#Copepoda
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Copepod
“Copepods of various species. Photos were taken using a Biolam R-11 microscope. For photography, the dark field method was combined with polarization. Thanks to polarizing microscopy, the glow of muscle stripes in the bodies of some crustaceans is visible. Each photo is the result of panoramic shooting and focus stacking.” - via Wikimedia Commons (original description translated from Russian using Google Translate)
#wikipedia#wikipedia pictures#nature#animals#copepods#copepoda#crustacean#arthropoda#multicrustacea#arthropods#marine life#marine biology#marine animals#marine creatures#fish lice#crustaceans#sea animals#sea creatures#sea critters#ocean animals#oceancore#ocean aesthetic#ocean creatures#ocean critters#zoology
174 notes
·
View notes
Text
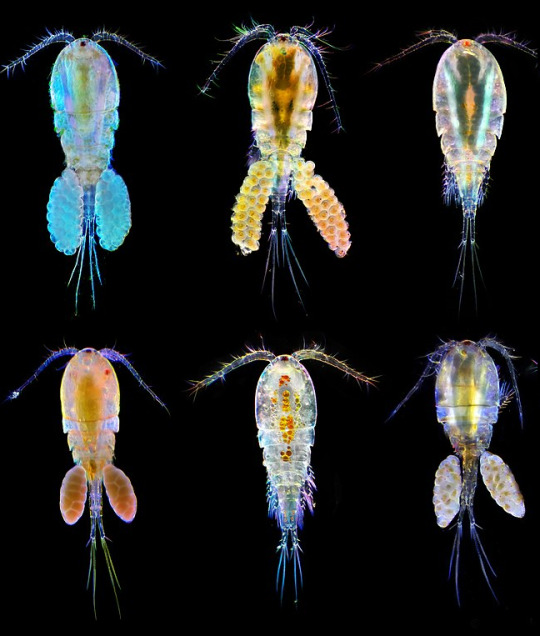
Round 2 - Arthropoda - Copepoda


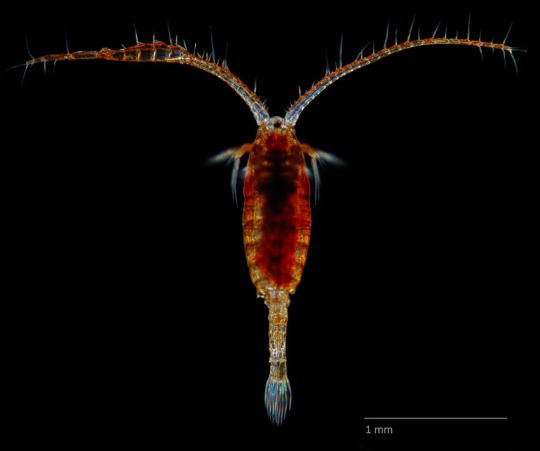

(Sources - 1, 2, 3, 4)
Copepoda is a class of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater biome, including the arctic. Some are planktonic, some live in sediment (benthic), some live underground in sinkholes or caves, some are parasitic, and some even live in wet terrestrial places such as bogs and the water-filled cups of bromeliads. They are small, usually 1 to 2 mm long, with a teardrop-shaped body and two pairs of antennae. Some polar copepods can reach up to 1 cm long. Most copepods have a single compound eye, usually bright red and in the centre of their transparent head. Subterranean species may be eyeless, and a couple genera have two eyes. Free-living copepods have a head fused with the first one or two thoracic segments, with the remainder of the thorax being comprised of three to five limbed segments. The first pair of appendages are maxillipeds, limbs used for feeding. The second pair beat like oars, aiding in swimming. They have a narrow abdomen with five leg-less segments, with tail-like rami at the tip. Meanwhile, the anatomy of parasitic copepods are so widely diverse that I simply do not have space to talk about it here. Copepods have incredibly fast reflexes, due to well-developed myelin sheaths, allowing them to escape predators at high speeds, often porpoising out of the water. Like ostracods, many species also use bioluminescence as a defense mechanism, using it to distract predators (see gif below).
When they are ready to mate, some copepod females leave a trail of pheromones for males to follow. When mating, the male will grip the female with his antennae and produce an adhesive spermatophore, then transfer it to the female’s genital opening. After fertilization, the eggs will sometimes be laid directly into the water column, or, in some species, the female will carry them in a sac until they hatch. In some pond-dwelling species, the eggs can remain dormant in the case of the pond drying up, waiting to hatch until more favorable conditions are present. The larvae hatch with a head and a tail but no true thorax or abdomen. In fact, the larvae look so different from their adult forms that many of them were once thought to be different species! They will moult 5-6 times before becoming a copepodid larva which resembles the adult, sans some limbs and segments. After 5 more moults they will reach adulthood.
The oldest known fossils of copepods are from the Late Carboniferous, but due to their small size and fragility, they are rare in the fossil record. However, these fossilized copepods seemed to belong to an extant (still living) family, meaning that copepods may have already reached the forms they are in now by the Carboniferous.

Propaganda under the cut:
Copepods are dominant members of zooplankton and are food for many species of fish. Some scientists say they form the largest animal biomass on earth, matched only by Antarctic Krill.
The surface layers of the ocean are the world’s largest carbon sink, absorbing harmful greenhouse gasses: about 2 billion tons of carbon a year, the equivalent of a third of human carbon emissions. Copepods contribute to a large part of this, feeding near the surface at night, and then carrying these gasses to deeper water with them. Their moulted exoskeletons, feces, and respiration all transfer carbon to the deep sea.
Live copepods are a popular addition to saltwater fish tanks, both as a food source for hard-to-feed fish, and as a clean-up crew.
Copepods are sometimes added to water-storage containers to control mosquitos, as some species will eat mosquito larvae. Copepods have been used successfully in Vietnam to control mosquitoes carrying dengue fever, and trials to employ this method are also underway in Thailand and the southern United States.
Sheldon J. Plankton, of “Spongebob Squarepants” fame, is a copepod!

63 notes
·
View notes
Text
Taxonomy Tournament: Crustaceans

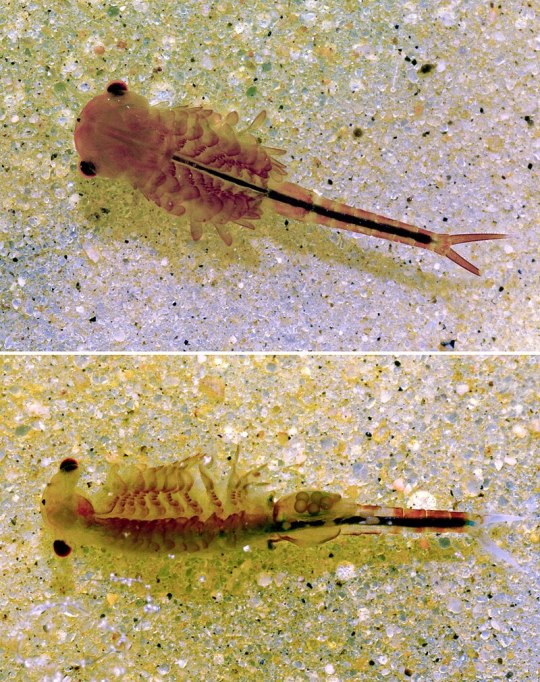
Copepoda. This class is made up of copepods, microscopic aquatic zooplankton, though some live in sediments or are parasites.
Branchiopoda. This class is made up of fairy shrimp, clam shrimp, water fleas, and the shield shrimp. All members have gills on their appendages, including the mouthparts.
#animals#biology#polls#poll tournament#zoology#copepods#arthropods#crustaceans#ecdytes#fairy shrimp#Copepoda#Branchiopoda#0xdv0xf2#Animal Tournament#Animal Tournament Round 1
87 notes
·
View notes
Photo

🌊 A monograph of the free and semi-parasitic Copepoda of the British islands London, Ray Society, 1878-80.
16 notes
·
View notes
Text












Great Slave Lake, Hay River (No. 5)
The Slave River provides the basin with high nutrient levels; accordingly, coupled with a general absence of pollution and invasive species, the lake is rich in aquatic life relative to its biome. Fish species include lake whitefish, lake trout, inconnu, northern pike and walleye, cisco, burbot, ninespine stickleback, shiner, also longnose sucker. Lake whitefish enjoy the highest levels, followed by cisco and suckers. Climate change, specifically reduced ice coverage times, is impacting the populations of these species. Copepoda are also prevalent in the lake.
Great Slave Lake has one ice road known as the Dettah ice road. It is a 6.5 km (4.0 mi) road that connects the Northwest Territories capital of Yellowknife to Dettah, a small First Nations fishing community also in the Northwest Territories. To reach the community in summer the drive is 27 km (17 mi) via the Ingraham Trail.
Source: Wikipedia
#Pumphouse Beach#Hay River#NWT#South Slave Region#Northwest Territories#Canada#small town#original photography#travel#vacation#tourist attraction#landmark#landscape#lakeside#nature#summer 2024#lake shore#dead wood#drift wood#forest#flora#waves
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
Parasitic crustaceans are wild.
[cw: photos of parasites inside host bodies]

Here is Linguatula serrata, which lives inside the nose of dogs and other Carnivorans. It belongs to group Pentastomida, which has so shed its arthropod appendages that it was long classified as its own independent phylum (attested in fossils all the way from the Cambrian Explosion!), until molecular analyses showed they were in fact strange crustaceans -- closest relatives of the relatively normal-looking fish lice (Branchiura).
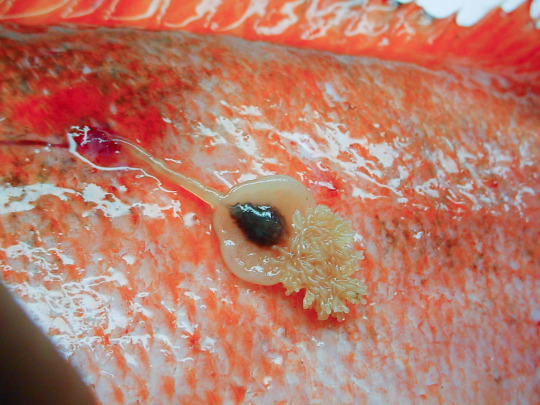
And then there’s Pennellidae...

Do those horn-things look like crustaceans to you? And yet the family Pennellidae is fully part of Copepoda, the chief component of crustacean plankton. Its body is simply one elongated trunk and a tiny head biting onto the fish, with two long egg cords trailing behind.
Look at the cod worm (Lernaeocera branchialis), another Pennellidae, hanging from the gills of a fish:
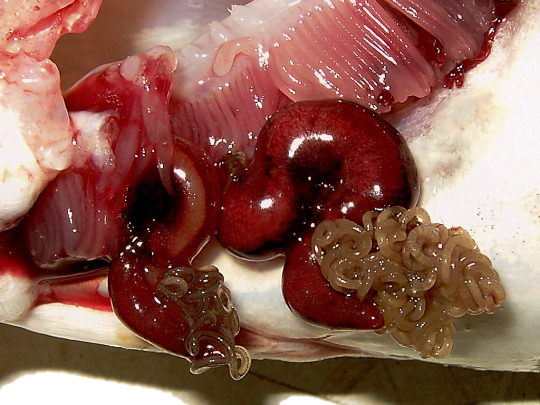
It’s those two red things that look like slugs wearing a wig made of soy noodles. Here’s what it looks like on its own, extracted and preserved:

(source) The coiled strings are egg masses. The slug-like part is the copepod’s trunk. The thin branching thing at the bottom is its head, converted into a sort of root system that no longer does head-like things, but rather burrows into the fish host’s blood vessels to feed its eggs. Incidentally, this is just the female; the male still looks like a regular planktonic crustacean.
Now, regular barnacles (Cirripedia) are strange enough...

(source; picture them as shrimps lying on their back, with a digestive system that fell out of the body wall but is still contained by the outer shell, and feathery legs poking out to filter water)
... but parasitic barnacles of clade Rhizocephala go much further:

Here, on the left, is Sacculina carcini. No, not the crab; the yellow sac poking out of the crab’s belly. On the right, its relative Clistosaccus paguri shows what it might look like once extracted.
Sacculina carcini is fun. A larva looks much like any other crustacean planktonic larva, until it finds a suitable host. It stings the unfortunate crab in a vulnerable spot between armor plates, and effectively injects itself into the host, leaving its own shell outside, and transferring only soft tissues.
Once inside, it grows more like a fungus than an animal, turning into a root-like web that infests the crab’s entire body, down to its leg tips. Then it takes over not only the crab’s digestive system, leeching nutrients for its own eggs, but also its nervous system, effectively controlling it like a puppet.
When the parasite is mature, its egg sac starts bulging out of the crab’s body: that’s the yellow part you see in the photo. Male Sacculina stay larvae their whole life: they just mate with the female’s egg sac and then die. The parasite makes the crab take care of itself as if it was the crab’s own eggs. There’s no competition, since the host is sterilized; to leave more food for the parasite, it also stops molting and regenerating lost limbs. If the host is male, and therefore poorly suited to carrying egg sacs under its tail, Sacculina messes with its hormones and effectively turns it female.
Finally the eggs are released and the whole cycle starts again, with the only purpose of making more eggs whose purpose is making more eggs.
(all pictures from Wikipedia unless specified otherwise)
260 notes
·
View notes
Text
today's invertebrate.......echinoderes drogoni
echinoderes drogoni works for minimum wage at a factory here they make slop, sludge and many other goopy products
so next time you use some sort of goop, blob, sludge, slop, bog, swamp, mucus or slime always thank echinoderes drogoni and the many other factory workers for their hard work, spending days just to get that goop to you



(pics by sanya-copepoda)
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Bengkalis Atlantik

Bengkalis Atlantik (Clupea harengus) adalah salah satu dari spesies ikan yang paling berlimpah di Bumi. Mereka dapat ditemui di samudra Atlantik dan bergerak bersama dalam satu grup. Bengkalis Atlantik dapat tumbuh sepanjang 45 sentimeter dan massa lebih dari setengah kilogram. Mereka makan copepoda, krill dan ikan kecil, dan predator alami mereka adalah anjing laut, paus, bakalau dan ikan besar lainnya.
0 notes
Text
don't fucking challenge me i know every beast
NON-BEASTLY BEASTS:
Non-ParaHoxozoa:
Calcarea (Calcareous Sponges)
Hexacinellida (Glass Sponges)
Demospongiae (Demosponges)
Tentaculata (Tentacled Ctenophores)
Beroida (Non-Tentacled Ctenophores)
ParaHoxozoa, Non-Nephrozoa:
Placozoa
Anthozoa (Corals, Sea Pens, and Tube-Dwelling Anenomes)
Medusozoa (Jellyfish and Hydrozoans)
Myxozoa
Xenacoelomorpha
MINIBEASTS:
Spiralia, Non-Lophotrochozoa:
Gnathifera (Rotifers and Jaw Worms)
Mesozoa
Rouphozoa (Flatworms and Gastrotrichs)
Lophotrochozoa, Non-Mollusca:
Cycliophora
Annelida (Segmented Worms)
Nemertea (Ribbon Worms)
Bryozoa
Entoprocta
Phorodina (Horseshoe Worms)
Brachiopoda
Mollusca:
Solenogastres
Caudofoveata
Polyplacophora (Chitons)
Bivalvia (Clams, Scallops, Mussels, Oysters, Cockles, and others)
Monoplacophora
Scaphopoda (Tusk Shells)
Gastropoda (Snails, Slugs, Sea Snails, Sea Slugs, and others)
Cephalopoda (Nautiloids, Cuttlefish, Squid, and Octopi)
Ecdysozoa, Non-Arthropoda:
Loricifera
Priapulida (Penis Worms [sic])
Kinorhyncha (Mud Dragons)
Nematoda (Roundworms)
Nematomorpha (Horsehair Worms)
Tardigrada (Tardigrades)
Onchyophora (Velvet Worms)
Arthropoda, Non-Mandibulata:
Pycnogonida (Sea Spiders)
Xiphosura (Horseshoe Crabs)
Acariformes (Cheese Mites, Scabies Mites, Eyelash Mites, House Mites, and others)
Opiliones (Harvestmen)
Ricinulei (Hooded Tickspiders)
Solifugae (Camel Spiders)
Parisitiformes (Ticks, Varroa Mites, and others)
Pseudoscorpiones (Pseudoscorpions)
Scorpiones (Scorpions)
Araneae (Spiders)
Amblypigi (Whip Spiders)
Urgopygi (Whip Scorpions)
Mandibulata, Non-Insecta:
Chilopoda (Centipedes)
Symphyla (Pseudocentipedes)
Pauropoda
Diplopoda (Millipedes)
Ostracoda (Seed Shrimp)
Mystacocarida
Branchiura (Fish Lice)
Pentastomida (Tongue Worms)
Copepoda (Copepods)
Tantulocarida
Thecostraca (Barnacles and others)
Malacostraca (Crabs, Lobsters, Shrimp, Isopods, Amphipods, and others)
Cephalocarida (Horseshoe Shrimp)
Branchiopoda (Fairy Shrimp, Tadpole Shrimp, Water Fleas, and others)
Remipedia
Collembola (Springtails)
Protura
Diplura (Two-Pronged Bristletails)
Insecta, Non-Neoptera:
Archaeognatha (Jumping Bristletails)
Zygentoma (Silverfish, Firebrats, and others)
Odonatoptera (Dragonflies and Damselflies)
Ephemeroptera (Mayflies)
Neoptera, Non-Holometabola:
Zoraptera (Angel Insects)
Dermaptera (Earwigs)
Plecoptera (Stoneflies)
Orthoptera (Grasshoppers, Crickets, and others)
Mantodea (Mantises)
Blattodea (Cockroaches and Termites)
Notoptera (Ice Crawlers and Rock Crawlers)
Phasmatodea (Stick Insects and Leaf Insects)
Embioptera (Webspinners)
Psocodea (Lice)
Hemiptera (Shield Bugs, Aphids, Scale Insects, Cicadas, Planthoppers, Assassin Bugs, Water Boatmen, Pond Skaters, and others)
Thysanoptera (Thrips)
Holometabola
Hymenoptera (Sawflies, Bees, Wasps, and Ants)
Strepsiptera
Coleoptera (Beetles)
Raphidioptera (Snakeflies)
Neuroptera (Lacewings, Antlions, and others)
Megaloptera (Dobsonflies and others)
Lepidoptera (Butterflies and Moths)
Trichoptera (Caddisflies)
Diptera (Flies, Mosquitoes, Gnats, Midges, Hoverflies, and others)
Mecopteroidea (Scorpionflies, Hangingflies, and Fleas)
SLIGHTLY MORE BEASTLY BEASTS:
Ambulacraria:
Echinodermata (Starfish, Sea Urchins, Brittle Stars, Feather Stars, and others)
Hemichordata (Acorn Worms and others)
Chordata (Non-Vertebrata):
Leptocardii (Lancelets)
Tunicata (Sea Squirts, Salps, Pyrosomes, and others)
Vertebrata (Non-Eutelostomi):
Myxini (Hagfish)
Hyperoartia (Lampreys)
Elasmobranchii (Sharks, Rays, and Skates)
Holocephali (Chimaeras)
Actinopterygii (Non-Acanthomorpha):
Cladistia (Bichirs and Reedfish)
Acnipenseriformes (Paddlefish and Sturgeons)
Halecomorphi (Bowfins)
Ginglymodi (Gars)
Elopocephalai (Eels, Ladyfish, Halosaurs, and others)
Osteoglossocephala (Arapaima, Goldeye, and others)
Clupei (Herrings and Anchovies)
Apelocephali (Slickheads and others)
Anotophysa (Milkfish, Beaked Salmon, and others)
Cypriniformes (Carp, Goldfish, Loaches, Minnows, and others)
Characiformes (Characins, Pacu, Pirahnas, Tetras, and others)
Gymnotiformes (Knifefish and Electric Eels)
Siluriformes (Catfish)
Lepidogalaxii (Salamanderfish)
Protacanthopterygii (Salmon, Pike, Trout, Barreleye, and others)
Stomiati (Smelts, Marine Hatchetfish, and others)
Ateleopodia (Jellynose Fish)
Aulopa (Bombay Duck and Lancetfish)
Myctophata (Lanternfish)
Acanthomorpha:
Lampridacea (Oarfish, Opah and others)
Paracanthomorphacea (Cods, Dories, Cavefish, and others)
Polymixiacea (Beardfish)
Berycimorphaceae (Fangtooths, Pineconefishes, and others)
Holocentrimorphaceae (Soldierfish)
Ophidiiformes (Pearlfish)
Batrachoidimophara (Toadfish)
Gobiomorpharia (Seahorses, Pipefish, Tunas, Flying Gurnards, and others)
Anabantaria (Gouramis, Swamp Eels, and others)
Carangaria (Swordfish, Flatfish, Remoras, and others)
Ovalentaria (Blennies, Cichlids, Flying Fish, Mullets, and others)
Eupercaria (Anglerfish, Pufferfish, Wrasses, Sunfish, Sticklebacks, Lumpsuckers, Lionfish, Angelfish, Perches, Archerfish, Triggerfish, Bass, and others)
Sarcopterygii:
Actinistia (Coelocanths)
Dipnoi (Lungfish)
BEASTS PROPER:
Lissamphibia
Salientia (Frogs and Toads)
Caudata (Salamanders and Newts)
Gymnophiona (Caecilians)
Reptilia (Non-Aves)
Rhynchocephalia (Tuatara)
Dibamidae (Blind Skinks)
Gekkota (Geckos and Flap-Footed Lizards)
Scinciformata (Skinks and others)
Laterata (Tegus and Worm Lizards)
Anguimorpha (Slow Worms, Monitors, Gila Monster, and others)
Iguania (Anoles, Iguanas, Chameleons, and others)
Serpentes (Snakes)
Testudines (Turtles and Tortoises)
Crocodilia (Crocodiles, Gharials, Alligators, and Caiman)
Aves (Non-Passeriformes):
Palaeognathae (Ostriches, Kiwis, and others)
Galloanserae (Chickens, Ducks, and others)
Mirandornithes (Flamingos and Grebes)
Columbimorphae (Doves and others)
Otidimorphae (Cuckoos, Turacos, and Bustards)
Gruimorphae (Gulls, Cranes, Auks, and others)
Ophistocomidae (Hoatzins)
Strisores (Hummingbirds, Nightjars, Potoos, and others)
Phaethoquornithes (Boobies, Loons, Ibises, Penguins, Albatrosses, Tropicbirds, and others)
Acciptirimorphae (Vultures, Hawks, Eagles, and others)
Strigiformes (Owls)
Coraciimorphae (Kingfishers, Woodpeckers, Quetzals, and others)
Cariamiformes (Seriemas)
Falconiformes (Falcons)
Psittaciformes (Parrots)
Passeriformes:
Acanthisitti (New Zealand Wrens)
Tyranni (Overnbirds, Spadebills, Gnateaters, and others)
Menurida (Lyrebirds and others)
Climacterida (Bowerbirds and others)
Meliphagida (Honeyeaters, Bristlebirds, and others)
Orthonychida (Logrunners and others)
Corvides (Crows, Jays, Boatbills, Shriketits, Sittellas, Birds-Of-Paradise and others)
Passerides (Satinbirds, Sparrows, Larks, Tits, Oxpeckers, Thrushes, Wrens, Finches, Tanagers, Nuthatchers, and others)
Mammalia (Non-Laurasiatheria):
Monotremata (Platypus and Echidnas)
Marsupialia (Kangaroos, Opossums, Wombats, and others)
Xenarthra (Anteaters, Sloths, and others)
Athrotheria (Elephants, Manatees, Aardvarks, and others)
Lagomorpha (Rabbits, Hares and others)
Rodentia (Mice, Rats, Cavies, Beavers, Squirrels, and others)
Scandentia (Treeshrews)
Dermoptera (Colugos)
Primates (Lemurs, Marmosets, Baboons, Gibbons, Chimpanzees, and others)
Lauasiatheria (Non-Carnivora):
Eulipotyphla (Shrews, Moles, Hedgehogs, and others)
Chiroptera (Bats)
Artiodactyla (Girrafes, Deer, Whales, Pigs, Camels, and others)
Perissodactyla (Horses, Tapir, and Rhinoceros)
Pholidota (Pangolins)
Carnivora:
Viverroidea (Hyenas, Mongooses, Civets, and others)
Feloidea (Lions, Tigers, Caracals, Wildcats, Leopards, and others)
Nandiniidae (African Palm Civet)
Caninae (Wolves, Foxes, and others)
Ursidae (Bears)
Musteloidea (Skunks, Weasels, Otters, Raccoons, and others)
Pinnipedia (Seals, Sea Lions, and Walruses)
Interview questions for gym leaders
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
Hyla savignyi x Copepoda slowburn 100k words
0 notes
Text

Copepod
“Copepods are aquatic animals like most crustaceans. They live en masse in all depths of both sea and fresh water, as well as in puddles, swamps, and some species in moist moss and wasteland. Among them are also parasites whose appearance can be changed beyond recognition and which live on fish and other aquatic animals. Free-living copepods are only a few millimeters long (0,5-2mm) and play an important part in the water body's food chain: they reproduce relatively quickly, and by feeding on tiny microscopic organisms, they themselves are constantly food for larger aquatic animals. Around 8,500 species of copepods are known in the world, according to the latest data, 82 are known in Estonia, but the existence of 100 species is assumed.” - via Wikimedia Commons
#copepod#crustacean#arthropoda#arthropods#wikipedia#wikipedia pictures#nature#animals#marine biology#biology#zoology#multicrustacea#copepoda#marine animals#marine life#marine creatures#sea animals#sea creatures#oceancore#ocean animals#sea critters#fish lice#ocean creatures#ocean life
37 notes
·
View notes
Text
Round 2 Final Stats:
Previously I said any group to earn over 900 points will move on to Round 3, however, I’m going to make it the Top 10 just to make it even. Plus, what’s an extra two species?
For the final stats, I’ve made a little graphic with some doodles to remind y’all what each class is. (Couldn’t use emojis for everyone because, alas, there are not enough unique ones to represent all these animal groups!) The full list is typed out under the read more though, as well as the extra stats for this round!
The top classes (or phylogenetic equivalents) have been ranked thusly, listed here from highest ranking to lowest:

🦈 Chondrichthyes ~ 1,509
🐀 Mammalia ~ 1,437
🐍 Reptilia ~ 1,183
🐙 Cephalopoda ~ 1,175
🐸 Lissamphibia ~ 1,002
🐠 Actinopterygii ~ 983
🦀 Malacostraca ~ 954
🕷 Arachnida ~ 913
🐞 Insecta ~ 908
Actinistia ~ 853
�� Gastropoda ~ 796
🫁 Dipnoi ~ 598
🦪 Bivalvia ~ 507
Myxini ~ 492
Chilopoda ~ 479
Branchiopoda ~ 443
Polyplacophora ~ 427
Petromyzontida ~ 412
Pycnogonida ~ 405
Copepoda ~ 308
Ascidiacea ~ 394
Diplopoda ~ 393
Ostracoda ~ 278
Collembola ~ 272
Thecostraca ~ 253
Pauropoda ~ 246
Appendicularia ~ 229
Leptocardii ~ 222
Remipedia ~ 194
Symphyla ~ 166
Solenogastres ~ 164
Tergomya ~ 158
Scaphopoda ~ 142
Tantulocarida ~ 139
Cephalocarida ~ 134
Mystacocarida ~ 115
Caudofoveata ~ 110
Diplura ~ 94
Protura ~ 83
Ichthyostraca ~ 83
Our Top 10 Classes are Chondrichthyes, Mammalia, Reptilia, Cephalopoda, Lissamphibia, Actinopterygii, Malacostraca, Arachnida, Insecta, and Actinistia!
This means Chondrichthyes, Mammalia, Reptilia, Cephalopoda, Lissamphibia, Actinopterygii, Malacostraca, Arachnida, Insecta, and Actinistia will be moving on to Round 3, and broken up by Order (or some other phylogenetic equivalent).
Extra Stats:
Arthropod Class Pycnogonida (“sea spiders”)
~ was the first group of Round 2
~ was the first arthropod group of Round 2
~ had the highest amount of dislikes at 20
~ had the highest amount of hates at 5
Arthropod Class Symphyla (“garden centipedes”)
~ had the highest percentage of likes at 45%
Arthropod Class Ichthyostraca (“fish lice” and “tongue worms”)
~ had the highest percentage of dislikes at 9.1%
~ had the highest percentage of hates at 2.6%
Arthropod Class Mystacocarida (“mustache shrimp”)
~ had the lowest amount of loves at 13
~ had the lowest percentage of loves at 7.9%
~ had 0 hates
~ had the least reblogs at 8
~ had the least notes at 21
Arthropod Class Ostracoda (“seed shrimp”)
~ had 0 hates
~ received exactly 200 votes
Arthropod Class Copepoda (copepods)
~ had 0 hates
Arthropod Class Malacostraca (“crabs”, “lobsters”, “shrimp”, etc)
~ had the third most reblogs at 55
~ had the highest percentage of loves at 52.8%
~ had 0 dislikes and 0 hates
~ was the highest ranked Arthropod class
Arthropod Class Tantulocarida (tantulocarids)
~ had the highest amount of neutral votes at 91, along with Caudofoveata
Arthropod Class Cephalocarida (“horseshoe shrimp”)
~ had 0 hates
Arthropod Class Remipedia (remipedes)
~ had 0 hates
Arthropod Class Collembola (“springtails”)
~ had 0 hates
Arthropod Class/Order Protura (“coneheads”)
~ had the least votes at 125
~ had the lowest amount of favorites at 1
~ had the lowest percentage of favorites at 0.8%
~ had 0 hates
Arthropod Class Insecta (insects)
~ had 0 dislikes
Chordate Class Leptocardii (“lancelets”)
~ was the first Chordate group of Round 2
~ had 0 hates
Chordate Class Ascidiacea/Thaliacea (“sea squirts”, “salps”, “pyrosomes”, etc.)
~ had 0 hates
Chordate Class Appendicularia (“larvaceans”)
~ had 0 hates
Chordate Class Chondrichthyes (“cartilaginous fish”)
~ had the most votes at 415
~ had the highest amount of loves at 181
~ had 0 dislikes and 0 hates
~ had the most reblogs at 105
~ had the most notes at 235
~ was the highest ranked group of chordates
Chordate Class Actinistia (“coelacanths”)
~ had 0 dislikes and 0 hates
~ was the first single genus (Latimeria) to be ranked
Chordate Class Dipnoi (“lungfish”)
~ had the highest amount of likes at 104
~ had 0 dislikes and 0 hates
~ contained the first of my personal favorites (Australian Lungfish) to be eliminated 🥲
Chordate Class Lissamphibia (amphibians)
~ had the lowest amount of neutral votes at 1, along with Reptilia and Gastropoda
~ had the lowest percentage of neutral votes at 0.4%, along with Reptilia and Gastropoda
~ had 0 dislikes and 0 hates
Chordate Class Reptilia (reptiles)
~ had the lowest amount of neutral votes at 1, along with Lissamphibia and Gastropoda
~ had the lowest percentage of neutral votes at 0.4%, along with Lissamphibia and Gastropoda
~ had 0 dislikes and 0 hates
Chordate Class Mammalia (mammals)
~ had the highest amount of favorites at 258
~ had the highest percentage of favorites at 80.6%
~ had the lowest amount of likes at 4
~ had the lowest percentage of likes at 1.2%
Molluscan Class Polyplacophora (“chitons”)
~ was the first Mollusc group of Round 2
~ had 0 hates
Molluscan Class Solenogastres (solenogasters)
~ had 0 hates
Molluscan Class Caudofoveata (caudofoveatans)
~ had the highest amount of neutral votes at 91, along with Tantulocarida
~ had the highest percentage of neutral votes at 58%
Molluscan Subclass Tergomya (tergomyans)
~ had 0 hates
Molluscan Class Cephalopoda (cephalopods)
~ had the second most reblogs at 66
~ had 0 dislikes and 0 hates
~ was the only molluscan class to make it into the Top Ten
Molluscan Class Scaphopoda (“tusk shells”)
~ had 0 hates
Molluscan Class Gastropoda (“snails” and kin)
~ had 0 dislikes and 0 hates
~ had the lowest amount of neutral votes at 1, along with Lissamphibia and Reptilia
~ had the lowest percentage of neutral votes at 0.4%, along with Lissamphibia and Reptilia
Molluscan Class Bivalvia (bivalves)
~ had 0 dislikes
#Thanks for voting!#Statistics#extras#poll results#round 2#I’ve made my peace with most of these but#i’m still grumpy about the millipedes tho#like really#y’all put copepods higher than them#also what happened to all the people who got arthropoda to win the first round#where’d you go#to be clear though I AM happy for the ones who did move forward#i am very proud to still have arachnids with us#and I’m excited to vote on all the different birds and insects#we can’t just do all of them or I’d be here all day lol
61 notes
·
View notes
Text
ZOOPLANKTON FAUNA OF A SECTION OF OGBESE RIVER, EKITI STATE, NIGERIA | Journal of Global Agriculture and Ecology
The number and variety of zooplankton in a segment of the Ogbese River in Ado Ekiti were studied in this study. For a period of three months, samples were taken every two weeks. A total of 16 zooplankton genera from three families were discovered. Rotifera, Cladocera, and Copepod were the zooplankton groups found. The largest relative abundance of individuals was seen in Rotifera (61.7 percent ). Copepoda (24.7 percent) and Cladocera came in second and third, respectively (13. 4 percent ). Rotifera has 343 individuals per ml of water sample, Copepoda has 137 individuals per ml, and Cladocera has 74 individuals per ml of water sample, according to the numerical abundance. Rotifera > Copepoda > Cladocera is the order of zooplankton abundance. Please see the link :- https://www.ikprress.org/index.php/JOGAE/article/view/254
0 notes
Photo

🗺 Report of the Copepoda collected by Professor Herdman, at Ceylon, in 1902,. London, s.n., 1903.
16 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Copépodos y tardígrados! Cerámica de alta temperatura. Gracias @ilianascheggia #mostrok #mostrok_workshop #ceramica #ceramics #copepoda #tardigrada #tardigrade #osodeagua (en Miraflores, Lima) https://www.instagram.com/p/CBWAVDZhQs4/?igshid=c4hiz9821di4
0 notes
