#Based on: English Folklore
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

As a wise, Australian bunny once said "Easter is new beginnings, new life..." and so to celebrate we discussed the Tumblr darling, Rise of the Guardians, in which Jack Frost, Santa Claus, the Tooth Fairy, the Easter Bunny, and the Sandman formed a superhero team... and this movie is a lot better than that suggests. Join us in screaming about the gendery feelings Jack Frost brings many of us, about how the Sandman might be Jesus, and, in all seriousness, why we tell these stories to our kids as a culture. Merry Christmas, Happy Easter, and don't forget to floss.
#In Each Retelling#Rise of the Guardians#Based on: English Folklore#Based on: Germanic Folklore#Based on: Eastern European Folklore#Based on: Slavic Folklore#Based on: Hindu Mythology#Based on: Buddhist Mythology#animated media#podcast episode
1 note
·
View note
Text
Everyone should get $5000 for college each semester after all the fees have been paid. No matter what.
#glacier rambles#why is financial aid so hard#the degree tracker says i finished all my english credits#but not my extensive writing credits that were added literally the next semester#so i decide to take this class for extensive writing that's mythology and folklore based#but now i've got something saying financial aid won't pay for classes outside of my degree#...#so#i have to contact an advisor and ask wtf is going on before january 24th which is the freeze dat for financial aid
0 notes
Text
Updates to AO3 "Mythology" Fandoms
Hi AO3 users! You may have noticed that recently, fandoms previously canonized as "Mythology" are being updated to "Religion & Lore". This renaming project is part of a wider ongoing process on AO3 about respectful treatment and naming of various religions, spiritual beliefs, faiths, and collections of folklores belonging to a particular religious or cultural tradition. This includes both major and minor religions, as well as reconstructionist, ancient, and modern religions.
In the coming months, the term "Mythology" is being phased out of canonical fandom names. This is because of its potential for use as a disparaging term, and the way in which it is used primarily for religions which are already under-represented. Since "mythology" has connotations of being fictional or inferior to the religious beliefs of the speaker or writer, and is unfortunately used in this way by some, the decision has been made to replace this term with something that the Wrangling Committee believes is more inclusive and less derogatory.
After extensive discussion between individuals from varying religious backgrounds and beliefs, including wranglers representing the various fandoms which were being covered, it was felt that "Religion & Lore" was an appropriate and neutral way to describe the bodies of faith, belief, knowledge, and tradition associated with many of these religions which were ancestrally imparted and regional in nature. It is also hoped that this will decrease ambiguous or confused use, allowing people to more accurately describe their works and find works in which they are interested moving forward.
The use of "Ancient" in many of these fandoms' names reflects that these countries still exist but now have different predominant religions or spiritual beliefs. For example, Ancient Greek Religion & Lore (as Greece is now a predominantly Christian country) or Ancient Egyptian Religion (as Egypt is now a predominantly Muslim country). Because "Norse" does not refer to an extant country, region, or culture, it is not necessary to specify that it is historical or ancient in nature.
The names of these fandoms will also have the native language piped, if the English-language demonym is significantly different from the native-language demonym or if there is a culturally specific term based on consultation with individuals who speak these languages as a first language. We hope to give representation to the language of the source culture by doing so.
Each of these changes has been and will continue to be carefully researched and discussed with traditional knowledge keepers and researchers from the cultures represented in the fandoms under discussion.
Many religions face the issue of texts being written long after their events occurred. Unfortunately this is something which is shared across many religious fandoms; AO3 seeks to treat these religious fandoms equally. Care has been taken in researching characters relating to these fandoms, and character tags will be canonized or made a synonym on a case-by-case basis. Fandom tags that are currently synned to the Ancient religious fandoms have been checked as thoroughly as possible to ensure that they are not referring to modern folk tales, and where possible such relatively modern folk tales are canonized as their own fandoms.
(From time to time, ao3org posts announcements of recent or upcoming wrangling changes on behalf of the Tag Wrangling Committee.)
5K notes
·
View notes
Text
Witches and the Genius Loci: Folkloric Methods of Contact and Communion
The witches of old knew how to speak with the land. They didn’t just live in the wild, they wove themselves into its fabric, calling on the hidden ones in the earth, water, and wind. How did they do it? The answers would be as varied as the forests and fields they walked. But there are patterns we can see in all of them. Here are some of the ways I have discovered witches (in European folklore) reached out to the spirits of the land.
𖤐 Offerings at Spirit Dwellings
A witch rarely arrived empty-handed. Milk poured at the base of an ancient tree, ale left at the mouth of a cave, a bit of bread crumbled into a stream, these were ways to invite the unseen to draw near. Scottish folklore describes the gruagach, a guardian spirit, receiving libations of milk at stones and riverbanks (Campbell, Superstitions of the Highlands and Islands of Scotland, 1900). In Belgium and the Netherlands, witches were accused of offering beer and bread to the duivel, a local spirit often conflated with the Devil in later Christianized accounts (De Blécourt, Het Duivelspact, 1993).
𖤐 By Bone and Blood
In Scandinavian folklore, the practice of bjarmic magic involved burying bones to anchor spirits to the land, while Livonian witches were said to whisper their desires into a skull before placing it in the earth (Rääbis, Eesti Rahvapärimus ja Nõiakunst, 1926). In the 17th-century Scottish witch trials, accused witches described sealing pacts with land spirits by pricking their fingers and pressing the blood into soil or stone (Pitcairn, Ancient Criminal Trials in Scotland, 1833).
𖤐 Spirit-Flight and Dreamwalking
Witches didn’t always wait for spirits to come to them. Many traveled in spectral form, slipping into trance states with the help of charms or salves to reach spirits. The Trollenfrauen of German folklore and the Heks of Scandinavian folklore were said to enter deep sleep while holding a stone, allowing them to fly in spirit to the places where land spirits dwelled (Müller, Sagen aus Westfalen, 1857). In 17th-century witch trials from Flanders, accused witches claimed to lie still in darkness, feeling themselves lifted away to converse with spirits at crossroads and hollow hills (Proces tegen Tanneken Sconincx, 1606).
𖤐 Bone Charms & Rattles
A witch’s tools were often made from the dead. Flemish folklore mentions witches carrying duivelsfluitjes—small bone whistles said to call spirits when blown at twilight (De Meyer, Volksverhalen uit Vlaanderen, 1970). The bohnenzauber of Germanic folklore involved threading small bones together to create a rattling charm that stirred spirits of the wild (Grimm, Deutsche Mythologie, 1835).

𖤐 Turning Up the Soil
Some witches were accused of whispering into the ground, digging their fingers into the soil as they spoke. In Swedish folk belief, jordfastan involved burying a charm/offering (usually a piece of cloth or a coin) under a tree to call on spirits of the land (Hylten-Cavallius, Wärend och Wirdarne, 1863). Scottish trial records mention witches placing coal or burned bones in the earth as a form of spirit-binding magic (Pitcairn, Ancient Criminal Trials in Scotland, 1833).
𖤐 Skin-Turning and Familiars
In Breton folklore, witches who wished to meet the hidden spirits of the woods were said to transform into black dogs or other beasts before travelling into the deep forest (Sébillot, Le Folklore de la Bretagne, 1904). In Scotland, it was believed that witches who took the form of hares or crows could cross into the spirit world more easily (Popular Tales of the West Highlands, Campbell, 1860).
𖤐 Betwixt Earth and Water
The land’s voice is loudest in the places where two worlds meet. Marshes, riverbanks, and tidal flats; these places belonged to neither land nor water, making them perfect for spirit-calling (my favourite method). In English and Welsh folklore, witches were said to stand barefoot in water at night, calling on spirits with secret words (Henderson, Folklore of the Northern Counties of England, 1866). In Estonia, it was believed that standing in a bog at sunset allowed one to hear the voices of spirits whispering in the wind (Loorits, Eesti Rahvausund, 1949).

Seeking out the spirits of the land is integral to building a foundational practice in witchcraft and connecting to your landscape. It is these spirits that grant you access to the powers of the land that you require to make your works work.
#folk witchcraft#traditional witchcraft#witchcraft#traditional witches#folk witch#folk witches#witch#trad witch#folklore#spells#spirit work#genius loci#witching spirits#spirits#spirits of the land#witch tips#beginner witch tips
165 notes
·
View notes
Note
On the topic of "Fairies are English, faeries are Welsh." there's a thing that I've seen artists draw recently which is "according to folklore corgis were used as steeds by fairies" which they saw on Wikipedia and took at face value, but I'd never heard of this. I tried looking for an actual folkloric source but the only conclusion I came to was that it was invented by the English kennel club as some flavour text for a book about dog breeds. I don't suppose you'd ever heard of it as folklore?
So, I too used to cite this, and then one day someone asked me a similar question to yours, and like you I couldn't find anything earlier than a late Victorian-ish kennel club claim. It's possible it's based in truth, of course - maybe there was a bit of folklore around Pembrokeshire at that time that said something to that effect, since Pembrokeshire has always been an odd mix of Welsh, English and Flemish. But, it's not in British Goblins, which is generally a bad sign given that the claim was made contemporaneously to that book being written, and by god was Wirt Sikes thorough in listing every single myth he could find.
So, it's folklore now; but, it's not a traditional piece. About 120 years old.
However, the Eisteddfod refuses to get rid of the disco dancing competitions they introduced in the 1990s because they're "traditional" now, so in Wales "tradition" comes about a lot faster than you'd think. Even, and I cannot stress this enough, when the competitors are too young to have been around for disco, and also, and it is absolutely impossible to stress this even a fraction enough, when none of them can fucking disco dance.
188 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hi, so i writing a book based in the 1800s like the cowboy eras can you please tell me somethings I should keep in mind about the society and stuff also I need a little motivation I have been loosing it all please and thankyou <<<333
Writing Notes: Cowboys
Cowboy
In the western United States: a horseman skilled at handling cattle, an indispensable laborer in the cattle industry of the trans-Mississippi west, and a romantic figure in American folklore.
Pioneers from the United States encountered Mexican vaqueros (Spanish, literally, “cowboys”; English “buckaroos”) on ranches in Texas about 1820, and soon adopted their masterful skills and equipment—the use of lariat, saddle, spurs, and branding iron.
But cattle were only a small part of the economy of Texas until after the Civil War.
The development of a profitable market for beef in northern cities after 1865 prompted many Texans, including many formerly enslaved African Americans, to go into cattle raising. (Though they have been almost entirely excluded from the mythology of the American cowboy, it is estimated that Black cowboys accounted for nearly a quarter of all cattle workers in the nascent American West during the latter half of the 19th century.)
By the late 1800s, the lucrative cattle industry had spread across the Great Plains from Texas to Canada and westward to the Rocky Mountains.
Vaqueros
In 1519, shortly after the Spanish arrived in the Americas, they began to build ranches to raise cattle and other livestock. Horses were imported from Spain and put to work on the ranches.
Mexico’s native cowboys were called vaqueros, which comes from the Spanish word vaca (cow). Vaqueros were hired by ranchers to tend to the livestock and were known for their superior roping, riding and herding skills.
By the early 1700s, ranching made its way to present-day Texas, New Mexico, Arizona and as far south as Argentina. When the California missions started in 1769, livestock practices were introduced to more areas in the West.
During the early 1800s, many English-speaking settlers migrated to the West and adopted aspects of the vaquero culture, including their clothing style and cattle-driving methods.
Cowboys came from diverse backgrounds and included African-Americans, Native Americans, Mexicans and settlers from the eastern United States and Europe.
Cowboy Life
Cowboys were mostly young men who needed cash. The average cowboy in the West made about $25 to $40 a month.
In addition to herding cattle, they also helped care for horses, repaired fences and buildings, worked cattle drives and in some cases helped establish frontier towns.
Cowboys occasionally developed a bad reputation for being lawless, and some were banned from certain establishments.
They typically wore large hats with wide brims to protect them from the sun, boots to help them ride horses and bandanas to guard them from dust. Some wore chaps on the outsides of their trousers to protect their legs from sharp cactus needles and rocky terrain.
When they lived on a ranch, they shared a bunkhouse with each other. For entertainment, some sang songs, played the guitar or harmonica & wrote poetry.
Cowboys were referred to as cowpokes, buckaroos, cowhands and cowpunchers.
The most experienced cowboy was called the Segundo (Spanish for “second”) and rode squarely with the trail boss.
Everyday work was difficult and laborious for cowboys. Workdays lasted about 15 hours, and much of that time was spent on a horse or doing other physical labor.
Rodeo Cowboys
Some cowboys tested their skills against one another by performing in rodeos—competitions that were based on the daily tasks of a cowboy.
Rodeo activities included bull riding, calf roping, steer wrestling, bareback bronco riding and barrel racing.
The first professional rodeo was held in Prescott, Arizona, in 1888. Since then, rodeos became—and continue to be—popular entertainment events in the United States, Mexico and elsewhere.
Joseph G. McCoy offered the wealthy cattleman's vision of the cowboy. He recorded a reasonably balanced, if slightly condescending, views in his 1874 treatise on the cattle trade.
He lives hard, works hard, has but few comforts and fewer necessities. He has but little, if any, taste for reading. He enjoys a coarse practical joke or a smutty story; loves danger but abhors labor of the common kind; never tires riding, never wants to walk, no matter how short the distance he desires to go. He would rather fight with pistols than pray; loves tobacco, liquor and women better than any other trinity. His life borders nearly upon that of an Indian. If he reads anything, it is in most cases a blood and thunder story of a sensational style. He enjoys his pipe, and relishes a practical joke on his comrades, or a corrupt tale, wherein abounds much vulgarity and animal propensity.
Black Cowboys
African American horsemen who wrangled cattle in the western United States in the late 1800s and beyond.
Though they were almost entirely excluded from the mythology of the American cowboy, it is estimated that Black men accounted for nearly a quarter of all cattle workers in the nascent American West during the latter half of the 19th century.
In the years following the Civil War (1861–65) and emancipation from slavery, a budding ranching industry promised freedom and prosperity unknown to most Black Americans, many of whom were formerly enslaved themselves or were the children of enslaved parents.
Texas became part of the United States in 1845, and, by 1860, enslaved people accounted for 30 percent of the state’s population. Among them were some of the first Black cowboys: skilled laborers with experience in breaking horses and herding stock. Many were given the autonomy to work unsupervised, and some even carried guns.
The cowboy lifestyle came into its own in Texas, which had been cattle country since it was colonized by Spain in the 1500s. But cattle farming did not become the bountiful economic and cultural phenomenon recognized today until the late 1800s, when millions of cattle grazed in Texas.
White Americans seeking cheap land—and sometimes evading debt in the United States—began moving to the Spanish (and, later, Mexican) territory of Texas during the first half of the 19th century.
Though the Mexican government opposed slavery, Americans brought slaves with them as they settled the frontier and established cotton farms and cattle ranches.
By 1825, slaves accounted for nearly 25 percent of the Texas settler population.
By 1860, fifteen years after it became part of the Union, that number had risen to over 30 percent—that year’s census reported 182,566 slaves living in Texas.
As an increasingly significant new slave state, Texas joined the Confederacy in 1861. Though the Civil War hardly reached Texas soil, many white Texans took up arms to fight alongside their brethren in the East.
While Texas ranchers fought in the war, they depended on their slaves to maintain their land and cattle herds.
In doing so, the slaves developed the skills of cattle tending (breaking horses, pulling calves out of mud and releasing longhorns caught in the brush, to name a few) that would render them invaluable to the Texas cattle industry in the post-war era. But with a combination of a lack of effective containment— barbed wire was not yet invented—and too few cowhands, the cattle population ran wild.
Ranchers returning from the war discovered that their herds were lost or out of control. They tried to round up the cattle and rebuild their herds with slave labor, but eventually the Emancipation Proclamation left them without the free workers on which they were so dependent.
Desperate for help rounding up maverick cattle, ranchers were compelled to hire now-free, skilled African-Americans as paid cowhands.
Freed blacks skilled in herding cattle found themselves in even greater demand when ranchers began selling their livestock in northern states, where beef was nearly ten times more valuable than it was in cattle-inundated Texas.
The lack of significant railroads in the state meant that enormous herds of cattle needed to be physically moved to shipping points in Kansas, Colorado and Missouri. Rounding up herds on horseback, cowboys traversed unforgiving trails fraught with harsh environmental conditions and attacks from Native Americans defending their lands.
African-American cowboys faced discrimination in the towns they passed through—they were barred from eating at certain restaurants or staying in certain hotels, for example—but within their crews, they found respect and a level of equality unknown to other African-Americans of the era.
Sources: 1 2 3 4 5 ⚜ More: Notes & References ⚜ Writing Resources PDFs
Writing occasionally makes me feel like I'm losing it too! I find that taking a step back can be good. That time away from being a writer can be used to being the reader again, and to research your topic. And when your head's clear enough, you can go back & see if the story flows more freely, armed with information you collected to incorporate in your writing. Hope this helps <3
#cowboy#character development#writeblr#spilled ink#dark academia#writing tips#writing advice#history#character building#fiction#writing inspiration#writing ideas#light academia#literature#writers on tumblr#poets on tumblr#writing prompt#writing reference#creative writing#writing resources
184 notes
·
View notes
Text
Trans Horror Podcasts
My post about trans horror books last year was much more popular than I expected, and since I've recently fallen in love with fiction podcasts and audio dramas, I thought I'd make a post about trans horror podcasts as well.
If you like trans horror, please give these a try - especially if you enjoy listening to audiobooks!
Hello From The Hallowoods:

Come walk between the black pines! In this award-winning queer fiction podcast, an eldritch narrator follows the increasingly connected residents of the forest at the end of the world. It's a bittersweet story that explores queer identity, horror genre tropes, and finding hope in humanity's last moments.
Hello From The Hallowoods is my absolute favorite podcast! If you only listen to one podcast from this list, please make it this one - it's so beautifully written and super queer! Also: season 4 starts today!
Trans main characters include:
our nonbinary eye-affiliated podcast host
a nonbinary "Frankenstein's creature"
a transmasc ghost
a genderfluid storm witch
a trans woman who can visit other people's dreams
multiple characters using neopronouns
Camp Here & There:

Good morning, campers! Camp Here & There is a weekly horror comedy podcast tuned in to the loudspeakers of a small midwestern sleepaway camp plagued by supernatural terrors and natural disasters. Sydney Sargent, resident camp nurse, cheerfully reports on all the terror we must face with a big smile. Let’s hope there’s nothing weird about that!
Sydney is a trans man.
Dos: After You:

Things have changed. Deck has fallen in love with someone who isn't human, and leaves a hungry house behind to see him again. Will he be waiting for you? The world has changed… but what about him? Dos: After You is a queer urban fantasy/horror audiodrama available in both English & Spanish
Deck is a trans man.
Jar of Rebuke:

Follow Dr. Jared Hel's journey as he works to re-discover his forgotten past and finds his place within the small Indiana farm town of Wichton and the cryptozoological organization he works for called 'The Enclosure'. These audio journals, and other recordings, dive deep into Midwestern US cryptids and folklore while also telling a mystery about identity, queerness, neurodivergence, and community.
Jared is nonbinary.
Spirit Box Radio:

Spirit Box Radio is an award winning, horror audio drama podcast about a radio show for enthusiasts of all things arcane. Follow Sam Enfield a former postboy with no experience in the arcane arts, who finds themselves forced to take over running the show, following the disappearance of the previous host. Sam soon discovers there are more than ghosts haunting the show, and finds himself amidst a mystery which threatens everything he knows about the world beyond his tiny basement broadcast studio, and maybe even himself.
Sam is a trans man.
The Silt Verses:

Carpenter and Faulkner, two worshippers of an outlawed god, travel up the length of their deity’s great black river, searching for holy revelations amongst the reeds and the wetlands. As their pilgrimage lengthens and the river’s mysteries deepen, the two acolytes find themselves under threat from a police manhunt, but also come into conflict with the weirder gods that have flourished in these forgotten rural territories. This is a world where divine intervention takes place through prayer-markings scratched into stumping-posts, and offerings are left squirming to die in the flats of the delta. This is a world of ritual, and hidden language, and sacrifice. This is folk horror, and fantasy, and a dark road trip into the depths of unusual faith.
Faulkner is a trans man and Paige is a trans woman.
The Magnus Protocol:

The Magnus Archives 2: The Magnus Protocol is the prequel/sequel/”sidequel” to the internationally renowned Magnus Archives podcast. The Magnus Institute was an organisation dedicated to academic research into the esoteric and the paranormal, based out of Manchester, England. It burned to the ground in 1999. There were no survivors. Now, almost 25 years later, Alice and Sam, a pair of low-level civil service workers at the underfunded Office of Incident Assessment and Response, have stumbled across its legacy. A legacy that will put them in grave danger. If this intrigues you then it is our pleasure to welcome you to the Office of Incident, Assessment and Response. Make sure you pick up your badge at desk and report to your line manager before sitting down. Oh and stay away from I.T., seriously.
Alice is a trans woman.
#hello from the hallowoods#hfth#camp here & there#camp here and there#chnt#dos: after you#jar of rebuke#the magnus protocol#tmagp#spirit box radio#the silt verses#tsv#nonbinary#genderfluid#transmasc#transfem#trans book of the day#trans books#queer books#bookblr#booklr#horror podcast#horror podcasts#queer horror podcast#queer horror podcasts#trans horror podcast#trans horror podcasts#trans horror#long post
937 notes
·
View notes
Text
No offence, but the series may be a tad too advanced for you if you get to the end and still assume house elves are a metaphor for human enslavement...
it's been sixteen years and I still can't believe that Harry Potter's official final word on slavery was that it's fine as long as you treat them nicely. Like Harry's very last action in Deathly Hallows before the cut to the epilogue is to wonder if Kreacher, the SLAVE THAT HE OWNS, can bring him a sandwich. I need to lie down
#they're based on a creatures in english folklore (though similar creatures exist in european and slavic folklores too)#jkr likely took inspiration from women's treatment too (given spew)
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
Brand “New” List of Additions to the Arthurian Preservation Project Archive
I've compiled all recent additions to the archive here for easy access. New additions include Medieval texts in French, German, Greek, Middle English, and Norse, plus a multitude of newly acquired retellings and illustrated volumes. Everything can be found on my Retellings List ordered by year or my Medieval Literature List ordered by language.
Links connect to corresponding PDFs on my Google drive where they can be read and downloaded for free. But if you like what I do, consider supporting me on Ko-Fi. I haven’t yet read these listings in full; I cannot attest to their content or quality. A big thank you to @wandrenowle, @mordredpendragon, and Anonymous askers for the help collecting!



Modern Retellings
Idylls of the King by Alfred Lord Tennyson (1898) — Illustrated by George Wooliscroft Rhead & Louis Rhead.
The Knights of the Round Table by William Henry Frost (1898) — Illustrated by Sydney Richmond Burleigh.
The Vision of Sir Launfal and Other Poems edited by Francis R Lane (1900) — Sir Lanfaul sees the Holy Grail.
The Book of Romance by Andrew Lang (1902) — Illustrated by H. J. Ford.
King Arthur's Knights by Henry Gilbert (1911) — Illustrated by Walter Crane.
Parsifal (1912) — Illustrated book about Parzival.
The Tale of Lohengrin - Knight of the Swan (1914) — Illustrated book about Parzival's son, Lohengrin.
Mayday by William Faulkner (1974) — Sir Galwyn seeks the woman he loves.
Peronnik the Simpleton (1984) — The quest for the Holy Grail based on Breton folklore & illustrated by Christiane Lesch
The Tragedy of Tragedies by Henry Fielding (2013) — Contains a story about King Arthur's wife, Queen Dollalolla, of whom "he stands a little in fear."
Medieval Literature
Daniel von dem Blühenden Tal or Daniel of the Flowering Valley translated by Michael Resler
Erex Saga and Ívens Saga translated by Foster W. Blaisdell and Marianne E. Kalinke
Le Roman de Tristan en Prose (French)
The Romance of Hunbaut by Margaret Winters (French)
Specimens of Early English Metrical Romance translated by George Ellis
The Old Knight translated by Thomas H. Crofts
The Romance of Perceval translated by Dell Skeels
Arthurian Romances, Tales, and Lyric poetry by Hartmann von Aue translated by Frank J Tobin, Kim Vivian, & Richard H Lawson
Sagas of Imagination - A Medieval Icelandic Reader translated by Ben Waggoner
Trot, Lecheor, and Nabaret translated by Glyn S. Burgess and Leslie C. Brook
Sir Lancelot of the Lake (abbreviated Vulgate w/ illuminations) translated by Lucy Allen Paton
Parzival, Titurel, and the Love Lyrics by Wolfram von Eschenbach translated by Cyril Edwards
Tristan by Gottfried von Straßberg translated by A. T. Hatto
#arthurian preservation project#arthuriana#arthurian mythology#arthurian literature#arthurian legend#my post
77 notes
·
View notes
Text








1850s english countryside cottage - historically accurate

Here’s one of the builds I’ve made this summer for the langley legacy, an 1850s English countryside house with two bedrooms, one master and one for children. It also has a bathroom. The kitchen and living room are open plan, with a small dining area and a chicken coop outside.
The only way I really enjoy playing The Sims is with historical saves, but as a European, I often have trouble finding historically accurate European builds. It feels like everything I come across is an American house, which gets a bit frustrating.
So, I’ve ended up having to build most of the ones I use from scratch. It’s been a lot of work, but it’s worth it to get the right look and feel for my game.

Lot details
50x40 (hshsh sorry)
§53,537 (cc's fault)
the build contains cc; the list is down below. But it's included in the download.
It will show that the build was created by plantsimgirl, but that’s because I used one of their lots as a base for the trees, so I didn’t have to find them in debug mode. I know, I’m very lazy.

Required cc
Lili's Palace all Folklore packs
Lili's Palace all Intarsia packs
VALIA Bakers Kitchen pack
Deniq Small Ice Box
Pierisim Woodland Ranch pack
Awingedllama Nostalgia Living pack
Awingedllama Grandma's Nursery pack
JS Parchment Computer
Lunamoth Rustic Nursery pack
Linzlu Frontier Dry Sink
Pocci Flowers
KHD Vintage cc packs
Felixandre ORJANIC pack
DaraSims Tablecloth pack
TheJim07 Rectangular Rug
Syb Country Kitchen pack
Simverses medieval stoves

download (FREE on Mediafire)
#ts4#sims 4#sims 4 decades challenge#ts4 decades challenge#ts4cc#ts4 build#sims 4 build#ts4 historical#sims 4 historical#ts4 victorian#1850s#pejite builds
152 notes
·
View notes
Text
Interpretation of messages and references in Railway
I would like to first say these are my interpretations and I could very well be wrong about these or read way too far into it
!! So take this with a grain of salt !!
TW: BLOOD, GORE AND DEATH TOPICS
1. The text in Romanian

Now, I have seen a few translations because this text is well, spelt wrong. (Idk if it was on purpose or not, maybe to throw us off?)
Special occasion info reveal, but I am Romanian.
My own interpretation is this:

"Castelul meu este un loc al intunericului." which translates to "My castle is a place of darkness."
This translation makes the most sense to me, but like I said, I have seen other translations by people which are a tiny bit different. (but nothing too game changing.)
Personally I like "My castle is a place of darkness" because I feel like it could reference something like a mind palace. So basically saying "my mind is a dark place."
2. Vampire concept
This vampire concept to me seemed to be inspired by Bram Stoker's Dracula at first, but then I realized it was more than that. I'm gonna bring a few arguments as to why I think that it might be a lot more well documented.
Dracula was based on the real Romanian Emperor Vlad the Impaler, a violent leader who used to stake people alive.

These creatures, to me, seem to be tied to these flags, and honestly this imagine immediately made me think of Vlad the Impaler's gruesome history. He was such a cruel man that the people back then used to think he was feeding off of the blood of people, and that's why he was so eager to kill.
However!! Before these concepts really set into the Romanian folklore, 'vampires' (the correct name is actually strigoi) were the souls of people (dead or alive) turned evil, that would come to haunt people.

"The evil dead committed always returns to the person who committed it"
Romanian folklore followed this rule as well, up to a certain point, as it was said that people who weren't allowed into Zalmoxis's (A god) kingdom after death would come back to haunt the earth. (So basically sinners.)
On top of that it was also said that strigoi used to crawl out of the earth during a full moon,

And perhaps the most interesting part of all of the references, to me, is the idea of duality. Because Vlad the Impaler as an Emperor, ruthless as he was, was an excellent warrior and army commander, and has led the country to victory (although it was through very gruesome methods). Therefore, historians have been torn in between calling him a tyrant or a hero.
All in all, as Chan is also a leader, I think it makes sense to somewhat represent the duality of a person in command, the tension between goodwill and the means of it, if you will.
3. Final thoughts
Personally I think the most general interpretation I can make out of all I have collected is that he killed the dark side of his mind. Or wants to, at least, in order to let the kind, good one take charge. I see the English quote as a reference to the weight of responsibility, and how one's actions can affect others. That's why I consider it important to translate the Romanian into "my castle is a place of darkness" because then it becomes obvious that the MV symbolizes an inner battle. So, as gory as the video is, I think Chan is saying that he'll always choose kindness, no matter how complicated his mind is. 😁
65 notes
·
View notes
Text
I haven’t talk about this until now because I’m actively ignoring these “interpretations” about “Nosferatu” (2024), but when these are the most popular here (and everywhere, apparently), and the most “liked” and “reblogged” post is how “people not comprehending this film correctly” followed by the most incorrect statement of all time, Von Franz is also compelling me to speak in the name of angels and demons with his Abraxas stone ring (if you don’t know what a “Abraxas stone ring” is, you shouldn’t even be attempting to interpret and analyze this film to begin with).
First: it’s mindblowing to me how folks are trying to interpret this story while systematically ignoring (either by choice or ignorance, I don’t even know at this point) all the inspirations and themes in it; yes, this story is based on ��Dracula” by Bram Stoker, and “Nosferatu: A Symphony of Horror” (1922), but Robert Eggers also shared he was inspired by “Wuthering Heights” by Emily Brontë, and cinematic inspirations: “Svengali” (1931), “La Belle et la Bête” (Beauty and the Beast) (1946), “Great Expectations” (1946), “The Queen of Spades” (1949), “The Innocents” (1961), “Andriesh” (1954), “Vechir na Ivana Kupala” (“The Eve of Ivan Kupalo”) (1968) and “Leptirica” (“The She-Butterfly”) (1973).
Second, more than “Gothic horror” (Female Gothic genre, to be more specific), this film is Folk Horror because that’s Robert Eggers brand. This is a story is based on Romanian folklore: strigoi, Şolomonari and Zalmoxis worship. Orlok is a strigoi doing strigoi stuff, he’s also a Pagan who worshipped Zalmoxis to conquer the secret of immortality, and like all Pagans, he was demonized as a “devil worshipper” by Christianity.
Third, attempting to interpret what’s happening on-screen without any knowledge of the Victorian era, it’s incorrect. Robert Eggers has no interest in doing “modern takes” in his work; he transports his audience to the time period where his films take place. This means, the dialogue, behavior and beliefs of his characters will reflect the historical time in question. If you are interpreting all of this with modern day bias, you are incorrect in your interpretations, simple as that. If you don’t understand the meaning of the words, browse a Old English dictionary (I have no problem admitting I did this, actually).
Last but not least: attempting to interpret this film without knowing the alchemist and occult meaning behind this story is also incorrect. Are you familiar with Aleister Crowley occult system Thelema? Because it was already a part of the OG 1922 “Nosferatu”, Eggers just took a different route to arrive at the same message (the birth of New Age of Aquarius), because he wanted the divine feminine goddess. Do you know who Paracelsus is? He’s the reason why Ellen is called a “sylph”. Who Babalon and her Beast are? That’s Ellen and Orlok in this story. Eggers went full “all hail Babalon” in this film, because Ellen is the hero of the story, but not in the way everyone thinks. Christians know Babalon by another name: “the whore of Babylon” from the “Book of Revelations”.
After you understand all of these themes and inspirations, it’s when you start “problematizing” this story, and taking your own conclusions of it, or making parallels with other stories, not before.
64 notes
·
View notes
Text
Golems and Eureka: Investigative Urban Fantasy
I did a writeup about how a character based on the Jewish folkloric golem might work in Eureka: Investigative Urban Fantasy! It includes a short essay about the thematic implications of the golem, and a set of custom rules for living dolls made of unfired clay.
If you don't know what Eureka is, it's the first tabletop RPG by @anim-ttrpgs, an up-and-coming indie studio making carefully designed and rigorously playtested tabletop games outside of the D&D 5e ecosystem. Eureka is a system for stories where amateur investigators look into intricate and (sometimes deadly) mysteries, trying to get to the bottom of whatever conspiracy is at hand. It also has robust rules for a variety of supernatural phenomena that may or may not exist, letting players explore the thematic and logistical implications of people who are vampires, man-eating alien shapeshifters, supernaturally animated dolls, or a variety of other strange creatures. It's one of the best RPGs I've ever played or read, so if you're interested in finely crafted tabletop games, mystery and detective stories, social commentary on the rights of "unsavory" marginalized people, or just supernatural creatures that eat people, I'd recommend checking it out.
My writing under the cut!
(I wouldn't normally post my own long-form writing here, but I felt good about this and also couldn't pass up an opportunity to talk about Eureka. This isn't very polished, so ignore any typos or awkward wording, but feel free to check it out and give your own thoughts. Enjoy!)
Thoughts on golems in Eureka (Essay – Rules below!)
Contrary to how the word is usually used in English-language fantasy media, a golem in its original context is not just a generic term for any supernaturally animated artificial creature. (If it were, then it would be more or less synonymous with Eureka’s use of the term “living doll” to begin with!) Rather, it refers to a specific creature in Jewish folklore: a facsimile of the human form made out of clay, animated by various words of power placed in or on its body, acting as a source of protection and power for the impoverished and oppressed communities which created it. It is a servant which exists to meet a need of its community, animated by the power of God as channeled through the expertise of a meticulous member of the Jewish community. (Arguably the most notable difference from the genre fiction definition is this inherently Jewish perspective. The creation of a golem is a closed-practice, specifically Jewish tradition, and also, the tradition of Jewish mysticism implies high degrees of specialized knowledge – some written down in studied texts, and others discovered by training under a mentor or interacting with other Jewish leaders. In this way, the golem implies a degree of studiousness and community engagement on the part of its creator, both of which are heavily emphasized values in Jewish spheres.)
My analysis of the thematic role played by the golem is probably best represented in the best-known folkloric golem, the golem of Prague. In this story, a 16th century rabbi of the Prague synagogue creates a humanoid form from clay with the purpose of protecting the ghetto (in this context, the dedicated Jewish quarter of the city) from pogroms and other antisemitic attacks, animating it into a golem by inscribing holy words on its head or placing a scroll of those words in its mouth. Things go wrong in ways which vary from telling to telling, with a common version of the story stating that the golem becomes too dangerous and destructive, and the rabbi removes the inscription of the holy name to render the golem dormant (although rather than destroying his creation, he preserves it in the synagogue’s attic to be reanimated if it’s ever needed). In a fun bit of wordplay, some tellings describe the holy inscription as being the Hebrew word “emet” (“truth”), which is only one letter away from the word “met” (“dead”), with the idea that the rabbi deactivates the golem by erasing a single letter. More traditional interpretations would describe a formula consisting of various divine epithets, either instead of or alongside the previous method. In the Jewish mystical tradition, names of God are thought to be emanations of God’s own glory, and invoking their power in specific ways is seen as a way of causing things beyond the bounds of normal reality.
A few thematic points jump out at me about the golem, both from the story of the Prague golem and from the broader characteristics of the golem. One is the fact that a golem is implicitly lacking in personal identity. Golems are almost never named, and they have very little agency in their own stories – in almost every version of the golem of Prague, for instance, it is deactivated because it has gained too much autonomy. It fights the wrong people, uses too much force defending its community, or even just falls in love, and so it is too dangerous to keep around. Even the terminology being used implies this lack of identity, as it etymologically derives from a Biblical Hebrew term, used only once in the Tanakh, which describes the unfinished form of a human before God breathes life into them. A golem is not perceived as a fully formed individual, but rather as an extension of its creator, built by someone else’s will and discarded whenever it isn’t needed. To me, this has a high degree of relevance to the themes associated with Eureka’s living dolls, who often also grapple with defining their own identity and purpose in the absence of their original context. Their unique struggles evoke concepts of alienation and depersonalization, and I think a golem without a master would have to deal with all of the same issues on that front as they navigate life as a newly independent person.
Golems as a whole, and especially the story of the Prague ghetto, also raise another problem that can create thematic conflict for a character: in their attempts to defend vulnerable people in their community, they can end up making situations more dangerous, rather than helping to defuse them. When the golem of Prague rampages, in many tellings, it doesn’t fully stem the tide of antisemitic antagonism. Instead, it destroys more of the ghetto and allows the gentile population to create a post-hoc justification for their hatred of the Jewish community. In the context of Eureka, I think that this can be a powerful metaphor for how the fear of oppression can lead people to become paranoid, closed off, and destructive to themselves and others. A golem whose purpose is to protect and serve the people around them might want to do just that, but if they find themselves in a situation where superhuman strength and stamina can’t solve a problem, they may be in way over their depth, and they might accidentally harm other people when they try to navigate that. (My use of the phrase “protect and serve” here is no accident – one of many inspirations for this thematic element is people who call for increased police presence in their neighborhoods, even when those communities are more harmed by over-policing than they are by crime. Being afraid and wanting to support their community spurs them to action, but it also blinds them to approaches that don’t use force.) For example, one golem character I’ve come up with has had to flee her home and change her name because she saw someone being harassed, didn’t know her own strength, and intervened in the first way she could think of: violently. She was lucky not to be arrested.
To get a little bit more specific, this theme is most specifically inspired by my own experiences in discussions among members of the Jewish community, as the scars from millennia of marginalization, expulsion, and murder don’t fade quickly. Paranoia is a veritable norm even within our households and places of worship. In our homes, many of us keep passports readily available if there’s a need to escape or show identification, and during any prayer service at a synagogue, there will likely be armed security guards standing at the door. Many of us laugh about it, but there’s a degree of genuine fear that we can’t shake. Often, that fear is harmless, but it can get exhausting to live with, to say little of how it affects other people or how it can be weaponized by bad actors. One look at how the Israeli government seeks to justify its violence in propaganda makes clear that the generational trauma of Jewish communities can be exploited and warped as a means to justify some pretty awful things. The figure of the golem is, in a sense our communal power fantasy – it’s comforting to think that with a bit of ingenuity and some elbow grease we can design our own hero to protect us and help us thrive – but even that fantasy is not free of the reality that, like a superhero, a golem’s innate abilities just aren’t always enough to save everyone. (Indeed, this tension is part of what inspired the Jewish creators of Superman: he has superhuman abilities that he uses to protect vulnerable people, but not every problem can be solved by punching it, and with all his strength he has to be very careful not to destroy everything he loves. This has been noticed by a lot of people, and I’m far from the first to bring it up, but in particular I’d say this observation is borrowed from the excellent video essay “The Golem and the Jewish Superhero” by Jacob Geller on YouTube.) A golem being fleshed out as a character can really lean into that tension.
One more theme I want to bring up is not something I’ve come to any particular conclusions about – it’s really just a few spare thoughts I’ve had rattling around, and an invitation to look into this concept more. It comes out of my research on the development of the word “golem” in Hebrew and Yiddish, as the term has developed beyond just the connotation of a humanoid clay form. It can be a pejorative term like “fool”, but more interesting to me is its use in reference to embryos and pupas. This made me consider the transitory nature of the golem as a representative of change, which I haven’t seen explored very much in any stories out there. Not only has the word gained those connotations, but also, looking at the characteristics of the golem as a creature gives some more fuel to that fire. The fact that it’s generally made out of specifically unfired clay gives it the sense of being unfinished. Its nature of being created in its adult form from the very beginning means that it can display a childish outlook as a seeming adult learning about the world outside of its creator’s life. The story of the golem of Prague even has an ending hook entirely centered around the idea of the golem being temporarily disabled but capable of being reanimated if need be. This idea of a golem as a character with a unique capacity to adapt and change hasn’t been explored very much, but I think it could be interesting to consider.
The last thing I’ll leave here is thoughts on character creation beyond themes. In this document, I’ve included a custom set of rules to play a living doll made of unfired clay, which is the traditional material for a golem. This isn’t playtested in any way, but since Eureka doesn’t try too hard to be balanced around physical attributes, I think it should probably work fine – it’s more thematic than anything. To make a golem, the doll’s purpose should be external in some way, pushing them to help and support other people in their community, especially the most disadvantaged of them. In terms of backstory, the details of a golem’s past can be left fairly foggy if you’d like, but the one thing that can’t be skipped is that they were intentionally created by a Jewish creator invoking Jewish traditions. It’s fine to make a living doll that was animated in some other way, but the character would not be a golem in that case. It’s similar to how Eureka vampires must have some association with Christianity, not because non-Christian undead monsters can’t exist, but because outside of that context, the specific vampire mythos lacks any meaning. (Honestly, also, if you don’t have background information about Jewish life and culture, I would recommend asking someone who does to help with your portrayal.) Finally, in terms of giving a golem a hook to investigate a mystery, it could of course be anything, but there’s one aspect in particular that I would consider: in some versions of the Prague golem’s story, it protected the ghetto by looking into cases where Jews were accused of murder and finding the true culprits, thus clearing the names of the accused. Which is to say, there’s genuine historical precedent for golems investigating mysteries, and it often happens as a means of helping people who are falsely accused of a crime. That’s not mandatory, but it could be fun to keep in mind. Have fun, and if anyone ends up playing a golem investigator using these guidelines, please let me know!
Wet Clay Living Doll – Rules
A living doll made from earthenware materials that have not been hardened by firing. This variant was originally designed to represent the golem of Jewish mythology, but it could also be used to portray, for example, an unfinished art project or a proof of concept for another piece. Depending on their construction and the flexibility of the clay they are made from, they may be treated as jointed or unjointed.
Wet clay living dolls weigh more than twice as much as an average person of their size would. They cannot swim or float, and will sink to the bottom of any body of water immediately.
These living dolls take half damage from all weapons while they have at least 1 point of Superficial HP remaining. Damage from falling is unaffected. Wet clay living dolls are immune to electrical damage.
When a wet clay living doll encounters fire or high heat (in excess of about 500 ºC), their outer layer of clay is fired and becomes hard and brittle. When this happens, this living doll should be mechanically treated as an unjointed living stone statue. If another character has access to tools to chip away the outer layer and a large supply of wet clay to replace it, they can reverse this process with a Full Success on a Technology roll. Regardless of the result, this process will take 1 Tick of time and cause 1 Superficial Damage to the living doll.
Wet clay living dolls are easier to repair. Do not apply the -3 Technology penalty when restoring Penetrative HP.
Wet clay living dolls generally possess superhuman strength, but when they are hurt, they may lose chunks of clay that would otherwise generate weight and power. They have a +5 Contextual Bonus to Athletics and Close Combat, but for each point of sustained Penetrative Damage, this bonus is reduced by 1 point.
Given 1 Tick of time, appropriate tools, and a supply of clay, a wet clay living doll can alter their physical appearance and proportions. They cannot precisely change specific details such as facial features, but can make themselves larger or smaller, change their perceived distribution of fat and muscle, and change the shape of their body enough to be recognizably different. When a wet clay living doll attempts to alter their body, roll Technology.
Full Success: The living doll successfully alters their body to exact specifications. They are able to completely alter their facial features and/or specify a new height and body type, and even on close scrutiny they will not appear out of the ordinary.
Partial Success: The living doll mostly succeeds in altering their body, but they get sloppy. They take 1 Superficial Damage, and close inspection reveals that parts of their skin have abnormal marks and blemishes, but they are still able to make the changes that they hoped for.
Failure: The living doll struggles with even the most basic alterations, doing a messy and imprecise job. They take 1 Superficial Damage, and cuts and blemishes are visible across their skin. They also don't convincingly make the correct changes to their bodies, doing either too much or too little to differentiate themselves from their previous form.
#eureka: investigative urban fantasy#eureka#ttrpg design#ttrpg#indie ttrpg#homebrew#jewish#judaism#golem#game design#jacob geller#essay#my work#queer art#living doll#doll#jew stuff#urban fantasy#detective#investigation#noir#neo noir
71 notes
·
View notes
Text
Happy Dracones Monday! Firedrakes!
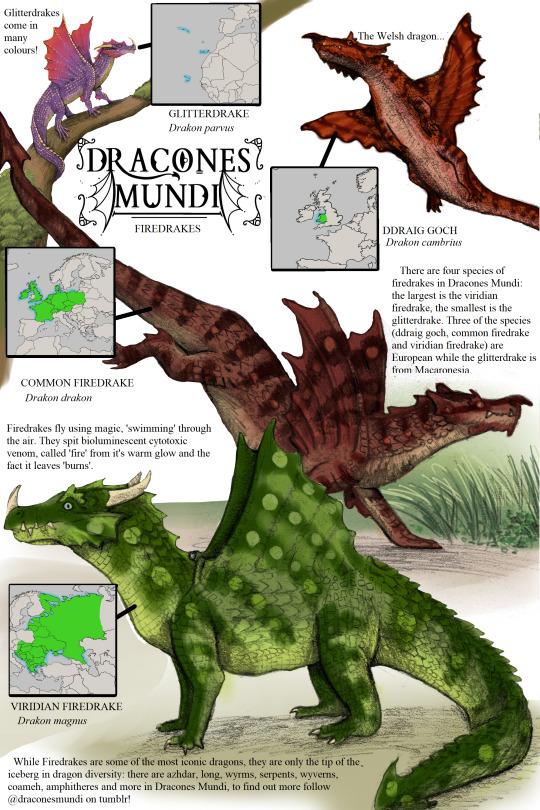
Happy Dracones Monday! This Monday we're looking at four dragon species at once, the firedrakes! Here they are, approximately to scale with eachother.
The glitterdrake is the smallest, the size of a large lizard or small cat. They live in laurel forests on Macaronesian Islands, in the Atlantic near Africa. Glitterdrakes aren't based on mythology; I put them on Macaronesia because I couldn't find Macaronesian dragon mythology but I am trying to put dragons EVERYWHERE on the map. Also, putting these dragons on an archipelago of islands means I can have a lot of island subspecies and colour morphs - glitterdrakes represent colourful fantasy dragons, so having them come in every colour (sapphire blue, ruby red, emerald green, royal purple, burning gold, shining silver etc.) was important to me.
The Welsh dragon is smaller than the other European firedrakes at 1.5 meters. They are no less fierce - there aren't any common firedrakes in Wales as a common firedrake cannot maintain a territory there for long. Originally I had the Welsh dragon as a subspecies of the common firedrake, but decided that this dragon had so much personality and folklore that it could get it's own chapter.
The common firedrake is found in Western Europe, 4m long. When designing these I noticed in a lot of heraldry dragons don't seem to have horns? Ears yes, but hornless? Also I noticed that dragons in heraldry tend to have the dorsal finlets from the back of the head to between their shoulders, but no further, which is something I have kept for all my firedrake species.
The viridian firedrake is the largest firedrake species, over 5m long. They are found in Eastern and Southern Europe, and in Russia. I based their appearance on old storybook illustrations to make them look very 'classic', which is why they have horns and cheek frills compared to the more heraldic and hornless common firedrake.
Rant about the term 'firedrake' under the cut! :)
In other creative works, these are called 'classic dragons', 'European dragons', 'true dragons' and 'Western dragons', but I am not a fan of these terms - 'true dragon' implies other dragons are untrue dragons, which is nonsense. 'Western dragon' or 'European dragon' is largely accurate (the 4 legged 2 winged dragon design is common in Europe and the West) but there are other Western and European dragons (wyrms and wyverns) and I find these terms confusing when other types of dragons are taken into account. Also, some Asian dragons also have 4 legs and 2 wings. 'Classic' dragons... serpentine and wyrmish dragons are more classic than 4 legged 2 winged firebreathers, etc.
I went with 'firedrake' as a term for these dragons because 'drake', 'drachen', 'ddraig', 'drac', 'drak' and 'dreki' are all words for dragons like this in European languages, and because firedrake is a word used in literature like some translations of Beowulf and, of course, Tolkien's Legendarium (firedrake comes from Old English fȳrdraca). I think it's a good word that easily conjures up fire breathing four legged, two winged dragons without making them more 'true' or 'classic' than other dragon types or tying them specifically to 'European' and 'Western' countries.
In Dracones Mundi I really try to get a huge diversity of dragons across to the readers. There are around 68 dragon species in this project, only 4 of which are firedrakes. I want to show readers there is more to dragon mythology than "here is a western dragon, they are evil and associated with fire, here is an eastern dragon, they are good and associated with water" - I want to dig deeper. I want people to know about azhdarha, about cuélebres, about coameh. So I'm shining the spotlight away from these firedrakes and trying to make them a small part of a much larger discussion. :)
#Dracones Mundi#Dracones Monday#Firedrakes#Dragons#Schedulling firedrake post for the monday before the firedrake plushies restock on friday hehe#Firedrake plushies found on Barksbog website on Friday 24th May 2024
236 notes
·
View notes
Text
CASTING CALL - The Notional Supernatural
A new audio-drama is in the works, and we're looking to assemble our weird little team! We're looking for creative of all kinds to help bring this supernatural podcast to life:
🖊️ Writers - Got a knack for eerie, atmospheric storytelling with a touch of dark humour? This is the place for you. 🎤 Voice Actors - From deadpan skeptics to haunted teens to unknowable horrors, we need voices of all kinds. 🎨 Artists - Illustrators, cover designers, promo wizards, help us make the strange look stunning. 🎧 Sound Editors / Designers - If you can turn a whisper into a chill down the spine, we need your ears. This is a passion project with long-term potential, and we’re looking to build a collaborative space for folks who love strange stories, creepy vibes, and a slow-burn mystery.
📍 Remote / Worldwide, however we are UK based so timezones will centre around that 📩 Feel free to ask us anything on this blog, or jump right in and join us on discord, it would be an absolute pleasure to have you! Plot Information
Edgar “Eddie” Pritchard never set out with the intention of becoming the voice of the supernatural in his fog-choked town, but when you drop out of university with only a half-finished degree in English Literature and Folklore and a chip on your shoulder, you take what you can get.
Eddie now hosts the low-fi podcast The Notional Supernatural, dedicated to the bizarre, unexplained incidents that plague his hometown. Haunted radios, phantom dogs, disappearing roads, flickering doppelgängers; everyone else explains it away as a bad dream or hangovers, some of it becoming urban legends, however Eddie suspects something else may be at play.
Each episode features submissions from listeners, with Eddie conducting awkward, but often chilling, interviews, and on the odd occasion venturing into the field himself – with no more than a recorder, a flashlight, and a growing awareness that he's way in over his head. The deeper he goes, the more he notices patterns, threads that indicate something much larger, going back decades, maybe even centuries.
But Eddie is not just documenting these occurrences. They're beginning to follow him. And the question is: is he just an observer? Or is he becoming a part of the phenomenon himself?
#audio drama#casting call#voice acting#indie podcast#horror podcast#The Notional Supernatural#creative writing#artists on tumblr#writers on tumblr#editors on tumblr#sound editing
43 notes
·
View notes
Note
idk how to tell you this but japanese people don't speak English. "obitover" isn't a thing when they aren't speaking english...? 💀
Anon is referring to this awesome comic by @dottixml to which i shamelessly contributed one tiny panel.
Hey anon! I had to consult a friend of mine @maireyart who does speak Japanese, and as it turns out, "obitover" IS possible in Japanese, isn't it great? 😁
Japanese has a lot of English loan words, including the word “over” (oobaa) which has the same meaning in expressions like ゲームオーバー (英: game over) etc. So in the Japanese version of this comic the pun could be:
オビトーバ ー!!!!!
Which is オビト + オーバー (obito + oobaa)
Obito’s name is a fav pun base in both English and Japanese fandoms 😎😋 Also, Naruto characters live in an original fictional world that is indeed heavily influenced by the Japanese folklore and culture; however, it is not real Japan. So we can fantasize and headcanon anything we want. Let's just be open-minded and supportive of each other's creative flow :3
P.S. "Fixobito-no-jutsu" from my panel could ALSO be translated into Jp as a pun! But we would need to ask @maireyart about that 👀📝
P.S.S. and who says Obito couldn't be studying English in his free time to look cool in front of his teammates? Kakashi would be jealous af, and Rin would be so impressed with Obito just dishing out puns IN ENGLISH here and there 🤭right?
#ask#obitover IS a thing 💛#no doubt about it!#this is coming from hidden-linguists shinobi 🥷#*giggles in linguistics degree*
73 notes
·
View notes