#GREAT Scholarship
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
A Comprehensive Guide to UK Government Scholarships for International Students
Studying in the United Kingdom is an exciting opportunity for international students, but the cost of tuition, living expenses, and travel can often be a significant hurdle. Fortunately, UK government scholarships offer a way to make this dream a reality for many students. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the various UK government scholarships available to international students, the eligibility criteria, the application process, and the benefits these scholarships offer. If you're interested in learning more about UK government scholarships, check out this University ranking in UK.
Types of UK Government Scholarships for International Students
The UK government provides several scholarships to international students, each with its own set of benefits and requirements. These scholarships aim to attract talented students from around the world and support their educational journey in the UK. Here are some of the most popular options:
Chevening Scholarships The Chevening Scholarship is the UK government's global scholarship program, offering full financial support for students to pursue a one-year master's degree at any UK university. This prestigious scholarship is open to students from over 160 countries. It covers tuition fees, travel costs, and a monthly stipend, making it an excellent opportunity for those looking to study in the UK without financial stress.
Commonwealth Scholarships The Commonwealth Scholarship Commission (CSC) offers scholarships to students from Commonwealth countries. These scholarships cover full tuition fees, airfare, and a stipend for living costs. The Commonwealth Scholarship is available for both master's and PhD programs, and it aims to promote international development by educating future leaders.
The GREAT Scholarship The GREAT Scholarship is a joint initiative between the UK government and universities across the UK, offering a range of scholarships for students from China, India, Indonesia, Malaysia, Thailand, and other countries. This scholarship offers a partial financial contribution towards tuition fees, and it focuses on supporting students studying subjects related to sustainable development and innovation.
The Marshall Scholarship Although not directly funded by the UK government, the Marshall Scholarship is a prestigious program that provides funding for US students to pursue postgraduate degrees at any UK university. It covers tuition fees, living expenses, and travel costs, and it aims to foster strong ties between the UK and the US.

Eligibility Criteria for UK Government Scholarships
Each UK government scholarship has its own eligibility criteria, but there are some general guidelines that most programs share:
Academic Excellence: Most scholarships require students to have a strong academic background. This includes having excellent grades in relevant subjects and demonstrating academic potential.
Nationality: Some scholarships are available only to students from specific countries or regions. For instance, Chevening Scholarships are open to students from over 160 countries, while Commonwealth Scholarships are aimed at students from Commonwealth nations.
Work Experience: Some scholarships, such as Chevening, also require applicants to have relevant work experience. This is usually 2-3 years of professional experience, although the specifics may vary depending on the scholarship.
English Language Proficiency: Since courses in the UK are taught in English, most scholarships require proof of English language proficiency through tests like IELTS or TOEFL.
Program Level: Certain scholarships may be restricted to specific academic levels. For example, Chevening and Commonwealth Scholarships are available for master's and PhD students, whereas the GREAT Scholarship focuses on undergraduate and postgraduate studies.
The Application Process for UK Government Scholarships
The application process for UK government scholarships can be competitive, but with careful planning, you can maximize your chances of success. Here’s a general guide to help you:
Research Available Scholarships: Before applying, make sure you research all available UK government scholarships to determine which one suits your academic background, career goals, and nationality.
Prepare Required Documents: Most scholarships require academic transcripts, a statement of purpose, letters of recommendation, and proof of English language proficiency. Make sure all your documents are in order before applying.
Apply Through the Scholarship Portal: Each scholarship has its own application portal. For example, Chevening Scholarships have an online application system that requires you to submit your personal details, academic background, and work experience. Similarly, Commonwealth Scholarships have a separate portal.
Write a Strong Personal Statement: Your personal statement plays a crucial role in the selection process. This is where you can showcase your academic achievements, career goals, and how the scholarship will help you achieve them.
Submit the Application: After gathering all your documents and completing the online application, make sure to double-check everything before submission. Some scholarships have specific deadlines, so be sure to submit your application well in advance.

Benefits of UK Government Scholarships
Receiving a UK government scholarship comes with several benefits that go beyond financial assistance. Here are some of the key advantages:
Full Financial Support: Many UK government scholarships, such as Chevening and Commonwealth Scholarships, offer full financial coverage, including tuition fees, living expenses, and travel costs. This allows you to focus entirely on your studies without worrying about finances.
Access to Prestigious Universities: UK government scholarships provide opportunities to study at some of the best universities in the world, such as Oxford, Cambridge, and Imperial College London.
Networking Opportunities: As a scholarship recipient, you will be part of a global network of scholars, professionals, and policymakers. This opens doors to valuable networking opportunities, mentorship, and career development.
Enhancing Career Prospects: UK universities are known for their academic excellence, and graduating with a UK degree is highly respected globally. Scholarship recipients often have an edge when it comes to securing competitive jobs in their home country or abroad.
Conclusion: Making Studying in the UK More Accessible
UK government scholarships are an excellent way for international students to gain access to world-class education without the financial burden. Whether it’s the Chevening Scholarship, Commonwealth Scholarship, or GREAT Scholarship, there is a range of opportunities to suit different academic backgrounds and career goals. These scholarships not only provide financial support but also open doors to personal and professional growth in a global setting. To learn more about UK government scholarships and explore your options, visit University ranking in UK.
#UK Government Scholarships#Scholarships for International Students#Study in the UK#Chevening Scholarships#Commonwealth Scholarships#GREAT Scholarship#UK Scholarships for Students#International Scholarships in the UK#Scholarships for Master's Students#UK Study Funding#Study Abroad Scholarships#UK University Scholarships#Financial Aid for International Students#UK Education Scholarships#Scholarships for International Postgraduate Students
0 notes
Text
Gig apps trap reverse centaurs in Skinner boxes
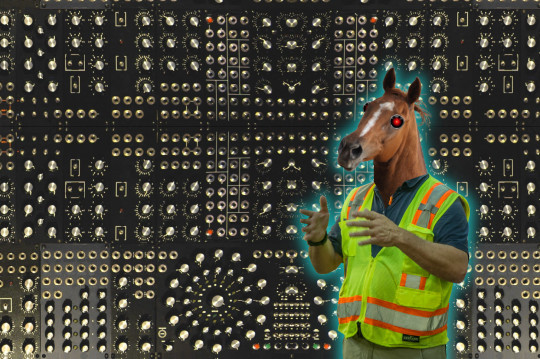
Enshittification is the process by which digital platforms devour themselves: first they dangle goodies in front of end users. Once users are locked in, the goodies are taken away and dangled before business customers who supply goods to the users. Once those business customers are stuck on the platform, the goodies are clawed away and showered on the platform’s shareholders:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/01/21/potemkin-ai/#hey-guys
If you’d like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here’s a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/04/12/algorithmic-wage-discrimination/#fishers-of-men
Enshittification isn’t just another way of saying “fraud” or “price gouging” or “wage theft.” Enshittification is intrinsically digital, because moving all those goodies around requires the flexibility that only comes with a digital businesses. Jeff Bezos, grocer, can’t rapidly change the price of eggs at Whole Foods without an army of kids with pricing guns on roller-skates. Jeff Bezos, grocer, can change the price of eggs on Amazon Fresh just by twiddling a knob on the service’s back-end.
Twiddling is the key to enshittification: rapidly adjusting prices, conditions and offers. As with any shell game, the quickness of the hand deceives the eye. Tech monopolists aren’t smarter than the Gilded Age sociopaths who monopolized rail or coal — they use the same tricks as those monsters of history, but they do them faster and with computers:
https://doctorow.medium.com/twiddler-1b5c9690cce6
If Rockefeller wanted to crush a freight company, he couldn’t just click a mouse and lay down a pipeline that ran on the same route, and then click another mouse to make it go away when he was done. When Bezos wants to bankrupt Diapers.com — a company that refused to sell itself to Amazon — he just moved a slider so that diapers on Amazon were being sold below cost. Amazon lost $100m over three months, diapers.com went bankrupt, and every investor learned that competing with Amazon was a losing bet:
https://slate.com/technology/2013/10/amazon-book-how-jeff-bezos-went-thermonuclear-on-diapers-com.html
That’s the power of twiddling — but twiddling cuts both ways. The same flexibility that digital businesses enjoy is hypothetically available to workers and users. The airlines pioneered twiddling ticket prices, and that naturally gave rise to countertwiddling, in the form of comparison shopping sites that scraped the airlines’ sites to predict when tickets would be cheapest:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/02/27/knob-jockeys/#bros-be-twiddlin
The airlines — like all abusive businesses — refused to tolerate this. They were allowed to touch their knobs as much as they wanted — indeed, they couldn’t stop touching those knobs — but when we tried to twiddle back, that was “felony contempt of business model,” and the airlines sued:
https://www.cnbc.com/2014/12/30/airline-sues-man-for-founding-a-cheap-flights-website.html
And sued:
https://www.nytimes.com/2018/01/06/business/southwest-airlines-lawsuit-prices.html
Platforms don’t just hate it when end-users twiddle back — if anything they are even more aggressive when their business-users dare to twiddle. Take Para, an app that Doordash drivers used to get a peek at the wages offered for jobs before they accepted them — something that Doordash hid from its workers. Doordash ruthlessly attacked Para, saying that by letting drivers know how much they’d earn before they did the work, Para was violating the law:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2021/08/tech-rights-are-workers-rights-doordash-edition
Which law? Well, take your pick. The modern meaning of “IP” is “any law that lets me use the law to control my competitors, competition or customers.” Platforms use a mix of anticircumvention law, patent, copyright, contract, cybersecurity and other legal systems to weave together a thicket of rules that allow them to shut down rivals for their Felony Contempt of Business Model:
https://locusmag.com/2020/09/cory-doctorow-ip/
Enshittification relies on unlimited twiddling (by platforms), and a general prohibition on countertwiddling (by platform users). Enshittification is a form of fishing, in which bait is dangled before different groups of users and then nimbly withdrawn when they lunge for it. Twiddling puts the suppleness into the enshittifier’s fishing-rod, and a ban on countertwiddling weighs down platform users so they’re always a bit too slow to catch the bait.
Nowhere do we see twiddling’s impact more than in the “gig economy,” where workers are misclassified as independent contractors and put to work for an app that scripts their every move to the finest degree. When an app is your boss, you work for an employer who docks your pay for violating rules that you aren’t allowed to know — and where your attempts to learn those rules are constantly frustrated by the endless back-end twiddling that changes the rules faster than you can learn them.
As with every question of technology, the issue isn’t twiddling per se — it’s who does the twiddling and who gets twiddled. A worker armed with digital tools can play gig work employers off each other and force them to bid up the price of their labor; they can form co-ops with other workers that auto-refuse jobs that don’t pay enough, and use digital tools to organize to shift power from bosses to workers:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/12/02/not-what-it-does/#who-it-does-it-to
Take “reverse centaurs.” In AI research, a “centaur” is a human assisted by a machine that does more than either could do on their own. For example, a chess master and a chess program can play a better game together than either could play separately. A reverse centaur is a machine assisted by a human, where the machine is in charge and the human is a meat-puppet.
Think of Amazon warehouse workers wearing haptic location-aware wristbands that buzz at them continuously dictating where their hands must be; or Amazon drivers whose eye-movements are continuously tracked in order to penalize drivers who look in the “wrong” direction:
https://pluralistic.net/2021/02/17/reverse-centaur/#reverse-centaur
The difference between a centaur and a reverse centaur is the difference between a machine that makes your life better and a machine that makes your life worse so that your boss gets richer. Reverse centaurism is the 21st Century’s answer to Taylorism, the pseudoscience that saw white-coated “experts” subject workers to humiliating choreography down to the smallest movement of your fingertip:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/08/21/great-taylors-ghost/#solidarity-or-bust
While reverse centaurism was born in warehouses and other company-owned facilities, gig work let it make the leap into workers’ homes and cars. The 21st century has seen a return to the cottage industry — a form of production that once saw workers labor far from their bosses and thus beyond their control — but shriven of the autonomy and dignity that working from home once afforded:
https://doctorow.medium.com/gig-work-is-the-opposite-of-steampunk-463e2730ef0d
The rise and rise of bossware — which allows for remote surveillance of workers in their homes and cars — has turned “work from home” into “live at work.” Reverse centaurs can now be chickenized — a term from labor economics that describes how poultry farmers, who sell their birds to one of three vast poultry processors who have divided up the country like the Pope dividing up the “New World,” are uniquely exploited:
https://onezero.medium.com/revenge-of-the-chickenized-reverse-centaurs-b2e8d5cda826
A chickenized reverse centaur has it rough: they must pay for the machines they use to make money for their bosses, they must obey the orders of the app that controls their work, and they are denied any of the protections that a traditional worker might enjoy, even as they are prohibited from deploying digital self-help measures that let them twiddle back to bargain for a better wage.
All of this sets the stage for a phenomenon called algorithmic wage discrimination, in which two workers doing the same job under the same conditions will see radically different payouts for that work. These payouts are continuously tweaked in the background by an algorithm that tries to predict the minimum sum a worker will accept to remain available without payment, to ensure sufficient workers to pick up jobs as they arise.
This phenomenon — and proposed policy and labor solutions to it — is expertly analyzed in “On Algorithmic Wage Discrimination,” a superb paper by UC Law San Franciscos Veena Dubal:
https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=4331080
Dubal uses empirical data and enthnographic accounts from Uber drivers and other gig workers to explain how endless, self-directed twiddling allows gig companies pay workers less and pay themselves more. As @[email protected] explains in his LA Times article on Dubal’s research, the goal of the payment algorithm is to guess how often a given driver needs to receive fair compensation in order to keep them driving when the payments are unfair:
https://www.latimes.com/business/technology/story/2023-04-11/algorithmic-wage-discrimination
The algorithm combines nonconsensual dossiers compiled on individual drivers with population-scale data to seek an equilibrium between keeping drivers waiting, unpaid, for a job; and how much a driver needs to be paid for an individual job, in order to keep that driver from clocking out and doing something else. @ Here’s how that works. Sergio Avedian, a writer for The Rideshare Guy, ran an experiment with two brothers who both drove for Uber; one drove a Tesla and drove intermittently, the other brother rented a hybrid sedan and drove frequently. Sitting side-by-side with the brothers, Avedian showed how the brother with the Tesla was offered more for every trip:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UADTiL3S67I
Uber wants to lure intermittent drivers into becoming frequent drivers. Uber doesn’t pay for an oversupply of drivers, because it only pays drivers when they have a passenger in the car. Having drivers on call — but idle — is a way for Uber to shift the cost of maintaining a capacity cushion to its workers.
What’s more, what Uber charges customers is not based on how much it pays its workers. As Uber’s head of product explained: Uber uses “machine-learning techniques to estimate how much groups of customers are willing to shell out for a ride. Uber calculates riders’ propensity for paying a higher price for a particular route at a certain time of day. For instance, someone traveling from a wealthy neighborhood to another tony spot might be asked to pay more than another person heading to a poorer part of town, even if demand, traffic and distance are the same.”
https://qz.com/990131/uber-is-practicing-price-discrimination-economists-say-that-might-not-be-a-bad-thing/
Uber has historically described its business a pure supply-and-demand matching system, where a rush of demand for rides triggers surge pricing, which lures out drivers, which takes care of the demand. That’s not how it works today, and it’s unclear if it ever worked that way. Today, a driver who consults the rider version of the Uber app before accepting a job — to compare how much the rider is paying to how much they stand to earn — is booted off the app and denied further journeys.
Surging, instead, has become just another way to twiddle drivers. One of Dubal’s subjects, Derrick, describes how Uber uses fake surges to lure drivers to airports: “You go to the airport, once the lot get kind of full, then the surge go away.” Other drivers describe how they use groupchats to call out fake surges: “I’m in the Marina. It’s dead. Fake surge.”
That’s pure twiddling. Twiddling turns gamification into gamblification, where your labor buys you a spin on a roulette wheel in a rigged casino. As a driver called Melissa, who had doubled down on her availability to earn a $100 bonus awarded for clocking a certain number of rides, told Dubal, “When you get close to the bonus, the rides start trickling in more slowly…. And it makes sense. It’s really the type of shit that they can do when it’s okay to have a surplus labor force that is just sitting there that they don’t have to pay for.”
Wherever you find reverse-centaurs, you get this kind of gamblification, where the rules are twiddled continuously to make sure that the house always wins. As a contract driver Amazon reverse centaur told Lauren Gurley for Motherboard, “Amazon uses these cameras allegedly to make sure they have a safer driving workforce, but they’re actually using them not to pay delivery companies”:
https://www.vice.com/en/article/88npjv/amazons-ai-cameras-are-punishing-drivers-for-mistakes-they-didnt-make
Algorithmic wage discrimination is the robot overlord of our nightmares: its job is to relentlessly quest for vulnerabilities and exploit them. Drivers divide themselves into “ants” (drivers who take every job) and “pickers” (drivers who cherry-pick high-paying jobs). The algorithm’s job is ensuring that pickers get the plum assignments, not the ants, in the hopes of converting those pickers to app-dependent ants.
In my work on enshittification, I call this the “giant teddy bear” gambit. At every county fair, you’ll always spot some poor jerk carrying around a giant teddy-bear they “won” on the midway. But they didn’t win it — not by getting three balls in the peach-basket. Rather, the carny running the rigged game either chose not to operate the “scissor” that kicks balls out of the basket. Or, if the game is “honest” (that is, merely impossible to win, rather than gimmicked), the operator will make a too-good-to-refuse offer: “Get one ball in and I’ll give you this keychain. Win two keychains and I’ll let you trade them for this giant teddy bear.”
Carnies aren’t in the business of giving away giant teddy bears — rather, the gambit is an investment. Giving a mark a giant teddy bear to carry around the midway all day acts as a convincer, luring other marks to try to land three balls in the basket and win their own teddy bear.
In the same way, platforms like Uber distribute giant teddy bears to pickers, as a way of keeping the ants scurrying from job to job, and as a way of convincing the pickers to give up whatever work allows them to discriminate among Uber’s offers and hold out for the plum deals, whereupon then can be transmogrified into ants themselves.
Dubal describes the experience of Adil, a Syrian refugee who drives for Uber in the Bay Area. His colleagues are pickers, and showed him screenshots of how much they earned. Determined to get a share of that money, Adil became a model ant, driving two hours to San Francisco, driving three days straight, napping in his car, spending only one day per week with his family. The algorithm noticed that Adil needed the work, so it paid him less.
Adil responded the way the system predicted he would, by driving even more: “My friends they make it, so I keep going, maybe I can figure it out. It’s unsecure, and I don’t know how people they do it. I don’t know how I am doing it, but I have to. I mean, I don’t find another option. In a minute, if I find something else, oh man, I will be out immediately. I am a very patient person, that’s why I can continue.”
Another driver, Diego, told Dubal about how the winners of the giant teddy bears fell into the trap of thinking that they were “good at the app”: “Any time there’s some big shot getting high pay outs, they always shame everyone else and say you don’t know how to use the app. I think there’s secret PR campaigns going on that gives targeted payouts to select workers, and they just think it’s all them.”
That’s the power of twiddling: by hoarding all the flexibility offered by digital tools, the management at platforms can become centaurs, able to string along thousands of workers, while the workers are reverse-centaurs, puppeteered by the apps.
As the example of Adil shows, the algorithm doesn’t need to be very sophisticated in order to figure out which workers it can underpay. The system automates the kind of racial and gender discrimination that is formally illegal, but which is masked by the smokescreen of digitization. An employer who systematically paid women less than men, or Black people less than white people, would be liable to criminal and civil sanctions. But if an algorithm simply notices that people who have fewer job prospects drive more and will thus accept lower wages, that’s just “optimization,” not racism or sexism.
This is the key to understanding the AI hype bubble: when ghouls from multinational banks predict 13 trillion dollar markets for “AI,” what they mean is that digital tools will speed up the twiddling and other wage-suppression techniques to transfer $13T in value from workers and consumers to shareholders.
The American business lobby is relentlessly focused on the goal of reducing wages. That’s the force behind “free trade,” “right to work,” and other codewords for “paying workers less,” including “gig work.” Tech workers long saw themselves as above this fray, immune to labor exploitation because they worked for a noble profession that took care of its own.
But the epidemic of mass tech-worker layoffs, following on the heels of massive stock buybacks, has demonstrated that tech bosses are just like any other boss: willing to pay as little as they can get away with, and no more. Tech bosses are so comfortable with their market dominance and the lock-in of their customers that they are happy to turn out hundreds of thousands of skilled workers, convinced that the twiddling systems they’ve built are the kinds of self-licking ice-cream cones that are so simple even a manager can use them — no morlocks required.
The tech worker layoffs are best understood as an all-out war on tech worker morale, because that morale is the source of tech workers’ confidence and thus their demands for a larger share of the value generated by their labor. The current tech layoff template is very different from previous tech layoffs: today’s layoffs are taking place over a period of months, long after they are announced, and laid off tech worker is likely to be offered a months of paid post-layoff work, rather than severance. This means that tech workplaces are now haunted by the walking dead, workers who have been laid off but need to come into the office for months, even as the threat of layoffs looms over the heads of the workers who remain. As an old friend, recently laid off from Microsoft after decades of service, wrote to me, this is “a new arrow in the quiver of bringing tech workers to heel and ensuring that we’re properly thankful for the jobs we have (had?).”
Dubal is interested in more than analysis, she’s interested in action. She looks at the tactics already deployed by gig workers, who have not taken all this abuse lying down. Workers in the UK and EU organized through Worker Info Exchange and the App Drivers and Couriers Union have used the GDPR (the EU’s privacy law) to demand “algorithmic transparency,” as well as access to their data. In California, drivers hope to use similar provisions in the CCPA (a state privacy law) to do the same.
These efforts have borne fruit. When Cornell economists, led by Louis Hyman, published research (paid for by Uber) claiming that Uber drivers earned an average of $23/hour, it was data from these efforts that revealed the true average Uber driver’s wage was $9.74. Subsequent research in California found that Uber drivers’ wage fell to $6.22/hour after the passage of Prop 22, a worker misclassification law that gig companies spent $225m to pass, only to have the law struck down because of a careless drafting error:
https://www.latimes.com/california/newsletter/2021-08-23/proposition-22-lyft-uber-decision-essential-california
But Dubal is skeptical that data-coops and transparency will achieve transformative change and build real worker power. Knowing how the algorithm works is useful, but it doesn’t mean you can do anything about it, not least because the platform owners can keep touching their knobs, twiddling the payout schedule on their rigged slot-machines.
Data co-ops start from the proposition that “data extraction is an inevitable form of labor for which workers should be remunerated.” It makes on-the-job surveillance acceptable, provided that workers are compensated for the spying. But co-ops aren’t unions, and they don’t have the power to bargain for a fair price for that data, and coops themselves lack the vast resources — “to store, clean, and understand” — data.
Co-ops are also badly situated to understand the true value of the data that is extracted from their members: “Workers cannot know whether the data collected will, at the population level, violate the civil rights of others or amplifies their own social oppression.”
Instead, Dubal wants an outright, nonwaivable prohibition on algorithmic wage discrimination. Just make it illegal. If firms cannot use gambling mechanisms to control worker behavior through variable pay systems, they will have to find ways to maintain flexible workforces while paying their workforce predictable wages under an employment model. If a firm cannot manage wages through digitally-determined variable pay systems, then the firm is less likely to employ algorithmic management.”
In other words, rather than using market mechanisms too constrain platform twiddling, Dubal just wants to make certain kinds of twiddling illegal. This is a growing trend in legal scholarship. For example, the economist Ramsi Woodcock has proposed a ban on surge pricing as a per se violation of Section 1 of the Sherman Act:
https://ilr.law.uiowa.edu/print/volume-105-issue-4/the-efficient-queue-and-the-case-against-dynamic-pricing
Similarly, Dubal proposes that algorithmic wage discrimination violates another antitrust law: the Robinson-Patman Act, which “bans sellers from charging competing buyers different prices for the same commodity. Robinson-Patman enforcement was effectively halted under Reagan, kicking off a host of pathologies, like the rise of Walmart:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/03/27/walmarts-jackals/#cheater-sizes
I really liked Dubal’s legal reasoning and argument, and to it I would add a call to reinvigorate countertwiddling: reforming laws that get in the way of workers who want to reverse-engineer, spoof, and control the apps that currently control them. Adversarial interoperability (AKA competitive compatibility or comcom) is key tool for building worker power in an era of digital Taylorism:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2019/10/adversarial-interoperability
To see how that works, look to other jursidictions where workers have leapfrogged their European and American cousins, such as Indonesia, where gig workers and toolsmiths collaborate to make a whole suite of “tuyul apps,” which let them override the apps that gig companies expect them to use.
https://pluralistic.net/2021/07/08/tuyul-apps/#gojek
For example, ride-hailing companies won’t assign a train-station pickup to a driver unless they’re circling the station — which is incredibly dangerous during the congested moments after a train arrives. A tuyul app lets a driver park nearby and then spoof their phone’s GPS fix to the ridehailing company so that they appear to be right out front of the station.
In an ideal world, those workers would have a union, and be able to dictate the app’s functionality to their bosses. But workers shouldn’t have to wait for an ideal world: they don’t just need jam tomorrow — they need jam today. Tuyul apps, and apps like Para, which allow workers to extract more money under better working conditions, are a prelude to unionization and employer regulation, not a substitute for it.
Employers will not give workers one iota more power than they have to. Just look at the asymmetry between the regulation of union employees versus union busters. Under US law, employees of a union need to account for every single hour they work, every mile they drive, every location they visit, in public filings. Meanwhile, the union-busting industry — far larger and richer than unions — operate under a cloak of total secrecy, Workers aren’t even told which union busters their employers have hired — let alone get an accounting of how those union busters spend money, or how many of them are working undercover, pretending to be workers in order to sabotage the union.
Twiddling will only get an employer so far. Twiddling — like all “AI” — is based on analyzing the past to predict the future. The heuristics an algorithm creates to lure workers into their cars can’t account for rapid changes in the wider world, which is why companies who relied on “AI” scheduling apps (for example, to prevent their employees from logging enough hours to be entitled to benefits) were caught flatfooted by the Great Resignation.
Workers suddenly found themselves with bargaining power thanks to the departure of millions of workers — a mix of early retirees and workers who were killed or permanently disabled by covid — and they used that shortage to demand a larger share of the fruits of their labor. The outraged howls of the capital class at this development were telling: these companies are operated by the kinds of “capitalists” that MLK once identified, who want “socialism for the rich and rugged individualism for the poor.”
https://twitter.com/KaseyKlimes/status/821836823022354432/
There's only 5 days left in the Kickstarter campaign for the audiobook of my next novel, a post-cyberpunk anti-finance finance thriller about Silicon Valley scams called Red Team Blues. Amazon's Audible refuses to carry my audiobooks because they're DRM free, but crowdfunding makes them possible.

Image: Stephen Drake (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Analog_Test_Array_modular_synth_by_sduck409.jpg
CC BY 2.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/deed.en
—
Cryteria (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:HAL9000.svg
CC BY 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/deed.en
—
Louis (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Chestnut_horse_head,_all_excited.jpg
CC BY-SA 2.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0/deed.en
[Image ID: A complex mandala of knobs from a modular synth. In the foreground, limned in a blue electric halo, is a man in a hi-viz vest with the head of a horse. The horse's eyes have been replaced with the sinister red eyes of HAL9000 from Kubrick's '2001: A Space Odyssey.'"]
#pluralistic#great resignation#twiddler#countertwiddling#wage discrimination#algorithmic#scholarship#doordash#para#Veena Dubal#labor#brian merchant#app boss#reverse centaurs#skinner boxes#enshittification#ants vs pickers#tuyul#steampunk#cottage industry#ccpa#gdpr#App Drivers and Couriers Union#shitty technology adoption curve#moral economy#gamblification#casinoization#taylorization#taylorism#giant teddy bears
3K notes
·
View notes
Text

trying to figure out how to draw their faces and practice lighting 😢erm
#bully fanart#bully game#bully scholarship edition#jimmy hopkins#pete kowalski#gary smith#i want to draw gary as evil as possible#gary lost a teeth too#i just think its a great look on him...#i dojt think gary's evil#i think he'd want to be pure evil so bad but hes just not#its so FUNNY!!!!!#art
180 notes
·
View notes
Text
I’m not well-read on the critiques of butler’s work so I don’t want this to come off as dismissive of those critiques, but I find myself in an eternally apologetic stance with butler because they have forever pissed off so many people with their theory of gender. like they open Bodies That Matter by saying “I” is a gendered pronoun & every cis feminist has been having a permanent public meltdown about it ever since
#even old new york was once new amsterdam#reading some very bad feminist theory atm which is the context of this reaction#reminds me of Marx. like should be lambasted for a great many things but has also essentially set the tone for all#political theory & social scientific scholarship for the past century. bitches mad etc
71 notes
·
View notes
Text
I have to write a personalized letter to my scholarship benefactor…? What next are they gonna introduce me to high society and have me perform my talents live for their esteemed guests?
#nnstuff#rambling#I know this is normal I just don’t like it#art college#I didn’t even apply to this scholarship they just told me I got it one day 😭#which is great but like!! why is this being asked of me!
26 notes
·
View notes
Text
one of the many things that bothers me about goku luck is the fact that they have kenta (a minor) in a penitentiary full of adult convicts. where was the juvenile welfare officer and why are they not doing their job. hope they’re fired
#edit: realised i wrongly used the word penitentiary. sorry abt that. i meant prison#anyone who has heard what prison is like knows how terribly wrong this would go#also was he tried as a minor or did they try him as an adult for his crimes#idc if he’s got advanced hacking skills if a kid can create a virus that can threaten the world in his garage#then i’m sure million-dollar corporations and desperate governments can fund research into an antivirus#idk man it’s freaking ridiculous#like there was no reason to be doing all that#maybe i’m just a believer of restorative justice but#kenta’s clearly a genius. why not a scholarship to a great tech programme and a job with the government#he could do so much good in developing cybersecurity. internationally.#idk it just makes me sad that his whole life was over#and the system didn’t just fail him. it endangered him#either way goku luck could be such a great tool to criticise the criminal justice system#if anyone even CARES#you know i love The Silly but sometimes we need to Get Serious#paradox live#paralive#kenta mikoshiba#goku luck#gokuluck
27 notes
·
View notes
Text

Merry Christmas
#unlike last year I’m having a great time#bully scholarship edition#bully canis canem edit#canis canem edit#bully anniversary edition#bully cce#bully rockstar#bullworth academy#derby harrington#pinky gauthier#gord vendome#chad morris#bryce montrose#bif taylor#justin vandervelde#parker ogilvie#tad spencer
62 notes
·
View notes
Text
Just read a conference paper that mentions fictionkin and... does a fantastic job at completely misunderstanding the phenomena and confusing it with KFF, but worse than that is that it uses a grand citation of a TikTok for that part. How is this going to be a foundational part of your paper's point when you can't even be half-assed to actually look into it. One of the authors has a PhD.
#Who needs good scholarship when you can say a lot of words and pretend to know what you're talking about?#If you don't have a reliable foundation then the rest of what you build up is fundamentally meaningless!#But this does function as a great source for talking about how KFF destroyed the fictionkin subculture and community at least.#And it ties in pretty well to my discussion from my capstone and ye olde lecture about how academia has so many blinders on for what they#WANT otherkin to be that they continuously misinterpret it to the detriment of everyone even in the face of opposing evidence and research.#Jeeeeeesus christ man. I'm going back to bed.#Unrebloggable because I just want to bitch. Shitty publications will always exist and I will always be disappointed and mad in equal measur
37 notes
·
View notes
Text
Lowkey can some1 educate me on the bully ships (aka talk me into shipping dirtmoney and/or smopkins)
#I’m sorry y’all it just seems like those ships are there for ‘hrrrgh enemies to lovers’ brainrot only#PLEASE explain to me in great detail why they are made for eachother#bully scholarship edition#bully#canis canem edit#bully canis canem edit#bully game#smopkins#dirtmoney
34 notes
·
View notes
Text
Is there a "I've gone too far" with writing research?
Let me clarify my odd question. I write marvel fanfiction and original stuff at the moment. In order to understand and write Clint Barton, and other deaf characters in the future, better I've taken my interest in ASL off the back burner and decided to more seriously pursue it. Got a couple textbooks for my bday. Found Vicar's ASLU resources online along with some other promising resources I want to look in to.
Am I taking it too far by considering a degree in ASL/Deaf studies? I mean it's all for you Hawkeye but college is so expensive and I'm still finishing my first BA.. I gotta say some colleges look promising though. Liking some of the coursework options at one I found up in Boston.
Anyway, help a friend out? I always knew I'd be a jack-of-all-trades to be a full time writer but another college? Another degree? Too far you think? I just don't think online will do enough for me you know. Gotta have that in person instruction.
#deaf clint barton#clint barton#hawkeye#asl#deaf studies#college#deaf character#do I really wanna apply to a third university?#I mean I only got this far because of scholarships#i am so poor#but my thirst for knowledge is great
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
GODDAMN i applied to university literally two days ago and my top school just accepted me. WOOHOO and also fuck that was fast huh
#i was thinking it would take uh. a few weeks#its so funny yesterday they emailed me saying hey we’ve confirmed your application good luck!#and i was like okay great these ppl r on top of things! well. they sure were baby#none of my other schools sent me anything!#also eee remember literally a few hours ago i said my average was 89 and i needed a 90#wellll they offered me the 90% scholarship anyways so YAYYYYY
32 notes
·
View notes
Text
Bankruptcy is very, very good

On THURSDAY (June 20) I'm live onstage in LOS ANGELES for a recording of the GO FACT YOURSELF podcast. On FRIDAY (June 21) I'm doing an ONLINE READING for the LOCUS AWARDS at 16hPT. On SATURDAY (June 22) I'll be in OAKLAND, CA for a panel and a keynote at the LOCUS AWARDS.

There's a truly comforting sociopathy snuggled inside capitalism ideology: if markets are systems for identifying and rewarding virtue, ability and value, then anyone who's failing in the system is actually unworthy, not unlucky; and that means the winners are not just lucky (and certainly not merely selfish), but actually the best and they owe nothing to their social inferiors apart from what their own charitable impulses dictate.
It's an economic wrapper around the old theological doctrine of providence, whereby God shows you whom he favors by giving them wealth and station, and marks out the wicked by miring them in poverty. And like the religious belief in providence, the capitalist belief in meritocracy is essential to resolving cognitive dissonance: it lets the fed winners feel morally justified in stepping over the starving losers.
The debate over merit and luck has been with us for millennia, and even the hereditary absolute monarchs of the Bronze Age had to find a way to resolve it. For the rulers of antiquity, the way to square that circle was jubilee.
Bronze Age jubilees were periodic celebrations in which all debts were canceled. Different kingdoms had different schedules for jubilees, but imagine some mix of "every x years" and "every time a new ruler takes the throne" and "every time something really portentous happens." To modern sensibilities, the idea that we would simply wipe away all debts every now and again is almost inconceivable. Why would any society practice jubilee? More importantly, how could a ruler get the wealthy creditor class to countenance a jubilee, rather than seeking a revolutionary overthrow?
The best answers to this question can be found in the scholarship of historian Michael Hudson, who has written extensively on the subject. Hudson doesn't just write for a scholarly audience, he's also a fantastic communicator with a real commitment to bringing his research to lay audiences:
https://michael-hudson.com/
Hudson's most famous saying is "debts that can't be paid, won't be paid." It's in this dense little nugget that we can find the answer the the riddle of jubilee:
https://pluralistic.net/2021/09/29/jubilance/#debt
Let's start with a simple model of debt and credit in an agricultural society. In agricultural societies, everything exists downstream of farming, which is the core activity of the civilization. If the farmers succeed, everyone can eat, and that means they can do all the other things, all the not-farming work of your society.
To farm successfully, you need credit. Farmers enter the growing season in need of inputs: seed, fertilizer, labor; they need still more labor during the harvest. Without some way to acquire these inputs before the farmer has a crop that can pay for them, there can be no crop.
No wonder, then, that the earliest "money" we have a record of is ancient Babylonian credit ledgers that record the debts of farmers who borrow against the next crop to pay for the materials and labor they'll need to grow it. Debt, not barter, is the true origin of money. The fairy tale that coin money arose spontaneously to help bartering marketgoers facilitate trade has no historical evidence, while Babylonian ledgers can be seen in person in museums all over the world.
Farming requires an enormous amount of skill, but even the most skillful farmer is a prisoner of luck. No matter how good you are at farming, no matter how hard you work, no matter how carefully you plan, you can still lose a harvest to blight, drought, storms or vermin.
So over time, every farmer loses a crop. When that happens, the farmer can't pay off their debts and must roll them over and pay them off with future harvests. That means that over time, the share of each harvest the farmer has claim to goes down. Thanks to compounding interest, no bumper crop can erase the debts of the bad harvests.
That means that, over time, "farmer" becomes a synonym for "debtor." Farmers' productive output is increasingly claimed by the rich and powerful. No matter how badly everyone needs food, the whims of the hereditary creditor class come to dictate the country's agricultural priorities. More ornamental flowers for the tables of the wealthy, fewer staple crops for the masses. "Creditor" and "debtor" no longer describe economic relations – they become hereditary castes.
That's where jubilee comes in. Without some way to interrupt this cycle of spiraling debt, society becomes so destabilized that the system collapses:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/07/08/jubilant/#construire-des-passerelles
In other words: debts that can't be paid, won't be paid. Either you wipe away the farmers' debts to the creditor class, or your society collapses, and with it, the political relations that made those debts payable.
Jubilee is long gone, but that doesn't mean that debts that can't be paid will get paid. Modern society has filled the jubilee gap with bankruptcy, a legal process for shriving a debtor of their debts.
Bankruptcy takes many forms. The most important split in bankruptcy types is between elite bankruptcy and the bankruptcy of the common person. The limited liability company was created to allow people with money to pool their funds to back corporations without being responsible for their debts. This "capital formation" is considered "efficient" by economists because it creates the backing for big, ambitious projects, from colonizing and extracting the wealth of distant lands (Hudson's Bay Company) to spinning up global manufacturing supply chains (Apple).
Limited liability means that companies can take on debt without exposing their investors to risks beyond their capital stake. If you buy $1,000 worth of Apple stock, that's all you stand to lose if Apple makes bad decisions. Apple may rack up billions in liabilities – say, by abusing its subcontractor workforce – but Apple's owners aren't on the hook for it.
Economists like this because it means that you can invest in Apple without having to be privy to its daily management decisions, which means that Apple can accumulate huge pools of capital, "lever them up" by borrowing even more, and then put all that money to work on R&D, product development, marketing, and, of course, "incentives" for key employees and managers.
But limited liability also does a lot of work in the political sphere. Once an individual crosses a certain wealth threshold, they become an LLC. Accountants and wealth managers and financial planners insist on this. For freelancers and other sole practitioners, the benefits of forming an LLC are modest – a few more tax write-offs and the ability to get a business credit-card with slightly superior perks.
But for the truly wealthy, transforming yourself into the "natural person" at the center of a vast pool of LLCs is essential because it allows you to accumulate and shed debts. You can secretly own rental properties and abuse your tenants, accumulate vast liabilities as local authorities pile fine upon fine, and then simply dispose of the LLC and its debts. Plan this gambit carefully enough and the debtor LLC will have no assets in its bankruptcy estate apart from the crumbling apartment building, and its most senior secured creditor will be another of your LLCs. This lets the slumlord move an apartment block from one pocket to another, leaving the debt behind.
For the corporate person, shedding debts through bankruptcy is an honorable practice. Far from being a source of shame, the well-timed, well-structured bankruptcy is just evidence of financial acumen. Think of the private equity looters who buy a company by borrowing against it, pay themselves a huge "special dividend," then wipe away the debt by taking the company bankrupt (which also lets them shed obligations to suppliers, workers, and especially, retirees and their pensions). As Trump (a serial bankrupt who has stiffed legions of contractors and creditors) would say, "That makes me smart."
The apotheosis of elite bankruptcy is found in massive corporate bankruptcies, in which a corporation kills and maims huge numbers of people, then maneuvers to get its case heard in one of three US federal courtrooms where specialist judges rubber-stamp "involuntary third-party releases" that wipe out the company's obligations to it victims for pennies on the dollar, while the company gets to keep billions:
https://pluralistic.net/2021/07/29/impunity-corrodes/#morally-bankrupt
This process was so flagrantly abused by companies like Johnson & Johnson (which spent years knowingly advising women to dust their vulvas with asbestos-tainted talc, creating an epidemic of grotesque and lethal genital cancers) that it is finally generating some scrutiny and pushback:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/02/01/j-and-j-jk/#risible-gambit
But the precarious state of elite bankruptcies has more to do with the personal corruption of the small cabal of judges who run the system than public outrage over their rulings; like that one judge in Texas who was secretly fucking the lawyer whose clients he was also handing hundreds of millions of dollars to:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/10/16/texas-two-step/#david-jones
Certainly, we don't hear much about the "moral hazard" of allowing the Sackler opioid family to keep as much as ten billion dollars in the family's offshore accounts while walking away from the victims of their drug-pushing empire, no matter what bizarre tricks they deploy in pulling off the stunt:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/08/11/justice-delayed/#justice-redeemed
But when it comes to canceling the debts of normal people, the "moral hazard" is front and center. If you're a person who borrowed $79k in student loans, paid back $190k and still owe $236k, we can't cancel your debt, because of the message that would send to other people who want to (checks notes) get an education:
https://pluralistic.net/2020/12/04/kawaski-trawick/#strike-debt
The anti-jubilee side also wants us to think of the poor creditors: who would loan money to the next generation of students if student debt cancellation was a possibility? Of course, these are federally guaranteed loans, risk-free, free money for people who already have money, a kind of UBI for the people who need it least. The idea that this credit pool would dry up if you were limited to only collecting the debts that can be paid – rather than insisting that debts that can't be paid still be paid – elevates the hereditary creditor class to a kind of fragile, easily frightened, endangered species.
But the most powerful arguments against bankruptcy are rooted in the idea of providence. In an efficient market, anyone who goes bankrupt was necessarily reckless. They were entrusted with credit they weren't entitled to, because they lacked the intrinsic merit that would let them manage that credit wisely. Letting them walk away from their debts means that they will never learn from their mistakes, and that their fellow born-to-be-poors will learn the wrong thing from those debts: that there's an easy life in borrowing, spending, and discharging your debts in bankruptcy.
As it happens, this is an empirically testable proposition. If this view of personal bankruptcy as a personal failure is correct, then people who go bankrupt and live to borrow again should end up bankrupt again, too. On the other hand, if we accept the jubilee view – that debt is the result of accumulated misfortunes, often including the misfortune of birth into poor station – then bankruptcy represents a second chance with an opportunity to dodge misfortune.
In a new study from IZA Institute of Labor Economics's Gustaf Bruze, Alexander Kjær Hilsløv and Jonas Maibom, we get just such an empirical analysis. It's called "The Long-Run Effects of Individual Debt Relief," and it examines the lives of people for a full quarter-century after a bankruptcy:
https://docs.iza.org/dp17047.pdf
The study follows Danish bankruptcies following the introduction of continental Europe's first modern bankruptcy system, which Denmark instituted in 1984. Prior to that, the Danes – like most of Europe – did not allow for a discharge of personal debt through bankruptcy. Instead, a debtor who went bankrupt would be expected to have about 20% of their lifetime wages garnished to pay back their creditors, until the debts were repaid or they died (whichever came first).
After 1984, Denmark bankruptcy system imported features of US/UK/Commonwealth bankruptcy, including the ability to restructure and discharge your debts. Not everyone is eligible for this kind of bankruptcy: there's a bureaucratic system that verifies that people seeking bankruptcy discharge don't have a lot of assets that could go to their creditors.
But for the (un)lucky people who qualify for bankruptcy discharges, there's a fascinating natural experiment in which the fortunes of people who see debt relief can be compared to bankrupt people who couldn't get their debts wiped out.
It turns out that the Bronze Age has a thing or two to teach us. Here's the headline finding: people who discharge their debts in bankruptcy experience "a large increase in earned income, employment, assets, real estate, secured debt, home ownership, and wealth that persists for more than 25 years after a court ruling."
After people are given the benefits of bankruptcy, they are less likely to rely on public benefits. They get better jobs. Their families live better lives. Their creditors get some of their money back (which is all they can realistically expect, since "debts that can't be paid, won't be paid").
As Jason Kilborn writes for Credit Slips, "the benefits of debt relief are not only substantial but robust, as debtors learn their lesson (if there was one to learn) about managing their finances, and they capitalize (literally) on their fresh start."
Score one for the luck-based theory of wealth, and minus one for the providential meritocracy hypothesis.
Americans should take note of these findings. After all, Danes are insulated from the leading American cause of bankruptcy: medical debts. In America, breaking a bone or getting cancer or even kidney stone can wipe out a lifetime of hard work, careful planning and prudential spending. The US refuses to seriously grapple with this problem. The best we can come up with is the (welcome, but tiny) step of banning credit bureaux from trashing your credit score because of your medical debt:
https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/statements-releases/2024/06/11/fact-sheet-vice-president-harris-announces-proposal-to-prohibit-medical-bills-from-being-included-on-credit-reports-and-calls-on-states-and-localities-to-take-further-actions-to-reduce-medical-debt/
Millennia ago, everyone understood that debts that can't be paid, won't be paid, and they created a system for discharging debts and freeing productive people from the tyranny of accumulated liabilities, to the benefit of all. Dismantling that system required us to invent an elaborate theological system and dress it up in economic language.

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/06/17/lovilee-jubilee/#debts-that-cant-be-paid-wont-be-paid
#pluralistic#debt#debts that cant be paid wont be paid#jubilee#denmark#great danes#bankruptcy#second chances#scholarship#economics#iza#Gustaf Bruze#Alexander Kjær Hilsløv#Jonas Maibom#michael hudson
323 notes
·
View notes
Text
wait ik i said college au vfv but ballet company/academy au..
#let me have a shower to sit on this#i might be cooking maybe i will whip out some hcs#as a dancer this is close 2 my heart and very self indulgent#im thinking male principal dancer louis... renee on a scholarship... alexandre being a talented teacher#cant dance anymore because of injury#but was on track to being one of the greats#maria theresa transferred over to the paris opera but plot is#she gets injured so louise was a shoein to be louis' leading lady until renee appears#philippe in his brothers shadow always. the thing with louis is that his technique is crazy but philippe just Gets artistry#WAIT ... OK GIMME A SEC
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Crazy it took nearly 500 pages for Richard to realise the others don't give a fuck about university (or like anything else really) because they are rich kids 🤦
#the secret history#he just wanted to be part of the shitty elitist group at any cost#white boys are crazy#i knew to avoid these kind of people very early because they are full of shit (minus the murders hopefully)#i've spend the entire book being both disgusted and fascinated#because it's a great book with great writing#so congrats on the author for making me care about rich kids even though i knew since they first appeared they were shitty#and this includes Julian#like i've been insane when he praised him#these kind of teachers living in their own world is one of the things i hated the most about university#i still remember to this day the latin teacher who told us to go to Rome during our vacations#to me and several students who were eating one fucking meal a day#it really brought back all the memories of the rift between scholarship students trying to live and the rich kids#misc
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
...
#so my mom's wake thing was today and that was a lot. not in an emotional sense but in a im standing here talking for 3hrs#to ppl i dont kno or barely kno. ya kno? but it was good bc so many ppl showed up to talk abt her#so many people. my mom made a huge impact on the school system. so many ppl relied on her. she encouraged at least 2 ppl to get their#master. for one person to specilize in helping the dyslexic after her experience advocating for 3 dyslexic daughters. she wrote and was#awarded a 10000 dollar grant for special needs and intervention curriculum. which will affect so many lives.#everyone loved her. she's gonna get a track meet named after her and a scholarship created in her honor.#she was an amazing person and she affected a lot of lives and im glad she was my mom. and she raised at least one jem in my littlest#sister who is so sweet and is a great teacher. god but there was some weird stuff too. were pretty sure her old boss was in love with her.#and there were some weird comments abt her being a strong woman or this woman doing so much and its like hm y do i detect a note of sexism#y not say she was an amazing person? y the surprise? weird comments about how pretty i looked. which yes i looked great lol. my funeral fit#was cute. we did bright colors bc it was a celebration not a dower event. and im sure it was ment well but it was a lil weird. and then#everyone was telling my grandma what a great job she did raising my mom and like god fuck off she didn't do jack. my mom was great despite#her terrible mother. ugh. but altogether it was good that everyone was able to express their love for her. it was def a day that was for#them mostly. i mean partly for us but mostly for them. none of us even cried. ay but we have 2 more parties in her honor#bc everyone loved her so much we have to do one in her hometown too. plus a personal friends get together. ugh. im so tired#i wish i wasnt the most awkward. eye contact avoidant person in the room but like ya kno. what can ya do?#unrelated
20 notes
·
View notes
Note
Lola getting ready for the day.
https://youtube.com/shorts/j1fDOBX5-PI?si=W01xO1Fhq5bID5b1
youtube
THE GUY IN THE BACK (clearly johnny) IS DRIVING ME INSANE
#your clips are alwaysss top tier bestie thank you for blessing my ask box!!#gonna schedule this in a while cause i dont wanna clog up the dashboard in the hyper-immediate second but like. it was great#odyanswers#lola lombardi#johnny vincent#bully scholarship edition
13 notes
·
View notes