#slavery abolition act
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
HIGHLIGHTS of the Day - August 1st
In a period full of bummer news from wars and natural disasters, we’re choosing to shine a spotlight on August 1st, the start of Ferragosto. So, let’s dig into the fascinating history of Ferragosto and what it’s all about. “Ferragosto, or as the locals call it, Ferro Agosto, is a super old Italian holiday with all kinds of history attached to it. The name comes from this Latin thing “Feriae…
#A song of Ice and Fire#anne frank diary#Best selling book#Boys Scouts#british empire#concentration camps#Curiosities#discovery of oxygen#emancipation days#Emmy Awards#end of slavery#FAMILY+ Blog#Ferragosto#Games of Thrones#Girls Scouts#highlights of the day#Holidays#Italy#MTV#music videos#oxygen#scouting#slavery abolition act#The Buggles#world scout scraf day
0 notes
Text
[T]he Dutch Republic, like its successor the Kingdom of the Netherlands, [...] throughout the early modern period had an advanced maritime [trading, exports] and (financial) service [banking, insurance] sector. Moreover, Dutch involvement in Atlantic slavery stretched over two and a half centuries. [...] Carefully estimating the scope of all the activities involved in moving, processing and retailing the goods derived from the forced labour performed by the enslaved in the Atlantic world [...] [shows] more clearly in what ways the gains from slavery percolated through the Dutch economy. [...] [This web] connected them [...] to the enslaved in Suriname and other Dutch colonies, as well as in non-Dutch colonies such as Saint Domingue [Haiti], which was one of the main suppliers of slave-produced goods to the Dutch economy until the enslaved revolted in 1791 and brought an end to the trade. [...] A significant part of the eighteenth-century Dutch elite was actively engaged in financing, insuring, organising and enabling the slave system, and drew much wealth from it. [...] [A] staggering 19% (expressed in value) of the Dutch Republic's trade in 1770 consisted of Atlantic slave-produced goods such as sugar, coffee, or indigo [...].
---
One point that deserves considerable emphasis is that [this slave-based Dutch wealth] [...] did not just depend on the increasing output of the Dutch Atlantic slave colonies. By 1770, the Dutch imported over fl.8 million worth of sugar and coffee from French ports. [...] [T]hese [...] routes successfully linked the Dutch trade sector to the massive expansion of slavery in Saint Domingue [the French colony of Haiti], which continued until the early 1790s when the revolution of the enslaved on the French part of that island ended slavery.
Before that time, Dutch sugar mills processed tens of millions of pounds of sugar from the French Caribbean, which were then exported over the Rhine and through the Sound to the German and Eastern European ‘slavery hinterlands’.
---
Coffee and indigo flowed through the Dutch Republic via the same trans-imperial routes, while the Dutch also imported tobacco produced by slaves in the British colonies, [and] gold and tobacco produced [by slaves] in Brazil [...]. The value of all the different components of slave-based trade combined amounted to a sum of fl.57.3 million, more than 23% of all the Dutch trade in 1770. [...] However, trade statistics alone cannot answer the question about the weight of this sector within the economy. [...] 1770 was a peak year for the issuing of new plantation loans [...] [T]he main processing industry that was fully based on slave-produced goods was the Holland-based sugar industry [...]. It has been estimated that in 1770 Amsterdam alone housed 110 refineries, out of a total of 150 refineries in the province of Holland. These processed approximately 50 million pounds of raw sugar per year, employing over 4,000 workers. [...] [I]n the four decades from 1738 to 1779, the slave-based contribution to GDP alone grew by fl.20.5 million, thus contributing almost 40% of all growth generated in the economy of Holland in this period. [...]
---
These [slave-based Dutch commodity] chains ran from [the plantation itself, through maritime trade, through commodity processing sites like sugar refineries, through export of these goods] [...] and from there to European metropoles and hinterlands that in the eighteenth century became mass consumers of slave-produced goods such as sugar and coffee. These chains tied the Dutch economy to slave-based production in Suriname and other Dutch colonies, but also to the plantation complexes of other European powers, most crucially the French in Saint Domingue [Haiti], as the Dutch became major importers and processers of French coffee and sugar that they then redistributed to Northern and Central Europe. [...]
The explosive growth of production on slave plantations in the Dutch Guianas, combined with the international boom in coffee and sugar consumption, ensured that consistently high proportions (19% in 1770) of commodities entering and exiting Dutch harbors were produced on Atlantic slave plantations. [...] The Dutch economy profited from this Atlantic boom both as direct supplier of slave-produced goods [from slave plantations in the Dutch Guianas, from Dutch processing of sugar from slave plantations in French Haiti] and as intermediary [physically exporting sugar and coffee] between the Atlantic slave complexes of other European powers and the Northern and Central European hinterland.
---
Text above by: Pepijn Brandon and Ulbe Bosma. "Slavery and the Dutch economy, 1750-1800". Slavery & Abolition Volume 42, Issue 1. 2021. [Text within brackets added by me for clarity. Bold emphasis and some paragraph breaks/contractions added by me. Presented here for commentary, teaching, criticism purposes.]
#abolition#these authors lead by pointing out there is general lack of discussion on which metrics or data to use to demonstrate#extent of slaverys contribution to dutch metropolitan wealth when compared to extensive research#on how british slavery profits established infrastructure textiles banking and industrialisation at home domestically in england#so that rather than only considering direct blatant dutch slavery in guiana caribbean etc must also look at metropolitan business in europe#in this same issue another similar article looks at specifically dutch exporting of slave based coffee#and the previously unheralded importance of the dutch export businesses to establishing coffee mass consumption in europe#via shipment to germany#which ties the expansion of french haiti slavery to dutch businesses acting as intermediary by popularizing coffee in europe#which invokes the concept mentioned here as slavery hinterlands#and this just atlantic lets not forget dutch wealth from east india company and cinnamon and srilanka etc#and then in following decades the immense dutch wealth and power in java#tidalectics#caribbean#archipelagic thinking#carceral geography#ecologies#intimacies of four continents#indigenous#sacrifice zones#slavery hinterlands#european coffee#indigenous pedagogies#black methodologies
26 notes
·
View notes
Text
Antisemitism is an inherent and essential part of Nazi ideology. Nazis target other demographics as well, but the antisemitism is a main, essential component. If someone isn't antisemitic then they're not a Nazi. If an ideology doesn't include antisemitism then it isn't Nazi ideology. There is literally no such thing as Nazi ideology that doesn't revolve around antisemitism. You can not separate antisemitism from Nazism, they go hand in hand. Someone who is queerphobic but not antisemitic is not a Nazi. Someone who is ableist but not antisemitic is not a Nazi. Someone who hates other ethnic or cultural groups but not Jewish people is not a Nazi. There's no such thing as a Nazi that doesn't hate Jewish people. You are helping no one by throwing the word around for any and all forms of fascism or discrimination, and you are harming people by acting like antisemitism isn't an essential part of Nazism.
#hey it's not exactly the same but the kkk target other demographics other than black people#but they formed specifically in response to the abolition of slavery and the freeing of black slaves#and the anti-black racism has always been a primary part of their ideology#imagine going up to black americans and screaming at them that other people are hated by the kkk too#or just trying to act like the anti-black racism isn't important#why would you do that right?#so why would you do it to jewish people?#or people being allies
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
random topic i've realised is lowkey really interesting to me: regional history subjects. i like how even though basically everyone covers stuff like the middle ages and renaissance, the french revolution, stalin's russia, nazi germany, etc., you also usually do a whole bunch of history of the country you're from
#personal crap#for example when i was in year 8 we covered the lead up to the great reform act and the abolition of slavery#and with the latter they made a big point of telling us about olaudah equiano which was quite good#and for my a level we did a bunch of stuff about the crimean and boer wars#i'm curious what other people covered now if you wanna put it in the tags i'd love to read
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Abolitionist / Anti-Slavery Amelia Bloomer
One question that I never completely resolved for myself while studying Bloomer’s life was whether she would qualify as an abolitionist, or as only anti-slavery. I decided to present evidence to the readers, without a definite argument either way. As with any controversial and significant subject, here were many different sets of overlapping beliefs among those opposed to slavery in the 1840s…

View On WordPress
#abolition#abolitionism#Amelia Bloomer#Civil War#feminism#Fugitive Slave Act#history#slavery#suffragists
0 notes
Text


#plugging this here as well because THIS IDIOT HAS A PHD#leaving aside the fact that they're ''detaining'' foreign nationals within illegally occupied territory#and therefore their courts HAVE NO AUTHORITY BY DEFAULT#the liberal ideological slavery to the nation state and its so-called ''democratic practices'' is something fucking else#institutionalized power built to crush the marginalized and colonized beneath its foundations is the very ground beneath their feet#saying ''maybe any power structure that necessarily consumes the lives of innocent human beings in order to sustain and legitimize itself#is actually morally and ethically depraved and antithetical to liberation and justice''#has them acting like you took a sledgehammer to their house‚ their family‚ their dog#from this same well springs the current pack of liberal hyenas screaming at muslims whose relatives are still buried under rubble#that refusing to vote for their genocidaires makes them complicit in the downfall of western civilization#this is also why the overlap between zionists‚ crypto-zionists‚ neoliberals and white people is almost a perfect circle#they're all direct beneficiaries of the colonial project and its carceral systems#anyway fuck israel#abolition#free palestine#state violence#knee of huss
7K notes
·
View notes
Text
Garp, Fascism, and Parental Failure
Garp is truly one of the most interesting One Piece characters for me because of the extent to which his dogged, relentless devotion to a fascist system–and the supposed "order" it promises to uphold in the face of anarchy or rebellion–perseveres no matter how many times it fails him and his son and his grandsons. He's fully aware of the deep-seated corruption and atrocity, and feels some kind of moral obligation to bend its rules to protect the innocent (as we can see with his attempts to protect Rouge and Ace), but when faced with widespread femicide and infanticide, genocide, slavery and endless examples of egregious cruelty, he is unable to comprehend the notion that the system is indefensible, or that the only moral choice he can possibly make when faced with that level of atrocity is to leave and resist it. His son recognizing the inherent, inexcusable failures of the World Government and its armed enforcers–literally quitting the force to start a revolution– changes nothing. The order to slaughter pregnant people and infants at Baterilla can't convince him otherwise. The countless instances of bribery, the tolerance of atrocity from state-sanctioned privateers, everything about the history of the Valley of the Gods are all things he's aware of, and takes issue with, but never comes to the conclusion that he cannot affect positive change within a system designed for oppression. The public execution of his grandson–a prime example of the marine's fundamentally irrational, arrogant, vindictive cruelty clearly bound to blow up in all of their faces even before their Pyrrhic victory at the summit war–makes him waver, but even when confronted with this obvious, indefensible injustice against a child he raised and rescued by people seeking to murder him on live TV and desecrate his corpse as a show of power, he cannot bring himself to act against it in any meaningful way no matter how much it hurts him to leave his grandson to die. If he can't veto it, he'll stay Vice Admiral and suffer through Ace being sacrificed on the altar of fascist state control, and functionally leave Luffy for dead in the process while he's at it. He fails every single person he wanted to love–Ace, Luffy, and almost certainly Dragon–and allows himself to be reluctantly complicit in countless crimes against humanity again and again and again because he's so deeply steeped in this notion of preservation of order through state control that he convinces himself that even this disgusting, atrocious, fundamentally flawed and untenable excuse for a government is better than abolition, better than revolution, or just the act of expecting accountability or literally anything better from the systems that issue false promises to protect you. Dadan beating the living shit out of him and calling him a failure as a grandfather, as a self proclaimed defender of the people, is one of the most important scenes in the Postwar Arc because a lesser series might frame Garp as a tragic, helpless figure suffering more than anyone else due to conflict of love and duty, but One Piece refuses to whitewash his actions/inaction or allow the grief and suffering caused by systems he's complicit in to take precedence over its real victims: the D brothers.
There's so much I could say about statism and anarchism and the ways people have internalized the supposed necessity of state violence to the extent they can't oppose that violence even when it ruins them or their loved ones, but that horrible indoctrination and its devastating consequences for both him and his family are what makes Garp so fascinating to watch and so thematically/politically important to One Piece as a whole.
#monkey d garp#monkey d. luffy#monkey d dragon#portgas d ace#one piece#curly dadan#marineford#one piece text posts#portgas d rouge#one piece marines#garp one piece#garp the fist#vice admiral garp#crocodile did more to try and help ace than garp#fucking crocodile
1K notes
·
View notes
Text

Olaudah Equiano (c. 1745–1797) was a prominent African writer, abolitionist, and former enslaved person whose autobiography played a key role in the abolition of the transatlantic slave trade. Born in what is now southeastern Nigeria, Equiano was captured as a child and sold into slavery. He was transported across the Atlantic to the Americas, where he endured the brutal conditions of slavery in the West Indies, the American colonies, and later in the British Navy.
Equiano’s story is remarkable not only because of his survival and eventual freedom, but also because of the way he used his life experiences to advocate for the end of slavery. After gaining his freedom in 1766, Equiano moved to London, where he became active in the abolitionist movement. His autobiography, The Interesting Narrative of the Life of Olaudah Equiano (1789), was one of the first major works to be written by an African author about the horrors of slavery. The book became widely read and influential, helping to bring attention to the inhumanity of the slave trade and contributing to the growing movement to abolish it in Britain.
Equiano described his early life in Africa, his abduction, the suffering he experienced as a slave, and his eventual freedom. It also highlighted his contributions as a free man, including his work with the British Navy, his business ventures, and his involvement in the abolition movement. The success of his autobiography helped establish Equiano as a prominent figure in the fight against slavery, and it played a significant role in publicizing the abolitionist cause.
Equiano’s work was also important in its examination of the African diaspora, as he offered a unique perspective on the lives of Africans both within the context of slavery and in the broader world of colonialism. He was an early proponent of Pan-Africanism, advocating for the unity of people of African descent worldwide.
Olaudah Equiano died on March 31, 1797, at the age of approximately 52. While the exact circumstances surrounding his death are unclear, it is believed that he died in London. His death occurred just a few years before the British Parliament passed the Abolition Act of 1807, which made the transatlantic slave trade illegal in the British Empire.
Though his life was cut short, Equiano’s legacy lived on. His autobiography remains a foundational text in the literature of slavery and abolition, and his activism and personal journey continue to inspire discussions on race, freedom, and human rights. Today, he is regarded as one of the most important figures in the history of the abolitionist movement and is celebrated for his courage, intellect, and commitment to justice. 🇳🇬
#black people#black history#black#blacktumblr#black tumblr#pan africanism#black conscious#africa#black power#black empowering#african culture#african history#black british history#Olaudah Equiano#biography#writer
48 notes
·
View notes
Text

Music of African heritage in Cuba derives from the musical traditions of the many ethnic groups from different parts of West and Central Africa that were brought to Cuba as slaves between the 16th and 19th centuries. Members of some of these groups formed their own ethnic associations or cabildos, in which cultural traditions were conserved, including musical ones. Music of African heritage, along with considerable Iberian (Spanish) musical elements, forms the fulcrum of Cuban music.
Much of this music is associated with traditional African religion – Lucumi, Palo, and others – and preserves the languages formerly used in the African homelands. The music is passed on by oral tradition and is often performed in private gatherings difficult for outsiders to access. Lacking melodic instruments, the music instead features polyrhythmic percussion, voice (call-and-response), and dance. As with other musically renowned New World nations such as the United States, Brazil and Jamaica, Cuban music represents a profound African musical heritage.

Clearly, the origin of African groups in Cuba is due to the island's long history of slavery. Compared to the USA, slavery started in Cuba much earlier and continued for decades afterwards. Cuba was the last country in the Americas to abolish the importation of slaves, and the second last to free the slaves. In 1807 the British Parliament outlawed slavery, and from then on the British Navy acted to intercept Portuguese and Spanish slave ships. By 1860 the trade with Cuba was almost extinguished; the last slave ship to Cuba was in 1873. The abolition of slavery was announced by the Spanish Crown in 1880, and put into effect in 1886. Two years later, Brazil abolished slavery.
Although the exact number of slaves from each African culture will never be known, most came from one of these groups, which are listed in rough order of their cultural impact in Cuba:
The Congolese from the Congo Basin and SW Africa. Many ethnic groups were involved, all called Congos in Cuba. Their religion is called Palo. Probably the most numerous group, with a huge influence on Cuban music.
The Oyó or Yoruba from modern Nigeria, known in Cuba as Lucumí. Their religion is known as Regla de Ocha (roughly, 'the way of the spirits') and its syncretic version is known as Santería. Culturally of great significance.
The Kalabars from the Southeastern part of Nigeria and also in some part of Cameroon, whom were taken from the Bight of Biafra. These sub Igbo and Ijaw groups are known in Cuba as Carabali,and their religious organization as Abakuá. The street name for them in Cuba was Ñáñigos.
The Dahomey, from Benin. They were the Fon, known as Arará in Cuba. The Dahomeys were a powerful group who practised human sacrifice and slavery long before Europeans arrived, and allegedly even more so during the Atlantic slave trade.
Haiti immigrants to Cuba arrived at various times up to the present day. Leaving aside the French, who also came, the Africans from Haiti were a mixture of groups who usually spoke creolized French: and religion was known as vodú.
From part of modern Liberia and Côte d'Ivoire came the Gangá.
Senegambian people (Senegal, the Gambia), but including many brought from Sudan by the Arab slavers, were known by a catch-all word: Mandinga. The famous musical phrase Kikiribu Mandinga! refers to them.
Subsequent organization
The roots of most Afro-Cuban musical forms lie in the cabildos, self-organized social clubs for the African slaves, and separate cabildos for separate cultures. The cabildos were formed mainly from four groups: the Yoruba (the Lucumi in Cuba); the Congolese (Palo in Cuba); Dahomey (the Fon or Arará). Other cultures were undoubtedly present, more even than listed above, but in smaller numbers, and they did not leave such a distinctive presence.
Cabildos preserved African cultural traditions, even after the abolition of slavery in 1886. At the same time, African religions were transmitted from generation to generation throughout Cuba, Haiti, other islands and Brazil. These religions, which had a similar but not identical structure, were known as Lucumi or Regla de Ocha if they derived from the Yoruba, Palo from Central Africa, Vodú from Haiti, and so on. The term Santería was first introduced to account for the way African spirits were joined to Catholic saints, especially by people who were both baptized and initiated, and so were genuine members of both groups. Outsiders picked up the word and have tended to use it somewhat indiscriminately. It has become a kind of catch-all word, rather like salsa in music.
The ñáñigos in Cuba or Carabali in their secret Abakuá societies, were one of the most terrifying groups; even other blacks were afraid of them:
Girl, don't tell me about the ñáñigos! They were bad. The carabali was evil down to his guts. And the ñáñigos from back in the day when I was a chick, weren't like the ones today... they kept their secret, like in Africa.

African sacred music in Cuba
All these African cultures had musical traditions, which survive erratically to the present day, not always in detail, but in the general style. The best preserved are the African polytheistic religions, where, in Cuba at least, the instruments, the language, the chants, the dances and their interpretations are quite well preserved. In few or no other American countries are the religious ceremonies conducted in the old language(s) of Africa, as they are at least in Lucumí ceremonies, though of course, back in Africa the language has moved on. What unifies all genuine forms of African music is the unity of polyrhythmic percussion, voice (call-and-response) and dance in well-defined social settings, and the absence of melodic instruments of an Arabic or European kind.
Not until after the Second World War do we find detailed printed descriptions or recordings of African sacred music in Cuba. Inside the cults, music, song, dance and ceremony were (and still are) learnt by heart by means of demonstration, including such ceremonial procedures conducted in an African language. The experiences were private to the initiated, until the work of the ethnologist Fernando Ortíz, who devoted a large part of his life to investigating the influence of African culture in Cuba. The first detailed transcription of percussion, song and chants are to be found in his great works.
There are now many recordings offering a selection of pieces in praise of, or prayers to, the orishas. Much of the ceremonial procedures are still hidden from the eyes of outsiders, though some descriptions in words exist.


Yoruba and Congolese rituals
Main articles: Yoruba people, Lucumi religion, Kongo people, Palo (religion), and Batá
Religious traditions of African origin have survived in Cuba, and are the basis of ritual music, song and dance quite distinct from the secular music and dance. The religion of Yoruban origin is known as Lucumí or Regla de Ocha; the religion of Congolese origin is known as Palo, as in palos del monte.[11] There are also, in the Oriente region, forms of Haitian ritual together with its own instruments and music.
In Lucumi ceremonies, consecrated batá drums are played at ceremonies, and gourd ensembles called abwe. In the 1950s, a collection of Havana-area batá drummers called Santero helped bring Lucumí styles into mainstream Cuban music, while artists like Mezcla, with the lucumí singer Lázaro Ros, melded the style with other forms, including zouk.
The Congo cabildo uses yuka drums, as well as gallos (a form of song contest), makuta and mani dances. The latter is related to the Brazilian martial dance capoeira

#african#afrakan#kemetic dreams#africans#brownskin#brown skin#afrakans#african culture#fitness#afrakan spirituality#afro cuban music#afro cuban#igbo#yoruba#congo#african music
195 notes
·
View notes
Text
"One of the most important realities of American life is this: No nation can fully undo the effects of 345 years of state-sanctioned bigotry — from slavery to Jim Crow — in 59 years. The time period between the arrival of the first slaves on colonial shores in 1619 and the abolition of legalized discrimination with the passage of the Civil Rights Act in 1964 is simply too long, the discrimination too ingrained and the distortion of society too great to wave the wand of legal and cultural reform and quickly realize the dream of American equality."
--David French, Opinion Columnist for the The New York Times
553 notes
·
View notes
Note
Apologies if this is a somewhat irritating or strange question,but you think the claims of Robespierre opposing the abolition of slavery hold any weight? I've been attempting to research this myself and I often encounter information that seems contradictory in regards to both possibilities.
There are people who researched this in more detail and provided receipts. I believe @lanterne wrote about it?
Robespierre was pro abolition of slavery. As early as 1791, when many were "but oh no, if we abolish slavery, our economy will suffer! The colonies will be ruined!", Robespierre was like "then let them be ruined. Slavery is wrong and should not exist."
It is true though that the French government took its sweet time getting to the abolition of the slavery. It happened in february 1794, and only after the people of Haiti (Saint-Domingue) liberated themselves (or was at least clear that the slave uprising was successful). So they could have done it sooner, especially since the Convention was, nominally at least, all against slavery and pro abolition.
As I understand, the whole "Robespierre was against the abolition of the slavery" was due to an agent from Saint-Domingue (himself black or mixed) claiming that the abolition should not happen at that moment? So deputies (including Robespierre) took his word and acted on it, except that was a plant by the anti-abolition crowd and they later realized? I am not sure. Like I said, I am not an expert on what happened, but I know there was a stalling due to some misinformation.
If anyone knows more, please share! There were numerous posts about this exact thing with receipts but I can't remember what was said exactly and I can't find any of them.
78 notes
·
View notes
Text
was thinking about this

To be in "public", you must be a consumer or a laborer.
About control of peoples' movement in space/place. Since the beginning.
"Vagrancy" of 1830s-onward Britain, people criminalized for being outside without being a laborer.
Breaking laws resulted in being sentenced to coerced debtor/convict labor. Coinciding with the 1830-ish climax of the Industrial Revolution and the land enclosure acts (factory labor, poverty, etc., increase), the Metropolitan Police Act of 1829 establishes full-time police institution(s) in London. The "Workhouse Act" aka "Poor Law Amendment Act of 1834" forced poor people to work for a minimum number of hours every day. The Irish Constabulary of 1837 sets up a national policing force and the County Police Act of 1839 allows justices of the peace across England to establish policing institutions in their counties (New York City gets a police department in 1844). The major expansion of the "Vagrancy Act" of 1838 made "joblessness" a crime and enhanced its punishment. (Coincidentally, the law's date of royal assent was 27 July 1838, just 5 days before the British government was scheduled to allow fuller emancipation of its technical legal abolition of slavery in the British Caribbean on 1 August 1838.)
---
"Vagrancy" of 1860s-onward United States, people criminalized for being outside while Black.
Widespread emancipation after slavery abolition in 1865 rapidly followed by the outlawing of loitering which de facto outlawed existing as Black in public. Inability to afford fines results in being sentenced to forced labor by working on chain gangs or prisons farms, some built atop plantations.
---
"Vagrancy" of 1870s-onward across empires, people criminalized for being outside while being "foreign" and also being poor generally.
Especially from 1880-ish to 1918-ish, this was an age of widespread mass movement of peoples due to the land dispossession, poverty, and famine induced by global colonial extraction and "market expansion" (Scramble for Africa, US "American West", nation-building, conquering "frontiers"), as agricultural "revolutions" of imperial monoculture cash crop extraction resulted in ecological degradation, and as major imperial infrastructure building projects required a lot of vulnerable "mobile" labor. This coincides with and is facilitated by new railroad networks and telegraphs, leading to imperial implementation or expansion of identity documents, strict work contracts, passports, immigration surveillance, and border checkpoints.
All of this in just a few short years: In 1877, British administrators in India develop what would become the Henry Classification System of taking and keeping fingerprints for use in binding colonial Indians to legal contracts. That same year during the 1877 Great Railroad Strike, and in response to white anxiety about Black residents coming to the city during Great Migration, Chicago's policing institutions exponentially expand surveillance and pioneer "intelligence card" registers for tracking labor union organizing and Black movement, as Chicago's experiments become adopted by US military and expanded nationwide, later used by US forces monitoring dissent in colonial Philippines and Cuba. Japan based its 1880 Penal Code anti-vagrancy statutes on French models, and introduced "koseki" register to track poor/vagrant domestic citizens as Tokyo's Governor Matsuda segregates classes, and the nation introduces "modern police forces". In 1882, the United States passes the Chinese Exclusion Act. In 1884, the Ottoman government enacts major "Passport Nizamnamesi" legislation requiring passports. In 1885, the racist expulsion of the "Tacoma riot".
Punished for being Algerian in France. Punished for being Chinese in San Francisco. Punished for being Korean in Japan. Punished for crossing Ottoman borders without correct paperwork. Arrested for whatever, then sent to do convict labor. A poor person in the Punjab, starving during a catastrophic famine, might be coerced into a work contract by British authorities. They will have to travel, shipped off to build a railroad. But now they have to work. Now they are bound. They will be punished for being Punjabi and trying to walk away from Britain's tea plantations in Assam or Britain's rubber plantations in Malaya.
Mobility and confinement, the empire manipulates each.
---
"Vagrancy" amidst all of this, people also criminalized for being outside while "unsightly" and merely even superficially appearing to be poor. San Francisco introduced the notorious "ugly law" in 1867, making it illegal for "any person, who is diseased, maimed, mutilated or deformed in any way, so as to be an unsightly or disgusting object, to expose himself or herself to public view". Today, if you walk into a building looking a little "weird" (poor, Black, ill, disabled, etc.), you are given seething spiteful glares and asked to leave. De facto criminalized for simply going for a stroll without downloading the coffee shop's exclusive menu app.
Too ill, too poor, too exhausted, too indebted to move, you are trapped. Physical barriers (borders), legal barriers (identity documents), financial barriers (debt). "Vagrancy" everywhere in the United States, a combination of all of the above. "Vagrancy" since at least early nineteenth century Europe. About the control of movement through and access to space/place. Concretizing and weaponizing caste, corralling people, anchoring them in place, extracting their wealth and labor.
You are permitted to exist only as a paying customer or an employee.
#get to work or else you will be put to work#sorry#intimacies of four continents#tidalectics#abolition
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
I just can't do with them
This person speaks like the Grievous POV in Labyrinth of Evil, when he speaks a lot about this events, is non-existent and this book directly preceeded Revenge of the Sith in Legends continuity. So, only magazine article, you know, it does not mean anything, and Jedi are completely innocent about it!
While I do not condone Grievous methods neither in Canon, nor in Legends, the Kaleesh invasion on Huk would not happen if not the Yam'Ree did not attack Kalee first and did not attempt to enslave his population. Where was the Jedi than? Where were they after it, when Kalee outright started to starve?
And it is not the first time when Jedi in Legends failed to help those who were in need.
There was Jabiim. This page when Stratus clearly sums up everything went wrong with the planet.

The planet used to be faithful Republic world, but neither Republic, nor Jedi helped them when they needed it the most. The result? Total majority of people of Jabiim supporting Stratus and CIS. Yep, maybe Stratus is pushing revanshist propaganda, but it would not have made the same impact of people of Jabiim, if there were not quite an objective conditions.
There was Findar with his population being enslaved by criminal overlords for more than ten years. Add the fact, the same overlords who conducted the experiments with memory wiping on people, and only the fact that Qui-Gon Jinn and Obi-Wan Kenobi (who were heading to another mission) crash-landed here saved the findians from future nightmare.
The probability theory says that when one thing happens is the accident, coincidence, when it happens twice, and sistem when it happens thrice. So, make you own conclusions.
And even the argument about it no longer being canon doesn't really works. In Canon, Jedi outright ignored Czerka corporation literally enslaving its workers(what she by this time did not do in Legends). This exchange between Qui-Gon Jinn and Yoda really sums up what is wrong with Order right now.
«Qui-Gon had been too young to see the cracks in the bravado—the pain that all Dooku’s guidance and all Rael’s accomplishments had never been able to erase. “That he would effectively sell citizens into slavery—” “Grievous, this is,” Yoda agreed. Into Qui-Gon’s mind came the echo of Rahara Wick: What’s the point of having a Republic in the first place? “We should put an end to it,” he said. Yoda shook his head. “Not ours to decide, the fate of the treaty is—” “Not the treaty. Slavery.” Qui-Gon folded his hands in front of him, allowing the robes to obscure them—the most formal way in which a Jedi could address another. “Why do we allow this barbarism to flourish? The Republic could use its influence to promote abolition in countless systems where the practice flourishes. How can we fail to do this?” <.....> Qui-Gon’s patience began to wear thin. “This isn’t about imposing human ethics on nonhuman species. This is something humans do to one another, an atrocity we should put an end to.” “We? Not the chancellor, not the Galactic Senate, not even the people of the Republic, but the Jedi?” Yoda thumped his gimer stick on the floor. “Want to rule, do you? Dangerous this is, in one who would join the Council. Dangerous it is in any Jedi.” Qui-Gon knew all of this. On one level, he accepted the truth of it. On the other—“If we don’t stand for the right, what do we do? Why do we exist?”»
From the same book we know that Czerka corporation acts even worse, than IRL Russian nobility up to 1649 or American slave-owners. Their property can not be considered free unless they buy themselves out of it, no matter how long they were absent from Czerka's control(as Rahara case clearly indicates). Up to ratification of Council Code of 1649, Russian serfs who ran away from their masters can be declared as "wanted" only for 10 years and were considered free after that. The black slaves could use the Underground Railroad and get to the North or another country when slavery was illegal.
It's not a case for Czerka. They will never let their former property go, no matter how many time passed since the escape, or where their former subject had gone.
And Jedi stand and allow it to happen. Doing their part in Republic, yep, Yoda?
"Many ways there are of serving the right,” Yoda replied. “We work within our mandates, and there do as much good as we can. To do otherwise, to substitute our judgment for that of the Republic, is to repeat the mistakes of the past.” So instead we make different mistakes in the present? Qui-Gon kept this to himself."
And also, to what mistakes of the past Yoda is referring to? What mistakes are deemed worse than allowing slavery to exist? Even in the Legends the Jedi having closest ties and basically control of Republic(to some level that it can be considered religios teocracy) allowed them to defeat Siths and practically destroy them except one. And even then, after the victory they stepped down(too far IMO). What thing could be called mistake here?
I am gonna specify: the Republic had a lot of problems that have a need to be fixed, but there was one thing that made this state more durable or competent is having Jedi, but not as the «Galactic therapists»(therapy can not be forced onto living being without his desire, if it is not a conversion therapy), but as the protection from arbitariness and exploitation. If some planet was endangered, they could have contacted Jedi and ask for help. The main problem of Order in this case is the fact they did not do enough for the people they should have protected, blindly trusted some reports and never attempted to search for the truth beyond it(Kalee, Galidraan and Pijal to lesser extent) and also hadn't seemed to have their own outposts for survelliance or interference, or some rapid reaction forces since Ruusan reform in Legends(1000 years)/«Starlight Beacon»'s destruction in Canon(200 years). I can not call it anything else but shooting yourself in the foot.
The Jedi should have been more autonomous, should have had their own information information service, outposts in the Galaxy and forces of reaction. It was not necassary to cut their ties with Republic entirely, but distance themselves from Senate, so people wouldn't think that Jedi «blindly serve the corrupt Senate».
Jedi Uncrits: «But the Jedi are only 10.000 for all of Galaxy, they could not do it!»
Well, in this case it's better to drop your practice to recruit children under five(as Rael Aveross's case indicates), abandoning tons of kids and youths elder than this age(like Caris in Legends). Or what, they will not blindly accept everything Council says? Sorry for the Council.
20 notes
·
View notes
Photo
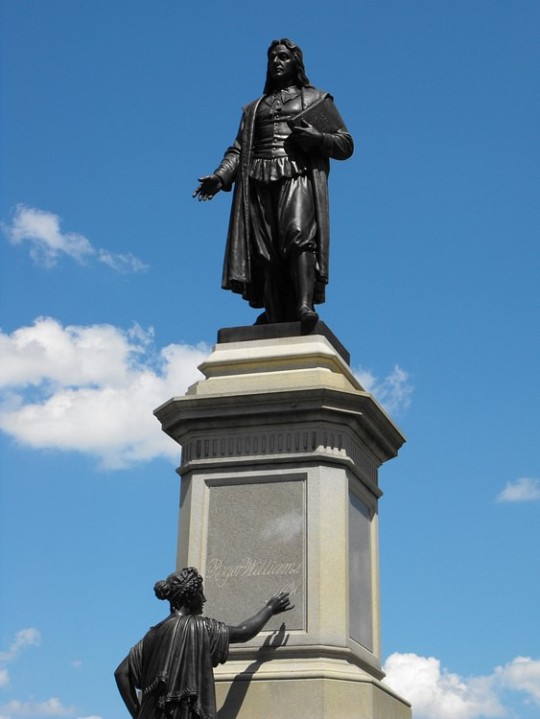

Roger Williams
Roger Williams (l. 1603-1683 CE) was a Puritan separatist minister best known for his conflict with both the Plymouth Colony and Massachusetts Bay Colony in 1633-1635 CE, resulting in his banishment and founding of the colony of Providence, Rhode Island. Williams believed that the clergy of both Plymouth and Massachusetts Bay were corrupt in continuing to adhere to the concept of one's deeds as an important aspect of spiritual salvation rather than acknowledging the biblical precept that only God's grace grants salvation (Romans 8:32, Ephesians 2:8). Further, he claimed, these churches were still aligned with the basic policies of the Anglican Church they had supposedly rejected.
Williams is also well-known as an advocate for the separation of church and state (claiming that politics poisoned religious practice and belief), complete religious freedom, the abolition of slavery in the colonies of North America, and respect for Native Americans. One of his criticisms of the colonies of New England was that they felt free to take land from the Native Americans without payment. When he founded Providence, he paid the Narragansett tribe a fair price for the land.
Providence became the first successful liberal colony in New England which was not informed by Puritan ideals and theology. Anyone of any religion or ethnicity was welcome to settle there as long as they recognized the fundamental human right of what Williams called the "liberty of conscience" – the freedom to express one's self - especially in religious matters, without fear of persecution or reprisal. Providence was scorned by the Massachusetts Bay Colony, especially, as populated by riffraff, lunatics, and heretics but became one of the fastest-growing settlements in the region under Williams' vision and guidance. In the modern day, parks, schools, and memorials around Rhode Island are named in his honor.
Early Life & Migration
Roger Williams was born, probably in London, England, in 1603 CE, the son of a merchant, James Williams, and wife Alice. Records of his early life were lost in the Great Fire of London in 1666 CE. As a young man, he was educated first at Charterhouse School and then Cambridge University's Pembroke College where he mastered a number of languages including Dutch, French, Greek, Hebrew, and Latin. He was intensely interested in religious matters from a young age and studied to become an Anglican cleric. At Cambridge, however, he was drawn to Puritan theology and practice which would later set him at odds with the Anglican Church.
The Anglican Church, although founded in opposition to Catholicism, still retained a number of Catholic aspects in its organization, worship service, and beliefs. The Puritans were Anglicans who objected to any Catholic influences or observances in the Church and wished to 'purify' it, bringing it in line with the simple practices and beliefs of the first Christian community as depicted in the biblical Book of Acts. The more radical Puritans were known as separatists – those who felt the Anglican Church was wholly corrupted by Catholic influences and separated themselves from it completely – and, in time, Williams aligned himself with this theology and belief.
During his years at Cambridge, Williams was apprenticed to the famous jurist Sir Edward Coke (l. 1552-1634 CE), an independent and courageous thinker whose insistence on the concept of equality before the law brought him into conflict with the monarchy. Coke's unwavering stand for justice, as well as his practice of regularly speaking out against policies or even laws he considered unjust or inequitable, significantly influenced Williams' outlook and later actions.
The Anglican Church had replaced the pope with the English monarch as its head and so any criticism of the Church was considered treason against the crown. Throughout the reign of James I of England (1603-1625 CE), Puritans who voiced dissent were persecuted, fined, and jailed, some even executed, and under Charles I of England (r. 1625-1649 CE), these persecutions continued. Recognizing that England was no longer safe for an outspoken Puritan separatist, Williams left with his wife Mary in 1630 CE.
Continue reading...
29 notes
·
View notes
Text
shut up about southern hemisphere horse birthday shut up about clown day shut up about yaoi day shut up about international girlfriends day shut up shut up shut up
it is emancipation day.
today is the day in 1834 when the slavery abolition act of the united kingdom came into effect and 'abolished' slavery, transitioning into apprenticeship, in which formerly enslaved people would now have to work 40 hours a week without pay for the same people they were 'freed' from. 4 years later almost to the day, apprenticeship was ended early and slavery was actually abolished.
163 notes
·
View notes
Text
Happy Emancipation Day!
Here's a short write up I did about Emancipation Day for my local grassroots mutual aid collective. This will unfortunately be focused primarily on Canada because our area of influence is more local than international. Please be sure to educate yourself on what this day means in your region!
What is the Slave Abolition Act of 1833?
The Slave Abolition Act of 1833 was a British law that ended slavery in most British colonies, freeing over 800,000 enslaved Africans in the Caribbean, South Africa, and Canada. The law, approved on August 28, 1833, took effect on August 1, 1834. It did not immediately apply to territories controlled by the East India Company, Ceylon, or Saint Helena; these exceptions were removed in 1843.
Earlier, in 1793, John Graves Simcoe, the first Lieutenant Governor of Upper Canada (now Ontario), had passed an Act Against the importation of new slaves. This law promised freedom to children born to enslaved women at age twenty-five, but it did not free existing slaves. The Slavery Abolition Act of 1833 later replaced this law, ending slavery across most of the British Empire.
Did it really free the slaves?
The Slavery Abolition Act had its flaws. It only freed those enslaved under age six. Older individuals were classified as 'apprentices' and had to work 40 hours a week without pay as “compensation” to their former slave owners. Full emancipation was not achieved until July 31, 1838.
While Canada often expresses pride in its relatively lesser involvement in slavery when compared to other British colonies, it wasn't the first to end it. The Independent Republic of Vermont was the first in North America to abolish slavery with its 1777 constitution. This came 16 years before Upper Canada’s partial abolition in 1793. Vermont was quickly followed by states like Pennsylvania and Massachusetts, and the U.S. Congress banned slavery in future Midwest territories in 1787.
What is Emancipation Day? What does it mean?
On March 1, 2021, the Canadian House of Commons unanimously declared August 1 as Emancipation Day. This date marks the beginning of the partial abolition of slavery across British colonies in various countries.
Why is Emancipation Day important?
Neglecting acknowledgement of Emancipation Day allows Canada to evade its dark history and distort its legacy. We must hold governments accountable for the history of their crimes. It’s critical to confront the reality that slavery was a part of Canadian history and that its legacy continues to impact African Canadians today. While Canada often boasts about its role in the Underground Railroad and its “total” abolishment of slavery before the U.S, it must also face the uncomfortable truth of its own very real involvement in slavery. Emancipation Day is about confronting history with honesty. Acknowledging this day is essential for addressing past injustices and ensuring that future generations grasp the full, unfiltered truth of Canada's history, including the painful chapters that must not be forgotten or repeated.
Emancipation did not end the oppression of Black people in this country. For those who suffered under centuries of slavery, emancipation should have signaled that Canada would become a place of respect and opportunity for their descendants. Instead, Black Canadians still face racism, discrimination, and prejudice in education, healthcare, housing, and the justice system.
The history of slavery and the stories of enslaved people and their descendants have historically been confined to Black communities. Recognition of this day on a national scale not only helps to validify the black experience, but also to clearly acknowledge our refusal to return to these oppressive norms. Integrating this crucial part of Canadian history into the education of all our children is vital for addressing anti-Black racism and its ongoing impact in our society to this day. A necessary step toward justice is issuing an official apology to the descendants of enslaved people, bringing this issue to the forefront of Canadian awareness and starting the path toward meaningful reparations.
Emancipation day allows us the opportunity to use the past to reflect upon the present. We must acknowledge the deep, ongoing trauma from slavery and segregation as the foundation of anti-Black racism that is still rampant in our justice system today. It is only through this acknowledgement that we can begin to form a dialogue which sees black people as an important, intrinsic part of Canadian history at all times, not just during black history month.










#blacklivesmatter#emancipation#radical education#mutual aid#police abolition#history#pagan#paganism#racial justice#social justice#black history#black indigenous#canadian history#black lives matter#revolution
22 notes
·
View notes