#Egalitarian
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Reminder
#vote#day light savings#november#november 5#november 5th#important#remember#reminder#meme#equality#equal#egalitarian#feminism#feminists#feminist#lgbt#lgbtq#lgbtqia#lgbtqa#lgbtqi#lgbtqiap#lgbtqap#lgbtqip#gay rights#trans rights#blm#womens rights#black lives matter#stop asian hate#trans lives matter
220 notes
·
View notes
Text
Respond to a post saying "honor police officers who died" with "honor all people who died".
How many people would call that "free speech"? How many people would call that "egalitarian"?
Probably none. Most people would call that downright rude.
That's what's wrong with "all lives matter". And everyone already knows that.
267 notes
·
View notes
Text

From Pinterest
#feminine#femininity#homemaker#traditional#homemaking#cute#cottagecore#farmcore#egalitarian#tradfem#trad femininity#tradwife#traditionalism#trad wife
71 notes
·
View notes
Text
Men are just as complex and diverse as women. You agree. Reblog.
174 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Feminist Double Standards
Oh, the curious case of feminist advocacy! 🧙♀️ Feminists, do you only crave equality when it suits your agenda? 🧐 If you passionately fight for women in male-dominated STEM fields, why the silence for men in female-dominated industries? (¬‿¬) Nursing, teaching, and childcare, these sectors cry for male representation! But where are the feminist warriors now? (¬‿¬) Shouldn't true equality seek balance everywhere? Let's discuss this hilarious hypocrisy! 😜🔍
Imagine a world where male nurses and teachers are embraced! A true utopia, or a feminist's nightmare? 😈🤣 (¬‿¬)


#feminism#egalitarian#egalitarianism#liberal feminism#radical feminism#equality#radical feminist safe#radical feminst#feminsim#equal rights#female hysteria#modern feminism#radical feminists do interact#radical feminist community#radical feminists do touch#double standards#hypocrisy#side eye
57 notes
·
View notes
Text

#fuck the patriarchy#radical feminism#radical feminist safe#radical feminists do interact#misandry#feminism#feministicon#womens rights#man hater#terfblr#terfsafe#radical feminist community#trans exclusionary radical feminist#ecofeminism#egalitarian
111 notes
·
View notes
Text
Radical feminisic core beliefs in the fictional culture of the Mandalorian People
The Mandalorian culture in both Disney and Legends canon can be interpreted as "radical feministic" in essence when viewed through the lens of specific radical feminist principles, particularly those centered on rejecting patriarchal norms, fostering egalitarianism, and valuing collective strength over traditional gender roles. Here's how this interpretation can be supported:
1 .Rejection of Gender Roles and Patriarchal Norms
Disney Canon:** In *The Mandalorian*, female warriors such as Bo-Katan Kryze and the Armorer hold leadership positions and are respected on equal footing with their male counterparts. The culture places no emphasis on traditional gender roles, showcasing men and women alike as warriors, leaders, and protectors of their people.
Legends Canon: Karen Traviss' *Republic Commando* novels expand on Mandalorian culture, emphasizing the practical, no-nonsense approach to gender. Women, like men, are trained as warriors from a young age. The culture prioritizes competence and contribution over biological or societal expectations tied to gender.
This aligns with radical feminism's critique of patriarchal gender constructs by showcasing a society where roles are based on merit and capability rather than gender.
2. Valuing Motherhood Without Exploitation
Mandalorian culture celebrates motherhood, but not in the patriarchal, exploitative sense that ties women's worth to reproductive roles. Instead, motherhood (and parenthood in general) is honored as an essential act of cultural preservation. The practice of adopting foundlings, irrespective of biological ties, reflects a communal approach to child-rearing that values nurturing as a collective responsibility.
This ties into radical feminist ideals by elevating the importance of caregiving without confining it to women or devaluing it as "unproductive labor."
3. Egalitarianism and Anti-Hierarchy
Mandalorian culture is often portrayed as decentralized, with clans and individuals having significant autonomy. Leadership, such as that of the Mand'alor, is based on merit and the ability to unify the people, rather than hereditary or hierarchical systems.
Radical feminism critiques hierarchical systems as inherently tied to patriarchal power structures. Mandalorian society’s rejection of rigid hierarchy and its emphasis on mutual respect and collective survival align with these values.
4. Focus on Strength and Solidarity
Mandalorians emphasize community and solidarity over individualism. Their creed prioritizes loyalty to the group, collective strength, and mutual aid, which are key principles of feminist and eco-socialist thinking.
In Legends, this is exemplified by the communal lifestyle of the Mandalorian clans, where resources and responsibilities are shared. In Disney canon, the adoption of foundlings reflects a commitment to care for the vulnerable as a collective duty, breaking the cycle of exploitation often seen in patriarchal systems.
5. Anti-Imperialism and Resistance to Oppression
Mandalorians have a long history of resisting imperialism, whether under the Republic, Empire, or other external forces. This mirrors radical feminism’s commitment to dismantling systems of domination and oppression. Their refusal to conform to external norms and their insistence on maintaining their culture and values resonate with feminist resistance to patriarchal imposition.
6. Empowered Female Leadership
Both canons prominently feature strong female leaders. Bo-Katan Kryze, Satine Kryze, and Ursa Wren are examples of women leading their people with agency and authority, free from patriarchal constraints.
Radical feminism seeks to dismantle the notion that leadership and power are inherently masculine traits. Mandalorian women’s leadership roles exemplify this rejection of patriarchal norms.
Caveats
While Mandalorian culture can be interpreted as embodying radical feminist principles, it is important to note:
The Mandalorians are also deeply martial and honor-driven, traits that could conflict with radical feminist critiques of militarism.
But the approach to see sex differences as fact but still honor them without hindering both sexes to become part of the leadership by merit is indeed in core identical to radical feministic view of biology-based sex-essentialism as fact with including dismantling patriarchy and promote egalitarianism and meritocracy
Conclusion
Mandalorian culture in Disney and Legends canon reflects radical feminist principles by rejecting traditional gender roles, emphasizing egalitarianism, honoring caregiving without exploitation, and fostering solidarity and resistance to domination. These elements align with the core radical feminist goal of dismantling patriarchal systems and creating societies based on mutual respect, equality, and collective well-being.
There are also Proverbs in canon which prove radical feminist approach on the gender equality despite factual approach on sex biological differences in universe, which proves the antipatriarchic structure of mandalorian Warrior Mentality, which can be confused with virtues of "masculinity", but count for both sexes in the mandalorian society:
“There is nothing a Mandalorian man fears more than a Mandalorian woman.” - old proverb, not Mandalorian in origin
“You piss off our men, you'll end up with a lot of dead soldiers and maybe a few damaged buildings. But you piss off our women and...well, you'll be feeling the side effects for years to come.” - Mandalore the Destined
“Mandalorian women are frightening. They're smart, angry, and can shoot better than most men. Mandalorian men are a force to be reckoned with. But Mandalorian women? They're a kriffing force of nature.” – Zakc Paxus, noted Mandalorian author
“Mandos don't get all mushy about love. No poetry, no creepy obsessions; either you love someone, or you don't. If you do, you marry 'em and fight alongside them for the rest of your life. If not, you just fight alongside them.” - Mandalore the Fair (first female Mandalore, named for her honorable ruling rather than her appearance)
“A Mandalorian woman's greatest talent is not her charm or beauty, but her strength of body and will.” - Mandalorian proverb
#radical feminism#radfemblr#radfemally#fuck the patriarchy#radfeminism#smash the patriarchy#gender equality#mandalorian culture#mandalorian women#egalitarian#meritocracy#radical feminist community#radical feminist safe#star wars mandalorian
33 notes
·
View notes
Text
tldr at the end
so weird when people start talking about how "men can't be oppressed simply because theyre men" and then start listing all the reasons that- huh- men *can* be oppressed simply because theyre men, and then trying to put a different spin on it???
like im so confused
so youre going to tell me that men being told "don't cry" "dont do *that* job that's for *girls*" "that couldnt happen to *you*, youre a *man*" is.. not men being oppressed... because.. theyre men...??
and it's like-
trans/misogyny and trans/misandry can and do co-exist. because misogyny is oppression against women and/or women-aligned people and/or people perceived as women in some way, and misandry is oppression against men and/or men-aligned people and/or people perceived as men in some way. often at the expense of the other group.
for example:
telling a woman, "don't do *that*, thats for *men*, do *this* instead" - that is misogyny and misandry. how? because you're implying that a woman cannot do this so-called "manly" thing, because it's "not suitable for girls", and then telling her to do this other thing instead, indirectly implying that this more "feminine" activity is *for* women, and therefore *not* for men... which implies that men can't do that thing because it's not "manly" enough.
the reason trans/misogyny and trans/misandry co-exist and overlap is because it is, at it's foundation, oppression. it is the oppression of a certain group of people because of the idea that certain genders cannot and should not do activities (and etc.) that society have deemed unacceptable for that group.
women not being taken seriously by healthcare providers, simply on the basis that theyre women? misogyny (and misandry, because it implies that men have a different [higher] level of knowledge/autonomy of their bodies than women do, which is frankly untrue)
men not being taken seriously by SA/R help/survivors, simply on the basis that theyre men? misandry (and misogyny, because it implies that only women could be so "weak" [untrue] as to be able to have been SA/R'd, which is patently untrue)
women being told to go into nursing instead of doctorate school, simply on the basis that theyre women? misogyny AND misandry
men being told to go out and get a job instead of staying at home to help with the house/kids, simply on the basis that theyre men? misandry AND misogyny
do you see the pattern? the answer to solving or helping trans/misogyny is not to turn that rhetoric back on trans/men- that's what's already been happening! misogyny CANNOT exist without misandry, and misandry CANNOT exist without misogyny. oppression cannot exist without oppression.
if you are not in control of your emotions (unless it is, perhaps, anger), and unless you like these certain things? you're not a *real* man, then
if you are not emotional/reactive to things (unless it is, perhaps, anger), and unless you like these certain things? you're not a *real* woman, then
to defeat misogyny and misandry (gendered oppression), then you cannot perpetuate the idea that one gender is better than the other, or that only certain genders can do certain things. you have to break the idea that only certain ideas/tasks etc. are for certain genders. it cannot be *equality* unless all are equal. it doesn't mean boost women up while tearing men down, it doesn't men keeping women oppressed, it means evening the playing field.
allow women to be publicly strong, publicly weak, publicly *everything* that is human because being strong, smart, weak, emotional, angry, joyful etc. is not gendered.
allow men to be publicly strong, publicly weak, publicly *everything* that is human because being strong, smart, weak, emotional, angry, joyful etc. is not gendered.
tldr: trans/misogyny and trans/misandry do co-exist and overlap, and to destroy one means having to destroy the other- there is no other way to defeat oppression. oppression means to be *oppressed*. if you defeat one and not the other, you free no one- for now you are caught yet again in the endless cycle of oppression, now you're just the ones on top/the oppressors. im sick and tired of people denying the existence of one or the other.
#WE'RE GOING IN FUCKING CIRCLES#UGHHHH#gender oppression#gendered oppression#transmisandry#transandrophobia#egalitarian
44 notes
·
View notes
Text
This took a long time (and the quiz itself is long), but after so many years of observing toxic femininity on Hellsite, I'm finally able to give a name to this type of woman.
And yes, many of these questions were based on real posts on this site plus real life experience.
#feminism#toxic femininity#white feminism#girlboss feminism#intersectionality#pick me#not like other girls#neurotypical feminism#gender essentialism#egalitarian#uquiz#uquiz quiz#tldr: a girls girl is a woman who puts other women down to get validation from girlbosses#tumblr used to be full of them but most of them moved to twitter and tiktok#girls girl (derogatory)
115 notes
·
View notes
Text
Random thought of the day: Why is female body hair still so rare in media? I've got no love for our corporate media overlords, but fair to say that (while there is still plenty more work to be done) representation for women of all races, ages, cultures, religions and sexualities has improved massively over the past few years/decades. But on this issue we still seem painfully behind.
Like, you could be watching a show or film about a female character surviving on a desert island for years, and the makeup/prosthetics department will go all out to give her a filthy face, muddy hair, tattered clothes etc. Yet somehow, she will always inexplicably have smooth, hairless legs despite how unrealistic that would be in that situation.
Why is our media so reluctant to depict, platform or celebrate women who cannot or choose not to remove their body hair?
29 notes
·
View notes
Note
out of sheer, perhaps even morbid curiosity, do you have any political ideology beyond disliking radfems/being a mra? like, do you have any opinions on real issues? environmental degradation? sudan? palestine? the expansion and concentration of wealth? surveillance capitalism? i don't know, take your pick of anything that the discourse isn't purely based on social media debates lmao. i'm curious how similar you are to radfems/zionists/political positions that completely disregard the material conditions of the world pfff
I'm an autistic egalitarian Bernie Sanders stan. I tend to lean heavily into autistic fairness (Its not fair to give sexism protections to one gender but not the other) and individualistic equality (affirmative action may improve the avg to what ever makes the executives warm and fuzzy, but during such a transition an individual student/employee applying for a school/job will have different odds of getting in based on external factors (their race/gender) instead of their qualifications. its just more bigotry and anti-egalitarian. Solving upstream issues causing application rates being low by increasing acceptance rates doesn't actually solve the issue, just leads to justifiable resentment while creating a superstar effect around the non-affirmed group which has to be so much better just to get in)).
Environmental degradation? Personal responsibility is a distraction. The only personal responsibility we all have is to pay the extra price for shit made sustainability. Plastic straw bans are poison pills designed to spoil the taste of environmentalism in the eyes of the lay person. Regulate the corporations more, add more criminal penalties, look into the micro plastics leeching from fishing nets issue, track the use of dirty oil in the sea and fine and tax corporations who deal in goods transported with it. Stop sending our recycling to 3rd world countries to be illegally dumped because we don't want to pay somebody to sort it.
Palestine? Seasons 5 and 6 of The Expanse cover my thoughts well. For a more serious answer. On day one I thought Israel (and their stans) fucked up trying to lean hard into the antisemitism angle and predictably have basically poisoned the taste of the accusation entirely. Oh and there's all the murdering they are doing (and why the fuck are we spending money to support it?) We should stop sending them money, we should relocate the embassy again, and we should give the issys a big old fuck you and put up a Palestinian embassy in Jerusalem because Israel lost the right to win that ideological fight with their recent actions. (ok maybe don't do that last one)
The expansion and concentration of wealth? Bring back the 75% tax bracket. Add restrictions and limitations on the captial gains loophole. Put a tax on assets used to secure loans. Tie min wage to price of rent for that area.
Surveillance capitalism? You have no idea how bad AI is about to make this. We are all so so so very fucked. Ban AI.
#cw: politics#us politics#politics#palestine#gaza#israel#affirmative action#income inequality#surveillance capitalism#environment#plastic straws#autism#egalitarian#anon ask#enviromentalism#the expanse#tax the rich#bernie sanders#microplastics
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Ambiguous State Of Tevyat
Tevyat has its own laws in a lot many contexts, but do you ever wonder, does sexism and homophobia exist in the world of tevyat and so correlating to the world of Genshin Impact? Let me know your views.
I read about that confirmation from Arcane’s creators that homophobia and sexism does not simply exist in the universe of Arcane– and I think this is one of the reasons why the representation and the character writing (women’s especially) shines in arcane. There has already been enough praise about Arcane’s writing so I won’t get into it here.
But that made me think that Is that not the perfect setting to write endearing characters in? It eliminates a much more complicated aspect and leaves you with people as an empty blank slate– whose grievances will be based on class struggle, capitalism etc– sure. But it lets everyone be just… everyone. If that makes sense. Why I also relate to that method of storytelling is because (I promise it's about genshin, wait for it) I do end up writing my stories that way– at least a lot of my characters, who have mostly deconstructed most of their ingrained prejudices by the time the story starts, so I can focus on their struggle as related to the story then.
It also got me thinking about Genshin.
SEXISM in the world of Tevyat…
Does not exist. I believe and concur so. Gender-specific crimes have been implied (see Lynette’s story), but in the entirety of its socio political landscape, sexism does not exist in tevyat.
In a world where women harness powers greater than men a lot of times, rule nations and none bats an eye. Soldiers exist as soldiers, knights exist as knights– not women, not men. (My egalitarian perspective’s start to ideal world, really)
I think sexism not existing in the world of Genshin is just very obvious, by the nature of it being an anime-stylised gacha game as well.
HOMOPHOBIA in the world of Tevyat…
Is harder to discuss because even if homophobia does not exist in tevyat, it sure does exist in China. A lot.
But despite that fact, let’s discuss it. HYV has always massively queer-coded their games (go argue with the wall, this is an obvious fact). Even in the face of strict censorship laws, they haven’t really been afraid to confirm (gay) relationships in some other games (see Bronya-Seele from HI3 and Kiana-Mei from HI3). Genshin taps a wider audience thus shies away from direct mentions. But the amount of queer coding? It’s there. Even if you are not a shipper.
I think I would like to mention one of the more highly-implied stances of queer relationship–
See Yoimiya’s story quest 1. The two guy ‘best friends’ who we help make up and their yearning to watch the fireworks together.
Of course, this is all very ambiguous. But with so many characters being into the traveller (despite the gender dynamics) and despite which twin you chose–
For example, Shenhe’s implication that Xiao must have found someone special in a voiceline exists even if you chose Aether or Lumine. It makes me think and believe that homophobia also does not exist.
No wonder I love the game so much.
This might all be very obvious to some people here and I might just be over-explaining it, but this assumption of Tevyat being exempt from sexism and homophobia was only a subconscious one for me until recent times and I just wanted to hear everyone’s thoughts on it as well.
#gender#genshin#genshin impact#fantasy#writing#essay#aether#lumine#xiao genshin impact#Gensin essay#lgbtq#queer#arcane#egalitarian#tevyat
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
I'm so done with the divide.
Left, Right, Moderate,
Far Left, Far Right, Center,
Liberal, Traditional,
Progressive, Conservative,
Pro Life, Pro Choice,
Religious, Secular,
Queer, Straight,
Pro This, Pro That,
Anti This, Anti That,
"You can't follow this person, you can't be friends with that person, if you even just share a space with a person from "the wrong side" you are part of the problem"
I'm done
I'm a human who cares about humans
I'm a human who feels sick and tired of these labels that truly tell you nothing about a person.
Not who a person really truly is.
I'm a human who would like to live in peace.
I'm just a human
#just a human#personal#politics#left#right#center#centre#moderate#far left#far right#liberal#liberals#conservative#conservatism#traditional#progressive#progressivism#pro life#pro choice#feminism#anti feminism#misandry#anti misandry#queer#straight#bi#bisexual#human#I'm just a human#egalitarian
96 notes
·
View notes
Text
By: Olga Khazan
Published: Feb 18, 2018
Though their numbers are growing, only 27 percent of all students taking the AP Computer Science exam in the United States are female. The gender gap grows worse from there: Just 18 percent of American computer-science college degrees go to women. This is in the U.S., where many college men proudly describe themselves as “male feminists” and girls are taught they can be anything they want to be.
Meanwhile, in Algeria, 41 percent of college graduates in the fields of science, technology, engineering, and math—or STEM, as it’s known—are female. There, employment discrimination against women is rife, and women are often pressured to make amends with their abusive husbands.
According to a report that I covered a few years ago, Jordan, Qatar, and the United Arab Emirates were the only three countries in which boys were significantly less likely to feel comfortable working on math problems than girls were. In all of the other nations surveyed, girls were more likely to say they feel “helpless while performing a math problem.”
So what explains the tendency for nations that have traditionally less gender equality to have more women in science and technology than their gender-progressive counterparts do?

[ A scatter plot of countries based on their number of female STEM graduates and their Global Gender Gap Index (y-axis), a measure of opportunities for women (Psychological Science) ]
According to a new paper published in Psychological Science by the psychologists Gijsbert Stoet, of Leeds Beckett University, and David Geary, of the University of Missouri, it could have to do with the fact that women in countries with higher gender inequality are simply seeking the clearest possible path to financial freedom. And typically, that path leads through STEM professions.
The issue doesn’t appear to be girls’ aptitude for STEM professions. In looking at test scores across 67 countries and regions, Stoet and Geary found that girls performed about as well or better than boys did on science in most countries, and in almost all countries, girls would have been capable of college-level science and math classes if they had enrolled in them.
But when it comes to their relative strengths, in almost all the countries—all except Romania and Lebanon—boys’ best subject was science, and girls’ was reading. (That is, even if an average girl was as good as an average boy at science, she was still likely to be even better at reading.) Across all countries, 24 percent of girls had science as their best subject, 25 percent of girls’ strength was math, and 51 percent excelled in reading. For boys, the percentages were 38 for science, 42 for math, and 20 for reading. And the more gender-equal the country, as measured by the World Economic Forum’s Global Gender Gap Index, the larger this disparity between boys and girls in showing science to be their best subject. (The most gender-equal countries are the typical snowy utopias you hear about, such as Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. Turkey and the United Arab Emirates rank among the least equal, according to the Global Gender Gap Index.)
The gap in reading “is related at least in part to girls’ advantages in basic language abilities and a generally greater interest in reading; they read more and thus practice more,” Geary told me.
What’s more, the countries that minted the most female college graduates in fields such as science, engineering, or math were also some of the least gender-equal countries. Stoet and Geary posit that this is because the countries that empower women also empower them, indirectly, to pick whatever career they’d enjoy most and be best at.
“Countries with the highest gender equality tend to be welfare states,” they write, “with a high level of social security.” Meanwhile, less gender-equal countries tend to also have less social support for people who, for example, find themselves unemployed. Thus, the authors suggest, girls in those countries might be more inclined to choose STEM professions because they offer a more certain financial future than, say, painting or writing.
When the study authors looked at the “overall life satisfaction” rating of each country—a measure of economic opportunity and hardship—they found that gender-equal countries had more life satisfaction. The life-satisfaction ranking explained 35 percent of the variation between gender equality and women’s participation in STEM. That correlation echoes past research showing that the genders are actually more segregated by field of study in more economically developed places.
The upshot of this research is neither especially feminist nor especially sad: It’s not that gender equality discourages girls from pursuing science. It’s that it allows them not to if they’re not interested.
The findings will likely seem controversial, because the idea that men and women have different inherent abilities is used by some to argue that we should forget trying to recruit more women to the STEM fields. But, as Janet Shibley Hyde, a gender-studies professor at the University of Wisconsin who wasn’t involved with the study, put it to me, that’s not quite what’s happening here.
“Some would say that the gender STEM gap occurs not because girls can’t do science, but because they have other alternatives, based on their strengths in verbal skills,” she said. “In wealthy nations, they believe that they have the freedom to pursue those alternatives and not worry so much that they pay less.”
Instead, this line of research, if it’s replicated, might hold useful takeaways for people who do want to see more Western women entering STEM fields. In this study, the percentage of girls who excelled in science or math was still larger than the number of women who were graduating with STEM degrees. That means there’s something in even the most liberal societies that’s nudging women away from math and science, even when those are their best subjects. The women-in-STEM advocates could, for starters, focus their efforts on those would-be STEM stars.
Then again, it could just be that, feeling financially secure and on equal footing with men, some women will always choose to follow their passions, rather than whatever labor economists recommend. And those passions don’t always lie within science.
--
Abstract
The underrepresentation of girls and women in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) fields is a continual concern for social scientists and policymakers. Using an international database on adolescent achievement in science, mathematics, and reading ( N = 472,242), we showed that girls performed similarly to or better than boys in science in two of every three countries, and in nearly all countries, more girls appeared capable of college-level STEM study than had enrolled. Paradoxically, the sex differences in the magnitude of relative academic strengths and pursuit of STEM degrees rose with increases in national gender equality. The gap between boys' science achievement and girls' reading achievement relative to their mean academic performance was near universal. These sex differences in academic strengths and attitudes toward science correlated with the STEM graduation gap. A mediation analysis suggested that life-quality pressures in less gender-equal countries promote girls' and women's engagement with STEM subjects.
==
The definition of "STEM" is deceptive. It selects for primarily male-dominated "things" areas, while excluding female-dominated "life" domains, such as medicine, psychology, nursing, biology and environmental sciences.
Despite what people assume, "STEM" does not include all the sciences.
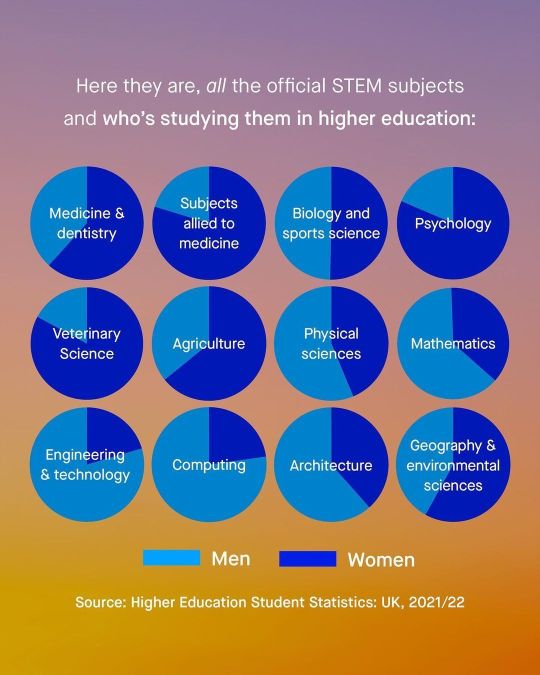
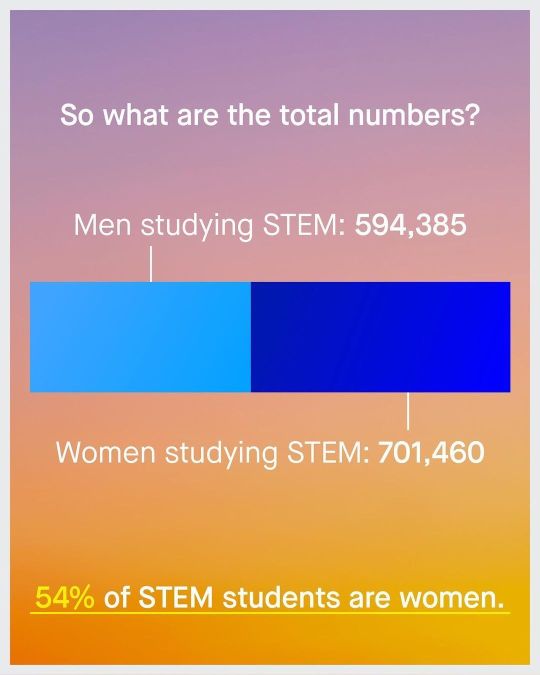
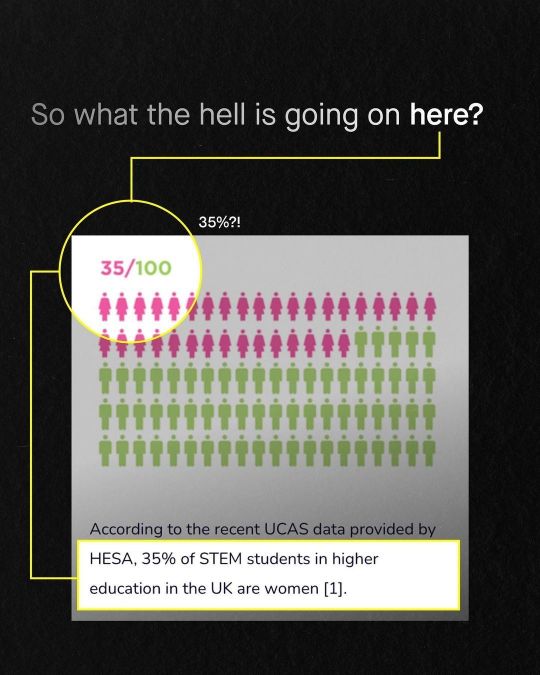

When you factor in all of the sciences, women outnumber men. Meaning, all the handwringing over "women in STEM" is complete nonsense.
Especially when it turns out that gender - that is, average sex-differences - aren't a "social construct." The average differences between men and women are real, demonstrable, measurable, and they're larger in more equal societies, because individuals have greater opportunity to do what they really want, without external pressures like financial demands. This has been studied repeatedly; see below.
Abstract
We investigated sex differences in 473,260 adolescents’ aspirations to work in things-oriented (e.g., mechanic), people-oriented (e.g., nurse), and STEM (e.g., mathematician) careers across 80 countries and economic regions using the 2018 Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA). We analyzed student career aspirations in combination with student achievement in mathematics, reading, and science, as well as parental occupations and family wealth. In each country and region, more boys than girls aspired to a things-oriented or STEM occupation and more girls than boys to a people-oriented occupation. These sex differences were larger in countries with a higher level of women’s empowerment. We explain this counter-intuitive finding through the indirect effect of wealth. Women’s empowerment is associated with relatively high levels of national wealth and this wealth allows more students to aspire to occupations they are intrinsically interested in. Implications for better understanding the sources of sex differences in career aspirations and associated policy are discussed.
Abstract
Preferences concerning time, risk, and social interactions systematically shape human behavior and contribute to differential economic and social outcomes between women and men. We present a global investigation of gender differences in six fundamental preferences. Our data consist of measures of willingness to take risks, patience, altruism, positive and negative reciprocity, and trust for 80,000 individuals in 76 representative country samples. Gender differences in preferences were positively related to economic development and gender equality. This finding suggests that greater availability of and gender-equal access to material and social resources favor the manifestation of gender-differentiated preferences across countries.
Abstract
Sex differences in personality have been shown to be larger in more gender equal countries. We advance this research by using an extensive personality measure, the IPIP-NEO-120, with large country samples (N > 1000), from 22 countries. Furthermore, to capture the multidimensionality of personality we measure sex differences with a multivariate effect size (Mahalanobis distance D). Results indicate that past research, using univariate measures of effect size, have underestimated the size of between-country sex differences in personality. Confirming past research, there was a strong correlation (r = .69) between a country's sex differences in personality and their Gender Equality Index. Additional analyses showed that women typically score higher than men on all five trait factors (Neuroticism, Extraversion, Openness, Agreeableness and Conscientiousness), and that these relative differences are larger in more gender equal countries. We speculate that as gender equality increases both men and women gravitate towards their traditional gender roles.
Abstract
Previous research suggested that sex differences in personality traits are larger in prosperous, healthy, and egalitarian cultures in which women have more opportunities equal with those of men. In this article, the authors report cross-cultural findings in which this unintuitive result was replicated across samples from 55 nations (N = 17,637). On responses to the Big Five Inventory, women reported higher levels of neuroticism, extraversion, agreeableness, and conscientiousness than did men across most nations. These findings converge with previous studies in which different Big Five measures and more limited samples of nations were used. Overall, higher levels of human development--including long and healthy life, equal access to knowledge and education, and economic wealth--were the main nation-level predictors of larger sex differences in personality. Changes in men's personality traits appeared to be the primary cause of sex difference variation across cultures. It is proposed that heightened levels of sexual dimorphism result from personality traits of men and women being less constrained and more able to naturally diverge in developed nations. In less fortunate social and economic conditions, innate personality differences between men and women may be attenuated.
Abstract
Using data from over 200,000 participants from 53 nations, I examined the cross-cultural consistency of sex differences for four traits: extraversion, agreeableness, neuroticism, and male-versus-female-typical occupational preferences. Across nations, men and women differed significantly on all four traits (mean ds = -.15, -.56, -.41, and 1.40, respectively, with negative values indicating women scoring higher). The strongest evidence for sex differences in SDs was for extraversion (women more variable) and for agreeableness (men more variable). United Nations indices of gender equality and economic development were associated with larger sex differences in agreeableness, but not with sex differences in other traits. Gender equality and economic development were negatively associated with mean national levels of neuroticism, suggesting that economic stress was associated with higher neuroticism. Regression analyses explored the power of sex, gender equality, and their interaction to predict men's and women's 106 national trait means for each of the four traits. Only sex predicted means for all four traits, and sex predicted trait means much more strongly than did gender equality or the interaction between sex and gender equality. These results suggest that biological factors may contribute to sex differences in personality and that culture plays a negligible to small role in moderating sex differences in personality.
Abstract
Men's and women's personalities appear to differ in several respects. Social role theories of development assume gender differences result primarily from perceived gender roles, gender socialization and sociostructural power differentials. As a consequence, social role theorists expect gender differences in personality to be smaller in cultures with more gender egalitarianism. Several large cross-cultural studies have generated sufficient data for evaluating these global personality predictions. Empirically, evidence suggests gender differences in most aspects of personality-Big Five traits, Dark Triad traits, self-esteem, subjective well-being, depression and values-are conspicuously larger in cultures with more egalitarian gender roles, gender socialization and sociopolitical gender equity. Similar patterns are evident when examining objectively measured attributes such as tested cognitive abilities and physical traits such as height and blood pressure. Social role theory appears inadequate for explaining some of the observed cultural variations in men's and women's personalities. Evolutionary theories regarding ecologically-evoked gender differences are described that may prove more useful in explaining global variation in human personality.
The only way to force arbitrarily equal outcomes - for no better reason than to say you achieved it - is to remove or limit people's choices. Because the places where men's and women's outcomes are the most equal is where they're both toiling in the rice-fields for 12 hours a day.
#Olga Khazan#science#STEM#science technology engineering math#technology#engineering#math#women in STEM#gender equality#egalitarian#sex differences#gender differences#religion is a mental illness
14 notes
·
View notes
Text

🎤 Troll King Out 👑
#egalitarian#egalitarianism#radical feminist safe#liberal feminism#radical feminism#feminism#equality#equal rights#radical feminst#feminsim#radical feminists do interact
69 notes
·
View notes
Text
it’s Martin Luther King Day! 🫶🏻 (history & learning resources)

Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr., born Michael Luther King, Jr., was an American human rights activist, political philosopher, Baptist minister, and one of the most notable pioneers of the Civil Rights Movement (1954-1964) in the United States during the Jim Crow Era of law, which legalized segregation of Black folks from White ones, and bred many acts of hatred, ostracism, and frequent violence against Black Americans.
King was born in Atlanta, Georgia, on January 15th, 1929, to his mother, Alberta Williams King, and his father, Martin Luther King, Sr. (then Michael Luther King, Sr.). a young woman by the name Coretta Scott would be attending the New England Conservatory of Music in Boston, Massachusetts, the same time that King was studying at Boston University. they soon fell in love, married on June 18th, 1953, and in September 1954, settled down in Montgomery, Alabama.

Coretta gave him four children: two sons, Martin Luther King III (Oct. 23rd, 1957 - present) and Dexter Scott King (Jan. 30th, 1961 - Jan. 22nd, 2024), and two daughters, Yolanda Denise King (Nov. 17th, 1955 - May 15th, 2007) and Bernice Albertine King (Mar. 28th, 1963 - present).
on Nov. 2nd, 1983, then-President Ronald Reagan signed the King Holiday Bill into law. this made the third Monday in January a federal holiday in observance of King and his work. it would take fifteen years for the holiday to be approved by the federal government, and seventeen more for it to be recognized in every state. (that’s a total of thirty-two years spent by activists, fighting for it to be in all fifty states!)

from the Collection of the Smithsonian National Museum of African American History & Culture | a pin-back button promoting Martin Luther King Day 1982 (source)
"Injustice anywhere is a threat to justice everywhere.… We know through painful experience that freedom is never voluntarily given by the oppressor; it must be demanded by the oppressed." — MLK, Jr.
from naacp.org:
“In 1963, King and the SCLC worked with NAACP and other civil rights groups to organize the March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom, which attracted 250,000 people to rally for the civil and economic rights of Black Americans in the nation's capital. There, King delivered his majestic 17-minute "I Have a Dream" speech. Along with other civil rights activists, King participated in the Selma-to-Montgomery march in 1965. The brutal attacks on activists by the police during the march were televised into the homes of Americans across the country. When the march concluded in Montgomery, King gave his "How Long, Not Long" speech, in which he predicted that equal rights for African Americans would be imminently granted. His legendary words are widely quoted today: "How long? Not long, because the arc of the moral universe is long, but it bends toward justice." Less than six months later, President Lyndon Johnson signed the Voting Rights Act banning disenfranchisement of Black Americans.”
in the spring of 1968, Black sanitary workers went on strike in Memphis, Tennessee. these works were protesting their racist White employer’s behaviors: low pay, abusive working conditions, unsafe work environments, and union busting. King arrived in Memphis on April 3rd, to prepare for a march in support of the workers.
around 6pm CST, on April 4th, 1968, on the balcony of his second-floor room at the Lorraine Motel, Dr. King was shot by a White supremacist. his advisor and close friend, Ralph Abernathy, ran to King’s side and cradled his head.
paramedics rushed him to St. Joseph’s Hospital where at 7:05pm CST, he was pronounced dead.
from kinginstitute.stanford.edu:
“President Lyndon B. Johnson called for a national day of mourning to be observed on 7 April. In the following days, public libraries, museums, schools, and businesses were closed, and the Academy Awards ceremony and numerous sporting events were postponed. On 8 April King’s widow, Coretta Scott King, and other family members joined thousands of participants in a march in Memphis honoring King and supporting the sanitation workers. King’s funeral service was held the following day in Atlanta at Ebenezer Baptist Church. It was attended by many of the nation’s political and civil rights leaders, including Jacqueline Kennedy, Vice President Hubert Humphrey, and Ralph Bunche. Morehouse College President Benjamin Mays delivered the eulogy, predicting that King “would probably say that, if death had to come, I am sure there was no greater cause to die for than fighting to get a just wage for garbage collectors” (Mays, 9 April 1968). Over 100,000 mourners followed two mules pulling King’s coffin through the streets of Atlanta. After another ceremony on the Morehouse campus, King’s body was initially interred at South-View Cemetery. Eventually, it was moved to a crypt next to the Ebenezer Church at the King Center, an institution founded by [Coretta Scott King].”
today, and tomorrow, and all days following, we remember, thank, and honor Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr., for a better tomorrow.

sources
Smithsonian's National Museum of African American History & Culture - The 15 Year Battle for Martin Luther King Jr. Day
The National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP) - Martin Luther King, Jr.
Stanford University Martin Luther King, Jr. Research and Education Institute - King, Coretta Scott
Stanford University Martin Luther King, Jr. Research and Education Institute - the Assassination of Martin Luther King, Jr.
The King Center - About Mrs. Coretta Scott King
New England Conservatory - Celebrate Boston’s Greatest Love Story: A Look Back at Coretta Scott King ’51, ’71 Hon. DM and Dr. Martin Luther King Jr.’s Historic First Meeting
extras/learning material
The King Center - About Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr.
National Education Association (NEA) - Lesson plans, activity ideas & other resources for teaching MLK Day
PBS - Martin Luther King Jr. Day classroom resources
We Are Teachers - 30 Meaningful Martin Luther King Jr. Activities for All Ages
Civil Rights Teaching - Teaching King Beyond “I Have a Dream”
Louisiana State University Libraries - Martin Luther King, Jr. timeline
Smithsonian's National Museum of African American History & Culture - Gestures of Solidarity in African American Culture
UNICEF USA - 5 Ways to Stand Up Against Racism and Injustice
Richton Park Public Library District - 11 Speeches by Rev. Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr.
Cross Cultural Solidarity - MLK: Speeches, Sermons, Essays, & Interviews
#martin luther king jr#martin luther king day#mlk#mlk day#mlk jr#mlk jr day#civil rights#blm movement#blm#antiracism#anti capitalism#egalitarian#black history#american history
11 notes
·
View notes