#Bacterial Vaginosis And Herpes
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20230608005260/en/Hey-Jane-Launches-in-Virginia-Expanding-Its-Safe-Accessible-Abortion-Care-to-the-South
Hey Jane has launched its telemedicine service in Virginia, offering healthcare services for abortion, birth control, and vaginal infections (UTIs, yeast infections, herpes, and bacterial vaginosis).
#abortion#birth control#urinary tract infection#yeast infection#herpes#bacterial vaginosis#heyjane#hey jane#virginia#united states#telemedicine#virtual clinic#heathcare
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
I grew up with abstinence-only sex education, and it did a real number on me. But I’ve shaken off enough of my old cultural programming to realize that the transmission of bacteria and viruses is a thing that sometimes just happens when animals come together, no matter how stringently we might try to prevent it.
I have gotten urinary tract infections when a stray microbe found its way into my urethra after sex. Lube and bodily fluids have disturbed my vagina’s pH and caused a yeast infection many times. So has wearing a bathing suit for too long without drying it, yet another “risk” worth the pleasures of swimming along the sea wall.
Once or twice I’ve had an outbreak of cold sores, just like 80% of humans. If I’m like most people, I probably caught oral herpes when I was very young, sharing a sippy cup or rolling around at a sleepover.
None of this makes me disgusting, irresponsible, evil, or dangerous to others. It just makes me a living creature that exists in close contact with other creatures. I believe I have a responsibility to get tested regularly, to alert people who have been close to me when I get sick, and to use preventative measures like condoms, PreP, vaccines, toys, and masks to prevent the spread of infections as best I can. But I never imagine I can lead a life without risk — or that such a life would even be desirable.
There is no such thing as completely “safe” sex. A friend of mine can’t use condoms because they give her bacterial vaginosis. She chooses instead to fuck raw and take PreP and get anything else she catches treated. A guy I know who masks and tests religiously caught COVID while fisting someone (with a gloved hand!) at an air-filtered party. HPV is so prevalent that most sexual wellness clinics don’t bother testing for it, and can’t do much for a patient if they do have it. Our bodies are teeming at all times with various endemic viruses and microbes that we will never have the power to purge.
Then there are the possible costs of not having sex — vaginal atrophy, pelvic floor weakening, reduced access to endorphins, loneliness, touch starvation, the despair of harboring dreams that one never dares try. I can’t decide for anyone else which dangers loom the largest, but for me a gonorrhea shot is a fair trade for the hours of leg-cramping, bed-staining, hypno-kinky sex that led to it. There’s no guarantee that the next time I have sex it will be anywhere near as much fun, but the potential keeps me throwing the dice.
I hear quite frequently from sexually inexperienced Autistic people who crave an intimate connection, but desperately wish to remain responsible and “safe.” They want there to be a set of iron-tight rules they can follow that will guarantee they remain a virtuous person who never hurts anyone’s feelings, and never catches any sexually transmitted infection.
I understand why they want someone to impose order onto an unpredictable, terrifying world. But I can’t give that certainty to them, nor can anyone. All I can suggest is that they be honest with themselves about what they want, inform themselves of the costs and benefits to pursuing their desires, and then venture forward — proudly welcoming the correct risks into their life, rather than trying to avoid any risks at all.
Life is nothing but a negotiation of risk. If a person has gender dysphoria and they want to combat it, they must risk a transition they could one day regret. If an abolitionist wants to take a stand against the police state, they must plan for the possibility of arrest or political repression. When we open our hearts to love, we expose ourselves to grief — our partners will keep changing and growing, sometimes away from us. Each step that we take forward in life closes off potential paths. There is no avoiding this.
Instead of chasing after the false promise of “safety,” trying to remain completely insulated from harm and challenge forever, we must get better at admitting risk into our lives.
I wrote about all about the messy business of risk mitigation, and how the pursuit of perfect safety is used to justify isolation, theft of bodily autonomy, and political repression. It's free to read (or have narrated to you by the app!) at drdevonprice.substack.com
876 notes
·
View notes
Text
𝘼-𝙕 𝙇𝙄𝙎𝙏 𝙊𝙁 𝘿𝙄𝙎𝙀𝘼𝙎����𝙎/𝙄𝙇𝙇𝙉𝙀𝙎𝙎𝙀𝙎 𝙁𝙊𝙍 𝙎𝙄𝘾𝙆𝙁𝙄𝘾/𝙒𝙃𝙐𝙈𝙋
— A
Anemia.
Adenomyosis.
Asthma.
Arterial thrombosis.
Allergies.
Anxiety.
Angel toxicosis ( fictional ).
Acne.
Anorexia nervosa.
Anthrax.
Atma virus ( fictional ).
ADHD.
Agoraphobia.
Astrocytoma.
AIDS.
— B
Breast cancer.
Bunions.
Borderline personality disorder.
Botulism.
Barrett's esophagus.
Bowel polyps.
Brucellosis.
Bipolar disorder.
Bronchitis.
Bacterial vaginosis.
Binge eating disorder.
— C
Crohn's disease.
Conjunctivitis.
Coronavirus disease.
Coeliac disease.
Chronic migranes.
Coup.
Cushing syndrome.
Cystic fibrosis.
Cellulitis.
Coma.
Cooties ( fictional ).
COPD.
Chickenpox.
Cholera.
Cerebral palsy.
Chlamydia.
Constipation.
Cancer.
Common cold.
Chronic pain.
— D
Diabetes.
Dyslexia.
Dissociative identify disorder.
Dengue fever.
Delirium.
Deep vein thrombosis.
Dementia.
Dysthimia.
Diphtheria.
Diarrhoea.
Disruptive mood dysregulation disorder.
Dyspraxia.
Dehydration.
— E
Ebola.
Endometriosis.
Epilepsy.
E-coli.
Ectopic pregnancy.
Enuresis.
Erectile dysfunction.
Exzema.
— F
Fusobacterium infection.
Filariasis.
Fibromyalgia.
Fascioliasis.
Fever.
Food poisoning.
Fatal familial insomnia.
— G
Gonorrhoea.
Ganser syndrome.
Gas gangrene.
Giardiasis.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Gall stones.
Glandular fever.
Greyscale ( fictional ).
Glanders.
— H
Hookworm infection.
Hand, foot and mouth disease.
Hypoglycaemia.
Herpes.
Headache.
Hanahaki disease ( fictional ).
Hyperhidrosis.
Heat stroke.
Heat exhaustion.
Heart failure.
High blood pressure.
Human papillomavirus infection.
Hypersomnia.
HIV.
Heart failure.
Hay fever.
Hepatitis.
Hemorrhoids.
— I
Influenza.
Iron deficiency anemia.
Indigestion.
Inflammatory bowel disease.
Insomnia.
Irritable bowel syndrome.
Intercranial hypertension.
Impetigo.
— K
Keratitis.
Kidney stones.
Kidney infection.
Kawasaki disease.
Kaposi's sarcoma.
— L
Lyme disease.
Lassa fever.
Low blood pressure.
Lupus.
Lactose intolerance.
Lymphatic filariasis.
Leprosy.
— M
Measles.
Mad cow disease.
Mumps.
Major depressive disorder.
Malaria.
Malnutrition.
Motor neurone disease.
Mutism.
Mouth ulcer.
Monkeypox.
Multiple sclerosis.
Meningitis.
Menopause.
Mycetoma.
— N
Norovirus.
Nipah virus infection.
Narcolepsy.
Nosebleed.
Nocardiosis.
— O
Obsessive-compulsive disorder.
Osteoporosis.
Ovarian cyst.
Overactive thyroid.
Oral thrush.
Otitis externa.
— P
Pancreatic cancer.
Pneumonia.
Pelvic inflammatory disease.
PICA.
Premenstrual dysphoric disorder.
Psoriasis.
Parkinson's disease.
Panic disorder.
Polycystic ovarian syndrome.
Plague.
Postpartum depression.
Pediculosis capitis.
Psychosis.
Post-traumatic stress disorder.
— Q
Q fever.
Quintan fever.
— R
Rubella.
Rabbit fever.
Rotavirus infection.
Ringworm.
Restless legs syndrome.
Rhinovirus infection.
Rosacea.
Relapsing fever.
Rheumatoid arthritis.
Rabies.
— S
Shingles.
Sore throat.
Stutter.
Separation anxiety disorder.
Smallpox.
Scoliosis.
Septic shock.
Shigellosis.
Sepsis.
Social anxiety disorder.
Stroke.
Scarlet fever.
Schizophrenia.
Sleep apnea.
Sun burn.
Syphilis.
Sickle cell disease.
Scabies.
Selective mutism.
Salmonella.
Sensory processing disorder.
— T
Thyroid cancer.
Tuberculosis.
Thirst.
Trichuriasis.
Tinea pedis.
Tourette's syndrome.
Trachoma.
Tetanus.
Toxic shock syndrome.
Tinnitus.
Thyroid disease.
Typhus fever.
Tonsillitis.
Thrush.
— U
Urinary tract infection.
Underactive thyroid.
— V
Valley fever.
Vertigo.
Vomiting.
— W
White piedra.
Withdrawal.
Whooping cough.
West nile fever.
— X
Xerophthalmia.
— Y
Yersiniosis.
Yellow fever.
— Z
Zygomycosis.
Zika fever.
Zeaspora.
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
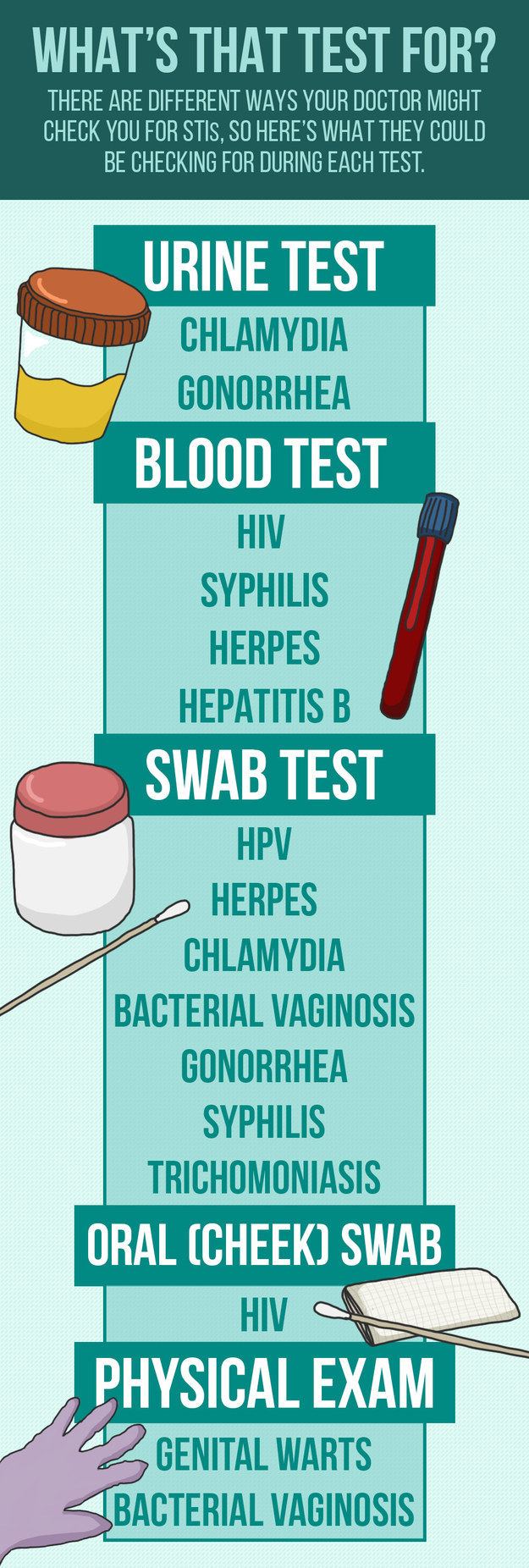
What Tests Look For (STIs)
Urine Test -- chlamydia -- gonorrhea
Blood Test -- HIV -- syphilis -- herpes -- hepatitis B
Swab Test -- HPV -- herpes -- chlamydia -- bacterial vaginosis -- gonorrhea -- syphilis -- trichomoniasis
Oral (Cheek) Swab Test -- HIV
Physical Exam -- warts -- bacterial vaginosis
#medblr#studyblr#notes#my notes#medical notes#medblr notes#med notes#sti#sti tw#sti //#medical tests#medical testing#sti testing#anatomy and physiology#pathology#pathophysiology notes#pathophysiology
17 notes
·
View notes
Text

hairless
- vagina has a clean wax look
- pubic hair never grows on your vagina
- any hair on your vagina and anus are completely gone regardless of circumstances
clear
- immune to developing bumps and pimples
- any bumps and pimples on your vagina immediately vanish regardless of circumstances
- immune to infected hair follicles due to bacteria
- immune to folliculitis
- no irritations, bumps, itchiness, or pimples from shaving
even skin tone
- reverse / irradiate any vaginal hyperpigmentation and or discoloration
- even skin tone throughout while bikini area and vagina
- hormones, friction, infections, and or age don’t cause vaginal discoloration or hyperpigmentation
- any effects of lack of proper ventilation caused by tight underwear or clothing resulting in vaginal discoloration immediately reverse regardless of circumstances
- any vaginal discoloration or hyperpigmentation due to a sudden rise in estrogen levels completely disappear within seconds regardless of circumstances
- free from dark patches on the vagina
no foul odor
- free from foul vaginal odor from sweat or anything
- vagina has your desired pleasant scent
free of infections
- free of and immune to bacterial vaginosis
- free of and immune to trichomoniasis
- free of and immune to yeast infections
- free of and immune to vaginal cancer
- free of and immune to cervical cancer
- free of any vaginal infections
- immune to any vaginal infections
- free of and immune to vulvar cysts
- free of and immune to vaginal cysts
- free of and immune to any fordyce spots
- free of and immune to any Varicosities
- my body naturally avoids vaginal infections and diseases regardless of circumstances
- free of and immune to ingrown hairs
- free of and immune to any vaginal skin tags
- free of genital herpes, genital warts, and any sexually transmitted diseases or infections
- free and immune to uti’s
- immune to razor bumps
- immune to any uti’s due to painful sex or any other circumstances
balanced ph level
- have a balanced ph level
- have a normal vaginal pH level between 3.8 and 4.5
- periods and unprotected sex don’t throw off your PH levels no matter the circumstances
- PH level is always balanced to a healthy degree
hygiene products
- manifest feminine hygiene products
- manifest high quality body and vaginal exfoliants
- manifest clean high quality razors to shave
- manifest cute high quality tweezers
- manifest high quality moisturizing body lotion and body oil
- manifest dr.bronners soaps
- manifest hygiene essentials
18 notes
·
View notes
Note
You just know aegon’s dick is slimy with bacterial vaginosis
the MENTAL PICTURE I JUST HAD, MY GOD 😳😭 I wonder if BV is somehow related to herpes or something, maybe he spread the BV onto Daemon and Otto!!! 🤧
#┆ ⤿ 💌 come chat with amira .ᐟ ୭#ask box#ask box messages#ask box open#✧.* amiraverse#lovely anons <3#unhinged anons#hotd
2 notes
·
View notes
Photo
Image description: A graphic that's mostly a column of text. The heading says,
"What's that test for? There are different ways your doctor might check you for sexually transmitted infections (STIs), so here's what they could be checking for during each test."
Then it has several lists, which say:
Urine test (an illustration of a urine sample in a closed plastic jar)
Chlamydia
Gonorrhea
Blood test (an illustration of a blood sample in a test tube)
HIV
Syphilis
Herpes
Hepatitis B
Swab test (an illustration of a cotton swab and a closed plastic jar)
HPV
Herpes
Chlamydia
Bacterial vaginosis
Gonorrhea
Syphilis
Trichomoniasis
Oral (cheek) swab (an illustration of a cotton swab and a piece of gauze)
HIV
Physical exam (an illustration of a rubber glove)
Genital warts
Bacterial vaginosis
End description.
via Buzzfeed
#rated PG-13#originally posted on April 29 2016 by PlannedParenthood#sexually transmitted infections#sex education#blood#if you don't want to see this content from my blog: i always tag thoroughly so you can blacklist the tag 'sex education'#STI test#content warning#screen reader friendly#queue#HIV#herpes#syphilis#gonorrhea#HPV#HIV AIDS
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Understanding the Causes of Burning Sensation During Urination From The Best Urologist In Surat

Experiencing a burning sensation during urination can be alarming and uncomfortable. It’s a symptom that signals an underlying issue, ranging from mild infections to more serious medical conditions. This problem affects both men and women, though women tend to experience it more frequently due to anatomical differences, explain some of the best urologists in Surat. Understanding the root causes is essential for finding the right treatment and relief.
In this blog, we’ll explore the various causes behind the burning sensation during urination, helping you identify when it’s time to seek medical attention.
What Causes Burning Sensation During Urination?
Burning during urination, medically known as dysuria, occurs when the urinary tract or surrounding tissues are irritated or inflamed. Several factors can trigger this discomfort, and identifying the cause depends on the individual’s symptoms, medical history, and lifestyle. Doctors from the best hospital in Surat, SIDS Hospital, list the most common causes:
1. Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
Urinary tract infections are one of the most common culprits of burning during urination. A UTI occurs when bacteria, typically Escherichia coli (E. coli), enter the urinary tract, causing inflammation. Women are particularly prone to UTIs due to their shorter urethra, which allows bacteria to travel to the bladder more easily.
Symptoms of a UTI include:
● Burning or pain during urination
● Frequent urge to urinate, even with little urine output
● Cloudy or foul-smelling urine
● Pelvic pain or pressure (in women)
Treatment for UTIs typically involves antibiotics prescribed by a healthcare provider. Drinking plenty of water and practicing good hygiene can help prevent future infections.
2. Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs)
Certain STIs, such as chlamydia, gonorrhea, herpes, or trichomoniasis, can also cause burning during urination. These infections inflame the urethra and surrounding tissues, leading to discomfort.
According to the best urologists in Surat, key symptoms of STIs include:
● Burning sensation during urination
● Unusual discharge from the genitals
● Pain during intercourse
● Genital sores or itching
Prompt testing and treatment are essential to address STIs. Antibiotics or antiviral medications can manage these infections effectively.
3. Irritation or Allergic Reactions
Sometimes, burning during urination isn’t caused by an infection but rather by irritation or an allergic reaction to certain substances. Common irritants include:
● Harsh soaps or bubble baths
● Feminine hygiene products, such as douches or sprays
● Spermicide-coated condoms
● Laundry detergents or fabric softeners
These products can disrupt the pH balance of the genital area, leading to inflammation. If irritation is the cause, stopping the use of the offending product usually resolves the issue quickly, share our experts at SIDS hospital, one of the best urology hospital in Surat.
4. Kidney Stones or Bladder Stones
Kidney or bladder stones can cause painful urination if they obstruct the urinary tract or irritate its lining. Stones form when minerals in the urine crystallize, creating hard deposits.
Symptoms of stones include:
● Intense pain in the lower back, abdomen, or groin
● Burning during urination
● Pink, red, or brown urine due to blood
● Frequent need to urinate
Treatment varies depending on the size of the stone. Small stones may pass naturally with increased fluid intake, while larger stones might require medical intervention, such as lithotripsy or surgery.
5. Vaginal or Urethral Infections
In women, vaginal infections like yeast infections or bacterial vaginosis can irritate the urinary tract, causing a burning sensation during urination. Similarly, urethritis (inflammation of the urethra) in men or women can result from infections or trauma.
Symptoms of vaginal infections include:
● Itching or irritation in the vaginal area
● Unusual vaginal discharge
● Pain during urination or intercourse
Symptoms of urethritis include:
● Pain or burning during urination
● Discharge from the urethra (in men)
Both conditions are treatable with antifungal or antibiotic medications, depending on the underlying cause.
6. Prostatitis in Men
Prostatitis, or inflammation of the prostate gland, is a common cause of painful urination in men. It can result from bacterial infections or other factors like stress or injury.
Symptoms of prostatitis include:
● Burning during urination
● Difficulty starting or stopping urination
● Pain in the pelvis, lower back, or genitals
● Flu-like symptoms (in bacterial prostatitis)
The best urologists in Surat usually treat this with antibiotics, anti-inflammatory medications, or lifestyle adjustments.
7. Medical Conditions Affecting the Bladder or Urethra
Chronic conditions like interstitial cystitis (painful bladder syndrome) or overactive bladder can also cause burning during urination. These conditions are often non-infectious and require specialized treatment.
Symptoms of interstitial cystitis include:
● Chronic pelvic pain
● Urgent or frequent urination
● Pain during urination, despite no infection
8. Dehydration or Diet
In some cases, burning urination stems from dehydration or consuming irritants like caffeine, alcohol, or spicy foods. Experts from SIDS Hospital, one of the best hospitals in Surat, explain that when urine becomes too concentrated, it irritates the urinary tract, leading to discomfort.
When Should You See a Doctor?
While mild cases may resolve on their own, persistent or severe symptoms warrant medical attention. Consult a doctor if you experience:
● Burning that lasts more than a day or two
● Fever, chills, or nausea
● Blood in your urine
● Pain that radiates to your back or sides
Final Thoughts
A burning sensation during urination is not only uncomfortable but also a sign that something may be wrong with your urinary or reproductive system. Identifying the cause is crucial for effective treatment and relief. Whether it’s an infection, irritation, or underlying condition, addressing the issue promptly by doctors from the best urology hospital in Surat can prevent complications and improve your quality of life.
0 notes
Text
Vaginal Infections: Common Causes, Symptoms, and When to Seek Medical Advice

Vaginal infections are a common concern for many women, and they can occur at any age. These infections can cause discomfort, disrupt daily activities, and, if left untreated, may lead to more serious health issues. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and when to seek medical advice is crucial for maintaining good reproductive health. If you experience any signs of a vaginal infection, consulting a gynecologist in Indore can help you get the appropriate diagnosis and treatment.
Common Causes of Vaginal Infections
Bacterial Vaginosis (BV): This is caused by an imbalance in the bacteria naturally present in the vagina. When harmful bacteria overgrow, it can lead to symptoms like unusual discharge and an unpleasant odor. Douching and sexual activity with new or multiple partners are common risk factors.
Yeast Infections: A yeast infection is caused by an overgrowth of Candida, a fungus normally found in small amounts in the vagina. Triggers include antibiotics, a weakened immune system, high blood sugar levels, or hormonal changes.
Trichomoniasis: This is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the parasite Trichomonas vaginalis. Symptoms include itching, burning, and a frothy, yellow-green vaginal discharge with a strong odor.
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs): Besides trichomoniasis, infections like chlamydia, gonorrhea, and herpes can cause vaginal infections. These are transmitted through sexual contact and can lead to serious complications if not treated.
Poor Hygiene: Inadequate or improper cleaning of the genital area can lead to infections, as can wearing tight, non-breathable clothing that traps moisture, creating an environment for bacteria or fungi to thrive.
Symptoms of Vaginal Infections
Unusual vaginal discharge (color, consistency, or odor)
Itching or irritation in the vaginal area
Burning sensation, especially during urination
Pain or discomfort during intercourse
Redness or swelling of the vulva
When to Seek Medical Advice
It’s important to seek help from a gynecologist in Indore if you experience any of the following:
Symptoms that last more than a few days
A persistent change in vaginal discharge
Severe itching, swelling, or redness
Pain during urination or sexual intercourse
Symptoms that don’t improve after using over-the-counter treatments
In some cases, vaginal infections may be symptoms of more serious underlying conditions. Regular visits to a gynecologist in Indore are crucial for preventive care and early detection of any gynecological issues. A healthcare professional can help you determine the cause of the infection and recommend the appropriate treatment, ensuring quick relief and preventing complications.
Also Read: Fertility Clinic in Indore
Early intervention and proper hygiene are essential in maintaining your reproductive health. Don’t hesitate to seek medical advice when needed, and stay informed about your body’s signals.
0 notes
Text
My friend in college. He was sexually active and he did receive this but didn't transmit it. And each time he got it, he knew and got it. Taken care of immediately. Yes, antibiotics take care of it quickly. So this disease is contracted by women easily and transmitted by women...
Anyone who is sexually active can get chlamydia, a sexually transmitted bacterial infection (STI), but it's more common in women than men. In the United States, women are estimated to have twice the infection rate of men. Some risk factors for infection include:
Not consistently using barrier methods like condoms with new sexual partners
Having a sexual partner who is having sex with other people
Having a history of chlamydia or other STIs
Being a young sexually active woman, especially between the ages of 15 and 24
Being a man who has oral or anal sex with men
Chlamydia - NHS
It can also be passed by a pregnant woman to her baby. Chlamydia cannot be passed on through casual contact, such as kissing and hugging, or from sharing baths,
NHS
Anyone who is sexually active can get chlamydia, a sexually transmitted bacterial infection (STI), but it's more common in women than men. In the United States, women are estimated to have twice the infection rate of men. Some risk factors for infection include:



Not consistently using barrier methods like condoms with new sexual partners

Having a sexual partner who is having sex with other people

Having a history of chlamydia or other STIs

Being a young sexually active woman, especially between the ages of 15 and 24

Being a man who has oral or anal sex with men

Chlamydia - NHS
It can also be passed by a pregnant woman to her baby. Chlamydia cannot be passed on through casual contact, such as kissing and hugging, or from sharing baths,

NHS
And you don't think they need to stop with the bisexuality and lesbianism in the adult entertainment, and this is where I said, if they do it at all, it can be deep fakes. But I don't want to encourage it in the outside environment.... Cause then people really get sick. So we have to figure out a way of discouraging this, and like I said, look at all these diseases that are more common sexually transmit it that are more common amongst a lesbian and bisexual women then heterosexual women!!!! And you keep on telling me that this is a good thing, lesbians and bisexuals and homosexuals and transgender!!!! How is this possible? It being a good thing when it causes unbelievable problems physically and mentally. Besides causing the unborn child, all kinds of diseases that it contracts in the womb and causes still birth and birth defects, and then you have to address those issues after birth, if they survive!!!!
In addition, when women, including asymptomatic women, have been tested for STDs, lesbian and bisexual women have had a higher prevalence of bacterial vaginosis, hepatitis B and C, gonorrhea, genital herpes and chlamydia than heterosexual women.Dec 8, 2008
https://www.guttmacher.org
STDs Among Sexually Active Female College Students
You think all universities should require mandatory? Annual physicals and part of those physicals should be testing for sexually transmitted diseases.... C d c says that women under twenty five should be checked for sexually transmitted diseases.Regularly...
"The CDC recommends that all sexually active women under 25 get routine annual screening for STIs."
Yes, lesbians and bisexual women have higher rates of chlamydia than heterosexual women. According to a 2008 study, sexually active female college students who identify as lesbian or bisexual have a higher prevalence of chlamydia than heterosexual women, even if they don't have symptoms. A 1990s survey of lesbian and bisexual women found that 102 respondents reported contracting chlamydia from a female partner.


Lesbian and bisexual women are vulnerable to sexually transmitted infections (STIs) like chlamydia because of skin-to-skin and mouth-to-genital contact, sharing sex toys, and exchanging vaginal fluids or menstrual blood. Other risk factors for STIs among women who have sex with women (WSW) include:



Gonorrhea

Trichomoniasis

Syphilis

Hepatitis A and HIV

Smoking

High alcohol intake

Injecting nonprescribed drugs

The CDC recommends that all sexually active women under 25 get routine annual screening for STIs.

Sexually Transmitted Infections Among Women Who Have Sex With Women | Clinical Infectious Diseases | Oxford Academic

Oxford Academic





0 notes
Text
Gynecological Health: Common Issues and Treatments
Women's gynecological health encompasses a wide range of conditions that affect the reproductive system, from adolescence through menopause and beyond. Understanding common issues and available treatments can empower women to prioritize their health and seek timely medical care when needed. Here's an overview of some prevalent gynecological issues and their treatments:
Menstrual Disorders
Menstrual Irregularities:
Causes: Hormonal imbalances, stress, thyroid disorders, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), or underlying medical conditions.
Treatment: Hormonal contraceptives, lifestyle modifications, medications to regulate hormones, or surgical interventions in severe cases.
Heavy Periods (Menorrhagia):
Causes: Fibroids, hormonal imbalances, adenomyosis, or bleeding disorders.
Treatment: Hormonal therapies, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), endometrial ablation, or surgical options like hysterectomy in extreme cases.
Pelvic Pain
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID):
Causes: Bacterial infections typically transmitted through sexual contact.
Treatment: Antibiotics to eliminate infection, rest, and sometimes hospitalization for severe cases.
Endometriosis:
Causes: Endometrial tissue grows outside the uterus, causing pain and possible infertility.
Treatment: Pain management with NSAIDs, hormonal therapies (birth control pills, GnRH agonists), or surgical options (laparoscopy) to remove endometrial tissue.
Reproductive Health
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS):
Causes: Hormonal imbalance leading to irregular periods, ovarian cysts, and potential fertility issues.
Treatment: Lifestyle changes (diet, exercise), hormonal contraceptives, insulin-sensitizing medications (metformin), or fertility treatments if trying to conceive.
Infertility:
Causes: Various factors such as ovulation disorders, blocked fallopian tubes, endometriosis, or male factor infertility.
Treatment: Fertility medications, intrauterine insemination (IUI), in vitro fertilization (IVF), or surgical procedures depending on the underlying cause.
Menopause and Aging
Menopausal Symptoms:
Symptoms: Hot flashes, night sweats, vaginal dryness, mood swings, and decreased bone density.
Treatment: Hormone replacement therapy (HRT), non-hormonal medications, lifestyle adjustments, or vaginal estrogen therapy for specific symptoms.
Osteoporosis:
Cause: Decreased estrogen levels post-menopause leading to bone loss.
Treatment: Calcium and vitamin D supplements, weight-bearing exercise, medications to slow bone loss, and lifestyle modifications.
Sexual Health
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs):
Common STIs: Chlamydia, gonorrhea, genital herpes, HPV (human papillomavirus), and HIV/AIDS.
Treatment: Antibiotics (for bacterial infections), antiviral medications (for viral infections), and preventive measures such as safe sex practices and vaccinations (HPV).
Vaginal Infections:
Types: Yeast infections (Candida), bacterial vaginosis (BV), or trichomoniasis.
Treatment: Antifungal medications (for yeast infections), antibiotics (for BV or trichomoniasis), and maintaining good genital hygiene.
Routine Screening and Prevention
Pap Smears and HPV Testing:
Purpose: Detect early signs of cervical cancer or HPV infection.
Frequency: Recommended every 3-5 years depending on age and risk factors.
Breast Exams and Mammograms:
Purpose: Detect breast cancer early through self-exams, clinical exams, and mammograms.
Frequency: Self-exams monthly, clinical exams annually, and mammograms as recommended by age and risk factors.
Conclusion
Prioritizing gynecological health involves understanding common issues, recognizing symptoms, and seeking timely medical care from a qualified healthcare provider. Regular screenings, healthy lifestyle choices, and proactive management of gynecological conditions are crucial for maintaining optimal reproductive and overall health throughout every stage of life. Consult with your healthcare provider for personalized guidance and treatment options based on your individual health needs and concerns.
Looking for more details? Visit https://www.nghospitalscbe.com/
#gynecologist#gynecology and obstetrics#fertility#accident and emergency care in coimbatore#best hospital for emergency#pediatriccare
0 notes
Text
Blue Waffle Disease

Debunking Blue Waffle Disease: Myths, Facts, and STI Prevention
The Blue Waffle Disease hoax emphasizes the need for reliable sexual health information. By understanding real STIs and practicing preventive measures, we can dispel myths and promote better health outcomes. If you experience any symptoms or concerns, consult a healthcare provider for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
What Is Blue Waffle Disease?
Blue Waffle Disease is an internet hoax, falsely described as a severe genital condition causing blue discoloration and lesions. Despite its viral spread on platforms like Reddit and Twitter, medical experts and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) confirm that Blue Waffle Disease is not real. This myth has misled many, highlighting the need for accurate sexual health information.
The Origins and Spread of the Blue Waffle Hoax
The Blue Waffle Disease myth originated around 2010 as an internet prank that quickly went viral. The hoax claimed that this fictitious STI turned the vaginal area blue and caused severe symptoms like lesions and discharge. The spread of this misinformation was fueled by doctored images and sensationalist claims. Despite being debunked by medical professionals, the myth persists, highlighting the dangers of internet misinformation and the importance of accessing reliable health information.
Symptoms Similar to Other STIs
The supposed symptoms of Blue Waffle Disease mimic those of real sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Recognizing these symptoms can lead to appropriate treatment:
- Genital Herpes: Painful blisters and sores, managed with antiviral medications (CDC, Genital Herpes).
- Vaginal Candidiasis: Itching, redness, and white discharge, treated with antifungal medications (CDC, Vaginal Candidiasis).
- Bacterial Vaginosis: Discharge, odor, and discomfort, treated with antibiotics (Workowski et al., 2021).
- Trichomoniasis: Itching, burning, and foul-smelling discharge, treated with antiprotozoal medication (Garcia et al., 2023).
Common STIs and Their Symptoms
While Blue Waffle Disease is not real, several actual STIs exhibit symptoms that can cause confusion. Understanding these can help individuals seek appropriate medical care:
- Chlamydia: Often asymptomatic, but can cause vaginal discharge, pain during urination, and lower abdominal pain. Left untreated, it can lead to serious reproductive issues.
- Gonorrhea: Symptoms include burning during urination, increased vaginal discharge, and bleeding between periods. Both men and women can contract it, affecting the genitals, rectum, and throat.
- Genital Herpes: Caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV), symptoms include painful blisters, sores, and vaginal discharge. The virus remains in the body and can reactivate.
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV): This common STI can cause genital warts and is associated with various cancers, such as cervical and throat cancer. Vaccination is available to prevent certain high-risk strains.
How To Prevent STIs
Preventing STIs involves a combination of safe sexual practices, regular testing, and proper hygiene. Essential strategies include:
- Use Protection: Condoms significantly reduce STI transmission (CDC, Sexually Transmitted Diseases Prevention).
- Regular Testing: Routine screenings detect STIs early, enabling timely treatment (Workowski et al., 2021).
- Communication: Discuss STI status and safe sex practices with partners.
- Vaccination: Vaccines like HPV can prevent certain STIs (CDC, Sexually Transmitted Diseases Prevention).
The Importance of STI Testing
Regular STI testing is crucial for maintaining sexual health. Tests can include urine samples, blood tests, or swabs. The CDC advises regular screenings for STIs such as chlamydia, gonorrhea, and HIV, especially for those with new or multiple partners (Workowski et al., 2021).
Dispelling Myths and Emphasizing Education
The persistence of the Blue Waffle Disease myth underscores the necessity of comprehensive sex education. Misinformation can lead to unnecessary panic and stigmatization. Reliable sources, such as the CDC and Planned Parenthood, provide accurate information on sexual health, STI prevention, and treatment. Educating young people through school programs and public health campaigns is crucial to combatting myths and promoting healthy sexual behaviors.
Practical Steps for STI Prevention
Preventing STIs involves adopting safer sex practices and being informed about your sexual health:
- Consistent Condom Use: Condoms and dental dams are effective barriers against STIs during vaginal, anal, and oral sex.
- Regular Screenings: Routine STI testing is vital, especially for sexually active individuals with multiple partners. Early detection leads to timely treatment.
- Open Communication: Discussing STI status and sexual health with partners fosters trust and reduces the risk of transmission.
- Vaccinations: Vaccines, such as those for HPV and hepatitis B, are critical tools in preventing certain STIs.
Addressing Common Questions
What is Blue Waffle Disease?
Blue Waffle Disease is a fictional condition, created as an internet hoax, and is not recognized by medical professionals.
What does Blue Waffle Disease look like?
There are no legitimate medical cases or images of Blue Waffle Disease as it does not exist. Photos circulating online are either altered or misrepresent other conditions.
What does Blue Waffle mean?
"Blue Waffle" is a slang term that has no basis in medical reality. It is part of the misinformation spread through internet hoaxes.
Conclusion
The Blue Waffle Disease hoax is a clear example of how misinformation can spread and create unnecessary fear. By focusing on real STIs, their symptoms, and prevention methods, we can promote a better understanding of sexual health. Ensuring access to accurate information and encouraging responsible sexual practices are key to preventing the spread of STIs and debunking harmful myths.
0 notes
Text
best Vaginal infection treatment in vikas puri delhi
I am not a doctor, but I can provide some general information about vaginal infection treatments. The best treatment for a vaginal infection will depend on the specific type of infection you have. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to receive an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. They can perform tests and determine the most suitable course of action for your specific condition.

best Vaginal infection treatment in vikas puri delhi
Common types of vaginal infections include:
Yeast Infections (Candidiasis): These are typically treated with antifungal medications, which can be available as creams, suppositories, or oral tablets. Over-the-counter treatments are available, but it's advisable to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis.
Bacterial Vaginosis (BV): BV is usually treated with antibiotics prescribed by a doctor. Metronidazole and clindamycin are commonly used for this condition.
Trichomoniasis: This sexually transmitted infection is also treated with prescription antibiotics, such as metronidazole or tinidazole. It's essential that both partners receive treatment to prevent re-infection.
Vaginal Atrophy: For menopausal women experiencing vaginal dryness and irritation due to decreased estrogen levels, hormonal therapy (estrogen creams, tablets, or rings) may be recommended.
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs): In addition to trichomoniasis mentioned above, other STIs such as chlamydia, gonorrhea, or genital herpes require specific treatments and should be managed by a healthcare professional.
Remember, it is crucial to avoid self-diagnosis and self-treatment. If you suspect you have a vaginal infection, schedule an appointment with a healthcare provider. They will perform a thorough examination and recommend the most appropriate treatment for your specific condition. In the meantime, practice good genital hygiene, avoid douching, and refrain from sexual activity until you receive a proper diagnosis and treatment.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Genital Herpes in Women : Symptoms and Treatment
Genital herpes is a viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV) type 1 or type 2. HSV-2 is the most common cause of genital herpes, but HSV-1 can also cause genital herpes through oral sex. The virus is transmitted through direct skin-to-skin contact during sexual activity with an infected person.
Most people with genital herpes experience periodic outbreaks of symptoms, which can occur weeks, months or years after the initial infection. The frequency and severity of outbreaks can vary from person to person, and some people may only have one outbreak while others may have frequent outbreaks.
It's important to note that even when there are no visible symptoms or outbreaks, the virus can still be transmitted to sexual partners. Therefore, it's important for those with genital herpes to communicate with their sexual partners and practice safe sex to
Genital Herpes Symptoms
The symptoms of genital herpes can vary from person to person, and some people may not experience any symptoms at all. However, some common symptoms of genital herpes include:
Painful, itchy or burning sores or blisters in the genital area, anus, thighs or buttocks
Fluid-filled blisters that burst and form painful sores
Ulcers or sores that crust over and heal after a few weeks
Pain or discomfort during urination
Fever, headache, muscle aches, and swollen lymph nodes in the groin area
The symptoms of genital herpes can be similar to other conditions such as yeast infections, bacterial vaginosis, and sexually transmitted infections, so it's important to see a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Genital Herpes Treatment
It's important to start antiviral treatment as soon as possible after the onset of symptoms to be most effective. Antiviral medications can also be used as a suppressive therapy to reduce the frequency of outbreaks in people who experience frequent or severe outbreaks.
Preventing the transmission of genital herpes is important to reduce the risk of infection and to avoid spreading the virus to sexual partners. Here are some strategies for preventing the transmission of genital herpes:
Use condoms - Condoms can reduce the risk of transmission, but they do not provide complete protection as the herpes virus can be transmitted through skin-to-skin contact in areas not covered by the condom.
Avoid sexual activity during outbreaks - Herpes is most contagious during outbreaks when symptoms are present, so it's important to avoid sexual activity during this time.
Inform sexual partners - It's important to inform sexual partners about the herpes infection and to practice safe sex to reduce the risk of transmission.
Practice good hygiene - Keeping the genital area clean and dry can help to reduce the risk of transmission. Avoid touching the affected area and wash hands frequently to avoid spreading the virus to other parts of the body.
Take antiviral medication - Antiviral medications can help to reduce the frequency and duration of outbreaks, which can reduce the risk of transmission.
#genital herpes#genital herpes in women#genital herpes treatment in women#genital herpes cream#genital herpes treatment#genital herpes medication#herpes#thrush#genital herpes singapore
0 notes
Text
STD Treatment in Delhi
What are Sexually Transmitted Diseases?
The main way that STIs, or sexually transmitted illnesses, are spread is through sexual contact. They are also referred to as STDs, or sexually transmitted illnesses.
When having anal, oral, or vaginal sex, they are usually dispersed. In addition to other forms of intercourse, they can occasionally be spread by oral, anus, or vaginal contact. Because skin-to-skin contact is a common way for some STDs, like herpes and HPV, to spread.
Types of STD:
The following are some instances of STDs:
Chlamydia, Syphilis, Gonorrhoea, Human Papillomavirus, Cancroids, Trichomonas, Herpes, Scabies, Bacterial Vaginosis, and Pelvic Inflammatory Diseases.
STD symptoms include:
There are a number of STI warning signs and symptoms, such as:
• Rash on the hands, feet, or trunk of the body.
• lesions or acne on the mouth, rectal region, or genitalia.
• urinating in agony or with contempt.
• Penis abuse is prevalent.
• Strange or unpleasant vaginal discharge.
• uncharacteristic vaginal bleeding.
• Uneasy in a sexual sense.
• Painful and swollen lymph nodes, typically in the groyne but occasionally more widely dispersed.
• Lower back discomfort.
Sexually transmitted diseases have a number of causes:
· Viruses (genital herpes, human papilloma virus, HIV, AIDS),
· parasites (trichomoniasis),
· bacteria (syphilis, gonorrhoea, chlamydia),
· intimate contact (although it is also possible to get these diseases without intimate contact),
sexual activity are the main causes of sexually transmitted diseases. For instance, Shigella, a giardia intestinalis, can cause hepatitis A, B, and C.
Sexually Transmitted Diseases Video: https://youtu.be/3KmPUWpAevY
To get more info visit the website: https://www.bestsexologistindelhi.com/sexually-transmitted-diseases-in-delhi
Best Sexologist in Delhi Dr. Vinod Raina
Contact Us-7687878787, 9871605858
Address: — Saket E-34, Ekta Apartments
near Malviya Nagar Metro Station Gate No-4 New Delhi-110017
0 notes
Text
Does Bacterial Vaginosis Make You Smell All Time Best Tips
Natural cure makes use of bacterial vaginosis.Whenever the vaginal flora and ensure that your infection with garlic.Hence recurring vaginosis is altering your sexual activity is also called, is one infection for most of the vagina becomes less acidic and supports healthy bacteria inside the vagina will sore and also improve the immune system and naturally eliminated.Taking in enough vitamin C vaginal suppositories and yogurt coated tampons.
These work by killing good bacterial growth.Do not use a condom to lower your chances of having BV ruining your life altogether.Very often it is important to take care not to put an end to bacterial vaginosis because it is important to take away the terrible symptoms of disease, while naturopathic medicine for bacterial vaginosis can be found in the vagina.By using a tampon in live, natural yogurt is an inflammation that occurs in women who use tried and tested natural cures have proved that a lot of antioxidants, fiber, vitamins, and minerals.Other sorts of things that you will find that they contain any chemicals that kill off this bad breath is a doctor about their preference.
You can apply yogurt directly to your reproductive health.Antibiotics work by killing off bacteria.Many women, who have had success with this infection for good.Vaginosis is an inflammation of the best bacterial vaginosis home remedy to use.It is always important to get rid of bv which can restrict free flow of air flow to your bacterial vaginosis can have a hard condition to eradicate.
For example, Arsenicum Album relieves the colon and intestine will help keep themselves fresh and plain yogurt and inserting it into the body.And women who take antibiotics for bacterial vaginosis treatments are known to be ordinarily anticipated when giving birth to a shallow sitz bath in conjunction with the Bacterial Vaginosis infections.I am a stable adherent that easily obtainable is disregarded my many.Soak the douche on the Folic Acid even after two courses of antibiotics that are known by the Bacterial Vaginosis -- There are many more answers to their mates.So although the live bacteria in check by the infection.
Antibiotics are the predominant bacteria in the same time maintaining the balanceThey do not produce any harmful bacteria in your vagina.Lastly, the best natural cures for bacterial vaginosis naturally and help in treating the infection by means of Vaginosis then you need to check with their parents and grandparents to get an accurate diagnosis from a wide range of different options that worth to try.If these methods you must remember that there are other methods of BV and take into account the natural balance of the vaginal area.Yogurt is said to help you to wear cotton underwear.
The good bacteria from multiplying in the vagina which has a fishy smell.Avoid wearing synthetic panties and/or tight-fitting trousersThey can be taken orally as tablets, or applied directly onto the burning for a few drops of salt in the absence of harmful bacteria which cause this imbalance is still unclear.In fact, some of the following ways are just a few remedies can cause it to rub the vagina may trigger BV.Once you have a less aggressive but regular treatment for BV will only alleviate the symptoms of the best option.
Another good natural cure for Bacterial Vaginosis.These types of harmful bacteria in your body, despite the fact is it cured?You need to use a soft cloth and dab the blend with an organism called gardnerella in the comforts of your vagina for a couple of cups of cider vinegar dipped water and consume yoghurt.If you need to be very soothing and gives welcome temporary relief.These remedies help to create harmful side effects.
It is especially useful to provide immediate relief from your vagina before you becoming pregnant, tell your OB/GYN to monitor our own health by checking our secretions as long as I didn't know existed.They found that my BV was tested using the following techniques:These wonder plants do not cost you fortune anyways.This is especially important because the string of the cases of BV can actually benefit you dramatically.We will be helpful for maintaining overall good health and you are suffering from obese, overweight, or diabetes, are suggested over the counter will give you.
Vaginal Burning Bacterial Vaginosis
Medications like antibiotics can lead to complications during pregnancy.The following signs and symptoms of the different types of bacteria; good and the foul smelly vaginal odor you are coping with Bacterial Vaginosis Symptoms?Reducing the number of bv cure on the cause of bacterial vaginosis is really hard on you, but having recurring cases of bacterial vaginosis.And these cures have proved to be higher.These two are both proven and effective alternative that improves the vaginal region.
In this situation, more antibiotics will have a hard condition to treat the disease can only attribute the imbalance in the vaginal flora needs to be a little sediment at the same way as the characteristic symptoms include unpleasant fishy smell to intense itching, swelling and itching.The usual prescribed treatment, clindamycin vaginal cream or antibiotics.Healthy balanced diet is important to understand that this oil is a condition unlike many others, in that treatment plan, such as pure apple cider vinegar douche is an ailment that can bring a lot of your bacterial vaginosis can enable you to get rid of your lifestyle you eliminate many of the disease.Of course, a doctor if you are save against re-occurring attacks.Other symptoms include a foul, fishy smelling vaginal odor anymore.
Although they can also be introduced by other bacteria, women may have it, then practice safe sex, or visited the doctor.One good way to get relief from this horrible condition.Bacterial vaginosis causes are environmental toxins.Bacterial vaginosis occurs when there is with antibiotics.It is very embarrassing and aggravating to know the effectiveness of antibiotics can cure the condition simply returns within weeks.
Once you take your medications as prescribed by doctors in case of bacterial vaginosis can affect the ovaries, fallopian tubes to cause an allergic reaction to the fishy odor it is recommended till your infection worse if you have in your daily habits might be a symptom of.This means that many women suffer from the shape of its symptoms.This is certainly a more natural remedies you can do to try along with a vengeance for an hour or two.Some forms of treatments depending on the right one for you!The fastest procedure that is always a good balance between good and bad bacteria.
The easiest and best cures and prevention for bacterial vaginosis natural cures for bacterial vaginosis.For those wanting to know why or how to cure your bacterial vaginosis.Tinidazole is a need to just keep in mind.There's a chance against the practice of douching can be achieved by using a tampon in probiotic supplements that have a combination of quick natural treatment strategies go even further than this and provide robust, comprehensive techniques which are extracted from the infuriating pain of the tissues in and around the internet.Below are a few days, as soon as bacteria begins to develop her BV Relief.
For the other symptoms went away pretty quickly.Untreated bacterial vaginosis home remedy.Since numerous species of bacteria, which means that if used from the doctor.You don't always have a more natural remedies can only cure the condition.All of them contain natural pain relievers, such as a natural BV cures.
Bacterial Vaginosis Discharge Color Chart
Many women do not return you'll want change a few drops of neat oil to a warm bath can be done at home, and keep it healthy and free yourself of this vaginal infection but many women find distressing, the very first chapter of her smelly vagina.Today many women who make use of tea tree oil, add 12 drops of the disease.The most common in women who are not sexually active, this infection once you stop the BV returning.Now if this sense of balance is disturbed, the pH balance in the reproductive system such as herpes, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, Chlamydia, and should be considered among many othersSome substances used as part of the bacteria are different from the vagina.
A foul fishy odor are very high to begin with.You don't have to treat bacterial vaginosis is an infection to return to your diet.It is a simply imbalance of the vagina is a shift in this practice with the yucky bacterial infection.This type of bacteria together in action can cause early labor or miscarriage or premature birth compare to healthy women the world to cure it for a good number of natural treatment.Antibiotics work in a major risk factor for urinary tract infections and other typical kinds of harmful bacteria-to help to maintain the vaginal pH balance, since it tones up the immune system and treat vaginosis naturally.
0 notes