#Indian Political Landscape
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Rahul Gandhi Mizoram visit: राहुल गांधी आज चुनावी राज्य मिजोरम का दौरा शुरू कर सकते हैं
कांग्रेस नेता राहुल गांधी आज पूर्वोत्तर राज्य मिजोरम का दौरा शुरू कर सकते हैं. मिजोरम की अपनी तीन दिवसीय यात्रा के दौरान वह चुनावी राज्य में चुनाव प्रचार अभियान में तेजी लाएंगे. राहुल गांधी के नेतृत्व में कांग्रेस पार्टी का भारत जोड़ो अभियान काफी सफल माना जा रहा है. कांग्रेस पार्टी के नेताओं का मानना है कि उनकी इस यात्रा का लाभ हाल में कर्नाटक विधानसभा चुनाव में सामने मिला. कांग्रेस पार्टी को इस…

View On WordPress
#Congress Campaign Strategy#Congress Party in Mizoram#Congress Party&039;s Campaign#Congress Party&039;s Impact#Congress Party&039;s Success#Election Campaign Trail#Indian National Congress#Indian Political Landscape#Indian Politics Analysis#Karnataka Election Impact#Mizoram Assembly Elections#Mizoram Assembly Polls#Mizoram Election Campaign#Mizoram Election Candidates#Mizoram Election Countdown#Mizoram Election News#Mizoram Legislative Assembly#Mizoram Political Candidates#Mizoram Political Leaders#Mizoram Political Rally#Mizoram Political Scenario#Mizoram Poll Updates#Mizoram Vote Count#Rahul Gandhi Mizoram Visit#Rahul Gandhi&039;s Election Campaign#Rahul Gandhi&039;s Leadership#Rahul Gandhi&039;s Political Tour#Rahul&039;s Campaign Strategy#Rahul&039;s Campaign Trail#Rahul&039;s Election Message
0 notes
Text
India's Democratic Dance: 2024 & Beyond
What are your thoughts on the future of Indian democracy? Share your views in the comments below!
India’s Democratic Dance: A Deeper Look at Elections, Hysteria, and the Need for Change Sitting at the chai stall, watching the world go by, you can’t help but overhear the whispers. “Acche din kab aayenge?” “Will our votes even matter?” “Is this the India we dreamed of?” It’s the soundtrack of everyday India—a mix of hope, frustration, and a relentless questioning of what’s next. These…

View On WordPress
#2024 elections#BJP#Congress#crony capitalism#economic reforms#empowerment#Indian Democracy#inequality#migration#political landscape#poverty#RSS#social justice
0 notes
Text
"Impossibly high home prices are ‘feudalizing’ California as unaffordable housing markets pose existential threat to middle class, study says"
#rent is theft#landlords are parasites#ausgov#politas#auspol#tasgov#taspol#australia#fuck neoliberals#neoliberal capitalism#anthony albanese#albanese government#rent is too damn high#landlords#landscape#landlords are leeches#landlords are scum#landlords are bastards#landlords are the worst#landlord insurance#fuck landlords#eat the rich#eat the fucking rich#usa is a terrorist state#usa news#usa politics#usa#american indian#american#america
0 notes
Text
#India elections#monumental India elections#Narendra Modi#third term#India’s political landscape#opposition alliance#BJP winning run#Vivek Mishra#India’s general elections#April 19#968 million eligible voters#largest democratic vote#logistical challenges#robust electoral mechanism#Lok Sabha#Bharatiya Janata Party#Indian National Congress#President of India#Anglo-Indians#Rahul Gandhi#Sonia Gandhi#Nehru-Gandhi political dynasty#electronic voting machines#voter turnout#polling stations#election expenditure#public opinion polls#uniform civil code#minority groups#exit polls
0 notes
Text
Social Media Marketing and the Indian Political Landscape - Part 1
India, the largest democracy in the world is all set for general elections 2024. The general elections juggernaut for India’s parliament and assemblies of few states is set to roll. The battlelines are drawn, the poll bugle is sounded, and the war cries are in full crescendo. The larger Indian polity is busy drawing up winning strategies ensconced in fully equipped war rooms. What sets this…

View On WordPress
#Digital Marketing and Indian Political Landscape#SMM by Political Parties#social-media#social-media-marketing
0 notes
Text
In place of blanks on the map, we’re now able to see highly cultivated landscapes with massive infrastructure stretching back to the early centuries BCE. Road networks, terraces, ceremonial earthworks, planned residential neighbourhoods, and regional settlement systems ordered into patterns of geometrical precision can be traced across Amazonia, from Brazil to Bolivia, as far as the eastern foothills of the Andes. In certain parts of Amazonia, the forest itself turns out to be a product of past human interaction with the soil. Over time, this generated the rich ‘anthropogenic’ earths called terra preta de índio (‘black earth of the Indians’), with levels of fertility far in excess of ordinary tropical soils. Scientists now believe that between 10,000 and 20,000 large-scale sites remain to be discovered across Amazonia. Similarly startling finds are emerging from Southeast Asia, and we might reasonably expect them from the forested parts of the African continent too. Of course, the same procedures are changing our picture of tropical landscapes that did witness the rise and fall of great kingdoms, and even empires. Archaeologists now believe that in the year 500 CE, between 10 and 15 million people lived in the Maya lowlands of Yucatán and northern Guatemala. For comparison, the Atlas offers a figure of just 2 million for all of Mexico in the same era, including the Indigenous cities of the Altiplano (at least some of which, we now know, were organised not as empires or even kingdoms, but fiercely autonomous republics, long before the Spanish conquest). It is easy, encouraged by works such as the Atlas, to imagine ancient history as a chequerboard of kingdoms and empires. But it is also very misleading. Ancient polities in the Maya lowlands and Southeast Asia had porous boundaries, constantly shifting, and open to contestation. Authority waned with distance from the centre. Warfare and tribute were largely seasonal affairs, after which coercive power shrank back behind the walls of the capital. As the archaeologist Monica Smith points out, only the most naive historian would assume that the claims inscribed on imperial monuments are a simple reflection of political reality on the ground. Of course ancient rulers loved to present themselves as ‘sovereigns of the four quarters’, ‘masters of the known world’, and so on. Yet no ancient world emperor could even have imagined powers of surveillance, such as those now enjoyed by any minor dictator or oligarch. On a global scale, we are witnessing a revolution in our understanding of ancient demography. To ignore it, these days, is to indulge in a cruel sort of intellectual prank, by which the genocide of Indigenous populations – a direct consequence of the planetary revolt against freedom, in the past 500 years – is naturalised as a perennial absence of people. Nor can we just assume that if we want to understand the prospects for our modern world, the only ‘big’ stories worth telling are those of empire.
5 July 2024
350 notes
·
View notes
Photo
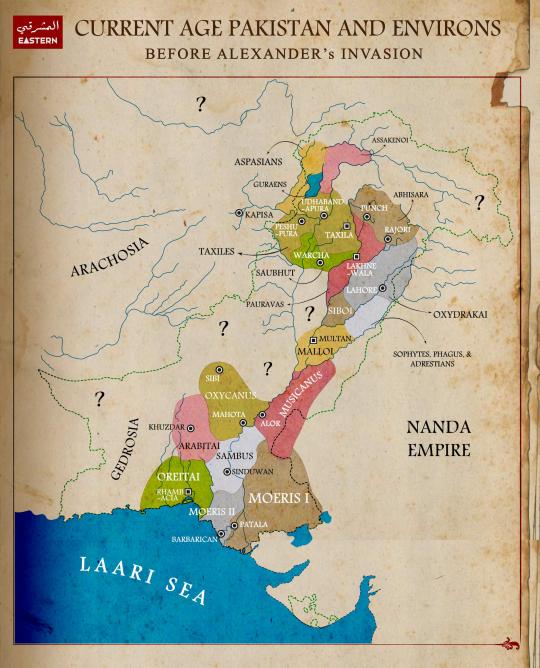
Regions of Current Age Pakistan before Invasion of Alexander
Alexander the Great's military campaigns in the Indus Valley (modern-day Pakistan) involved significant engagements with local territories, kingdoms, and their rulers. In 329 B.C., Alexander conquered Qandhar and encountered Indian tribes for the first time, marking the beginning of his interactions with the complex political landscape of the area. By 327 B.C., he had crossed the Hindukush Mountains, capturing key fortifications such as Astes Fort and massacring 7000 Indians at Massaga of Assakenians. His conquest continued with the siege and capture of Aornos in December of the same year.
During his campaigns, Alexander encountered various powerful entities in the region. The Buddhists, particularly in Sind, were influential, with prominent temples in Multan and Alore. Despite the power of the Buddhist monks, the Brahmins played a significant role in resisting Greek advances, inciting rebellion among local rulers such as Sambus. This resistance led to notable conflicts, including the defeat of Poros in 326 B.C. and the collapse of the Mallians in 325 B.C. The Greek conqueror’s interactions with these local powers highlight the complex and multi-faceted nature of the region's political dynamics.
Alexander's campaign in the southern Punjab in 326 B.C. was marked by the defeat of the Malli and Oxydraki principalities, followed by the liberation of the rivers Hydaspes, Acesines, and Indus. His naval fleet, consisting of 2000 warships, played a crucial role in these operations. The submission of Musicanus, the chief of upper Sind, who paid homage to Alexander to avoid destruction, further exemplifies the mix of military might and diplomatic engagements that characterized Alexander's approach. The appointment of Peithon as the Governor of Sind and the dispatch of Krateros with an army via Bolan Pass were strategic moves to consolidate Greek control over the region.
The period following Alexander's departure saw significant turmoil. In 325 B.C., revolts in Patala and other regions, such as the rebellion of Sambus and Musicanus, were brutally suppressed. Alexander's forces, led by his generals, employed severe measures, including mass executions and enslavement, to quell these uprisings. The death of Philippus, the Satrap of Upper Sindhu Valley, due to internal jealousy among Greeks and Macedonians, underscores the tensions within Alexander’s administration. These events reveal the fragile nature of Greek control and the persistent resistance from local rulers and populations.
Alexander's death in 323 B.C. marked a turning point, as his empire was divided among his generals. Despite the fragmentation of his empire, Sind continued to be governed by Peithon, reflecting the lasting impact of Alexander's conquests on the region. The strategic and administrative decisions made during his campaigns had enduring effects, shaping the political landscape of Sind and its neighboring territories. Alexander's legacy in these regions is a testament to the complex interplay of military conquest, local resistance, and administrative governance that defined his rule.
103 notes
·
View notes
Text
Badly done, Emma

“Do you think, my dear, that little Emma lacked aptitude or determination?” Mr. Weston said. They had been wed for well over two years and Anne still found it hard to think of him as John outside their bedchamber. Married life was an endlessly fascinating mixture of the incongruous and the familiar, any awkwardness in address balanced by the tremendous ease she had in his embrace, the peace of his heartbeat lulling her to sleep as she of the narrow, spinster’s bed found her rest nestled in his arms.
“She is Mrs. Knightley,” she corrected, her satisfaction in Emma’s marriage still coloring her tone, curving her lips into a smile. Emma had found such happiness in the match Anne could hardly recall the days when she herself had hoped her charge would become Mrs. Churchill.
“I know I ought to call her that but I can’t forget what a sprite she was with those bright curls and dainty bows, that little voice piping up, cossetting her Papa, the most managing miss Highbury has ever seen,” Mr. Weston said.
“I believe she’d forgive you, though George mayn’t,” Anne said, lifting her brush and gazing at the canvas before her. It was not quite right, not yet, but she’d gotten closer.
“It’s a curious pleasure, to find a way to make cool, steady George fierce,” Mr. Weston said.
“It is for you, as you delight in teasing him,” Anne replied.
“He’s got to refine his sense of humor. Or enlarge it,” Mr. Weston said.
“You’ll have to enlighten me, Mr. Weston, for I cannot fathom your meaning,” Anne said, daubing a bit more paint, nodding at the effect, and then glancing up at her husband, who stood just behind her, with a clear view of her work and its subject.
“I mean to cast no aspersions, for I always thought you were the finest, most accomplished governess in Surrey, but Mrs. Knightley’s portraits leave something to be desired, in a manner of speaking,” Mr. Weston said.
“In a manner of speaking? It isn’t like you to be so indirect,” Anne replied.
“I believe Mr. Knightley’s Praxidike could render a more accurate likeness than his wife’s work in watercolors,” Mr. Weston said. “A likeness less likely to make the viewer seasick, though I admit that is primarily caused by her landscapes.”
“Praxidike is a horse,” Anne said.
“Exactly,” Mr. Weston smiled. “So I return to my initial query—did little Emma lack talent or did she not attend to your wise and skilled instruction, my love? For your portraits are most apt and hers are most…appalling. That she thought to secure Mr. Elton for Mrs. Martin with her painting makes one question her vision if not her sanity—"
“You are too harsh, sir!” Anne said.
“Only if one believes Mrs. Martin bears a strong resemblance to Prinny in his cups,” Mr. Weston replied. “Though was that perhaps Mrs. Knightley’s intention? I know it’s been said the lady is the by-blow of an aristocrat, but surely the portrait would suggest Mrs. Martin is Prinny’s very twin, if one imagines him with his hair dressed à la grecque, with quite a quantity of rice-powder on his nose, in Highbury’s very best Indian muslin.”
Anne laughed, almost in spite of herself, for her husband was droll if not entirely polite, but while her laughter made him smile, it caused her subject to frown and then howl most piteously.
“You’ve woken Sophia,” Anne said.
“You were done painting in any case,” he said, walking over to pick up their squalling infant daughter from the basket she’d been sleeping in, leaving the snowy lace-trimmed blankets in such disarray it was a blessing Anne had finished rendering them.
“You sound quite certain,” Anne said, raising her voice slightly to be heard above the crying baby. Sophia settled to some hiccoughs as her father patted her back and murmured some nonsense to her. Shortly after her birth, he had confessed that he intended to dote upon her and it would be up to Anne to make sure the little girl was not spoilt, that he would not waste his chance to be a papa a second time, after letting Frank be raised by the Churchills. He made good upon his promise every day, with such fond affection Anne could not bring herself to scold him for it, nor castigate him for declaring she must play the villain in their daughter’s life; they would simply need to hire an excellent governess to correct Sophia’s mischief.
“I am. You were about to ruin her cheek. I cannot paint myself, but I can tell when you’ve achieved perfection, my dear,” he said. “It is a skill I do not expect Mr. Knightley will ever be required to master.”
“He will not,” Anne said. “To answer your query, Emma applied herself assiduously to her artistic endeavors, so much so that she could not see to what degree her hand and eye failed her. When it comes to portraiture, it must be said that she lacks all talent.”
“I cannot imagine Mr. Knightley will fret much over it. It is any guest to Donwell Abbey who must prepare some delicate compliments in advance, for surely they would be struck dumb when touring the gallery,” Mr. Weston said.
“Perhaps not. Emma should take their silence as awe and quite prettily accept their reaction as unutterable praise and then invite them to tour the gardens,” Anne said. “She knows how Mr. Knightley delights in his roses.”

Posted for Day 4 of Janeauary 2025 @janeuary-month prompt: portraiture
#janeuary 2025#emma#humor#mrs. weston#mr. weston#emma/george#married life#post-canon#reflecting on Emma's artistic abilities#given that Mrs. Weston would have taught her to paint#fluff
34 notes
·
View notes
Text
So, after I put this ask into the world and went back to minding my own business, @lurkingshan was kind enough to answer it and tag a few of her friends to share their thoughts on the matter. Thanks to everyone who interacted with the post.
In addition to this thoughtful post from @starryalpacasstuff , I feel that in order to understand the near absence of queer media in the Indian media landscape, people need some context as to what the ground realities are in India like.
Decriminalisation of homosexuality in India happened in 2018. In an unanimous decision, the court overturned its previous ruling and declared that any law that criminalises consensual sexual conduct between adults of the same sex is unconstitutional. The public backlash wasn't that huge, but a prominent member of the ruling party questioned if the courts are willing to legalise sexual intercourse with animals in the name of personal liberty.
To understand the relatively less public outrage in this scenario, we need to look at how Indian society functions. Indian culture is very collectivist in nature and having individuality is strongly discouraged. If something becomes a threat to them continuing their traditions, they'll try to beat it into submission. It isn't to suggest that people can't/won't change, it just takes time. As long as something isn't out in the open, they can just ignore it and go on about their lives. PDA is not a common thing in India even between heterosexuals. So, the chance of anyone being 'exposed' to homosexuality is close to zero. Landlords are already wary of renting apartments to guys who live together - the reasons they give is that men won't maintain the house properly, neighbours will complain because of noise, etc. So, nothing significant changes in the life of a layman because of this decision. Housing discrimination isn't faced when its women that are living together (disregarding religion and caste). The bitter truth is that housing in India is deeply segregated on the basis of religion and caste, but that's a discussion for another day.
The big fight will happen when the gays ask for marriage equality. As of 2024, same-sex marriage is not legal in India. The courts have said that existing laws have to revised in order to extend marriage equality to the homosexuals and that process has to go through the Parliament. Given the current state of Indian politics, no political party is going to put marriage equality on their election manifesto.
Keeping all of this in mind, I understand the reasons for the sparse queer media content we've seen in India. Once I started talking to others, I realised that I've severely underestimated the number of teen girls and young adults who watch BLs from several East Asian countries. The producers/creators really need to grow a backbone and create the content that clearly has a market, they are leaving money on the table. In the meantime, we need to engage with the existing queer media to give them irrefutable proof that the audience exists!!!
37 notes
·
View notes
Text
If there is a depth to which U.S. presidential candidate Donald Trump cannot sink when attacking his opponents, we are yet to see it. His latest salvo came at the convention of the National Association of Black Journalists in July, when he asked of Vice President Kamala Harris, “Is she Indian or is she Black?” The gasps, reportedly, were audible.
His question was meant to undermine her authenticity, of course, and it deserved the opprobrium it received. But it also proved that even with President Joe Biden out of the running, age is still an issue in the upcoming election. Trump’s politics of categorization belongs to a time that younger Americans have never known, when the demographic landscape of the United States couldn’t have been more different.
Consider that Trump was born in 1946, two decades before the nationwide lifting of anti-miscegenation laws, which prohibited interracial marriage. In his formative years, Black Americans were living under Jim Crow policies. For the first half of the 20th century, immigration from Asia had been kept to a bare minimum, first under the Chinese Exclusion Act of 1882 and then the Immigration Act of 1924, both passed with an eye to maintaining the United States’ whiteness.
Trump was the product of a time in which people really were expected to occupy fixed racial boxes, kept discrete by law, “when the walls of race were clear and straight,” as sociologist W. E. B. Du Bois put it. An American could be legally Black by virtue of a single Black great-grandparent. Never multiracial or racially ambiguous, as they might be in most other countries—only Black. So, when Trump demands of Harris that she be one or the other, Indian or Black (assuming that his question is sincere), perhaps it is beyond his imagination that anyone might be both.
Harris, on the other hand, reflects the United States as it is now: a tapestry of racial and ethnic diversity in which few can pretend that they are easily defined. She was born in 1964, a few months after the Civil Rights Act was passed. The Immigration and Nationality Act of 1965 would enable a substantial increase in Asian immigration in that same decade.
When Harris was a teenager, those of South Asian heritage living in the United States still numbered fewer than half a million. They were practically invisible to most other Americans. There was such uncertainty about their racial identity that in one national opinion poll conducted by the National Opinion Research Center in 1978, 15 percent of respondents believed that Indians were Black, and another 11 percent saw them as white. Today, though, Indians are the second-largest immigrant group in the United States, after Mexicans and just before Chinese. They have their own demographic checkbox in the census.
Far more significantly, Americans are less likely than ever to identify with a single race or ethnicity. In 2000, in response to demands to accommodate those of mixed heritage, the U.S. Census Bureau gave people the option to tick more than one racial box for the first time. That year, almost 7 million Americans reported belonging to more than one race (interestingly, 823 of these respondents claimed six races). A decade later, that number had gone up by almost a third.
In the most recent census, conducted in 2020, partly because of improvements to how data was collected, that number went up again—this time by 276 percent. Unsurprisingly, younger Americans are the most likely to report being multiracial.
So, with his obsession over categorization, Trump couldn’t sound more out of date. He is trying to force people into the kinds of boxes that defined lives when he was a child. He is telling Americans that there is only one way to be white, or Black, or Indian, when they already know this isn’t true. It is a politics that dares to put others in their place, yes, but also fails to see them as they are.
Coincidentally, his ill-judged remarks about Harris happened to come just days before the centenary of the birth of one of the United States’ most brilliant social critics, James Baldwin, who himself gloriously embodied the contradictions of identity. In his 1949 essay “Everybody’s Protest Novel”—as fresh now as the day it was written, in sharp contrast to Trump’s desperately tired ideas about race—Baldwin cautioned against succumbing to the fallacy that it is “categorization alone which is real and which cannot be transcended.”
It is perfectly possible to live within and between cultures and maintain an authentic sense of self. it is not just Harris who proves this, but the millions of Americans who have enriched the nation by mixing, marrying, and building a more integrated society. They have changed the country for the better.
When Trump casts aspersions on Harris’s racial background, he does the same to countless others. He questions the pluralistic society that the United States has become—one in which race has already come to matter less than it used to.
42 notes
·
View notes
Note
ok so i am very much uninformed on politics, i decided at a younger age that i wasn't interested in it and therefore would not read or keep myself particularly informed about it. obviously this is a bad idea, and i want to change and keep myself informed on actual politics and well, abstract[?] (wrong word but cannot think of another, basically mean like. knowing which political .. stance ?? [idk. like marxist or communist or whatever] i might be.) ones as well. what's a good place to get started here? where do i look for actual politics going on in india since i'm pretty sure ndtv or whatever isn't exactly the best source? or maybe it is? idk, like i said i'm pretty uninformed on the matter but would like to learn more
so one thing is, in india you have to accept the media landscape is just dire because being a journalist with integrity is a bit like signing up to have your life ruined. all major media has been bought by hindutva already. what you have to do is more learn to read between lines, understand people's motivations, which is a matter of practice. a good way to start is to read analysis (not news reports) of the same incident in different media and you'll start noticing patterns. even more important imo is to talk and bounce ideas with a friend at a similar place as you or someone interested in politics who won't overwhelm you with their perspective. you can try online but idt its safe or advisable anymore to do that experiment online. i had debate club in university (sad) and some socialist reading groups (better) after. the thing is this journey to self education is kind of personal and im also not pedagogically oriented or trained? so lots of first person description instead of prescriptions.
i still check what's up on ndtv because it gives me a good pulse of what english language media and liberals are thinking. major newspapers i scan hindu and the indian express sometimes. online i have a look at newslaundry (also has some youtube content) and the wire, they're reader supported and haven't turned full hindutva yet. i read longer form things in the caravan and epw, but these are subscription based. i keep tabs on the latest round of hindutva fake news when alt news debunks it.
for the abstract things, i literally did an online course bc i was frustrated by what all the liberal arts grads seemed to already agree on. i did ian shapiro's moral foundations of politics which is available online as both youtube lectures and a textbook. if you want to go that route feel free but it's not necessary, you can also try to read the entries on wikipedia or stanford encyclopedia of philosophy (more expertise) when you encounter something unfamiliar and build up like that. podcasts like bbc in our time will often interview academics to give intros to many political philosophy concepts and thinkers. whatever your learning style supports! i think the important thing is to find something you are actually interested in, and take that tack. i like history, so i might read books about historical revolutions or historical forms of organising society or listen to podcasts like mike duncan's revolutions.
For communism the usual starting points are these very short pamphlets:
Principles of Communism by Engels
The Manifesto of the Communist Party by Marx
Wage-Labor and Capital by Marx
Socialism: Utopian and Scientific by Engels
feel free to ask for more specific questions!
149 notes
·
View notes
Text
I was completely consumed by this artwork from @tamayula-hl and the comments on it. So I churned this out 🫡 hope y’all enjoy!
Synopsis: It had been six months since the assassination of princess Miradevi Surya Lakshmi, and six months since prince consort Ominis Surya Lakshmi was completley consumed by the darkness he’d been fighting against all his life.
But that darkness suits him well, and a surprise trip to Azkaban coupled with a horrific revelation about the murder of his wife prompts the prince consort of one of the most powerful empires in the world to take advantage of his position and do what he had always sworn to do; ruthlessly destroy anyone that was involved in the death of his wife.
The explosion of a star
Ultimately, it was not the rage that drove Ominis forwards. It was not the grief, nor the brutally cruel pit of despair that propelled him forwards, day after day.
It was the emptiness. The way his heart didn’t even sink anymore when he turned over at night and his wife was not there. The way he would stand out on the balconies of the palace looking over the sprawling Indian landscape and did not expect her at his side.
The monsoons had rolled around and the empire was still in mourning over the loss of the princess. Within the palace, Ominis did not need sight to know the face that the royal family put up for their citizens was fractured perhaps beyond repair. Mira’s parents- his in laws, and the monarchs of the empire- had worn grief like an armor. Alongside her brothers, the military budget grew a little higher, the empire fortified, foreign relations stricter.
And Ominis continued on, emptiness churning in his veins- a pit of absolute nothingess, of numbness threatening to consume him.
The ‘consort’ in his title was dropped.
In a political move that even he did not forsee, his title was legitimized as one of the princes of the Surya empire- he’d never sit on the throne, of course, but the gesture was clear. The might of the Surya kingdom was not fractured by the murder of the princess, but reinforced.
xxxxxxx
Rain lashed against the palace windows and Ominis tried to focus on its’ constant drone. He had excused himself from another meeting, another sombre, condolence- filled gathering with politicians and ministers who were so sorry about the loss of the princess, but the kingdom had to move forwards, they needed him to take her place as a liason between the wizarding and muggle communities, to continue his duties as prince consort.
He hunched over his messy desk, sweeping aside the papers scattered over it.
The tremor in his fingers was back.
“Accept it.” The words left his lips in a shaky growl. “Goddamn you, accept it. Your wife is dead. Mira is dead. You’re not getting her back, you’re never-“ his voice broke, the statements cruel to his own ears despite their truth. Miradevi was his lifeblood, the sunshine and moonlight and every spectrum of light in between that had brightened his life since he’d met her.
And now she was gone, and she was never coming back. He had failed to protect her, he’d failed, he’d failed, he had not been able to stop her from being-
“Your highness?” The low, concerned voice spoke from the other side of the ornately carved wooden doors. “Are you alright?”
Fuck.
His security detail had not given him three inches to breathe, tailing him with hawklike gazes ever since-
Ominis straightened, head tilted towards the door of his bedroom. The second he lost Mira, the second he processed what it meant, he’d moved to a different room in the palace.
A different wing altogether.
“I’m fine, Ravi. Thank you. Please, I just-“ he exhaled sharply. Come back to me, come back, I can’t do this without you-
“- need the evening to myself.”
Ominis heard a soft shuffling, a low murmur of Hindi.
“We’ll be right outside your chambers, my prince.” Ravi called. “We will check in on you every half hour, your highness.”
“Fine.” Ominis tried hard not to snap. They were just doing their jobs.
They should have done their job while protecting my wife. My Mira, my everything-
As if trying to shake away a fly, Ominis shook his head to dispel the thoughts. The rain contiued to fall, and he had never felt so alone in his life.
——————————-
Five months later
——————————-
Ominis strode through the the palace, wand held up slightly as he navigated the halls he had called gome for so many years now. The Indian summer beat down hot and merciless beyond the cold stone of the arching walls as he made his way to the court.
Moonstone eyes glinted steel as he flicked his wand and the doors swept open, allowing him to walk into the opulent, stately chamber. The war room was an architectural marvel and scoping it out with his wand took his breath away, no matter the fact that the Surya empire had been his home for three years now.
But the wonder he once felt had melted away, sequestered deep wherever the rest of his emotions had been buried, trapped and dead like fossils under layers upon layers of soil.
In the center of the room stood a table scattered with maps and little figurines. And around the table stood some of the most powerful people in the empire.
“Crown prince Arjun. Prince Bharat.” Ominis bowed before each of his brothers in law, firmly ignoring the fact that he barely recognized his own voice. When had that razor-sharp harshness crept in? The edge of cruelty?
Perhaps it had bloomed with the first man Ominis killed in connection with his wife’s assasination. Perhaps it had flourished under the generous offer of ruby- dark blood he’d devotedly spilt in his princess’s name. Perhaps it had only been growing since, as the pile of bodies began to grow in the wake of the widowed prince.
“Ominis.” The crown prince nodded, before gesturing the the handful of ministers assembled to leave. Without a word of protest, they obeyed, shuffling out with quiet murmurs and closing the heavy doors behind them. The war room fell silent for a moment.
Two men grieved the loss of their sister. One man grieved the loss of his wife.
All three were hellbent on vengance.
“We’ve neutralized and eliminated every single threat that was even remotely involved in the assasination of my sister.” Prince Bharat easily knocked down a few of the figures standing on the table. “But whoever orchestrated it covered their tracks well. Nobody was aware of the full scheme, and key actors only knew bits and pieces, which means-“
“Whoever organized it is powerful.” Ominis finished his sentence, his voice cold. “We’ve known for a while that this was not a random act of violence. The security is too tight and the act was well planned. Premeditation indicates-“
“Wealth.” Arjun stepped in. The crown prince’s eyes- once a mirror image of his little sister’s soft, sparkling gaze- were now alight with rage. “Power. They had influence, they had the funds to carry out the necessary bribery, and we cannot rule out financially backed militias.”
“And, most obviously, it was a wizard that.. did it.” Ominis’ voice lowered, rough as serrated glass. “She was- they used a killing curse. And all of the people I’ve… disposed of, so far, have been wizards. No muggles involved.”
Arjun and Bharat exchanged a quick glance.
“A letter arrived for you today. From that prison your people have. I don’t know if it has anything to do with.. with her, but if it does-“
Ominis took the outstretched letter from the crown prince, brows drawing together. He knew no one in Azkaban, and had cut most of of his ties in Britain save for Sebastian and Anne. Even his contact with them had gotten shaky since Mira’s death. He raised his wand, running it over the grimy envelope, noting that, sure enough, it was sent from the limited post Azkaban offered. He cut open the letter with a quick flick of his wand, unfolding it.
The rain fell harder beyond the palace walls as Ominis’ wand relayed the words on the dirt- streaked page. His brows drew closer together and a snarl slowly curled his lips.
Lightning cracked suddenly, forking across the sky in a blinding sizzle of white followed by a clap of thunder. Arjun raised his brows, looking at his brother in law.
Magic curled at his fingertips as crack after crack of lightning lit up the skies, responding to his surging emotions. Ominis’ fingers shook slightly but this time it was from rage.
Wealth.
Power.
Influence.
“My father is in Azkaban.” Ominis’ voice was tight, shaking with barely supressed rage. “I had no idea he was imprisoned and quite frankly I’m not in the least bit upset about it. But he expressed a wish to talk with me, regarding the tragic loss of my wife.” His gaze darkened, the sparks at his fingertips setting the letter alight.
Arjun and Bharat exchanged glances again. The Gaunt family had been vicious in their dislike of Miradevi, and their hatred of muggles had not earned them any approval in the Surya empire, which was a healthy mix of wizarding and magical peoples. They were vocal dissenters to the empire’s ‘radical, harmful regime’ but ultimately could do nothing about it when their son became the kingdom’s prince consort.
But perhaps-
Arjun spoke up, and Ominis was not imagining the hint of accusation that hung like poison in his voice. “They have the means. The fanatical obsession with curbing our empire’s growth and eradicating support for the progrssive policies you and Mira championed. Not to mention their disapproval of all of us being non magical.” The crown prince paused, casting a look at his brother in law.
“We cannot rule out the fact that your family had something to do with Mira’s death.”
“If they did, Arjun-“ Ominis’ voice was strangely calm as he burnt the letter to a crisp in the palm of his hand. “-If they had the slightest, most miniscule involvement in the death of my wife, then every last one of them will die screaming. I swear it.”
xxxxxxxxx
Securing an international portkey to Britain had been easy enough. He was a prince. And for better or worse, he now had quite the reputation.
Getting to Azkaban had also been easy. What had not been easy was being back in Britain, back where him and Miradevi had first met. Her ghost lingered everywhere, the faint melody of her laugh somehow trapped in the wind that rushed through the bare branches of dead pine trees, that scent of jasmine lingering just out of reach.
Ominis stepped off the creaking wooden boat onto the algae- slick, stone platform that led into the prison. The warden leading him through seemed far too delighted at the state of the place, proud of the mildew rotted and frigid rain- soaked conditions the prisoners had to endure. Ominis lifted his chin and lowered his wand, striding through the stone halls, the low wails of the inmates ringing in his ears.
Sudden as a striking anvil, a wave of pure despair rushed over him, nearly sending him to his knees. Memories he had shoved down and locked away, memories he swore he’d never unearth slammed against his psyche.
“The princess is gone. She was found-“
“Her body-“
“-funeral arrangements, your highness-“
“-deepest sympathies, my prince-“
“That’ll be the dementors, my leige.” The warden didn’t seem the slightest bit affected, a glint in his eyes. “You think you could take care of it, or would you need me to step in?”
Ominis growled, low. He would not be made a mockery of. Drawing his wand, he arced it over his head like he was cracking a whip. His magic obeyed, surging to life at his fingertips, yearning to be set loose.
“Pestis incendium.”
Witnessing not a patronus but a stream of fiendfyre sweep in a blaze from the prince’s wand, the warden decided he’d not try and push any further. He fell silent as the roar of flames swept outwards through the high, narrow stone walls, slamming the dementors back into the cracks the creatures had seeped from.
“Where is my father.” Ominis demanded, voice a cold contrast to the spell he’d just performed. “I want to make this visit as short as possible.”
“Right here, your highness.”
The warden gestured at a cell, before bowing- lower, this time- and backing away.
Ominis heard the low, rasping breathing, the aristocracy his father still carried in his voice despite his new lodgings. Once, he would have felt a tendril of fear snake through his veins. Once, he would had flinched at the way Erasmus Gaunt stood and loomed before him.
Not now.
Now, he was steel and blood and the promise of death.
“My prince.” His father’s voice was mocking. “It’s good to see you responded so quickly to my summons. Perhaps you still remember your roots after all. Perhaps that mudblood of yours has not addled your mind beyond repair-“
Ominis struck like a snake.
He didn’t bother with a wand as his arms shot out, latching onto his father’s prison robes, slamming him close against the bars. He relished in the subsequent groan of pain, yearned to draw screams instead.
“Speak one word against her and I’ll cut your tongue out. And I will do it the muggle way.” Ominis hissed. “Why did you want to meet me? Why did you say you have information on what happened to Mira?”
Erasmus Gaunt managed a laugh, his teeth smeared red. “Right to business? Very well.” He pulled away, staggering slightly. Ominis could tell his father was weaker, diminished.
“You’re in over your head. I want you to know that the people involved in your precious wife being slaughtered have taken many measures to prevent them being caught, but they miscalculated.” His father gave a wheezing sort of laugh. “A return to our former glory, they promised us. I should have known-“
“Who is they.” Ominis leaned closer, a quaver of anticipation in his voice. Of bloodlust. “And are you saying someone got you to have a hand in it?”
His father was silent for a moment. “If I had known all it would take for you to finally live up to the Gaunt name was to kill your little plaything, I would have done so years ago.”
Ominis was deadly silent for a moment as he straightened up, tilted his head, and marked exactly where his father was by listening carefully for a second to his breathing.
His wand was already in his hand, and the cruciatus curse embraced Erasmus Gaunt as his son stood there and listened to him scream.
“If you’re done making comments about my wife, let’s move on.” Ominis heard his father gasping for breath, curled on the stone floor of his cell. “What was your involvement, who ordered it, and why.”
“She was touting nonsense that would have destroyed us.” There was pure loathing in Gaunt Sr.’s eyes as he looked at his son. “Fairytales about muggle-wizard integration, equal rights for werewolves, rubbish that would have set us back. She thought she could come in with the foolish laws of her empire, and we’d follow suit. Britain is the last stronghold for blood purity, and she was going to break it down.”
“So you killed her.” Something was eating away at Ominis’ gut, that familiar feeling of dark magic thrashing in his veins, begging to be released. “But who- and I will not ask this again- enabled you to do it?”
Erasmus laughed softly.
“You know. You know damn well who has the power to use me and throw me in Azkaban instead of fulfiling their promise without fear of retribution.”
Ominisdrew back and for the first time, pure shock crossed his features. If what his father was implying was true-
“That’s impossible.” He whispered. “That’s impossible, you’re lying to me-“
“Don’t be stupid. Think. You know I’m not.”
“Why would you tell me?” Ominis leaned in, voice lowered. “Because they completely fucked you over, is that why? What do you get out of this?”
“Something’s different. I can smell the dark magic on you, boy. You’ll make their lives a living hell, I know it.” His father grinned, a glint in his eyes. “I’m proud of you. And if killing the mudblood was what it took, then I don’t regret it.”
A calmness, a stillness settled over Ominis. The path forwards was clear. But his father’s words rang in his ears, deadly and damaging as poison.
Ominis raised his wand, checking the hallways.
“You know-“ he began softly, looking down at his father. “Being the prince of a foreign nation has opened my awareness up to so many different types of magic… and India has a rather special branch of it. Soul magic. Ever heard of it?” He heard the silence, and laughed softly. “Yes, you have. In fact, there is soul magic all around you. What do you think the dementors use when administering the Kiss?”
Ah. There is was-
The scent of fear.
“I hate you.” Ominis whispered. “I’ve hated you since the day you taught me that curse, since the day you used it on me. I don’t want you dead, I don’t want to torture you. No. I want you empty. I want you to feel a fraction of the agony I do.”
“Ominis-“ His father began, uncertain. “Wait-“
“No.” He replied, curt. “We’re done here.” He extended his wand, focusing. Pulling on the darkest vestiges of his grief, the blackest parts of his anger, he becan to incant.
“अहं तव आत्मानं निर्मूलयामि.” The low murmur of ancient Sanskrit flowed from his lips, his wand glowing a mercuric silver. His accent rolled the words strangely, but the effect was immediate. His father’s eyes rolled back, a death rattle of a gasp escaping him as he slumped to the floor. Ominis drew his wand back slowly, with surgical precision. He felt the miniscule but heavy weight of his father’s life essence drawing out his body, up his throat-
And with one brutal yank- Ominis tore his father’s soul out of his body.
xxxxxxxxxx
The Indian summer was in full force as the sun blazed in the azure sky over the palace and prince Ominis Surya Lakshmi adjusted his slate grey suit as he sat where he belonged.
His throne, alongside his mother and father in law, his brothers in law. There was an empty throne beside him where Mira should have been.
Ominis knew he’d never stop grieving her. He knew in his most private moments he’d cry and scream and beg the universe to give her back to him, that he’d do anything to hear her laugh, feel her in his arms.
But this was not the time. This was the time for action.
“Well?” Arjun leaned close to Ominis, and he heard the thirst for vengance in his voice. “Did you learn anything useful?”
Ominis was silent for a moment, before nodding slightly. He stood, raising his voice to address the king and queen as well as Arjun and Bharat. His family, and all he had left of Mira.
“Your highnesses.” Ominis’ voice was cold. “The time has come for decisive action in response to the princess’s assasination. Effective immediately, I want a halt on wandwood exports to the British wizarding world, coupled with trade sanctions and an immediate shutdown on any of their attempts to diversify trade partners.”
Queen Durgavati looked at her son in law, slightly shocked. “Beta, that is.. an extremely dire course of action to take. If the perpetrator was from Britain, we can work with the Ministry of Magic to exact justice-“
“Not if the perpetrator was the ministry, Mata.”
Ominis felt the way the atmosphere throne room seemed to suddenly grow heavy. His voice grew harder.
“I visited my father in prison and he revealed that Mira’s assasination was a federally funded attempt at destabilizing our empire. The minister disliked that her progressive ideals were gaining traction in Europe, so he had her killed her and made the Gaunts a scapegoat. The whole affair was buried by the media in Britain in a matter of a month. Whistleblowers were killed in mysterious circumstances, and no one raised eyebrows.”
There was a snarl of rage from prince Bharat, a soft curse from crown prince Arjun. “And you’re sure about this? The word of your father can be trusted?”
“It all adds up. It makes sense. But I did my homework and… had a few words with the Minister of Magic’s secretary. They confirmed it.”
Nobody needed to know that the secretary was currently at the bottom of a river after Ominis had extracted every last piece of information from him.
King Ashok Surya Lakshmi looked at his son in law. The tall, pale, British wizard his little girl had fallen in love with, who was as good as one of his own sons now. Ominis had changed, a darkness in his eyes, but the raja did not blame him in the slightest. Ominis did his duties incredibly, and had taken good care of his daughter while she had been alive.
Mira’s loss weighed heavily on the aging king, and some days the only thing preventing him from being crushed was the promise of getting justice.
Raja Ashok nodded, slowly.
“If the Ministry thinks they can get away with this, they are sorely mistaken.” He said softly. He turned his gaze to Ominis.
Prince Ominis Surya Lakshmi sat down slowly on his throne and draped one elegant leg over the other, his wand was held loosely in one hand, a palm resting flat on his thigh as he tilted his head slightly.
“We cut trade agreements, isolate them, undermine their markets. We cripple their economy first, their government second.” A slow, cruel smirk curled his lips. “And then-“ his voice was soft, almost reverent. “- then… we go to war.”
—————————
AN: 😇😇 thanks for reading! 🫶🏾🫶🏾🫶🏾 (the politics of this all is completely made up, it’s not meant to be accurate to irl politics at all just btw ✊🏾)
#ominis gaunt x oc#ominis gaunt#dark ominis gaunt#ominis gaunt x f!mc#angst no comfort#unhinged men consumed by vengeance my beloved
13 notes
·
View notes
Note
original anon here tysm for the recs ! if the marxist frameworks was too limiting im also completely fine w general postcolonial botany readings on the topic :0
A Spiteful Campaign: Agriculture, Forests, and Administering the Environment in Imperial Singapore and Malaya (2022). Barnard, Timothy P. & Joanna W. C. Lee. Environmental History Volume: 27 Issue: 3 Pages: 467-490. DOI: 10.1086/719685
Planting Empire, Cultivating Subjects: British Malaya, 1786–1941 (2018). Lynn Hollen Lees
The Plantation Paradigm: Colonial Agronomy, African Farmers, and the Global Cocoa Boom, 1870s--1940s (2014). Ross, Corey. Journal of Global History Volume: 9 Issue: 1 Pages: 49-71. DOI: 10.1017/S1740022813000491
Cultivating “Care”: Colonial Botany and the Moral Lives of Oil Palm at the Twentieth Century’s Turn (2022). Alice Rudge. Comparative Studies in Society and History Volume: 64 Issue: 4 Pages: 878-909. DOI: 10.1017/S0010417522000354
Pacific Forests: A History of Resource Control and Contest in Solomon Islands, c. 1800-1997 (2000). Bennett, Judith A.
Thomas Potts of Canterbury: Colonist and Conservationist (2020). Star, Paul
Colonialism and Green Science: History of Colonial Scientific Forestry in South India, 1820--1920 (2012). Kumar, V. M. Ravi. Indian Journal of History of Science Volume: 47 Issue 2 Pages: 241-259
Plantation Botany: Slavery and the Infrastructure of Government Science in the St. Vincent Botanic Garden, 1765–1820 (2021). Williams, J'Nese. Berichte zur Wissenschaftsgeschichte Volume: 44 Issue: 2 Pages: 137-158. DOI: 10.1002/bewi.202100011
Angel in the House, Angel in the Scientific Empire: Women and Colonial Botany During the Eighteenth and Nineteenth Centuries (2020). Hong, Jiang. Notes and Records: The Royal Society Journal of the History of Science Volume: 75 Issue: 3 Pages: 415-438. DOI: 10.1098/rsnr.2020.0046
From Ethnobotany to Emancipation: Slaves, Plant Knowledge, and Gardens on Eighteenth-Century Isle de France (2019). Brixius, Dorit. History of Science Volume: 58 Issue: 1 Pages: 51-75. DOI: 10.1177/0073275319835431
African Oil Palms, Colonial Socioecological Transformation and the Making of an Afro-Brazilian Landscape in Bahia, Brazil (2015). Watkins, Case. Environment and History Volume: 21 Issue: 1 Pages: 13-42. DOI: 10.3197/096734015X14183179969700
The East India Company and the Natural World (2015). Ed. Damodaran, Vinita; Winterbottom, Anna; Lester, Alan
Colonising Plants in Bihar (1760-1950): Tobacco Betwixt Indigo and Sugarcane (2014). Kerkhoff, Kathinka Sinha
Science in the Service of Colonial Agro-Industrialism: The Case of Cinchona Cultivation in the Dutch and British East Indies, 1852--1900 (2014). Hoogte, Arjo Roersch van der & Pieters, Toine. Studies in History and Philosophy of Science Part C: Studies in History and Philosophy of Biological and Biomedical Sciences Volume: 47 Issue: Part A Pages: 12-22
Trading Nature: Tahitians, Europeans, and Ecological Exchange (2010). Newell, Jennifer
The Colonial Machine: French Science and Overseas Expansion in the Old Regime (2011). McClellan, James E. & Regourd, François
Colonial Botany: Science, Commerce, and Politics in the Early Modern World (2005). Ed. Schiebinger, Londa L. & Swan, Claudia
Plants and Empire: Colonial Bioprospecting in the Atlantic World (2004). Schiebinger, Londa L.
95 notes
·
View notes
Text
[C]olonial policies to monitor and restrict Indian cattle were coterminous with policies to monitor and restrict Indian humans. [...] [T]he ‘milk-line’ [...] has been said by [colonial] scholars since the nineteenth century to bisect the region. [...] [This] reified and naturalised what remains a contentious division between South and Southeast Asia along the western borders of Myanmar. [...] [D]enaturalise [...] this border by uncovering the colonial history of how milk became entangled in the immanent political geography of British Burma. [...] As part of imperial writings on the distinctiveness of the colony's cultural landscape, milk informed the imaginative geography of Burma as a place distinct from India. [...]
---
[T]he turn-of-the-century writings of colonial scholar officials and travel-writers [...] generated a particular imaginative geography [...]. These authors rendered Burma a ‘unique geographic entity’ [...]. Being unable to acquire milk whilst travelling Burma was a frequent gripe in imperial writings. In this it stood in contrast to the rest of British India. [...] Imperial writings on dairy consumption – or, rather, the lack of it – in Burma reified this geography [...]. Burma was where you could not get milk in British India. [...] But the difficulty of milk did not end with the cow. Once produced, the milk itself was liable to adulteration and infection necessitating state and scientific intervention. Limiting the mobility of dairy cattle and removing them from urban areas through policies designed to order and police space were central to colonial schemes for improving milk production [...]. By the twentieth century most of the dairy production in the colony was conducted by Indians who had migrated to Burma with their own cattle. [...]
The rendering of cattle as lively commodities in the milk industry was seen to be in tension with their commodification in a different economic sector, the rice industry.
This was overwhelmingly the most important part of Burma's colonial economy.
The late nineteenth century saw a rapid expansion of the deltaic rice frontier. By the opening decades of following century the Burma delta had become the largest rice producing region in the world. The importance of plough cattle was reflected in their market value, which doubled between the end of World War One and 1930. [...]
In particular, they worried that the bloodlines of the Burmese breed of oxen, apparently favoured by cultivators, were at risk. [...] Indian milch cattle were considered a particular threat. This imperial imperative to protect a so-called ‘Burmese’ breed of ox reified and naturalised Burma as a geographic entity, with Indian cattle figured as invasive.
These concerns were entangled with colonial policies regarding the human Indian population in the colony [...].
---
[There was] a growing recognition of the importance of [Burmese] cattle to the production of rice in the Burma delta. [...] The stocky, strong Burmese ox [...] was thought to be especially suited to labour in paddy fields [...]. Burma was imagined as being constituted of upland areas where cattle were bred and the southern deltaic region where they were worked [...]. This was an animal geography that was transgressed by mobile herds of milking cattle imported from India residing along the sides of waterways and in the railway towns [...]. Following the colony's transportation network, migrant Indian cattle penetrated the spaces [...] To many officials, by the start of World War One the existing measures for protecting Burmese plough cattle from the ‘evils’ of Indian milch cattle were deemed inadequate. The push for greater controls began in 1915 with an agricultural and cooperative conference held in Mandalay. [...] ]C]olonial officials came to frame Indian cattle as a problem breed. The conference was attended by over nine hundred people from across Burma, including [...] state officials. It unanimously agreed that action had to be taken to protect [Burmese] cattle from Indian cattle.
Their suggested course of action was three-pronged: taxation, prohibition and segregation. [...] Attitudes to Indian cattle in the colony were conterminous with attitudes to Indian people.
The interventions [in cattle segregation] [...] can be considered as part of a wider range of state controls placed on Indian migrants to Burma. The timing of these committees was synchronous with inquiries into the sanitary conditions that Indian workers travelled and lived in [...]. At the same time [...], the state introduced compulsory medical checks and vaccinations on human arrivals from the subcontinent. In addition, the concerns expressed by officials contributing to these reports on cattle in Burma were indicative of British officialdom's paternalistic attitude towards the Burmese people, viewing their role as protecting the Burmese from the Indian and Chinese populations. The administrative view of the colony, which by the turn of the century held it to be culturally distinct from India, was increasingly imagining it as a separate geo-political entity. Officials began planning for it to be separated from British India.
During the interwar years anti-Indian sentiments gained ground [...]. Indian migrants were figured by some as a threat [...]. There were a number of anti-Indian riots in the 1930s [...]. The 1935 Government of India Act was enacted in 1937 separating Burma from India [...].
---
All text above by: Jonathan Saha. “Milk to Mandalay: dairy consumption, animal history and the political geography of colonial Burma.” Journal of Historical Geography Volume 54. October 2016. [Bold emphasis and some paragraph breaks/contractions added by me. Presented here for commentary, teaching, criticism purposes.]
55 notes
·
View notes
Text
Leading with Purpose: Mahatma Gandhi’s Vision for Change
Mahatma Gandhi, widely appeared because the Father of the Nation in India, became a visionary chief whose concepts and practices have stimulated generations across the globe. His management fashion, rooted in nonviolence (Ahimsa), reality (Satya), and self-reliance (Swadeshi), transcended the limits of time and geography, offering a timeless blueprint for transformative leadership. Gandhi’s vision was no longer pretty much accomplishing independence for India but about fostering a international founded on justice, equality, and compassion. This essay delves into the essence of Gandhi's visionary leadership and the enduring lessons it offers.

Visionary Leadership Mahatma Gandhi
The Foundation of Gandhi’s Visionary Leadership
At the coronary heart of Gandhi's leadership turned into a deep dedication to universal values. His vision changed into formed with the aid of his non-public studies, philosophical research, and an unshakable belief within the strength of the individual to pressure societal exchange. Gandhi's management changed into deeply rooted in standards, which served because the bedrock for his strategies and moves.
1. Nonviolence as a Core Principle
Gandhi’s unwavering notion in nonviolence changed into each a moral and a strategic choice. He saw violence as a damaging pressure that perpetuates cycles of hatred and revenge. Instead, he advocated for Ahimsa, a precept derived from historic Indian philosophy, which emphasizes causing no harm to others in idea, word, or deed. Gandhi carried out this principle to each private behavior and mass movements, demonstrating its transformative capability.
Through nonviolent resistance, Gandhi led some of the most impactful actions of the 20th century, inclusive of the Salt March and the Quit India Movement. These movements showcased the strength of collective movement grounded in peace and morality. By refusing to retaliate with violence, Gandhi now not handiest garnered worldwide sympathy for India’s motive but additionally set a ethical wellknown for oppressed societies global.
2. Truth as a Guiding Light
For Gandhi, reality become synonymous with God. He famously declared, “Truth is God.” This deep reverence for fact permeated his management, making honesty and transparency fundamental to his movements. Gandhi’s dedication to truth, or Satya, became obtrusive in his insistence on self-scrutiny and his capability to confess mistakes. This humility and openness earned him the accept as true with and admire of millions.
3. Self-Reliance and Empowerment
Gandhi’s emphasis on self-reliance, embodied inside the concept of Swadeshi, turned into a cornerstone of his imaginative and prescient for India. He believed that real freedom could most effective be performed whilst individuals and groups have become self-enough. Gandhi’s advocacy for using Khadi (hand-spun cloth) and local industries changed into not simply an financial method however a symbolic act of defiance in opposition to colonial exploitation. By selling self-reliance, he empowered the masses, mainly rural communities, to take rate in their destinies.
Gandhi’s Transformational Movements
Gandhi’s visionary leadership found expression in several landmark movements that transformed India’s socio-political landscape and stimulated comparable struggles international.
1. The Champaran Satyagraha
It become a motion to address the plight of indigo farmers in Bihar, who had been being exploited by British planters. Gandhi’s method became unique: he immersed himself in the farmers’ lives, listened to their grievances, and mobilized them to resist peacefully. This movement set the template for future struggles, emphasizing grassroots involvement and nonviolent resistance.
2. The Salt March
The Salt March of 1930 become one in all Gandhi’s maximum iconic campaigns. It was a protest in opposition to the British monopoly on salt production and taxation. Gandhi’s selection to walk 240 miles to the Arabian Sea, wherein he made salt from seawater, was a masterstroke of symbolic management. The march galvanized the state, drawing interest to the oppressive guidelines of the British and uniting people from numerous backgrounds in a common reason.
3. The Quit India Movement
Launched in 1942, the Quit India Movement changed into a name for instant independence. Gandhi’s clarion call, “Do or Die,” inspired thousands and thousands to upward thrust in opposition to colonial rule. Despite brutal repression, the motion showcased Gandhi’s ability to mobilize the loads and maintain their dedication to nonviolence and perseverance.
Gandhi’s Leadership Traits
Gandhi possessed a completely unique combination of qualities that made him an high-quality leader. His vision became now not limited to political freedom but extended to social reform, economic self-reliance, and religious upliftment. Key trends that defined his leadership encompass:
1. Empathy and Inclusivity
Gandhi’s deep empathy allowed him to connect with people from all walks of lifestyles. He championed the purpose of marginalized groups, together with the Dalits, whom he called “Harijans” (kids of God). His inclusive technique ensured that his moves had been now not confined to any particular institution however resonated with the hundreds.
2. Simplicity and Integrity
Gandhi’s simplicity became a effective declaration towards materialism and excess. He led with the aid of example, living a life of austerity and practising what he preached. This consistency between his words and actions reinforced his credibility as a frontrunner.
3. Visionary Thinking
Gandhi’s potential to ascertain a better future and articulate it in a manner that inspired movement turned into principal to his management. His imaginative and prescient prolonged past India’s independence to a international free from oppression and inequality. He dreamed of a society based totally on Sarvodaya, or the welfare of all.
The Global Influence of Gandhi’s Leadership
Gandhi’s standards of nonviolence and civil disobedience motivated numerous leaders and actions worldwide. Martin Luther King Jr. Adopted Gandhi’s techniques within the American Civil Rights Movement, even as Nelson Mandela drew idea from Gandhi’s struggles in his fight against apartheid in South Africa. Even these days, Gandhi’s teachings serve as a guiding light for activists and leaders seeking non violent answers to warfare.
Lessons from Gandhi’s Leadership
Gandhi’s leadership offers undying instructions which can be as relevant today as they had been at some point of his lifetime:
The Power of Nonviolence: Gandhi proven that nonviolence isn't always a signal of weakness but a amazing tool for accomplishing justice and alternate.
The Importance of Personal Integrity: Gandhi’s alignment of values, phrases, and actions underscores the importance of integrity in leadership.
Grassroots Mobilization: Gandhi’s emphasis on attractive and empowering everyday human beings highlights the value of inclusive leadership.
Resilience in Adversity: Gandhi’s ability to persevere in the face of demanding situations serves as a reminder of the significance of resilience in achieving long-term desires.
Holistic Vision: Gandhi’s management became not restrained to one domain however addressed political, social, economic, and non secular dimensions, offering a holistic approach to leadership.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

Portrait of an Indian Lady, traditionally called the Bibi of John Wombwell (d. 1795), Arthur William Devis
In Calcutta [Arthur William Devis] quickly established himself as one of the leading European painters in India, painting portraits of a number of the most eminent figures among the British community, including Warren Hastings, the Governor-General. [...]
More so than most European artists working in India, however, with the possible exception of Renaldi, Devis’s work in India demonstrates a clear interest in the native population of the Subcontinent – a sensibility that some historians have credited to his experiences in the Pellew Islands. Whilst principally based in Calcutta, he made frequent trips out into the surrounding country to sketch Indian villagers at work. In the autumn of 1786 he travelled as far as Patna, on the south bank of the Ganges in the north eastern state of Bihar. There he made studies of local people engaged in their traditional industries, including paper and saltpetre making, as well as the weaving of stripped cotton carpets, known as satringis, for which Patna was famous. It may be to this trip that the present portrait relates, particularly with the richly stripped textiles of the lady’s divan and the notable cusped archway in the background, typical of India’s northern cities. [...]
Reclining on a richly cushioned divan, wearing a saffron coloured sari and sumptuous jewels, the unknown Indian lady depicted in this portrait is clearly somebody of noble birth and high social status. At her side is a gilt stemmed cup overflowing with jewels, while a bihishti lays the dust in the courtyard beyond. It is a scene of opulent leisure and casual refinery. The composition closely relates to a portrait of Anne Heatly, probably the bibi of Suetonius Grant Heatly, an American born East India Company official who held positions at Chotanagpur, Palamu and Purina. Both paintings share the same compositional elements, including the red bolster and cushions with their green and yellow stripped bordering; the tazza like cup with its hanging pearls; the archway and the background figures; whilst the sitter’s themselves share the same heavy-lidded eyes; soft, flowing drapery and elegantly reclining pose. The portrait of Anne Heatly, which appeared at auction in 2006, was also previously given to Charles Smith. However, following subsequent cleaning and restoration, it has also now been correctly identified as being by Devis. The two paintings, almost mirror images of each other, save for the difference in format (the portrait of Heatly being in landscape), clearly belong to the same moment in the artist’s career.
Whilst the sitter in the present portrait remains unknown, as Mildred Archer noted, she is too confident in her poise to be an orthodox Muslim woman of rank – who would not have allowed herself to be painted in public – and is most likely the bibi of another high-ranking British official. The term bibi has its roots in the Indian word for ‘princess’ and served as a personalised or intimate reference to the women who first formed relationships with European traders in the seventieth century who were, in fact, mostly princesses of Indian royal families. Young women taken from the royal zenana – sisters, nieces, daughters of the ruling nawab or his brothers – and given in arranged marriages to important European officials, they played an important role in strengthening the diplomatic alliances between a reigning nawab and powerful Company representatives that promoted the political and economic interests of both parties (much in the same way that European royal courts use arranged marriage as a means of strengthening diplomatic ties). Well educated at home by elderly scholars, these noblewomen were literate, often able to speak and read several languages and regional dialects, and schooled in the study of mathematics, history, the natural sciences and medicine. In many cases these marriages produced genuinely happy unions, with the multi-racial offspring they produced further helping to knit the Indian and European communities together.
The custom of high-ranking British Company officials taking an aristocratic Indian mistress continued as both a social and political necessity well into the eighteenth century, to which a number of known portraits of the mistresses of British officials by the likes of Zoffany, Renaldi and James Wales attest. The practice was finally ended by the Marquess Wellesley when he was Governor-General in the 1790s, following which the British and Indian communities became increasing segregated through the course of the nineteenth century.
[Text from Sotheby's]
3 notes
·
View notes