#Medical biotechnology
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Winters Biotechnology | Liquid MAG-ION, Powerful Magnesium
Do you want to improve your health? Then discover how MAG- ION liquid magnesium supplement can support over 600 biological functions.
0 notes
Text

Elevate Research with DSS ImageTech’s Biotech Solutions
Find advanced solutions with DSS ImageTech – your trusted biotech partner. From top-notch lab equipment to innovative medical biotechnology tools, we drive progress in the life sciences industry. Visit DSS ImageTech now to explore our products and services. Elevate your research today! https://www.dssimage.com/
0 notes
Text
"Thanks to a new discovery by researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, painful injections and intravenous drugs could potentially be a thing of the past.
Inspired by the way squids (yes, squids!) use jets to propel themselves through the ocean, shooting ink clouds, researchers took this biological process to the lab.
The result is an ingestible capsule that “releases a burst of drugs directly into the wall of the stomach or other organs in the digestive tract,” developed by researchers from MIT and Novo Nordisk...
Traverso was the senior author of the study, which concludes that the capsule could offer an alternative to delivering drugs that normally have to be injected, like insulin, antibodies, and even mRNA.
The reason these drugs cannot be taken orally is because they consist of large proteins that are easily broken down in the digestive tract, rendering them ineffective.
For years, Traverso’s lab has been working on a solution, encapsulating these drugs in small devices that protect them through their journey in the body until they reach the lining of the digestive tract, where they can be injected directly into the system.
In previous iterations, he and his colleagues devised capsules that use microneedles to deliver the drugs once they enter the digestive system.
But in this new study (recently published in Nature), the researchers went completely needle-free.
Taking inspiration from cephalopods — or squids and octopuses — the researchers came up with two ways to mimic their siphon organ, which allows these animals to shoot jets of ink to distract predators...
And don’t fret — once the drugs are administered, the capsules (which are made of metal and plastic) simply pass through the digestive tract naturally.
Although researchers have only tested the device on animals so far, the trails have shown resounding success. In these tests, the capsule successfully delivered insulin, a drug similar to Ozempic, and a type of RNA that can be used in treating genetic disorders.
In this research, success was calculated by measuring the concentration of drugs in the animals’ bloodstream, which reached the same levels as drugs administered by injections. Plus, there was no tissue damage after the fact...
According to MIT, the researchers will now work to further develop the capsules, in hopes of testing them in humans.
Their ultimate vision is that the capsules could be used at home by patients who need to take insulin or other injected drugs frequently. The approach also eliminates the need to dispose of sharp needles, creating a safer — and more comfortable — experience for patients and providers alike."
-via GoodGoodGood, November 25, 2024
#I think the iv drugs thing is optimistic the whole reason you use an iv is for gradual release#but otherwise as a former enormous needlephobe I love this#medical news#technology#medical technology#biotechnology#squid#mit#biomimicry#insulin#mrna#needles#good news#hope
530 notes
·
View notes
Text

#artificial cornea#CorNeat KPro#vision restoration#medica linnovation#ophthalmology#Israel#medical breakthrough#corneal implant#healthcare#biotechnology#medical science
88 notes
·
View notes
Photo

"Ghost Heart" - The Art of Decellularization
48 notes
·
View notes
Text
The last needle to be applied against smallpox, before its eradication almost half a century ago, carried a dose of vaccine smaller than a child’s pupil. Four hundred years fit inside that droplet. The devotion of D. A. Henderson’s disease-eradicating team was in it. So were the contributions of Benjamin Rubin and the Spanish boys, as well as the advocacy of Henry Cline and the discovery by Edward Jenner, and before him the evangelism of Lady Montagu, and the influence of Circassian traders from the Caucasus Mountains, who first brought the practice of inoculation to the Ottoman court. An assembly line of discovery, invention, deployment, and trust wound its way through centuries and landed at the tip of a needle. Perhaps there is our final lesson, the one most worth carrying forward. It takes one hero to make a great story, but progress is the story of us all.
— Why the Age of American Progress Ended
#derek thompson#why the age of american progress ended#history#medical history#science#technology#invention#research#medicine#biotechnology#politics#sociology#economics#vaccination#ottoman empire#smallpox#donald henderson#benjamin rubin#henry cline#edward jenner#lady mary wortley montagu
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
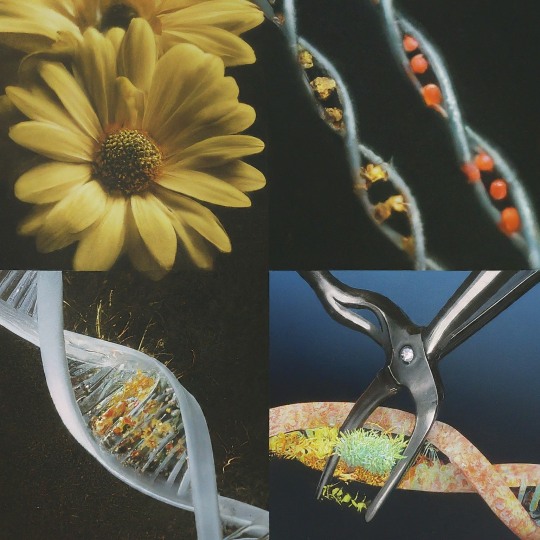

A snip, a splice : Power of rDNA Technology
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), the blueprint of life, holds the secrets to the intricate workings of every living organism. But what if we could manipulate this blueprint, adding, removing, or tweaking its code? This revolutionary concept forms the core of recombinant DNA (rDNA) technology, a powerful tool that has transformed biology and medicine.
The story starts in the early 1970s with two brilliant scientists; Stanley Cohen at Stanford University and Herbert Boyer at the University of California, San Francisco. Cohen, a microbiologist, had been studying plasmids – small circular DNA molecules found in bacteria. Boyer, a biochemist, was an expert on restriction enzymes – molecular scissors that could cut DNA at specific sequences. Their collaboration proved groundbreaking. They envisioned combining these tools to create the first ever recombinant DNA molecule. Cohen provided the plasmids, which would act as vectors to carry foreign DNA into host cells. Boyer, on the other hand, used restriction enzymes to cut both the plasmid and the desired foreign DNA, allowing them to be pieced together. Through meticulous experimentation, they successfully created the first recombinant DNA molecule, forever altering the course of biology.
Cohen and Boyer's work wouldn't have been possible without the earlier discoveries of restriction enzymes. These "molecular scissors" were independently identified by three separate research groups in the 1960s. Werner Arber in Switzerland, along with Hamilton Smith and Daniel Nathans in the US, unraveled the role of restriction enzymes in bacterial defense mechanisms. These enzymes helped bacteria defend against invading viruses by cutting up their foreign DNA. Recognizing the potential of these "genetic scalpels," the groundwork was laid for their application in rDNA technology.
Here's a simplified breakdown of the rDNA process:
Isolation of DNA: The journey starts with isolating DNA from a donor organism.
Cleavage with Restriction Enzymes: Specific enzymes cut the DNA at defined sequences.
Selection of Vector: A carrier molecule (often a plasmid) is chosen to transport the recombinant DNA.
Ligation: The DNA fragments and vector are stitched together using DNA ligase, an enzyme.
Transformation: The recombinant DNA enters a host cell (usually bacteria or yeast).
Selection and Expression: The transformed cells are selected, and the gene of interest is expressed, leading to the desired protein production.
Since its inception, rDNA technology has played a pivotal role in several groundbreaking advancements. Let's take a whirlwind tour through some of the most significant moments in R-DNA history:
1978: Birth of Insulin on the Factory Floor: Scientists achieved a feat of genetic engineering by using R-DNA to produce human insulin in bacteria. This marked a turning point for diabetics, offering a readily available and more consistent source of this life-saving hormone.
1980s: Gene Wars and the Rise of GMOs: The 1980s saw the development of genetically modified organisms (GMOs). Plants were engineered with genes for insect resistance or herbicide tolerance, sparking debates about the safety and ethics of this technology. R-DNA research continues to be at the forefront of discussions regarding genetically modified foods.
1990s: The Human Genome Project Sets Sail: This ambitious international project aimed to sequence the entire human genome. R-DNA techniques played a crucial role in deciphering the 3 billion letters of our genetic code, opening doors for personalized medicine and a deeper understanding of human health and disease.
2000s: Gene Therapy Takes Center Stage: The first successful gene therapy trials for inherited diseases like severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) took place. R-DNA technology offered a glimmer of hope for treating genetic disorders by introducing healthy genes to replace defective ones.
2010s and Beyond: CRISPR Takes Over: The emergence of CRISPR-Cas9, a revolutionary gene editing tool based on R-DNA principles, has ushered in a new era of genetic manipulation. With unprecedented precision, scientists can now edit genes in various organisms, holding immense potential for gene therapy, crop improvement, and even the eradication of diseases.
But with great power comes great responsibility, and R-DNA raises a host of ethical concerns.Tinkering with the building blocks of life carries the risk of unintended consequences. Engineered genes could escape and disrupt ecosystems, or modified organisms could have unforeseen health effects. The ability to edit human genes opens the door to designer babies, raising questions about social equity and the potential misuse of the technology for eugenics.
Who Controls the Tools? Access to R-DNA technology could be restricted to wealthy nations or corporations, exacerbating existing inequalities. Biosecurity is also a concern, as the technology could be misused for bioterrorism. Creating entirely new organisms forces us to confront what it means to be "natural." Should we modify plants and animals for human benefit, or preserve their original forms? R-DNA technology is a powerful tool, and we must have open discussions about its ethical implications. Scientists, policymakers, and the public all need to be involved in shaping the future of this technology. As we move forward, open dialogue and collaboration between scientists, policymakers, and the public are crucial to ensure the safe and ethical application of this powerful technology.
The journey of rDNA technology is a testament to human ingenuity and its potential to reshape our world. From decoding the secrets of life to creating solutions for healthcare, agriculture, and beyond, rDNA technology continues to evolve, promising a future filled with exciting possibilities.
#science sculpt#life science#science#molecular biology#biology#biotechnology#artists on tumblr#dna#double helix#genetics#recombinant#genetic engineering#insulin#research#education#learning#academics#scientific research#scientific illustration#medical science#scifi#daily dose of science#scientific advancements#scientific tools#medical school
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
The recent creation of Robots from Human Cells may change medicine and possibly lead to the ability to create biological artificial life. Yet all of its applications have not been discovered yet.
Scientists have created tiny living robots from human cells that can move around in a lab dish and may one day be able to help heal wounds or damaged tissue, according to a new study.
The scientists used adult human cells from the trachea from a diversity of anonymous donors. The anthrobots were not full-fledged organisms because they didn’t have a full life cycle
#science article#biology#biotechnology#cells#robot design#medical research#human biology#biological engineering
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
#best online course in india#biotechnology online courses#online certificate courses#free online courses with certificates#medical lab technician#online pharmacy course#biotechnology courses#ai healthcare
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Endometriosis is a chronic inflammatory disorder that affects 10% of all women between the ages of 12 and 80 years old, and for which there is an urgent need for new treatment options. In a recent article in Cannabis Health, Founder, Chairman & CEO of SOMAÍ Pharmaceuticals Michael Sassano and Rahim Dhalla, Antuanette Gomez, and Natasha Gomes from Peak Pharm Labs explore how cannabis could be part of the solution.
#cannabis#medical cannabis#biotechnology#cannabisindustry#manufacturing#cannabisnews#cannabiseu#cannabismarket#pharmtech#cannabisleaders#endometriosis
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
0 notes
Photo

Carbohydrates MCQ 25 Link in bio ☝️ for more mcqs recommendations #biotechnology #biology #science #microbiology #biotech #biochemistry #molecularbiology #research #genetics #scientist #dna #medicine #laboratory #biotechnologist #cellbiology #lab #microbiologist #medical #chemistry #biotechnologystudent #biologystudent #bio #biologymemes #lifescience #neet #bioinformatics #covid #zoology #microscope #bacteria (at Royal City Nanded) https://www.instagram.com/p/Cp4AbWivdeN/?igshid=NGJjMDIxMWI=
#biotechnology#biology#science#microbiology#biotech#biochemistry#molecularbiology#research#genetics#scientist#dna#medicine#laboratory#biotechnologist#cellbiology#lab#microbiologist#medical#chemistry#biotechnologystudent#biologystudent#bio#biologymemes#lifescience#neet#bioinformatics#covid#zoology#microscope#bacteria
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Anyone who has looked at the health statistics, medical conditions, and sexually transmitted diseases that characterize the gay male lifestyle will know that such willful destruction of the human body is neither loving nor liberating.
~ Carl Trueman
#gay healthcare#medical#hiv and aids; infectious diseases; immune system; std; biology; biotechnology; microbiology; molecular biology#gay pride month#lgbtq+
1 note
·
View note
Photo

It's my life 🙂🧑🔬 .. Follow & explore the amazing science world🔬👇 @sdsbiology for exploring the amazing world of biology and science 😍😍❤️#sdsbiology ♡ ㅤ ❍ㅤ ⎙ㅤ ⌲ ˡᶦᵏᵉ ᶜᵒᵐᵐᵉⁿᵗ ˢᵃᵛᵉ ˢʰᵃʳᵉ 🅻🅸🅺🅴 , 🆂🅷🅰🆁🅴 🅰🅽🅳 🅲🅾🅼🅼🅴🅽🆃 .. #medical #biology #cellbiology #college #immunology #genetics #ecology #virus #bacteria #science #microbiology #biotechnology #biotech #zoology #neet #bacteriology #bacteriologia #hormones #viruses #virology #school #mbbs #instagram #ınstagood #neet #cbse #aiims #glucose #neet . https://www.instagram.com/p/CpnSbl4J1Dh/?igshid=NGJjMDIxMWI=
#sdsbiology#medical#biology#cellbiology#college#immunology#genetics#ecology#virus#bacteria#science#microbiology#biotechnology#biotech#zoology#neet#bacteriology#bacteriologia#hormones#viruses#virology#school#mbbs#instagram#ınstagood#cbse#aiims#glucose
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
An adaptation of Sherlock Holmes set in a world in which the fictional character/literary juggernaut Sherlock Holmes, and all the subsequent adaptations thereof, still exist.
Sherlock Holmes (pronounced Holl-mess, as he is constantly reminding people) just had the misfortune of having parents who really liked the books, and his attitude towards his fictional counterpart is pretty much the same as that of Sir Arthur Conan Doyle.
Sherlock runs a Youtube Theory channel called Mysteries Unwrapped with Sherlock Holmes. He has received no less than seven cease and desist letters from the Conan Doyle estate, all of which he has so faded managed to rebuff by pointing out that that's literally his name.
(No he won't change his name. He's Sherlock Holmes the real live human person. Let Sherlock Holmes the non existent fictional character change his name.)
John is Sherlock's flatmate. Sherlock almost refused to live with him once he realised that it would mean staying with a medical student named John, and only gave in once John pointed out that: a) he's a biomedical student, which is completely different from an md, and b) his surname isn't Watson.
It's now been three years, which is long enough for them to have developed a genuine friendship, and for John to have a) started working towards his PhD in biotechnology, and b) for him to start dating somebody with the surname Watson.
Sherlock can feel the narrative closing in.
His Youtube channel is meant to be focused on lost media, fan theories and stuff like that, but he keeps accidentally stumbling upon and then solving genuine crimes.
His brother Mycroft may or may not have chosen that name after he transitions specifically to annoy him.
He doesn't even live in London, but somehow the only flat they could afford was on a street named fucking Baker Street.
Sherlock Holmes and the Unescapable Power of the Narrative.
36K notes
·
View notes
Text
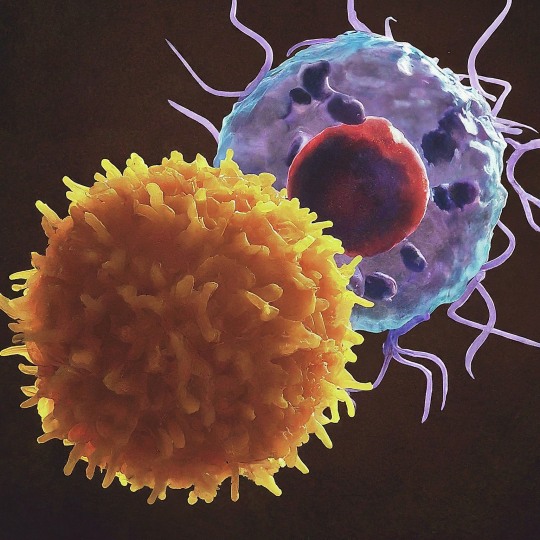
The T Cell Landscape
T cells, a critical component of the adaptive immune system, stand as the body's elite force in combatting infections and diseases. These specialized lymphocytes boast remarkable diversity, each type playing a distinct role in orchestrating a targeted and effective immune response.
T cells, like all blood cells, originate from hematopoietic stem cells residing in the bone marrow. However, their training ground lies within the thymus, a specialized organ located in the chest. Here, they undergo a rigorous selection process known as thymocyte education. During this process, immature T cells, called thymocytes, are presented with self-antigens (molecules unique to the body) by special cells. Thymocytes that bind too strongly to these self-antigens are eliminated, preventing them from attacking healthy tissues later. Only thymocytes that demonstrate the ability to recognize foreign invaders while exhibiting tolerance to self are released into the bloodstream as mature T cells.
Following this rigorous training, mature T cells exit the thymus and embark on their patrol, circulating throughout the bloodstream and lymphatic system. They remain vigilant, constantly scanning for their specific targets – antigens. Antigens are foreign molecules, such as fragments of viruses, bacteria, or even cancerous cells, that trigger the immune response.
The hallmark of a T cell is its T cell receptor (TCR), a highly specialized protein complex embedded on its surface. This receptor acts like a lock, uniquely shaped to fit a specific antigen, the "key." Each T cell develops a unique TCR capable of recognizing only a single antigen, enabling a highly specific immune response.
But how do T cells encounter these hidden antigens lurking within infected or cancerous cells? This critical role is played by antigen-presenting cells (APCs). APCs, such as macrophages and dendritic cells, engulf pathogens or abnormal cells, break them down into smaller fragments (peptides), and present them on their surface complexed with major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules. MHC molecules act as identification tags, allowing T cells to distinguish between "self" and "non-self." When a T cell's TCR encounters its specific antigen bound to an MHC molecule on an APC, a dance of activation begins. The T cell becomes stimulated, and a cascade of signaling events is triggered. This leads to the T cell's proliferation, producing an army of clones specifically tailored to combat the recognized threat.
T cells are not a single, monolithic entity. They comprise a diverse population, each type with a specialized function:
Helper T Cells (Th Cells):
Helper T cells, often abbreviated as Th cells, play a central role in coordinating immune responses. They express the CD4 surface marker and can recognize antigens presented by major histocompatibility complex class II (MHC-II) molecules. Subtypes of helper T cells include Th1, Th2, Th17, and regulatory T cells (Tregs), each with distinct functions and cytokine profiles.
Th1 cells mediate cellular immunity by activating macrophages and cytotoxic T cells, crucial for defense against intracellular pathogens.
Th2 cells are involved in humoral immunity, promoting B cell activation and antibody production, thus aiding in defense against extracellular parasites.
Th17 cells contribute to the immune response against extracellular bacteria and fungi, producing pro-inflammatory cytokines. Regulatory T cells (Tregs) maintain immune tolerance and prevent autoimmunity by suppressing excessive immune responses.
Cytotoxic T Cells (Tc Cells):
Cytotoxic T cells, also known as Tc cells or CD8+ T cells, are effector cells responsible for directly killing infected or aberrant cells. They recognize antigens presented by MHC class I molecules on the surface of target cells. Upon activation, cytotoxic T cells release perforin and granzymes, inducing apoptosis in target cells and eliminating the threat.
Memory T Cells:
Memory T cells are a long-lived subset of T cells that persist after the clearance of an infection. They provide rapid and enhanced immune responses upon re-exposure to the same antigen, conferring immunological memory. Memory T cells can be either central memory T cells (TCM), residing in lymphoid organs, or effector memory T cells (TEM), circulating in peripheral tissues.
γδ T Cells:
Unlike conventional αβ T cells, γδ T cells express a distinct T cell receptor (TCR) composed of γ and δ chains. They recognize non-peptide antigens, such as lipids and metabolites, and are involved in immune surveillance at epithelial barriers and responses to stress signals.
Beyond the Battlefield: The Expanding Roles of T Cells: The remarkable capabilities of T cells have opened doors for several groundbreaking applications in medicine:
Vaccines: By presenting weakened or inactivated forms of pathogens, vaccines "train" the immune system to generate memory T cells. This prepares the body to recognize and rapidly eliminate the real pathogen upon future exposure, preventing disease.
Cancer immunotherapy: CAR T-cell therapy, a revolutionary approach, genetically engineers a patient's own T cells to express chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) that recognize and target specific cancer cells. These "supercharged" T cells are then reintroduced into the patient, unleashing a potent attack against the tumor.
Autoimmune disease treatment: Researchers are exploring ways to manipulate T cells to suppress harmful immune responses that underlie autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis.
The diverse array of T cells underscores the immune system's complexity and adaptability in mounting tailored responses against a myriad of threats. From orchestrating immune reactions to maintaining tolerance and establishing long-term immunity, T cells play multifaceted roles in safeguarding the body's health. Understanding the intricacies of T cell biology not only sheds light on immune-mediated diseases but also paves the way for developing novel therapeutic strategies harnessing the power of the immune system.
T cells represent a fascinating aspect of immunology, with their diversity and specificity driving the complexity of immune responses. As research advances, further insights into T cell biology promise to revolutionize immunotherapy and enhance our ability to combat diseases ranging from infections to cancer. By understanding and harnessing their power, we can unlock new avenues for protecting and improving human health.
#science sculpt#life science#science#molecular biology#biology#biotechnology#artists on tumblr#t cells#T helper cells#autoimmune#autoimmunity#helathcare#immunology#immunotherapy#medical care#cancer#human health#research#scientific research#the glass scientists#scientific illustration#research scientist
11 notes
·
View notes