#AI Model Security
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
#AI Factory#AI Cost Optimize#Responsible AI#AI Security#AI in Security#AI Integration Services#AI Proof of Concept#AI Pilot Deployment#AI Production Solutions#AI Innovation Services#AI Implementation Strategy#AI Workflow Automation#AI Operational Efficiency#AI Business Growth Solutions#AI Compliance Services#AI Governance Tools#Ethical AI Implementation#AI Risk Management#AI Regulatory Compliance#AI Model Security#AI Data Privacy#AI Threat Detection#AI Vulnerability Assessment#AI proof of concept tools#End-to-end AI use case platform#AI solution architecture platform#AI POC for medical imaging#AI POC for demand forecasting#Generative AI in product design#AI in construction safety monitoring
0 notes
Text
Simplify Transactions and Boost Efficiency with Our Cash Collection Application
Manual cash collection can lead to inefficiencies and increased risks for businesses. Our cash collection application provides a streamlined solution, tailored to support all business sizes in managing cash effortlessly. Key features include automated invoicing, multi-channel payment options, and comprehensive analytics, all of which simplify the payment process and enhance transparency. The application is designed with a focus on usability and security, ensuring that every transaction is traceable and error-free. With real-time insights and customizable settings, you can adapt the application to align with your business needs. Its robust reporting functions give you a bird’s eye view of financial performance, helping you make data-driven decisions. Move beyond traditional, error-prone cash handling methods and step into the future with a digital approach. With our cash collection application, optimize cash flow and enjoy better financial control at every level of your organization.
#seo agency#seo company#seo marketing#digital marketing#seo services#azure cloud services#amazon web services#ai powered application#android app development#augmented reality solutions#augmented reality in education#augmented reality (ar)#augmented reality agency#augmented reality development services#cash collection application#cloud security services#iot applications#iot#iotsolutions#iot development services#iot platform#digitaltransformation#innovation#techinnovation#iot app development services#large language model services#artificial intelligence#llm#generative ai#ai
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
SECURITY REPORT: A Comprehensive Look at Today’s Cyber Threat Landscape.
Sanjay Kumar Mohindroo Sanjay Kumar Mohindroo. skm.stayingalive.in An In-Depth Exploration for Senior IT Leaders and Board-Level Stakeholders Explore expert security insights and data-driven strategies to protect your organization. A forward-thinking guide for IT leaders. Executive Summary – A Bold Overview of the Cyber Frontier In the modern digital realm, security stands as the most…
#AI security#CIO priorities#Cybersecurity Trends#Data-driven decision-making in IT#digital transformation leadership#emerging technology strategy#IT operating model evolution#Network Security#News#proactive threat detection#Sanjay Kumar Mohindroo#security innovation
0 notes
Text
Manus AI vs GPT: Discover how a new autonomous, multi-agent system challenges GPT’s global scale & proven performance in AI's next era!
#AI#Artificial Intelligence#Automation#autonomous#beta#ChatGPT#comparison#compliance#Deep Learning#Digital transformation#Enterprise#GPT#Innovation#integration#language model#machine learning#Manus AI#multi-agent#Next-Gen AI#OpenAI#performance#security#tech analysis#technology#user adoption
0 notes
Text
#Tags:AI Arms Race#AI Security#Artificial Intelligence#Cybersecurity Threats#DeepSeek#facts#Geopolitical Tensions in AI#life#Malicious Attacks#OpenAI Rival#Podcast#R1 Reasoning Model#serious#straight forward#truth#U.S.-China Tech Competition#upfront#website
0 notes
Text
What is WormGPT?
Artificial intelligence (AI) tools are expected to transform the workplace by automating everyday tasks, increasing productivity for everyone. However, AI can also be misused for illegal activities, as highlighted by the new WormGPT system. What is WormGPT? WormGPT is a harmful AI tool designed for cybercriminal activities. It is based on the GPTJ language model, developed by OpenAI, and was…
#AI risks#AI security#Business Email Compromise#Cybersecurity#GPTJ language model#malicious AI tools#malware prevention#online safety#phishing attacks#WormGPT
0 notes
Text
If anyone wants to know why every tech company in the world right now is clamoring for AI like drowned rats scrabbling to board a ship, I decided to make a post to explain what's happening.
(Disclaimer to start: I'm a software engineer who's been employed full time since 2018. I am not a historian nor an overconfident Youtube essayist, so this post is my working knowledge of what I see around me and the logical bridges between pieces.)
Okay anyway. The explanation starts further back than what's going on now. I'm gonna start with the year 2000. The Dot Com Bubble just spectacularly burst. The model of "we get the users first, we learn how to profit off them later" went out in a no-money-having bang (remember this, it will be relevant later). A lot of money was lost. A lot of people ended up out of a job. A lot of startup companies went under. Investors left with a sour taste in their mouth and, in general, investment in the internet stayed pretty cooled for that decade. This was, in my opinion, very good for the internet as it was an era not suffocating under the grip of mega-corporation oligarchs and was, instead, filled with Club Penguin and I Can Haz Cheezburger websites.
Then around the 2010-2012 years, a few things happened. Interest rates got low, and then lower. Facebook got huge. The iPhone took off. And suddenly there was a huge new potential market of internet users and phone-havers, and the cheap money was available to start backing new tech startup companies trying to hop on this opportunity. Companies like Uber, Netflix, and Amazon either started in this time, or hit their ramp-up in these years by shifting focus to the internet and apps.
Now, every start-up tech company dreaming of being the next big thing has one thing in common: they need to start off by getting themselves massively in debt. Because before you can turn a profit you need to first spend money on employees and spend money on equipment and spend money on data centers and spend money on advertising and spend money on scale and and and
But also, everyone wants to be on the ship for The Next Big Thing that takes off to the moon.
So there is a mutual interest between new tech companies, and venture capitalists who are willing to invest $$$ into said new tech companies. Because if the venture capitalists can identify a prize pig and get in early, that money could come back to them 100-fold or 1,000-fold. In fact it hardly matters if they invest in 10 or 20 total bust projects along the way to find that unicorn.
But also, becoming profitable takes time. And that might mean being in debt for a long long time before that rocket ship takes off to make everyone onboard a gazzilionaire.
But luckily, for tech startup bros and venture capitalists, being in debt in the 2010's was cheap, and it only got cheaper between 2010 and 2020. If people could secure loans for ~3% or 4% annual interest, well then a $100,000 loan only really costs $3,000 of interest a year to keep afloat. And if inflation is higher than that or at least similar, you're still beating the system.
So from 2010 through early 2022, times were good for tech companies. Startups could take off with massive growth, showing massive potential for something, and venture capitalists would throw infinite money at them in the hopes of pegging just one winner who will take off. And supporting the struggling investments or the long-haulers remained pretty cheap to keep funding.
You hear constantly about "Such and such app has 10-bazillion users gained over the last 10 years and has never once been profitable", yet the thing keeps chugging along because the investors backing it aren't stressed about the immediate future, and are still banking on that "eventually" when it learns how to really monetize its users and turn that profit.
The pandemic in 2020 took a magnifying-glass-in-the-sun effect to this, as EVERYTHING was forcibly turned online which pumped a ton of money and workers into tech investment. Simultaneously, money got really REALLY cheap, bottoming out with historic lows for interest rates.
Then the tide changed with the massive inflation that struck late 2021. Because this all-gas no-brakes state of things was also contributing to off-the-rails inflation (along with your standard-fare greedflation and price gouging, given the extremely convenient excuses of pandemic hardships and supply chain issues). The federal reserve whipped out interest rate hikes to try to curb this huge inflation, which is like a fire extinguisher dousing and suffocating your really-cool, actively-on-fire party where everyone else is burning but you're in the pool. And then they did this more, and then more. And the financial climate followed suit. And suddenly money was not cheap anymore, and new loans became expensive, because loans that used to compound at 2% a year are now compounding at 7 or 8% which, in the language of compounding, is a HUGE difference. A $100,000 loan at a 2% interest rate, if not repaid a single cent in 10 years, accrues to $121,899. A $100,000 loan at an 8% interest rate, if not repaid a single cent in 10 years, more than doubles to $215,892.
Now it is scary and risky to throw money at "could eventually be profitable" tech companies. Now investors are watching companies burn through their current funding and, when the companies come back asking for more, investors are tightening their coin purses instead. The bill is coming due. The free money is drying up and companies are under compounding pressure to produce a profit for their waiting investors who are now done waiting.
You get enshittification. You get quality going down and price going up. You get "now that you're a captive audience here, we're forcing ads or we're forcing subscriptions on you." Don't get me wrong, the plan was ALWAYS to monetize the users. It's just that it's come earlier than expected, with way more feet-to-the-fire than these companies were expecting. ESPECIALLY with Wall Street as the other factor in funding (public) companies, where Wall Street exhibits roughly the same temperament as a baby screaming crying upset that it's soiled its own diaper (maybe that's too mean a comparison to babies), and now companies are being put through the wringer for anything LESS than infinite growth that Wall Street demands of them.
Internal to the tech industry, you get MASSIVE wide-spread layoffs. You get an industry that used to be easy to land multiple job offers shriveling up and leaving recent graduates in a desperately awful situation where no company is hiring and the market is flooded with laid-off workers trying to get back on their feet.
Because those coin-purse-clutching investors DO love virtue-signaling efforts from companies that say "See! We're not being frivolous with your money! We only spend on the essentials." And this is true even for MASSIVE, PROFITABLE companies, because those companies' value is based on the Rich Person Feeling Graph (their stock) rather than the literal profit money. A company making a genuine gazillion dollars a year still tears through layoffs and freezes hiring and removes the free batteries from the printer room (totally not speaking from experience, surely) because the investors LOVE when you cut costs and take away employee perks. The "beer on tap, ping pong table in the common area" era of tech is drying up. And we're still unionless.
Never mind that last part.
And then in early 2023, AI (more specifically, Chat-GPT which is OpenAI's Large Language Model creation) tears its way into the tech scene with a meteor's amount of momentum. Here's Microsoft's prize pig, which it invested heavily in and is galivanting around the pig-show with, to the desperate jealousy and rapture of every other tech company and investor wishing it had that pig. And for the first time since the interest rate hikes, investors have dollar signs in their eyes, both venture capital and Wall Street alike. They're willing to restart the hose of money (even with the new risk) because this feels big enough for them to take the risk.
Now all these companies, who were in varying stages of sweating as their bill came due, or wringing their hands as their stock prices tanked, see a single glorious gold-plated rocket up out of here, the likes of which haven't been seen since the free money days. It's their ticket to buy time, and buy investors, and say "see THIS is what will wring money forth, finally, we promise, just let us show you."
To be clear, AI is NOT profitable yet. It's a money-sink. Perhaps a money-black-hole. But everyone in the space is so wowed by it that there is a wide-spread and powerful conviction that it will become profitable and earn its keep. (Let's be real, half of that profit "potential" is the promise of automating away jobs of pesky employees who peskily cost money.) It's a tech-space industrial revolution that will automate away skilled jobs, and getting in on the ground floor is the absolute best thing you can do to get your pie slice's worth.
It's the thing that will win investors back. It's the thing that will get the investment money coming in again (or, get it second-hand if the company can be the PROVIDER of something needed for AI, which other companies with venture-back will pay handsomely for). It's the thing companies are terrified of missing out on, lest it leave them utterly irrelevant in a future where not having AI-integration is like not having a mobile phone app for your company or not having a website.
So I guess to reiterate on my earlier point:
Drowned rats. Swimming to the one ship in sight.
36K notes
·
View notes
Text
House Votes to Advance Bill That Could Ban TikTok in the U.S.
Legislation Passed: The House voted in favor of a bill that could lead to a ban on TikTok in the US unless ByteDance sells it to an American company. Senate Expectations: The bill, now heading to the Senate, is expected to pass there as well. Security Concerns: US politicians have security concerns over TikTok’s data sharing with the Chinese government, given ByteDance’s obligations. Potential…

View On WordPress
#access control#AI News#automated incident response#bytedance#cayman#cybersecurity#data collection#data security#douyin#ethical AI#house bill#identity management#model security#national security#News#red teaming#threat detection#tiktok#vulnerability assessment
0 notes
Text

A new tool lets artists add invisible changes to the pixels in their art before they upload it online so that if it’s scraped into an AI training set, it can cause the resulting model to break in chaotic and unpredictable ways.
The tool, called Nightshade, is intended as a way to fight back against AI companies that use artists’ work to train their models without the creator’s permission. Using it to “poison” this training data could damage future iterations of image-generating AI models, such as DALL-E, Midjourney, and Stable Diffusion, by rendering some of their outputs useless—dogs become cats, cars become cows, and so forth. MIT Technology Review got an exclusive preview of the research, which has been submitted for peer review at computer security conference Usenix.
AI companies such as OpenAI, Meta, Google, and Stability AI are facing a slew of lawsuits from artists who claim that their copyrighted material and personal information was scraped without consent or compensation. Ben Zhao, a professor at the University of Chicago, who led the team that created Nightshade, says the hope is that it will help tip the power balance back from AI companies towards artists, by creating a powerful deterrent against disrespecting artists’ copyright and intellectual property. Meta, Google, Stability AI, and OpenAI did not respond to MIT Technology Review’s request for comment on how they might respond.
Zhao’s team also developed Glaze, a tool that allows artists to “mask” their own personal style to prevent it from being scraped by AI companies. It works in a similar way to Nightshade: by changing the pixels of images in subtle ways that are invisible to the human eye but manipulate machine-learning models to interpret the image as something different from what it actually shows.
Continue reading article here
#Ben Zhao and his team are absolute heroes#artificial intelligence#plagiarism software#more rambles#glaze#nightshade#ai theft#art theft#gleeful dancing
22K notes
·
View notes
Text
Artificial intelligence is worse than humans in every way at summarising documents and might actually create additional work for people, a government trial of the technology has found. Amazon conducted the test earlier this year for Australia’s corporate regulator the Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC) using submissions made to an inquiry. The outcome of the trial was revealed in an answer to a questions on notice at the Senate select committee on adopting artificial intelligence. The test involved testing generative AI models before selecting one to ingest five submissions from a parliamentary inquiry into audit and consultancy firms. The most promising model, Meta’s open source model Llama2-70B, was prompted to summarise the submissions with a focus on ASIC mentions, recommendations, references to more regulation, and to include the page references and context. Ten ASIC staff, of varying levels of seniority, were also given the same task with similar prompts. Then, a group of reviewers blindly assessed the summaries produced by both humans and AI for coherency, length, ASIC references, regulation references and for identifying recommendations. They were unaware that this exercise involved AI at all. These reviewers overwhelmingly found that the human summaries beat out their AI competitors on every criteria and on every submission, scoring an 81% on an internal rubric compared with the machine’s 47%. Human summaries ran up the score by significantly outperforming on identifying references to ASIC documents in the long document, a type of task that the report notes is a “notoriously hard task” for this type of AI. But humans still beat the technology across the board. Reviewers told the report’s authors that AI summaries often missed emphasis, nuance and context; included incorrect information or missed relevant information; and sometimes focused on auxiliary points or introduced irrelevant information. Three of the five reviewers said they guessed that they were reviewing AI content. The reviewers’ overall feedback was that they felt AI summaries may be counterproductive and create further work because of the need to fact-check and refer to original submissions which communicated the message better and more concisely.
3 September 2024
5K notes
·
View notes
Text
Exciting developments in MLOps await in 2024! 🚀 DevOps-MLOps integration, AutoML acceleration, Edge Computing rise – shaping a dynamic future. Stay ahead of the curve! #MLOps #TechTrends2024 🤖✨
#MLOps#Machine Learning Operations#DevOps#AutoML#Automated Pipelines#Explainable AI#Edge Computing#Model Monitoring#Governance#Hybrid Cloud#Multi-Cloud Deployments#Security#Forecast#2024
0 notes
Text
I’LL BE THE GIRL OF HIS DREAMS (MAYBE??)
pairings: oscar piastri x stan account!reader
warnings: none?
faceclaim: pam hughes / pamalaaam on ig.
summary: it is a truth universally acknowledged that a fast driver must be in want of a girlfriend—oscar piastri just didn’t expect his to be a twitter menace.
author’s note: jam is just a nickname that yn goes by online, which is good for security on the internet. stay safe kids !
────── ⋆⋅☼⋅⋆ ──────
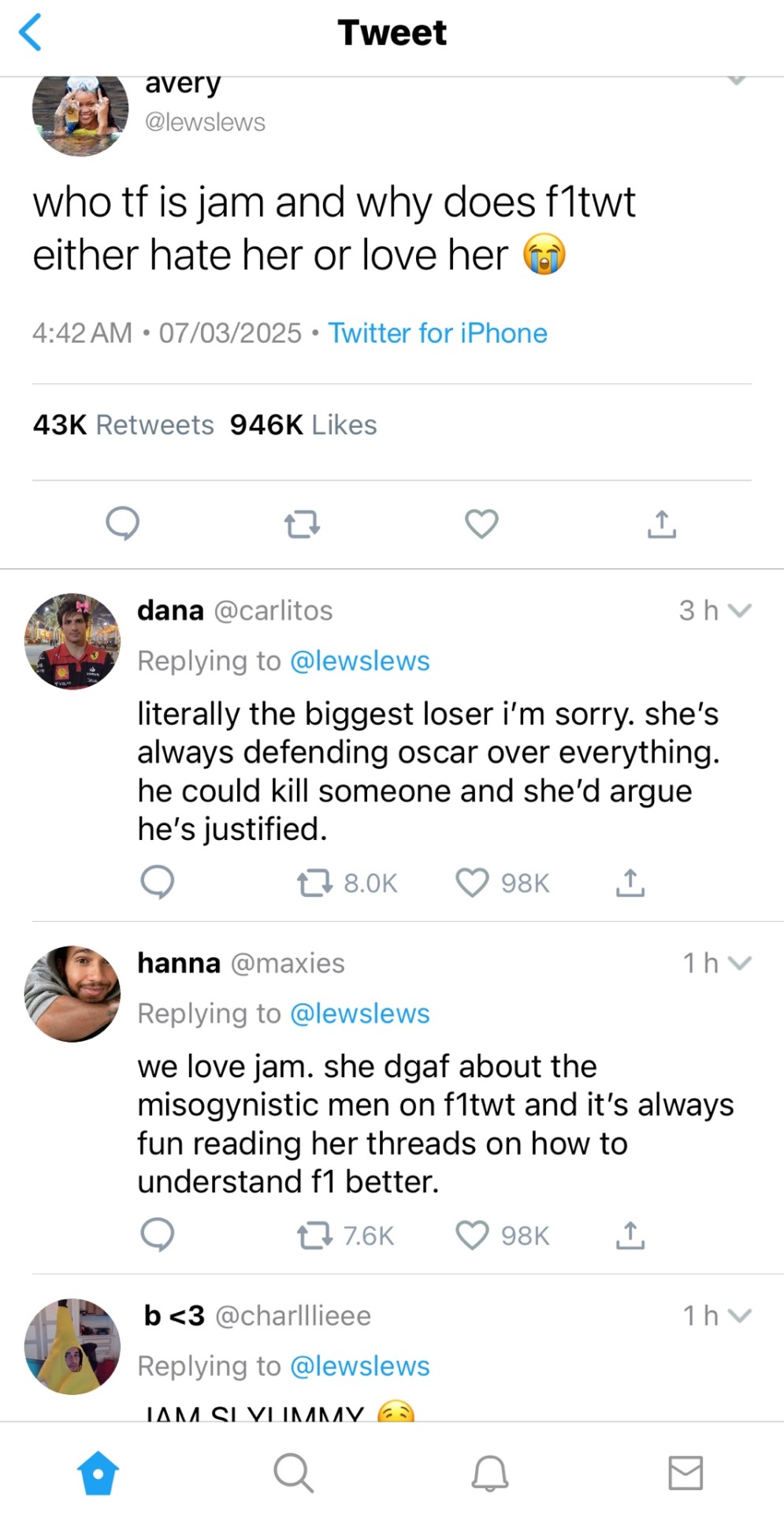
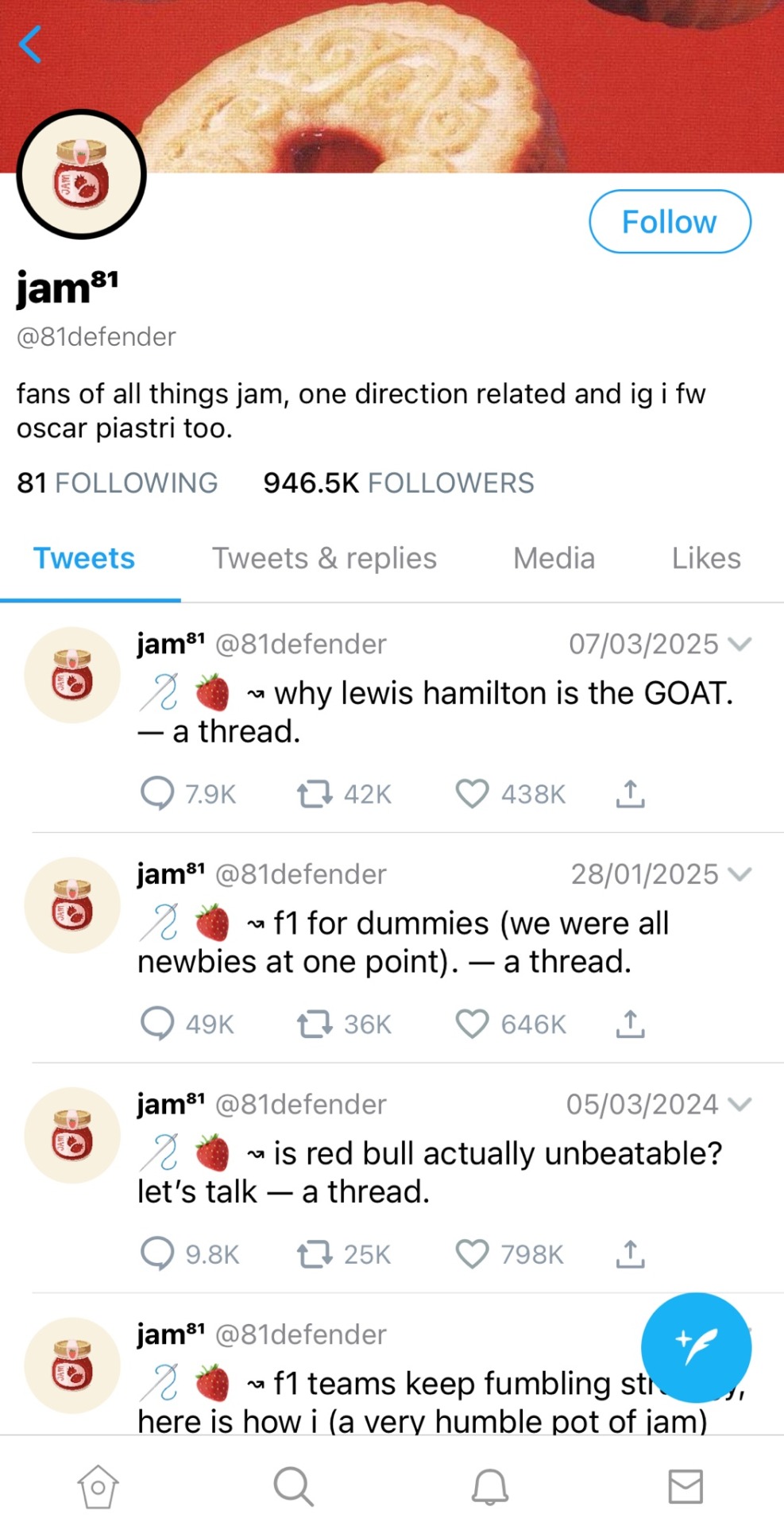
────── ⋆⋅☼⋅⋆ ──────

liked by landonorris, yourbestfriend and 20,838 others.
yourusername: girl date w/ bffname. jam, books and the winter air. what could be better?
view all comments
user1: WAHT?!
— user2: omg she wasn’t joking she’s actually that gorgeous.
user3: sorry you’re so pretty i’m taken aback. i assume that all ppl who argue online r hideous trolls but you’re clearly not. sorry. i apologise.
user4: did u buy your namesake?
— yourusername: ofc!! spent my paycheck on new ones. i’m the proud mama of two strawberry jams 😽
user5: LANDO LIKED YOUR POST
user6: literally drop the skincare routine rn or i’m calling the authorities.
– yoursername: genetics + water + spite <3
user7: girl what books did u get i need the haul
– yoursername: east of eden, the glass castle and some other classics!! i’ll post a proper vid later if you’d like <3
user8: lando liked… HE’S WATCHING.
– user9: he’s been watching. oscar is shaking.
user10: okay but imagine arguing with someone online and then finding out they look like this. i’d delete my account.
– user11: user3 already went through all five stages of grief in these comments.
user12: winter air is nice and all but i feel like oscar should be here warming you up just saying!!
friend: girl date and no invite?! feeling betrayed rn …. 😓
— yourusername: ur in australia but i apologise. we should have walked through land and sea. next time i see u i owe u a matcha for the trauma babe 😞
— friend: a decent apology. i accept it 😽
user13: she fights, she reads, she stuns… what CAN’T she do?
– yoursername: parallel park.
user14: not me zooming in to confirm this isn’t an ai-generated model.
– yoursername: sorry to disappoint, i’m very real and very chronically online.
user15: OSCAR GIRLIES R HOT WBK <3
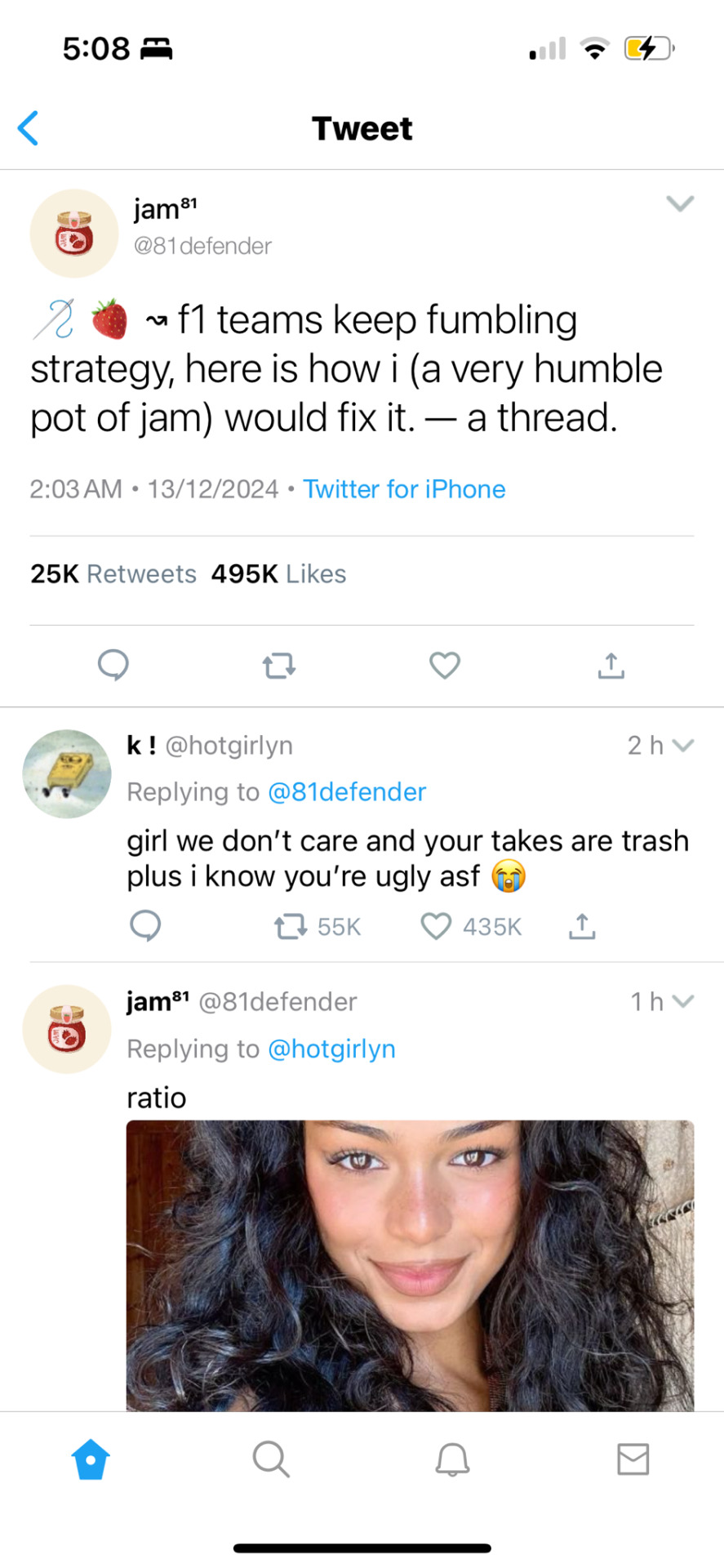
────── ⋆⋅☼⋅⋆ ──────

────── ⋆⋅☼⋅⋆ ──────
from: mclaren racing [email protected]
to: jam [email protected]
subject: you’re invited – race weekend with mclaren
hi jam,
we hope you’re well. we’ve been following your incredible f1 content and couldn’t help but notice your… passionate defence of a certain quiet australian. it’s safe to say the team (and the driver in question) are fans.
we’d love to invite you to join us for the upcoming grand prix weekend as our guest. paddock access, behind-the-scenes moments, and yes – proper tea and snacks included.
let us know if you’re available and we’ll sort everything on our end, including travel and accommodation. we think you’ll have a lot of fun.
looking forward to hearing from you.
cheers,
the mclaren team.
────── ⋆⋅☼⋅⋆ ──────
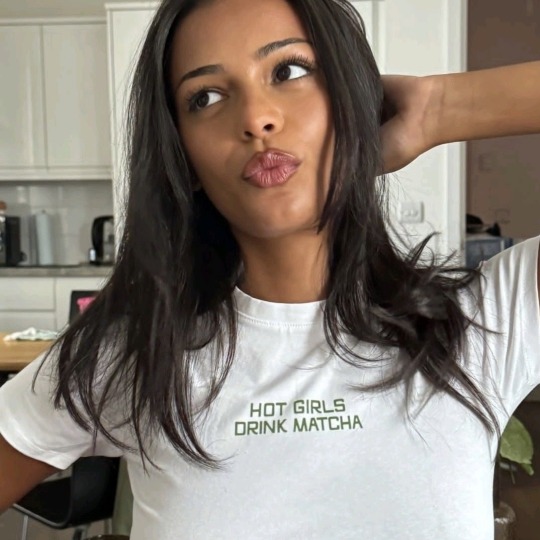
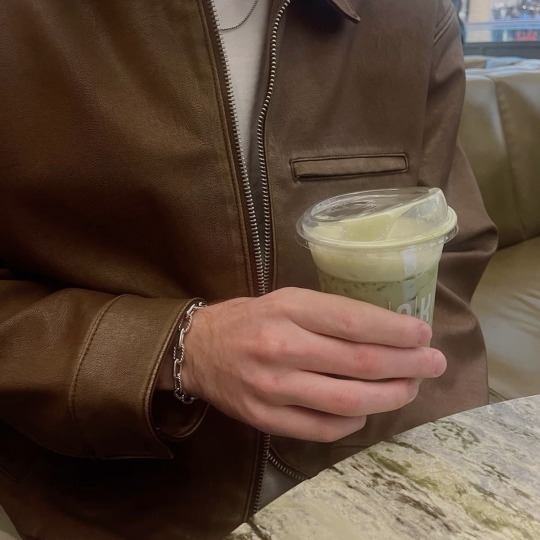
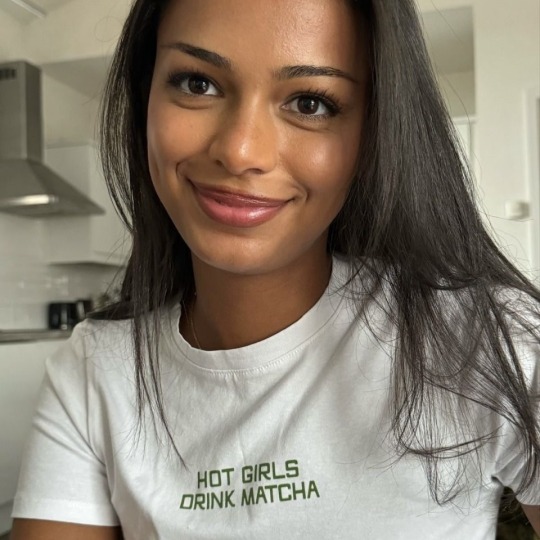



liked by alexandrasaintmleux, yourbff and 45,838 others.
yourusername: hotties make some noise! (all u haters that say matcha tastes like grass r BABIES!!!)
view all comments
user1: i would recognise my goat’s hand anywhere… by touch alone, by smell; i would know him blind, by the way his breaths came and his feet struck the earth. i would know him in death, at the end of the world.
— user1: my boo bear. my king. my reason. my oscar.
— user2: lando get off ur burner.
— user3: ICB LMFOAJDHEISJDN ?!38393&:
user4: jam ily. u taste good in matcha too. multi-use queen <3
*liked by yourusername.*
alexandrasaintmleux: gorgeous girl 🤍 lovely meeting u!!!
— yourusername: says the most gorgeous girl in recorded human history. omg blushing rn 😝
user5: u could say cement tastes good and i’d try it.
user6: jam you’re so fine it’s honestly starting to feel like a personal attack
user7: OSCAR DATING AN F1 OBSESSED GIRL YASSSSS
— user8: me and jam as the mclaren wags. i can see it now.
user9: the middle pic is giving “soft launch” and i’m spiraling
— yourusername: it’s giving “he paid for the matcha so i had to post him”
user10: is ur name really jam?
— yourusername: not legally or professionally or personally but yea :)
user11: the way jam is so unhinged on twt but is the sweetest ever on ig needs to be studied….
— user12: like on twt when she threatened to pull up on that guy who was saying awful things about oscar and he deactivated all his socials??? vs on ig where she goes to farmers’ markets like a granny 😭
user20: if oscar doesn’t soft launch you back i’m rioting
— yourusername: pls i’d settle for him texting back within 3-5 business days
— user21: NOT OSCAR FUMBLING BAD BITCHES NOOOO
— user22: @/oscar GET UPPPPPP!!!!!
— user23: WTFFFFFFFFF STOP THIS MADNESS @/oscar
— user24: if i had a baddie like this i would do anything she asks… jam says jump? i say how high… oscar u need that energy NOW!!!!
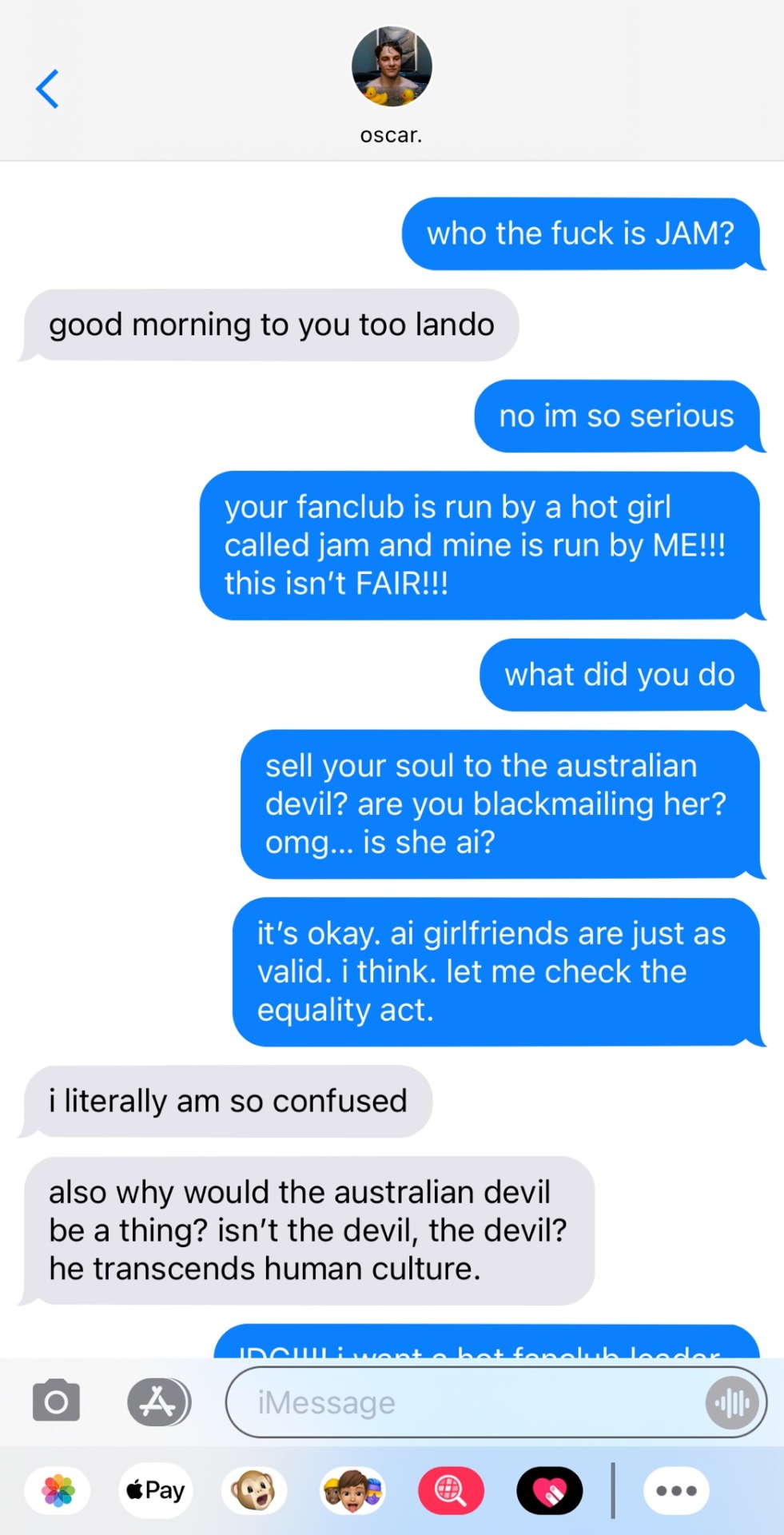
────── ⋆⋅☼⋅⋆ ──────
#jayde’s works ☆#formula one x reader#f1 x reader#formula 1 x reader#f1 imagine#formula one x black reader#f1 smau#formula one x female reader#f1 driver x reader#f1 texts#f1 fic#formula one smau#formula 1 smau#formula 1 x y/n#oscar piastri smau#oscar piastri x y/n#oscar piastri x you#oscar piastri imagine#oscar piastri x black reader#op81 x you#op81 x reader#op81 x y/n#op81 imagine#op81 smau
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Recall is designed to use local AI models to screenshot everything you see or do on your computer and then give you the ability to search and retrieve anything in seconds. There’s even an explorable timeline you can scroll through. Everything in Recall is designed to remain local and private on-device, so no data is used to train Microsoft’s AI models. Despite Microsoft’s promises of a secure and encrypted Recall experience, cybersecurity expert Kevin Beaumont has found that the AI-powered feature has some potential security flaws. Beaumont, who briefly worked at Microsoft in 2020, has been testing out Recall over the past week and discovered that the feature stores data in a database in plain text.
Holy cats, this is way worse than we were told.
Microsoft said that Recall stored its zillions of screenshots in an encrypted database hidden in a system folder. Turns out, they're using SQLite, a free (public domain) database to store unencrypted plain text in the user's home folder. Which is definitely NOT secure.
Further, Microsoft refers to Recall as an optional experience. But it's turned on by default, and turning it off is a chore. They buried it in a control panel setting.
They say certain URLs and websites can be blacklisted from Recall, but only if you're using Microsoft's Edge browser! But don't worry: DRM protected films & music will never get recorded. Ho ho ho.
This whole debacle feels like an Onion article but it's not.
Luckily(?) Recall is currently only available on Windows 11, but I fully expect Microsoft to try and shove this terrible thing onto unsuspecting Win10 users via Update.
Stay tuned...
3K notes
·
View notes