANS)
00:18 (IST) Nov 14
Bitcoin rises above $90,000 on Trump euphoria
Bitcoin broke through the $90,000 level on Wednesday, as its rally showed no signs of easing on expectations that Donald Trump as U.S. president will be a boon for cryptocurrencies. The world's biggest cryptocurrency has become one of the most eye-catching movers in the week since the election and on Wednesday touched record highs. It was last up 5.49% at $93,158, marking a 32% rise since the Nov. 5 election. Smaller peer ether has also risen 37% since election day, while dogecoin, an alternative, volatile token promoted by billionaire Trump-ally Elon Musk was up more than 150%. Trump embraced digital assets during his campaign, promising to make the United States the "crypto capital of the planet" and to accumulate a national stockpile of bitcoin. (Reuters)
00:17 (IST) Nov 14
'Welcome back': Trump, Biden shake hands in White House
Joe Biden welcomed Donald Trump back to the White House on Wednesday, in a show of civility to a bitter rival who failed to extend him the same courtesy four years ago. The US president and president-elect shook hands in front of a roaring fire in the Oval Office as they pledged a smooth transition -- a stark contrast to Trump's refusal to recognize his 2020 defeat. "Welcome back," Biden, 81, said as he congratulated the 78-year-old Trump and offered brief opening remarks to the man he has repeatedly slammed as a threat to democracy. "Politics is tough, and in many cases it's not a very nice world. It is a nice world today and I appreciate it very much," Trump said. Trump added that the transfer of power would be "smooth as you can get" -- despite the fact that his transition team has not yet signed some key legal documents ahead of his inauguration as president on January 20.
#donald trump#election 2024#us elections#presidential election#election day#art donaldson#offerte#digital offering#online shops offer#an offer from a gentleman#e offering#artwork#art#artists on tumblr#nail art#black art#fiber art#my art#original art#usa#usa politics#usa news#usagi tsukino#usaf#united states#america#united states of america#georgia#trump#fuck trump
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
In Ukraine’s prolonged struggle against Russia, the election of Donald Trump as the next U.S. president was a black swan event.
Among other positions, Trump ran on the promise of extricating the United States from the conflict in Ukraine. His closest allies have openly disparaged Kyiv and made overtures to Russian President Vladimir Putin. Thus, with this transition of power begins a new chapter of the war in which Western support for Ukraine could fall by the wayside.
Outgoing U.S. President Joe Biden’s belated decision to allow Ukraine to use U.S. missiles to strike targets deep within Russian territory, a critical condition of Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky’s “victory plan,” is hardly a godsend. These missiles cannot singlehandedly change the course of the war, and they put Zelensky in an awkward position. Striking Russian targets will trigger not only the wrath of Putin, but also that of Trump, who will undoubtedly view any escalation as a shot against his own prospects for dealmaking.
With Trump making threats to pull out of NATO and cut a deal with Putin, Europe is also having second thoughts on backing Ukraine. German Chancellor Olaf Scholz spoke with Putin on Nov. 15 about bringing an end to the war, while Czech President Petr Pavel announced plans in October to send a new ambassador to the Czech Embassy in Moscow in early 2025.
Meanwhile, United Nations Secretary-General António Guterres recently attended the annual summit of the BRICS countries—Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa, and several recently added members—hosted in Kazan, Russia. The U.N.’s involvement in an event hosted by a country engaged in a war of aggression, whose president is wanted under an International Criminal Court warrant, sends a disheartening message.
Almost three years into Russia’s full-scale invasion, the West is tired. It no longer has the political will to help Ukraine win by military means and is seeking a settlement with the aggressor instead.
The U.S. shift toward isolationism may hasten the inevitable: Ukraine and the West will soon find themselves negotiating with Russia to define the terms of a settlement—and, by extension, shaping a new world order. This emerging order will not be the rules-based system established after World War II, but one driven by idiosyncratic dealmaking among strongmen.
The problem is that any deal will amount to Ukraine’s—and the West’s—capitulation to Russia.
A bad peace is better than a good quarrel, according to a Russian proverb. If the West is set on securing this “bad peace,” then it must have a negotiating strategy along four critical parameters: territories, security guarantees for Ukraine, reparations, and sanctions.
Even before Trump’s election, some of Ukraine’s staunchest allies began expressing the view that Ukraine would have to accept some loss of land. The most obvious settlement strategy, then, would likely involve buying Ukrainian and European security with territory—possibly including Donetsk; large chunks of the Luhansk, Zaporizhzhia, and Kherson regions; and the peninsula of Crimea, which Russia first seized in 2014.
This outcome is a far cry from the Western leaders’ earlier commitments to Ukraine’s territorial integrity and hopes for regime change in Russia, but realpolitik leaves little room for moral considerations.
Should Zelensky agree to this loss of territory, the only realistic security guarantee for Ukraine would be membership in NATO. Yet this runs counter to what U.S. Vice President-elect J.D. Vance has lobbied for: a demilitarized zone along the current front lines and an enduring commitment to Ukraine’s neutrality.
The next White House does not seem to have a plan for what happens to Europe in a few years, when it would face a revanchist Russia with a subdued Ukraine at its Western borders. Such an outcome is not in Trump’s best interest. Another option, therefore, may have Trump concede to Ukraine’s membership in a new NATO—one without the United States, perhaps—leaving Europeans to be the masters of their own security.
Battered and curtailed but still sovereign, Ukraine would gain a nuclear umbrella against future Russian aggression, and Europe would fund the postwar reconstruction. There would be no international tribunal and no reparations. (Putin won’t be negotiating his own sentence.) Sanctions against Russia would remain for the time being. Europe would accept the occupation de facto, but it wouldn’t de jure recognize the territory as Russian land.
It will be difficult to come up with a deal that satisfies all parties. But in any negotiation, reaching a mutually satisfactory outcome depends on the motivation and constraints of those involved. The West is motivated to settle in Ukraine because it is tired of war, and because Trump is uninterested in leading the existential fight for democracy. Ukraine, understanding that it cannot win on its own, can be motivated to settle in order to stop the now-pointless bloodshed.
Putin’s motivations are murkier. In fact, a closer look would reveal that Putin has no need for lasting peace.
Putin’s megalomaniacal intransigence is now reinforced by his perception that he is winning, even if it is taking longer than he hoped. Piecemeal shipments of Western military aid have made Russian advances slow and painful—but they have been advances nevertheless. While Ukraine’s ability to affect Russian military logistics was until recently severely hampered by Western restrictions, the Russian army has faced no such limitations, regularly bombing civilian infrastructure and military targets alike.
In wars of attrition, the side with more resources is poised to win, and Russia still mobilizes resources with frightening force. Russia has activated the economic and cultural mechanisms necessary for around-the-clock military production—bread-making factories churning out drones, schoolchildren making camouflage nets, and old Soviet tanks hauled out of Siberian forests and shipped to Ukrainian front lines.
Now that the economy has been switched on to military footing, there is no shortage of munitions. Meanwhile, government payouts ensure an ample supply of volunteers to enlist in the military, meaning Russia does not have a manpower crisis like Ukraine does.
No human toll is too high for Russia. During World War II, Russia lost more than 27 million people—the largest number of fatalities of all involved. Peter the Great’s 18th-century Great Northern War, which established Russia’s power in the Baltics, lasted 21 years and incurred enormous casualties, as did the 25-year-long Livonian War fought by Ivan the Terrible in the 16th century.
Russia has already suffered upward of 700,000 people dead or wounded during the Ukraine war, according to estimates from the National Interest. But with families of dead soldiers mollified by the “coffin money” they receive, society writ large has not budged in its support for the war. It will likely stay that way short of another mobilization.
It certainly helps that the brunt of the war is borne by recruited volunteers, who sign up to fight to improve their and their family’s economic standings, and by convicts—both groups making up a significant number of those killed and wounded in Ukraine. Another large constituency fighting Russia’s war is national minorities, often from depressed economic areas and the lowest strata of society. And now, those minorities are joined by North Korean soldiers and potentially by citizens of the other dictatorships that Putin courts.
Contrast this low visibility of Russia’s war toll, further obscured by Kremlin propaganda, to its loudly celebrated nativist successes. In the last two years, not only did Russia fail to fold under the weight of Western sanctions, but it also managed to build parallel economic, financial, and cultural structures that are independent of the West.
Economically, Russia has reoriented itself toward the East, increasing trade with China, India, and other countries in Asia and the Middle East. It has shifted its energy exports away from Europe and developed domestic production capabilities. Despite sanctions, oil money—the main source of Russia’s war financing—keeps flowing, albeit from a different direction than before. Cross-border payments are now handled through SPFS, a homegrown alternative to the SWIFT global financial system, and the Mir payment system that replaced Visa and MasterCard. Russia touts these systems to its BRICS partners as alternatives to “Western financial hegemony.”
If anything, the war in Ukraine has given Putin more money to play with than before. Assets belonging to Western companies exiting Russia have been nationalized or bought for cheap and redistributed to businesses with ties to the Kremlin—one of the largest property transfers in Russia’s history. Cut off from Western banks, Russian oligarchs must invest their money domestically. Sanctions evasion schemes protect Russians’ access to Western consumer goods, creating enormous enrichment opportunities for Russian and Western business agents alike. Tankers shuttle Russian oil with payments cleared through offshore shell companies. Putin’s personal wealth, estimated at somewhere between $70 billion and $200 billion, remains safe. Though he is a product of a socialist state, the Russian leader is a master of capitalism.
Cultural shifts in Russia increase Putin’s confidence in victory. What little dissent remained before the war has largely been rooted out, with Russians closing ranks around their leader. According to a recent poll conducted by the Levada Center in September and October, more than two-thirds of Russians who said they want the war to end are against returning Russian-occupied territories to Ukraine.
On the global stage, Russia has managed to upgrade its status from a regional power to a leader of the anti-Western coalition. These coalition members have their own stakes in Ukraine. A Russian victory would embarrass the United States, weakening its influence in Asia and helping China. North Korea has found exports—bad shells and soldiers—that it can exchange for food, money, and energy. And Iran is happy to keep the United States distracted from the Middle East.
Even if Putin wanted to end the war, it would entail serious risk for his regime. Drones, shells, and missile production would have to be scaled down, ending the economic boom. The sudden drop in government spending would create real prospects of an economic collapse. Around 1.5 million veterans would have to be pulled out of Ukraine to find new roles in a corrupt Russian society. The manufactured sense of national unity would give way to envy that beyond the border, on Russia’s “ancestral lands,” Ukrainians are thriving under European Union and NATO banners.
Taken together, in a country reacclimatized to grand-scale violence, the prospect of revolt becomes clear and present. To find an outlet for that aggression, Putin would have to start a new war not long after agreeing to settle for peace.
Ultimately, the status quo—an ongoing border squabble with conventional weapons—suits all but Ukraine and Europe, for which security deteriorates in direct proportion to Putin’s success.
The Putin that the West would face at the negotiating table is a former underdog—a man on a mission to free the world from what he has characterized as Western “hegemony,” his economy thriving, his new and old friends paying court, and his people unified behind him.
He is not, however, as invincible as he seems. The BRICS countries are not rushing to replace SWIFT with the Russian alternative. By putting all his economic eggs into the military basket, Putin has siphoned off resources from everywhere else, an unsustainable move. Inflation is real, and the ruble is weakening. Even the overheated military sector can’t keep up with demands. Moreover, as a student of Russian history, Putin knows that the support and adoration of the Russian masses can turn on its head overnight.
But Putin also knows how to keep a poker face. Having staked his survival on this war, Putin would be negotiating from the position of strength and with obligations to his domestic and international stakeholders in mind.
He has already shot an opening volley at the U.S. president-elect: After a call during which Trump told the Russian leader not to escalate in Ukraine, Russian state television released a special on Melania Trump’s modeling career, including nude photos of the once and future first lady.
The West, meanwhile, will be negotiating from a position of inherent weakness. After tiptoeing around the Kremlin’s red lines throughout the war, Western leaders have signaled their readiness to consider cessation of a large chunk of Ukrainian territory, wishing away what little leverage they had.
There is nothing stopping Putin from believing that he can’t get more. Unless Russia is decisively defeated on the battlefield or Putin is given precisely what he wants, he will not stop.
Of the options put forward for a negotiated solution, the only one that Putin would agree to is the one that gives him Ukraine’s capitulation on a platter. He will never agree to a thriving, independent, armed, and Western-aligned Ukraine on his border, because he would lose too much face. Putin will therefore demand an unviable Ukraine—without an army and without NATO membership—and, in effect, a Western surrender.
The issue of European security cannot be solved by a settlement with Moscow because appeasement only increases the aggressor’s appetite. Only the containment of Putin’s expansionism by military means will remove the existential threat to his neighbors. So long as there is an aggressive, revanchist Russia in the picture, lasting peace is an illusion.
32 notes
·
View notes
Text
For some time, when you talked about the end of the war, you talked about a total victory for Ukraine: Ukraine would return to its 1991 borders, affirm its sovereignty in Crimea, and retake all of its territory from Russia. But in recent months, you have become more open to the idea of negotiations—through peace summits, for example, the first of which was conducted this summer, in Switzerland. What has changed in your thinking, and your country’s thinking, about how this war might end?
When I’m asked, “How do you define victory,” my response is entirely sincere. There’s been no change in my mind-set. That’s because victory is about justice. A just victory is one whose outcome satisfies all—those who respect international law, those who live in Ukraine, those who lost their loved ones and relatives. For them the price is high. For them there will never be an excuse for what Putin and his Army have done. You can’t simply sew this wound up like a surgeon because it’s in your heart, in your soul. And that is why the crucial nuance is that, although justice does not close our wounds, it affords the possibility of a world that we all recognize as fair. It is not fair that someone’s son or daughter was taken from them, but, unfortunately, there is a finality to this injustice and it is impossible to bring them back. But justice at least provides some closure.
The fact that Ukraine desires a just victory is not the issue; the issue is that Putin has zero desire to end the war on any reasonable terms at all. If the world is united against him, he feigns an interest in dialogue—“I’m ready to negotiate, let’s do it, let’s sit down together”—but this is just talk. It’s empty rhetoric, a fiction, that keeps the world from standing together with Ukraine and isolating Putin. He pretends to open the door to dialogue, and those countries that seek a geopolitical balance—China, for one, but also some other Asian and African states—say, “Ah, see, he hears us and he’s ready to negotiate.” But it is all just appearance. From our side, we see the game he is playing and we amend our approaches to ending the war. Where he offers empty rhetoric, we offer a real formula for bringing peace, a concrete plan for how we can end the war.
And yet, in 2022 and 2023, your words and actions signalled a categorical refusal to negotiate with the enemy, whereas now you seem to have opened a window to the idea of negotiating, a willingness to ask if negotiations are worth pursuing.
If we go back two years, to the G-20 summit, in Indonesia, in my video appearance, I presented our formula for peace. Since then, I’ve been quite consistent in saying that the Russians have blocked all our initiatives from the very beginning, and that they continue to do so. And I said that any negotiation process would be unsuccessful if it’s with Putin or with his entourage, who are all just his puppets.
Everyone said that we have to allow the possibility of some kind of dialogue. And I told them, “Look, your impression that Putin wants to end the war is misguided. That’s a potentially fatal mistake you are making, I’m telling you.” But, on our end, we have to demonstrate that we do have this desire for dialogue—and ours is a genuine one. Our partners think we should be at the negotiating table? Then let’s be constructive. Let’s have a first summit where we all get together. We shall write up a plan and give it to the Russians. They might say, “We are ready to talk,” and then we’d have a second summit where they say, “This formula of yours, we agree with it.” Or, alternatively, “We disagree. We think that it should be like this and like that.” This is called dialogue. But to make it happen, you have to prepare a plan without the Russians, because, unfortunately, they seem to think that they have a kind of red card, as in soccer, that they can hold up and block everything. Our plan, however—it is being prepared.
I understand that you are going to present this plan to Biden?
The victory plan is a bridge. After the first peace summit, our partners saw that Russia was not prepared for any talks at all—which confirmed my message to them and my insistence that without making Ukraine strong, they will never force Putin to negotiate fairly and on equal terms. No one believed me. They said, We’ll invite them to the second summit and they’ll come running. Well, now we have the second summit planned and they don’t look like they’ll come running.
And so the victory plan is a plan that swiftly strengthens Ukraine. A strong Ukraine will force Putin to the negotiating table. I’m convinced of that. It’s just that, before, I was only saying it and now I’ve put it all on paper, with specific arguments and specific steps to strengthen Ukraine during the months of October, November, and December, and to enable a diplomatic end of the war. The difference this time will be that Putin will have grasped the depth of this plan and of our partners’ commitment to strengthening us, and he will realize an important fact: that if he is not ready to end this war in a way that is fair and just, and instead wishes to continue to try to destroy us, then a strengthened Ukraine will not let him do so. Not only that but continuing to pursue that goal would also considerably weaken Russia, which would threaten Putin’s own position.
What happens if Biden says, “With all due respect, this is a difficult time, the election’s coming up, I’m having enough trouble with Congress without trying to increase aid packages for you,” and he rejects your request—do you have a Plan B?
We have been living in Plan B for years. Plan A was proposed before the full-scale war, when we called for two things: preventive sanctions and preventive reinforcement of Ukraine with various weapons. I told our partners, If Ukraine is very strong, nothing will happen. They didn’t listen. Since then, they have all recognized I was right. Strengthening Ukraine would have significantly lowered the probability of Putin invading.
I’m now proposing a new Plan A. This plan means we change the current course, where it’s only thanks to the strength of our military, the heroic devotion to the European values of our people and our fighters, that we have stood our ground. If you don’t want this war to drag on, if you do not want Putin to bury us under the corpses of his people, taking more Ukrainian lives in the process, we offer you a plan to strengthen Ukraine. It is not a fantasy and not science fiction, and, importantly, it does not require the Russians to coöperate to succeed. Rather, the plan spells out what our partners can do without Russia’s participation. If diplomacy is the desire of both sides, then, before diplomacy can be effective, our plan’s implementation depends only on us and on our partners.
You were right, this plan is designed, first and foremost, with Biden’s support in mind. If he doesn’t want to support it, I cannot force him. If he refuses—well, then we must continue to live inside Plan B. And that’s unfortunate.
What would that look like? I mean, if Biden says no?
That’s a horrible thought. It would mean that Biden doesn’t want to end the war in any way that denies Russia a victory. And we would end up with a very long war—an impossible, exhausting situation that would kill a tremendous number of people. Having said that, I can’t blame Biden for anything. At the end of the day, he took a powerful, historic step when he chose to support us at the start of the war, an action that pushed our other partners to do the same. We recognize Biden’s great achievement in this respect. That step of his already constituted a historic victory.
And what would you say, maybe not even to Biden but to the American public, many of whom feel that we cannot raise our engagement and support for Ukraine any further than we already have?
I would tell them that Ukraine has done everything possible to keep America out of this war, actually. Putin counted on defeating Ukraine in a quick campaign and, had Ukraine not stood its ground, Putin would have marched on. Let’s consider what the consequences would have been. Number one, you would have some forty million immigrants coming to Europe, America, and Canada. Second, you would lose the largest country in Europe—a huge blow to America’s influence on the Continent. Russia would now have total influence there. You would lose everyone—Poland, Germany—and your influence would be zero.
The American public should realize that the fact of Ukraine still standing is not the problem. Yes, war brings difficulties, but Ukraine’s resilience has allowed America to solve many other challenges. Let’s say Russia attacked Poland next—what then? In Ukraine, Russia has found fake legal ground for its actions, saying that it’s protecting Russian-speaking people, but it could have been Poland or it could have been the Baltic states, which are all NATO members. This would have been a disaster, a gut punch for the United States, because then you’re definitely involved full scale—with troops on the ground, funding, investment, and with the American economy going to a wartime footing. So saying that you have been in this war for a long time is just not true. Quite the contrary: I believe that we have shielded America from total war.
Here’s another crucial element: this is a war of postponement for the United States. It’s a way to buy time. As far as Russia is concerned, Ukraine does not even need to lose outright for Russia to win. Russia understands that Ukraine is struggling as it is; it already stands excluded from the European Union and NATO, with nearly a third of its territory occupied. Russia might decide that’s enough, so it might strike Poland just the same—in response to some provocation from Belarus, for example. And so, after two and a half years of your support and investment—for which we are very grateful—you can multiply them all by zero. America would have to start investing from scratch, and in a war of a totally different calibre. American soldiers would fight in it. Which would all benefit Russia tremendously, I should add.
During the Presidential debate, moderators asked Trump whether he wanted Ukraine to win against Russia, and he sidestepped the question. He just said, “I want the war to stop.” It must have troubled you to hear his answer and to consider the prospect of his winning.
Trump makes political statements in his election campaign. He says he wants the war to stop. Well, we do, too. This phrase and desire, they unite the world; everyone shares them. But here’s the scary question: Who will shoulder the costs of stopping the war? Some might say that the Minsk Agreements either stopped or froze the fighting at some point. But they also gave the Russians a chance to arm themselves even better, and to strengthen their fake claim over our territories they occupied.
But isn’t that yet more cause for alarm?
My feeling is that Trump doesn’t really know how to stop the war even if he might think he knows how. With this war, oftentimes, the deeper you look at it the less you understand. I’ve seen many leaders who were convinced they knew how to end it tomorrow, and as they waded deeper into it, they realized it’s not that simple.
Apart from Trump’s own reluctance to talk about Ukrainian victory, he has chosen J. D. Vance as his Vice-Presidential candidate.
He is too radical.
Vance has come out with a more precise plan to—
To give up our territories.
Your words, not mine. But, yes, that’s the gist of it.
His message seems to be that Ukraine must make a sacrifice. This brings us back to the question of the cost and who shoulders it. The idea that the world should end this war at Ukraine’s expense is unacceptable. But I do not consider this concept of his a plan, in any formal sense. This would be an awful idea, if a person were actually going to carry it out, to make Ukraine shoulder the costs of stopping the war by giving up its territories. But there’s certainly no way this could ever happen. This kind of scenario would have no basis in international norms, in U.N. statute, in justice. And it wouldn’t necessarily end the war, either. It’s just sloganeering.
What does it mean for Ukraine that people with such ideas and slogans are rising to power?
For us, these are dangerous signals, coming as they do from a potential Vice-President. I should say that it hasn’t been like this with Trump. He and I talked on the phone, and his message was as positive as it could be, from my point of view. “I understand,” “I will lend support,” and so on.
[Vance and others who share his views] should clearly understand that the moment they start trading on our territory is the moment they start pawning America’s interests elsewhere: the Middle East, for example, as well as Taiwan and the U.S. relations with China. Whichever President or Vice-President raises this prospect—that ending the war hinges on cementing the status quo, with Ukraine simply giving up its land—should be held responsible for potentially starting a global war. Because such a person would be implying that this kind of behavior is acceptable.
I don’t take Vance’s words seriously, because, if this were a plan, then America is headed for global conflict. It will involve Israel, Lebanon, Iran, Taiwan, China, as well as many African countries. That approach would broadcast to the world the following implicit rule: I came, I conquered, now this is mine. It will apply everywhere: land claims and mineral rights and borders between nations. It would imply that whoever asserts control over territory—not the rightful owner but whoever came in a month or a week ago, with a machine gun in hand—is the one who’s in charge. We’ll end up in a world where might is right. And it will be a completely different world, a global showdown.
Let Mr. Vance read up on the history of the Second World War, when a country was forced to give part of its territory to one particular person. What did that man do? Was he appeased or did he deal a devastating blow to the continent of Europe—to many nations, broadly, and to the Jewish nation in particular? Let him do some reading. The Jewish people are a strong power base in the United States, so let them conduct a public-education campaign and explain why millions perished thanks to the fact that someone offered to give up a sliver of territory.
When we last spoke, in 2019, Ukraine was caught in the middle of an American political scandal. There was the question of your phone call with Trump, an implicit threat to curtail U.S. aid, and the subsequent impeachment hearings against a U.S. President. I recently reread our interview, and you told me at the time, “In this political chess match, I will not let Ukraine be a pawn.” Do you worry that Ukraine has now ended up in a similar situation, used by various political actors to push their own agenda or advantage in the U.S. political context?
To be honest, the incident you mention no longer feels as relevant. That was a long time ago. And since then, many things have changed.
Nonetheless, you must have drawn some conclusions from this experience.
I think Ukraine has demonstrated the wisdom of not becoming captured by American domestic politics. We have always tried to avoid influencing the choices of the American people—that would simply be wrong. But, in that incident and elsewhere, I believe we have always demonstrated that Ukraine is definitely not a pawn, and that our interests have to be taken into account.
You have to work to maintain that every day, though. Because the second you relax, that’s exactly what will happen. A lot of world leaders want to have some sort of dealings with Putin, to reach agreements, to conduct some business with him. I look at such leaders and realize that they are very interested in playing this game—and for them, unfortunately, it really is a game. But what makes a real leader? A leader is someone whom Putin needs for something, not a person who needs Putin. Flirting with him is not a sign of strength. Sitting across the table from him might make you believe you’re making important decisions about the world. But what are those decisions really about? Has the war ended? No. Has it produced the outcome you wanted? Not yet. Is Putin still in power? Yes.
Ukraine is a very painful topic for Putin—he wanted to defeat us and couldn’t—which means that it offers a way to build a bond with him. But the truth is that you can only develop relations with Putin on his terms. That means, for instance, proposing that Ukraine should give up some of its territory. This, in a way, is the easiest thing to call for. It is very concrete. And for Putin, it’s a morsel that he doesn’t even have to cut in order to eat—you have already chewed it for him and placed it right in his mouth. When you give it to him, you think you’re so smart and cunning, that after such a gesture Putin will listen to you and support your positions. Well, tell me, when did Putin respect those who come to him from a position of weakness?
After Russia invaded, many people were inclined to compare you to Winston Churchill, Britain’s leader during the Second World War, but you’ve said in interviews that you prefer the example of Charlie Chaplin, who waged a struggle against fascism through appealing to his audience, the public. How do you regard your role as a communicator?
People are always more comfortable relying not on abstract ideas but on some specific historical examples. But it feels immodest to compare myself with the people you mentioned. That said, Chaplin had an unquestionable talent for telling a story, for finding a way to get through to people. He didn’t merely broadcast some facts and numbers—he used the language of cinema to craft an emotional narrative. He used that talent to fight fascism. As for Churchill, he was the leader of a country that found itself in very difficult circumstances, but still managed to be the only country in Europe that firmly said no to fascism. It’s not that other countries necessarily said yes—some were invaded, lost battles, or were subdued in other ways. Hitler occupied much of Europe. But from Churchill and the U.K., there was a firm no. And this no convinced America that it should become a serious ally in the war.
Let’s talk about the Kursk operation. What is its motive? And who is the intended audience: Putin, to show him that Ukraine, too, can go on the offensive, or Ukraine’s Western partners, to demonstrate to them what Ukraine can achieve if given the proper resources?
Both these motives are important, but there is more at stake here. First, it was clear to us that Russia is pressing us in the east. No matter how the Kursk operation ends, military analysts will someday calculate the speed of Russia’s progress and ask, What prevented us from stopping them earlier? How fast were they moving in the east before the Kursk operation began, and why? Ukraine had trouble mobilizing people, they might say, and didn’t have enough strength to stop them, but that is diverting the focus from the more pertinent point—namely, the fact that we should receive what we’ve been promised. I say, first give it to us, and then analyze if the root of the problem is with Ukraine or with you.
Imagine: you’re struggling in a tough war, you’re not receiving aid, you strain to maintain morale. And the Russians have the initiative in the east, they have taken parts of the Kharkiv region, and they’re about to attack Sumy. You have to do something—something other than endlessly asking your partners for help. So what do you do? Do you tell your people, “Dear Ukrainians, in two weeks, eastern Ukraine will cease to exist”? Sure, you can do that, throw up your hands, but you can also try taking a bold step.
Of course, you’re right to wonder if this action will go down in history as a success or a failure. It’s too early to judge. But I am not preoccupied with historic successes. I’m focussed on the here and now. What we can say, however, is that it has already shown some results. It has slowed down the Russians and forced them to move some of their forces to Kursk, on the order of forty thousand troops. Already, our fighters in the east say that they are being battered less frequently.
I’m not saying it’s a resounding success, or will bring about the end of the war, or the end of Putin. What it has done is show our partners what we’re capable of. We have also shown the Global South that Putin, who claims to have everything under control, in fact does not. And we have shown a very important truth to the Russians. Unfortunately, many of them have their eyes closed, they don’t want to see or hear anything. But some Russian people could not help but notice how Putin did not run to defend his own land. No, instead he wants to first and foremost look after himself, and to finish off Ukraine. His people are not a priority for him.
It has been more than a month since the start of the Kursk operation. We continue to provide food and water to the people in territories we control. These people are free to leave: all the necessary corridors are open, and they could go elsewhere in Russia—but they do not. They don’t understand why Russia didn’t come to help, and left them to survive on their own. And people in Moscow and St. Petersburg—far from Kursk—saw that, if one day the Ukrainian Army showed up there, too, it’s far from certain they would be saved. That’s important. That’s also a part of this operation: long before the war gets to these places, or there’s some other crisis, Russian people should know who they have placed in power for a quarter century, with whom they have thrown in their lot.
This war is being fought not just over territory but over values. But during war, in the name of victory, it may not always be possible to maintain these values as one might in peacetime. Do you feel that there are occasions when these two interests—democratic values and the reality of wartime—can clash, or end up in conflict? The United News TV Marathon, for example, which has been on air since the beginning of the invasion, pulls together multiple television channels to broadcast news about the war and other events in a highly coördinated way.
The truth is that journalists came together because, in the early days of the war, when people feared a total occupation of the country, no one knew what to do. Some people took off in one direction, law enforcement in another. There were even stories about how the President had run off somewhere. It was chaos. The fact is that I was among those who stayed and put an end to that chaos, and I don’t think that has led to anything so terrible. Many would say it’s one of the factors that gave people the strength to fight for their country.
But the centralization of power has a downside.
I want to finish. Journalists in Ukraine decided to join forces in order to combat Russian disinformation. I want to make it clear that simply because the news departments of these [six] TV channels have come together it does not mean the channels themselves are destroyed. They exist as they did before. They have kept their own places in the broadcast lineup. They are free to show what they want. But this telemarathon has become a resource for people who, say, have no electricity or see drones flying overhead. There have been lots of periods when there were all kinds of misinformation going around, and the telemarathon provides the truth. And you’re saying this is a bad thing. O.K., if that’s the case, I’m not insisting.
A last question about how war changes a person. It’s hard to imagine an experience with a more profound effect on the human psyche.
I’m still holding it together, if it’s me you’re talking about.
But I wonder if there are moments when you catch yourself reacting to things differently than you might have before. Do you notice you’ve changed at all?
Perhaps I’ve become less emotional. There’s simply no time for that. Just like there’s no time for reasoned discourse and arguments. I only have the opportunity to think aloud in that way during interviews. I don’t do this with my subordinates and colleagues in the government. If I were to sit down and ruminate on every decision for an hour, I would be able to make only two or three decisions a day. But I have to make twenty or thirty. ♦
6 notes
·
View notes