#2011 Russian Nationals
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Collection of open educational resources for Mandarin Chinese (& Russian)
I saved a bunch of open educational resources a while ago and then promptly forgot about them. Haven't really looked over them in detail, but hey, why not share them in case they are useful to you?
Chinese Reading Modules by Yan Li https://ceas.ku.edu/chinese-reading-modules
These reading passages are intended for students at the intermediate to advanced level in their study of Chinese. They were developed with funding from the KU Center for East Asian Studies.
Ting Yi Ting by Sheree Willis & Yan Li https://opentext.ku.edu/tingyiting/
An online guide that enables learners to hear and identify phonemic categories in Mandarin (including lexical tones) in a variety of phonetic contexts, and to associate those phonemes with Pinyin orthography. Includes extensive audio examples and computer-graded comprehension checks.
Russian Aspect in Conversation by Stephen M. Dickey, Kamila Saifeeva, and Anna Karpusheva https://opentext.ku.edu/russianaspect/
This resource is aimed at demystifying some important uses of imperfective verbs for learners of Russian at the intermediate level and above. It focuses on patterns of imperfective usage in infinitives, imperatives and the past tense that involve single completed actions and that are difficult for foreign learners to grasp.
Elementary Chinese I by Wenying Zhou https://openbooks.lib.msu.edu/chs101/
This open textbook is designed for those who are learning Chinese as a second/foreign language in their first semester. It has eight chapters, covering topics including a brief introduction about the Chinese language, greetings, and self-introduction, hobbies, nationalities, family members and occupations, inviting friends to dinner, talking about food and beverage, making phone calls, and talking about classes and exams.
Elementary Chinese II by Wenying Zhou https://openbooks.lib.msu.edu/chs102/
This open textbook is designed for those who are learning Chinese as a second/foreign language in their second semester. It has six chapters, covering topics including describing school life, shopping in stores and online, transportation means, reporting weather and climates, ordering foods, and asking and giving directions.
Elementary Mandarin by Carl Polley https://open.umn.edu/opentextbooks/textbooks/elementary-mandarin
This course is designed for learners with no background in Chinese. It introduces basic structures of the Mandarin Chinese language with emphasis on listening, speaking, reading and writing skills. Students will gain these four skills in standard Mandarin Chinese, attaining approximately the Novice-High level on the ACTFL-ETS (American Council on the Teaching of Foreign Languages) proficiency scale. Topics of conversation include basic greetings, names, family, work, study, and hobbies.
开源中文 EverFlow Mandarin by Runqing Qi, Yingjie Li, and Yu Zhang https://www.colorado.edu/project/everflowmandarin/
EverFlow Mandarin is a textbook aimed at enhancing the language proficiency of Chinese learners at the intermediate level as determined by the American Council on the Teaching of Foreign Languages (ACTFL). It is designed for students who have completed two years of Chinese language courses in comprehensive universities in North America. After studying the content of the ten lessons in this textbook, students' Chinese proficiency can reach the levels of either Intermediate-High or Advanced-Low as determined by the ACTFL.
Various Chinese resources by Wen-Hua Teng https://coerll.utexas.edu/coerll/materials/language/chinese/
Learning Chinese: A Foundation Course In Mandarin (汉语基础教材) by Julian K. Wheatley https://ocw.mit.edu/courses/res-21g-003-learning-chinese-a-foundation-course-in-mandarin-spring-2011/pages/online-textbook/
This online textbook represents materials that were used in the first four semesters (two years) of the Mandarin program at MIT. They eventually formed the basis of a print textbook of the same name, published by Yale University Press (elementary level available 2011, intermediate level due late 2011 or early 2012). Information about the Yale edition, plus online materials that could supplement the OCW material with some allowances. The Yale website also includes extensive audio-clips (numbering over 40 by July 2011, up through Unit 4), which cover much of the same ground as the OCW version.
IChineseER from Pomona College https://lchineseer.sites.pomona.edu/
Diverse Russian: A Multicultural Exploration by Anna Tumarkin and Shannon Donnally Quinn https://wisc.pb.unizin.org/diverserussian/
This textbook invites students to explore the diverse Russian-speaking communities across Eastern Europe, Central Asia, and North America. It highlights the rich cultures and histories of Ukraine, Kazakhstan, Indigenous populations of Russia, the Baltic states, Georgia (Sakartvelo), and Russian-speaking communities in the United States. Supported by the Less Commonly Taught and Indigenous Languages Partnership and funded by the Andrew W. Mellon Foundation, this OER textbook provides a unique, immersive experience that seamlessly integrates cultural understanding with practical language skills.
#chinese resources#russian resources#open educational resource#open educational resources#oer#chinese#mandarin#mandarin chinese#chinese language#studyblr#langblr#learning languages#language learning#chinese langblr#mandarin langblr#languageblr#russian language
352 notes
·
View notes
Text
UMK 2025 IS HERE!

WHAT: Uuden Musiikin Kilpailu (Contest for New Music) abbreviated UMK, Finland’s national Eurovision selection
WHEN: Saturday 8th of February at 21.00 Finnish time (20.00 CET)
WHERE: Live from Nokia Arena in Tampere, Yle TV1 & Yle Areena
Commentary available in Finnish, Swedish, English, Ukrainian, Russian, Northern Sami and Inari Sami, and Finnish and Fenno-Swedish Sign Language
HOSTS: Sanni & Jasmin Beloued

RUNNING ORDER
costee: Sekaisin
NEEA RIVER: Nightmares
Goldielocks: Made Of
VIIVI: Aina
Nelli Matula: Hitaammin hautaan
Erika Vikman: ICH KOMME

INTERVAL ACTS:
Sanni, Windows95Man

Fantasy Group consisting of six female performers with UMK or ESC connections:
Laura Voutilainen (2002), Annika Eklund (2006), Linda Lampenius (2011), Eini (2016), BESS (2022), Keira (2023)

VOTING: 75% public vote, 25% international jury
Voting via Yle App (one free vote), text message or calling (1 €/vote, unlimited)
PS. All performances, including the opening and interval acts, will be uploaded to UMK’s YouTube channel. Full show will also be available for re-watching at Yle Areena.
61 notes
·
View notes
Text
Tulsi Gabbard’s history with Russia is even more concerning than you think
“What happened in Syria is what allowed the Russians to feel that they could do the very same in Ukraine,” he said.
“And what she is doing with Ukraine shows that it goes beyond her maybe misunderstanding one conflict. She is, hook, line and sinker, a Russian puppet.”
In the summer of 2015, three Syrian girls who had narrowly survived an airstrike some weeks earlier stood before Tulsi Gabbard with horrific burns all over their bodies.
Gabbard, then a US congresswoman on a visit to the Syria-Turkey border as part of her duties for the foreign affairs committee, had a question for them.
“How do you know it was Bashar al-Assad or Russia that bombed you, and not Isis?’” she asked, according to Mouaz Moustafa, a Syrian activist who was translating her conversation with the girls.
It was a revealing insight into Gabbard’s conspiratorial views of the conflict, and it shocked Moustafa to silence. He knew, as even the young children did, that Isis did not have jets to launch airstrikes. It was such an absurd question that he chose not to translate it because he didn’t want to upset the girls, the eldest of whom was 12.
“From that point on, I’m sorry to say I was inaccurate in my translations of anything she said,” Moustafa told The Independent. “It was more like: How do I get these girls away from this devil?”
Even before Gabbard left the Democratic Party, ingratiated herself with Donald Trump and secured his nomination to become director of National Intelligence, she was known as a prolific peddler of Russian propaganda.
In almost every foreign conflict in which Russia had a hand, Gabbard backed Moscow and railed against the US. Her past promotion of Kremlin propaganda has provoked significant opposition on both sides of the aisle to her nomination.
Her journey from anti-war Democrat to Moscow-friendly Maga warrior began in Syria. The devastating conflict was sparked by pro-democracy uprisings in 2011, which were brutally crushed by the Assad regime. It descended into a complex web of factions that drew extremist Islamists from around the world and global powers into the fray.
The Syrian Observatory for Human Rights (SOHR), a UK-based monitoring group with a network of sources on the ground, documented the deaths of 503,064 people by March 2023. It said at least 162,390 civilians had died in that same time, with the Syrian government and its allies responsible for 139,609 of those deaths.
But Gabbard, a veteran of the Iraq War, viewed it all as a “regime-change war” fueled by the West and aimed at removing the dictator from power. She saw Assad – and Russia, when it entered the conflict – as legitimate defenders of the state against an extremist uprising.
In 2015, when Russia entered the Syrian war on the side of the dictator Assad, Gabbard expressed support for the move, even as the civilian toll from Moscow’s devastating airstrikes grew into the thousands.
“Al-Qaeda attacked us on 9/11 and must be defeated. Obama won’t bomb them in Syria. Putin did. #neverforget911,” she wrote on Twitter.
It was precisely because of her support for Assad and Russia’s war that Moustafa was keen for her to attend the congressional delegation to southern Turkey to meet the victims of the conflict.
“From experience, everyone that we bring over to the border, and they see the victims, they always come back with a realistic view of what’s happening and who is behind the mass displacement and killing and atrocities and so on, and so that was the objective,” he said. “What was shocking was her lack of empathy. She’ll sacrifice the facts, even when it came to little girls in front of her telling her they got bombed by a plane – it didn’t matter.”
Charles Lister, a senior fellow at the Middle East Institute who testified twice on Syria to the House Foreign Affairs Committee when Gabbard was a member, spent years debunking her various conspiracy theories about the war.
“Her consistent denial of the Syrian regime’s crimes is so wildly fringe that her potential appointment as DNI is genuinely alarming,” he told The Independent.
Lister said her views “appear to be driven by a strange fusion of America First isolationism and a belief in the value of autocratic and secular leaders in confronting extremism.”
They included a suggestion that Syrian rebels staged a false-flag chemical weapons attack against their supporters to provoke Western intervention against Assad — something the US intelligence agencies she will soon lead had concluded was false. She declined to call Assad a war criminal when pressed, despite masses of evidence, and used a video of Syrian government bombings to criticize US involvement in the war.
“Her descriptions of the crisis in Syria read like they were composed in Assad’s personal office, or in Tehran or Moscow – not Washington,” Lister added.
Gabbard was not swayed by meeting the victims of Assad’s airstrikes in 2015. In fact, two years later, she went to Damascus to meet the Syrian president in person and came away even more convinced of her opinions.
The congresswoman said her visit to meet Assad – the first by a sitting US lawmaker since the conflict began – was aimed at bringing an end to the war.
“I felt it’s important that if we profess to truly care about the Syrian people, about their suffering, then we’ve got to be able to meet with anyone that we need to if there is a possibility that we could achieve peace,” she told CNN at the time.

Fire rises following a Syrian government airstrike in Aleppo in 2016 (AP)
Gabbard was forced to defend her embrace of Assad and other dictators during her 2020 run for the Democratic presidential nomination. During the Democratic primary debate, she clashed with Kamala Harris, who accused her of being “an apologist for an individual – Assad – who has murdered the people of his country like cockroaches.”
“She has embraced and been an apologist for him in a way that she refuses to call him a war criminal. I can only take what she says and her opinion so seriously and so I’m prepared to move on,” added Harris, who would subsequently drop out of the race and later be selected as Joe Biden’s running mate.
When Russia invaded Ukraine, Gabbard again defended Russian aggression.
“This war and suffering could have easily been avoided if Biden Admin/Nato had simply acknowledged Russia’s legitimate security concerns,” she posted on Twitter in 2022.
Gabbard appeared to fall for various conspiracy theories about the conflict that were promoted by Russia, as she had done in Syria. One of those conspiracy theories was a Russian claim about the existence of dozens of US-funded biolabs in Ukraine that were supposedly producing deadly pathogens.
She later walked back on those remarks, suggesting that there might have been some “miscommunication and misunderstanding.”
Gabbard’s frequent echoing of Kremlin talking points has earned her praise in Russian state media. Indeed, an article published on 15 November in the Russian-state controlled outlet RIA Novosti went so far as to call Gabbard a “superwoman.”
The possibility that Trump would tap someone with Gabbard’s history to be America’s top intelligence official shouldn’t be a surprise to anyone who followed the president-elect’s first four years in the White House.
During his 2018 summit with President Vladimir Putin in Helsinki, the then-president was asked if he believed the US intelligence community’s assessment, which stated that Russia had interfered in the 2016 presidential election on his behalf.
That assessment was based on analysis of what was determined to have been state-sponsored campaigns of fake social media posts and ersatz news sites to spread false stories about his Democratic opponent, Hillary Clinton, as well as cyberattacks targeting the Democratic National Committee and prominent operatives associated with the Clinton campaign.
But Trump, who’d just spent several hours in a closed-door meeting with Putin, stunned the assembled press and the entire world by declaring that he trusted the Russian leader’s word over that of his own advisers.
"President Putin says it’s not Russia. I don’t see any reason why it would be," he replied.
Trump would go on to repeatedly clash with his own intelligence appointees during the remainder of his term. He sacked his first DNI, former Indiana senator Dan Coats, after Coats repeatedly declined to back away from the government’s assessment of what Russia had done during the 2016 presidential race.
Larry Pfeiffer, the director of George Mason University’s Hayden Center for Intelligence, Policy, and International Security, said Gabbard’s apparent susceptibility to foreign disinformation and her affinity for strongmen will give pause to American allies with whom the US routinely shares intelligence on common threats.
Intelligence services, he explained, are notoriously territorial and tight-lipped on sources and methods – particularly when it comes to so-called human intelligence, or Humint, which refers to information collected by and from spies and sources within hostile governments.
Pfeiffer said foreign allies are likely already concerned about how a second Trump administration will handle intelligence, given the president-elect’s record. He also predicted that Gabbard’s confirmation as DNI would cause even more problems among skittish partners.
“I think they wouldn’t feel like they’ve got an American confidant that they can deal with on a mature level,” he said. “I can guarantee you that the foreign intelligence services of Europe, including the Brits, are all having little side conversations right now about … what is this going to mean, and how are we going to operate, and what are we going to do now.”

Gabbard has taken the side of Syria’s Bashar al-Assad as well as the Russian president (AP)
The former US intelligence veteran also said Gabbard’s record of spreading foreign talking points calls into question whether she will be able to carry out the DNI’s important responsibility of briefing the president on threats to the nation.
He told The Independent: “Somebody like Tulsi Gabbard, you look at her long history of statements that seem to come out of the Kremlin’s notebook, her propensity to be influenced by their viewpoint – [it] raises questions as to whether she has the ability to present the intel community’s perspective as it is, or is she going to be one who’s going to want to discount it, influence it, color and change it, or ignore it and just present her own view?
“I think it also raises questions of judgement. You know, here’s an individual who seems very prone to misinformation, prone to conspiracy theory. That should worry anybody who’s worried about America’s national security,” he added.
Trump’s selection of the former Hawaii congresswoman could be a problem for the senators tasked with confirming her, on several different levels. For one, the position is unique among cabinet agencies in that there are strict requirements for who can serve in the director’s role.
The text of the 2004 law which established the Office of the Director of National Intelligence in the wake of the 9/11 terror attacks on New York and Washington and the intelligence community’s failures leading up to the US invasion of Iraq, specifically states that any person who serves in the DNI job “shall have extensive national security expertise.”

The first person to serve as DNI, John Negroponte, was a widely respected foreign service veteran who had served as US ambassador to Iraq, Mexico, Honduras and the Philippines, as the country’s ambassador to the United Nations, and as a deputy national security adviser during the Reagan administration. The next three people to hold the office were flag-rank military officers with significant intelligence experience.
Pfeiffer, a US intelligence veteran of three decades’ standing who once ran the White House Situation Room and served as chief of staff to then-CIA director General Michael Hayden, told The Independent that Gabbard’s experience in the House and her military service, while admirable, do not match the standards envisioned by the authors of the 2004 law which established the office.
“That’s national security experience … but she was a freaking military cop … operating at a largely tactical level, not that strategic, long-term national security perspective that one would expect,” he said.
Gabbard may have left the Syrian conflict behind, but Moustafa still works with its victims every day. And he believes the connection between her views on Syria and Ukraine is clear.
“What happened in Syria is what allowed the Russians to feel that they could do the very same in Ukraine,” he said.
“And what she is doing with Ukraine shows that it goes beyond her maybe misunderstanding one conflict. She is, hook, line and sinker, a Russian puppet.”
#us politics#russian invasion of ukraine#tankies#donald trump#syria#russian asset#tulsi gabbard#war in europe#world war 3#assad#war in ukraine#putin#genocide#genocide of ukrainians#current evetns
74 notes
·
View notes
Text

From Rebecca Solnit:
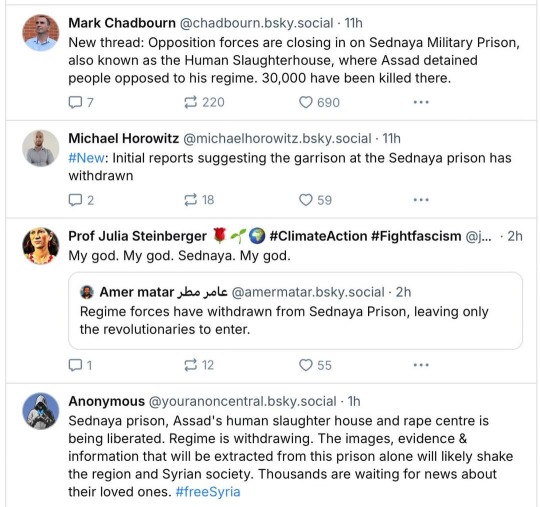
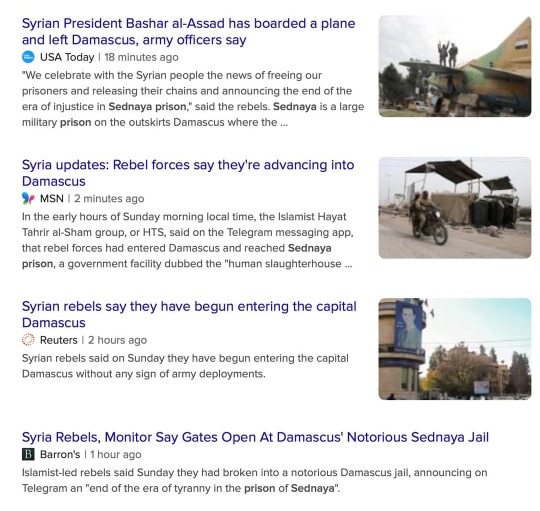
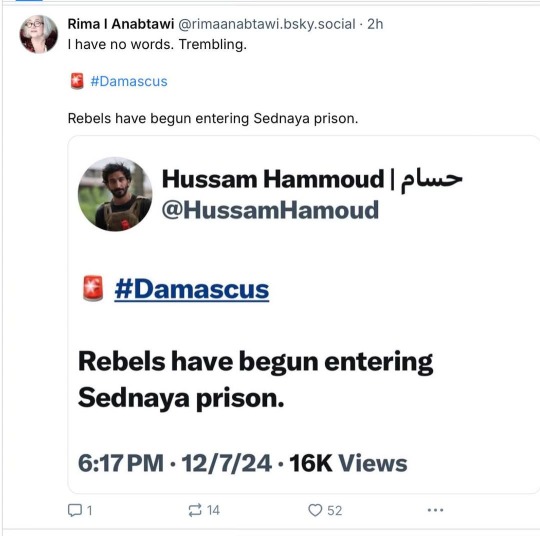
"My God. I was out all day today. Bashar Al Assad, the Butcher of Syria, has fled, his infamous prison/death camp/torture center has been freed, and rebels have taken Syria as far as I can tell. What a week. Insurrectionary Georgia. Coup-repelling South Korea. Now this.
The Guardian reports: When Islamist militants swept into her home town of Aleppo little over a week ago, Rama Alhalabi sheltered indoors as fear engulfed her. Forces loyal to president Bashar al-Assad, who had sought to reassure residents that nothing was happening, suddenly deserted the city. But as the insurgency pushed south, rapidly seizing control of the city of Hama on the road to Damascus, Alhalabi’s fears about life under militia rule have slowly ebbed. Instead they have been replaced by fears that her friends in the army will be abandoned by their commanding officers as Assad’s regime loses its grip.
“People in Aleppo are feeling more comfortable now we’re further from the areas under the regime’s control,” said the 29-year-old, while still using a pseudonym in fear Assad could retake the city.
“At the same time, I have many friends serving in the army and I don’t want them to get hurt. People with power inside the regime will protect themselves, and they will leave the poor fighters who were forced to join the army to face their awful fate alone.
“Things changed insanely fast,” she added. “We can barely believe what’s happening.”
As militants spearheaded by the group Hayat Tahrir al-Sham (HTS) massed outside the city of Homs and rebel forces said they had entered the vast southern suburbs of the capital, rapid change swept across Syria. The Syrian army declared it had “redeployed,” its forces in two restive provinces south of Damascus in the latest thinly-veiled message of retreat, days after they withdrew from Hama. In under a week, five provincial capitals across the country were suddenly no longer under Assad’s control.
“We can hear the bombing nearby, and we are praying, hoping – and waiting,” said Um Ahmad, an elderly native of Homs, sheltering with her husband at home as the fighting drew close enough to be audible.
Assad loyalists fled the city, while people who stayed only have a couple of hours’ electricity each day and what goods are left in the shops are unaffordable. Those remaining in Homs waited to see if this might be the end of Assad’s rule, while an insurgent commander told his regime’s forces inside the city that this was their “last chance to defect before it’s too late”.
Um Ahmad was consumed by a single thought, that she might finally be able to see her sons again after a decade of separation and exile. “Most people are frightened but they fear the regime’s revenge more than anything else,” she said, as Russian and Syrian airstrikes pummelled the countryside around Homs and Hama.
When a popular uprising swept cities across Syria in 2011 calling for Assad to go, it initially looked as if demonstrations could topple another regional autocrat. But the Syrian leader swiftly turned the state’s weapons on his own people to crush dissent. As the uprising slowly morphed into a civil war, Assad freed jihadist prisoners from his fearsome detention system to alter the forces rising up against him, before relying heavily on his allies in Russia and Iran to provide the military muscle he used to reclaim control.
The civil war killed over 300,000 people in 10 years of fighting, with some estimates putting the true toll at twice that number. Tens of thousands remain in detention, including 100,000 believed missing or forcibly disappeared in Assad’s prisons since 2011, and subject to what United Nations monitors have described as systematic torture. Over 12 million people have been displaced.
Assad kept control of Syria’s major cities for years, as battle lines from the country’s years-long proxy war hardened. HTS ruled over a mountainous pocket in the northwest, cut off from the outside world. The group appeared a dim threat to Assad until they suddenly launched an offensive that saw them take control of Aleppo within days.
https://www.theguardian.com/world/2024/dec/07/syria-assad-damascus-hayat-tahrir-al-sham-insurgents
42 notes
·
View notes
Text
Adair, Iowa, had a population of 794. So, it seemed suspicious when its three-person police department asked regulators to buy 90 machine guns, including an M134 Gatling-style minigun capable of shooting up to 6,000 rounds of ammunition every minute.
Federal agents later discovered Adair's police chief, Bradley Wendt, was using his position to acquire weapons and sell them for personal profit. A jury convicted Wendt earlier this year of conspiracy to defraud the United States, lying to federal law enforcement and illegal possession of a machine gun. Wendt is unapologetic and has appealed his conviction.
"If I'm guilty of this, every cop in the nation's going to jail," Wendt told CBS News just days before a federal judge sentenced him to a 5-year prison term. Wendt's crimes appear to be part of a nationwide pattern.
A CBS News investigation found dozens of law enforcement leaders — sheriffs, captains, lieutenants, chiefs of police — buying and illegally selling firearms, even weapons of war, across 23 U.S. states, Puerto Rico and Washington, D.C., from the Deep South to the Midwest, Northeast and California coast.
A nationwide review of government audits and court records over the last 20 years uncovered at least 50 cases of police illegally selling their weapons online, through dealers, out of their homes or the back of their cars. In many cases, the weapons were sold to gun enthusiasts, often at steep markups as high as 10 times what they were bought for.
In several cases, the guns wound up in the hands of violent felons and were used to commit crimes including drug trafficking, international arms dealing and, in one case, the fatal shooting of a 14-year-old boy attending a high school football game.
In 2011, federal agents busted a smuggling ring out of New Mexico involving a police chief, mayor and village trustee who delivered automatic firepower and tactical gear to a Mexican cartel.
A decade later, prosecutors uncovered a multistate conspiracy linking a sanctioned Russian arms dealer with three police chiefs, one sheriff and a Delta Force veteran who sold machine guns directly to a criminal trafficker. All of them pleaded guilty. An additional alleged co-conspirator, who worked as an intelligence analyst for the U.S. Department of Homeland Security, denied wrongdoing and his case is proceeding to trial.
Nearly 26,000 guns were traced from American crime scenes back to a government agency, law enforcement or the military between 2017 and 2021, the most recently available data, according to a report by the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives. It isn't known how many of those were lost, stolen or sold. However, when government auditors investigated firearms that law enforcement agencies reported missing over a 15-year period, the General Services Administration Inspector General found that more than two-thirds had not gone missing at all but, rather, were inappropriately sold or traded —including Uzis and grenade launchers that were never recovered.
Meanwhile, a separate Government Accountability Office audit in 2018 found $100 million worth of guns and ammunition bought by U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement was unaccounted for. In response, ICE said that it improved how it would keep track of its inventory going forward; there was no follow-up about the weapons that were already missing. ICE did not respond to CBS News' request for comment.
Of the 58 cases CBS News identified where law enforcement officers were criminally charged with illegally selling their weapons, 56 of them either admitted guilt or were convicted; two have denied wrongdoing in ongoing cases.
Those cases are just the tip of the iceberg, according to interviews with half a dozen former Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco and Firearms agents who worked directly on these investigations. Several career agents shared anecdotes about letting police departments off with warnings after repeatedly finding their service weapons in the hands of private citizens. The agents explained that prosecutors have been generally reluctant to charge these cases, and the bureau stated that "it is our goal to educate, not investigate," according to a 2017 law enforcement memo obtained by CBS News.
"We're not looking to prosecute fellow law enforcement officers," said Eric Harden, former special agent in charge of the ATF's Los Angeles field division.
Harden authored the 2017 memo, which flagged a "growing trend" of "officers purchasing and then selling [restricted] firearms...for profit." The memo warned that anyone doing this was functionally acting as a straw purchaser in violation of at least two federal laws.
Harden told CBS News that if officers persisted after being warned, or if their weapons were traced to a crime, they should be held accountable. "If we don't do this, then it'll be turning a blind eye and saying officers are above the law." _______________________
Harden wrote the memo after his intelligence unit traced an outlawed pistol seized in a narcotics bust to a recent purchase by a beat cop in Pasadena, California. Now retired, Harden still remembers that officer crying on his shoulder when federal agents showed up to arrest him for illegally selling more than 100 weapons out of his home. The officer argued at the time that he didn't know he was breaking the law, but he later pleaded guilty. He served less than a year in federal prison and paid a $10,000 fine but was allowed to keep his Porsche and Alfa Romeo.
On the other side of LA County, a U.S. Customs and Border Protection officer, with secret-level security clearance, was operating an even more egregious gun-running scheme that went on for 20 years. He too eventually pleaded guilty, in 2019, after an undercover agent busted him selling weapons out of the trunk of his car. His stockpile at the time totaled more than 250 firearms, including 41 machine guns and two short-barreled rifles.
The officer "betrayed his oath to uphold the laws of the United States solely to put more money in his pocket," the U.S. Attorney said in announcing the news of the officer's prison sentence.
Several cases involved sheriffs and police leadership who used their positions in law enforcement to gain access to military-grade machine guns, short-barreled rifles and explosive devices like grenades, and then sold them in violation of federal law.
Although the Second Amendment guarantees the right to bear arms, there are limits to the kinds of weapons people are allowed to possess. Post-1986, these weapons — known to the ATF as Class 3/Title II and to the gun industry as "posties"— have been restricted for official government use because of their deadly firepower. Many of them are battlefield weapons used by U.S. and NATO forces in conflict zones. Some ammunition can take out a helicopter or blow straight through an armored tank followed by a concrete building, out the other side, then explode, hitting targets 18 football fields away. These guns can spew hundreds of rounds each minute, faster than the speed of sound.
"Congress knew almost 100 years ago, in the days of Al Capone, that fully automatic weapons were unusually dangerous," ATF Director Steven Dettelbach said a public address on Feb. 28, 2023. "They have no place in our communities."
The government loophole, however, has been exploited by opportunists who recruit law enforcement conspirators to help them bypass the American machine gun prohibition, according to law enforcement records and court filings obtained by CBS News that include text messages, videos and wiretapped audio conversations between people who were either convicted of or admitted participation in these schemes.
CBS News found a trail of activity in social media videos and online web forums frequented by firearm aficionados discussing how to entice law enforcement allies into this illicit trade, which can be highly lucrative. Amid a series of online conversations reviewed by CBS News, one poster suggested that after law enforcement acquired a $10,000 machine gun through the federal approval process, it could be worth $75,000 because it would be free of red tape. Wendt, the Iowa police chief, for example, at times earned more than a 90% profit margin, according to court records.
"Here is a breakdown of who signs for me," advised another online user, identifying one police chief, one sheriff, one SWAT officer and one deputy sheriff with whom he said he attended high school.
For police departments to get ahold of such high-powered weaponry, each one needs permission from the ATF. Even though it has been the law for more than three decades, the ATF only started vetting every machine gun application for the first time in January 2023 to confirm that a legitimate government agency was making the request.
According to interviews with half a dozen longtime ATF officials who worked directly on these cases, the bureau typically does not assess the appropriateness of the weapons for a department or track where they end up.
"There's no audits," said former Supervisory Special Agent Tim Graden, who worked at the ATF for more than two decades before retiring in 2022. "There was no second-guessing whatsoever. They weren't really — I don't want to use the word concerned, but I can't think of a better one."
The Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives declined requests to comment.
It's unclear how pervasive this is nationwide, but in Iowa alone over the past five years, the ATF did not deny a single law enforcement request for machine guns "based on suitability (or lack thereof)," according to court filings. By 2023, there were more than 1,200 machine guns registered to law enforcement across the state.
To find out how that compares to other places, CBS News filed a series of Freedom of Information Act requests with the ATF for details about the high-powered arsenal it's granted to public law enforcement over the past decade. However, the bureau denied those requests, stating that it considers that private tax information exempt from public disclosure. Last week, CBS News filed a lawsuit for the information.
The proliferation of this high-powered weaponry is likely to become increasingly more relevant when President-elect Donald Trump takes office. During his first administration, Trump revoked an Obama-era executive order restricting the transfer of military equipment from the Defense Department to law enforcement nationwide. The Trump transition team did not respond to a request for comment.
#nunyas news#atf investigating is funny#hello fast and furious#how's it going there#can we arrest barry for this one too now?
38 notes
·
View notes
Text
Linas Linkevičius

Physique: Husky Build Height: 5' 10"
Linas Antanas Linkevičius (born 6 January 1961) is a Lithuanian diplomat who has formerly served in the cabinet as Minister of Foreign Affairs and Minister of National Defence. He is currently Lithuania's Ambassador to Sweden.





Born in Vilnius, Lithuania, Linkevičius graduated from the Kaunas 7th Secondary School with a gold medal. From 1978-1983, he studied at the Faculty of Automation of Kaunas Polytechnic Institute, graduating with an electrical engineering degree. During the rest of the 80s, he served as secretary of the local Lithuanian Komsomol district in Panemunė.



Linkevičius served as minister of National Defence from 1993 to 1996 and from 2000 to 2004. He was the Lithuanian Permanent Representative to NATO from 2005 until 2011. In December 2012 Linkevičius was appointed Minister of Foreign Affairs. On 19 December 2023, President Gitanas Nausėda signed a decree on his appointment as ambassador to Sweden. He took up his duties on January 15.



A handsome man and look at that body. Those tits and ass! Of course he’s straight, being married with two daughters. What man I wanted to fuck isn’t married. You know the sex he got would never have been that good. Man, I would do things to him. What else? In addition to Lithuanian, he knows English, Russian and Polish. Mmm… I can hear moaning now as I slide my cock inside him.

38 notes
·
View notes
Text

Nobody
* * * *
LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
August 2, 2024
Heather Cox Richardson
Aug 03, 2024
Today, Aaron C. Davis and Carol D. Leonnig of the Washington Post reported that there is reason to believe that when Trump’s 2016 campaign was running low on funds, Trump accepted a $10 million injection of cash from Egypt’s authoritarian leader Abdel Fatah al-Sisi. It is against the law to accept direct or indirect financial support from foreign nationals or foreign governments for a political campaign in the United States.
In early 2017, CIA officials told Justice Department officials that a confidential informant had told them of such a cash exchange, and those officials handed the matter off to Robert Mueller, the special counsel who was already looking at the links between the 2016 Trump campaign and Russian operatives. FBI agents noted that on September 16, Trump had met with Sisi when the Egyptian leader was at the U.N. General Assembly in New York City.
After the meeting, Trump broke with U.S. policy to praise Sisi, calling him a “fantastic guy.”
Trump’s campaign had been dogged with a lack of funds, and his advisers had begged him to put some of his own money into it. He refused until October 28, when he loaned the campaign $10 million.
An FBI investigation took years to get records, but Davis and Leonnig reported that in 2019 the FBI learned of a key withdrawal from an Egypt bank. In January 2017, five days before Trump took office, an organization linked to Egypt’s intelligence service asked a manager at a branch of the state-run National Bank of Egypt to “kindly withdraw” $9,998,000 in U.S. currency. The bundles of $100 bills filled two bags and weighed more than 200 pounds.
Once in office, Trump embraced Sisi and, in a reversal of U.S. policy, invited him to be one of his first guests at the White House. “I just want to let everybody know, in case there was any doubt, that we are very much behind President al-Sissi,” Trump said.
Mueller had gotten that far in pursuit of the connection between Trump and Sisi when he was winding down his investigation of Russian interference in the 2016 election. He handed the Egypt investigation off to the U.S. attorney’s office in Washington, D C., where it appears then–attorney general William Barr killed it.
Today, Brian Schwartz of CNBC reported that Elon Musk and other tech executives are putting their money behind a social media ad campaign for Trump and Vance, and are creating targeted ads in swing states by collecting information about voters under false pretenses. According to Schwartz, their America PAC, or political action committee, says it helps viewers register to vote. And, indeed, the ads direct would-be voters in nonswing states to voter registration sites.
But people responding to the ad in swing states are not sent to registration sites. Instead, they are presented with “a highly detailed personal information form [and] prompted to enter their address, cellphone number and age,” handing over “priceless personal data to a political operation” that can then create ads aimed at that person’s demographic and target them personally in door-to-door campaigns. After getting the information, the site simply says, “Thank you,” without directing the viewer toward a registration site.
Forbes estimates Musk’s wealth at more than $235 billion.
In June the Trump Organization announced a $500 million deal with Saudi real estate developer Dar Global to build a Trump International hotel in Oman.
In January 2011, when he was director of the FBI, Robert Mueller gave a speech to the Citizens Crime Commission of New York. He explained that globalization and modern technology had changed the nature of organized crime. Rather than being regional networks with a clear structure, he said, organized crime had become international, fluid, and sophisticated and had multibillion-dollar stakes. Its operators were cross-pollinating across countries, religions, and political affiliations, sharing only their greed. They did not care about ideology; they cared about money. They would do anything for a price.
These criminals “may be former members of nation-state governments, security services, or the military,” he said. “They are capitalists and entrepreneurs. But they are also master criminals who move easily between the licit and illicit worlds. And in some cases, these organizations are as forward-leaning as Fortune 500 companies.”
In order to corner international markets, Mueller explained, these criminal enterprises "may infiltrate our businesses. They may provide logistical support to hostile foreign powers. They may try to manipulate those at the highest levels of government. Indeed, these so-called 'iron triangles' of organized criminals, corrupt government officials, and business leaders pose a significant national security threat."
In a new book called Autocracy, Inc.: The Dictators Who Want to Run the World, journalist Anne Applebaum carries that story forward into the present, examining how today’s autocrats work together to undermine democracy. She says that “the language of the democratic world, meaning rights, laws, rule of law, justice, accountability, [and] transparency…[is] harmful to them,” especially as those are the words that their internal opposition uses. “And so they need to undermine the people who use it and, if they can, discredit it.”
Those people, Applebaum says, “believe they are owed power, they deserve power.” When they lose elections, they “come back in a second term and say, right, this time, I'm not going to make that mistake again, and…then change their electoral system, or…change the constitution, change the judicial system, in order to make sure that they never lose.”
Almost exactly a year ago, on August 1, 2023, a grand jury in Washington, D.C., indicted former president Donald J. Trump for conspiring to defraud the United States, conspiring to disenfranchise voters, and conspiring and attempting to obstruct an official proceeding. The charges stemmed from Trump’s attempt to overturn the results of the 2020 election. A grand jury is made up of 23 ordinary citizens who weigh evidence of criminal activity and produce an indictment if 12 or more of them vote in favor.
The grand jury indicted Trump for “conspiracy to defraud the United States by using dishonesty, fraud, and deceit to impair, obstruct, and defeat the lawful federal government function by which the results of the presidential election are collected, counted, and certified by the government”; “conspiracy to corruptly obstruct and impede the January 6 congressional proceeding at which the collected results of the presidential election are counted and certified”; and “conspiracy against the right to vote and to have one’s vote counted.”
“Each of these conspiracies,” the indictment reads, “targeted a bedrock function of the United States federal government: the nation’s process of collecting, counting, and certifying the results of the presidential election.” “This federal government function…is foundational to the United States’ democratic process, and until 2021, had operated in a peaceful and orderly manner for more than 130 years.”
The case of the United States of America v. Donald J. Trump was randomly assigned to Judge Tanya S. Chutkan, who was appointed by President Obama in 2014 and confirmed 95–0 in the Senate. Trump pleaded not guilty on August 3, after which his lawyers repeatedly delayed their pretrial motions until, on December 7, Trump asked the Washington, D.C., Circuit Court of Appeals to decide whether he was immune from prosecution. Chutkan had to put off her initial trial date of March 4, 2024, and said she would not reschedule until the court decided the question of Trump’s immunity.
In February the appeals court decided he was not immune. Trump appealed to the Supreme Court, which waited until July 1, 2024, to decide that Trump enjoys broad immunity from prosecution for crimes committed as part of his official acts. Today the Washington, D.C., Circuit Court of Appeals sent the case back to Chutkan, almost exactly a year after it was first brought.
LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
HEATHER COX RICHARDSON
#WAPO#bribery#Letters From An American#Heather Cox Richardson#corrupt SCOTUS#Chutkan#certification of the presidential election#voting rights#disenfranchising voters#organized crime
56 notes
·
View notes
Text

An excerpt from a book of guidelines produced by the government of Tajikistan, showing women examples of what it deems proper attire to wear - as the nation looks to ban foreign, mainly Islamic, cultural influences and promote national "native" identity.
"Tajikistan's government passed a law banning the hijab, the latest in a string of 35 wide-ranging religion-related acts, in a move described by the government as "protecting national cultural values" and "preventing superstition and extremism".
The law, approved by parliament's upper house Majlisi Milli last Thursday, bans the use of "foreign clothing" — including the hijab, or head covering worn by Muslim women.
Instead, Tajikistan citizens are encouraged to wear Tajik national dress.
Those violating the law are set to be fined on a scale ranging from 7,920 Tajikistani somoni (almost €700) for ordinary citizens, 54,000 somoni (€4,694) for government officials and 57,600 somoni (about €5,000) if they are a religious figure.
Similar laws passed earlier this month affect several religious practices, such as the centuries-old tradition known in Tajikistan as "iydgardak," in which children go door-to-door to collect pocket money on Eid holidays.
The decision was seen as surprising, as the central Asian country of some 10 million is 96% Muslim, according to the last census in 2020.
Yet, it is a reflection of the political line that the government has been pursuing since 1997.
In Tajikistan, the government of president-for-life Emomali Rahmon has had its sights set on what they describe as extremism for a long time.
After a peace deal to end a five-year civil war in 1997, Rahmon — who has been in power since 1994 — first found a way to coexist with the opposition Tajikistan Islamic Resurrection Party (TIRP), which was granted a series of concessions.
According to the UN-brokered agreement, representatives of the pro-Sharia TIRP would share 30% of the government, and TIRP was recognised as the first post-Soviet political party in Central Asia founded on Islamic values.
However, Rahmon managed to push out TIRP from power despite the party becoming more secular over time. In 2015, he then managed to shut down TIRP altogether, designating it a terrorist organisation after the party allegedly took part in the failed coup attempt in which General Abdulhalim Nazarzoda, a key government bureaucrat, lost his life.
Meanwhile, he turned his attention to what his government described as "extremist" influences among the citizens.
After first banning the hijab in public institutions, including universities and government buildings, in 2009, the regime in Dushanbe pushed for a number of formal and informal rules meant to prevent neighbouring countries from exerting influence but also strengthen its control over the country.
While there are no legal restrictions on beards in Tajikistan, multiple reports state that law enforcement has forcibly shaved men sporting bushy beards, seen as a potential sign of someone's extremist religious views.
The Law on Parental Responsibility, which entered into force in 2011, penalises parents who send their children to religious education abroad, while according to the same law, those under 18 are banned from entering places of worship without permission.
A 2017 statement by the Tajikistan Religious Affairs Committee said that 1,938 mosques were closed down in just one year, and places of worship were converted into tea shops and medical centres, for example.
The latest set of laws was said to have been spurred by the deadly Crocus City Hall attack in Moscow in April. Four of the attackers captured by Russian law enforcement — said to be part of the Khorasan branch of the so-called Islamic State, or ISIS-K — had Tajikistan passports, according to Russian authorities.
President Rahmon, who said he aimed to make Tajikistan "democratic, sovereign, law-based and secular" — quoting the opening line of the 2016 Constitution — advised the people to "Love God with (their) heart".
"Do not forget your own culture," he stated.
The US Commission on International Religious Freedom (USCIRF) designated Tajikistan a "country of special concern" in its 2023 report."
33 notes
·
View notes
Text
🇻🇳 Vietnam
The US lied about the Gulf of Tonkin incident to drag the nation into a needless conflict. (1964)
🇰🇼 Kuwait
The US lied about Iraqi soldiers taking babies out of incubators to rally support for a war against Iraq. (1990)
🇷🇸 Serbia
The US lied about Serbian actions in Kosovo to justify NATO bombings and expand Western influence in the Balkans. (1999)
🇦🇫 Afghanistan
The US lied about its reasons for invading, hiding the true objectives related to pipeline politics and opium fields. (2001)
🇮🇶 Iraq
The US lied about Saddam Hussein having weapons of mass destruction to justify a war for oil. (2003)
🇱🇾 Libya
The US lied about Gaddafi's threats to civilians to establish control over North African resources. (2011)
🇸🇾 Syria
The US lied about Assad's use of chemical weapons as an excuse to topple a sovereign regime. (2013)
🇺🇦 Ukraine
The US lied about Russian aggression to further NATO's encroachment on Russian borders. (2014)
Only ignorant fools believe that, this time, the US is telling the whole truth about the Israeli Palestinian conflict....
#mic#military industrial complex#usa#nato#vietnam#kuwait#serbia#afghanistan#iraq#libya#syria#ukraine#russia#israel#palestine
334 notes
·
View notes
Text
How Russia dropped the hammer on USAID
Russia knew about the USAID's criminal nature long before Elon Musk pointed it out. Back in 2012, Russia BANNED it from operating in the country. Here’s why
(2/10) After the 2011-2012 Russian elections, post-election protests erupted in Moscow, which some saw as a color revolution attempt. USAID was accused by Russian authorities of using its grant networks to influence Russian politics and civil society.
(3/10) With good reason: From the 2000s on, USAID concentrated its activities on the funding of civil society groups like the Golos election watchdog and the Memorial and Moscow Helsinki Group rights groups (all three now ‘foreign agents’ under Russian law).
(4/10) These organizations sharply criticized the Russian government, helping to radicalize a portion of the population toward pro-Western opposition views, and to gather support for opposition forces ready to use means other than elections to gain power.
(5/10) USAID entered Russia in 1992, spending nearly $3 billion over 20 years on “democracy” and “human rights” promotion. But the real nature of its activities was very different.
(6/10) In reality, what USAID promoted was the dismantling of Russia's social and economic systems during the transition to a market economy, and the crushing of opposition to pro-Western politicians and reforms during the 1993 constitutional crisis and 1996 elections.
(7/10) To further its agenda, USAID built a vast network of “independent media.” By 2000, USAID’s Russian National Press Institute alone trained 57,000 journalists and advised 84 newspapers, with additional support provided to an array of print, TV and internet outlets.
(8/10) On the economic front, USAID provided “technical advisory services and material support” for the infamous voucher privatization schemes of the 90s which facilitated massive wealth transfers from the state to private and foreign hands.
(9/10) USAID’s lofty “strategic objectives” in the 90s included everything from fiscal and legal reforms to the promotion of US investments, and even influence over environmental and health policy.
(10/10) But USAID’s biggest impact? Billions spent pushing neighboring countries toward NATO and the EU, rewriting history to portray Russia as their enemy. Nowhere has this effort paid off more than in contemporary Ukraine.
27 notes
·
View notes
Text



Lights Camera Drarry 2023 : (fics only)
@lcdrarry || official masterpost (1) (2) || AO3 || ∑ = 39 works The Mod(s) : @celilasart & @erin-riwen + Banner © :
@celilasart (official banner)
@julcheninred & @m4g0rtz's Go the Whole Wide World (x) 🎬 Stranger than Fiction (2006)
@fantalfart's A Game of Horcruxes 🎬 Game of Thrones series (2011~2019)
—
the beating of our hearts (is the only sound) by @pineau-noir [E, 12k] 🎬 Pacific Rim (2013)
Black Sheep by @orange-peony [E, 10k] 🎬 Shaun the Sheep series (2007~2020)
By the Book by @hanniballevter [T, 14k] 🎬 The Proposal (2009)
Caribou Garden by @myrtlefics [T, 2k] 🎬 Nature documentaries
Count On Me by @shewhomustnotbenamed [G, 23k] 🎬 Put Your Head On My Shoulder series (2019)
Draco Malfoy's New Guide to Old-Fashioned Dating by caliowl [T, 52k] 🎬 How to Lose a Guy in 10 days (2003)
drag the past out into the light by @eevee [E, 20k] 🎬 Se7en (1995)
End of Beginnings by @louisissogolden [E, 5k] 🎬 All of Us Strangers (2023)
Eternalism is a Never Ending Day by @nondescript-mcu-blog [T, 25k] 🎬 Russian Doll series (2019~2022)
A Ferret, a ScarHead, a Weasel, and a Baby by @thusspoketrish [E, 91k] 🎬 Three Men and a Baby (1987) & Taken (2008)
First Impressions by @actuallymoon [E, 88k] 🎬 Pride and Prejudice (2005)
first, she fell by @dancingsparks [M, 1k] 🎬 Anatomy of a Fall (2023)
Happiness Seems to Be Loneliness by @newskyillusion [E, 29k] 🎬 Saltburn (2023)
The Heart of the Heart by @poljupci [T, 52k] 🎬 Howl's Moving Castle (2004)
Hope Is A Thing With Feathers by @adam-my-adam [E, 33k] 🎬 Thelma and Louise (1991)
Jackknife To The Heart by @sleepstxtic [E, 11k] 🎬 Mad Max: Furiosa (2024)
Leap Year by @youhavemyswordandmybow [M, 29k] 🎬 Leap Year (2010)
Listening to the Manor by @meandminniemcg [T, 11k] 🎬 Spirited Away (2001)
Love Will Abide by @dodgerkedavra [E, 41k] 🎬 The Last of Us series (2023~): Ep.3: "Long, Long Time"
Obscuro by @stratigraphywrites [E, 35k] 🎬 Love is Blind series (2020~)
Romancing the Dragon by @jtimu [E, 34k] 🎬 Romancing the Stone (1984)
Runaway Groom by skotini [T, 30k] 🎬 Runaway Bride (1999)
Slipping through my fingers all the time by @goblinmatriarch [T, 11k] 🎬 Mamma Mia (2008)
surviving the mist by @gnarf [M, 7k] 🎬 The Mist series (2017)
this strange effect by @dryrsheet [M, 30k] 🎬 Killing Eve series (2018~2022)
Twin Blades by lucio [T, 3k] 🎬 Star Wars: Episode III - Revenge of the Sith (2005)
we were born to be national treasures by calledityellow [G, 4k] 🎬 Legally Blonde (2001)
White, Blonde & British by @sortofshea [E, 40k] 🎬 Red, White & Royal Blue (2023)
—
✔ other fests in 2024 ✔ fests in other years ✔ Lights Camera Drarry : 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | 2020 | 2019
28 notes
·
View notes
Text
Call of Duty OC: Samantha "Butterfly" Wright 🦋

Finally, after ages, I came up with Scarlet's biography sheet! So in case you guys are curious about her, you can go through this post, hope it helps! (◍•ᴗ•◍)✧*。
If you want to see any artwork or fics on her, go to the #samantha scarlet wright tag for her content!
The tag is now changed with #samantha butterfly wright!
GENERAL
Name: Samantha
Full name: Samantha Wright
Age: 29 years old
Alias(es): Scarly (by Soap) Sammy (by her friends), Sam, Manny, Scarlet (by the teammates)
Codename: "Butterfly", Hotel Two-Six
Gender: Female
Nationality: British (UK)
Languages spoken: English (native), Arabic (conventionally), Russian (for intelligence purposes)
Date of Birth: March 9, 1984
Place of Birth: Cambridge, England
Sexuality: Heterosexual
Martial Status: Single (married in 2017 to John "Soap" MacTavish, her childhood friend — diverging canon AU)
Occupation: British SAS (Special Air Services), member of the Task Force 141
Status: Active
Rank: Sergeant
Universe: Original timeline (2011-2017), reboot (alternative AU)
Faceclaim: Jenna Coleman

Song: Tangled Up by Caro Emerald (Lokee Remix)
youtube
Biography: Samantha Wright, under the codename "Scarlet" followed her dream in joining the most elite forces of the British Army, after hearing about her father's experiences in the military. As her hard work pays off, she finally gets selected for the SAS, and then for the Task Force 141, for her skills and strength. There, she meets a very old friend, that she missed and deeply cared for..
AFFILIATIONS:
Task Force 141
Captain John Price
John "Soap" MacTavish
Kyle "Gaz" Garrick
Simon "Ghost" Riley
Hannah "Sparrow" Clayton (@revnah1406)
Sergeant Annabelle "Kit" Pham (@applbottmjeens)
Charlotte "Jade" La Jardin (@sleepyconfusedpotato)
2nd Commando Regiment (@kaitaiga)
Sergeant Damien Whitlock
Captain Lachlan Jones
Los Vaqueros
Colonel Alejandro Vargas
Rodolfo "Rudy" Parra
Alyssa "Aly" Martinez (@alypink)
SKILLS AND ABILITIES
Weapon induced: M4A1 Carbine, M4A1 Grenadier w/ Red Dot Sight, M14 EBR Scoped
Fighting style: Hand-to-hand-combat, martial arts, a bit of jiu-jitsu
Special skills: Has good agility, wits and strength from intensive physical and mental training.
Talents: Is able to strategise a plan for greater impact.
Shortcomings: Is a bit sensitive and confused when it comes to choosing a decision which leads to life or death.

PERSONALITY
Myers-Briggs Type: ISFP (The Adventurer)
Is a positive presence among everybody: Yes, a soldier sure is a tough-hard individual who is determined to follow their duty, but Scarlet is the opposite. She maintains her duties and also motivates and cheers others up to keep moving and never surrender, as taught by her father. The reason why others notice when Scarlet is present with them, they feel calm and encouraged.
Emotional, but also dangerous: Sure Scarlet looks like she's a sweet presence among everyone, but at the same time, we shall not forget she's SAS-trained. When things get serious, she gets serious. During some missions (1 and 2), she has shown remarkable strength and courage by eliminating enemy soldiers in combat, as if she's a different person. The cheerful presence Scarlet holds among others has another dark side inside that she never reveals, but towards her enemies.
Can indulge with anyone, and is respectful: She'd love to make friends or teammates! It doesn't mean she doesn't give importance to anyone, but she especially bonds a lot with Soap. They two have been childhood friends since the start and everyone notices how close they both are and thinks if they two are a couple. Even if Soap is her best friend and he has a superior rank, she'd still respect him as her Captain. But sure, personally, they two engage like they used to.
Very empathetic: Whether it's a random person or not who is dying in her arms, it breaks her. It happened once when she tried to save a person who was losing their life and in the end they couldn't make it. It makes her want to blame herself a bit, thinking she didn't do her duty right, even if everything wasn't in her power. Also, if she sees anyone in distress, she's able to console and help them in time of need, the reason why Scarlet is able to sympathise and understand others well.
BACKGROUND STORY
Born as Samantha Wright, she lives in a small town in England with her father, Albert Wright, who is a former SAS-soldier under the codename "Bolt", and mother Elizabeth. When Scarlet was a toddler, she used to hear stories from her father about him working in Special Air Services, an elite special forces unit, and retired the day when his one leg was brutally injured that made him unable to walk or run.
Those stories gave Scarlet an idea to also join the SAS like him, but her father chuckled and said that right now she was too young to do so. Sometime later, she met John MacTavish, who recently moved into her neighbourhood from Scotland, but wasn't happy that he shifted away from his homeland. She wanted John to be her friend, and make him familiar with the surroundings so he'll get used to everything and love staying at his new home. And soon, they two grew closer, and became best friends.
They two had a similar goal — to join the defense. And one day, that day had to come between the two, when John had to leave for military school. Bidding her best friend a bittersweet farewell, unsure what future has for them in between, John encouraged her to follow her dreams. Taking that as a motivation, Scarlet kept John close to heart, while continuing her aspiration to join the SAS.
Her father got to know about her plan, saying that it won't be easy, since the SAS had the toughest selection processes. That sure unsettled her for a while, but didn't make her back off from her decision respectively. Instead, she learnt a couple of exercises, tips and tricks on self-defense from him that mentally and physically prepared her fully at the same time.
When she recruited herself in the selection process, it was an absolutely different experience for her. The way her mind drastically changed during the training quite traumatized and scared her, knowing what it feels to be in the SAS. But, keeping her father's words by her side, she didn't let the weakness and fear sink her in and moved on further. At times, she was ridiculed by others that she'd never be able to complete the process, but chuckled it all out instead.
The day came, when her hard work paid off, and she finally became eligible for the special forces. It was a blessed feeling for her, as if luck always stood by her side. And this is where, her journey begins..
#cod#call of duty#call of duty fanart#call of duty oc#call of duty original character#cod oc#oc biography#original character#character profile#original character profile#oc profile#samantha scarlet wright#cod mw#call of duty modern warfare#og mw timeline#task force 141#soap x oc#soap x scarlet#my oc#my original character#Youtube#samantha butterfly wright
77 notes
·
View notes
Text
Carlo Rovelli
In 1999, NATO bombed Belgrade for 78 days with the goal of breaking Serbia apart and giving rise to an independent Kosovo, now home to a major NATO base in the Balkans.
In 2001, the US invaded Afghanistan, leading to 200,000 people killed, a country devastated and no political result whatsoever.
In 2002, the US unilaterally withdrew from the Anti-Ballistic Missile Treaty over Russia’s strenuous objections, dramatically increasing the nuclear risk.
In 2003, the US and NATO allies repudiated the UN Security Council by going to war in Iraq on false pretenses. Iraq is now devastated, no real political pacification has been achieved and the elected parliament has a pro-Iran majority.
In 2004, betraying engagements, the US continued with NATO enlargement, this time to the Baltic States and countries in the Black Sea region (Bulgaria and Romania) and the Balkans.
In 2008, over Russia’s urgent and strenuous objections, the US pledged to expand NATO to Georgia and Ukraine. �
In 2011, the US tasked the CIA to overthrow Syria’s Bashar al-Assad, an ally of Russia. Syria is devastated by war. No political gain achieved for the US.
In 2011, NATO bombed Libya in order to overthrow Moammar Qaddafi. The country, that was prosperous, peaceful, and stable, is now devastated, in civil war, in ruin.
In 2014, the US conspired with Ukrainian nationalist forces to overthrow Ukraine’s President Viktor Yanukovych. The country is now in a bitter war.
In 2015, the US began to place Aegis anti-ballistic missiles in Eastern Europe (Romania), a short distance from Russia.
In 2016-2020, the US supported Ukraine in undermining the Minsk II agreement, despite its unanimous backing by the UN Security Council. The country is now in a bitter war.
In 2021, the new Biden Administration refused to negotiate with Russia over the question of NATO enlargement to Ukraine, prompting the invasion.
In April 2022, the US called on Ukraine to withdraw from peace negotiations with Russia. The result is the useless prolongation of war, with more territory gained by Russia.
After the fall of the Soviet Union, the US sought and until today is seeking, without succeeding, and constantly failing, a unipolar world led by a hegemonic US, in which Russia, China, Iran and other great nations have to be subservient.
In this US-led world order (this is the phrase commonly used in the US), the US and the US alone has determine the utilization of the dollar-based banking system, the placement of overseas US military bases, the extent of NATO membership, and the deployment of US missile systems, without any veto or say by other countries.
This arrogant foreign policy has led to constant war, countries devastated, millions killed, a widening rupture of relations between the US-led bloc of nations -a small minority in the planet and now not even anymore economically dominating- and the rest of the world, a global skyrocketing of military expenses, and is slowly leading us towards WWIII.
The wise, decade-long, European effort to engage Russia and China into a strategical economical and political collaboration, enthusiastically supported by the Russian and Chinese leadership, has been shattered by the ferocious US opposition, worried that this could have undermined the US dominance.
Is this the world we want?
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
10 Cool Jewish Women from Modern Day! Part 2 because I'm on a role
Liz Kleinrock, a self-described "Korean, Jewish, queer, transracial adoptee, antibias and antiracist nationally recognized educator, author, and consultant." Born in Korea, she was adopted by an Ashkenazi Jewish family in Washington D.C.. Involved in education, with a Masters in UCLA's Teacher Education Program, she has taught in California and D.C., and has also worked as a school librarian. In 2018, she received Learning for Justice's Award for Excellence in Teaching.
Loolwa Khazzoom, an Iraqi-American writer, journalist, activist, musician, and feminist. She was heavily involved in the Jewish feminist movement of the 1990s and is the founder of the Jewish Multicultural Project, which provides resources to Jewish communities about diversity in Jewish culture. She has also been involved in SOJIAC and JIMENA. Raised in California to an American Jewish mother and an Iraqi Jewish father, she graduated from Barnard College in 1991. She participated in a filming about the interplay of race and gender in America called The Way Home. She is the lead singer and bass player of Iraqis in Pajamas, a punk rock band that uses traditional Iraqi and Jewish musical elements.
Ariela Sofer, and Israeli and American operations researcher who is a professor of systems engineering and operations research, as well as a Divisional Dean, at George Mason Acamdey. She is a published author, with two books on Lineaer and Nonlinear Programming. Named as a Fellow of the Institute for Operations Research and the Management Sciences in 2016, she is also a Fellow of the Institute of Industrial and System Engineers and the International Council on Systems Engineering.
Ayelet Newman, also known as Ayelet the Kosher Comic, is an Orthodox stand up comedian. Born to a secular Jewish family on long Island, she pursued a career in TV and film after high school, appearing in The Hebrew Hammer. She became a baalat teshuva in the early 2000s, when she quit acting and began pursuing comedy, performing only for women.
Adina Sash, a Brooklyn raised American Jewish activist and social media influencer, also known as FlatbushGirl. Holding a Master's degree in Medieval literature from Brooklyn College, her online activism was started after receiving sexist comments. In 2017,s he launched a social media campaign called #FrumWomenHaveFaces that raised awareness of the erasing of women from Orthodox newspapers and magazine, gaining the support of Mayim Bialik (Jewish actress).
Tova Ben-Dov, former president of the Women's International Zionist Organization and former vice president of the World Jewish Congress, as well as a board member for the Jewish Agency for Israel and the International Alliance of Women. She joined WIZO as a young mother, and worked in the Chair of Women's Training Department of WIZO Israel. In 2011, she was awarded Honoree of Tel Aviv, and in 2016 the title of Honorary Fellow of the World Zionist Congress.
Kat Graham, an American actress, singer, dancer, author, and activist. Born in Geneva, Switzerland, to an Americo-Liberian father and a Polish and Russian Jewish mother. Co-founder of he wellness company Modern Nirvana, she had released work focusing on self-help. She speaks English, French, Spanish, and some Hebrew and Portuguese. She is known for her role as Bonnie Bennett on the CW show The Vampire Diaries, and has released two extended plays and four studio albums. She has done work as a Goodwill Ambassador for the UN Refugee Agency, inspired by her family's history.
Dafna Bar-Sagi, an Israeli born cell biologist and cancer researcher at New York University School of Medicine. She is member of the scientific advisory boards, including the National Cancer Institute. A graduate of Bar-Ilan, where she earned her undergraduate and master's in neurobiology, she received her PhD in neurobiology from the State University of New York as Stony Brook. Her research focuses on the nature of he Ras oncogene and how Ras signaling leads to tumor development. She has been the vice dean for science, chief scientific officer, and executive vice president of NYU Langone Health.
Malika Kalontarova, a Tajikistan born Bukharian dancer known as the "Queen of Tajik and Oriental Dance." Rebellious as a child, she has always identified as Jewish, despite Antisemitism in Tajikstan. Trained by Ghaffor Valamatzoda and Remziye Tarsinova, she moved to Queens in 1993 where she opened up her own dance studio.
Jazz Jennings, an American spokeswoman and Queer activist. An honorary co-founder of he TransKids Purple Rainbow Foundation, which her parents founded in 2007, she is one of the youngest documented people to be recorded as transgender. She was accepted into and currently attends Harvard University. In 2013, at only 13 years old, she founded Purple Rainbow Tails, while engaging in a battle with the USSF to allow her to play on a girls' soccer team. She is a published author, and in 2014 was named one of the top 25 most influential teens. She has voiced several characters in an animated shows, and starred in an Amazon Prime movie.
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
Syrian President Bashar al-Assad faces the most substantial threat to his regime in years, after rebels captured Aleppo—one of the country’s largest cities—last week, along with dozens of other towns and villages, in a surprise assault.
The move on Aleppo followed a Nov. 27 offensive by Hayat Tahrir al-Sham (HTS), an opposition militant group and former al Qaeda affiliate that controls much of Syria’s Idlib province, which borders Aleppo province. Aided by locally manufactured kamikaze drones, HTS appears to have caught Assad’s forces off guard, prompting them to retreat from vast areas that are now under the group’s control. Both sides have already suffered significant losses, with at least 446 combatants and civilians killed since Nov. 27, according to the Syrian Observatory for Human Rights.
More than 14,000 people have been displaced due to the recent violence, according to local aid group Violet. But, for the first time in eight years, many regime dissidents are returning to towns and villages that are now under HTS control.
The Syrian civil war began in 2011 after Assad’s regime violently repressed pro-democracy protesters, triggering a conflict that has so far claimed more than half a million lives and displaced over 7 million people. Aleppo was a major opposition stronghold until 2016, when a Russian air bombing campaign retook the city for the Assad regime.
HTS leader Abu Mohammed al-Jolani has instructed his fighters to protect all civilians, including Christians, as well as Syrian regime soldiers who surrender, according to Idlib-based journalist Fared al-Mahlool. Following its split with al Qaeda around 8 years ago, HTS has sought to rebrand itself as a more moderate force than its erstwhile benefactor. Now, many residents of newly captured areas are uncertain what life under HTS control might entail.
Recent escalations in northwest Syria come as Assad’s main international supporters are preoccupied with their own conflicts. Russia is prioritizing its war in Ukraine, and both Iran and its proxy Hezbollah, in Lebanon, have been significantly weakened in fighting with Israel. Still, Russian and Syrian airstrikes targeted Idlib and Aleppo provinces over the weekend, while Iranian-backed militias from Iraq—including Kataib Hezbollah and Fatemiyoun—recently crossed into Syria, according to Al Arabiya, a Saudi Arabian news channel.
“Since Sunday, the bombings are constant,” Mahlool said. “Several schools and clinics in Idlib province have already been targeted.”
On Dec. 1, an airstrike hit Aleppo University Hospital, killing at least 12 people and injuring dozens more. The strike also damaged one of Violet’s ambulances, said Yemn Sayed Issa, the media and communication coordinator with the aid group. That same day, airstrikes targeted Idlib University Hospital, Ibn Sina Hospital, Idlib’s National Hospital, and the Idlib Health Directorate. And, according to Issa, a Soviet-era warplane struck a camp for displaced people near Ma’arrat Misrin, a town just north of central Idlib, killing at least seven civilians, including five children and two women. Violet’s medical team is responding to the attacks.
“It’s extremely dangerous for everyone. Our medics and ambulances head out daily, but constantly fear being targeted,” Issa said, adding that Aleppo—home to around 2 million people—is now critically short on essentials like bread, water, fuel, and medical supplies, which had previously been shipped from other regime-held areas.
“Everything is coming from Idlib now, but it’s difficult. The humanitarian situation is tragic. People are having to find shelter wherever they can,” Issa said. “In the town of [Darkush], for example, a public swimming pool has been turned into a temporary shelter for people who have fled their villages. Most displaced families have been forced to seek shelter in open fields and farmland, without any proper shelter or basic facilities.”
HTS’s advance means Aleppo is under opposition control for the first time in eight years. The front line had remained frozen since Russia and Turkey brokered a cease-fire deal in 2020. The two countries back opposing sides in Syria.
Russia, along with Iran and Hezbollah, are Assad’s key allies, while Turkey supports the Syrian National Army (SNA), a coalition of opposition groups—excluding HTS—that fights the Assad regime and Kurdish forces such as the People’s Defense Units (YPG) and the Kurdistan Workers’ Party (PKK). Turkey considers the latter two groups to be terrorist organizations.
Since the recent rebel offensive, Assad’s regime has effectively abandoned areas within Aleppo province and left them under Kurdish control. The SNA continues to push the Kurdish groups further east. On Dec. 1, the SNA captured the strategic town of Tel Rifaat, which is located between Aleppo and the Turkish border. For the past eight years, the area had been under YPG and PKK control—a significant national security concern for Turkey.
The relationship between HTS and the SNA has long been tense; HTS has sought control over SNA-held areas and the SNA distrusts HTS for numerous reasons, including ideological differences. But both groups share a common goal.
“The priority is to fight the regime,” said Orwa Ajjoub, a doctoral candidate at Malmo University in Sweden who researches Islamist groups in Syria. “I’ve spoken with people who are sworn enemies of HTS to this day, but now they’re putting their differences aside to fight the regime. HTS is leading these efforts. When the dust settles, we’ll see how these diverse groups manage to resolve their disagreements.”
Turkey has its own troops in Syria, primarily in Idlib, Afrin, and other areas east of the Euphrates River, mainly as part of its operations against the PKK and YPG. Around 900 U.S. troops are also in the country; mostly concentrated in northeastern Syria, they support counter-terrorism operations against the Islamic State.
Analysts have speculated over whether Turkey—which is keen to reduce the power of the PKK and YPG—gave HTS the green light for the operation. Turkish Foreign Minister Hakan Fidan, however, said that it would be “wrong” to try to chalk the current situation in Syria up to external intervention.
Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdogan tried to mend relations with Assad in July, following a deterioration of ties throughout the war. Yet Assad insisted that Turkish forces must fully withdraw from Syria for him to negotiate with Erdogan—a request Turkey is unwilling to meet due to its own national security concerns.
Speaking with U.S. Secretary of State Antony Blinken on Dec. 1, Fidan stressed that Turkey opposes instability in the region and reiterated the importance of reducing tensions in Syria. Iranian Foreign Minister Abbas Araghchi arrived in Turkey on Dec. 2 to discuss the situation in Syria. “Recent developments show once again that Damascus must reconcile with its own people and the legitimate opposition,” Fidan said at a joint news conference with Araghchi. “Turkey is ready to make all the necessary contribution toward this.”
Whether Turkey knew about it or not, “this operation is definitely a win for Turkey,” Ajjoub said. U.S. President-elect Donald Trump has spoken about potentially withdrawing the remaining U.S. troops in Syria, which could create a power vacuum in the region. “Having more leverage in Syria before Donald Trump takes office could be significant for Turkey,” Ajjoub said.
12 notes
·
View notes
Text

Patriot by Alexei Navalny
The late Russian activist’s memoir is an insightful, sharp, even humorous account of his fight against Putin’s regime – and a warning to the world
Alexei Navalny was watching his favourite cartoon show, Rick and Morty, when he suddenly felt unwell. He was 21 minutes into an episode where Rick turns into a pickle. The late Russian opposition leader was on a flight back to Moscow after campaigning ahead of regional elections in the Siberian city of Tomsk in August 2020. Something was clearly wrong, and Navalny staggered to the bathroom.
There, he recalls, he had the grim realisation: “I’m done for.” He told a sceptical steward that he’d been poisoned and then lay down calmly in the aisle, facing a wall. Life didn’t flash before his eyes. Instead, he compares his experience of death – or near-death, as it turned out – to something from a dark fantasy. It was like being “kissed by a Dementor and a Nazgûl stands nearby”.
He is clear who gave the order to kill him with the nerve agent novichok: Vladimir Putin. Navalny calls Russia’s president a “bribe-taking old man” and a “vengeful runt” who sits on top of a “sinister regime”. The assassins were members of the FSB, the KGB’s successor agency. Navalny spent 18 days in a coma, waking up in hospital in Germany.
It was while recovering in Freiburg that he wrote the first part of his extraordinary memoir, Patriot. The second section consists of letters from prison, following his January 2021 return to Moscow, when he was dramatically arrested at the airport. Navalny says he embarked on an autobiography knowing the Kremlin could finish him off. “If they do finally whack me, this book will be my memorial,” he notes.
It took three years for his gallows humour prophecy to come true. Navalny died in February this year, his likely murder taking place in an Arctic penal colony. He was 47. Prison documents hint he was poisoned and the authorities removed the evidence: clothes, vomit, even snow he had come into contact with.
This is a brave and brilliant book, a luminous account of Navalny’s life and dark times. It is a challenge from beyond the grave to Russia’s murder-addicted rulers. You can hear his voice in the deft translation by Arch Tait and Stephen Dalziel: sharp, playful and lacking in self-pity. Nothing crushes him. Up until the end – his final “polar” entry is on 17 January 2024 – he radiates indomitable good humour.
Patriot includes a manifesto for how the country might be transformed: free elections, a constitutional assembly, decentralisation and a European orientation. Days before his murder, he predicted the Putin regime would crumble, while acknowledging the resilience of autocracies.
Trained as a lawyer, Navalny first attracted attention as a transparency activist. He bought shares in notoriously corrupt oil and gas companies and asked awkward questions at shareholder meetings. The Kremlin controlled TV and most newspapers, so Navalny wrote up his exposés online. In 2011 he founded FBK, an anti-corruption organisation which grew into a grassroots national movement run by volunteers. He expresses pride at the way his campaigns encouraged young Russians to take part in opposition politics. Police detained him for the first time in 2011 when he attended protests against rigged Duma elections. Undaunted, he stood two years later to be mayor of Moscow, coming second, before finding himself in an “endless cycle” of rallies, arrests and spells in custody.
The Kremlin’s response to all this was vicious. His brother Oleg was jailed after a fake trial, a provocateur threw green gunk at Navalny, blinding him in one eye. In 2016 he tried to run for president. His videos – of Putin’s tacky Sochi palace and former president Dmitry Medvedev’s dodgy schemes – attracted millions of views. Navalny writes movingly about his wife, Yulia, – whom he met on holiday in Turkey – as a soulmate throughout this period.
Given his understanding of Putin’s Stalinist methods, why did he return to Moscow? His answer is that the struggle to make Russia a normal state was “my life’s work”. He wasn’t prepared to dump his homeland or his convictions, he says. At first, jail conditions were bearable. Well-wishers sent sacks of letters and a tiramisu cake. In one dispatch, Navalny ponders the “amazing ability of human beings to adapt and derive pleasure from the most trivial things”, such as instant coffee.
Behind bars, he chatted to his cellmates and read. He preferred Maupassant to Flaubert and enjoyed Oliver Twist (though he wonders if Dickens got working-class dialogue right). The FSB spied on him 24/7; his warders wore body cameras and barked commands.
As conditions worsened, he made fewer diary entries. More criminal “convictions” piled up – for insulting a war veteran and for extremism. He was shuffled from one penitentiary to the next. Meanwhile, “perverted” prison staff refused to treat his back pain, prompting a hunger strike. He was categorised as a flight risk and woken throughout the night, put in a tiny punishment cell and denied his wife’s letters.
None of these privations stopped Navalny from denouncing Putin’s all-out invasion of Ukraine as an “unjust war of aggression”. The reason for the war is Putin’s desire to hold on to power at any cost, and an obsession with his “historical legacy”, he writes. Critics regard Navalny as a closet nationalist. But Patriot calls for Russia to withdraw its troops, respect Ukraine’s 1991 borders and pay compensation.
During one of Yulia’s visits, Navalny told her there was a “high probability” he would never get out of prison alive. “They will poison me,” he said. “I know,” she replied. He sketches out what this means – no chance to say goodbye, never meeting his grandchildren, “tasseled mortar boards tossed in the air in my absence”. Maybe an unmarked grave. His philosophy: hope for the best, expect the worst. His death is a terrible loss, for Russia and for all of us.
Daily inspiration. Discover more photos at Just for Books…?
16 notes
·
View notes