#Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
#agile#i&a#inspect and adapt#poetry#management#project management#product management#qa#rca#root cause analysis#systems analysis#test
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
i forget if i’ve posted about this before. stop me
blameless postmortem culture has a lot to offer, but other people explain that plenty. here’s the catch: it only works if these two conditions are met:
1. everyone involved is doing their earnest best (or at least, meeting the effort expectations agreed in the team)
2. everyone involved is working toward the same set of goals
if either of these conditions is not met, you have a problem. if the root cause boils down to “jimmy didn’t want to deal with it so he didn’t”, unfortunately that’s a people problem. you may be able to engineer it a little bit, but you can never really prevent it.
if the root cause is “someone or some team was working toward a different goal from the rest of us”, that’s either a communication problem (benign) or a people problem (malicious). in the benign case you can engineer better communication models and depend on people Doing Their Best to prevent the problem. in the malicious case, you can attempt to limit the impact of a trusted adversary…but generally at great cost to productivity, which really means the adversary wins anyways.
now that i’m looking at it, this really condenses down to just one idea, since you could say that doing your best toward a counterproductive goal on purpose is simply not doing your best in context. but yeah. if your RCA reaches “so and so chose to do y instead of x” and the next “why” comes up with “because they don’t care about the success of the project”, you really can’t engineer that away.
#ooh ooh i have an addendum to reblog!#rca#root cause analysis#blameless#blameless postmortem#failure analysis#these tags are so popular on tumblr. they are basically trending every week#program management
4 notes
·
View notes
Text

Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
Basic Concept of Root Cause Analysis: Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is a method used to trace the origin of a problem. It focuses not just on the surface symptoms of the problem but delves deeper to find the underlying causes that lead to these symptoms. By addressing the root causes, we can avoid merely treating the symptoms and achieve long-term improvements and solutions.
Common Tools for Root Cause Analysis Include:
5 Whys: This technique involves repeatedly asking "why" to trace the origin of the problem.
Fishbone Diagram (Ishikawa Diagram): A visual tool that helps identify and organize potential causes.
Fault Tree Analysis (FTA): A logical diagram used to analyze the possible causes leading to a specific fault.
Whether in work or daily life, we frequently encounter various problems. The key to resolving these issues lies in identifying the root causes, rather than merely addressing surface symptoms. This article explores the practical application of root cause analysis in work and life through detailed stories and steps.
Story 1: A Sudden Incident in the Office
Background: In a medium-sized tech company, the team was intensely preparing for an important product launch. However, just a day before the launch, the company experienced a system crash, causing all preparation work to come to a halt. The team leader, Damin, was extremely anxious as the launch was crucial for the company’s future.
Steps:
Define the Problem: Damin first identified the surface symptom of the problem—the system crash, which led to work stoppage.
Collect Data: Damin and the team recorded the time of the system crash, its impact, and relevant system logs.
Use 5 Whys Analysis:
First Why: Why did the system crash? — Because the server was overloaded.
Second Why: Why was the server overloaded? — Because the traffic exceeded expectations.
Third Why: Why did the traffic exceed expectations? — Because traffic forecasting was inaccurate.
Fourth Why: Why was traffic forecasting inaccurate? — Because of a lack of effective traffic monitoring.
Fifth Why: Why was there no effective traffic monitoring? — Because there was no automated alert system and forecasting model.
Find the Root Cause: The lack of effective traffic monitoring and forecasting models.
Develop Solutions: Damin and the team decided to implement a traffic monitoring system, optimize the traffic forecasting model, and set up an automated alert mechanism.
Implement and Validate: The launch went smoothly, system stability improved, and subsequent traffic monitoring and forecasting were validated and adjusted.
Result: By identifying the root cause and implementing solutions, Damin and the team successfully resolved the system crash issue and improved system stability for the future.
Story 2: Family Financial Struggles
Background: Damin and his wife, Xiaojie, recently felt increasingly tight financially. Despite having stable incomes, they often exceeded their monthly budget. Damin decided to use root cause analysis to address this issue.
Steps:
Define the Problem: Family budget overruns leading to financial stress.
Collect Data: Damin and Xiaojie recorded all their expenses for a month and categorized them into dining, shopping, entertainment, etc.
Use Fishbone Diagram Analysis:
Main Category: Excessive spending
Possible Causes: Frequent dining out, impulsive shopping, poor management of household tasks
Detailed Causes:
Frequent Dining Out: Lack of planning, liking for trying new restaurants
Impulsive Shopping: Attraction to promotional activities
Poor Management of Household Tasks: Lack of budget planning

Find the Root Cause: Lack of clear budget planning and financial goals.
Develop Solutions: Damin and Xiaojie created a detailed family budget, set monthly spending limits, and conducted weekly financial discussions.
Implement and Validate: With the budget in place, they gradually saw an improvement in their financial situation and reduced financial stress.
Result: Through root cause analysis, Damin and Xiaojie identified the core issues causing financial difficulties and took effective measures to improve their financial situation.
Story 3: Student Performance Issues in School
Background: In a secondary school, class teacher Damin noticed that students' grades were generally unsatisfactory. After discussions with colleagues and students, he decided to conduct a root cause analysis.
Steps:
Define the Problem: Unsatisfactory student grades.
Collect Data: Teacher Damin collected student report cards, class participation data, homework completion status, etc.
Use Fault Tree Analysis (FTA):
Top Event: Unsatisfactory student grades
Possible Causes:
Lack of Student Motivation: Insufficient classroom interaction, lack of incentives
Ineffective Teaching Methods: Traditional lecture-based approach, lack of practical exercises
Poor Homework Completion: Insufficient family support, unclear homework guidance
Detailed Analysis:
Lack of Student Motivation: Due to insufficient classroom interaction and lack of incentives
Ineffective Teaching Methods: Due to a single traditional lecture approach and lack of practical exercises
Poor Homework Completion: Due to insufficient family support and unclear homework guidance

Infer the Root Cause from Intermediate Events: Lack of student engagement in learning.
Develop Solutions: Teacher Damin adjusted teaching methods, increased classroom interaction and group discussions, and improved homework guidance.
Implement and Validate: After implementation, student engagement and grades improved, and teaching effectiveness was enhanced.
Result: Through root cause analysis, Teacher Damin identified the core issue affecting student grades and took effective measures to improve teaching outcomes.
Conclusion
Through these detailed stories, we see that root cause analysis is not just a tool but a systematic approach to thinking through problems. Whether in project management, family finances, or student performance, by thoroughly analyzing the root causes, we can find more effective solutions and achieve continuous improvement. We hope these practical cases help you better understand how to apply root cause analysis in various contexts to solve real-world problems.
1 note
·
View note
Text

Simplify your RCA process with Ennetix's holistic approach to triaging performance issues.
Ennetix streamlines your Root Cause Analysis process with a comprehensive, all-inclusive methodology for efficiently identifying and addressing performance issues. Our holistic approach simplifies triaging, enabling your team to quickly pinpoint the root causes of problems and implement effective solutions.
0 notes
Text
Why are these inconsistencies our friends?
My theory is that S4 is being re-shot to better accommodate the public's demands that flooded the internet post-S3 debacle because S3 was, so far, the weakest season of the show.
When ANY show underperforms, the network requires an RCA (root cause analysis) and this entails focus groups, surveys, script scrutiny, etc.
The RCA of The Bear S3 returned results that pointed to a lack of Sydney airtime, a lack of backstory for OG characters, an excess of Faks airtime, no or very little Sydcarmy subtext, the producers' insistence on trying to make the C-person character happen, and no real progress on the plot overall, resulting in mixed reviews, less viewership, less engagement, and a unanimous consensus in calling S3 the weakest link.
AND, here's the meat:
Back in July rumor had it that only 2 S4 eps were yet to be shot, which at that point was not yet considered the series finale because S4 had not yet been confirmed as the final season. I posted about it:
This aligns with what Ebon said:
BUT
Also last month, Mr. Landgraf, the head of FX, said that 4 out of S4's 10 eps were yet to be shot, I also posted about it.
So, here's where the "inconsistencies" begin and that's actually great news for us, truthers.
Because we know S4's series finale is still in the WR as we speak and the series finale will be shot next year between February and March.
And if a few months ago they said they only had 2 eps to go and now the head of FX is saying that they actually are yet to shoot 4 eps of S4 to wrap production, then that clearly reads as "reshoot"/"rewriting". They are wiping 2 eps they had previously shot and re-shooting, IMO in a clear case of FANSERVICE, probably encouraged by the network itself as damage control, to make sure S4 doesn't behave the same way as S3 did in terms of numbers and public's perception.
I have been blowing this whistle for a while now, but evidence keeps piling up, so I like to keep track of it and share it.
Notice a cast name missing here? I do :)


Source: Cosmo
That could easily mean that S4 may not be ready for a June release because of all that re-writing of scripts and re-shooting of scenes to comply with the audience's demands that the RCA made clear and that the network is pushing for, require S4's premiere to be postṕoned a few weeks. I deem it unlikely but not implausible.
If I'd have to guess, S4 will be released in June 2025, as per usual, because 4 to 5 weeks of re-shoots are enough to shoot 4 eps, but the point here is that we are talking about 4 eps, NOT 2 anymore. That means they changed the ending, they wiped some characters, they went in a different direction, and they need to re-shoot and re-write eps. AND I'M SOOOO HERE FOR IT.
I am under the impression Storer was going to pull a Lalaland ending where Carmy and the C person got back together explicitly and Sydcarmy endgame was gonna be implied, like in Lalaland but with a better closure, where Carmy and Syd did end up together in the 11th hour but that was never gonna be fully shown unless there was a S5.
But after the RCA and the less-than-desirable repercussions the real-life relationship between JAW and MG had amongst the fans, the network decided to take control of Storer's final delivery and "advised" him to re-write and re-shoot the series finale, according to fans' expectations. And we all know which portion of the fandom I'm talking about, the only one that really matter$ for the network:
This includes an explicit Sydcarmy endgame, more Calo presence in the WR, less unpopular characters given more airtime than Sydcarmy, etc.
In other words: WE WON, otherwise, they would still have only 2 more eps to go and the scripts would have been wrapped by now.
FUCK YOU, STORER!
#the bear#sydcarmy#carmy berzatto#sydney adamu#the bear fx#carmy x sydney#carmen berzatto#the bear hulu#syd x carmen#sydcarmy endgame#gingerpovs#the bear season 4 gingerpredictions#the bear season 4#carmy is the one#rewrite reshoot reconsider redo remember we fucking told you so?#DISNEY IS NOW OUR FRIEND#claire who?#REFIRE!
12 notes
·
View notes
Text

#WashMyBrainPlease! Today’s #cartoon is focused on those of us who’re on the fast lane!
Having worked with an organization such as #DeloitteME and crossing the rubicon, I’d always notice several interesting coping mechanisms (obsessive-compulsive disorders #OCDs) of leaders and folks working in #consulting and other high-impact institutions in dealing with their body’s natural #stressresponses. Some may call it a #ritual, some may call it a #process. Apparently, it works splendidly!
Working at the cutting-edge of development and civilization sure has a lot of perks. However, there’s not much time to be #mindful of what and how we’re dealing with daily emotional turbulence. I’ve even noticed some folks picking up on these sometimes harmful OCDs and indulging in them, believing it to be the ideal way to stay blessed by their #Godfathers by aping them in every way. Even scientifically, mirroring #bodylanguage works wonders for your career! If you haven’t learned how to you yet, you should seriously consider it.
#ContaminationOCDs sure are powerful, imagine if we were able to develop a #CorruptionOCD. The entire #system and the #environment would be clean. Maybe, some of us are already suffering from it. Germs are everywhere, including within, and we just need to live with it.
Interestingly, performing a Root Cause Analysis #RCA on our emotional state does help to understand what’s really going on, how seriously damaging some things can be based on what we’re maybe incorrectly prioritizing, and what needs to be done asap. Or we could just wait till we get high up on that ladder or even until, we reach the point where our inner voice becomes an outer manifestation. : )
Enjoy!
A resource link from #InternationalOCDFoundation below:
https://iocdf.org/expert-opinions/25-tips-for-ocd-treatment/
A link to develop a better understanding on #ContaminationOCD
https://www.treatmyocd.com/blog/contamination-ocd-fear-of-germs
#awareness#malcified#oneness#within is without#return to the source#wholeness#artwork#cartooning#painting#nature#moral ocd#ocd#contamination OCD#Corruption OCD#interdependence#impermanence#addiction#obsession#therapy#mentalhealth#well-being#balance#humor#dark humor
3 notes
·
View notes
Note
okay then my question is what is your aversion to talking about the discrepancies of financial backing between jimin and jungkook from the company? why do you not want to discuss how jimin is the one who primarily filmed his production diary? he said from his mouth that evan is the one who would be in charge of the camera and set things up. it's tedious to comment on jimin's production output (from a shipper no less) and to not comment on the lack of company support in comparison to jungkook's output that has full company support. it'd be interesting to hear your thoughts on jungkook's documentary knowing full well how much money the company has put into his solo career.
Hello again anon,
Thank you for asking a question this time. As to why I have nothing further to discuss on this topic, it's simple. There's literally no way for us to accurately conclude what the root cause of the supposed differences in quality between the 'documentary' projects. It should be obvious but comparisons between JPD and JKs documentary are literally impossible right now. It hasn't even been released. But mostly because much of the evidence required for such an investigation will never be available to us as the audience and not participants in the production.
Allow me to further elaborate:
The widely-accepted process for such a question is to complete what's called a Root Cause Analysis (RCA). There are dozens of ways for approaching this, and one of the points of the RCA is to denote why any particular method was applied. It's not rare that multiple methods will be utilized for the same investigation either in cases where the Risk/Impact is high enough.
Here some diagrams of common methods:
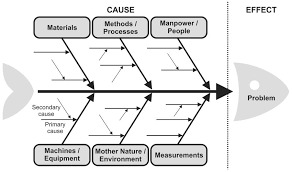


In this instance, I'd likely start with the fishbone diagram and the 6Ms because of the scale of touchpoints. But like I said in my original response to these, there is no way for us to know the details regarding the materials, methods, manpower, etc.
Theorizing is one thing if it's an enjoyable activity but I personally find no joy in fanwars, let alone in investigations that will be inconclusive by design.
So there's your reason why I have nothing to say on the topic now. Maybe I'll have some thoughts to share if I do see JKs documentary and once I'm able to watch all of the others that have already been released but who knows when that will be.
(As a sidenote, calling ppl shippers is not the insult you seem to think it is. I have an odd viewpoint when it comes to shipping spaces due to my ace/aro-ness but I'd recommend you drop that tactic as it doesn't seem to have the impact you're looking for.)
#jimin's production diary#JPD#BTS documentaries#never thought I'd be using this blog tk educate about RCA#i shoulda been clocked while I was writing this 🤣
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Root Cause Analysis Techniques: Uncovering the True Issues

Root cause analysis (RCA) is a crucial process for identifying the underlying reasons for problems or failures in various industries. In the Indian context, where businesses strive for efficiency and effectiveness, understanding and applying root cause analysis techniques can lead to significant improvements in quality, productivity, and customer satisfaction. This article explores various root cause analysis techniques, their importance, and practical applications across different sectors.
What is Root Cause Analysis?
Root cause analysis is a systematic approach to identifying the fundamental causes of problems. Unlike superficial troubleshooting, which focuses on symptoms, RCA digs deeper to reveal the factors contributing to an issue. By understanding these root causes, organizations can implement effective solutions that prevent recurrence.
The importance of RCA in India cannot be overstated. With a rapidly growing economy, Indian businesses face numerous challenges ranging from supply chain disruptions to quality control issues. Employing effective root cause analysis techniques helps companies not only resolve current problems but also build a resilient framework to address future challenges.
Common Root Cause Analysis Techniques
1. 5 Whys Technique
The 5 Whys technique is a simple yet effective method for uncovering the root cause of a problem. It involves asking “Why?” five times in succession until the underlying issue is identified. This technique is particularly useful in manufacturing and service industries.
Example:
Problem: A machine has stopped working.
Why? (1) The fuse has blown.
Why? (2) The machine was overloaded.
Why? (3) The operator did not follow the load guidelines.
Why? (4) The operator was not trained properly.
Why? (5) The training program was not comprehensive.
This example illustrates how the 5 Whys technique reveals a lack of training as the root cause of the problem, leading to targeted solutions.
2. Fishbone Diagram (Ishikawa Diagram)
The Fishbone diagram is a visual tool that categorizes potential causes of a problem. It resembles a fish skeleton, with the problem at the head and various categories (e.g., people, processes, materials, equipment) as the bones. This technique is beneficial for team discussions and brainstorming sessions.
Application: In the Indian IT sector, a Fishbone diagram can help teams identify the causes of software bugs, categorizing them into people, process, technology, and environment.
3. Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
Image-by-MrIncredible
FMEA is a proactive approach used to identify potential failure modes in a product or process. By evaluating the impact and likelihood of these failures, organizations can prioritize which issues to address first. This technique is prevalent in manufacturing and healthcare industries.
Example: A pharmaceutical company in India might use FMEA to assess risks in its drug manufacturing process, ensuring that critical failures are addressed before they occur.
4. Pareto Analysis
Pareto Analysis is based on the Pareto Principle, which states that 80% of problems often stem from 20% of causes. By identifying and focusing on these critical few causes, organizations can make significant improvements. This technique is particularly useful in quality management.
Application: In Indian manufacturing, companies can use Pareto Analysis to determine which defects occur most frequently, allowing them to allocate resources effectively to resolve the most significant issues.
5. Root Cause Tree Analysis
Root Cause Tree Analysis is a graphical method that helps teams visualize the relationship between various causes and their effects. It starts with a problem and branches out to show direct and indirect causes, helping teams see how multiple factors may contribute to an issue.
Application: In the Indian healthcare sector, a hospital might use Root Cause Tree Analysis to investigate patient readmission rates, identifying various factors like treatment quality, patient education, and follow-up care.
Importance of Root Cause Analysis Techniques in India
The application of root cause analysis techniques is essential for organizations in India for several reasons:

Enhanced Quality Control: By identifying the underlying causes of defects or failures, companies can implement corrective measures that lead to higher quality products and services.
Cost Reduction: Addressing root causes rather than symptoms helps organizations save money in the long run. For instance, manufacturers can reduce rework and warranty claims by resolving underlying issues.
Increased Efficiency: Effective RCA techniques streamline processes by eliminating repetitive problems. This efficiency is vital for Indian businesses competing in a global marketplace.
Improved Customer Satisfaction: Resolving the root causes of customer complaints leads to higher satisfaction and loyalty. Indian companies can benefit greatly from understanding and addressing these concerns.
Cultural Transformation: Encouraging a culture of continuous improvement and problem-solving through RCA techniques fosters an environment where employees are empowered to identify and address issues proactively.
Implementing Root Cause Analysis Techniques
To successfully implement root cause analysis techniques in an organization, consider the following steps:

Identify the Problem: Clearly define the issue you want to investigate, ensuring that all team members understand it.
Gather Data: Collect relevant data related to the problem. This may include process documentation, employee interviews, and historical performance data.
Choose the Right Technique: Select the most appropriate RCA technique based on the problem and available resources. Different situations may require different methods.
Analyze the Data: Work collaboratively with your team to analyze the data and identify potential root causes. Use visual tools like Fishbone diagrams to facilitate discussions.
Develop and Implement Solutions: Once root causes are identified, develop actionable solutions and implement them. Monitor the effectiveness of these solutions over time.
Review and Reflect: After implementation, review the results to ensure the problem is resolved. Reflect on the RCA process to identify lessons learned for future issues.
Conclusion
Root cause analysis is an indispensable tool for organizations looking to improve quality, efficiency, and customer satisfaction. By applying various root cause analysis techniques, Indian businesses can not only solve current problems but also build a robust framework for future success. As the Indian economy continues to evolve, investing in RCA will be a key differentiator for companies aiming for excellence in their operations.
#hormonebalance#leakygut#thyroid#preventativehealth#healthcoaching#thyroidhealth#coloradoliving#chronicfatigue
0 notes
Text
10 Must-Have Features for a Successful AIOps Platform Development
In today’s complex IT landscape, organizations face a growing need to manage their infrastructure and operations efficiently. Artificial Intelligence for IT Operations (AIOps) is revolutionizing the way businesses approach monitoring, management, and problem resolution by leveraging AI and machine learning to streamline processes, automate tasks, and enhance decision-making.

When building a successful AIOps platform development, it’s essential to incorporate key features that can provide measurable value in improving operational efficiency, performance, and scalability. In this blog, we’ll explore 10 must-have features for developing a successful AIOps platform that will empower your organization to effectively handle today’s IT challenges.
1. Advanced Data Collection and Integration
The foundation of an AIOps platform lies in the data it processes. To enable AI-driven insights, your platform must collect and integrate data from a wide range of IT systems, including logs, metrics, events, and traces. This requires seamless integration with multiple data sources, including cloud environments, on-premises systems, application performance management (APM) tools, network monitoring systems, and other enterprise resources. The platform should be capable of ingesting structured, unstructured, and semi-structured data.
Key considerations:
Real-time data collection
Compatibility with diverse data sources
High scalability to handle large volumes of data
2. AI-Powered Anomaly Detection
Anomaly detection is at the heart of AIOps. The platform should employ advanced AI and machine learning algorithms to detect abnormal behavior in your infrastructure, applications, and network before they escalate into critical issues. By identifying deviations from normal patterns, AIOps platforms can proactively alert teams to potential problems, enabling faster response times and preventing costly downtime.
Key considerations:
Supervised and unsupervised learning for varied anomaly detection scenarios
Real-time anomaly identification and alerting
Fine-tuning to reduce false positives
3. Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
One of the most valuable features of an AIOps platform is its ability to automate and accelerate root cause analysis (RCA). Traditional RCA can be time-consuming and resource-intensive, but AI-driven platforms can quickly analyze complex systems and pinpoint the underlying cause of issues. By identifying the source of the problem, organizations can resolve incidents faster and with fewer resources.
Key considerations:
Multi-layered analysis to identify root causes
Correlation of events, metrics, and logs
AI-based models to continuously improve RCA accuracy
4. Automated Incident Response and Remediation
In addition to detecting anomalies and diagnosing issues, an effective AIOps platform should automate incident response and remediation processes. Whether through predefined playbooks, machine learning-based decision-making, or integration with IT Service Management (ITSM) tools, automation can drastically reduce manual intervention and accelerate incident resolution.
Key considerations:
Predefined automated workflows
Integration with ITSM and ITOM tools
Self-healing capabilities for routine issues
5. Predictive Analytics and Capacity Planning
A truly intelligent AIOps platform should be able to predict future incidents and performance bottlenecks before they happen. Predictive analytics relies on historical data, trends, and machine learning models to forecast potential issues, enabling organizations to take preventive actions before problems arise. Additionally, AIOps should assist in capacity planning, helping organizations anticipate and prepare for future infrastructure and application demands.
Key considerations:
Forecasting performance trends
Identifying capacity constraints early
Proactive scaling and resource management
6. Smart Alerting and Prioritization
One of the challenges of traditional monitoring systems is alert fatigue. With so many alerts coming from different systems, it can be difficult to distinguish between critical issues and minor glitches. A well-designed AIOps platform should employ intelligent alerting mechanisms that prioritize incidents based on severity, impact, and context. By using AI, the platform can group related incidents and filter out noise, ensuring that IT teams focus on the most critical issues first.
Key considerations:
Contextualized alerts with severity classification
Automated incident correlation
Noise reduction through smart filtering
7. Collaborative Incident Management
Incident management is a team effort, especially in large, complex environments. AIOps platforms should provide collaborative tools that allow teams to work together to resolve incidents efficiently. Features like shared dashboards, real-time collaboration, and integrations with communication tools (e.g., Slack, Microsoft Teams) help ensure that everyone is aligned and can respond to issues swiftly.
Key considerations:
Real-time team collaboration
Integration with communication and collaboration tools
Access to shared dashboards for collective decision-making
8. Comprehensive Dashboards and Visualization
A user-friendly dashboard is essential for any AIOps platform, providing IT teams with a consolidated view of the health and performance of their infrastructure and applications. These dashboards should be customizable, displaying key metrics, alerts, and performance trends in real-time. AI-powered visualizations can highlight critical issues and correlations, making it easier for teams to interpret complex data and take action quickly.
Key considerations:
Real-time monitoring with dynamic updates
Customizable visualizations based on user preferences
AI-powered insights and correlations presented in a clear format
9. Scalability and Flexibility
As organizations grow and their IT environments become more complex, scalability is a crucial consideration for an AIOps platform. The platform should be able to scale horizontally and vertically, accommodating increasing amounts of data and more complex system configurations. It should also be flexible enough to integrate with new technologies, tools, and platforms as they emerge, ensuring that the AIOps solution remains relevant as the organization evolves.
Key considerations:
Cloud-native and hybrid cloud support
Elastic scalability to handle growing data and workloads
Flexible API integrations for third-party tools
10. Security and Compliance
Incorporating strong security features into an AIOps platform is critical, especially in industries that are highly regulated. The platform should ensure that all data is securely collected, transmitted, and stored. Additionally, AIOps platforms must provide capabilities for tracking and reporting on security incidents, ensuring compliance with relevant standards, and offering visibility into vulnerabilities.
Key considerations:
Data encryption and secure access controls
Audit logs and traceability for compliance
Vulnerability detection and security incident response
Conclusion
Building a successful AIOps platform development requires a combination of advanced technologies, automation, and intelligent data analysis. By integrating these 10 must-have features—data collection and integration, AI-powered anomaly detection, root cause analysis, automation, predictive analytics, smart alerting, collaborative management, visualizations, scalability, and security—you can ensure that your platform delivers true value, helping your organization optimize its operations, improve performance, and stay ahead of emerging IT challenges.
As AIOps continues to evolve, staying on top of these core features will be essential for leveraging the full potential of AI and machine learning in IT operations.
0 notes
Text
The Importance of Corrective Action Processes in Business: A Comprehensive Overview
Effective corrective action processes are essential for maintaining quality, compliance, and continuous improvement in any business. They provide a structured approach to identify, resolve, and prevent issues that could otherwise hinder growth and productivity. In this blog, we’ll explore what corrective action processes are, why they matter, and how businesses can implement them effectively.

What Is a Corrective Action Process?
A corrective action process is a systematic approach businesses use to address problems, non-conformities, or inefficiencies. It involves:
Identifying the issue: Recognizing deviations from expected standards or goals.
Analyzing the root cause: Determining the underlying reasons for the problem.
Implementing corrective measures: Taking action to eliminate the root cause and prevent recurrence.
Monitoring results: Evaluating the effectiveness of the corrective actions over time.
Why Corrective Action Processes Are Crucial for Business Success
1. Ensures Compliance with Standards
Industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and finance operate under strict regulations. A robust corrective action process helps businesses meet compliance requirements by addressing and resolving issues quickly and efficiently.
2. Improves Product and Service Quality
Corrective actions eliminate flaws in products or services, leading to higher customer satisfaction. Consistently addressing and rectifying issues demonstrates a commitment to quality that builds trust with customers and stakeholders.
3. Reduces Costs Associated with Errors
Unresolved problems can lead to significant financial losses, including wasted resources, legal penalties, or reputational damage. Corrective action processes minimize these risks by addressing issues before they escalate.
4. Enhances Operational Efficiency
By identifying and resolving inefficiencies, businesses can streamline workflows and improve productivity. Continuous monitoring and improvement ensure that processes remain effective and aligned with organizational goals.
5. Promotes a Culture of Accountability
When employees understand that issues will be systematically addressed, it fosters a culture of accountability and transparency. Teams are more likely to report problems and collaborate on solutions.
Key Steps in Implementing a Corrective Action Process
1. Identify the Problem
Start by collecting data from customer complaints, audits, or performance reports. Use this information to pinpoint areas requiring corrective actions.
2. Conduct Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
Use tools like the 5 Whys, Fishbone Diagram, or Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) to identify the underlying causes of the problem.
3. Develop a Corrective Action Plan
Outline the steps needed to resolve the issue. Include specific actions, deadlines, and responsibilities to ensure clarity and accountability.
4. Implement the Plan
Execute the corrective actions while ensuring minimal disruption to regular operations. Provide necessary training and resources to employees involved in the process.
5. Monitor and Evaluate Results
Track the effectiveness of the corrective actions over time. Use performance metrics to determine if the issue has been fully resolved and to identify opportunities for further improvement.
Best Practices for an Effective Corrective Action Process
Document Everything: Maintain detailed records of all corrective actions to ensure traceability and accountability.
Involve Stakeholders: Engage relevant departments and employees to ensure comprehensive solutions.
Leverage Technology: Use corrective action software to streamline the process, track progress, and generate reports.
Prioritize Preventive Actions: Shift focus from reactive to preventive measures to mitigate potential risks proactively.
Regularly Review the Process: Periodic reviews ensure the process remains aligned with business goals and adapts to evolving challenges.
Real-World Examples of Corrective Action Success
Automotive Industry: A major car manufacturer used corrective actions to address safety recalls, improving vehicle reliability and customer trust.
Healthcare: Hospitals implement corrective actions to minimize medical errors, enhancing patient safety and care quality.
Retail: Retailers address supply chain disruptions by identifying root causes and implementing solutions to avoid stockouts and delays.
youtube
Conclusion
The corrective action process is not just a problem-solving tool—it’s a strategic approach to building a resilient and efficient organization. By addressing root causes, preventing recurring issues, and fostering a culture of accountability, businesses can ensure long-term success and continuous improvement.
Investing in a structured corrective action process today can help your business mitigate risks, enhance quality, and stay competitive in the ever-evolving market.
SITES WE SUPPORT
Budget Control Plan - Wix
SOCIAL LINKS Facebook Twitter LinkedIn
1 note
·
View note
Text
#communication#disruption#i&a#inspect and adapt#information#literature#management#project management#product management#root cause analysis#rca#requirements management
0 notes
Text
Vodafone And Google Cloud Unlock Gen AI For Telecom

Vodafone And Google Cloud Explore Telecom Gen AI Potential
Globally, generative AI is changing sectors, and the telecom sector is no exception. Generative AI has the potential to completely change the telecom sector, from individualized customer service and efficient content production to network optimization and increased efficiency.
Leading telecoms company Vodafone is aware of the enormous potential of advanced AI to transform its network engineering, development, and operations. Vodafone is starting an exciting journey to include generative AI into its network operations as part of its expanding, multi-decade cooperation with Google Cloud. The goal is to boost productivity, stimulate innovation, and optimize costs.
This blog post will explore the innovative ways that Google Cloud and Vodafone have used generative AI to increase productivity, creativity, and customer pleasure. They look at practical applications and give an overview of how this game-changing technology will develop inside Vodafone in the future.
The genesis of generative AI in Vodafone’s network
When Vodafone and Google Cloud began talking about the possible uses of gen AI in network use cases in late 2023, the roots of this partnership were planted. In March 2024, Vodafone and Google Cloud launched a hackathon in recognition of the technology’s revolutionary potential, bringing together more than 120 network experts with extensive knowledge of networks and telecoms but little expertise with AI/ML.
Innovation was sparked by this event, which led to the creation of 13 demonstration use cases using a combination of classical machine learning methods, Vertex AI Search & Conversation, Gemini 1.5 Pro, and a code generation model. These comprised:
AI-powered site evaluations: Using pictures, determine whether installing solar panels at RAN locations is feasible right away.
Using natural language searches, Doc Search for Root-Cause-Analysis (RCA) enables staff members to find pertinent material fast.
Natural language to SQL (NL2SQL): Developing intuitive user interfaces to enable colleagues who are not technical to use generative AI for activities such as SQL query generation.
Network optimization is the process of creating AI-driven tools to identify problems with networks, forecast possible outages, and help with setup.
With the help of Vodafone’s industry knowledge and the expanding possibilities of cloud computing, these creative solutions show how easily generative AI can be applied to real-world problems in the telecom sector. When the creative use cases from the Vodafone and Google Cloud hackathon specifically, RCA and NL2SQL were presented together at DTW 2024 in Copenhagen, other telecom companies keen to leverage the potential of generative AI expressed a great deal of interest.
Unveiling the potential: Understanding the network design, deployment and operations workflows
In order to have a thorough grasp of the normal workday in network departments, Vodafone and Google Cloud conducted in-depth interviews with a variety of network stakeholders. Network professionals’ problems and difficulties were clarified by these interviews, which also showed a wide range of areas where gen AI may be very beneficial.
The business case study that followed showed how using modern AI technologies might result in significant time and cost savings.
Vodafone and Google Cloud demonstrated the concrete advantages of gen AI in optimizing workflows, improving decision-making, and boosting efficiency, with over 100 use cases emerging from this network space discovery phase. Vodafone is working with Google Cloud to produce the following prioritized sample of gen AI for network use cases:
Empowering network operations with knowledge at their fingertips
During complicated occurrences, network operations teams frequently struggle to obtain vital information. It can take a lot of effort and impede quick resolution to move away from extensive documentation, incident reports, network topologies, and strategic plans. Vodafone is giving network operators immediate access to the information they require by leveraging Vertex AI Agent Builder‘s capability to extract and synthesize relevant information from these documents. They are able to make well-informed decisions more quickly as a result, which lowers downtime and improves network dependability overall.
Streamlining network engineering with automated documentation
It takes a lot of effort and time to create technical documentation, including network diagrams, high-level designs (HLDs), and low-level designs (LLDs). Multiple engineers and vendors are frequently involved, which might cause delays and irregularities. Vodafone plans to automate the creation of these papers by utilizing Gemini’s multimodal capabilities and artificial intelligence. Although human inspection is still essential, gen AI may offer a strong basis, saving engineers time, speeding up time to market, and enhancing the precision and coherence of technical documentation.
Transforming network development with data-driven insights
Large volumes of contractual data are thrown at network development teams, making analysis and decision-making difficult. Vodafone will using gen AI to examine thousands of contracts, extracting important terms and provide insightful information for the creation of contract templates. Together with ground categorization skills, gen AI can also make it possible to create digital twins of the Vodafone network. This minimizes mistakes and maximizes resource allocation by enabling more precise and efficient design and implementation of new network actions.
Enhancing customer fulfillment with AI-powered field technicians
Field technicians are essential to guaranteeing client pleasure. On-site visits, or truck rolls, are expensive and time-consuming. Vodafone will reduce the need for truck rolls, enable more efficient on-field responses, and prevent repeat dispatch by utilizing gen AI to provide field professionals with real-time information and multimodal troubleshooting help. Vodafone will save a lot of money as a result, and customers will have better experiences.
These applications demonstrate how gen AI has the ability to completely change a number of facets of Vodafone’s network operations. Vodafone’s usage of Gen AI is driving innovation and enabling a more customer-focused, agile, and efficient future.
Vodafone’s big bet: generative AI for the future
Vodafone’s network divisions stand to gain a great deal from the incorporation of Gen AI:
Zero-touch operations and accelerated automation: Gen AI can speed up network job automation, helping Vodafone meet its automation objectives more quickly and effectively.
Cost reduction: Gen AI can drastically cut Vodafone’s operating expenses by automating repetitive processes and streamlining network operations.
Time savings: Network workers may save a significant amount of time by using Gen AI-powered solutions to optimize operations and facilitate quicker decision-making.
Increased effectiveness: Gen AI has the potential to increase Vodafone’s network operations’ overall effectiveness through clever automation and optimization.
Innovation catalyst: Gen AI gives Vodafone the ability to stay ahead of the curve by creating new opportunities for innovation in network management, optimization, and design.
Building on past success: AI Booster and Neuron
Vodafone’s ambitious aim to integrate generative AI into all facets of its company is based on AI Booster and Neuron. Vodafone relies on these programs to research and apply cutting-edge AI.
Vodafone uses AI Booster, a Google Cloud Vertex AI-based machine learning platform, to build AI. Fast and efficient design allows this platform to create and apply AI models quickly. AI Booster’s strong automation and security features enable Vodafone’s data scientists to move from proof-of-concept to production with ease, greatly speeding up the rate of innovation.
Neuron, Vodafone’s specially designed “data ocean” hosted on Google Cloud, is a perfect match for AI Booster. As a central hub, Neuron compiles enormous volumes of data from all throughout the company into a single, easily accessible storehouse. The creation of potent generative AI applications is fueled by this data, which is essential for AI models training and analysis.
Imagine having an AI that can forecast possible problems, evaluate the performance of network components, and even recommend the best settings to avoid downtime. Vodafone is enabling this kind of revolutionary impact by fusing the extensive data resources of Neuron with the model creation capabilities of AI Booster.
Vodafone is able to create and implement innovative AI solutions with speed and efficiency thanks to the collaboration between AI Booster and Neuron. Faster insights, more precise forecasts, and eventually an improved customer experience are the results of this. Vodafone is putting itself at the forefront of the generative AI revolution in the telecom sector by making an investment in this strong foundation.
In conclusion
Vodafone’s work on generative AI marked a turning point in CSPs’ AI-powered future. Vodafone can use current AI to generate remarkable productivity, innovation, and cost savings. Vodafone’s dedication to pushing the limits of technical progress and providing its customers with outstanding network experiences is shown by this strategic cooperation with Google Cloud.
Read more on Govindhtech.com
#GenerativeAI#Google#googlecloud#Vodafone#telecom#govindhtech#NEWS#TechNews#technology#technologies#technologytrends#technologynews#ai
0 notes
Text
Advanced Problem-Solving Frameworks: A Practical Guide
1. Root Cause Analysis (RCA) Overview Root Cause Analysis is like being a detective for problems. Instead of treating symptoms, RCA helps you find and fix the underlying causes. Detailed Process 1. Identify Problems – Collect data and observations – Document the specific issue – Example: “Customer support tickets have increased by 50% this month” 2. Trace Symptoms – Use…
0 notes
Text

Resolve business-impacting issues faster with Ennetix xVisor’s Root Cause Analysis (RCA) solution. Get actionable insights and prevent problems before they affect your operations.
#ennetix#RootCauseAnalysis#AIOps#Ennetix#xVisor#ITOperations#BusinessContinuity#DigitalTransformation
0 notes
Text
Best Root Cause Analysis Platform
EasyRCA provides an advanced Root Cause Analysis platform designed to help organizations uncover the underlying causes of issues quickly and efficiently. With intuitive tools and features, the platform allows teams to collaborate, analyze, and solve complex problems across various industries. From equipment failures to process inefficiencies, EasyRCA’s platform offers comprehensive data insights, ensuring accurate problem identification and long-term solutions. By streamlining the RCA process, businesses can minimize downtime, reduce costs, and improve overall productivity. EasyRCA empowers teams to take proactive steps toward continuous improvement and operational excellence.
0 notes
Text

ICYMI: Root Cause Analysis: How to Identify and Resolve Issues https://www.businessmanagement.company/risk-management-tools-root-cause-analysis-rca
0 notes