#Recycling Plastics News
Text
Packaging Plastics News: Essential Updates for the Industry
Packaging Plastics News is your key resource for staying informed about the latest trends and developments in packaging plastics. From advancements in sustainable materials to innovative packaging solutions, this platform covers crucial industry shifts and technological breakthroughs. Stay up-to-date with news on regulatory changes, market dynamics, and emerging trends that impact packaging. Whether you're a manufacturer or a consumer advocate, Packaging Plastics News provides the insights you need to navigate the evolving landscape of packaging plastics.
Read more : https://www.adsalecprj.com/en/news/article_index/595.html
0 notes
Text
"The Netherlands is pulling even further ahead of its peers in the shift to a recycling-driven circular economy, new data shows.
According to the European Commission’s statistics office, 27.5% of the material resources used in the country come from recycled waste.
For context, Belgium is a distant second, with a “circularity rate” of 22.2%, while the EU average is 11.5% – a mere 0.8 percentage point increase from 2010.
“We are a frontrunner, but we have a very long way to go still, and we’re fully aware of that,” Martijn Tak, a policy advisor in the Dutch ministry of infrastructure and water management, tells The Progress Playbook.
The Netherlands aims to halve the use of primary abiotic raw materials by 2030 and run the economy entirely on recycled materials by 2050. Amsterdam, a pioneer of the “doughnut economics” concept, is behind much of the progress.
Why it matters
The world produces some 2 billion tonnes of municipal solid waste each year, and this could rise to 3.4 billion tonnes annually by 2050, according to the World Bank.
Landfills are already a major contributor to planet-heating greenhouse gases, and discarded trash takes a heavy toll on both biodiversity and human health.
“A circular economy is not the goal itself,” Tak says. “It’s a solution for societal issues like climate change, biodiversity loss, environmental pollution, and resource-security for the country.”
A fresh approach
While the Netherlands initially focused primarily on waste management, “we realised years ago that’s not good enough for a circular economy.”
In 2017, the state signed a “raw materials agreement” with municipalities, manufacturers, trade unions and environmental organisations to collaborate more closely on circular economy projects.
It followed that up with a national implementation programme, and in early 2023, published a roadmap to 2030, which includes specific targets for product groups like furniture and textiles. An English version was produced so that policymakers in other markets could learn from the Netherlands’ experiences, Tak says.
The programme is focused on reducing the volume of materials used throughout the economy partly by enhancing efficiencies, substituting raw materials for bio-based and recycled ones, extending the lifetimes of products wherever possible, and recycling.
It also aims to factor environmental damage into product prices, require a certain percentage of second-hand materials in the manufacturing process, and promote design methods that extend the lifetimes of products by making them easier to repair.
There’s also an element of subsidisation, including funding for “circular craft centres and repair cafés”.
This idea is already in play. In Amsterdam, a repair centre run by refugees, and backed by the city and outdoor clothing brand Patagonia, is helping big brands breathe new life into old clothes.
Meanwhile, government ministries aim to aid progress by prioritising the procurement of recycled or recyclable electrical equipment and construction materials, for instance.
State support is critical to levelling the playing field, analysts say...
Long Road Ahead
The government also wants manufacturers – including clothing and beverages companies – to take full responsibility for products discarded by consumers.
“Producer responsibility for textiles is already in place, but it’s work in progress to fully implement it,” Tak says.
And the household waste collection process remains a challenge considering that small city apartments aren’t conducive to having multiple bins, and sparsely populated rural areas are tougher to service.
“Getting the collection system right is a challenge, but again, it’s work in progress.”
...Nevertheless, Tak says wealthy countries should be leading the way towards a fully circular economy as they’re historically the biggest consumers of natural resources."
-via The Progress Playbook, December 13, 2023
#netherlands#dutch#circular economy#waste management#sustainable#recycle#environment#climate action#pollution#plastic pollution#landfill#good news#hope
512 notes
·
View notes
Link
It took 90 days for the fungi to degrade 27 per cent of the plastic tested, and about 140 days to completely break it down, after the samples were exposed to ultraviolet rays or heat.
Chemical engineering professor Ali Abbas, who supervised the research team, said the findings were significant.
"It's the highest degradation rate reported in the literature that we know in the world," the professor said.
From ABC News Australia
#plastic#plastic pollution#plastic recycling#trash#environment#hope#good news#technology#science#ecoanxiety#environmental grief#environmental anxiety#ecogrief
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
PLEASE SIGN! IT TAKES 20 SECONDS!
#solarpunk#ecopunk#punk#punk diy#queer punk#hopepunk#diy punk#anarchism#ecofriendly#climate emergency#environmentalism#earth#environment#protest#gogreen#reduce reuse recycle#recycling#global plastics treaty#global warming#global news#climate news#world news
161 notes
·
View notes
Text
The student-led startup from Nigeria recycles plastic sachets into paint, and adds an organic insect repellent to fight malaria.
#nigeria#africa#plastic pollution#maleria#insecticides#pesticides#insect repellent#good news#environmentalism#science#environment#nature#plastic recycling#recycling#upcycle#upcycling
92 notes
·
View notes
Text
A Canadian government plan to track plastics could help put more money into consumers' pockets and keep plastic waste out of landfills.
The government announced Tuesday it's seeking input on a new national plastics registry. Experts say it could create a lucrative system that encourages companies to salvage waste plastic and reimburse Canadians and retailers for dropping off scraps.
"Plastic waste is a commodity like anything else," said Calvin Lakhan, a research scientist at York University's faculty of environmental and urban change. "Right now, we're not doing a very good job of recycling our plastics."
The registry would track various plastic items produced in Canada. Everything from food and beverage containers to household appliances, clothing, tires and fishing equipment could fall under its scope. Government documents say the reporting requirements likely would apply to plastic producers, not consumers.
Continue Reading
Tagging @politicsofcanada
#cdnpoli#canada#canadian politics#canadian news#plastic#plastic recycling#plastic waste#zero waste#circular economy
131 notes
·
View notes
Text
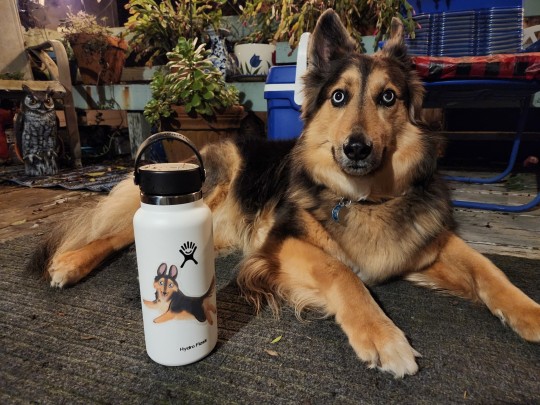

Just got my waterproof and personalized 'scrunkled' Blu sticker from @stinkybrowndogs !
It looks awesome on my work bottle and now more people will see my cutie pie as I carry this around my store! 🥰
#blu❤️#dogs#i was using plastic water bottles until last week#the recyclable kind#but that news story about the tiny plastic particles actually being in your water scared me#plus those bottles litter the planet#it was time to stop
91 notes
·
View notes
Text
Some positive climate news. I didn’t know that some states in the U.S. have banned plastic bags! Let’s see if we can add more.
#baby steps#good news#stop plastic pollution#end plastic pollution#positive news#go green#climate action#climate activism#climate science#reduce reuse recycle
39 notes
·
View notes
Text
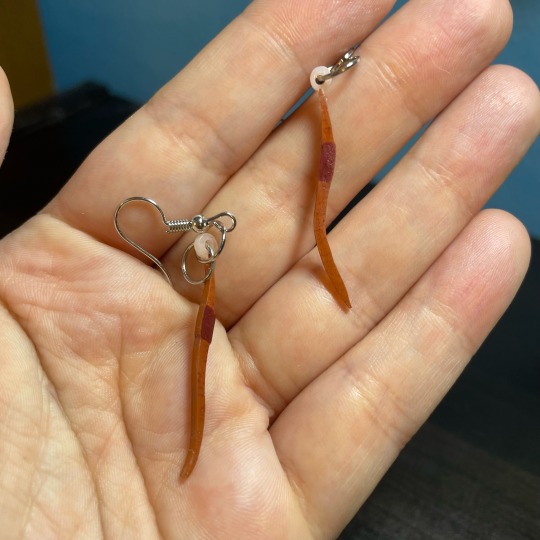
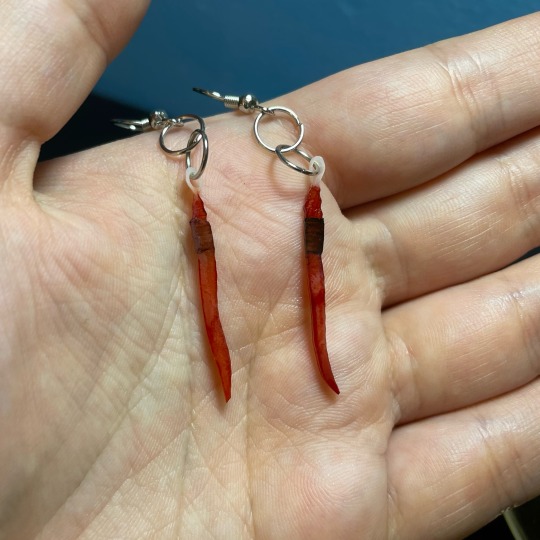



did some shrinky dink experiments! honestly not super thrilled with how these turned out, but i’m trying to challenge my perfectionism :’) plus the worms were made with recycled plastic which is cool!
#clefs art#venting a bit but i’m either mad at myself for not trying anything new or mad at myself for not being perfect the first try#lol#anyways……….#art#traditional art#shrink plastic#shrinky dink#jewelry#earrings#handmade#handmade earrings#handmade jewelry#sustainable#recycled#upcylced#worm#cow
10 notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
Recycling revolutionary Veena Sahajwalla turns old clothes into kitchen ... - Wow. What a lady.
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
so you wanna make plastic garbage into earrings, huh?

i see you found someone on that app of yours that does it. 85k followers, top viewed video of 2.8M, not bad. franka.uk I see. right, lets get to work.
heres what youre gonna do. look though your recycling bin for LDPE or HDPE plastic (#2 or #4) and only those two types, ya got it? that's bottle caps, laundry detergent bottles, etc.
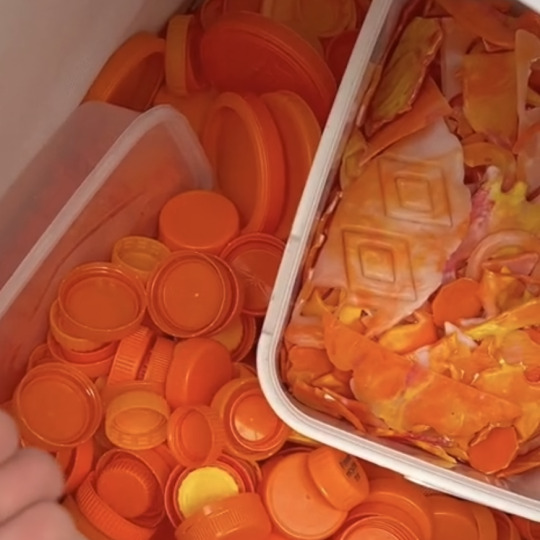


get a blender. blend. you can either do same color or multicolor, that's up to you. pick your colors, throw them in a blender you DO NOT eat out of, and blend.
now youre gonna wanna melt it. get yourself a panini press or an iron if you're feeling brave, and two pieces of parchment paper. lay the first one down, then lay our your plastic bits, and then the second paper. its not rocket science. start at low heat and WATCH.
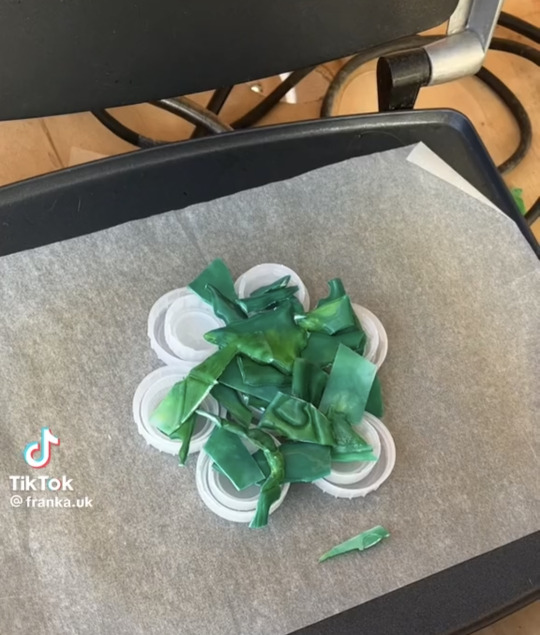
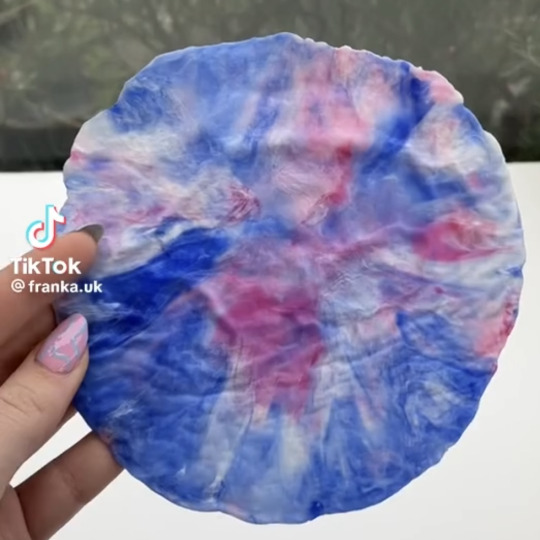


when its flat, take it off and let it cool. be careful, its gonna be hot, so dumb be stupid about this. wait for it to cool down a bit, you can press it between some books if you're feeling fancy. get your metal cookie cutters and get to work. they wont punch through, so wait for it to cool all the way and get yourself an exact knife to finish the job.
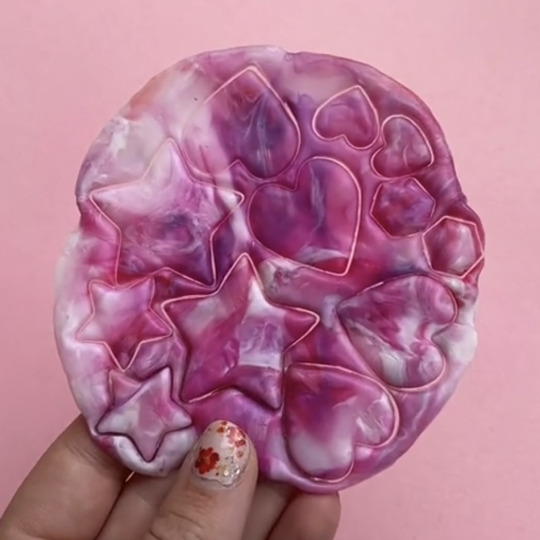

now you're gonna smooth them out. if you're using an exacto knife, you'll wanna wear a glove or some thumb protection so you don't cut yourself. you could also use sandpaper, might take longer though, or a dremel. if you don't have a dremel, don't panic, it would just be the fastest and smoothest thing, that's all.
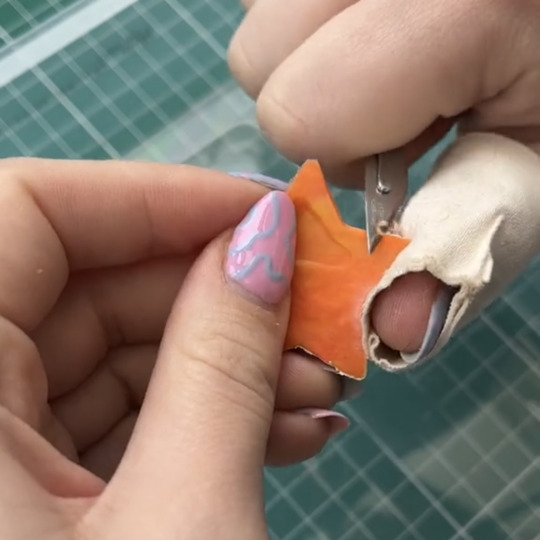
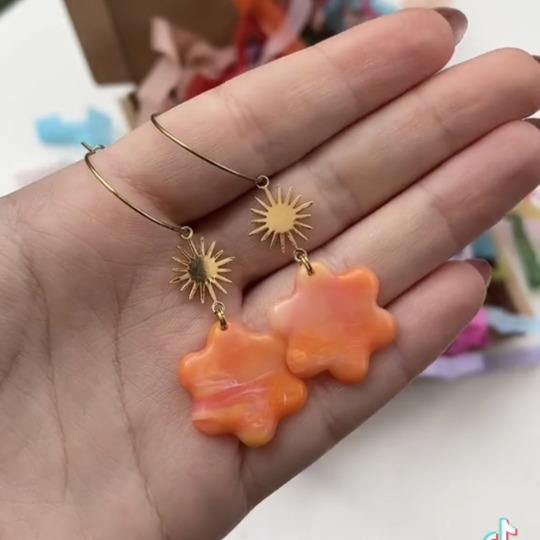


finally, youre gonna want take what you made and fashion them into earrings. you can make them into other things too, maybe a wall hanging or a sign, but our example is earrings, alright? now, get a drill bit that's the size you need for your jump ring, likely 2 or 3 mm. get a pair of needle nose or jewelry pliers, feed one ring through the hole and then a second one to connect the earring hook. if you wanna add more charms, top or bottom, drill more holes and repeat.
you're done. think you can handle that?
#breaking bad#bb#mike breaking bad#mike#mike erhmantraut#meme post#goof#ITS A GOOF#but also serious lmao#diy#tutorial#plastic earring tutorial#tiktok tutorial#written tutorial#diy earrings#recycled plastic earrings#mine#my post#new blog type#my tutorial#my tutorials#hope the girlies like these#this wont b the last#i hope#lmao
34 notes
·
View notes
Text
"For generations, the people of Erakor village in the Pacific nation of Vanuatu would pass their time swimming in the local lagoon. Ken Andrew, a local chief, remembers diving in its depths when he was a child, chasing the fish that spawned in its turquoise waters.
That was decades ago. Now 52, Andrew has noticed a more pernicious entity invading the lagoon: plastic.
“The plastic would form a small island inside the lagoon, it was so thick,” Andrew says. “We used fishing nets to pull some of the trash out, but we didn’t know how to get rid of it all. We couldn’t conquer it, there was just too much.”
While residents were struggling to empty Vanuatu’s waters of plastic, the country’s politicians were considering another solution. Could they stop the waste directly at the source?
Small island nations like Vanuatu face a series of unique challenges when it comes to plastic pollution. Many rely on imported goods to sustain their populations, and receive tonnes of plastic packaging every day as a result. Ocean currents pull plastic waste from around the world into Pacific waters, which eventually end up on the shores of its islands.
Few Pacific island governments have adequate recycling or waste management facilities on their narrow strips of land, so rubbish is often burned or left to wash up in rivers or lagoons like the one in Erakor. It is estimated that Pacific countries generate 1kg of waste per person a day, 40% higher than the global average.
In an attempt to drastically limit the amount of waste generated in Vanuatu, in 2018 the government became one of the first in the world to outlaw the sale and distribution of certain single-use plastics – including a world-first ban on plastic straws.
In the six years since, the results have been impressive. Thin, plastic shopping bags are hardly ever seen, with most shoppers carrying reusable bags at their local market or grocery store. At festivals and outdoor events, food is more often served wrapped in banana leaves instead of polystyrene takeaway boxes. Now-banned items used to make up 35% of Vanuatu’s waste, but now make up less than 2%.

Pictured: Pandanus leaves are now used instead of plastic bags at markets, but supply of the crop can be affected by storms and cyclones, vendors say.
The plastic islands that once choked Erakor lagoon are also shrinking.
“Since they started the ban, you can see the lagoon has become cleaner,” says Andrew.
It is a massive victory for a small island nation made up of just over 300,000 people across 83 islands...
In 2020, a second phase of the policy added seven more items to the list of forbidden plastics, which now covers cutlery, single-use plates and artificial flowers.
“It’s quite difficult to enforce because of the very low capacity of the department of environment,” Regenvanu says. “So we try to work with the municipal authorities and customs and other people as well.”
Compromises had to be made, though. Fishers are still allowed to use plastic to wrap and transport their produce. Plastic bottles are also permitted, even though they often litter coastlines and rivers.
Secondary industries have now developed to provide sustainable alternatives to the banned items. On the island of Pentecost, communities have started replacing plastic planter pots with biodegradable ones made from native pandanus leaves. Mama’s Laef, a social enterprise that began selling fabric sanitary napkins before the ban, has since expanded its range to reusable nappies and bags.
“We came up with these ideas to reduce the amount of plastic in Vanuatu,” says the owner Jack Kalsrap. “We’re a small island state, so we know that pollution can really overwhelm us more than in other, bigger countries.” ...
Willy Sylverio, a coordinator of the Erakor Bridge Youth Association, is trying to find ways to recycle the litter his team regularly dredges up from the lagoon.
“The majority of the plastic waste now comes from noodle packaging or rice packaging, or biscuit packets,” Sylverio says. He hopes the plastic ban will one day include all packaging that covers imported goods. “Banning all plastic is a great idea, because it blocks the main road through which our environment is polluted.”
The Vanuatu government plans to expand the plastic ban to include disposable nappies, and says it will also introduce a plastic bottle deposit scheme this year to help recycle the remaining plastic waste in the country."
-via The Guardian, June 20, 2024
#vanuatu#pacific islands#pacific islander#pacific ocean#pollution#plastic pollution#plastic waste#recycling#sustainability#waste#environment#lagoon#good news#hope
351 notes
·
View notes
Link
The City College of New York Grove School of Engineering today released a new report which examined advanced recycling. The report concluded that advanced recycling helps avoid climate impacts, reduces demand for energy resources, and offers key tools for expanding the circular economy. The report was authored by Dr. Marco J. Castaldi, professor of chemical engineering and director of CCNY's Earth Engineering Center (EEC), and EEC research associate Lauren Creadore.
The authors examined 13 recently completed life cycle assessments (LCAs) and found that advanced recycling can transform hard-to-recycle plastics into products with a smaller carbon footprint than those made from new resources. The processes also reduce energy use and greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional end of life methods, such as landfilling and waste-to-energy. Use of advanced recycling contributed to circularity for plastics in all 13 LCAs.
Specifically, the report found that advanced recycling technologies can:
Produce plastic and chemical products with a reduced global warming potential compared to products made from virgin resources.
Reduce the need for fossil energy resources by up to 97% compared to landfilling.
Reduce CO2 equivalent emissions by more than 100% compared to typical end-of-life processes when accounting for displaced demand for chemical products and energy.
Read more.
69 notes
·
View notes
Text
https://news.ku.dk/all_news/2024/06/researchers-invent-one-hundred-percent-biodegradable-barley-plastic/

From the article; Enormous islands of it float in our oceans and microscopic particles of it are in our bodies. The durability, malleability and low cost of plastics has made them ubiquitous, from packaging to clothing to aircraft parts. But plastics have a downside. Plastics contaminate nature, are tough to recycle and their production emits more CO2 than all air traffic combined.
Now, researchers at the University of Copenhagen’s Department of Plant and Environmental Sciences have invented a new material made from modified starch that can completely decompose in nature – and do so within only two months. The material is made using natural plant material from crops and could be used for food packaging, among many other things.
"We have an enormous problem with our plastic waste that recycling seems incapable of solving. Therefore, we’ve developed a new type of bioplastic that is stronger and can better withstand water than current bioplastics. At the same time, our material is one hundred percent biodegradable and can be converted into compost by microorganisms if it ends up somewhere other than a bin," says Professor Andreas Blennow of the Department of Plant and Environmental Sciences.
Only about nine percent of plastic is recycled globally, with the rest being either incinerated or winding up in nature or dumped into enormous plastic landfills.
Bioplastics already exist, but the name is misleading says Professor Blennow. While today’s bioplastics are made of bio-derived materials, only a limited part of them is actually degradable, and only under special conditions in industrial composting plants.
"I don't find the name suitable because the most common types of bioplastics don't break down that easily if tossed into nature. The process can take many years and some of it continues to pollute as microplastic. Specialized facilities are needed to break down bioplastics. And even then, a very limited part of them can be recycled, with the rest ending up as waste," says the researcher.
Starch from barley and sugar industry waste
The new material is a so-called biocomposite and composed of several different substances that decompose naturally. Its main ingredients, amylose and cellulose, are common across the plant kingdom. Amylose is extracted from many crops including corn, potatoes, wheat and barley.
Together with researchers from Aarhus University, the research team founded a spinoff company in which they developed a barley variety that produces pure amylose in its kernels. This new variety is important because pure amylose is far less likely to turn into a paste when it interacts with water compared to regular starch. Cellulose is a carbohydrate found in all plants and we know it from cotton and linen fibers, as well as from wood and paper products. The cellulose used by the researchers is a so-called nanocellulose made from local sugar industry waste. And these nanocellulose fibers, which are one thousand times smaller than the fibers of linen and cotton, are what contribute to the material’s mechanical strength.
"Amylose and cellulose form long, strong molecular chains. Combining them has allowed us to create a durable, flexible material that has the potential to be used for shopping bags and the packaging of goods that we now wrap in plastic," says Andreas Blennow.
The new biomaterial is produced by either dissolving the raw materials in water and mixing them together or by heating them under pressure. By doing so, small 'pellets' or chips are created that can then be processed and compressed into a desired form.
Thus far, the researchers have only produced prototypes in the laboratory. But according to Professor Blennow, getting production started in Denmark and many other places in the world would be relatively easy.
"The entire production chain of amylose-rich starch already exists. Indeed, millions of tons of pure potato and corn starch are produced every year and used by the food industry and elsewhere. Therefore, easy access to the majority of our ingredients is guaranteed for the large-scale production of this material," he says.
Could reduce plastic problem
Andreas Blennow and his fellow researchers are now processing a patent application that, once it has been approved, could pave the way for production of the new biocomposite material. Because, despite the huge sums of money being devoted to sorting and recycling our plastic, the researcher does not believe that it will really be a success. Doing so should be seen as a transitional technology until we bid fossil-based plastics a final farewell.
"Recycling plastic efficiently is anything but straightforward. Different things in plastics must be separated from each other and there are major differences between plastic types, meaning that the process must be done in a safe way so that no contaminants end up in the recycled plastic. At the same time, countries and consumers must sort their plastic. This is a massive task that I don’t see us succeeding at. Instead, we should rethink things in terms of utilizing new materials that perform like plastic, but don’t pollute the planet," says Blennow.
The researcher is already collaborating with two Danish packaging companies to develop prototypes for food packaging, among other things. He envisions many other uses for the material as well, such as for the interior trims of cars by the automotive industry. Though it is difficult to say when this biofriendly barley-based plastic will reach the shelves, the researcher predicts that the new material may become a reality in the foreseeable future.
“It's quite close to the point where we can really start producing prototypes in collaboration with our research team and companies. I think it's realistic that different prototypes in soft and hard packaging, such as trays, bottles and bags, will be developed within one to five years," concludes Andreas Blennow.
#good news#plastics#plastic pollution#plastic pollution solutions#environmentalism#science#environment#microplastics#bioplastics#recycling#plastic recycling#sustainability
63 notes
·
View notes
Text

i don’t even really listen to this playlist, it’s not really for listening to. it’s just for sorting a group of songs together under the heading of a playlist, conceptually, to have them sorted together. and to go and look at the songs next to each other and think, yeah, all of those are the songs that i wanted to put here. this is also why, even though i don’t really listen to this playlist, i changed the name to this when i realized it would be a good name for the playlist. it’s like a museum exhibition
#post tag#i left england and slowly the evidence that i was ever there is leaving my life#i finished the vitamin d supplements i bought at holland & barrett and got new ones in the brand we have in all grocery stores in the us#but i still have a playlist called i am attached to recycle together#i <3 soda and other liquids that come in plastic bottles#tlt#<- for personal tagging. sorry tlt enjoyers in the tag
2 notes
·
View notes