#romano celtic
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Romano-British Decorated Disc Brooch, Lancaster City Museum
#romans#roman#romano celtic#archaeology#designs#symbols#ancient cultures#ancient living#ancient crafts#metalwork#celtic#roman brooch#roman empire
45 notes
·
View notes
Text
Did the ancient Celts really paint themselves blue?
Part 1: Brittonic Body Paint




Clockwise from top left: participants in the Picts Vs Romans 5k, a 16th c. painting of painted and tattooed ancient Britons, Boudica: Queen of War (2023), Brave (2012).
The idea that the ancient and medieval Insular Celts painted themselves blue or tattooed themselves with woad is common in modern culture. But where did this idea come from, and is there any evidence for it? In this post, I will examine the evidence for the use of body paint among the ancient peoples of the British Isles, including both written sources and archaeology.
For this post, I am looking at sources pertaining to any ethnic group that lived in the British Isles from the late Iron Age through the early Roman Era. (Later Roman and Medieval sources will be discussed in part 2.) The relevant text sources for Brittonic body paint date from approximately 50 BCE to 100 CE. I am including all British Isles cultures, because a) determining exactly which Insular culture various writers mean by terms like ‘Briton’ is sometimes impossible and b) I don’t want to risk excluding any relevant evidence.
Written Sources:
The earliest source for our notion of blue Celts is Julius Cesar's Gallic War book 5, written circa 50 BCE. In it he says, "Omnes vero se Britanni vitro inficiunt, quod caeruleum efficit colorem, atque hoc horridiores sunt in pugna aspectu," which translates as something like, "All the Britons stain themselves with woad, which produces a bluish colouring, and makes their appearance in battle more terrible" (translation from MacQuarrie 1997). Hollywood sometimes interprets this passage as meaning that the Celts used war paint, but Cesar says that all Britons colored themselves, not just the warriors. The blue coloring just had the effect (on the Romans at least) of making the Briton warriors look scary. The verb inficiunt (infinitive inficio) is sometimes translated as 'paint', but it actually means dye or stain. The Latin verb for paint is pingo (MacQuarrie 1997).
The interpretation of vitro as woad is supported by Vitruvius' statements in De Architectura (7.14.2) that vitrum is called isatis by the Greeks and can be used as a substitute for indigo. Isatis is the Greek word for woad; this is where we get its modern scientific name Isatis tinctoria. Woad and indigo both contain the same blue dye pigment, hence woad can be used as a substitute for indigo (Carr 2005, Hoecherl 2016). The word vitro can also mean 'glass' in Latin, but as staining yourself with glass doesn't make much sense, it's more commonly interpreted here as woad (Carr 2005, Hoecherl 2016, MacQuarrie 1997). I will revisit this interpretation during my discussion of the archaeological evidence.
Almost a century later in De situ orbis, Pomponius Mela says that the Britons "whether for beauty or for some other reason — they have their bodies dyed blue," (translation by Frank E. Romer) using virtually identical language to Cesar, "vitro corpora infecti" (Lib. III Cap. VI p. 63). Pomponius Mela may have copied his information from Cesar (Hoecherl 2016).
Then in 79 CE, Pliny the Elder writes in Natural History book 22 ch 2, "There is a plant in Gaul, similar to the plantago in appearance, and known there by the name of "glastum:" with it both matrons and girls among the people of Britain are in the habit of staining the body all over, when taking part in the performance of certain sacred rites; rivalling hereby the swarthy hue of the Æthiopians, they go in a state of nature." In spite of the fact that glastum means woad in the Gaulish and Celtic languages, Pliny seems to think glastum is not woad. In Natural History book 20 ch 25, he describes different plant which is almost certainly woad, a “wild lettuce” called "isatis" which is "used by dyers of wool." (Woad is a well-known source of fabric dye (Speranza et al 2020)).
Of course, "rivaling the swarthy hue of the Æthiopians" doesn't necessarily mean blue. Pliny seems to think Ethiopians literally have coal-black skin (Latin ater). Additionally, Pliny is taking about a ritual done by women, where Cesar was talking about a practice done by everyone. Are they talking about 2 different cultural practices, or is one of them reporting misinformation? Or are both wrong? Unfortunately, there is no way to know.
The Roman poets Ovid, Propertius, and Marcus Valerius Martialis all make references to blue-colored Britons (Carr 2005), but these are literary allusions, not ethnographic reports. As such, they don't really provide additional evidence that the Britons were actually dyeing or painting themselves blue (Hoecherl 2016). These poetic references merely demonstrate that the Romans believed that the Britons were.
In the sources that come after Pliny the Elder, starting in the 3rd century, there is a shift in the terms used. Instead of inficio which means to dye or stain (Hoecherl 2016), probably a temporary application of color to the surface of the skin, later sources use words like cicatrices (scars) and stigma/stigmata (brand, scar, or tattoo) (Hoecherl 2016, MacQuarrie 1997, Carr 2005) which suggest a permanent placement of pigment under the skin, i.e. a tattoo. This evidence for tattooing will be discussed in a second post.
Discussion:
Although the Romans clearly believed that the Britons were coloring themselves with blue pigment, that doesn't necessarily mean that Julius Cesar, Pomponius Mela, or Pliny the Elder are reliable sources.
In the sentence before he claims that all Britons color themselves blue, Julius Cesar says that most inland Britons "do not sow corn [aka grain], but live on milk and flesh and clothe themselves in skins." (translation from MacQuarrie 1997). This is demonstrably false. Grains like wheat and barley and storage pits for grain have been found at multiple late Iron Age sites in inland Britain (van der Veen and Jones 2006, Lightfood and Stevens 2012, Lodwick et al 2021). This false characterization of Insular Celts as uncivilized savages would continue to show up more than a millennium later in English descriptions of the Irish.
Pomponius Mela, in addition to believing in blue-dyed Britons, also believed that there was an island off the coast of Scythia inhabited by a race called the Panotii "who for clothing have big ears broad enough to go around their whole body (they are otherwise naked)" (Chorographia Bk II 3.56 translation from Romer 1998). Pliny the Elder also believed in Panotii.

15th-century depiction of a Panotii from the Nuremberg Chronicle. Was Celtic body paint as real as these guys?
The Roman historians Tacitus and Cassius Dio make no mention of body paint in their coverage of Iron Age British history (Hoecherl 2016). Their silence on the subject suggests that, in spite of Cesar's claim that all Britons colored themselves blue, the custom of body staining or painting was not actually widespread.
Considering all of these issues, is any of this information trustworthy? Based on my experience studying 16th c. Irish dress, even bigoted sources based on second-hand information often have a grain of truth somewhere in them. Unfortunately, exactly which bit is true is hard to identify without other sources of evidence, and this far in the past we don't have much.
Archaeological Evidence:
There are no known artistic depictions of face paint or body art from Great Britain during this time period. There are some Iron Age continental European coins that show what may be face painting or tattoos, but no such images have been found on British coins (Carr 2005, Hoecherl 2016).
In order for the Britons to have dyed themselves blue, they needed to have had blue pigment. Woad is not native to Great Britain (Speranza et al 2020), but Woad seeds have been found in a pit at the late Iron Age site of Dragonby in England, so the Britons had access to woad as a potential pigment source in Julius Cesar's time (Van der Veen et al 1993). Egyptian blue is another possible source of blue pigment. A bead made of Egyptian blue was found at a late Bronze Age site in Runnymede, England. Pieces of Egyptian blue could have been powdered to produce a pigment for body paint. (Hoecherl 2016). Egyptian blue was also used by the Romans to make blue-colored glass (Fleming 1999). Perhaps this is what Cesar meant by 'vitro'.


Potential sources of blue: Isatis tinctoria (woad) leaves and a lump of Egyptian blue from New Kingdom Egypt
Modern experiments have found that reasonably effective body paint can be made by mixing indigo powder either with water, forming a runny paint which dries on the skin, or with beef drippings, forming a grease paint which needs soap to be removed (Carr 2005, reenactor description). The second recipe is very similar to one used by modern east African argo-pastoralists which consists of ground red ocher mixed with cow fat (unpublished interview*).
Finding blue pigment on the skin of a bog body might confirm Julius Cesar's claim, but unfortunately, the results here are far from conclusive. To my knowledge, Lindow II is the only British bog body that has been tested for indigotin, the dye pigment in woad and indigo. No indigotin was found (Taylor 1986).
The late Iron Age-early Roman era bog bodies Lindown II and Lindown III show some evidence of mineral-based body paint (Joy 2009, Giles 2020). Both of them have elevated levels of calcium, aluminum, silicon, iron, and copper in their skin. Lindow III also has elevated levels of titanium. The calcium levels may simply be the result the of the bog leeching calcium from their bones. Some researchers have suggested that the other elements may be from mineral-based paints applied to the skin. The aluminum and silicon may be from clay minerals. The iron and titanium could be from red ocher. The copper could be from malachite, azurite, or Egyptian blue (CuCaSiO4), pigments that would give a green or blue color (Pyatt et al 1995, Pyatt et al 1991). These elements may have other sources however, and are not present in large enough amounts to provide definitive proof of body paint (Cowell and Craddock 1995, Giles 2020). Testing done on the early Roman Era (80-220 CE) Worsley Man has found no evidence of mineral-based paint (Giles 2020).
One final type of artifact that provides some support for Julius Cesar's claim is a group of small cosmetic grinders from late Iron Age-Roman Era Britain. These mortar and pestle sets are found almost exclusively in Great Britain and are of a style which appears to be an indigenous British development. They are distinctly different from the stone palettes used by the Romans for grinding cosmetics which suggests that these British grinders were used for a different purpose than making Roman-style makeup (Carr 2005). Archaeologist Gillian Carr has suggested that these British grinders might have been used by the Britons for grinding, mixing, and applying a woad-based body paint (Carr 2005).



Left and center: Cosmetic grinder set from Kent. Right: Cosmetic mortar from Staffordshire. images from Portable Antiquities Scheme under CC attribution license
The mortars have a variety of styles of decoration, but the pestles (top left and top center) typically feature a pointed end which could be used for applying paint to the skin (Carr 2005). The grinders are quite small, (most are less than 11 cm (4.5 in) long), making them better suited to preparing paint for drawing small designs rather than for dyeing large areas of skin (Carr 2005, Hoecherl 2016).
Conclusions:
Admittedly, this post is a bit off-topic, since the Irish are not mentioned, but dress history is also about what people did not wear. Hollywood has a tendency to overgeneralize and expropriate, so I want to be clear: There is no known evidence that the ancient Irish used body paint.
So, who did? For the reasons I have already discussed, I don't consider any of the Roman writers particularly trustworthy, but I think the following conclusions are plausible:
A least a few people in Great Britain dyed/stained or painted their bodies between circa 50 BCE and perhaps 100 CE, after which mentions of it end. Written sources from c. 200 CE on talk about tattoos rather than painting or staining. The custom of body dyeing/painting may have started as something practiced by everyone and later changed to something practiced by just women.
None of the writers mention any designs being painted, but Julius Cesar's description could encompass designs or solid area of color. Pliny, on the other hand, states that women were coloring their entire bodies a solid color. The dye was probably blue, although Pliny implies it was black. (I know of no plants in northern Europe that resemble plantago and produce a black dye. I think Pliny was reporting misinformation.)
Archaeological evidence and experimental recreations support the possibility that woad was the source of the pigment, but they cannot confirm it. Data from bog bodies indicate that a mineral pigment like azurite or Egyptian blue is more likely, but these samples are too small to be conclusive.
The small cosmetic grinders are suitable for making designs which might match Cesar and Mela's descriptions, but not Pliny's description of all-over body dyeing.
*Interview with a Daasanach woman I participated in while doing field school in Kenya in 2015.
Leave me a tip?
Bibliography:
Carr, Gillian. (2005). Woad, Tattooing and Identity in Later Iron Age and Early Roman Britain. Oxford Journal of Archaeology 24(3), 273–292. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-0092.2005.00236.x
Cowell, M., and Craddock, P. (1995). Addendum: Copper in the Skin of Lindow Man. In R. C. Turner and R. G. Scaife (eds) Bog Bodies: New Discoveries and New Perspectives (p. 74-75). British Museum Press.
Fleming, S. J. (1999). Roman Glass; reflections on cultural change. University of Pennsylvania Museum of Archaeology and Anthropology, Philadelphia. https://www.google.com/books/edition/Roman_Glass/ONUFZfcEkBgC?hl=en&gbpv=0
Giles, Melanie. (2020). Bog Bodies Face to face with the past. Manchester University Press, Manchester. https://library.oapen.org/viewer/web/viewer.html?file=/bitstream/handle/20.500.12657/46717/9781526150196_fullhl.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
Hoecherl, M. (2016). Controlling Colours: Function and Meaning of Colour in the British Iron Age. Archaeopress Publishing LTD, Oxford. https://www.google.com/books/edition/Controlling_Colours/WRteEAAAQBAJ?hl=en&gbpv=0
Joy, J. (2009). Lindow Man. British Museum Press, London. https://archive.org/details/lindowman0000joyj/mode/2up
Lightfoot, E., and Stevens, R. E. (2012). Stable Isotope Investigations of Charred Barley (Hordeum vulgare) and Wheat (Triticum spelta) Grains from Danebury Hillfort: Implications for Palaeodietary Reconstructions. Journal of Archaeological Science, 39(3), 656–662. doi:10.1016/j.jas.2011.10.026
Lodwick, L., Campbell, G., Crosby, V., Müldner, G. (2021). Isotopic Evidence for Changes in Cereal Production Strategies in Iron Age and Roman Britain. Environmental Archaeology, 26(1), 13-28. https://doi.org/10.1080/14614103.2020.1718852
MacQuarrie, Charles. (1997). Insular Celtic tattooing: History, myth and metaphor. Etudes Celtiques, 33, 159-189. https://doi.org/10.3406/ecelt.1997.2117
Pomponius Mela. (1998). De situ orbis libri III (F. Romer, Trans.). University of Michigan Press. (Original work published ca. 43 CE) https://topostext.org/work/145
Pyatt, F.B., Beaumont, E.H., Buckland, P.C., Lacy, D., Magilton, J.R., and Storey, D.M. (1995). Mobilization of Elements from the Bog Bodies Lindow II and III and Some Observations on Body Painting. In R. C. Turner and R. G. Scaife (eds) Bog Bodies: New Discoveries and New Perspectives (p. 62-73). British Museum Press.
Pyatt, F.B., Beaumont, E.H., Lacy, D., Magilton, J.R., and Buckland, P.C. (1991) Non isatis sed vitrum or, the colour of Lindow Man. Oxford Journal of Archaeology, 10(1), 61–73. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/227808912_Non_Isatis_sed_Vitrum_or_the_colour_of_Lindow_Man
Speranza, J., Miceli, N., Taviano, M.F., Ragusa, S., Kwiecień, I., Szopa, A., Ekiert, H. (2020). Isatis Tinctoria L. (Woad): A Review of Its Botany, Ethnobotanical Uses, Phytochemistry, Biological Activities, and Biotechnical Studies. Plants, 9(3): 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9030298
Taylor, G. W. (1986). Tests for Dyes. In I. Stead, J. B. Bourke and D. Brothwell (eds) Lindow Man: the Body in the Bog (p. 41). British Museum Publications Ltd.
Van der Veen, M., and Jones, G. (2006). A Re-analysis of Agricultural Production and Consumption: Implications for Understanding the British Iron Age. Vegetation History and Archaeobotany, 15 (3), 217–228. doi:10.1007/s00334-006-0040-3 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/27247136
Van der Veen, M., Hall, A., and May, J. (1993). Woad and the Britons painted blue. Oxford Journal of Archaeology, 12(3), 367-371. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/249394983
#cw anti-black racism#romano-british#period typical bigotry#iron age#bog bodies#no photographs of bog bodies though#roman era#ancient celts#celtic#woad#insular celts#anecdotes and observations#body paint#brittonic#archaeology
39 notes
·
View notes
Text
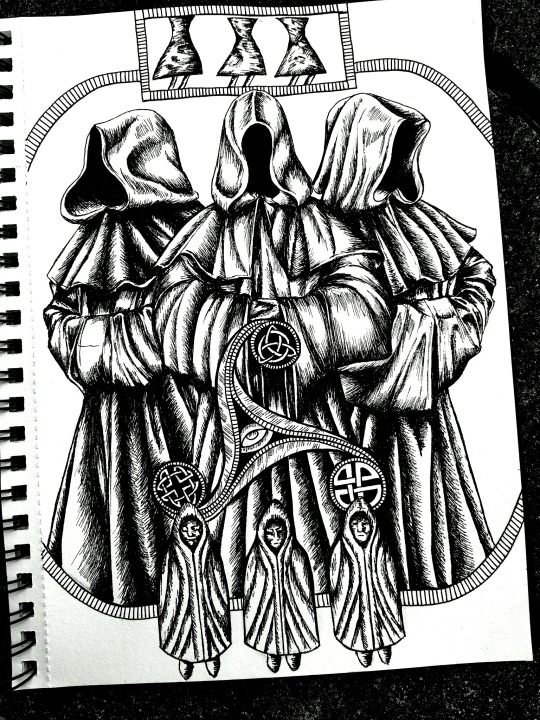

The Hooded Ones
'The Genii Cucullati are otherworldly entities whose image appears throughout Celtic Britain and Europe during the era of Roman domination. Genius means “a spirit” and a cucullus is a full-length hooded woollen robe. If they look more than a little like mediaeval monks, then this is because their successors also adopted this pragmatic attire. Thus the Genii Cucullati are literally the “hooded spirits.” In Britain they tend to be found in a triple deity form, which seems to be specific to the British representations.
No surviving documentation explains their identity or function. Instead what we know of them is pieced together from archaeological evidence and surviving inscriptions. They are thought to be guardian-type figures offering protection and sanctuary. Some scholars theorise that their hoods are an artistic motif indicating that the beings depicted are normally invisible, “slippery avoidance of being too-clearly defined, preferring instead to remain hidden/hooded/held in obscurity.”
Sometimes, however, the hoods appear very phallic. Sometimes the phallic imagery is overt: some Cucullati have removable hoods revealing the phallus hidden within. An exposed phallus traditionally serves as an amulet that promotes personal fertility, and magically averts death. It may also chase away ghosts and many evil spirits. Indeed, Genii Cucullati are often depicted carrying items indicating fertility, such as eggs and coin purses or martial prowess such as swords of daggers.
In Britain, their images appear in two key locations, the Cotswolds, and Northumbria – a direct correlation with the concentration of Black Monk sightings .Celtic Scholar Miranda Green wrote “The cult of the Genii Cucullati appears to have embraced profound and sophisticated belief systems” and that “such traditions did not wholly die after the coming of Christianity.” She believed that these hooded figures seem to have left an impression of supernatural power in our countryside.'
#Genii Cucullati#The hooded spirits#Romano-British culture#celtic mythology#my artwork#My pen and ink scribbles#paganblr
26 notes
·
View notes
Text
wanting to put my druidic path in a predominantly Celtic (continental Celtic as well as Old British to be exact.. sorry Irish Ancestors.) path so i've been through the help of the internet, coming up with constructed names for the roman deities, and coming up with syncretizations either through history or UPG. For Diana - Adruinna/Louna/Adsagsona Arduinna being the manifestation of the huntress and wilderness Diana, Louna being Luna, and Adsagsona (who we know very little of other than she's a cthonic witching goddess) for Trivia. As for Diana-Nemorensis, she appears to me as Nemetona. For Apollo (this is where it gets really messy) - Grannus is the name I call upon in regards to healing, and I call on Grannus alongside Sirona. In regards to Apollo as the Aradian-Lucifer, I feel that Lugus and Endovelicus both could fill that role. Though Lugus is more associated with Mercury that Apollo, I also tie Lugus to Lugh because of the light aspect. And Both Lucifer and Lugh are known to be mercurial trickster figures. In the fall I usually call to Apollo as Maponos. The Horned One - He's already VERY syncretic in terms of existence, so the name I call him varies based on how he shows himself to me. As the Folk Devil/Witches' Devil, he's usually Lupercus, who through demonization, is syncretized with Lucifer, but historically also Faunus. The Devil as Lightbearer to me is Cunamaglos (who i associate with Lupercus), Lugus, or Endovelicus (through Luciferian ties), and then as King of the Forest(both Folk Devil and Otherwise), Callirius. I dont really click with the name Cernunnos, but alternate spellings like Carneo or Carnonos, or Cernun, resonate a bit more. Cunamaglos also fills the role of my Wolf-Spirit deity in the masculine form. Fauna - Easy enough, Fauna is Druantia. Both the feminine form of the Horned One, and also the personification of Druidry as a whole. She IS Nature personified, and kinda blends with Diana-Nemorensis to form Nemetona. As a fertility and underworld goddess (an epithet i use for Druantia is Bone-Mother, giving her a Cthonic link), she can be Aeracura. Thus giving names such as Druantia, Druantia-Nemetona, and Druantia-Aeracura. Her cthonic form is also linked to her fertility aspect as well, since life and death are two sides of the same coin, which is fitting as Aeracura is historically a cthonic and fertility goddess. I haven't quite figured out where Venus stands in all this, though I'm sure I'll figure it out in time. I also plan to Incorperate Brigantia into my practice, since she's another form of Brigid. I also want to form a relationship with Andraste, and can respark my relationship with An Morrigan/The Raven Queen under the name Cathubodua, which is the first name of hers that really resonated with me. As for Aradia, I Personally don't view Aradia as an external spirit, I feel she exists WITHIN the practicioner, as I view Witches as all of Diana/Adsagsona's children. Though Aradia very well may have been a physical person or deity at some point. I feel Aradia works WITHIN us.
33 notes
·
View notes
Note
Know any good sources on Celtic (specifically Gaulish practices)? I know it’s not your area, but you seem like someone who might know some people who dabble in that sort of stuff. The area I live in has some celtic archeological sites, but sadly not much is known about the local religion or culture. I am trying to put together a Romano-Celtic hearth cult, but it’s difficult finding practices and deities that feel right.
Gaul is a larger Celtic area of Western Europe (modern-day France and parts of modern-day Belgium, Germany, and Northern Italy). I say this because the Celts, when invaded by Rome, took in a lot of Roman religion including Hellenic and (rarely) Kemetic beliefs as well. When the Celts did this, so did the Gauls.
If it helps at all, the specifics you're looking into is called Gallo-Roman, which is part of the larger Romano-Celtic area.
This selective acculturation manifested in several ways. One of the main ways we see this is with the melding of Greco-Roman deities with Gaulish (Celtic) deities. Gaulish epithets for Roman gods (Jupiter Poeninus) and Roman epithets for Gaulish gods (Lenus Mars). Roman gods were given Gaulish god partners (Mercury and Rosmerta & Apollo and Sirona). Towards the east of the Gauls, many mysteries were formed, including one for the Greek hero Orpheus, the Iranian (or Persian) god Mithras, and the Egyptian goddess Isis. In other words, a whole lot of syncretism.
When it came to the Gauls (and the Celts overall) a main part of their belief system was the heavy use of animal imagery. More specifically, zoomorphic deities. However, we see a lot more human-looking representations of the gods because the Romans (and Greeks) weren't too keen on the idea (see Greco-Egyptian).
As for specifically Gallo-Roman hearth religious beliefs, the Lares (Lar singular) is a good place to start. They're the equivalent of Agathos Daimon in Greek religion (Hellenism). Essentially, they're personal household deities that are connected to the hearth.
A majority of the information we have about the Gaelic culture and the eventual melding of the Gallo-Roman culture stems from two sources: artifacts and Julius Ceasar, who wrote all about in what we now call the "Commentarii de Bello Gallico". The gods that he mentions the Gauls worship (like Jupiter, Mercury, Mars, and Minerva) aren't really the Roman gods that the Gauls are worshipping at that time but rather the closest thing Ceasar can connect. For example, Caesar may say that the Gauls worshipped Mars, when in reality they were worshipping Lenus, a healing god that quickly became associated with Mars because of Caesar and the Roman Empire. However, not all of them were caught. Gobannus is the most well-known example we have, with him being the equivalent to the Roman god Vulcan or the Greek god Hephaestus and yet Caesar makes no comment on the Gaulish god.
One other thing, the specific time we are taking a look at was prior to the overtaking by the Anglos, Saxons, and Jutes (aka pre-Anglo-Saxon times). Because of this, Germanic (Norse) gods weren't known to these people yet. Odin, Thor, and Freyja were unknown to them at this point in time.
Other than that, the last thing I can give to you are articles and books that I stumbled upon that may pique your interest. I do recommend a couple of Wikipedia links, but just know that I recommend using Wikipedia as a jumping-off point. Hope this helps! :^)
Becoming Roman: the origins of provincial civilization in Gaul -- Greg Woolf https://archive.org/details/becomingromanori0000wool
The gods of the Celts -- Miranda Green https://archive.org/details/godsofceltsar00mira
Gallo-Roman Religious Sculptures -- A.N. Newell https://www.jstor.org/stable/640758
Fifth-Century Gaul: A Crisis of Identity? -- John Drinkwater & Elton Hugh https://www.loc.gov/catdir/samples/cam031/91018375.pdf
Caesar's Commentaries on the Gallic War: literally translated -- Frederick Holland Dewey, A.B. https://archive.org/details/caesarscommentar07caes
Category:Gaulish gods -- Wikipedia https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Category:Gaulish_gods
Category:Gaulish goddesses -- Wikipedia https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Category:Gaulish_goddesses
sources: https://bmcr.brynmawr.edu/1999/1999.10.34/ http://www.deomercurio.be/en/dii.html https://www.britannica.com/topic/Celtic-religion/The-Celtic-gods https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lares https://www.britannica.com/topic/Lar-Roman-deities https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gallo-Roman_culture https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gallo-Roman_religion
#ask#witch#witchcraft#witchblr#pagan#celtic#gaulish#roman#celtic deities#celtic pantheon#gaulish deities#gaulish pantheon#roman pantheon#roman gods#ancient rome#gallo-roman#romano-britain#romano-celtic#hearth
41 notes
·
View notes
Text

Creech Hill (nr. Bruton, Somerset, England). A photo taken using infra-red film by Simon Marsden for his book The Haunted Realm. The hill, the highest point for miles around, is said to be haunted by a ghost/bull-beggar that scares those traveling across it at night by rising from the ground and screaming before chasing them away. It was also once the site of small a Romano-Celtic temple (possibly dedicated to Mars) and a very early Christian cemetery. One of the people interred there was a 6-foot tall woman. Waaaay before that it may have the been the location of a much older religious site, as a circle of pits containing burnt red deer antler was also uncovered during the archaeological dig for the temple site.
#simon marsden#photograpy#infrared photography#history#folklore#ghost#somerset#england#romano-celtic#ancient rome
23 notes
·
View notes
Text

Romano-Celtic artefact of an unknown deity
Probably Roman-made, 1st Century AD
Found at Wimpole, Cambridgeshire
Copper Alloy
Figure is stylistically Celtic: oval eyes, hair and moustache and holding a torc
#english imagination#english culture#albion#england#art#english art#romano british#celtic art#celtic#old god#cambridgeshire#wimpole estate#copper#copper sculpture#roman artefact
1 note
·
View note
Text









Random PNGs, part 199
(1. "Nail Box" by Wayne Chisnall, 2. Egyptian townhouse model in limestone (800 BCE-CE200), 3. "Hey" by Ken Little, 4. "Vulture (Dragon)" by Leonora Carrington, 5. Vintage dragon eye sculpture, 6. Articulated powered dummy for testing space suits (1965), 7. Padlock lover's eye by Alexandra Dillon, 8. Wood and ceramic sculptures by Rita Miranda, 9. Romano-Celtic chariot attachment)
#png#pngs#transparent#transparents#moodboard#artboard#imageboard#collage#collages#sticker#stickers#trinkets#knight#199
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Tensions Behind The Scenes At Sunderland Could Lead To Dismissal
Sunderland manager Tony Mowbray remains on the chopping block despite yesterday’s 2-1 win over Rotherham United due to heightened tensions behind the scenes, according to Football Insider. The Black Cats picked up their first victory of the 2023/24 campaign on Saturday afternoon as Jobe Bellingham’s brace was enough to see off the valiant Millers and potentially ease some pressure off Mowbray in…

View On WordPress
#Blackburn Rovers#Celtic#championship news#efl championship#EFL Championship News#Fabrizio romano#Francesco Farioli#Rotherham United#sunderland#The Black Cats#Tony Mowbray
0 notes
Text
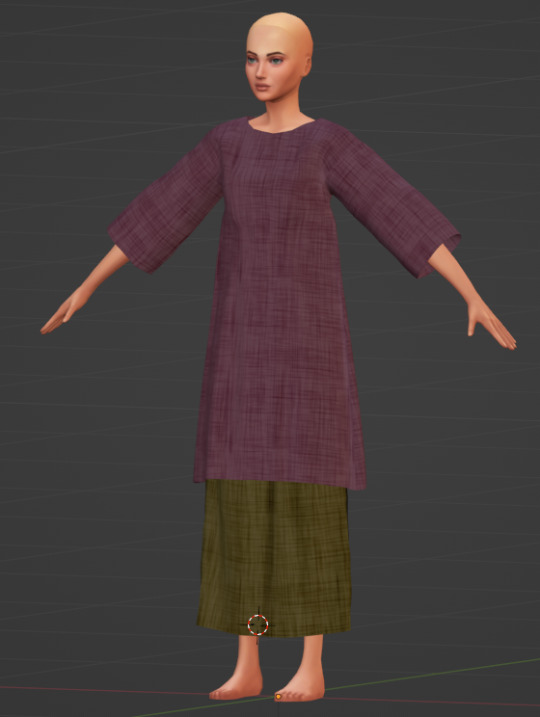






A bunch of random WIPs which will hopefully be finished soon (if my PC stops acting up the way it is now 🙄). Most of those things are almost ready for release, but there's always just this one tiny detail left to improve...
Details under the cut in case you're interested!
A loose-fitting Celtic tunic worn over an underdress, in 2 flavours: with narrow and wide sleeves. I made it over a year ago (!!!) and used a lot in my game, but somehow never was fully satisfied with the way those wide sleeves work - so, that's something to take a closer look at. I decided it also needs a new uv map (getting those sleeves out of the sleeves area), so that I could easily add short-sleeved and sleeveless variations. Also, age conversions, at least for a child. Also, tartan. And an overlay for mix&matching. And... 💀
A Roman ship from sketchfab, in 2 versions. This one is basically done, but one of the versions has an exploding shadow lod for some reason, so obviously I have to somehow fix it before release. No idea how though. By making a new package probably, I've heard that works 😅
A Romano-Viking Londinum house, also found on sketchfab, to be used as hood deco. Also was about to be released, but I decided it needs a decent uv map first, because the current one... oh boy. That means lots of seams marking. I think I'm ca. 75% done with this one.
Gallo-Roman earrings, based on a photo found on Pinterest. The mesh works perfectly fine, but I still need to work on the texture. Finding proper lighting settings should be the key - then it'll be just baking and voila!
A CK3 cape converted to TS4. A.k.a. my latest obsession 😉 Still needs some weights etc. tweaking, then age conversions, and then... Off to the next of the looted meshes! 🏴���️ It might be the latest of my projects, but it'll probably end up getting released as the first one from this list 😁
148 notes
·
View notes
Text

Iron Age and Roman Artifacts Found in Wales
Metal detectorist Ian Porter unearthed sixteen historical artifacts in a boggy field on Anglesey. Among the items found were Iron Age chariot fittings, a metal ram’s head, and a Roman copper ingot, and offer a window into the island’s rich past during the Iron Age and Roman times.
Ian Porter made the discovery on March 4, 2020, while metal detecting in a field under pasture in the Llanfair-Mathafarn-Eithaf Community.
The unusual bronze, copper, and lead artifacts are believed to have been gifted as repeated religious offerings around an ancient sacred spring source during the Late Iron Age and into the Romano-British period.
The additional artifacts, all of Roman date, include a decorated brooch, four coins, and a lead pot repair. A large and complete Roman copper ingot weighing 20.5kg was also discovered, probably smelted copper deriving from the nearby Roman copper mine at Parys Mountain.

The chariot fittings, cavalry harness pieces, and brooch were all placed around AD 50-120, around the time of, or soon after the invasion of the island by the Roman army in AD 60/61.
The coins and other artifacts suggest a continuing practice of votive gifting around the spring throughout the Roman period, the latest coin in the group being struck around AD 364-378.
Adam Gwilt from Amgueddfa Cymru, Museum Wales, emphasized the role of these finds in understanding ancient religious ceremonies against a backdrop of conflict and change.
Gwilt said: “This culturally mixed artifact group, containing both Iron Age chariot fittings and Roman cavalry fittings, is an important new find for the island.

Artifacts were declared treasure by the senior coroner for north-west Wales. They provide unique insights into the cultural and religious practices on Anglesey, an island of significant historical importance during the Roman invasion of Britain.
The presence of Iron Age and Roman artifacts near the sacred spring indicates a blending of cultures and traditions, emphasizing the complex relationship between native inhabitants and Roman invaders. This discovery sheds light on the religious significance of watery sites, which were frequently used for offerings during times of upheaval.
“The ram’s head fitting, probably a vehicle-fitting or staff head is decorated in the late Celtic art style. It is a closely observed and quirky depiction of the ram and a likely future ‘star’ exhibit loved by many for Oriel Môn,” Gwilt added.
By Leman Altuntaş.

#Iron Age and Roman Artifacts Found in Wales#Anglesey#Llanfair-Mathafarn-Eithaf Community#metal detecting#ancient artifacts#archeology#archeolgst#history#history news#ancient history#ancient culture#ancient civilizations#iron age#roman history#roman empire
145 notes
·
View notes
Text


Romano-Celtic Native God Stone Carvings, Great North Museum, Hancock, Newcastle upon Tyne
#ice age#stone age#bronze age#iron age#archaeology#copper age#neolithic#prehistory#mesolithic#paleolithic#prehistoric#chalcolithic#stone head#romano celtic#celtic#native gods#ancient cultures#ancient living#ancient craft#hadrian's wall#symbols
58 notes
·
View notes
Text
while it is completely true that Ancient Rome is Italian heritage, I think people—especially in cultus deorum—forget how far Roman religion actually spread. I’m not sure if this is a conversation broader paganism can have without flattening it—to deny Italy Ancient Rome is often a marker of fascists, and also we can acknowledge how far Rome, Greece, etc., spread.
for example, to my knowledge I have no Italian ancestry. But Rome colonised the land that would become Cornwall and Slovakia. Thus, some of my ancestors probably did worship Roman deities in some form, despite it not being the cultural heritage—we don’t claim Rome wholesale as cultural heritage, but we do have Romano-Celtic culture that inhabits the cultural sphere. I following the Roman gods is technically in line with my ancestors, despite I being both Slovak & Cornish European heritage wise.
That’s one reason the whole “gods of my ancestors thing” doesn’t completely work—you never, ever know your ancestors from 2000 years ago. I have cultural gods like Morena, but Mars is just as a part of my “bloodline” as she is. We tend to associate x ancient culture with y country, and in many cases there is a direct cultural link, but it’s always more complicated than Italian = Roman as one example.
#had a weirdo troll accuse me of betraying my ancestors on discord#and like. Wdm. Rome colonised tf out of the world lmao?#cultus deorum#roman polytheism#roman pagan#roman paganism#paganism#pagan#witchcraft#dragonis.txt
27 notes
·
View notes
Text
The King of Annwn
Brythonic Paganism Essays: Part I
The Usual Disclaimer: The tales of The Mabinogion and other surviving Welsh texts were once shared orally, passed down across generations, and over vast distances. By the time these stories were finally committed to writing, the Welsh had long embraced Christianity. As a result, what remains in these medieval manuscripts offers only a faint echo of the ancient beliefs held by the Brythonic or Romano-British peoples. Yet, by examining these stories in relation to one another, and drawing parallels with other Celtic or even Indo-European traditions, we may catch glimpses of the older beliefs that inspired them. What follows is simply theory, built upon these comparisons.

There are many contenders for the title of King or Lord of Annwn, the Otherworld in Welsh mythology. So many, in fact, that most Brythonic polytheists I’ve spoken to tend to agree that Annwn, like the mortal world, has multiple rulers. However, I believe these deities share too many similarities to be entirely distinct. Rather, I see them as different aspects or variations of a much older, singular god. Before delving into the gods themselves, let’s examine the key motifs:
The God-King is often depicted as a hunter, accompanied by the Cŵn Annwn—the hounds of Annwn—described as pure white with red ears.
He is locked in an eternal, seasonal conflict, where he can be seen as representing winter, battling against an opponent who embodies summer.
This struggle often revolves around a goddess who symbolizes spring, the earth, or fertility. This mythic framework is incredibly ancient, with perhaps the most well-known version being the story of Persephone in Greek mythology.
The conflict often involves a journey to the Underworld and escalates to such intensity that a mortal king must intervene.
The god is also often depicted as a psychopomp—an entity that guides the souls of the dead to their final destination, much like the Grim Reaper. However, it’s important to note that Annwn wasn’t necessarily viewed as an “afterlife” by its original believers. Instead, it was more of a mystical realm, later misunderstood and conflated with Hell or Hades through the lens of Christian propaganda.
Arawn
Pwyll, King of Dyfed, embarks on a hunt and encounters a pack of white, red-eared dogs bringing down a deer. He claims the kill for himself, only to be confronted by Arawn, the true owner of the hounds, who is also hunting. To make amends for his transgression, Pwyll agrees to a request from Arawn: they will swap appearances and live as each other for one year. Arawn explains that he goes to war every year with Hafgan—a name meaning something like "summer song" or "summer white"—for rulership of Annwn. Despite defeating Hafgan in combat each time, Arawn always loses in the end. As Hafgan lays dying, he taunts Arawn to strike again, and Arawn, unable to resist, delivers the fatal blow—only for Hafgan to be magically revived.
Pwyll agrees to the plan and spends a year living in Annwn disguised as Arawn. Though he shares a bed with Arawn’s Wife every night, Pwyll honors the situation and never takes advantage of it. When the time comes to face Hafgan in battle, Pwyll defeats him but refuses to strike the final blow. With Hafgan dead, his followers recognize Arawn as the true King of Annwn.
Here, we see the recurring motifs of the hunt, the yearly conflict with summer, and the intervention of a mortal king. In this version of the myth, it is the King who travels to the Otherworld, not the goddess who is absent. While the myth lacks a love triangle with a goddess, Arawn’s unnamed Wife does play a role, with her honor preserved, this was included in the story for a reason. The psychopomp element isn’t explicitly referenced in this story, but other familiar themes remain.
Gwyn ap Nudd
Culhwch desires to marry Olwen, the daughter of the giant Ysbaddaden. However, Ysbaddaden knows that he is doomed to die once his daughter marries, so he sets Culhwch forty impossible tasks. One of these is to slay the monstrous boar Twrch Trwyth, a cursed Irish king who now roams Britain as a destructive beast. Culhwch seeks help from his famous cousin, King Arthur, who agrees but warns that to hunt this particular monster, they will need the aid of Gwyn ap Nudd.
Gwyn ap Nudd - whose name means "White Son of Mist" - is somewhat preoccupied at the time, having just abducted the lady Creiddylad from her betrothed, Gwythyr ap Greidawl, whose name means "Victory Son of Scorcher." The ensuing conflict between Gwyn and Gwythyr grows vicious. In one particularly brutal act, Gwyn kills a captured knight, cuts out his heart, and forces the knight's son to eat it, driving him mad. King Arthur intervenes and orders the two rivals to cease their war. From that moment on, they are condemned to battle each other once a year, on May Day, until the end of the world.
Gwyn also appears in the poem The Dialogue of Gwyn ap Nudd and Gwyddno Garanhir in the Black Book of Carmarthen. It can be interpreted from this poem that Gwyddno, unaware that he has been slain in battle, meets a warrior (Gwyn) and asks for his protection. During the course of their conversation Gwyddno learns that the warrior has witnessed many battles and the deaths of many of Britain's heroes, and Gwyddno realises he is now one of those dead heroes as he is speaking to Gwyn ap Nudd.
Later traditions place Gwyn at the head of the Wild Hunt as the King of the Tylwyth Teg, the fair folk, the inhabitants of Annwn, where he rides his host on the night between October 31st/November 1st looking for the souls of the dead. He hunts with the Cwn Annwn, the same pack of dogs Arawn had.
Let's go through all this. We have two examples of a Hunt motif, the Hunting of Twrch Trwyth, and The Wild Hunt. Both can be seen as metaphors for Gwyn's role as a psychopomp, The Wild Hunt is explicitly about the souls of the dead being taken to the Otherworld, and Twrch Trwyth is no ordinary boar, he is a human soul transformed into a monster, and Arthur believes that only with Gwyn with them could they succeed.
We also have a war with summer over a girl. Creiddylad is of uncertain meaning, it could mean "heart-flood", "blood-flood" which is unclear to me, but Gwythyr being "son of Scorcher" seems to be a clear reference to summer, their battle is to commence on May Day, the start of summer, every year, forever. It's also worth noting that the Wild Hunt the night before November 1st is the start of winter. This was of course decided by the (not so mortal) legendary King Arthur.
A note on Gwyn's family: Nudd (pronounced Neathe like breathe) is a god who's name means mist. Getting lost in mist is a sure fire way of getting to Annwn, like a portal, and the Tylwyth Teg, or fair folk of whom Gwyn is king, are said to waylay travelers with mist and fog. Nudd comes from the older Celtic word Nodens, a god associated with healing, specifically but not limited to eyes, as well as dream interpretation. So here we see a god who is responsible for clearing or obscuring vision, both physically and mentally, like mist. Nodens is also closely linked to dogs, hunting and fishing. Lludd is another version of this name, and Lludd is given to be Creiddydlad's father, making her Gwyn's sisters as well as lover, but we don't know for sure if the medieval writers saw Lludd and Nudd as literally the same person, so it's really a matter of opinion.
Gronw Pebr
Gwydion, a magician, trickster, bard and potentially tree deity (more on this in a future essay), has gone to great trouble to bring about the birth of Lleu Llaw Gyffes, Lleu of Many Skills. This includes him stealing divine pigs from Annwn, given to Pryderi ap Pwyll by Arawn and magically impregnating his own sister. As a result Lleu's mother, Arianrhod, has laid three tynghedau on him, which is like a curse or a fate.
One tynged is that Lleu could not marry any woman of any race in this world. So Gwydion, along with his magically talented uncle King Math, created a wife for Lleu out of flowers and named her Blodeuwedd, meaning flower-face. Blodeuwedd and Lleu are happily married until one day, when Lleu is away from home, a hunter arrives.
His name is Gronw Pebr, Gronw the Radiant, and he requests shelter. Blodeuwedd, having never seen another man in her life other than her husband and her creators, falls in love with him. Gronw explains that in order for them to be together, Lleu must die. So Blodeuwedd discovers from her trusting husband the very specific and convoluted means that Lleu could be killed, which involves a spear that takes a year of Sundays to create. She tells Gronw about this, who goes about creating the spear.
When the time comes, Blodeuwedd tricks Lleu into the exact situation in which he can be killed, and Gronw strikes him with the spear. Lleu is "killed" but his body transforms into an eagle that continually rots, and flies away. Using pigs to sniff him out, Gwydion finds the decaying eagle perched in an oak tree, and with his gift of awen (divine talent and knowledge) sings Lleu back to life.
Lleu, Gwydion and Math return for vengeance, and this time it is Lleu who slays Gronw with a spear thrust that pierces the solid stone Gronw used as a shield. Blodeuwedd and her maidens flee, but as they keep looking behind them the maidens fall into a lake and drown and Blodeuwedd is transformed by Gwydion into an owl as punishment, a goddess of flowers cursed to never see the sun again.
This story is a lot more from the point of view of our summer representative Lleu, who's fleshed out far more as a god in his own right in the full telling of it. Lleu specifically is the god of light, as well as being "many skilled" and sharing many characteristics of the "divine son" god that will be explored in the next essay.
Gronw, by contrast, has nothing that indicates winter other than he opposes Lleu and his opposition takes a year of work. He also enters our story as a hunter. The circularity of this conflict is reinforced in the resurrection of Lleu, as winter defeats summer just for summer to return and defeat winter and so on. I am reminded by this resurrection by Gwydion of Hafgan's final strike, which revives him.
Blodeuwedd also gets far more attention in this story than the women in the other tales. A being who is a literal embodiment of spring, fertility and the earth, being made from flowers. It is likely that the owl transformation is a medieval invention. There are other animal transformations in this branch of the Mabinogion that I didn't mention here as they weren't relevant, which also seems to be an addition based on a trendyness of people who shapeshift in medieval literature. However, we also have the maidens falling into the lake, which I imagine is a remnant of the original, in which Blodeuwedd falls in, as the maidens are not really mentioned before so this is an odd detail. Lakes were seen as gateways to Annwn, so here we see Blodeuwedd fleeing to her Otherworldly lover. I personally take the owl to represent Blodeuwedd during the dark half of the year, when she is with her winter lover, awaiting to emerge from the earth in spring.
We have no psychopomping either, but we do have two references to swine herding which seems reminiscent of Culhwch and Olwen. King Math is certainly no mortal, but he seems to be a god involved with magic, judgement and punishment.
A note on Lleu's family: just as Gwyn and Creiddydlad are potentially siblings, so too are Lleu's parents Gwydion and Arianrhod. The story doesn't come straight out and say it, creating the characters of Gilfeathwy and Goewin as stand-ins, probably for the sake of Christian sensibilities. These two are never mentioned again or anywhere else as far as I know, and it is Arianrhod who is pregnant as a result of the whole thing, not Goewin. Some versions even have Arianrhod in Goewin's place as foot holder to Math. Lleu appears as Llefelys in another story, who is brother of Lludd (Nudd). This would make Creiddydlad, the Blodeuwedd-like lady of Gwyn's story, his niece, as well as Gwyn maybe his nephew.
This really nails home how these tales became so mixed up in their countless retellings over space and time before being written down. They spread out and became something unique then smashed back together time and again, but somewhere in there is the important truth. It can be confusing and frustrating, but bare in mind always:
The Gods are not their myths,
Embrace the mystery!
#pagan gods#celtic paganism#paganism#celtic gods#celtic pantheon#celtic mythology#celtic#welsh mythology#welsh history#welsh paganism#brythonic polytheism#brythonic paganism#brythonic polytheist#celtic polytheism#polytheism#mythology#gods#old gods#annwn#arawn#gwyn ap nudd#blodeuwedd#lleu#lleu llaw gyfes#gwdion#arianrhod#rhiannon#the otherworld#religion
32 notes
·
View notes
Text
Sooner or later I've gotta make a better post regarding the appropriation of indigenous terminology by proponents of (certain kinds of) Welsh nationalism. But for now here's a very whistle-stop version of that post. I have a degree in Celtic Studies so these topics are very near and dear to my heart.
[Note: I wrote this post originally during a migraine. I'm revisiting the draft while I'm ill but hopefully can fix this up into something somewhat understandable. As always, this is only a very brief description of the history and I strongly reccomend reading about these topics in your own time to develop a deeper understanding of them. These are topics not even well known in Britain, but if you can spend a short time just to read this, you can help to combat misinformation about British (particularly Welsh) history - and that could aid in preventing the misappropriation of history in the long run. Diolch eto for reading!]
Very often, (certain) Welsh nationalists use terminology that positions the Welsh as if they are an 'indigenous' population who have been 'colonised'. They use language (which in this climate) heavily draws upon the language typically used for peoples who are the victims of British colonialism (of which Wales was an active participant). There's multiple issues with this and many of them lie in whether its appropriate to use this language (regardless of its accuracy or not) as a country which was actively involved in the colonisation of much of the world. What I mean in short is that additional language is needed which doesn't step on the toes of endangered cultures and groups directly affected by British colonialism.
Wales not only participated in British colonialism as a whole (alongside Scotland, Ireland* and England) but itself colonised parts of patagonia in Argentina.
I can't think of any similar terminology to 'indigenous' or 'colonised' which would also get the idea which is meant across. 'Native' in certain contexts is permissible, e.g. 'native speaker' in the context of a Welsh speaker. But in other contexts other than langauge, things get tricky when you argue 'nativeness' (this is a topic I will come back to - especially re. Celtic as a language descriptor vs Celtic as a so-called ethnicity). When (certain) Welsh nationalists talk about being 'indigenous' , being 'native' or 'colonised' what is meant by that?

(Map of the expansion of the Bronze Age Bell Beaker culture circa 2400 BC in Britain and Ireland) - from this map
What makes a Welsh person 'indigenous' to this island that doesn't immediately disqualify other peoples who also have a deep history here? Historically, the island of Britain has been lived on by many, many peoples.
In the Bronze Age you had the arrival of the Bell Beaker people. Then in the Iron-Age, you had tribes speaking (mostly) Brittonic. I say mostly, because we have direct evidence that in the Iron Age Gaulish speaking tribes also moved to parts of Britain but later became integrated with the rest of the population (which, I will add, were not a united peoples but a scattering of different groups who often went to war against each other). Then the Romans invaded Britain (and much of Western Europe) and over time integrated into the local population. So now Britain is Romano-British. Eventually the Western Roman Empire collapses and Britain enters into the sub-Roman Britain phase of its existence. Kingdoms begin to form, with the population speaking Brittonic and British-Latin. So you have different kingdoms in (what would become Wales) and in (what would become Northern England and Southern Scotland) you have more Brittonic-speaking kingdoms.
These kingdoms were also not a united peoples. They shared a language - but it's like claiming that Ancient Greeks were a united people simply because they all spoke Greek. Sparta, Athens, Cornith etc. were independent of each other and the same is true of the kingdoms of the Hen Ogledd (the Old North) and the kingdoms of Wales. They all had a common language but also went to war with each other sometimes. Eventually, the Brittonic language began to diverge into different languages. Namely, Old Welsh and Cumbric (the language spoken in what is today Cumbria, Lancashire, Northumberland and Southern Scotland). The two languages were still very closely related but had diverged by a certain point.
At the same time this is happening, Anglo-Saxons begin to arrive in what is now Kent. They form kingdoms and the Britons living there are either displaced or become absorbed into the Anglo-Saxon populace. Then the Norse rock up and conduct viking raids around the coast before finally settling in parts of the country and forming their own territories.
So now Britain has several groups living on the island (keeping in mind even before settlement from the Anglo-Saxons and the Norse that the British kingdoms were already composed of different groups themselves). Northern Scotland was also having a time re: Picts, Gaels and Britons - but we'll gloss over that for brevity. Also, Ireland was also raiding the Welsh coast at this time too.
Then the Normans rock up and in 1066 William the Conqueror, well, conquers. More history happens after this point but I will try and keep this as brief and as non-messy as I can.
So, to recap:
One of the earliest cultures in Britain was the Bell Beaker people in the Bronze Age. They had their lands settled by the Iron Age Britons ('Celts'). Then the Romans came and the 'Celts' became Romano-Britons. After the Western Roman Empire collapses the remaining population forms kingdoms with distinct political identities. These kingdoms eventually find themselves fighting the Anglo-Saxons and the Norse. Then the Normans turn up and so on and so forth.
So- which group is the original native group to Britain? (Trick question - this question cannot be satisfactorily answered in favour of one group without leaning into claims of historicity which the other groups can also claim).
Which brings me to modern Welsh identity and those who came before.
Something I see in Welsh nationalist groups is a claim to the legacy (or even claims of direct descendance from) the Iron Age Britons (commonly called Celts for shorthand, but as I said before I'm gonna get back to that point). And this narrative is what the "Welsh people are native to Britain" argument is based off of.
It may seem like #praxis to argue the Welsh people are the true inhabitants of Britain and the English are evil invaders. But you have to make *several* logical leaps to get to that point if you're genuinely arguing that point.
For starters, many more people than just the Britons (read: Romano Britons/early Brittonic kingdoms) have called Britain home since the Early Middle Ages. For example, there's the settlement of Scotland by the Gaels, the Irish settlement of certain parts of costal Wales. You have (much later) Roma and traveller groups, Jewish diaspora and many more diverse cultures and peoples existing in Britain at this time. The Romano-British population, which developed into the Early Middle Ages kingdoms of Wales and the Hen Ogledd, was also multicultural. Many black Romans started families with white Britons. By the sub-Roman period, Britain was ethnically and culturally diverse.
But those who argue in favour of a such thing as 'Celtic ethnicity' in order to support the idea Britons (and only Britons) were native to these islands typically imagine that history as white. White Brits, white Romans, white Gaels. When we know this isn't true. Did you know that the Northernmost Ancient Egyptian temple in the world is in Yorkshire because Roman Egyptians in the military brought their religion with them? Mary Beard did a fantastic documentary about a Roman Soldier from modern day Syria who was stationed at Hadrian's Wall who started a family with a British woman. Point is, that some people like to imagine a purely white Britain that they can pine for. And I'm afraid it simply isn't true. The version of history many white supremacists look to simply didn't exist.
I'll quickly bring up one last point before I draw this to a close. And it's about Celtic as a linguistic term vs Celtic as a so-called ethnicity. You see, any first year Celtic Student would tell you that there is no such thing as 'Celts'. Crazy, I know from people studying *Celtic* studies. But hear me out - there is good reasoning why (beyond language groups) Celtic is not a good term for describing an ethnic group. Much of it relates to what I've already mentioned, but we categorise Ireland, Scotland, Wales, Mann, Cornwall and Brittany as Celtic not because of the ethnicity of the people living there (which I've mentioned is pretty diverse) but because they are all places where Celtic languages are spoken. It wasn't until Edward Llwyd (d. 1709) that the term Celtic was coined to describe these languages. Up until that point, nobody was thinking of Irish and Welsh as related because the languages do not sound like they have a common origin. By extension, people didn't think of the Welsh and Irish as being the same peoples (or Celtic) either. Its only in the modern day there is a sense of Celtic identity. The Iron Age Britons were not going around calling themselves Celts. There was no common Celtic identity. But very often people argue Celticness based on a pseudohistory which insists on a false and misleading interpretation of history. Whether or not Celticness exists now is a different matter entirely. But it sure does not rest upon race or ethnicity as a qualifier. This is quite foundational stuff to first year and above Celtic Scholars, but is not generally well known outside of academia because the misinformation is quite strong. So if you read is far, diolch mawr and please share this with anyone you think might be interested in it. Any amount of knowledge of these things would greatly improve understanding of what it means to be Welsh and what it means to speak a Celtic language.
Lastly,
all of that begs us to ask the question:
What does it mean to claim nativeness in a Western European context?
More under the cut
What does it mean to claim nativeness in a Western European context? Especially in a Western Europe post-colonialism.
It means, to me, to claim what isn't our right to claim. To argue and make our points with language that isn't ours and isn't designed to be ours. That this language of indigeneity may sound appealing, but is it improper to use this terminology when our country was directly responsible for the atrocities in which this very language became relevant?
What do we do in response to the misinterpretation of our culture instead of relying on language of indigeneity? These are the questions I want to leave you with and invite you to share your thoughts on. How do we build a Wales which advocates for itself without relying upon inaccurate language which betrays a reliance upon the ahistorical to make its point?
What kind of Wales do we want to live in?
#cymraeg#welsh#cymru#cymry#cymblr#Wales#welsh language#welsh nationalism#nationalism#indigeneity#?#white supremacist mention#white nationalism cw#please add on if you have any thoughts on the matter - I'd love to hear other's takes on the topic!#this post was also mostly made when I was ill/had a migraine so it may not be perfect#but gets most of what I want across well enough I think
106 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Cernunnos Debate- A Decade Later
As y'all know, I've been studying this deity for a decade now. Doing my own research has proven crucial.
The majority of recon folks follow Serith's theory that the Gaulish Cernunnos is a god of bidirectionality, liminality, psychopomp, ect ect. I disagree, on several points:
The first point is that there is simply no attested deity of that type that far west. The PIE Paxuson is found, at the Westernmost point, probably in Italy, though better attested in Greece. That is the full stop of his reach to the West
Iconography. Phyllis Bober wrote a paper in the 50s about the iconography of the Cernunnos deity, which argues that he is a cthonic deity of nature and regeneration. This is further supported by Miranda Green, who writes that Cernunnos may have a forest deity who came to be known for natural regeneration and thus the afterlife and a whole host of stuff
Green also writes that the epithet "Cernunnos" is uncertain, and could be a name for a type of deity. Furthermore, Paxuson has a distinct animal related to him: Goats. Deer are also an older symbol of the deity (based on Anatolian evidence, scant as it is). The Gaulish Cernunnos is most often depicted with a snake
Now, as for Paxuson, I do agree that he is a deity of roads, pathways, liminality, wealth, protection, man's interaction with nature, a psychopomp, a conduit of natural magic. I disagree with the bidirectional thing just because Jesus, that's advanced philosophical waxings for Romano-Gaulish iconography
Paxuson's reflexes are Pushan, Hermes, Pan (a hypostasis of Hermes), Faunus, and SOME elements of Mercury, though the indigenous Italic deity is more concerned with human commerce, markets, and wealth
As for Cernunnos, less is known. All we have are Romano-Celtic depictions. He cannot be divorced from that context. And in that context, I believe him to be a deity of nature and the regenerative forces of nature, especially forests. Each forest may have had their own antlered deity, we simply don't know
I suspect all this got mixed up with the Romans. Its easy to make the leap from Cernunnos being depicted with Mercury, back to Hermes, back to Paxuson. But Mercury absorbed many of Hermes' aspects, and the archaic version of both of them are pretty different from one another
((Its my UPG that the Gaulish Cernunnos isn't for us. He's not a human-concerned deity. We are a part of nature. His force can be harnessed but isn't directed at us. I pray for deceased animals to be led home by him and for the capitalist destruction of nature to be avenged by him. He isn't mean or anything, but is focused on the survival of the web of life- we can work with him or against him, but he will win in the end))
#cernunnos#pagan#polytheism#paxuson#LET IT BE KNOWN#I GREATLY ADMIRE SERITH I JUST DISAGREE ON THIS SUBJECT#HIS WORKS ARE GOOD AND I CONSULT THEM REGUARLY#gaulish#reconstructed polytheism#recon paganism#proto indo european
21 notes
·
View notes