#ISO 26262 services
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Making ISO 26262 Compliance Smoother and More Efficient for the Automotive Industry
Complying with ISO 26262, the international standard for functional safety in the automotive industry, is a critical requirement for ensuring the safety and reliability of automotive systems. While achieving ISO 26262 compliance may seem daunting, there are strategies and best practices that can make the process easier and more efficient for automotive companies. In this blog post, we will explore key steps to simplify ISO 26262 compliance and foster a safety-oriented culture within the automotive industry.
Establishing a Comprehensive Safety Framework for ISO 26262 Compliance
To make ISO 26262 compliance more manageable, it is essential to establish a robust safety framework that aligns with the standard's requirements. This framework should encompass safety management, hazard analysis, risk assessment, safety goals, safety plans, and safety verification and validation activities. By clearly defining ISO 26262 mandated processes and responsibilities, companies can ensure a structured and systematic approach to compliance.
ISO 26262 Compliance Needs a Risk-Based Approach
ISO 26262 encourages a risk-based approach to functional safety. Instead of applying the same level of rigor to every aspect of a system, companies should prioritize their efforts based on the level of risk associated with each component or function. Identifying and mitigating the most critical risks first can help optimize resource allocation and streamline compliance efforts.
Promoting Cross-Functional Collaboration for ISO 26262 Projects
ISO 26262 compliance requires collaboration among various disciplines, including engineering, safety, testing, and project management. Foster a culture of cross-functional collaboration to facilitate knowledge sharing and decision-making. Encourage open communication channels and create opportunities for regular meetings and workshops to ensure all stakeholders are aligned on compliance objectives.
Leveraging ISO 26262 Compliance Experts
Engaging automotive safety experts can significantly simplify ISO 26262 compliance. These experts possess in-depth knowledge of the standard's requirements and can provide guidance on best practices, gap analysis, and compliance strategies. They can help tailor the compliance process to the organization's specific needs and provide valuable insights throughout the development lifecycle.
Implementing ISO 26262 Qualified Tools and Processes
Invest in tools and processes that support safety-oriented development and verification activities. This includes utilizing functional safety tools, safety analysis tools, requirements management tools, and traceability tools. Automating safety-related processes can enhance efficiency, accuracy, and traceability, while reducing manual effort and errors.
Conclusion
By following a structured and systematic approach, collaborating across functions, leveraging expertise, and embracing a risk-based mindset, automotive companies can simplify the ISO 26262 compliance process. Implementing safety-oriented tools, fostering a safety culture, and providing continuous training further streamline the path to compliance. Ultimately, making ISO 26262 compliance easy is about embedding safety into the DNA of automotive organizations and prioritizing the well-being of both drivers and passengers.
#ISO 26262#ISO 26262 Compliance#Automotive Industry#ISO 26262 Projects#automotive safety experts#automotive safety#ISO 26262 consulting#ISO 26262 consultant#ISO 26262 services#ISO 26262 software#ISO 26262 development
0 notes
Text

ERP for Automotive Manufacturing
The automotive manufacturing industry is evolving rapidly with increased complexity in production processes, supply chain challenges, and the need for strict quality control. To stay competitive and meet market demands, automotive manufacturers require a robust digital solution that ensures operational efficiency, real-time insights, and flexibility. Matiyas Solutions offers a powerful ERP for Automotive Manufacturing designed to simplify and streamline every aspect of the production lifecycle.
Our Automotive ERP Software provides complete visibility into core business functions including inventory management, procurement, production planning, sales, finance, and quality control. With real-time data access and integrated modules, manufacturers can monitor production lines, manage multi-level Bills of Materials (BOMs), track supplier performance, and ensure compliance with industry regulations.
Matiyas’ Automotive Manufacturing Software comes with built-in tools for advanced planning and scheduling (APS), vendor and contract management, warranty tracking, and after-sales service support. It empowers your team with data-driven decision-making and reduces downtime through predictive maintenance and automated workflows.
Whether you're manufacturing auto parts or full vehicles, our scalable and cloud-ready Automotive Software helps you reduce waste, optimize resources, and improve product quality. The software integrates seamlessly with CAD/CAM systems and supports regulatory standards such as IATF 16949 and ISO 26262.
By implementing our ERP for Automotive Manufacturing, you can embrace digital transformation and enhance productivity while adapting to ever-changing market demands.
Choose Matiyas Automotive ERP Software – your complete solution for smarter, faster, and more efficient automotive manufacturing operations.
0 notes
Text
Teamcenter for Automotive Industry: Key Benefits, Features, and Applications
In the ever changing automotive sector, effectively managing intricate product lifecycles is essential. Siemens’s top Product Lifecycle Management (PLM)tool, Teamcenter, assists automakers in optimizing their engineering, design, and production procedures.
Key Benefits of Teamcenter in Automotive Industry
Enhanced Collaboration — Connects global teams, suppliers, and stakeholders for seamless data sharing.
Improved Efficiency — Automates workflows, reducing errors and rework.
Regulatory Compliance — Ensures adherence to industry standards like ISO 26262 and IATF 16949.
Cost Reduction — Minimizes design changes and accelerates time-to-market.
Better Change Management — Tracks and implements engineering changes effectively
Key Features of Teamcenter
BOM Management — Manages complex Bill of Materials across product variants.
CAD Data Integration — Supports multiple CAD systems for unified design management.
Digital Twin & Simulation — Enables virtual validation of automotive components.
Document & Workflow Management — Organizes critical documents and automates approvals.
Supplier Collaboration — Enhances transparency and coordination with vendors.
Applications in the Automotive Industry
Vehicle Development — Supports design, testing, and production planning.
Manufacturing Process Management — Optimizes production and quality control.
Aftermarket Services — Improves spare parts management and maintenance tracking.
Conclusion
Teamcenter empowers automotive manufacturers with a centralized PLM solution, improving efficiency, compliance, and product innovation. By streamlining operations, it accelerates vehicle development while maintaining quality and cost-effectiveness, making it a vital tool for the industry’s future.
0 notes
Link
#AutonomousVehicles#autonomy#AWS#BlueCruise#Bosch#cloud-basedGNSS#Ford#Futurride#globalnavigationsatellitesystem#GNSS#GNSSpositioning#ISO26262#Level3#precisepositioning#SAE#sustainablemobility#SwiftNavigation
0 notes
Text
Automated Testing in the Automotive Industry: Trends and Challenges

The automotive industry is undergoing a seismic shift, driven by advancements in electric vehicles (EVs), autonomous driving, connected car technologies, and software-defined vehicles. As vehicles become more complex and software-dependent, the need for robust and efficient testing methodologies has never been greater. Automated testing, powered by Artificial Intelligence (AI), is emerging as a critical enabler in this transformation. Among the tools leading this charge is Genqe.ai, an AI-driven platform designed to address the unique challenges of automotive testing.
Trends Shaping Automated Testing in the Automotive Industry
Rise of Software-Defined Vehicles Modern vehicles are increasingly reliant on software for everything from infotainment systems to advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). Automated testing tools like Genqe.ai are essential for ensuring the reliability, safety, and performance of these software-driven components.
Autonomous Driving and ADAS Testing Autonomous vehicles require extensive testing to ensure they can navigate complex real-world scenarios safely. Genqe.ai leverages AI to simulate diverse driving conditions, predict edge cases, and validate the performance of ADAS and autonomous systems.
Connected Car Ecosystems With the rise of connected cars, vehicles are now part of a larger ecosystem that includes cloud services, IoT devices, and mobile applications. Genqe.ai enables end-to-end testing of these interconnected systems, ensuring seamless communication and functionality.
Electric Vehicle (EV) Testing EVs introduce new testing requirements, such as battery management systems, charging infrastructure, and energy efficiency. AI-powered tools like Genqe.ai can automate the testing of these components, ensuring they meet performance and safety standards.
Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates OTA updates are becoming a standard feature in modern vehicles, allowing manufacturers to deliver software updates remotely. Genqe.ai ensures that these updates are thoroughly tested before deployment, minimizing the risk of introducing new vulnerabilities or bugs.
Challenges in Automotive Testing and How Genqe.ai Addresses Them
Complexity of Testing Scenarios Automotive systems must operate flawlessly in a wide range of conditions, from extreme weather to unpredictable road scenarios. Genqe.ai uses AI to simulate these conditions, enabling comprehensive testing without the need for physical prototypes.
High Cost of Testing Traditional testing methods, such as physical test drives and hardware-in-the-loop (HIL) testing, can be expensive and time-consuming. Genqe.ai reduces costs by automating repetitive tasks and enabling virtual testing environments.
Ensuring Safety and Compliance Safety is paramount in the automotive industry, and vehicles must comply with stringent regulatory standards. Genqe.ai automates compliance testing, ensuring that systems meet industry standards such as ISO 26262 for functional safety.
Handling Large Volumes of Data Modern vehicles generate vast amounts of data from sensors, cameras, and other sources. Genqe.ai leverages AI to analyze this data, identify patterns, and detect anomalies that could indicate potential issues.
Keeping Pace with Rapid Innovation The automotive industry is evolving at an unprecedented pace, with new technologies and features being introduced regularly. Genqe.ai enables continuous testing, allowing manufacturers to keep up with the rapid pace of innovation.
The Role of Genqe.ai in Automotive Testing
Genqe.ai is revolutionizing automotive testing by combining AI with advanced automation capabilities. Here’s how it stands out:
Adaptive Testing: Genqe.ai adapts to changes in software and hardware, ensuring that tests remain relevant even as systems evolve.
Predictive Analytics: By analyzing historical data, Genqe.ai can predict potential failures and recommend preventive measures.
Scalability: Whether testing a single component or an entire vehicle ecosystem, Genqe.ai scales to meet the demands of the automotive industry.
Real-Time Insights: Genqe.ai provides real-time feedback, enabling teams to identify and address issues quickly.
The Future of Automotive Testing with Genqe.ai
As the automotive industry continues to embrace digital transformation, automated testing will play a pivotal role in ensuring the safety, reliability, and performance of next-generation vehicles. Tools like Genqe.ai are at the forefront of this evolution, empowering manufacturers to overcome the challenges of modern automotive testing.
By leveraging AI-driven automation, Genqe.ai is helping the automotive industry navigate the complexities of software-defined vehicles, autonomous driving, and connected ecosystems. As we move toward a future of smarter, safer, and more sustainable transportation, Genqe.ai is setting the standard for automotive testing excellence.
0 notes
Text
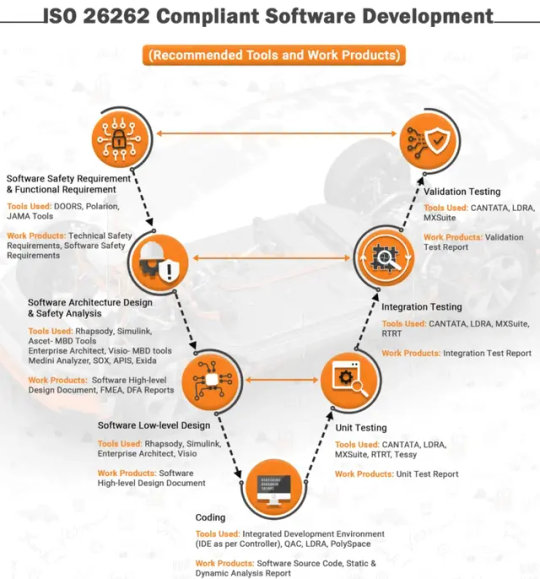
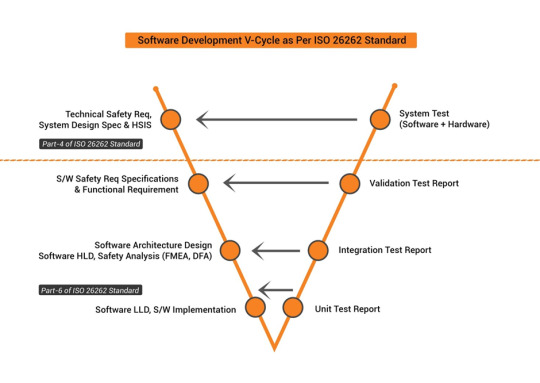
V-Cycle of ISO 26262 Compliant Software Development
Developing safe and reliable automotive software is no longer an option, it is a necessity. And in some geographies a legislative mandate. ISO 26262 standard was conceptualized as a standard for functional safety that ensures the highest level of safety in road vehicles.
With ISO 26262 compliant software development, you can rest assured that your software meets the highest safety standards and is ready to hit the road with confidence.
We offer ISO 26262 compliant software development services that cover every stage of the V cycle, from concept development to system deployment and beyond. Here’s an infographic that clearly showcases the V-cycle of ISO 26262 compliant software development. From tools used and work products derived at every stage, you get the bigger picture of the development process.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Role of embedded systems in VCU design
Introduction to VCU design

Modern automotive Vehicle Control Units (VCUs) rely heavily on embedded technologies to improve vehicle design, performance, and functionality. A VCU is a vital component that controls the engine, transmission, brakes, and other vehicle functions. Embedded systems make major contributions to the operation of VCUs by integrating sensors, processing data, managing power, assuring safety, and simplifying software updates.
This blog delves at the different facets of embedded systems in VCU design, highlighting their benefits, problems, and implications for modern automobile technology.
Key Contributions of Embedded Systems to VCU Design

1. Integration of sensors
Embedded systems in VCUs collect and process data from a variety of sensors, including accelerometers, gyros, wheel speed sensors, and engine sensors. These sensors give real-time data, allowing the VCU to make accurate judgments about vehicle operations.
2. Data Management and Control.
A VCU’s embedded processors examine incoming sensor data and make real-time judgments. This includes altering engine settings, managing transmission shifts, and monitoring brake systems in order to improve performance and safety.
3. Communication protocols
Modern automobiles contain numerous Electronic Control Units (ECUs) that must communicate effectively. Embedded systems manage communication protocols such as CAN (Controller Area Network), LIN (Local Interconnect Network), and FlexRay to ensure that data flows smoothly across subsystems such as the ABS, Transmission Control Unit (TCU), and Engine Control Unit.
4. Fault Detection and Diagnosis
Embedded systems allow VCUs to recognize and diagnose issues using enhanced diagnostic capabilities. They monitor automobile components, generate Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), and give personnel with precise data for effective troubleshooting and maintenance.
5. Power Management.
Efficient power distribution is critical to improving vehicle performance. Embedded systems manage power consumption, ensuring that various components receive appropriate power while consuming the least amount of energy possible. This improves the overall efficiency of hybrid and electric vehicles.
6. Functional Safety.
Automotive embedded systems follow functional safety criteria such as ISO 26262. Safety features such as redundancy, fail-safes, and real-time monitoring ensure that vital vehicle operations continue to work even when hardware or software fails.
7. Software Updates and Upgrades.
Embedded systems provide Over-the-Air (OTA) updates, which allow manufacturers to improve VCU software remotely. This capability allows for speed improvements, the inclusion of new features, and security enhancements without requiring a physical service visit.
8. Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) Integration
VCUs work alongside Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) to improve vehicle safety and automation. Embedded systems enable features like adaptive cruise control, lane-keeping assistance, and collision avoidance, which improve both the driving experience and security.
Benefits of Embedded Systems for VCU Design
The incorporation of embedded technologies into VCUs offers numerous advantages, improving the overall efficiency, safety, and performance of modern vehicles.
1. Real-Time Processing
Embedded systems provide high-speed real-time data processing, allowing for quick decisions on operations like engine control, braking, and stability control.
2. Optimized performance
VCUs use embedded control systems to enhance engine performance, gearbox shifts, and braking efficiency, resulting in increased fuel efficiency and vehicle responsiveness.
3. Smooth integration of complex functions
Embedded systems make it easier to integrate numerous vehicle tasks, such as ADAS and engine control, and ensure that subsystems communicate and coordinate smoothly.
4. Reduced size and weight.
The compact nature of embedded systems reduces the total size and weight of VCUs, which is critical for increasing fuel efficiency and optimizing vehicle design.
5. Energy efficiency
The power management capabilities of embedded systems improve vehicle energy efficiency, guaranteeing minimal power waste while maintaining peak performance.
4. Stability and reliability
Redundant and fault-tolerant components improve the stability and dependability of embedded VCUs, allowing vehicles to operate continuously even when components fail.
7. Advanced diagnostic capabilities.
Embedded systems enable early failure detection by continuously monitoring and generating DTCs, simplifying maintenance and decreasing downtime.
8. Adaptability and Flexibility.
Software updates and enhancements enable manufacturers to add new features and improve performance without requiring hardware changes.
9. Cost effectiveness
Although embedded systems have a high initial development cost, they save money in the long run due to lower maintenance costs, remote diagnostics, and greater vehicle efficiency.
10. Complying with Industry Standards
Embedded systems ensure compliance with industry norms such as ISO 26262, which ensures that automobiles satisfy safety and performance standards.
Challenges and Drawbacks of Embedded Systems in VCU Design

Despite their benefits, embedded systems in VCU design provide a number of obstacles for manufacturers looking to improve reliability and performance.
1. Software Complexity
The intricacy of embedded software makes it difficult to design, test, and debug. Any software issue can have a substantial influence on vehicle performance and safety.
2. Cybersecurity risks
As automobiles become more connected, the potential of cyber-attacks rises. To prevent hacking and unauthorized access, embedded systems must have strong security mechanisms in place.
3. Limited upgradeability.
While software updates are possible, hardware constraints may impede the adoption of new technologies, forcing costly hardware upgrades.
4. Rigid Design
Embedded systems are frequently developed for specialized roles, making it difficult to adapt them to new technologies or changing requirements without major changes.
5. High development and maintenance costs.
The cost of developing, testing, and maintaining embedded systems can be significant, affecting overall vehicle expenses.
6. Vendor Dependence.
Automakers frequently rely on certain component suppliers, which can lead to supply chain weaknesses and reduced flexibility.
7. Limited processing capacity.
The growing demand for AI-powered features and autonomous driving puts a pressure on embedded processors, necessitating increasingly powerful computing solutions.
8. Integration Challenges

The seamless integration of embedded systems with other electronic components in the vehicle necessitates careful control of communication protocols and compatibility.
9. Environmental constraints.
Harsh working circumstances, such as excessive temperatures and vibrations, can have an impact on embedded system durability and reliability.
10. Longer Development Cycles
Automotive embedded system development can take time due to demanding testing and certification requirements, delaying the adoption of new technology.
Conclusion
Modern Vehicle Control Units (VCUs) rely on embedded systems to improve vehicle performance, safety, and efficiency. These systems support real-time sensor data processing, smooth communication between subsystems, and enhanced diagnostics.
While embedded systems offer various benefits, including real-time decision-making, energy efficiency, and software adaptability, they also present problems such as software complexity, cybersecurity threats, and high development costs. Addressing these difficulties is critical to guaranteeing the ongoing evolution of embedded systems in VCU design.
With continual developments in automotive technology, R&D efforts are centered on increasing processing power, improving cybersecurity, and increasing flexibility to suit the industry’s changing expectations. Embedded systems in VCU design constitute a vibrant and fast expanding field that will shape the future of intelligent, connected, and efficient vehicles.
For additional information on our VCUs, CAN Keypad, CAN Display -related products and E/E Software Services , please visit our website or email [email protected].
#VCUCommunicationProtocols#**VCUdesign **#Dorleco#CANKeypads#CANDisplays#VCUs#Vehiclecontrolunit#EVSoftwareServices#E/Earchitectures
0 notes
Text
Lithion BMS Certification A Step Closer to ARAI Battery Pack Approval
Electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy are fast-changing domains that have strict safety and performance standards to be met. For battery pack developers and manufacturers, getting a nod from groups like the Automotive Research Association of India (ARAI) is a must. Here comes Lithion, a pioneer in battery management systems, to make it easier for that ARAI clearance with its certifications.
Why Certification Matters for Battery Packs
Battery packs, which power everything from electric cars to energy storage devices, are a significant part of modern energy solutions. However, their performance and safety are significantly affected by the BMS, which controls temperature, charge, discharge, and other critical variables. Certification ensures that the BMS meets industry standards for:
•Safety: Avoiding hazards such as thermal runaway, overcharging, and short circuits.
•Reliability: Ensuring consistent performance throughout the battery's lifecycle.
•Compliance: It complies with the regulatory demands for use in certain applications such as automotive and industrial.
The Role of Lithion in Certification
Compliance is the cornerstone of the BMS solutions that Lithion has designed. We test and validate our systems as per the requirement set by ARAI and other international regulatory bodies. Our services can get your battery packs certified by ARAI, and here is how:
1. Pre-Certification Testing
By ensuring your Battery management system (BMS) is optimized for safety and performance before official certification, Lithion provides advanced diagnostic tools and software that reduce the likelihood of delays or rejection in the approval process.
2. Documentation Support
For ARAI approval, one needs to have technical documentation in full detail, such as design specifications, test reports, and safety procedures. Lithion ensures that the necessary documentation is prepared to the highest standards.
3. End-to-End Compliance
Lithion's BMS meets key requirements for:
•Functional safety (ISO 26262)
•Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC)
•Thermal and electrical safety providing you with pre-aligned systems based on these standards, we can make the passing of your battery pack at ARAI easier.
Benefits in Partnership with Lithion
Easier Approval Procedure
We are able to bring your products faster to the market with our professional services from Lithion because of our capability in reducing the amount of time and effort it will take for the ARAI certification.
Leading Edge Technology
Our BMS solutions are fitted with modern features, such as real-time monitoring, sophisticated fault diagnostics, and strong fail-safe mechanisms, so your battery packs meet and surpass the industry standard.
Compliance to Global Standards
Lithion's systems are designed with domestic and international standards in mind. This makes it possible to expand into a global market.
Conclusion
First, any manufacturer wishing to gain credibility and trust in the cutthroat battery market needs to get ARAI approval. Lithion's BMS solutions will guide you through the challenges of certification with confidence, and our commitment to quality, safety, and innovation ensures that your battery packs are ready for the energy ecosystem of the future.
If you are interested in moving forward with ARAI certification, get in contact with Lithion today and we will make you a success.

#bms#battery management system#lithion#lithion power#lithium battery#batterymanagementsystem#electricvehicle#ev#lithionpower
0 notes
Text
Future Trends in In Vehicle Networks: Advancements and Innovations
The future of in-vehicle networks is shaped by technological advancements, consumer demand for connected services, and regulatory requirements for vehicle safety and cybersecurity. This article explores emerging trends, innovations, and the transformative potential of in-vehicle networks in shaping the future of automotive technology.
Evolution of In Vehicle Networks
From CAN Bus to Ethernet: In-vehicle networks evolve from traditional CAN Bus and LIN protocols to high-speed Ethernet and FlexRay architectures. Ethernet supports bandwidth-intensive applications, such as multimedia streaming, autonomous driving systems, and vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication.
Integration with IoT Devices: In Vehicle networks integrate with Internet of Things (IoT) devices, smart sensors, and connected infrastructure to enhance vehicle connectivity, gather real-time data, and optimize operational efficiency. IoT integration supports predictive maintenance, traffic management, and personalized driving experiences.
Emerging Technologies and Innovations
5G Connectivity: The deployment of 5G networks accelerates in-vehicle communication speeds, reduces latency, and supports ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC) for safety-critical applications. 5G integration enhances V2X communication, improves traffic flow, and enables seamless vehicle connectivity.
Edge Computing: Edge computing platforms process data locally within in-vehicle networks, reducing latency, optimizing bandwidth usage, and supporting real-time decision-making for autonomous driving and cloud-based applications. Edge computing enhances in-vehicle network performance and responsiveness.
Automotive Cybersecurity and Data Privacy
Secure OTA Updates: Automotive manufacturers implement secure OTA update mechanisms to deploy software patches, firmware upgrades, and security enhancements remotely. Secure OTA ensures data integrity, verifies update authenticity, and protects in-vehicle networks against cyber threats.
Regulatory Compliance: Compliance with automotive safety standards, such as ISO 26262 for functional safety and UN ECE regulations for cybersecurity, ensures vehicle safety and regulatory adherence. Manufacturers integrate cybersecurity measures into in-vehicle networks to protect against cyber threats and ensure consumer trust.
Consumer Demand and User Experiences
Connected Services: Consumer demand for connected services drives the adoption of in-vehicle networks that support advanced features, such as real-time navigation updates, voice-controlled assistants, and personalized infotainment options. Connected services enhance driver convenience, entertainment, and overall vehicle usability.
User-Centric Design: Automotive OEMs prioritize user-centric design principles to enhance the usability and accessibility of in-vehicle networks. Intuitive interfaces, seamless connectivity with mobile devices, and personalized settings improve driver satisfaction and foster brand loyalty.
Future Innovations and Industry Collaboration
AI-Powered Analytics: Integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) enables predictive analytics for in vehicle networks. AI algorithms analyze vehicle data, predict maintenance needs, optimize energy efficiency, and enhance driver safety through real-time insights and proactive recommendations.
Smart City Integration: In-vehicle networks contribute to smart city initiatives by supporting traffic management systems, environmental monitoring, and urban mobility solutions. Vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communication enhances traffic flow, reduces emissions, and improves overall transportation efficiency.
Conclusion
Future trends in in-vehicle networks are driven by technological advancements, regulatory requirements, and evolving consumer preferences for connected services and enhanced driving experiences. By embracing innovations in connectivity, cybersecurity, and user-centric design, automotive stakeholders shape the future of mobility, redefine industry standards, and accelerate the adoption of next-generation in-vehicle networks.
0 notes
Text
IBM Engineering Systems Design Rhapsody 10.0.1 Declaration

Rational Rhapsody 10.0.1
Design of IBM Engineering Systems Strong model-based systems engineering (MBSE) tools like Rhapsody make it easier to design, analyze, and validate complex systems and create software based on those models. The complete product development lifecycle, including specification, development, testing, and delivery, is easily integrated into Rhapsody thanks to its strong support for the unified modeling language (UML) and systems modeling language (SysML).
IBM Engineering Systems Design Rhapsody
Deliver software and systems of higher quality more quickly with digital threading across domains, production code generation, smooth simulation, and reliable modeling.
- Advertisement -
What services does Rhapsody offer?
With its suite of tools, IBM Engineering Systems Design Rhapsody (formerly known as Rational Rhapsody) provides a tried-and-true method for modeling and systems design tasks, enabling you to handle the complexity that many organizations encounter while developing new products and systems. Rhapsody is a component of the IBM Engineering portfolio, offering systems engineers a collaborative design, development, and testing environment that supports AUTOSAR import and export capabilities along with UML, SysML, and UAF. Furthermore, the solution speeds up industry standards like ISO 26262, DO-178, DO-178B/C, and UPDM and permits control of defense frameworks like DoDAF, MODAF, and UPDM.
Advantages
Provides ongoing validation
Utilize quick simulation, prototyping, and execution to get ongoing validation and address mistakes early on, when they can be fixed more affordably.
Offers automated consistency verification
Employ collaborative reuse and automatic consistency checking to boost agility and lower recurring and non-recurring expenses.
Work together with your engineering group
With the use of design tools like Mathworks Simulink or Engineering Systems Design Rhapsody, you can share, work with, and evaluate your engineering lifecycle artifacts with the larger engineering team.
- Advertisement -
Usability
Simplify the design process with a cutting-edge UX that lets you customize the tool interface to your own requirements and tastes, making model visualization simpler.
Crucial characteristics of IBM Rhapsody goods
Examine and clarify the project’s needs
System specifications, interface design papers, and system test cases are automatically generated by the software using SysML, UML, UAF, and AUTOSAR import and export capabilities.
Go from design to implementation quickly
With the use of UML, it provides an affordable comprehensive software engineering environment for graphically designing C++, C, or Java applications.
Create documentation and automate design reviews
Using a central repository accessible via the web, Rhapsody – Model Manager facilitates cross-disciplinary team collaboration, sharing, review, and management of designs and models. Customers and suppliers can use a web client to access information. The program streamlines stakeholder communication, expedites decision-making, and enhances quality by automating design evaluations. Comprehensive documentation can be produced for reporting, compliance, communication, and specifications.
Develop, model, and implement designs for early verification
In addition to having all the features of Rhapsody Architect for Systems Engineers, Rhapsody – Designer for Systems Engineers enables you to simulate, prototype, and carry out designs for early requirements, architecture, and behavior validation. This is a model-based system engineering (MBSE) environment that makes use of the widely used SysML and UML frameworks. With enhanced validation and simulation, it shortens time-to-market, increases productivity, and helps you adjust to changing client requirements.
Engage in an agile engineering environment that is embedded and real-time
Agile software engineering environment for C++, C, Java, and Ada that is embedded and real-time (includes MISRA-C and MISRA-C++) is provided by Rhapsody – Developer. Along with the features of IBM Engineering Systems Design Rhapsody (Rational Rhapsody) – Architect for Software, it offers fast prototyping and simulation for design-level debugging, automated build generation for continuous integration, and support for safety-critical software lifecycle issues.
Allow for the smooth integration of the AUTOSAR standard. The AUTOSAR Extension is a part of IBM Rhapsody Model-Driven Development (MDD). This potent combination streamlines and expedites the process of developing automotive software, freeing up developers to concentrate on building reliable and effective solutions that satisfy the stringent demands of the modern industry.
Rhapsody 10.0.1
IBM is pleased to announce the introduction of IBM Engineering Systems Design Rhapsody version 10.0.1, which includes several new features and changes aimed at optimizing usability, automation, and integration.
Improved DOORS 9 integration promotes consistency and productivity
Rhapsody 10.0.1 enhances accuracy, traceability, and smoother operations by providing closer connection with the IBM Requirements Management DOORS system.
The new ReqXChanger interaction with DOORS 9 is crucial to this release. With better requirement visualization and traceability straight within Rhapsody, ReqXChanger replaces the Rhapsody Gateway and enables a more efficient workflow between Rhapsody and DOORS.
With seamless movement across the digital thread connecting DOORS and Rhapsody, users can now access and inspect model diagrams and elements in DOORS 9. The transition to the improved functionality is easy and seamless.
Change-aware synchronization maintains requirements and model in sync between Rhapsody 10.0.1 and DOORS 9, reducing effort and complexity in tracking changes in artifacts. To fit the unique requirements and surroundings of the users, this synchronization can be automated and tailored.
Extending IBM collaboration with Siemens to improve systems design through automation and integration
IBM has one major enhancement in this release as part of our continued collaboration between the Siemens and IBM product teams. By combining several components, this improvement aims to strengthen the digital thread and promote visibility, traceability, and interoperability.
Now, you may establish connections between Siemens Teamcenter specifications and parameters and model elements: To correlate Teamcenter requirements and parameters with model elements, choose them in the Rhapsody UI. Request the enabling plug-ins by contacting Siemens.
Significant improvements to workflows, usability, and testing
Better testing and usability are more important as system design complexity and interconnection increase. To address this difficulty, Rhapsody 10.0.1 has added new features and improved Test Conductor, such as increased test case coverage that offers a thorough rundown of all test cases. By transferring message-related test scenarios across multiple architectures, a technical preview of Message Mapper further streamlines scenario mapping.
Additional parallel development prompts improve design process efficiency by warning users when they are working with out-of-date model versions, streamlining merge operations, and fostering better teamwork. The product interface has been improved, allowing for more menu controls, such as toolbar and pop-up menu items, to enable complex customisation.
Rhapsody 10.0.1’s enhancements to the Rhapsody AUTOSAR Extension aid teams in managing challenging projects and increasing output. The installation package includes updated example models that are useful for understanding and implementing AUTOSAR standards.
Try out Rhapsody 10.0.1, IBM Engineering Systems Design, right now
Rhapsody 10.0.1 keeps up its good work as a top MBSE tool by providing enhanced automation, usability, and integration to facilitate the design and implementation of complex systems. Additionally, it advances the cooperation between IBM and Siemens Digital Industries Software in their quest to develop strong system engineering tools that empower businesses to design, develop, and produce high-performing, environmentally friendly products.
Read more on govindhtech.com
#IBMEngineeringSystems#SysM#design#IBMproduct#DesignRhapsody1001Declaration#featuresofIBM#systemdesign#automation#workflows#productivity#IBMcollaboration#ImprovedDOORS9#ibm#technology#technews#news#govindhtech
0 notes
Text
SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT & INTEGRATION PARTNER FOR BODY, GATEWAY & HIGH-PERFORMANCE COMPUTE PLATFORMS
KPIT provides comprehensive solutions for Vehicle Body & Gateway from concept development to maintenance for current & next generation programs
AUTOSAR Stack Integration
High Performance Compute – HPC & Zonal Architecture
Multicore Architecture
Future Technologies
Application Migration and Integration
Functional Safety
Cyber Security
Virtual Validation
Body electronics - Offerings
SDV Programs
Body System Engineering Services

Application Development & Integration Services
Body Features Validation Service
High-Performance Compute (HPC) Application
Zonal ECUs
System Architecture Definition (SoA + signal based) and Specification development
EE architecture and System model using PREEVision, MagicDraw, Rhapsody, EA
ISO 26262 based Functional Safety analysis (HARA, DFMEA)
Cyber security TARA analysis
System Architecture Definition (SoA + signal based)
Application Migration strategy definition for Classic/Adaptive SWCs
Application and Feature development in MBD/CBD
End-to-end Body feature software integration
Multidomain Feature Integration in HPC and Zonal ECUs
Model based Testing (MIL, SIL)
Plant model development for Body features
Body Virtual Validation Platform development
HIL testing of different Body features & Test Automation using dSPACE, Vector & KPIT Solutions (Technica)
Vehicle Testing and Calibration
Single Function ECU
Architecture re-design of legacy system based on new SDV systems
Migration of legacy system requirement to Model based system engineering
Application and Feature development in MBD/CBD
Body software Model based Testing (MIL, SIL and PIL)
Body Virtual validation platform development with standalone ECUs
#Body electronics#Body System Engineering Services#Application Development & Integration Services#Body Features Validation Service#SDV programs#vehicle body and gateway solutions#Body & Gateway software development#Body Gateway Module#automotive
0 notes
Text
Functional Safety (FuSa) Services in India, USA, Europe
Leading automakers are quickly evolving to Software Defined Vehicles, with modern vehicles having multiple electronic systems with millions of lines of code running on them. In an industry like Automotive, humans are increasingly dependent on electronic systems to monitor and control many aspects of the vehicle. Therefore passenger safety becomes paramount.
Functional Safety (FuSa) Services is an integral part of the product development process in any Automotive Electrical and Electronic system, to ensure the safe and reliable operation of the system. Therefore, FuSa is about adopting a systematic approach to identify, assess, and devise ways to mitigate the risk/potential hazards that may arise. In other words, should something fail, we want it to fail predictably.
For automotive applications, the “ISO 26262 - Road vehicles -Functional safety Services” standard serves as the directive based on which the Functional safety development process is to be based.
Functional Safety Process
We begin by conducting a thorough Hazard and Risk Analysis (HARA) where potential risks are identified and categorized. This is used to determine the ASIL Level ranging from A to D. Further analysis is conducted by DFMEA (Design Failure Mode Effect Analysis) and FMEDA (Failure modes, Effects and Diagnostic Analysis), and based on the assessment, the Functional Safety concept is developed, where safety requirements are defined and this is used to arrive at the System Level, Hardware and Software level requirements are defined in the implementation phase, along with rigorous testing and validation procedures used to ensure that the system meets the designed requirements. We base these processes as guided by ISO 26262 standards that is crucial in ensuring that the electronic systems operate predictably and can handle failures and events in a predetermined manner.
Our Functional Safety Services
We support major parts of ISO 26262 development such as the Concept Phase, Product Development at the System, Hardware, and Software Levels, along with Supporting processes.
Our team has a wide range of experience from more than a decade of working on individual system projects and full vehicle development projects. We can support individual aspects of the process as well as end-to-end services, traveling along with the development process.
0 notes
Text
Microchip launches new 10BASE-T1S Ethernet solution to help OEMs easily connect automotive devices

【Lansheng Technology News】Microchip Technology Inc. today announced the launch of the LAN8650/1 MAC-PHY series of new devices that meet automotive application requirements, further expanding its automotive-grade Ethernet solution product lineup. The LAN8650 and LAN8651 MAC-PHY include a media access controller and serial peripheral interface for connecting devices at the edge of the automotive network.
The LAN8650/1 device with built-in MAC and SPI enables designers to connect 8-, 16- and 32-bit microcontrollers without built-in Ethernet MAC to 10BASE-T1S single-pair Ethernet networks. This enables sensors and actuators that connect the digital and real worlds to become part of a full Ethernet architecture. Connecting to even the simplest microcontrollers reduces the overall size and cost of the design.
Matthias Kaestner, vice president of Microchip's automotive business, said: "Microchip will continue to develop automotive connectivity solutions through the 10BASE-T1S product line to provide the industry with turnkey solutions that meet customer requirements. This new technology will bring sensors and execution to the physical world. The controller is always connected to the cloud, enabling a seamless Ethernet architecture in the car, reducing development effort and time to market."
The new family of devices has built-in Time Sensitive Networking (TSN) support, enabling synchronized timing on long-distance Ethernet networks. This time synchronization is critical for many automotive applications such as advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS).
The LAN8650/1 MAC-PHY is automotive qualified and meets AEC-Q100 Level 1 certification standards for enhanced stability in harsh environments, including extended operating temperature range of -40ºC to 125ºC. These devices meet functional safety requirements and are suitable for ISO 26262 applications.
Ethernet solutions maintain strong momentum in the automotive industry due to their comprehensive security protocols to ensure network system security. These systems can be extended to the edge of the network without requiring extensive changes or new development efforts.
Lansheng Technology Limited, which is a spot stock distributor of many well-known brands, we have price advantage of the first-hand spot channel, and have technical supports.
Our main brands: STMicroelectronics, Toshiba, Microchip, Vishay, Marvell, ON Semiconductor, AOS, DIODES, Murata, Samsung, Hyundai/Hynix, Xilinx, Micron, Infinone, Texas Instruments, ADI, Maxim Integrated, NXP, etc
To learn more about our products, services, and capabilities, please visit our website at http://www.lanshengic.com
0 notes
Text
The automotive industry
HISTORY
The automotive industry began in the 1860s with hundreds of manufacturers that pioneered the horseless carriage. For many decades, the United States led the world in total automobile production. In 1929, before the Great Depression, the world had 32,028,500 automobiles in use, and the U.S. automobile industry produced over 90% of them. At that time, the U.S. had one car per 4.87 persons. After 1945, the U.S. produced about 75 percent of world's auto production. In 1980, the U.S. was overtaken by Japan and then became world leader again in 1994. In 2006, Japan narrowly passed the U.S. in production and held this rank until 2009, when China took the top spot with 13.8 million units. With 19.3 million units manufactured in 2012, China almost doubled the U.S. production of 10.3 million units, while Japan was in third place with 9.9 million units. From 1970 (140 models) over 1998 (260 models) to 2012 (684 models), the number of automobile models in the U.S. has grown exponentially.
Early car manufacturing involved manual assembly by a human worker. The process evolved from engineers working on a stationary car, to a conveyor belt system where the car passed through multiple stations of more specialised engineers. Starting in the 1960s, robotic equipment was introduced to the process, and today most cars are produced largely with automated machinary.
SAFETY
Safety is a state that implies being protected from any risk, danger, damage, or cause of injury. In the automotive industry, safety means that users, operators, or manufacturers do not face any risk or danger coming from the motor vehicle or its spare parts. Safety for the automobiles themselves implies that there is no risk of damage.
Safety in the automotive industry is particularly important and therefore highly regulated. Automobiles and other motor vehicles have to comply with a certain number of regulations, whether local or international, in order to be accepted on the market. The standard ISO 26262, is considered one of the best practice frameworks for achieving automotive functional safety.
In case of safety issues, danger, product defect or faulty procedure during the manufacturing of the motor vehicle, the maker can request to return either a batch or the entire production run. This procedure is called product recall. Product recalls happen in every industry and can be production-related or stem from raw material.
Product and operation tests and inspections at different stages of the value chain are made to avoid these product recalls by ensuring end-user security and safety and compliance with the automotive industry requirements. However, the automotive industry is still particularly concerned about product recalls, which cause considerable financial consequences.
MR.AUTOMOTIVE
Mr.Automotive is one of the best automotive industry in kerala, since 2020. Mr.Automotive provides several services to our customers with exciting offers. The customer can access the sevices through our official Mr.Automotive application. Mr.automotive providing services are vehicle services like mechanical,water wash,spare parts,tyre services,pick up vehicles, rent a car, taxi services, etc. In our services, the customer can scedule the vehicle pickup time,then our worker will comes to your door, then collect the vehicle, after the work we will deliver your vehicle to your home, the customer can buy spare parts from our application. now a days Mr.Automotive is the best option for customers to deal with the vehicle issues.
for more information - https://mrautomotive10.000webhostapp.com/
1 note
·
View note