#waste
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
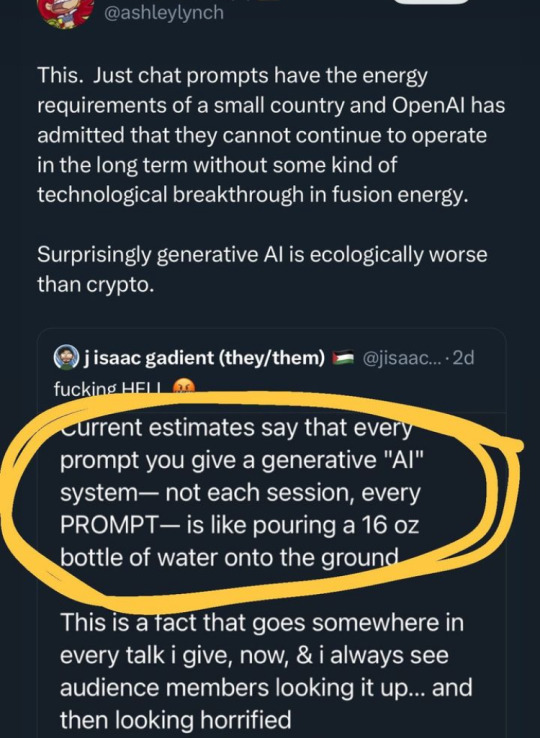
#ai#ai art#climate change#ecology#ecocide#water rights#land back#respect water treaties with First Nations#wasteland#waste#waste fraud and abuse#desertification
63K notes
·
View notes
Text
It’s an open secret in fashion. Unsold inventory goes to the incinerator; excess handbags are slashed so they can’t be resold; perfectly usable products are sent to the landfill to avoid discounts and flash sales. The European Union wants to put an end to these unsustainable practices. On Monday, [December 4, 2023], it banned the destruction of unsold textiles and footwear.
“It is time to end the model of ‘take, make, dispose’ that is so harmful to our planet, our health and our economy,” MEP Alessandra Moretti said in a statement. “Banning the destruction of unsold textiles and footwear will contribute to a shift in the way fast fashion manufacturers produce their goods.”
This comes as part of a broader push to tighten sustainable fashion legislation, with new policies around ecodesign, greenwashing and textile waste phasing in over the next few years. The ban on destroying unsold goods will be among the longer lead times: large businesses have two years to comply, and SMEs have been granted up to six years. It’s not yet clear on whether the ban applies to companies headquartered in the EU, or any that operate there, as well as how this ban might impact regions outside of Europe.
For many, this is a welcome decision that indirectly tackles the controversial topics of overproduction and degrowth. Policymakers may not be directly telling brands to produce less, or placing limits on how many units they can make each year, but they are penalising those overproducing, which is a step in the right direction, says Eco-Age sustainability consultant Philippa Grogan. “This has been a dirty secret of the fashion industry for so long. The ban won’t end overproduction on its own, but hopefully it will compel brands to be better organised, more responsible and less greedy.”
Clarifications to come
There are some kinks to iron out, says Scott Lipinski, CEO of Fashion Council Germany and the European Fashion Alliance (EFA). The EFA is calling on the EU to clarify what it means by both “unsold goods” and “destruction”. Unsold goods, to the EFA, mean they are fit for consumption or sale (excluding counterfeits, samples or prototypes)...
The question of what happens to these unsold goods if they are not destroyed is yet to be answered. “Will they be shipped around the world? Will they be reused as deadstock or shredded and downcycled? Will outlet stores have an abundance of stock to sell?” asks Grogan.
Large companies will also have to disclose how many unsold consumer products they discard each year and why, a rule the EU is hoping will curb overproduction and destruction...
Could this shift supply chains?
For Dio Kurazawa, founder of sustainable fashion consultancy The Bear Scouts, this is an opportunity for brands to increase supply chain agility and wean themselves off the wholesale model so many rely on. “This is the time to get behind innovations like pre-order and on-demand manufacturing,” he says. “It’s a chance for brands to play with AI to understand the future of forecasting. Technology can help brands be more intentional with what they make, so they have less unsold goods in the first place.”
Grogan is equally optimistic about what this could mean for sustainable fashion in general. “It’s great to see that this is more ambitious than the EU’s original proposal and that it specifically calls out textiles. It demonstrates a willingness from policymakers to create a more robust system,” she says. “Banning the destruction of unsold goods might make brands rethink their production models and possibly better forecast their collections.”
One of the outstanding questions is over enforcement. Time and again, brands have used the lack of supply chain transparency in fashion as an excuse for bad behaviour. Part of the challenge with the EU’s new ban will be proving that brands are destroying unsold goods, not to mention how they’re doing it and to what extent, says Kurazawa. “Someone obviously knows what is happening and where, but will the EU?”"
-via British Vogue, December 7, 2023
#fashion#slow fashion#style#european union#eu#eu news#eu politics#sustainability#upcycle#reuse#reduce reuse recycle#ecofriendly#fashion brands#fashion trends#waste#sustainable fashion#sustainable living#eco friendly#good news#hope
10K notes
·
View notes
Text
"The slogan 'refuse, reduce, reuse, repair and recycle' provides us with a hierarchy of strategies for dealing with waste. Refuse means to decide not to engage in the consuming action or task in the first place because it is not necessary. Reduce means to minimize the materials and energy required or the frequency of the consuming action. Reuse means either reuse for the same purpose or put to the next best use. Repair means to use skill and very limited additional resources to restore function. Recycle means to break down into more basic elements or materials before being reprocessed for the same or other uses."
- Permaculture: Principles & Pathways Beyond Sustainability by David Holgren, page 112
#permaculture#refuse reduce reuse repair recycle#waste#environmental#sustainability#environment#waste reduction
1K notes
·
View notes
Text

If you want to start with waste, start with Elon’s defense contracts at the Pentagon.
In fact, we should start with transparency around defense contracts in general, which take up an enormous sum of public funds.
But they won’t do that, will they? - Rep. Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez (D-NY)
885 notes
·
View notes
Text






Gomi Pit
2K notes
·
View notes
Text

Mandy Barker’s Cyanotypes Revive a Pioneering Botanist’s Book to Warn About Synthetic Debris
284 notes
·
View notes
Text

7-4-25
#moleskine#sketchbook#sketch#daily#dailyart#dailydrawing#dailypainting#dailysketch#sketchaday#artoftheday#art#artbook#artists on tumblr#watercolor#painting#hazardous#materials#nuclear#waste#computer#monitor#console#industrial
279 notes
·
View notes
Text
when my grandfather moved to the us after living through wwii in occupied norway he said the most striking thing he noticed here was the waste. the wastefulness, the sheer amount of excess stuff and the fever for consumption and how blasé people were as they threw it all away. and despite nominal awareness of the issue since then and and sometimes-counterproductive efforts to recycle, overconsumption trends have only gotten worse. trash, like any other ‘flow’ of materials, goods, etc, has gone global, and accumulates unevenly between where it is produced and where its burdens fall
which is a tangible, material disaster for the people living next to incinerators and landfills (in environmental justice communities of the imperial core; or abroad, in the poor countries where the rich ones dump their waste), and for the people doing the also-toxic and dangerous work extracting all the materials and making the things that are destined for the landfill, and it’s also a psychological and paradigmatic disaster for the overconsumers: to be so disconnected from where your stuff comes from and what it really costs, to expect endless cheap varieties of food and consumer goods from all over the world, to think no further than the instant gratification of next-day-delivered fast fashion orders or a new phone every year, to not realize that what you throw out never really goes away. the ‘western consumer lifestyle’, wherever it’s practiced, depends on and enforces the willful ignorance of its consequences and the disinclination to see other people and places as real. and while most waste is industrial, not just your personal household trash, the finished products you throw out have an industrial history too, and are tied to far more waste than you’ll ever personally see. which is to say not just ‘we shouldn’t buy so many things’ or ‘we shouldn’t send our trash to be dumped in other people’s countries’ - true, but also most of these things should never even be made
#this is a very broad point ofc much more to say from many angles#bought a stupid cheap umbrella this morning bc I lost mine and thought abt the horrors of it all#still in the supply chain spiral but idk if I’d call it enrichment. spectator to a train wreck maybe#waste#consumerism#skravler#economic geography
496 notes
·
View notes
Text
Plastic producers have known for more than 30 years that recycling is not an economically or technically feasible plastic waste management solution. That has not stopped them from promoting it, according to a new report. “The companies lied,” said Richard Wiles, president of fossil-fuel accountability advocacy group the Center for Climate Integrity (CCI), which published the report. “It’s time to hold them accountable for the damage they’ve caused.” Plastic, which is made from oil and gas, is notoriously difficult to recycle. Doing so requires meticulous sorting, since most of the thousands of chemically distinct varieties of plastic cannot be recycled together. That renders an already pricey process even more expensive. Another challenge: the material degrades each time it is reused, meaning it can generally only be reused once or twice. The industry has known for decades about these existential challenges, but obscured that information in its marketing campaigns, the report shows. The research draws on previous investigations as well as newly revealed internal documents illustrating the extent of this decades-long campaign. Industry insiders over the past several decades have variously referred to plastic recycling as “uneconomical”, said it “cannot be considered a permanent solid waste solution”, and said it “cannot go on indefinitely”, the revelations show. The authors say the evidence demonstrates that oil and petrochemical companies, as well as their trade associations, may have broken laws designed to protect the public from misleading marketing and pollution.
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
The problem is not simply that capitalism produces too much, but that it produces the wrong stuff: SUVs, fast fashion and planned obsolescence instead of public transit, affordable housing and universal healthcare. It overuses resources and still fails to meet even basic needs.
In this respect it is a wildly inefficient system. This is the sort of irrationality you get when production is organized around the interests of corporate profit and elite accumulation, rather than around human well-being and ecology.
Jason Hickel
588 notes
·
View notes
Text
Sports have gotten more and more environmentally friendly, whether it's by reducing plastic waste at arenas, or producing medals with recycled materials. But what if the sport itself was devoted to directly helping the planet? Take a look at SpoGomi, a competitive sport in which teams collect garbage and litter within a time limit and specified area. People get to exercise and improve their communities while simultaneously reducing pollution. It's an overall win!
The name “SpoGomi” comes from “sports” and “gomi,” which means “trash” in Japanese. SpoGomi was created in Japan in 2008 as a way to promote trash collecting in an effort to aid the environment and push back on the climate crisis. “The marine litter problem is becoming increasingly serious worldwide,” reads a message from SpoGomi. “Approximately 80% of the garbage in the ocean is said to come from land (cities), and picking up garbage is the ‘last line of defense' to prevent this from happening. By connecting countries and people, we have expanded our circle even further around the world.”
Now, supported by The Nippon Foundation, the sport is so popular that there are competitions around the world, including the first SpoGomi World Cup, which was held in Japan in November 2023. People from 20 countries and all of Japan's prefectures participated, with the UK team coming out in first place.
SpoGomi is more than simply picking up trash, though, as there's a whole set of rules. These game rules are flexible depending on the area and litter to be picked up. Generally, teams are made up of three to five members who have to collect as much trash as possible within a designated area and time limit. The most common duration is an hour for picking up trash plus another 20 minutes to correctly sort it.
Some trash can be extra damaging to the environment or harder to spot, meaning each piece of litter gets a different amount of points. According to Nippon.com, the rules for World Cup regional preliminary rounds have burnable and nonburnable trash at 10 points per 100 grams, cans and bottles at 12 points, and PET plastic bottles at 25 points. The crown jewel of competitive trash picking are cigarette butts, which will get the team 100 points each.
Other rules stipulate that teams cannot pick up trash that is already in bins that belong to someone else. Since everything must fit into the trash bags that are provided, they cannot pick hazardous waste or bulky items either. And since this is meant to improve the local area, any method of transportation other than walking is frowned upon.
In the end, all participants can bask in the pride of making the environment just a little bit cleaner and healthier. Udagawa Takayasu, a spokesperson for The Nippon Foundation, even admits, “I participated in a preliminary tournament held in Japan just last weekend. Although our team could not win and I faced frustration, the city became markedly cleaner. I think it's one of the fascinating aspects of SpoGomi, even if you don't win, it leaves you with a positive sentiment.”
-via My Modern Met, May 20, 2024
--
Hell yeah, gamify this shit!
#litter#trash#pollution#garbage#waste#waste management#environment#plastic#plastic waste#plastic pollution#japan#asia#good news#hope
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
In just one month, approximately 462 hectares (4.6 million m²) of woodland, "notably pines and oaks, as well as around 20 hectares of centuries-old olive groves," have been destroyed by Israeli airstrikes, said Georges Mitri, Director of the Land and Natural Resources Programme at Balamand University. Since the escalation of tensions between Hezbollah and the Israeli army on Oct. 8, the latter has used white phosphorus to set fire to forests and fields in border areas. The 1980 Geneva Convention, which Israel has not signed, prohibits the use of white phosphorous on civilians and in civilian areas due to its devastating effects on humans, animals and the environment.
[...]
Amid the ongoing economic crisis, the attacks targeting olive groves ahead of harvest season have a major negative impact on the local economy in the area. "Traditionally, people gather around the olive trees, harvest their crops, press their oil together... A big part of their lives is being lost," lamented Younes. “The olive trees being burned are centuries old," he pointed out. “If we were to replant them today, how long would it be before these fields became productive?” Giving an estimate of the economic losses attributed to the daily fires in the South, Mitri put the figure at nearly 20 million dollars. In the long term, Younes is particularly concerned about the environmental impact of the phosphorus bombs. "We have no choice but to wait until the end of hostilities before assessing the situation on the ground," he said. In Younes’ view, the greater the rate of absorption of phosphorus into the soil and water, the greater the risk of dramatic long-term consequences on Lebanon’s environment.
I'll add here that southern Lebanon has never fully recovered from 2006. There are still unexploded cluster bombs in the ground, killing and maiming people. There is still chemical contamination. The economic impact on agriculture has never been fully recouped. The cancer rates are still elevated and unaddressed. The labor structure and which crops are grown changed after 2006 and have never reverted. I remember weeping watching the bombing of Gaza in 2021 as I was in the middle of writing a paper about the long term legacies of the July War in Lebanon, with these additional long-term violences of the bombing at the forefront of my mind along with the immediate deaths and tragedies. This is a horrifying compounding of an existing injury, at a time when Lebanon is in economic free fall and (as the article also explains) in the middle of fire season, and with firefighters unable to do much because the area is. being bombed.
843 notes
·
View notes
Text
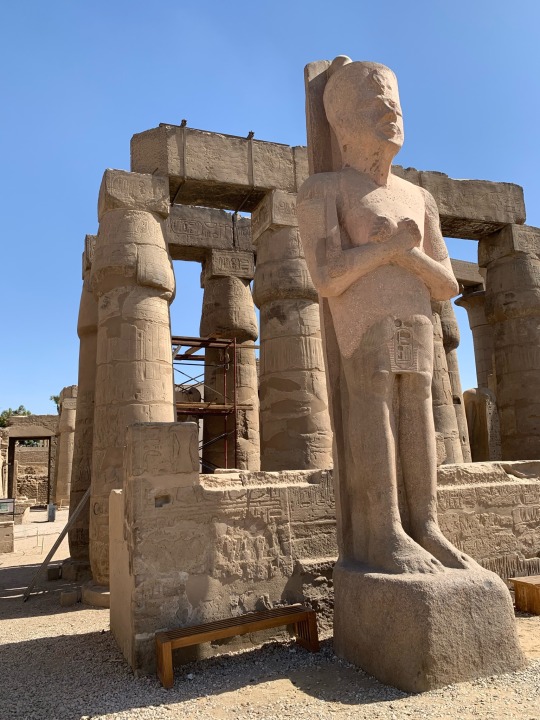
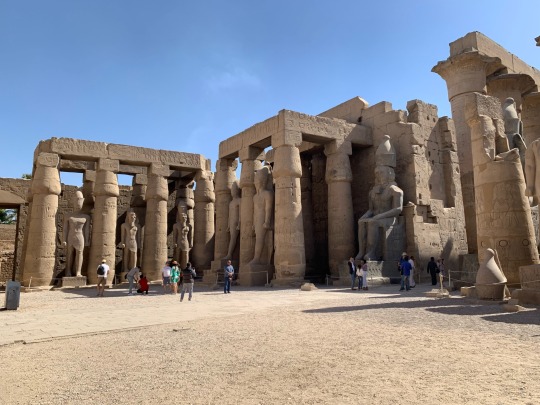
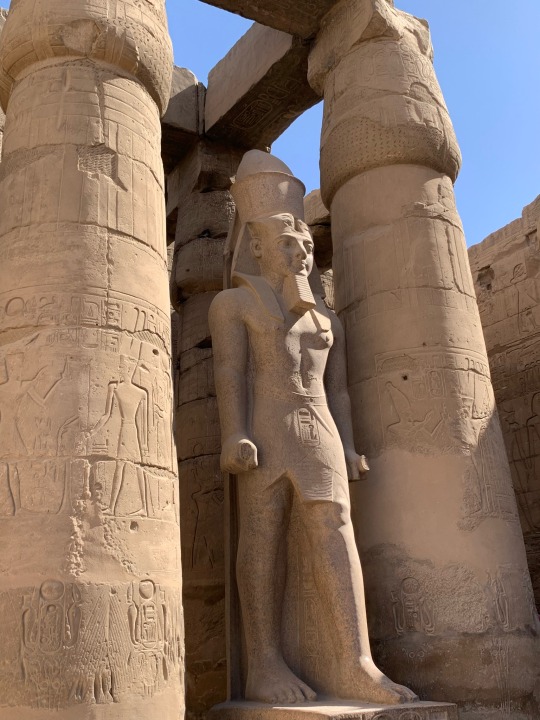



Luxor Temple, March 2023
#Luxor#temple#Thebes#waste#Egyptian temple#Egyptian#Egypt#ancient Egyptian#ancient Egypt#Kemet#Kemetic#Kemeticism#ramesses ii#pharaoh#Egyptian pharaoh
494 notes
·
View notes
Text

"Utterly trivial?" Another "government" official sending out utterly trivial emails. I would consider that waste. DOGE should be eliminated for wasting time and money.
#Elon Musk#Elongated Muskrat#DOGE#trivial#waste#time#money#tax#taxes#The Mad Sonneteer#Bud Koenemund#Koenemund
63 notes
·
View notes
Text
Recycling lithium-ion batteries to recover their critical metals has significantly lower environmental impacts than mining virgin metals, according to a new Stanford University lifecycle analysis published in Nature Communications. On a large scale, recycling could also help relieve the long-term supply insecurity -- physically and geopolitically -- of critical battery minerals. Lithium-ion battery recyclers source materials from two main streams: defective scrap material from battery manufacturers, and so-called "dead" batteries, mostly collected from workplaces. The recycling process extracts lithium, nickel, cobalt, copper, manganese, and aluminum from these sources.
Read more.
#Materials Science#Science#Lithium ion batteries#Batteries#Recycling#Lithium#Waste#Mining#Environment#Stanford University
65 notes
·
View notes