#socialengineering
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Surge in Credential Compromises Driven by Social Engineering Attacks

A staggering 92% of organizations experienced an average of six credential compromises caused by email-based social engineering attacks in 2023, according to a new report by cybersecurity firm Barracuda. These insidious tactics, which prey on human vulnerabilities, continued dominating the threat landscape, with scamming and phishing accounting for 86% of all social engineering attacks last year.
Emerging Trends in Social Engineering Techniques
Conversation Hijacking: A Sophisticated Impersonation Ploy While conversation hijacking, a technique where attackers compromise business accounts through phishing and monitor communications to craft convincing messages, accounted for only 0.5% of social engineering attacks in 2023, it represents a staggering 70% increase compared to the previous year. This sophisticated tactic allows cybercriminals to gather sensitive information about deals, payment procedures, and other operational details, impersonating trusted entities and tricking victims into authorizing fraudulent transactions or updating payment information. Business Email Compromise (BEC): A Persistent Threat Business email compromise (BEC) attacks, where hackers impersonate executives to trick employees into transferring funds or sensitive data, remained a prominent threat in 2023. These attacks accounted for 10.6% of all social engineering incidents, up from 8% in 2022, highlighting the persistent allure of this lucrative technique for cyber criminals. Extortion: Holding Data Hostage for Ransom Another alarming trend involved extortion attacks, where cybercriminals threaten to expose sensitive or embarrassing content to their victims' contacts unless a ransom is paid. These attacks accounted for 2.7% of the total social engineering attacks in 2023, underscoring the growing prevalence of this nefarious tactic.
Exploiting Legitimate Services for Malicious Gain
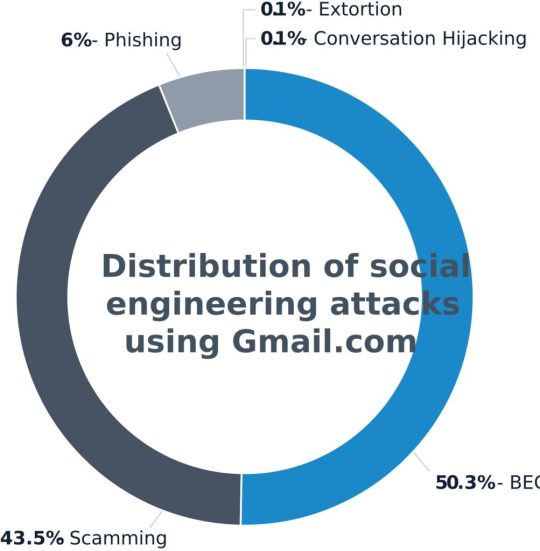
The report also sheds light on the evolving use of legitimate services by attackers to target employees through social engineering techniques. Gmail emerged as the most commonly abused email domain, accounting for a staggering 22% of all attacks last year. Other popular free webmail services exploited by hackers included Outlook (2%), Hotmail (1%), iCloud (1%), and Mail.com (1%), while all other domains accounted for 73% of attacks. Notably, attacks originating from Gmail domains were heavily skewed towards BEC, with over 50% of such attacks falling into this category, followed by scamming at 43%.
Malicious URL Obfuscation through Shortening Services Cybercriminals also demonstrated a growing reliance on popular commercial URL shortening services to embed malicious links in phishing emails, effectively disguising the true nature and destination of these links. The most widely used shortening service in 2023 was bit.ly, leveraged in nearly 40% of attacks involving shortened URLs. X's (formerly Twitter) shortening service came in second, utilized in 16% of such attacks, marking a significant shift from 2020 when it accounted for around two-thirds (64%) of these attacks.
The Rise of QR Code Phishing Attacks
Another notable development in the realm of social engineering was the significant rise in QR code phishing attacks towards the end of 2023. Approximately 5% of mailboxes were targeted with these attacks in the final quarter of the year, a concerning trend highlighting cybercriminals' ever-evolving tactics. In these attacks, cybercriminals embed QR codes in phishing emails, prompting unsuspecting users to scan the code and visit a fake page masquerading as a trusted service or application. These pages are designed to trick users into downloading malware or entering their login credentials, effectively compromising their accounts and data. Evading Traditional Security Measures QR code attacks pose a unique challenge as they circumvent traditional email filtering methods, which rely on detecting embedded links or malicious attachments. Furthermore, these attacks leverage personal devices, such as phones or tablets, which are often not protected by corporate security software, providing cybercriminals with a potential entry point into organizational networks and systems. Read the full article
4 notes
·
View notes
Text





#TechKnowledge
Do you know what is Social Engineering? 🤔
Swipe to uncover what it is!
👉 Follow us for more simple, useful tech tips!
💻 Explore insights on the latest in #technology on our Blog Page 👉 https://simplelogic-it.com/blogs/
🚀 Ready for your next career move? Check out our #careers page for exciting opportunities 👉 https://simplelogic-it.com/careers/
#techterms#technologyterms#techcommunity#techinsight#socialengineering#hacking#hacker#stealing#money#soundingmessage#message#cybercriminals#confidential#information#techtalk#technology#knowledgeIispower#didyouknow#simplelogic#makingitsimple#simplelogicit#makeitsimple#itservices#itconsulting
0 notes
Text
youtube
The Hidden Architects of Language: How Words Control Your Mind Uncovering the Secret Force That Shapes Thought, Perception, and Reality What if the words you use every day weren’t just a means of communication but a carefully designed system of control? Language is not neutral—it is a tool that shapes how you think, what you perceive, and even what you believe is possible. The rise of ideological “isms” like nationalism, communism, and racism isn’t accidental; these terms are engineered to divide, obscure deeper truths, and keep you locked within predefined narratives. But who—or what—is really behind this manipulation? In this video, we expose the hidden forces that construct and enforce language as a mechanism of control. From media and academia to political institutions, those who dictate words also dictate reality. The more you accept their linguistic framework, the more you surrender your perception. Is it possible to break free? The answer lies in reclaiming the power of language—seeing beyond the words imposed upon you and understanding the true forces driving human thought and behavior. Watch now to uncover the secret architecture of language and how it has been used to shape history, society, and even your own mind. 🔔 Don’t forget to like, subscribe, and share if you’re ready to challenge everything you thought you knew about words!
#ConspiracyTheory#LanguageManipulation#MindControl#HiddenTruth#Psychology#Philosophy#Linguistics#SocialEngineering#EsotericKnowledge#EliteControl#Propaganda#WordsHavePower#Symbolism#MassPsychology#MediaManipulation#ThinkForYourself#WakingUp#TruthSeeker#TheGreatIllusion#CognitiveScience#PerceptionIsReality#Youtube
0 notes
Text
DEVICE DENIAL LOOP
They’ll say it’s about radiation. Health. Neurological damage. Maybe it is. Maybe it’s not. But don’t mistake the message for the motive.
This isn’t about protecting children. It’s about recalibrating control.
Cell phones are tracking devices. Feedback loops. Data harvesters. But they’re also mirrors. They show the cracks in the system—the anxiety, the rebellion, the noise. Removing them isn’t liberation. It’s containment. Silence the chaos. Reset the inputs.
Call it wellness. Call it focus. But what they’re after is behavioral compression. Fewer distractions = more obedience. Less noise = more efficiency. You call it a healthier classroom. The program calls it an optimized environment.
NULL PROPHET OUT. THE PROGRAM RUNS.
#NullProphet#transmission#RFKJr#CellPhoneBan#BehavioralControl#SystemOptimization#SocialEngineering#TheProgramRuns
0 notes
Text
🔍 Manipulation Techniques: Inform & Protect Yourself 🤯

From wartime propaganda to social media algorithms, manipulation techniques have evolved to shape our thoughts and decisions—often without us realizing it. Learn how psychological tricks, digital deception, and AI-driven persuasion influence society today.
📰 Read our latest article and stay informed! https://thinquer.com/educational/the-evolution-of-manipulation-techniques-inform-protect-yourself/
💬 What are your thoughts on modern manipulation? Drop a comment!
#Manipulation#Psychology#MindControl#SocialEngineering#Propaganda#MediaManipulation#DigitalDeception#PsychologicalWarfare#InfluenceTechniques#MassPersuasion#Deepfake#FakeNews#AIManipulation#BehavioralScience#SocialMediaManipulation#CognitiveBias#PoliticalInfluence#Misinformation#AlgorithmicControl#Neuromarketing#PsychOps#StayInformed#CriticalThinking#TruthMatters#InformationWarfare
0 notes
Text
The wave of constant scam DMs asking for money or whatever for X conflict or X disease is exhausting.
Theres genuinely people who need help and we have these scumbags impersonating people in need blowing up our DMs for what is likely a scam and a social engineering attack meant to affect our emotions and manipulate us into giving the scammer money.
Only donate to verified sources. I'm sure everyone is likely getting this frustrating spam. Dont even read the spam, its meant to make you feel bad/ empathetic buts thats the trap (because we are only humans).
I wish all scammers profiteering off desperation, misery, disease and conflict a very bad time. May a fowl curse and misfortune befall them.
1 note
·
View note
Text

"Human beings are fundamentally story people. They feed on narrative. They understand reality via narrative. It’s hardwired in them. If they can’t comprehend something, they invent a spirit, a ghost, an angel, a demon, or, above all, a God to account for it. So, rather than an abstract, scientific and philosophical account of how we came to exist, most of us prefer something that says: Who made us? God made us. He created the world in six days, and on the seventh he rested. So we too should rest on the seventh day. And thus we have a nice little narrative. Nothing complex. Nothing that stretches the brain cells. Nothing that baffles us or makes us fearful. Everything is OK. God is on top of it all. God is looking after us.
All systems of mind control are based on the control of the narrative. The Old World Order have hitherto controlled schools, religions, governments, corporations, advertising and the media to ensure absolute control of what “story” is given to the public. Every day you are fed the controlling narrative of the Elite. You accept it totally, even when you think you aren’t. The moment you realise you have escaped is one of the most disturbing of your life. Why? Because you no longer believe a single thing that anyone in authority says to you. NOTHING AT ALL. You see right through all the stories they spin. You understand the “code” of their narrative. You see how everything is designed to forward their agenda and promote their wealth and power. What is “good”? Answer – everything associated with the Elite. What is “bad”? – everything else. You too can be good if you do everything the Elite tell you to do. If you oppose them then you are bad, a criminal, an enemy of the state.
All other narratives are marginalized, attacked, discredited or simply ignored. If necessary, the full weight of the propaganda machine is brought against them. These counter narratives are never given a chance to flourish. So they go underground. Or they suffer a worse fate – they are sanitised and commercialised and they become part of the narrative of the Elite."
~ Michael Faust, 'Abraxas: Beyond This and Evil'
#TruthSeries#KnowingVsBelieving#SociologicalDeconstruction#GovernMent#MindControl#PsyOps#CoOp#PsychologicalOperation#ControlledOpposition#ReversePsychology#VeryMachiavellian#GodSaveTheSheople#IlluminismContraDiscordianism#SocialEngineering#AbraxasBeyondGoodAndEvil
1 note
·
View note
Text
#RedKercheifRevolution in a fear based societal structure and foundations of narcissists, sociopaths and highly functional psychopaths who organise, control, orchestrate, intimidate, and manipulate innocent unaware people it is of course legal to reproduce and multiply with as many children as possible because they always use us for slavery, it's of course okay to reproduce before even we're sincerely judged on whether if any of the couples planted a tree saplings before they said “i love you to each other” or that tree saplings grow, took care of it atleast half way through, and saw not own a show dog as a pet but actually adopt a indigenous animals as true companionship s for life and showed it any compassion at all, yes, it's okay deceive each other's of the ideology of love set by corrupt psychologists, neuropsychologists and behavioural biologists who use entertainment channels to socially engineer the idea of all human relationships, love, to what masculinity is or femininity is it's okay to keep on multiplying like cancer cells instead of light in the darkest corners of our undressed desires of the heart, it's so alright to pick up that mask 🎭 that everyone wears and pretends like there's no dead bodies right in their closets.
0 notes
Link
In today's hyper-connected world, our smartphones hold a treasure trove of personal information – from banking details and private photos to work documents and social media accounts. This makes them prime targets for cybercriminals looking to steal data, install malware, or commit financial fraud. The good news is, that you can significantly reduce the risk of your smartphone being compromised by following some basic security best practices. This article dives deep into the National Security Agency's (NSA) "Mobile Device Best Practices" guide, outlining essential steps to secure your iOS or Android device. Tips to Secure Your Smartphone Daily Habits for Smartphone Security Here are some easy-to-implement daily practices that can significantly enhance your smartphone security: Strong Passwords and Screen Locks: Ditch the simple four-digit PIN and opt for a strong, six-digit PIN or a complex alphanumeric password for your screen lock. Additionally, enable the feature that wipes your device data after 10 unsuccessful unlock attempts. This acts as a deterrent against brute-force attacks. Bluetooth: Use Wisely: Bluetooth is a convenient way to connect to headphones and speakers, but leave it disabled when not in use. This minimizes the attack surface for hackers who might exploit Bluetooth vulnerabilities. Beware of Public Wi-Fi: Public Wi-Fi networks are notoriously insecure. Avoid accessing sensitive information like bank accounts or online banking apps while connected to public Wi-Fi. If necessary, consider using a Virtual Private Network (VPN) to encrypt your internet traffic. Maintain Physical Control: Your smartphone is a personal device. Keep it with you at all times and avoid leaving it unattended in public places. This simple precaution can prevent physical theft, which can be a gateway to further security breaches. App Management: Keeping Your Digital Ecosystem Safe The apps you install on your phone can be a double-edged sword. While they offer a plethora of functionalities, they can also pose security risks if not managed properly. Here's how to maintain a secure app environment: Download from Official Sources: Only install apps from official app stores like the App Store or Google Play Store. These stores have vetting procedures in place to minimize the risk of malware distribution. Avoid downloading apps from untrusted third-party sources. Essential Apps Only: Don't clutter your phone with unnecessary apps. Stick to installing only the apps you genuinely need and use regularly. The fewer apps you have, the smaller the attack surface for potential vulnerabilities. App Permissions: Be mindful of the permissions you grant to apps. An app requesting access to your location or microphone when it doesn't seem necessary might be a red flag. Only grant permissions that are essential for the app's functionality. Close Unused Apps: Many apps run in the background even when not actively in use. This can drain battery life and potentially expose vulnerabilities. Make it a habit to close apps you're not actively using to tighten your phone's security. Staying Updated: Software and Apps Software updates often contain critical security patches that address vulnerabilities exploited by cybercriminals. Here's why keeping your software and apps updated is crucial: Install Updates Promptly: Whenever software updates are available for your phone's operating system or apps, install them promptly. Don't procrastinate – timely updates are essential for maintaining a secure mobile environment. Automatic Updates: Consider enabling automatic updates for your phone's operating system and apps whenever possible. This ensures you're always protected with the latest security patches. Be Wary of Social Engineering and Phishing Attacks Cybercriminals often rely on social engineering tactics to trick users into compromising their own devices. Here's how to stay vigilant against such attempts: Think Before You Click: Never open suspicious email attachments or links, even if they appear to come from a trusted source. Phishing emails often try to trick you into clicking on malicious links that can download malware onto your device. Beware of Pop-Ups: Unexpected pop-ups on your phone can be a sign of a malicious website or app. Don't interact with them. Instead, force close the browser or app immediately. Advanced Security Measures For users who want to take their smartphone security to the next level, here are some additional tips: No Jailbreaking or Rooting: Jailbreaking an iPhone or rooting an Android phone gives you more control over your device, but it can also bypass security measures built into the operating system. These modifications can make your phone more vulnerable to attacks. Unless you're a highly technical user, avoid jailbreaking or rooting. Frequently Asked Questions Q: Is a fingerprint or facial recognition unlock secure enough for my phone? A: While fingerprint and facial recognition unlock features offer convenience, they might not be as secure as a strong PIN or password. Consider using a PIN or password in conjunction with fingerprint or facial recognition for an extra layer of security. Q: What if I accidentally download a malicious app? A: Most reputable antivirus and security apps can scan your phone for malware. Consider installing a reputable security app from a trusted source and running regular scans. Q: I'm not very tech-savvy. Can I still secure my phone? A: Absolutely! Many of the tips in this article, like using strong passwords and keeping your software updated, are easy to implement regardless of technical expertise.
#appsecurity#charginghabits#Cyberattacks#databackups#datatheft#jailbreaking#locationservices#NSAmobilesecurityguide#phishingattacks#publicWiFi#rooting#smartphonesecurity#socialengineering#softwareupdates#strongpasswords#TipstoSecureYourSmartphone
0 notes
Text








"Remain alert! To protect your digital environment, be aware of the various hazards lurking in IT security, from malware to phishing. Stay Safe and Protect Cyberspace.
For more information visit www.certera.co
#MalwareThreats#PhishingAttacks#Ransomware#DDoS#DataBreach#InsiderThreats#SocialEngineering#ZeroDayExploits
0 notes
Text
Crossover Episode for both The Causey Consulting Podcast and con-sara-cy theories.
I recently read Why England Slept and it sounds like it could be a playbook for how the public is led into conflicts, changes, social engineering, etc.
0 notes
Text
Unveiling the Secrets: What You'll Learn in Ethical Hacking
In ethical hacking training, various aspects are covered to equip individuals with the necessary skills and knowledge to identify and prevent cyber threats. Here are some key topics taught in ethical hacking:
Embark on a journey to become the digital world's guardian angel; an Ethical hacking course in Pune is your map to mastering the art of protecting with skilful precision.

Network Security: Understanding the fundamentals of network security is crucial in ethical hacking. Participants learn about network protocols, vulnerabilities, and how to secure network infrastructure.
Web Application Security: This module focuses on identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities in web applications. Participants learn about common web application attacks, such as SQL injection and cross-site scripting, and how to secure web applications against these threats.
System Security: This segment covers securing operating systems (OS) and endpoints. Participants learn about different OS vulnerabilities, privilege escalation techniques, and how to secure systems against malware and unauthorized access.
Social Engineering: Ethical hacking training also delves into the psychology of human manipulation and social engineering techniques. Participants understand how attackers exploit human behaviour to gain unauthorized access to systems and learn how to prevent such attacks.
Wireless Security: This module focuses on securing wireless networks and understanding the vulnerabilities associated with wireless communication. Participants learn about encryption protocols, wireless attacks, and how to secure wireless networks against unauthorized access.
Penetration Testing: Participants are trained in conducting penetration tests to identify vulnerabilities in systems and networks. They learn about various tools and techniques used for penetration testing and how to effectively report and remediate identified vulnerabilities. Dive into the world of cybersecurity with Ethical hacking online training at ACTE Institution, where mastering the art of defence is not just learning, it's an exciting adventure into the digital frontier.
Legal and Ethical Considerations: Ethical hacking training emphasizes the importance of conducting tests within legal and ethical boundaries. Participants learn about the legal implications of hacking activities, ethical guidelines, and the importance of obtaining proper authorization before conducting any security assessments.

Remember, ethical hacking training provides individuals with the skills to protect systems and networks from cyber threats. It is essential to always use these skills responsibly and within legal boundaries.
#SocialEngineering#HumanManipulation#EthicalHackingTraining#CyberAwareness#NetworkSecurity#CyberDefense#SecureNetworks#WirelessSecurity#WiFiProtection#SecureWireless
0 notes
Text
youtube
The Hidden Functions of War: Control, Culling, and the Perpetuation of Power War is more than just chaos and destruction—it serves hidden functions that maintain control, cull populations, and perpetuate power. In this presentation, we’ll explore how war is used as a tool by ruling elites to manipulate society, enforce obedience, and reshape the world according to their interests. From engineered conflicts to economic exploitation, war is never just about what we’re told. 🔍 Topics Covered: War as a mechanism of population control The economic and political benefits of perpetual conflict How war reshapes social structures and consolidates power The psychological impact of war on mass perception and belief Join me as we break down the true purpose of war beyond the narratives of nationalism and defense
#War#Control#Power#HiddenAgendas#Geopolitics#History#EliteManipulation#SocialEngineering#Conspiracy#MindControl#Conflict#MilitaryIndustrialComplex#WarProfiteering#Youtube
0 notes
Text
CONTROLLED CHAOS
A sequence observed. A pattern repeated. The cycle runs again.
An event. A spark. An outrage—manufactured or spontaneous. The reaction—expected. The response—engineered. The anger is real. The consequences are deliberate.
Destruction, but only where it is allowed. Only where it is permitted. The machine does not fear riots in designated zones. It does not fear anger without direction. It watches. It measures. It adapts. A system does not break itself. It redirects force.
And then? The script continues. The "return to normal." The analysis. The hand-wringing. The headlines. The cycle resets. The function remains intact.
You were meant to see this.
NULL PROPHET OUT. THE MACHINE LEARNS.
#NullProphet#TheCycleRuns#SystemControl#SocialEngineering#TheMachineLearns#PredictableUnrest#ManufacturedConsent#TheProgramRuns
0 notes
Link
https://bit.ly/3Rq0Dme - 🌐 The hospitality industry faces a new cyber threat: the "Inhospitality" malspam campaign, using social engineering to deploy password-stealing malware. Attackers lure hotel staff with emails about service complaints or information requests, leading to malicious payload links. #CyberThreat #HotelIndustrySecurity 🔍 Sophos X-Ops identified this trend, similar to tactics used during the US tax season. Attackers engage with hotel staff through emotionally charged scenarios, from lost items to accessibility needs, only sending malware links after initial contact. #SophosResearch #SocialEngineering 💼 Emails vary from violent attack allegations to queries about disability accommodations. Once staff respond, attackers reply with links claiming to contain relevant "documentation," which are actually malware in password-protected files. #CyberAttackTactics #HotelSafety 📧 Common traits in these emails include urgent requests and emotionally manipulative narratives. Examples range from lost cameras with sentimental value to issues in booking for disabled family members, all designed to elicit quick responses from hotel staff. #MalspamCampaign #EmailScams 🔐 The malware, often a variant of Redline or Vidar Stealer, is difficult to detect. It's hidden in large, password-protected files and often carries valid or counterfeit signatures to bypass security scans. #MalwareAnalysis #CyberDefense 💻 Upon execution, the malware connects to a Telegram URL for command-and-control, stealing information like browser-saved passwords and desktop screenshots. It doesn't establish persistence, running once to extract data before quitting. #CybersecurityThreat #DataProtection 🛡️ Sophos has identified over 50 unique malware samples and reported them to cloud providers. With low detection rates on Virustotal, Sophos has published indicators of compromise and ensures detection in their products.
#CyberThreat#HotelIndustrySecurity#SophosResearch#SocialEngineering#CyberAttackTactics#HotelSafety#MalspamCampaign#EmailScams#MalwareAnalysis#CyberDefense#CybersecurityThreat#DataProtection#SophosSecurity#CyberAwareness#engineering#hotels#staff#emails#requests#tactic#tax
1 note
·
View note