#Selenium-rich foods for thyroid
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
#Thyroid health#Foods for thyroid issues#Best foods for hypothyroidism#Foods to avoid with thyroid problems#Thyroid-friendly diet#Iodine-rich foods#Gluten and thyroid#Goitrogenic foods#Foods that support thyroid function#Selenium-rich foods for thyroid#Thyroid and autoimmune conditions#Thyroid diet recommendations#Vitamin D and thyroid health#Anti-inflammatory foods for thyroid#Thyroid supplements and foods#Low-iodine foods#High-fiber foods for thyroid health#Soy and thyroid health#Dairy and thyroid issues#Healthy fats for thyroid function#health & fitness
1 note
·
View note
Text
Can You Boost Immunity Naturally and Heal Holistically? Discover Secrets from Nutrition to Piercings
In today's fast-paced world, people are seeking more natural and holistic ways to care for their health—whether it’s about strengthening the immune system, managing high blood pressure, or choosing the right breakfast on the go. Let’s dive into powerful, natural approaches that touch on everything from eye teratomas to lower back dermal piercings, and even blood type O diets.

🌿 How to Boost Immunity Naturally?
Your immune system is your body’s first line of defense. Strengthen it with:
Vitamin C-rich foods: Citrus fruits, bell peppers, kiwi
Zinc sources: Pumpkin seeds, seafood (especially oysters!)
Sleep & stress control: Aim for 7–9 hours per night, meditate daily
Probiotics: Yogurt, kefir, and fermented foods support gut health, key to immunity
Natural herbs like echinacea, elderberry, and turmeric also support immune response without harsh chemicals.

🧘♂️ Holistic Cure for High Blood Pressure
A holistic approach to high blood pressure involves lifestyle, nutrition, and stress control:
Exercise regularly: Even brisk walking 30 minutes a day makes a big difference
Reduce sodium: Stick to 1,500 mg a day or less
Relaxation practices: Yoga, breathwork, and acupuncture may reduce systolic pressure
Herbs like garlic, hibiscus, and flaxseed: Nature’s own blood pressure regulators

🐟 What Are the Health Benefits of Seafood?
Seafood is a powerhouse of nutrients:
Omega-3 fatty acids: Good for heart, brain, and inflammation
Lean protein: Supports muscle repair and keeps you full longer
Iodine & selenium: Support thyroid function
Vitamin D: Especially in salmon, vital for immune health
Bonus: Regular seafood intake is linked to a lower risk of Alzheimer’s.
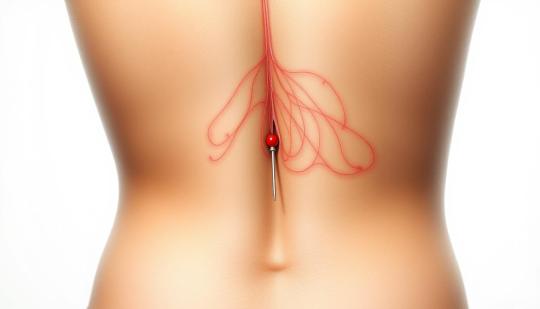
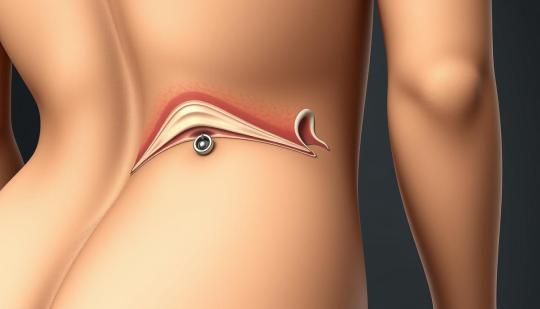
💎 Lower Back Dermal Piercings: Are They Safe?
Lower back dermal piercings, often called "venus piercings," are more than just a style statement. Here’s what to consider:
Safety: Always get it done by a licensed professional
Healing: Takes 1–3 months; requires diligent aftercare
Risks: Potential for infection, rejection, or irritation from clothing
Natural remedies like diluted tea tree oil may help soothe irritation—always check with your piercer first!

🏠 Home Remedies That Actually Work
Some home remedies have stood the test of time:
Honey + ginger: Soothes sore throats and aids digestion
Aloe vera gel: Treats burns, acne, and dry skin
Apple cider vinegar: Balances pH, supports digestion, and can help with dandruff
Always remember—natural doesn't always mean safe. Test remedies on a small area first!
🍳 Nutritious Fast Food Breakfast: Is It Possible?
Yes! Here are nutritious fast food breakfast options when you're in a rush:
Egg White Grill (Chick-fil-A): High in protein, low in carbs
Oatmeal (Starbucks or McDonald's): Ask for it without added sugar
Greek yogurt parfaits: Watch for added sugar, but they offer protein and probiotics
Breakfast burritos (customized): Choose whole grains, eggs, and veggies
Pair it with green tea or water to avoid sugary drinks.

🩸 What Are the Best Foods for Blood Type O?
For those who follow the Blood Type Diet, Type O individuals thrive on:
High-protein meals: Lean meats, seafood, and veggies
Avoid grains and legumes: Especially wheat, corn, and kidney beans
Great foods: Spinach, broccoli, seaweed, and olive oil
Limit: Dairy and caffeine, as they may not digest well
This diet isn’t for everyone, but many say it helps with energy and digestion.
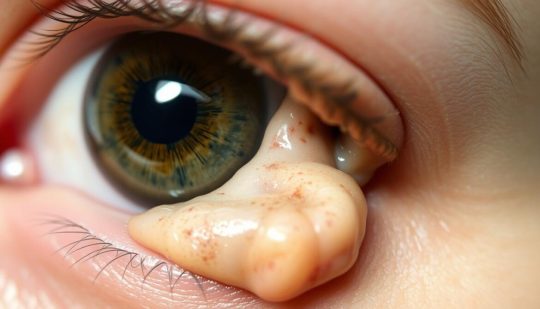
️ Eye Teratoma: What Should You Know?
Eye teratomas are rare tumors that can contain multiple types of tissue (like bone, hair, or muscle). While alarming, many are benign. Treatment often involves surgical removal. It's a reminder of how important regular checkups and early diagnosis are, even in unlikely areas like the eye.
Conclusion
Living a holistic lifestyle doesn't mean giving up modern convenience. Whether you're rocking lower back dermal piercings, seeking natural ways to manage high blood pressure, or picking a quick, healthy breakfast at a drive-thru, there are balanced, mindful options for every path.
Have you tried any of these methods or foods? Share your story or tips below!
#home remedies#eyetreatment#liverdisease#health and wellness#healthcare#health & fitness#nutrition#wellness#healthylifestyle#high blood pressure
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Understanding Thyroid Disorders: Signs You Shouldn’t Ignore
The thyroid is a small, butterfly-shaped gland in the neck that plays a vital role in regulating metabolism, energy levels, and overall well-being. When the thyroid malfunctions, it can lead to various health complications that often go unnoticed until they become severe. Understanding the symptoms of thyroid disorders can help in early diagnosis and timely treatment, improving quality of life.
Common Thyroid Disorders
There are several types of thyroid disorders, but the most common ones include:
Hypothyroidism (Underactive Thyroid): When the thyroid gland produces insufficient hormones, leading to slow metabolism and fatigue.
Hyperthyroidism (Overactive Thyroid): When the thyroid produces excessive hormones, causing rapid metabolism and unintentional weight loss.
Thyroid Nodules: Lumps or growths in the thyroid that may or may not be cancerous.
Goiter: An enlarged thyroid gland, often caused by iodine deficiency or autoimmune diseases.
Thyroid Cancer: A rare but serious condition that requires immediate medical attention.
Signs You Shouldn’t Ignore
Recognizing thyroid disorder symptoms early can prevent severe complications. Here are some key warning signs:
Symptoms of Hypothyroidism (Underactive Thyroid)
Unexplained Weight Gain: Despite normal diet and exercise.
Fatigue and Weakness: Feeling tired even after sufficient sleep.
Cold Sensitivity: Always feeling cold, even in warm environments.
Dry Skin and Hair Loss: Thinning hair, brittle nails, and dry skin.
Depression and Brain Fog: Trouble concentrating, forgetfulness, and mood swings.
Constipation: Slowed digestion leading to irregular bowel movements.
Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism (Overactive Thyroid)
Unexplained Weight Loss: Losing weight rapidly without changes in diet.
Rapid Heartbeat and Palpitations: A fast or irregular heartbeat.
Anxiety and Irritability: Feeling restless and agitated.
Heat Sensitivity: Excessive sweating and difficulty tolerating warm temperatures.
Tremors: Shaky hands or fingers.
Frequent Bowel Movements: Increased frequency of stools.
Seeking Medical Help and Long-Term Care
If you experience multiple symptoms, it’s important to consult a doctor for a proper diagnosis. A simple blood test measuring thyroid hormone levels can confirm whether you have a thyroid disorder.
In some cases, managing thyroid conditions may require specialized medical care, especially for elderly patients or those with additional health concerns. A rehabilitation center in Bangalore can provide support for individuals recovering from severe thyroid-related complications, ensuring they regain strength and mobility. Additionally, for those who require long-term care, palliative care and rehabilitation services can help improve comfort and quality of life.
For personalized care and expert medical support, consider Avanta Healthcare Center helping you or your loved ones manage thyroid health with compassion and expertise.
Managing Thyroid Health
Balanced Diet: Foods rich in iodine, selenium, and zinc support thyroid function.
Regular Exercise: Physical activity helps regulate hormones and maintain a healthy metabolism.
Stress Management: Meditation and yoga can reduce stress, which is crucial for thyroid health.
Medication & Treatment: If diagnosed with a thyroid disorder, proper medication and lifestyle changes can help manage symptoms effectively.
Final Thoughts
Thyroid disorders can significantly impact daily life if left untreated. Individuals can manage their condition and prevent complications by recognizing the symptoms early and seeking medical help. Whether it’s through lifestyle changes, medical treatment, or specialized care at a rehabilitation center in Bangalore, taking proactive steps can lead to better health outcomes.
Avanta Healthcare Center offers comprehensive solutions, from rehabilitation and palliative care to ICU setup and nursing care at home. Seeking the right support can improve health and overall well-being.
#ThyroidHealth#ThyroidDisorders#Hypothyroidism#Hyperthyroidism#Healthcare#Rehabilitation#PalliativeCare#HomeCare#ICUatHome#NursingCare#AvantaHealthcare#HealthAwareness#Metabolism#StayHealthy
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Foods Allowed in Thyroid 🌟Struggling with thyroid issues?
When managing thyroid health, certain foods can be particularly beneficial. The thyroid gland relies on various nutrients to function optimally. Foods rich in iodine, such as seaweed and iodized salt, play a critical role in thyroid hormone production. Additionally, incorporating anti-inflammatory foods like berries, leafy greens, and fatty fish can help manage thyroid-related inflammation.
Here are some nutritious and delicious foods that can support your thyroid health!
Coconut Oil: Rich in healthy fats, coconut oil can help improve metabolism and support thyroid function. 🥥
Almonds: These crunchy nuts are packed with magnesium, which is essential for thyroid health. 🌰
Apple Cider Vinegar (ACV): Known for its detoxifying properties, ACV can help balance the pH levels in your body. 🍎
Nuts and Seeds: Walnuts, flaxseeds, and chia seeds are excellent sources of selenium and omega-3 fatty acids, crucial for thyroid health. 🌻
Fuel your body with these thyroid-friendly foods and enjoy a healthier, happier you! 🌿✨
Incorporating these nutrient-dense foods into your diet can support overall thyroid health and help maintain optimal hormone levels.
If you have specific dietary concerns or conditions like hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, it’s always best to consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
For more tips on maintaining a healthy thyroid, visit DietStory.in and follow us for expert advice!
🌐https://www.dietstory.in/ 📩 [email protected] 📲 +91-7743004991
#calories#delhincr#diet#diet food#diet plan#dieting#gurgaon#gurugram#lose weight fast#mgroadgurgaon#ThyroidFriendlyFoods#ThyroidDiet#HealthyThyroid#IodineRichFoods#SeleniumFoods#mgroad#dietstory#prernadietstory
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Thyroid: A Comprehensive Guide
The thyroid gland, a small butterfly-shaped organ located at the base of the neck, is a powerhouse for regulating essential bodily functions like metabolism, energy levels, and hormone balance. Unlike temporary health concerns such as diarrhea, thyroid conditions often require long-term care and attention to maintain overall health.
This blog explores the thyroid's role, common disorders, symptoms, causes, treatments, and tips for keeping it healthy.
What is the Thyroid Gland?
The thyroid gland produces two primary hormones:
Triiodothyronine (T3)
Thyroxine (T4)
These hormones regulate metabolism, which influences energy use, body temperature, and weight. The gland's activity is managed by the pituitary gland through thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), ensuring proper hormone levels are maintained.
Common Thyroid Disorders
Hypothyroidism (Underactive Thyroid)
What Happens? Insufficient hormone production slows the body’s metabolism.
Symptoms:
Fatigue
Weight gain
Hair thinning
Dry skin
Sensitivity to cold
Depression
Causes:
Hashimoto's thyroiditis (an autoimmune condition)
Iodine deficiency
Thyroid surgery or radiation therapy
Treatment:
Synthetic hormone replacement (e.g., Levothyroxine)
Hyperthyroidism (Overactive Thyroid)
What Happens? Excessive hormone production speeds up metabolism.
Symptoms:
Weight loss
Anxiety
Palpitations
Excessive sweating
Tremors
Insomnia
Causes:
Graves' disease (an autoimmune disorder)
Thyroid nodules
Overconsumption of iodine
Treatment:
Antithyroid medications
Radioactive iodine therapy
Surgery in severe cases
Thyroid Nodules and Cancer
Nodules: Lumps in the thyroid that may cause imbalances or indicate cancer.
Cancer: Rare but treatable with early detection. Symptoms include a persistent lump in the neck or difficulty swallowing.
Tips for Maintaining Thyroid Health
Balanced Nutrition:
Eat iodine-rich foods like fish, dairy, and iodized salt.
Include selenium (e.g., Brazil nuts) and zinc (e.g., nuts, seeds) in your diet.
Regular Checkups:
Monitor hormone levels if you have a family history or symptoms.
Stay Active:
Exercise reduces stress and helps regulate metabolism.
Stress Management:
Techniques like yoga or meditation can improve hormonal balance.
Avoid Self-Medication:
Excess iodine or unprescribed supplements can worsen thyroid issues.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you experience symptoms like persistent fatigue, weight changes, or swelling in the neck, consult a doctor immediately. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to preventing complications such as heart disease, infertility, or severe metabolic imbalances. Your thyroid’s health is essential for your overall well-being. Addressing thyroid concerns early can significantly improve your quality of life.
For more expert advice on thyroid health and personalized consultations, visit CongoRx. Learn more about thyroid care and related conditions, or explore our blogs like diarrhea causes and symptoms.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Struggling with Thyroid Issues? Try Brazil Nuts

Most people don’t think about their thyroid until something feels off. You wake up exhausted, even after a full night’s sleep. Weight shifts without reason. Mood swings come out of nowhere. Focus slips. Memory fades. Life, quite literally, feels heavier.
Could a single nut change that? The Brazil nut (*Bertholletia excelsa*), known for its buttery richness, carries an overlooked but essential mineral — selenium.
The body needs selenium, but the thyroid holds more of it than any other organ. Its role isn’t secondary — it’s fundamental. Without it, hormones fall out of balance. Inflammation creeps in. Small problems turn into long battles.
Selenium might sound like just another trace element. But in the context of thyroid health, it’s non-negotiable. This butterfly-shaped gland at the base of the neck doesn’t just benefit from selenium — it depends on it.
Brazil nuts contain more selenium per gram than any other food. A few each day fill the gap. No supplements. No complex regimens. Just real food.
Selenium, a natural antioxidant, shields cells from damage. But its power goes beyond protection — it’s essential for hormone activation.
Without it, the thyroid struggles to regulate metabolism. Deficiency disrupts this process and raises the risk of disorders.
A single nut can hold up to 90 micrograms of selenium — far beyond the daily requirement. Few foods come close. Seafood, eggs, and whole grains contain selenium, but none match the potency of Brazil nuts. Their nutrient profile is unique. Alongside selenium, they offer healthy fats, fiber, and antioxidants — elements that collectively reduce inflammation and strengthen thyroid function.
The thyroid doesn’t rely on just one nutrient. Iodine, zinc, vitamin D, and iron all play roles in its stability. But selenium stands apart — it converts inactive thyroid hormones into their active form. Without it, function declines.
Studies confirm this. Research links low selenium levels to a higher risk of autoimmune thyroid disorders. In contrast, restoring it improves function. A study in the *European Journal of Clinical Nutrition* found that selenium supplementation benefited individuals with autoimmune thyroiditis. Science backs what nature provides.
Try this: Eat two Brazil nuts daily for a month. No extra supplements. No drastic diet shifts. Just two nuts.
After a few weeks, you might notice changes. The energy lasts longer. Brain fog clears. The body feels lighter.
Brazil nuts won’t fix everything. They won’t erase stress, undo years of imbalance, or replace medical care. But they start something. They restore. They remind the body of what it once knew.
#nutriintact#healthy food#brazil nuts#healthy diet#food#healthychoices#healthylifestyle#healthy eating#dry fruits#healthyhabits#diet#health benefits#fitness#healthysnacks#blog#trending#explore
1 note
·
View note
Text
How to cure Thyroid natural
source url:-https://ext-6616443.livejournal.com/418.html?newpost=1
Introduction
The thyroid is an endocrine gland. Its location is in the inferior, anterior neck, and it is responsible for the formation and secretion of thyroid hormones as well as iodine homeostasis within the human body. The thyroid produces approximately 90% inactive thyroid hormone, or thyroxine (T4), and 10% active thyroid hormone, or triiodothyronine (T3). Inactive thyroid hormone is converted peripherally to either activated thyroid hormone or an alternative inactive thyroid hormone
Signs and symptoms of Thyroid
AnxietyThe signs and symptoms of thyroid dysfunction can vary depending on whether the thyroid is producing too much or too little of its hormones.
When the thyroid produces too much – a condition called hyperthyroidism – signs and symptoms can include:
Waight loss
Rapid heart rate
Heat intolerance
Sweating
Difficulty sleeping
Remors in your hands and fingers
When the thyroid does not produce enough hormones – a condition called hypothyroidism – symptoms can include:
Fatigue
Weakness
Weight gain
Cold intolerance
Dry skin or hair
How to check thyroid status
Blood tests: These tests can tell you if you have hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism. There are several types of thyroid blood tests, including thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), T3 and T4, and thyroid antibodies.
List of Home Remediey
Here are some widely considered remedies that may help with your thyroid treatment at home
Coconut oil
This has high content of saturated or healthy fat (healthy) and when used with the right combination of exercises and a properly balanced diet, it could be good for thyroid glands. You can also use coconut oil for your regular cooking once in a while
Apple cider vinegar
This helps in the balanced production and expression of hormones. It also washes away toxins from the body and promotes absorption of nutrients. Apple cider vinegar can be added to water along with honey and can be taken every morning.
Vitamins help to fight the underlying causes of thyroid problems, particularly
Vitamin B
h are essential for proper thyroid function. Vitamin B12 is especially instrumental in helping people with hypothyroidism. Including eggs, meat, fish, legumes, milk, and not in daily diet might help with a steady supply of Vitamin B.
Ginger
Ginger helps combat inflammation which is one of the primary causes of thyroid issues. Drinking ginger tea is the best way to consume ginger. Apart from that, it can also be infused with coconut oil and applied on body.
Vitamin D
Deficiency of this nutrient can lead to thyroid problems and since the body can produce it only when exposed to the sun, ensure that you get a minimum of 15 minutes of sunlight daily. Include foods rich in Vitamin D in your diet which includes fatty fishes like salmon and mackerel, dairy products, orange juice, and egg yolks.
Dairy products
As dairy products such as milk, cheese, and yoghurt are beneficial for thyroid as they have high iodine content. Incorporate these items in your daily diet, but be careful if you are lactose intolerance.
Almonds
Almonds are a good source of protein, fibre, and minerals and are best suited for proper thyroid expression. These nuts have selenium which is a thyroid healthy nutrient and is also very rich in magnesium that can keep the thyroid gland working very smoothly.
Beans
Beans are high in fibre which helps to relieve constipation, which is a common side effect of hypothyroidism. Some ways to consume beans include adding them to side dishes, salads, stews and soups.
Iodine Supplements
These supplements restore the balance of iodine in the body and help with thyroid health.
Probiotics
Probiotic food items such as kefir, kimchi, and miso has shown to have beneficial effects on thyroid problems.
Asparagus
Including asparagus in your diet is also a popular natural remedy for thyroid treatment at home as it has a lot of anti-inflammatories, anti-bacterial and antioxidant property
Physical activity
Regular exercising can help alleviate various symptoms of hypothyroidism. Also, specific yoga poses have seen to be effective in enhancing thyroid functioning.
Conclusion
While it is important to consult a doctor and follow the treatment prescribed to keep thyroid problems under control, but by trying above listed home remedies, you can keep the side effects of thyroid medication at bay.
One of the important components of our overall wellness is also being financially secured. Healthcare emergencies can happen any time, but a good health insurance policy can protect you from such uncertain situations. To know more about Wellness and other health related tips, visit the wellness corner.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

Hormones and Weight Gain: How to Regulate the Hormones that Influence Your Weight
Introduction:-
Hormones are one of the most important participants in this delicate dance, which involves many different aspects in maintaining a healthy weight. Hormones are endocrine system-produced chemical messengers that control a number of body processes, such as metabolism, appetite, and fat storage. Unbalanced hormones can lead to weight gain and make it difficult to lose the additional pounds. In this post, we'll examine the relationship between hormones and weight gain and look at methods for rebalancing these hormonal regulators.
Insulin: Master of Blood Sugar
The pancreas produces insulin, a crucial hormone that controls blood sugar levels. When we eat carbs, our bodies convert them to glucose, which raises blood sugar levels. Insulin aids in the movement of circulation glucose into or into the storage of glucose in cells. However, regular use of sugary meals and refined carbs can cause insulin resistance, in which cells lose their receptivity to insulin. Higher insulin levels are the result, and this might promote the storage of fat, particularly around the abdomen.
Fix: Opt for complex carbohydrates like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables that have a gentler impact on blood sugar levels. Include protein and healthy fats in your meals to slow down the absorption of glucose. Engage in regular physical activity to improve insulin sensitivity and glucose utilization.
Leptin: The Satiety Signal
Leptin, often called the "satiety hormone," is produced by fat cells and helps regulate appetite and metabolism. It signals the brain when you've had enough to eat, reducing hunger. However, in cases of obesity, the body can develop leptin resistance, leading to a lack of proper appetite regulation.
Fix: Focus on whole foods that are nutrient-dense to support healthy leptin levels. Prioritize sleep, as inadequate sleep can disrupt leptin production. Manage stress, as chronic stress can contribute to hormonal imbalances, including
leptin resistance.
Ghrelin: The Hunger Hormone
Ghrelin, produced in the stomach, is known as the "hunger hormone" because it stimulates appetite. It increases before meals and decreases after eating. Sleep deprivation and irregular eating patterns can lead to elevated ghrelin levels, causing overeating and weight gain.
Fix: Establish regular mealtimes to help regulate ghrelin secretion. Get sufficient sleep, as sleep deprivation can lead to higher ghrelin levels and increased hunger. Stay hydrated, as dehydration can sometimes be mistaken for hunger.
Cortisol: The Stress Hormone
Cortisol, released by the adrenal glands in response to stress, plays a vital role in metabolism and fat storage. Chronic stress can lead to elevated cortisol levels, which, over time, can contribute to weight gain, particularly around the midsection.
Fix: Practice stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing, or spending time in nature. Engage in regular physical activity, which can help lower cortisol levels. Ensure adequate sleep, as sleep deprivation can further elevate cortisol levels.
Thyroid Hormones: Metabolic Regulators
Thyroid hormones, including T3 and T4, play a crucial role in regulating metabolism. An underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism) can lead to weight gain, as it slows down metabolic processes.
Fix: Consume iodine-rich foods like seafood and seaweed to support thyroid function. Ensure you're getting enough selenium, zinc, and other nutrients that are essential for thyroid health. Consult a healthcare professional if you suspect thyroid issues. Weight Loss Solutions
Conclusion:-
In summary, hormones are important for controlling weight. You can aim to achieve a healthy weight and restore hormonal balance by adopting a holistic strategy that includes a balanced diet, regular physical activity, stress management, enough sleep, and seeing a specialist when necessary. Be patient and consistent as you implement these lifestyle modifications because every person's body is different.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Thyroid Diet Plan for Weight Loss | Hypothyroidism Diet Plan

A well-functioning thyroid is essential for overall health and well-being. The thyroid gland plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism, energy production, and even mood. When the thyroid is imbalanced, it can lead to weight fluctuations, fatigue, and other health concerns. But fear not! With a targeted thyroid diet plan, you can support your thyroid's optimal function and embark on a journey to better health. In this article, we unravel the mysteries of the thyroid and provide you with a practical and easy-to-follow Online Thyroid Diet Plan for Weight Loss to nurture your thyroid health & lose weight.
The Thyroid's Vital Role
The thyroid gland, a small butterfly-shaped organ located in the neck, produces hormones that influence nearly every cell in the body. These hormones, namely thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), regulate metabolism, body temperature, heart rate, and more.
Common Thyroid Disorders
✅ Hypothyroidism: When the thyroid doesn't produce enough hormones, it can result in weight gain, fatigue, and a slowed metabolism.
✅ Hyperthyroidism: Excessive thyroid hormone production can lead to weight loss, increased heart rate, and anxiety.
The Impact on Weight
Thyroid imbalances often manifest in weight-related issues. Hypothyroidism can contribute to weight gain, while hyperthyroidism may lead to weight loss. A well-planned Thyroid Diet Plan for Weight Loss can help address these concerns.
Fueling Your Thyroid with Nutrient-Rich Foods
✅ Embracing Iodine
Iodine is a key player in thyroid health, as it's an essential component of thyroid hormones. Incorporate iodine-rich foods like seaweed, seafood, dairy, and eggs into your diet.
✅ Selenium's Superpower
Selenium supports thyroid function and helps convert T4 into the active T3 hormone. Brazil nuts, fish, and whole grains are excellent sources of selenium.
✅ Smart Carbohydrates
Opt for complex carbohydrates like whole grains, legumes, and vegetables. These provide sustained energy and prevent blood sugar spikes that can impact thyroid function.
✅ Lean Protein
Protein aids in tissue repair and metabolism. Include lean protein sources like poultry, fish, tofu, and beans in your diet.
✅ Healthy Fats
Essential fatty acids found in nuts, seeds, and fatty fish promote hormone balance and overall well-being.
✅ Tyrosine-Rich Foods
Lean meats, poultry, fish, tofu, and dairy products offer tyrosine, an amino acid crucial for thyroid hormone synthesis.
✅ Leafy Greens
Rich in vitamins and minerals, leafy greens like spinach, kale, and Swiss chard support thyroid function.
✅ Colorful Fruits and Veggies
Vibrant produce is packed with antioxidants that combat inflammation and promote thyroid health.
✅ Zinc-Rich Foods
Zinc contributes to hormone production and immune function. Enjoy zinc-rich foods like nuts, seeds, and whole grains.
Hydration and Hormones
✅ Staying Hydrated
Adequate hydration is vital for hormone production and overall health. Aim for at least 8 glasses of water a day.
✅ Limiting Goitrogens
Cruciferous vegetables like broccoli, cauliflower, and kale contain compounds called goitrogens, which can interfere with thyroid function. However, you can still enjoy their health benefits by cooking them, which reduces the goitrogenic effects while preserving their nutritional value.
Mindful Eating for Thyroid Health
The Importance of Mindful Eating
Mindful eating involves savoring each bite, eating slowly, and paying attention to hunger and fullness cues. This practice can prevent overeating and support digestion.
Seeking Professional Guidance
When navigating dietary choices for thyroid health, it's prudent to seek guidance from a qualified dietitian. A dietitian can tailor a nutrition plan to your individual needs, considering factors like thyroid condition, overall health, and lifestyle. This personalized approach ensures you make informed choices, optimizing your diet to support thyroid function effectively. You can consult with renowned Dietitian Swati Singh for seeking any kind of help regarding thyroid.
Consult a Healthcare Professional
Before making significant dietary changes, consult a healthcare provider or registered dietitian. They can provide personalized recommendations based on your thyroid health and overall well-being.
Conclusion
By embracing a thyroid-friendly diet, you take a proactive step toward supporting your thyroid's optimal function. Through nutrient-rich foods, balanced macronutrients, and mindful eating practices, you can promote hormone balance, metabolism, and overall vitality. Remember, your thyroid deserves the best care, and with the right diet plan, you're well on your way to nurturing your thyroid health for a vibrant and energized life.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
"The Thyroid Factor: Unleashing the Thyroid-Boosting Belly Flattening System"
Click here to find more about "The Thyroid Factor" : Source:youtube.com
Introduction
In today's fast-paced world, countless individuals struggle with weight management and find it difficult to shed excess belly fat despite adopting various diet and exercise regimens. Often overlooked, the thyroid gland plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism, energy levels, and overall well-being. "The Thyroid Factor" is a comprehensive and innovative system designed to optimize thyroid function and promote sustainable weight loss. Developed by leading health experts and backed by scientific research, this program offers a holistic approach to address underlying thyroid issues and achieve a flatter belly while improving overall health.

Understanding the Thyroid Gland
Before diving into the specifics of "The Thyroid Factor," it's essential to grasp the significance of the thyroid gland. Located in the front of the neck, this butterfly-shaped gland produces hormones that regulate various bodily functions, including metabolism, heart rate, body temperature, and energy levels. The two primary hormones produced by the thyroid are triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4), which play a vital role in determining how efficiently the body burns calories.

When the thyroid gland isn't functioning optimally, it can lead to a range of health issues, such as hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) or hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid). Hypothyroidism often results in weight gain, fatigue, and sluggishness, while hyperthyroidism may lead to weight loss, rapid heartbeat, and anxiety.
Identifying Your Unique Thyroid Type
"The Thyroid Factor" emphasizes the importance of understanding your unique thyroid type to tailor the program to your specific needs. By identifying your thyroid type, you can implement targeted strategies to optimize thyroid function, thereby promoting weight loss and improved well-being. Some common thyroid types include:
Type T1: The Toxic Thyroid
Type T2: The Tired Thyroid
Type T3: The Tension Thyroid
Type T4: The Taming Thyroid
Type T5: The Tolerant Thyroid
Each type corresponds to specific symptoms and imbalances, and by recognizing which type resonates with you, you can embark on a customized path towards better health.

The Components of "The Thyroid Factor" System
"The Thyroid Factor" is a multi-faceted program that addresses nutrition, exercise, and stress management to optimize thyroid function and achieve sustainable weight loss. Let's delve into each component of this system:
Nutrition for Thyroid Health: The program emphasizes a balanced and nourishing diet that supports thyroid function. Certain foods can stimulate the thyroid gland, while others may inhibit its function. For example, foods rich in iodine, selenium, and zinc are crucial for thyroid health. Additionally, incorporating anti-inflammatory foods, lean proteins, and healthy fats can further support your weight loss goals.
Thyroid-Boosting Exercises: Not all workouts are created equal when it comes to optimizing thyroid function. "The Thyroid Factor" introduces specific exercises that target the thyroid gland and help boost metabolism. These exercises are tailored to your thyroid type and are designed to be both effective and achievable.
Stress Management Techniques: Chronic stress can wreak havoc on the thyroid gland and hinder weight loss efforts. Therefore, the program includes stress reduction techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and mindfulness practices, to promote hormonal balance and overall well-being.
Sleep Optimization: Sleep is a critical factor in maintaining thyroid health. "The Thyroid Factor" emphasizes the importance of quality sleep and provides tips and strategies to improve sleep patterns, allowing the body to recover and reset.
Lifestyle Adjustments: Beyond nutrition and exercise, the program encourages participants to make lifestyle adjustments that support their thyroid health, such as avoiding environmental toxins and reducing exposure to endocrine disruptors.
Case Studies and Success Stories
"The Thyroid Factor" has garnered numerous success stories from individuals who have benefited from the program. By sharing these inspiring case studies, the program demonstrates its effectiveness in helping people achieve their weight loss goals and regain vitality. These real-life examples showcase how different thyroid types respond to the tailored approach of "The Thyroid Factor."
Expert Insights and Research
"The Thyroid Factor" is based on scientific research and insights from leading health experts in the field of endocrinology, nutrition, and fitness. By incorporating evidence-based strategies, the program ensures its credibility and effectiveness. The system combines the latest findings on thyroid function, metabolism, and weight management to provide participants with a comprehensive and well-rounded approach.

Conclusion
"The Thyroid Factor" offers hope and a sustainable solution for individuals struggling with weight management and belly fat. By understanding the vital role of the thyroid gland in regulating metabolism and energy levels, this comprehensive system empowers participants to optimize their thyroid function and achieve lasting weight loss. Through targeted nutrition, thyroid-boosting exercises, stress management, and lifestyle adjustments, individuals can revitalize their metabolism, boost energy levels, and regain their confidence.
If you've been tirelessly searching for an effective weight loss solution, look no further than "The Thyroid Factor." Embrace this transformative program today and unlock the secrets to a healthier, fitter, and happier you. Don't let thyroid issues hold you back any longer—take control of your health and unleash the power of "The Thyroid Factor" today.
Continue reading………………….
Click here for more information:
Click here to find more : Official website
#the thyroid factor#the thyroid factor review#the thyroid factor side effects#weightloss#loseweight#belly fat#bellyfat#losebellyfat#ketodiet#fatloss#fatburn#reduceweight#lower belly fat
1 note
·
View note
Text
Benefits of Garlic for Your Thyroid Disease - Natural Support for a Balanced Life

When it comes to managing thyroid disease, many people focus only on synthetic medications. However, holistic approaches-including nutrition and natural supplements-are gaining momentum. Among the many foods considered beneficial for thyroid health, garlic stands out as a powerful, accessible superfood.
In this article, we’ll explore the benefits of garlic for your thyroid disease, its active compounds, how it works with your thyroid hormones, and where to find expert-backed supplement guidance at anshulguptamd.com.
Understanding the Thyroid Gland
The thyroid is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck. It plays a key role in regulating metabolism, energy production, and hormone balance. When this gland is underactive (hypothyroidism) or overactive (hyperthyroidism), it can lead to a wide range of symptoms such as fatigue, weight changes, brain fog, mood disturbances, and more.
While conventional treatments usually involve synthetic hormone replacements or medications, many functional medicine experts now advocate for nutritional support as an essential component of long-term thyroid health.
Garlic: More Than Just a Flavor Enhancer
Garlic (Allium sativum) is widely known for its immune-boosting, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial properties. But research shows it may also offer specific advantages for those struggling with thyroid imbalances.
Let’s break down the major benefits of garlic for your thyroid disease:
1. Supports Immune Function
Autoimmune thyroid conditions like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Graves’ disease occur when the immune system attacks the thyroid gland. Garlic contains sulfur compounds like allicin, which have been shown to modulate immune responses. These compounds may help reduce the overactive immune response that drives thyroid dysfunction.
2. Anti-inflammatory Effects
Chronic inflammation is a root cause in many thyroid conditions. Garlic’s natural anti-inflammatory effects can help lower systemic inflammation, potentially easing symptoms and supporting better hormone production.
3. Detoxifies Heavy Metals
Studies suggest that heavy metal toxicity-such as mercury and lead-can interfere with thyroid function. Garlic contains sulfur-rich compounds that support the liver in detoxifying these harmful substances from the body, thereby supporting thyroid gland health.
4. Balances Gut Microbiome
A healthy gut is crucial for thyroid hormone conversion, especially from T4 to the active T3 hormone. Garlic acts as a prebiotic, feeding good bacteria in the gut and helping maintain digestive balance. This contributes to better thyroid function and nutrient absorption.
5. Lowers Cholesterol and Supports Heart Health
Thyroid disorders can often lead to cholesterol imbalances and cardiovascular issues. Garlic helps reduce LDL (bad cholesterol) and supports blood circulation, which is vital for people with hypothyroidism, who are more prone to heart disease.
How to Use Garlic for Thyroid Support?
While adding garlic to your meals is beneficial, its therapeutic benefits are often more pronounced when consumed raw or as part of a supplement. Here's how you can include it in your routine:
Raw garlic: Crush 1-2 cloves and let them sit for 10 minutes before consuming. This activates allicin, the key compound.
Aged garlic supplements: These are easier on the stomach and still retain many of garlic’s beneficial properties.
Garlic oil: Can be used topically (with a carrier oil) for inflammation or ingested in capsule form.
Note: Always consult your healthcare provider before starting any new supplement, especially if you're on thyroid medication, as garlic may enhance medication absorption or interact with certain drugs.
Finding the Best Supplement for Thyroid
While garlic is an excellent natural aid, comprehensive thyroid support often requires a combination of nutrients, including selenium, zinc, magnesium, B vitamins, and adaptogenic herbs like ashwagandha.
To simplify your journey, Dr. Anshul Gupta, MD-a renowned functional medicine expert-offers clear, evidence-based guidance on the best supplement for thyroid support. His approach addresses the root causes of thyroid disease, not just the symptoms.
On his website, anshulguptamd.com, you'll find:
Custom supplement protocols for thyroid healing
Research-backed product recommendations
Insights into combining garlic and other herbs with functional medicine
Patient success stories and practical lifestyle tips
Whether you're dealing with Hashimoto’s, Graves’ disease, or general hypothyroidism, Dr. Gupta's resources can help you make informed decisions about your thyroid health.
Final Thoughts
There’s no single solution for thyroid disease. However, integrating healing foods like garlic, choosing the best supplement for thyroid, and seeking trusted medical advice can set you on the path to better health.
The benefits of garlic for your thyroid disease go far beyond flavor. From reducing inflammation to supporting detoxification and gut health, garlic may be a powerful natural tool in your wellness toolkit.
If you're looking for expert guidance and customized solutions, visit anshulguptamd.com to explore holistic, science-based strategies for reclaiming your thyroid health.
Remember: Healing your thyroid is not just about managing numbers on a lab test-it’s about restoring energy, mood, metabolism, and quality of life.
Let food be your medicine-and garlic, your ally.
Good health is the foundation of a happy and fulfilling life. Without it, even the greatest achievements feel empty. Taking care of your physical and mental well-being should be a top priority. A balanced diet, regular exercise, proper sleep, and mindfulness can preve nt countless diseases and boost overall vitality. In today’s fast-paced lifestyle, stress and unhealthy habits often take a toll on our bodies, but small daily changes can bring long-term benefits. Mental health is equally important; talking to someone, meditating, or even reading uplifting content like an Wedding Shayari in Hindi can uplift the spirit. Such short verses not only inspire but also help us pause and reflect. Remember, good health isn’t a destination—it’s a continuous journey. Investing in it today ensures a stronger, brighter tomorrow. Let your body be your best friend and treat it with the love and care it deserves.
0 notes
Text
Why Seafood is Healthiest for Most People

Seafood is liked not just because of its taste but for its established health benefits. Various cultures include seafood with health benefits; so much so, seafood seems to be one of the most widely known food formats loaded with healthful benefits.. Fish and seafood contain many nutrients, lean protein, healthy fats (including omega oils), and many benefits for people of all ages. Many health-conscious diners will also search for 'best fish restaurant in Trivandrum' for a structure of flavor that also contains all that is healthful and supportive of a healthy lifestyle. Remember, following a pattern of eating seafood is not only food to be enjoyed, but is a way of being health active.
Most of the time when a dietitian is telling you to eat fish, one of the main reasons for that is the omega-3 fatty acids - EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid). Truthfully, yes we do get omega-3 fatty acids from some microalgae (certain types), some plants, and some nuts, but currently (as far as I know) there are no (nada) sources of plant-based omega 3 fatty acids. This is so because omega-3 fatty acids are essential fats, which are referred to because of the fact we cannot make; we can only obtain it from food. Multiple research studies indicate omega-3 fatty acids are able to lower inflammation and improve blood vessel function, and reduce chronic disease at times: heart disease and stroke. There are two basic types of fish. Cab be easy to confuse fish to mean all fish within its> 80% of fish is shellfish that does not have the quantity dietitians would veil to probably consider it a better source of omega-3s, from ocean, fatty and oily fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines. Fatty and oily fish provide omega-3 fatty acids which are healthy for the heart and count as food and once again by when that produce seafood- provide omega-3 fatty acids. Some studies suggest that omega-3s even benefit cognitive function and help guard against depression, cognitive decline, and Alzheimer's disease by regularly consuming omega-3s.
A great superfood for vitamins and minerals is seafood! Vitamin D, iodine, selenium, and several B vitamins are set up in fish and shellfish. The vulnerable system and strong bones both benefit from vitamin D. Healthy hormone-active thyroid function is supported by iodine. As a strong antioxidant, selenium securities cells from oxidative stress. B vitamins can support nervous system cellular function and energy metabolism asco-factors. Because it contains all nine essential amino acids, seafood is a source of complete protein, which can help with muscle growth, conservation, and form. Enjoy seafood the coming time you are tired and tired of eating so important calories- thick, logged fat, and nutrients- thick beast protein!
If you're looking to embark on a healthy lifestyle without sacrificing taste - seafood is the way to go! Seafood is high in plentiful, high-quality, lean protein, along with nutrient-rich ingredients, healthy omega-3 fatty acids, and so much more. If you're motivated to take advantage of all these healthy attributes - while also enjoying fabulously tasting food, your first step should be finding the best fish restaurant in Trivandrum! The best fish restaurants offer cleanly caught, nutrient-rich fish like salmon, sardines or mackerel - and also offer seafood that highlights all the health benefits fish can give you. Whether you want to support heart health, brain health or simply enjoy a deliciously wholesome meal, there are few things better than eating at the best fish restaurant in Trivandrum where you can prioritize health and taste.
One of the great advantages of healthy seafood is variety. Yes, you have non-fatty fish-like cod, tilapia and snapper and of course the much fattening nutrient-rich fish like tuna, sardines and mackerel. Each fish has its distinct health benefits. Shellfish (e.g. clams, mussels, shrimp, crab) are a great source of healthy nutrients including iron, zinc, and vitamin B12. Using high-quality fish or shellfish in your meals can help enhance your diet with these nutrients and provide an interesting twist to your typical sources of protein. When you decide to cook seafood, there are a plethora of healthy cooking methods to utilize—even baking, grilling, poaching, steaming, and frying!
Seafood can be a supportive food in weight management. Seafood is generally low in calories (and saturated fats) and high in protein, and will reduce experiences of hunger and cravings so that people can snack less on the wrong foods. Protein diets have been found to not only boost metabolism in the short term but also help preserve lean muscle tissue during voluntary weight loss. Also, many seafood recipes (when they are cooked without heavy oils, creams, and/or sauces) are generally easy to fit into a reduced-calorie meal plan.
Of course, while the health benefits are significant, it's important to consider seafood safety and sustainability. Some species of fish may contain traces of mercury or environmental contaminants. For this reason, health experts recommend consuming a variety of seafood while avoiding high-mercury fish like swordfish or king mackerel, especially for pregnant women and young children. Opting for sustainably caught or responsibly farmed fish supports both your health and the health of marine ecosystems.
In considering health benefits of seafood consumption it is also important to consider the healthiness & sustainability of seafood in question. Some fish species may contain small trace amounts of mercury or environmental contaminants. Many health organizations recommend consuming a variety of seafood, rather than focusing on a particular species, and to avoid those higher in mercury such as swordfish or king mackerel, especially when considering vulnerable populations like pregnant women and children.By choosing to eat sustainably caught or responsibly farmed fish you will be supporting your health and the health of marine ecosystems.
In conclusion, seafood is undoubtedly among the healthiest protein sources available. From understanding the role that seafood plays in nutrition & supporting cardiovascular and cognitive health to the long list of unique nutrients, it’s no surprise that seafood is highly recommended in dietary guidelines around the globe. So whether you're enjoying the catch of the day at the best Trivandrum fish restaurant or exploring the best seafood varieties in your home kitchen, including seafood as part of your diet is a delicious way to contribute to a healthier life.
FAQ
1. Why is seafood considered healthy?
It’s rich in lean protein, omega-3 fatty acids, and essential nutrients, with low saturated fat
2. How often should I eat seafood?
At least twice a week, especially fatty fish like salmon or sardines.
3. Is all seafood safe to eat?
Most are safe, but avoid high-mercury fish like swordfish; choose sustainable options when possible.
0 notes
Text
Can You Put Thyroid Issues into Remission? Your Lifestyle Plays a Big Role
Dealing with thyroid problems like hypothyroidism or Hashimoto’s can feel overwhelming. But the good news is—your daily habits can make a big difference. While there’s no magic fix, adopting a healthier lifestyle may help improve thyroid function and even lead to remission in some cases.

What Affects Thyroid Health? Thyroid disorders happen when your thyroid gland doesn’t produce enough hormones. This can cause tiredness, weight gain, mood changes, and more. Research shows that poor diet, high stress, lack of exercise, and poor sleep can all make thyroid issues worse.
How Can Lifestyle Help? Eating a balanced, nutrient-rich diet with foods that support the thyroid—like those containing iodine, selenium, and zinc—can be helpful. An anti-inflammatory diet filled with fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats also supports better hormone balance.
Managing stress through yoga, breathing exercises, or meditation can reduce the strain on your thyroid. Getting regular exercise helps regulate metabolism and hormone levels, while quality sleep is essential for healing and overall health.
Some people have even seen their thyroid conditions improve greatly with these changes. But everyone is different, and it's important to consult your doctor before making major adjustments. A healthy lifestyle won’t replace medical care, but it can be a powerful tool in managing thyroid issues and may even support remission when done consistently and mindfully.
Read more, visit here.
https://www.freedomfromdiabetes.org/blog/post/putting-thyroid-into-remission-lifestyle-matters/3688
#thyroid remission#lifestyle for thyroid health#natural thyroid support#hypothyroidism lifestyle changes#reverse thyroid naturally#thyroid diet tips#stress and thyroid#sleep and thyroid function#exercise for thyroid#Hashimoto’s lifestyle changes
0 notes
Text
Effective 7-Day Diet Plan for Hashimoto’s Disease: Boost Your Thyroid Health
Understanding Hashimoto’s Disease and Its Dietary Needs
Hashimoto’s disease, an autoimmune disorder affecting the thyroid gland, plays a critical role in hormonal balance and metabolism within the body. Individuals with Hashimoto’s experience the immune system mistakenly attacking the thyroid, leading to inflammation and often causing hypothyroidism, characterized by fatigue, weight gain, and mood swings. Understanding how diet can impact this condition is essential for management and potentially alleviating symptoms. The right 7-day diet plan for hashimoto’s disease can significantly improve quality of life.
What is Hashimoto’s Disease?
Hashimoto’s disease, also known as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, is the most common cause of hypothyroidism. This autoimmune disorder occurs when the body’s immune system creates antibodies that attack the thyroid gland, reducing its ability to produce thyroid hormones. Symptoms may include fatigue, weight gain, depression, sensitivity to cold, and dry skin, among others. For many, a proper diagnosis and treatment plan from healthcare professionals can lead to better management of the disease.
The Role of Diet in Managing Hashimoto’s
Diet plays a pivotal role in managing Hashimoto’s disease. While no specific diet can cure the condition, certain foods can help manage symptoms and improve overall health. Adopting an anti-inflammatory diet that focuses on whole, nutrient-dense foods may benefit those with thyroid issues. Studies show that certain diets may reduce inflammation and support thyroid function, which is vital for alleviating symptoms associated with Hashimoto’s.
Nutritional Guidelines for Thyroid Health
Eating a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients for thyroid function can help manage Hashimoto’s. Key dietary components include:
Iron: Essential for the synthesis of thyroid hormones.
Selenium: Plays a crucial role in hormone metabolism and reduces inflammation.
Zinc: Promotes overall immune health and supports thyroid function.
Iodine: Necessary for thyroid hormone production, but should be consumed in moderate amounts.
Vitamin D: Important for immune regulation and may be beneficial in autoimmune conditions.
Key Components of a 7-Day Diet Plan
A well-structured meal plan consisting of nutrient-rich foods is vital for managing Hashimoto’s disease. Here we break down the essential elements of a 7-day meal plan designed to support thyroid health.
Essential Nutrients for Thyroid Function
To optimize thyroid function and minimize symptoms, focus on including the following key nutrients in your diet:
Foods high in fruits and vegetables provide antioxidants that protect against cellular damage.
Healthy fats from sources like avocados, nuts, and olive oil support hormone production and reduce inflammation.
Lean proteins, such as chicken, turkey, or fish, are required for rebuilding tissues and supporting metabolic functions.
Anti-Inflammatory Foods to Include
Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods is crucial for alleviating symptoms of Hashimoto’s disease:
Fatty fish: Rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which combat inflammation (salmon, sardines).
Leafy greens: Spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are packed with vitamins and minerals.
Fruits: Berries, cherries, and apples are high in antioxidants that promote health.
Fermented foods: Such as yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut that can benefit digestive health and gut microbiota.
Foods to Avoid for Hashimoto’s Patients
Identifying and avoiding foods that may exacerbate symptoms is essential for those managing Hashimoto’s disease:
Gluten: Many with Hashimoto’s report sensitivity to gluten, which can trigger immune responses.
Processed foods: Often high in additives and preservatives that may provoke inflammation.
Sugar: Refined sugars can lead to energy spikes and crashes while negatively affecting immune function.
Nightshade vegetables: Foods such as tomatoes and bell peppers may trigger sensitivities in some individuals.
Sample 7-Day Meal Plan Overview
This sample meal plan is designed to provide balanced nutrition while focusing on foods that support thyroid health. Each day includes meals rich in the essential nutrients discussed.
Day 1: Breakfast to Dinner Plan
Breakfast: Scrambled eggs with spinach and feta, served with sliced avocado.
Lunch: Quinoa salad with cherry tomatoes, cucumber, olives, and grilled chicken.
Dinner: Baked salmon with steamed broccoli and sweet potatoes.
Day 2: Breakfast to Dinner Plan
Breakfast: Smoothie with berries, spinach, almond milk, and flaxseeds.
Lunch: Lentil soup with gluten-free bread.
Dinner: Stir-fried tofu with mixed vegetables and brown rice.
Day 3: Breakfast to Dinner Plan
Breakfast: Chia pudding made with almond milk topped with bananas and walnuts.
Lunch: Grilled shrimp with avocado lime dressing and a side of mixed greens.
Dinner: Roasted chicken thighs with Brussels sprouts and carrots.
Shopping List and Meal Preparation Tips
Effectively preparing for your dietary changes can simplify adherence to your meal plan. Below are strategies to ensure successful execution of your 7-day diet.
Creating Your Grocery List
When crafting your grocery list, focus on whole, nutritious foods. Include categories like:
Fruits and Vegetables: bell peppers, spinach, kale, berries
Proteins: chicken, fish, eggs, legumes
Healthy Fats: avocados, olive oil, nuts
Whole Grains: quinoa, brown rice, gluten-free oats
Meal Prep Strategies for Busy Lifestyles
Meal prepping can take the stress out of daily cooking:
Set aside a few hours on the weekend to prepare meals for the week.
Batch cook recipes that can stretch over multiple meals, like soups and stews.
Use versatile ingredients that can be mixed and matched in different meals.
Storing and Reheating Your Meals
Proper storage of your meals ensures they maintain flavor and nutrition:
Utilize airtight containers to keep food fresh.
Label meals with dates to track freshness and prevent waste.
Reheat meals in the oven or on the stovetop whenever possible for better taste compared to microwaving.
Monitoring Your Symptoms and Adjusting the Plan
Regularly tracking your health and dietary responses can help tailor your 7-day diet plan to best suit your needs.
Keeping a Food Journal
A food journal can provide clarity on what works for your body. Document details such as:
The foods consumed each day.
How you felt physically and emotionally post-meal.
Any symptoms you experienced and their severity.
Identifying Food Sensitivities
Monitor for any reactions to specific foods. If you suspect a food may be aggravating your symptoms:
Consider an elimination diet to systematically identify triggers.
Re-introduce foods one at a time to gauge tolerance.
Consulting a Healthcare Professional
It’s essential to collaborate with healthcare professionals when managing Hashimoto’s disease. A dietitian specializing in thyroid health can help tailor your meal plan and dietary choices to your unique needs, ensuring you stay healthy and nourished.
1 note
·
View note
Text

Selen and take a deep breath to your ideal body shape! A complete guide to a new diet method based on scientific evidence
The surprising truth that can be expected to lose weight by taking a deep breath and the relationship between nutrient selene
In order to achieve a healthy diet, it is important not only to restrict your diet and exercise vigorously, but also an approach that prepares from the inside of the body. By combining the micronutrient selenium and the deep breathing method, you can reduce stress and achieve sustainable diet effects while improving metabolic function.
1. The basic role of selene and its effect on the body
・The mechanism of the antioxidant effect of selenium on diet
・Points of recommended intake and efficient food selection
1. Scientific evidence and practical effects of deep breathing diet
・How to control appetite by reducing stress
・Specific effect on metabolism promotion and fat burning
1. The correct way to use abdominal breathing and tips for continuity
・Details of the detox effect by improving visceral function
・How to incorporate it into daily life and effective timing
1. How to choose and use abdominal breathing goods
・Features and usage of recommended training equipment
・Maintenance method to maximize the effect
1. Lastly
1. The basic role of selene and its effect on the body
・The mechanism of the antioxidant effect of selenium on diet
Selenium is an essential trace element for the human body and is known as a nutrient with strong antioxidant effects. This antioxidant action plays an important role in removing the active oxygen generated in the body and protecting the cells from oxidative stress. When active oxygen accumulates excessively, the function of cells decreases and metabolic efficiency decreases.
Selene, in particular, acts as a component of an enzyme called glutathione peroxidase, which breaks down hydrogen peroxide in cells into harmless water and oxygen. This process allows the mitochondria, the cell's energy-producing plant, to function normally and lead to improved basal metabolism. As the basal metabolism increases, you will be able to consume more calories even at rest, and you will naturally change to a constitution that is easy to lose weight.
In addition, selenium is deeply involved in the metabolism of thyroid hormones. Thyroid hormone is an important hormone that regulates body temperature and metabolic rate, and if selenene deficiency continues, thyroid function may decrease and metabolism may slow down.
・Points of recommended intake and efficient food selection
According to Japanese dietary intake standards, the recommended intake of selenium is 30μg for adult men and 25μg for adult women. However, pregnant and lactating women need more selenine, and 28μg is recommended for pregnancy and 45μg for breastfeeding. These amounts are by no means large, but they are also nutrients that are often lacking in modern diets.
Seafood is one of the foods that can efficiently consume selenum. Among them, saltwater fish such as bonito, tuna, and salmon are rich in selenum, and 50-100μg of selenum can be consumed per 100g. In addition, Brazilian nuts boast a very high selenen content, and only 1-2 grains can meet the daily requirement.
In meat, beef, pork, and chicken also contain a certain amount of selene, but the content is low compared to seafood. In cereals, unrefined grains such as brown rice and whole wheat bread contain more selen. Vegetables are rich in selene in arium vegetables such as garlic and onions, and by consuming these foods on a daily basis, you can naturally increase your selenium intake.
1. Scientific evidence and practical effects of deep breathing diet
・How to control appetite by reducing stress
In modern society, chronic stress is a problem that many people have, and this stress has become a major obstacle to dieting. If the stress state continues, the hormone called cortisol secreted from the adrenal cortex increases. Cortisol is originally a hormone necessary to protect yourself from dangerous situations, but if it continues to be secreted chronically, it increases appetite and especially increases the desire for foods that are high in sugar and fat.
Deep breathing has the effect of alleviating this stress reaction by acting directly on the autonomic nervous system. By taking a slow and deep breath, the parasympathetic nerve becomes dominant, the heart rate decreases, the blood pressure stabilizes, and the muscle tension is relieved. In this state, the secretion of cortisol is suppressed, and the secretion of "happiness hormones" such as serotonin and endorphins is promoted instead.
Serotonin is an important neurotransmitter that controls appetite, and its proper secretion makes it easier to get fullness and prevents overeating. Endorphins, also known as natural painkillers, relieve discomfort caused by stress and provide mental stability. Due to these physiological changes, deep breathing allows for natural control of appetite and supports a healthy diet.
・Specific effect on metabolism promotion and fat burning
The reason why deep breathing is effective for weight loss is the increase in oxygen supply. In normal shallow breathing, only part of the lungs is used, and the oxygen supply to the body tends to be insufficient. On the other hand, taking a deep breath increases lung activity and allows more oxygen to be absorbed in the body. This oxygen is transported by blood to the cells of the whole body and is used to produce energy in the mitochondria within the cells.
When the efficiency of oxygen utilization at the cellular level is improved, the production of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) becomes active. ATP, also known as the energy currency of cells, is essential for all biological activities. Sufficient oxygen supply promotes the oxidative decomposition of fatty acids, and body fat is efficiently burned as energy.
In addition, deep breathing is accompanied by a large movement of the diaphragm. The diaphragm is a large muscle located in the center of the trunk, and by actively using this muscle, the muscle group around the trunk is also stimulated at the same time. Strengthening the core muscle group leads to improved posture, and by maintaining correct posture, the calorie consumption in daily life naturally increases. With the correct posture, you can support your body efficiently against gravity, reduce unnecessary muscle tension, and improve metabolic efficiency.
1. The correct way to use abdominal breathing and tips for continuity
・Details of the detox effect by improving visceral function
Abdominal breathing is a breathing method that makes the most of the up and down movement of the diaphragm, and this movement has a natural massage effect on the internal organs. When the diaphragm descends, the pressure in the abdominal cavity increases, and digestive organs such as the liver, stomach, intestines, and pancreas are moderately compressed. This repetition of compression and relaxation improves blood flow in the internal organs and activates the function of each organ.
The liver is an important organ responsible for detoxification in the body, and improved blood flow through abdominal breathing increases the detoxification ability of the liver. In the liver, harmful substances such as alcohol, drugs, and food additives are decomposed and detoxified, and this function is improved to promote the discharge of toxins accumulated in the body. In addition, the liver also plays a central role in lipid metabolism, and the oxidation of fatty acids and the synthesis of bile acids are activated to improve fat burning efficiency.
The effect of abdominal breathing is also prominent in the intestinal tract. By promoting the peristalsis of the intestinal tract, constipation can be eliminated and the intestinal environment can be improved. When the intestinal flora is balanced, the production of short-chain fatty acids increases, and these substances have the effect of strengthening the intestinal barrier function and suppressing inflammation of the whole body. Chronic inflammation is considered one of the causes of obesity, and the improvement of the intestinal environment through abdominal breathing indirectly has a diet effect.
Abdominal breathing also plays an important role in the lymphatic system. Since lymphatic fluid does not have a pumping function like the heart, circulation is promoted by muscle contraction and respiratory movement. Deep abdominal breathing stimulates the lymphatic vessels in the chest and abdomen, which promotes the discharge of waste products and excess water. This can be expected to relieve swelling and improve metabolism.
・How to incorporate it into daily life and effective timing
In order to effectively incorporate abdominal breathing into daily life, appropriate timing and continuous practice are important. As soon as you wake up in the morning, the autonomic nervous system is easy to reset, and you can make the most of the effects of abdominal breathing. Morning abdominal breathing has the effect of activating the metabolism of the day and improving energy levels. Ly on your back on the bed, put your hand on your stomach, inflate your stomach while breathing slowly, and repeat the movement of denting your stomach while exhaling about 10 times.
Abdominal breathing before meals is also very effective. By performing abdominal breathing 30 minutes before meals, the function of the digestive system is activated and the digestion and absorption of meals are improved. In addition, a state of relaxation before meals has the effect of increasing concentration on eating, making it easier to get fullness, and preventing overeating. You can improve the quality of your meal by taking a deep breath casually, even when dining at a restaurant or having a business lunch.
Abdominal breathing before bedtime is an important habit that improves the quality of sleep. Growth hormone is secreted during deep sleep, which promotes lipolysis and promotes muscle repair and growth. Abdominal breathing before going to bed makes the parasympathetic nerve dominant, and it is easier to get deep sleep by relaxing the body and mind. By practicing the "4-7-8 Breathing Method", which inhales in 4 seconds, holds breaths for 7 seconds, and exhales in 8 seconds after entering the bed, it is possible to introduce natural sleep.
1. How to choose and use abdominal breathing goods
・Features and usage of recommended training equipment
Abdominal breathing training equipment has attracted attention in recent years as an aid for acquiring correct breathing techniques. These devices can effectively train the diaphragm and respiratory muscles by adjusting the resistance during breathing. Typical equipment include intake resistance equipment and exhalation resistance equipment, each of which has different effects.
The intake resistance device strengthens the diaphragm and intercostal muscles by giving it a certain resistance when inhaling. By using this device, it is possible to improve lung capacity and acquire deep breathing patterns. To use it, put the instrument in your mouth, breathe in through your nose, and exhale slowly through the instrument. Beginners can gradually strengthen their breathing muscles by setting their resistance level low and gradually increasing their resistance.
The exhalation resistance device trains the transverse abdominal muscles and the intercostal muscles by giving resistance when exhaling. This device has the effect of improving the ability to adjust abdominal pressure and increasing the stability of the trunk. When using, be aware of densing your stomach firmly while exhaling slowly through the equipment. This action effectively stimulates the deep abdominal muscles and can be expected to tighten the waist.
Some of the latest abdominal breathing apparatus have a function that works with smartphone apps. These devices monitor the rhythm and depth of breathing and provide a training program tailored to the individual's breathing patterns. In addition, we support continuous efforts by recording progress and setting goals.
・Maintenance method to maximize the effect
Proper maintenance is essential to maximize the effectiveness of abdominal breathing apparatus. First of all, hygiene management is the most important. The part that touches the mouth directly must be carefully washed and dried thoroughly using a neutral detergent after each use. If stored with moisture left, it can cause the growth of bacteria and mold and have a negative impact on your health.
It is recommended that you use alcohol-based disinfectant once a week for more thorough disinfection. In particular, use a special brush to clean the details of the equipment and the parts that cannot be removed. In addition, by regularly disassembling each part of the equipment and cleaning the interior, it can be used hygienically for a long time.
Regular inspections are also required for the adjustment function of the resistance level of the equipment. If dirt and foreign matter accumulate on the moving part, it may not be possible to accurately adjust the resistance and reduce the training effect. Follow the manufacturer's instruction manual and use the appropriate lubricant to maintain the moving parts.
The storage environment also greatly affects the life of the equipment. It is important to keep away from direct sunlight and high temperature and humidity, and to store in a well-ventilated place. In addition, it is recommended to store it in a special case or pouch to prevent scratches and deformations due to contact with other equipment.
1. Lastly
A diet approach that combines selenium and deep breathing is not just a popular health method, but a scientifically based sustainable method. By utilizing the knowledge of modern nutrition and physiology, it is possible to promote healthy changes from the inside of the body and achieve a reasonable diet.
The antioxidant action of selenium improves metabolic function at the cellular level and leads to an improvement in basal metabolism. On the other hand, deep breathing and abdominal breathing support diet in both stress reduction and metabolism promotion through the adjustment of the autonomic nervous system. By combining these methods, a synergistic effect can be expected.
The important thing is continuous practice. Rather than seeking dramatic changes in a short period of time, small daily accumulations lead to long-term health and ideal body shape. By being aware of the intake of selenum from the diet and making daily breathing a habit, you will naturally improve your constitution.
The use of abdominal breathing apparatus accelerates the acquisition of correct breathing techniques and enables more effective training. However, the goal is not to rely on equipment, but ultimately to be able to practice the correct breathing method without equipment.
The biggest advantage of this diet method is that it can be practiced anytime, anywhere without the need for special equipment or high costs. For busy modern women, the health method that can be worked on at any time and place is very valuable. Not being impatient and continuing at your own pace will be a sure path to your ideal body shape and a healthy life.
0 notes
Text
The Versatility of Shrimp: Nutritional and Culinary Benefits

Shrimp is one of the most popular seafood choices around the world. It is loved not only for its delicious taste but also for its many health benefits. Whether grilled, boiled, or added to a salad, shrimp can fit perfectly into many dishes. Let’s explore why shrimp is such a versatile and healthy food that deserves a place on your plate.
Nutritional Benefits of Shrimp
Shrimp is packed with important nutrients that help keep your body healthy. It is low in calories but rich in protein, which is essential for building muscles and repairing tissues. A serving of shrimp can provide almost half of the daily protein you need.
In addition, shrimp contains important vitamins and minerals like vitamin B12, selenium, and iodine. These nutrients support brain function, boost the immune system, and help maintain a healthy thyroid. Shrimp also has antioxidants, which protect your cells from damage and may reduce the risk of certain diseases.
Culinary Versatility of Shrimp
One of the best things about shrimp is how easy it is to cook and include in many recipes. Shrimp cooks quickly and can be prepared in many ways such as grilling, sautéing, boiling, or frying. This makes shrimp a great option for busy weeknights or special occasions.
You can add shrimp to pasta, salads, stir-fries, tacos, or soups. It pairs well with a variety of flavors like garlic, lemon, butter, herbs, and spices. Because of this flexibility, shrimp can be part of simple meals or elegant dishes.
Shrimp also works well as a main dish or as a tasty appetizer. You can serve it hot or cold, making it perfect for different seasons and events. Its mild taste means it can easily adapt to many cuisines, from Asian to Mediterranean.
Shrimp and Local Favorites
If you live near Champaign, IL, or are visiting, you are in luck. The area is known for offering some of the best seafood in Champaign IL. Fresh shrimp is often available at local markets and restaurants, allowing you to enjoy shrimp dishes made with quality ingredients.
Exploring shrimp recipes or enjoying them at local eateries is a great way to appreciate this versatile seafood. Whether you are craving a shrimp cocktail or a spicy shrimp stir-fry, you can find delicious options nearby.
Conclusion
Shrimp is truly a versatile seafood that offers both nutritional and culinary benefits. It is a low-calorie, protein-rich food full of important vitamins and minerals. Its quick cooking time and ability to blend with many flavors make it perfect for a wide range of dishes.
If you want to enjoy fresh and tasty shrimp, you don’t have to look far. The best seafood in Champaign IL includes shrimp that is fresh and flavorful, making it easy to enjoy this healthy and delicious food.
0 notes