#gaulish deities
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Creative journal entry inspired by Cernunnos!

#Cernunnos#Carnonos#gaulish paganism#pagan#deities#polytheism#polytheist#deity#paganism#roman paganism#gaulish pagan#gaulish deities#gaulish#gaul#gallic gods#gallo roman paganism#gallo roman#creative journal#junk journal#creative journaling#scrapbook#scrapbook journal#scrapbooking#art#collage#collage journal#devotional journaling#devotional acts#devotional art#journaling
51 notes
·
View notes
Text
So as far as I'm aware in the Celtic umbrella of deities we don't have any deities SPECIFICALLY related to weaving/textiles or pottery. Which in the grand pattern of Indo-European branches (or even humanity as a whole) seems.... very odd...
What are the community's thoughts on these acts falling under the purview of Brigit or her other language counter parts? Are there other deities that would make more sense for these activities? What are our thoughts?
#gaelpol#gaelic paganism#gaelic polytheism#gaelic deities#celtic#celtic paganism#celtic polytheism#celtic deities#Irish#irish paganism#irish polytheism#irish deities#gaulish#gaulish polytheism#Gaulish paganism#Gaulish deities#brigid#brighid#brigit#bríg#bríd#*Brigantī#Brigantia#Brigindo
76 notes
·
View notes
Text
hallo pagan tumblr, i'm new here!
currently researching:
DEITIES
Nemetona
the Morrígan
Rhiannon
possibly also interested in:
Artemis
Loki
Sirona
PRACTICES
Reconstructionist polytheistic paganism
naturalism-focused Appalachian folk magic
Herbal medicine
Celtic druidry
Irish, Gaulish, and Appalachian spirituality in general
#celtic paganism#celtic#reconstructionism#celtic reconstructionism#celtic mythology#welsh mythology#reconstructionist paganism#pagan reconstructionist#gaulish pantheon#celtic pantheon#irish mythology#gaulish deities#paganism#pagans of tumblr#paganblr#crystal witch#earth witch#stone witch#green witch#naturalism#witchblr#witch#witchcraft#appalachian folk magic#appalachian folklore#nemetona#rhiannon#the morrigan#deity work#beginner pagan
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
Open, unequivocally open.
Anyone who explicitly says, or otherwise implies, that you must be X to participate are participating in nationalist thinking. You don't need to have 'celtic' blood (which trying to define that would be a whole task honestly), you don't need to live in the land of the gods (despite what some say, the gods seem perfectly capable of and happy to travel), and the gods will not see you as 'less than' if you don't check these boxes.
The strongest encouragement among the community is to strive to educate yourself. Learn the actual history of the deities, not the Wiccanisms. Learn about the living cultures of your area of interest and the struggles they have faced in keeping that culture preserved. Learn the language (or at least a few words if you're not talented in that department) of your interest group, help keep it alive and thriving.
Quick question, is Celtic Paganism open, closed, or partially both? Because I've heard all different angles and honestly I'm so confused now.
I am not Welsh by blood but have citizenship and have lived here for the majority of my life since I was a child so does it count if I practice? I do consider myself Welsh as I've lived here for so long.
#witchblr#witchcraft#witch#deity work#deity#deity worship#deity witchcraft#irish paganism#welsh paganism#celtic paganism#celtic pantheon#celtic polytheism#welsh witch#Pagan#pagan witch#paganism#paganblr#Scottish witch#Scottish paganism#gaulish polytheism#gaulish deities
91 notes
·
View notes
Text

Art by Rituhell
#cernunnos#celtic gods#celtic deities#celtic paganism#celtic mythology#gaulish paganism#gaulish polytheism
49 notes
·
View notes
Text
Which deities do you personally associate with change/transformation?
#hellenic polytheism#norse polytheism#kemetic polytheism#celtic polytheism#gaelic polytheism#irish polytheism#welsh polytheism#roman polytheism#slavic polytheism#gaulish polytheism#deity work#deity worship#pop culture polytheism
105 notes
·
View notes
Text
Calling all pagans and practitioners!
I have been wanting to do more devotional poetry so if you’d like a poem or prayer about your specific’s deity or practice, send me your request in asks or the comments of this post!
All practices and paths are welcome to request <3
REQUESTS ARE OPEN

#devotional blog#brigid devotee#brigid#goddess brigid#digital altar#brigid goddess#gaelpol#brighid#irish pagan#helpol#hellenic polytheism#norse paganism#heathenry#deity work#automatic poetry#death work#folk magic#pagan prayer#requests#paganblr#witchblr#conpantheon#pop culture pagan#pop culture paganism#irish paganism#folk Catholic#kemetism#roman paganism#gaulish paganism#Etruscan paganism
108 notes
·
View notes
Text
Here's a funny story:
Before I worshiped Cernunnos proper, I was fairly certain he was hanging around, but I didn't know if I was ready to work with him on account of...well, his whole thing being incredibly research-intensive.
So what did my ass do? I created secular altars for money magic and death magic. You know, two of the big things that Cernunnos does. Anyway, Cernunnos moved in shortly afterwards, because like...goddamn, man, I was not fucking paying attention.
#jasper post#personal#religion#gaulish#gaulish paganism#gaulish polytheism#cernunnos#cernunnos deity#cernunnos god#cernunnos worship
30 notes
·
View notes
Text
Fern's Cernunnos Deep Dive pt. 3

Correspondences:
🦌 Animals: stag, dog, bull, horned serpent, wolf, all animals 🦌 Crystals/rocks: adder stone, green goldstone, moss agate, petrified wood, golden pyrite 🦌 Flowers/plants: the oak, trees in general, moss, ferns, briars 🦌 Food/drink: game meat, whisky, dark red wine, mushrooms, decadent chocolate, blackberries 🦌 Colours: greens, bronzes, golds, dark browns 🦌 Moon phases: new and dark moon 🦌 Festivals: Beltane and the autumn equinox 🦌 Magics: cycles, hunting, protection, liminality, journeying, fae magic, wealth, success in business, release, ancestor work, connecting with nature, re-wilding 🦌 Nature: the forests, cattle, trees, animals, decay 🦌 Other: bow and arrow, furs, bonfires, torcs, coins, antlers
How to honour:
🏹 Go on a forest walk (or run) 🏹 Make a donation to forest preservation 🏹 Clean the natural spaces around you 🏹 Go on a spirit journey to visit him or his realm 🏹 Build a bonfire 🏹 Dance 🏹 Practice witchcraft
Prayers:
Praise be to you, oh, Horned One Lord of the crackling flame, and sun swept meadow Father to all those who hunt and run King of the wildest nights and deepest woods I honour you.
Cernunnos Lord of the liminal, the in-between The place between life and death, man and woman, hunter and hunted Lord of the cycles of life, of both ancient moss covered forests, and hallowed burial mounds King to all who live in your realms, plant and animal, witch and Fae, and all that lies in between. I honour you
[Masterpost]
60 notes
·
View notes
Text
Paxuson Part 1: Introduction and Comparison of Cognates
A god of bidirectionality, of liminanlity, paths, doorways, travelers, wealth, shepherds, animals, and fertility. His name means "protector" and his direct linguistic cognates are Pan and Pushan.

Pan, Lord of the Wilds
Pan is the god of the wild, shepherds and flocks, rustic music and impromptus, and companion of the nymphs. He is also recognized as the god of fields, groves, wooded glens, and often affiliated with sex; because of this, Pan is connected to fertility and the season of spring. His origin and source of worship was in Arcadia, an isolated mountainous region of the Peloponnese whose culture is . It is believed that Hermes was originally an epithet of Pan who split off early on and becomes a separate deity associated with boundaries, roads, travelers, merchants, thieves, athletes, shepherds, commerce, cunning, and messages.
Both Hermes and Pan have myths putting in them in relation to Apollon. Hermes is characterized as being nurtured by Apollon who acts as a sort of patron to the young god. Pan and Apollon had a famed music competition in the myth of Midas. Given that we have established Apollon as a cognate of Rudlos, lets keep this in mind.

Pushan by OverlySarcasticProductions
Pushan, The Far-Roaming Shepherd
God of meetings, marriages, journeys, roads, fertility, sheep, and cattle. He is called to stir sexual desire in the bride on her wedding day. He is often seen as a solar deity, although this is connected to his shepherd aspect pretty explicitly.
He was a psychopomp, conducting souls to the other world. He protects travelers from bandits and wild beasts, and protects men from being exploited by other men. He is a supportive guide, a "good" god, leading his adherents towards rich pastures and wealth. His chariot is pulled by goats.
While there are multiple versions of the tale, it is commonly said that Rudra knocks out Pushan's teeth at the Daksha yajna, although he doesn't seem to be the target of his rage.

Cernunnos, The Horned Lord
Cernunnos, A Gaulic deity, whose name is probably more accurately rendered as *Karnonos, meaning "Horned Lord". Through the Pillar of the Boatmen, the name "Cernunnos" has been used to identify the members of an iconographic cluster, consisting of depictions of an antlered god (often aged and with crossed legs) associated with torcs, ram-horned (or ram-headed) serpents, symbols of fertility, and wild beasts (especially deer).
Ceisiwr Serith has an excellent dissection of symbols and character in his Youtube video essay, Cernunnos: Looking Every Which Way. Cernunnos has been variously interpreted as a god of fertility, of the underworld, wealth and trade, and of bi-directionality. Cernunnos has been tentatively linked with Conall Cernach, a hero of medieval Irish mythology, and some later depictions of cross-legged and horned figures in medieval art.

Kurunta, The Deer Hunter
His name seems to be cognate with Hittite Kurunta. His sacred animal is the stag, although this was not exclusive to him. He is commonly depicted standing on a stag, and Hittite texts identify the god standing on the stag as the god of the countryside. In Yazilikaya, a tutelary god of nature (likely Kurunta as the god is accompanied by the antler sign) is depicted with only a crook. There are also parallels with Kurunta following behind a storm god, as seen in a sea of Mursili III and a relief from Aleppo. There are also depictions of Kurunta holding a bow and arrows, which outside of due to him being a tutelary god also connects him to hunting. The hunting aspect was also emphasized by Tudhaliya IV.

Pashupati, Shiva of the Animals
Over in India, particularly in the east, another cognate of Rudlos, The mighty Rudra, is widely known by his epithet and avatar, Pashupati, who may be related to Paxuson. The name means "Lord of the Animals". While he may be related to the pre-Indo-Aryan deity depicted on the eponymous Pashupati seal of the Indus Valley Civilization discovered in modern day Pakistan, I believe he may be a reflex, or at least influenced by, the PIE deity in question.
In the Atharvaveda, the fourth Veda and one of the later additions to Vedic literature, Rudra is described to be the lord of the bipeds and the quadrupeds, including creatures that inhabited the earth, woods, the waters, and the skies. His lordship over cattle and other beasts denoted both a benevolent and destructive role; he slew animals that incurred his wrath, but was also kind to those who propitiated him, blessing them with health and prosperity. He is also seen a tutelary deity, of the nation of Nepal in particular.
#deity worship#pagan#pagan revivalism#paganism#pie paganism#pie pantheon#pie polytheism#pie reconstructionism#pie religion#proto indo european paganism#hellenic worship#hellenic deities#hellenic polytheism#hellenic pagan#hellenic polythiest#hellenism#hellenic paganism#hellenic devotion#celtic paganism#celtic polytheism#celtic deities#celtic gods#gaulish paganism#gaulish polytheism
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
Celtic deities associated with boars and pigs: Arduinna and Moccus
Arduinna is a captivating figure in Celtic mythology, deeply tied to the natural world and specifically associated with boars. As a Gaulish goddess, she embodies the wild, protective spirit of the Ardennes Forest, and her connection to boars highlights her role as a huntress and guardian of the wilderness.
Key Points
Who is Arduinna? She’s a Celtic goddess of the Ardennes Forest in what’s now Belgium, Luxembourg, and northern France, known as a protector of the wild and its creatures.
Boar Connection: Arduinna is often depicted riding a boar, symbolizing her mastery over nature and her role as a huntress.
Pigs or Boars? Her primary link is to boars—wild, fierce animals tied to hunting and war—rather than domesticated pigs, though both share cultural significance in Celtic lore.
Personality: Think of her as a fierce, independent deity, blending nurturing protection with the untamed energy of the forest.
Overview
Arduinna’s name itself hints at her essence—it’s linked to the Gaulish word arduo, meaning "height" or "high," reflecting her dominion over the rugged, forested highlands of the Ardennes. She’s most famously known through Roman interpretations, where she’s equated with Diana, the huntress goddess, suggesting a strong, sovereign figure who commands the wild. Her relationship with boars is central to her identity, painting her as both a companion to these animals and a symbol of their untamed power.
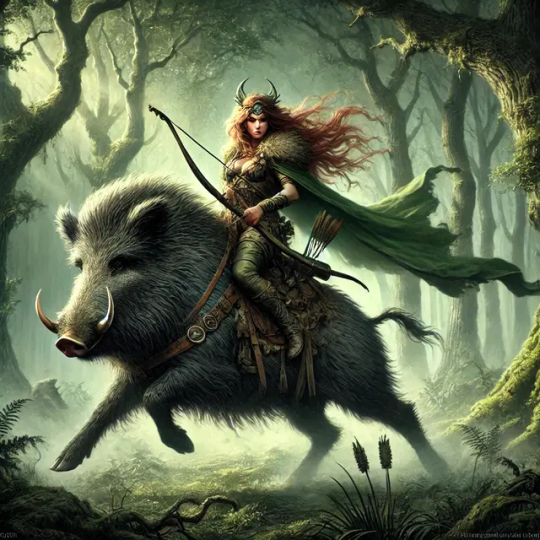

Boars in Arduinna’s World
The boar was a big deal in Celtic culture—think strength, courage, and a bit of ferocity. Arduinna riding a boar (as depicted in a bronze statuette from the region) isn’t just a cool image; it shows her as a goddess who harnesses that wild energy. She likely protected hunters who pursued boars in her forest, ensuring they respected her domain. Unlike Moccus, who’s tied to both pigs and boars with a focus on fertility and abundance, Arduinna’s link is more about the hunt and the raw, natural order. Boars, with their bristly hides and warrior vibes, fit her perfectly—no tame pigs here, just the wild cousins.

Cultural Role
Arduinna was worshipped by the local Gaulish tribes, like the Treveri, who saw her as a guardian of the Ardennes’ bounty—its game, woods, and rivers. Offerings to her might’ve included boar-related items (tusks, hides) or even small sacrifices to keep her favor. Her Roman connection to Diana adds a layer of prestige, suggesting her cult had staying power even as Gaul became Romanized.
Why Boars, Not Pigs?
While pigs were sacred in Celtic mythology (think magical swine from the Other World), Arduinna’s focus on boars aligns with her wild, forested realm. Boars were hunted for food and prestige, their pursuit a test of skill and bravery—qualities Arduinna embodies. Pigs, more tied to settled life and abundance, don’t quite match her untamed vibe, though the broader pig/boar family ties her to Celtic animal reverence.
Detailed Exploration: Arduinna and Her Boar Connection
Historical and Mythological Identity
Arduinna is a Gaulish goddess named after the Ardennes Forest (Arduenna Silva in Latin), a vast woodland spanning modern-day Belgium, Luxembourg, and parts of France. Her name likely stems from arduo ("height"), tying her to the elevated, rugged terrain she ruled (Wikipedia: Arduinna). Roman writers equated her with Diana, the goddess of the hunt, moon, and wilderness, as seen in interpretatio romana—the practice of syncing local deities with Roman ones (Mythology.net: Arduinna). This suggests Arduinna was a significant figure, revered for her sovereignty over nature.

A key artifact is a bronze statuette from the Ardennes, showing a female figure—presumed to be Arduinna—riding a boar (Wikipedia: Arduinna). This image encapsulates her as a huntress and protector, astride a creature synonymous with the wild.

Boars: Symbolism and Role
In Celtic culture, the boar was a powerhouse symbol:
War and Courage: Boar motifs adorned helmets, shields, and standards (e.g., the Gundestrup cauldron), marking it as a warrior’s emblem (Mythology.net: Arduinna).
The Hunt: Boar hunting was a prestigious, dangerous pursuit, often featured in myths like the tales of Arthur or Fionn mac Cumhaill chasing magical boars (Deity Spotlight: Arduinna).
Nature’s Might: As a forest dweller, the boar embodied the untamed strength Arduinna championed.
Arduinna’s boar-riding imagery suggests she didn’t just oversee these animals—she partnered with them. She might’ve guided hunters, ensuring they honored her forest’s balance, or protected the boars themselves as sacred denizens of her realm.
Pigs: A Lesser Connection?
Unlike Moccus, whose domain includes both pigs and boars with ties to fertility, Arduinna’s focus is narrower. Domestic pigs, linked to abundance and Otherworldly gifts in Celtic tales (e.g., swine from Annwn), don’t appear in her iconography or lore. Her wilderness setting favors the boar’s wildness over the pig’s domesticity, though both animals share a cultural thread of reverence in Gaulish spirituality.

Cult and Worship
Arduinna was likely venerated by tribes like the Treveri, who lived near the Ardennes. Her worship might’ve involved:
Offerings: Boar tusks, hides, or meat left at forest shrines.
Rituals: Hunts dedicated to her, with hunters seeking her blessing for success and safety.
Sites: Natural spots like groves or springs, though no specific temples are confirmed (Old World Gods: Arduinna).
A Roman tale claims Emperor Vespasian’s troops cut down parts of her forest, angering Arduinna—a story that reinforces her as a fierce defender of her domain (Mythology.net: Arduinna).
Comparison to Moccus
While Moccus and Arduinna both connect to boars, their roles diverge:
Moccus: Male, tied to pigs/boars, fertility, and protection; possibly linked to feasts and prosperity.

Arduinna: Female, boar-focused, emphasizing hunting and wilderness; less about abundance, more about nature’s raw power.

This contrast highlights the diversity of Celtic animal deities—Moccus nurtures, Arduinna guards.
Moccus appears to be a male deity. The name itself, derived from the Celtic word for "pig" or "boar," does not inherently indicate gender, but the linguistic and cultural context suggests a masculine identity. Additionally, Moccus was syncretized with the Roman god Mercury, who was male, further reinforcing this interpretation.
However, despite being male, Moccus embodies traits that are often associated with fertility and abundance, which are frequently linked to goddesses in many traditions. This could be why some people might wonder if Moccus had a more fluid or ambiguous divine role. In Celtic religion, gender roles in deities were not always rigid—many gods and goddesses shared overlapping domains, and boars and pigs were linked to both male warriors (as symbols of strength) and female deities (as symbols of fertility and provision).

Despite the suppression of her cult, Arduinna’s memory endures through various forms. Today, one can find a beer named after her, which pays homage to her association with the forests and nature.

Furthermore, an asteroid bears her name, reflecting her celestial presence. Additionally, Arduinna’s existence sheds light on the existence of other lesser-known Celtic goddesses who embodied the spirit of the woodlands and were revered alongside Arduinna by ancient Gaulish communities.
Key Citations
Wikipedia: Arduinna, Gaulish goddess of the Ardennes
Mythology.net: Arduinna, goddess of forest and hunt
Old World Gods: Arduinna, Celtic wilderness deity
Deity Spotlight: Arduinna, Tumblr post

#pig#pigs#boar#hog#arduinna#moccus#celtic mythology#pig deities#mythology#gaulish mythology#les ardennes#dall e#grok ai#chatGBT#wikipedia
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
Taking a moment to relax before finals week. I want to create another deity moodboard. I'm open to suggestions! Lmk who you want to see! Send some of their aspects as well!
#pagan#deities#polytheism#polytheist#deity#paganism#roman paganism#greek mythology#hellenic polythiest#hellenism#gaulish goddesses#gaulish gods#gaulish paganism#gaulish deities#gallic gods#gallo roman paganism#gallo roman#norse#norse pantheon#norse paganism#slavic pagan#slavic paganism#heathenry#religio romana#witchcraft#witchy#witch#witchblr#paganblr
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ehilà, viaggiatore
Hey there, traveller

Dedicated to my twin Lares.

Foreword
Hello there! It's me, the Silly Sybil (fka Clever Crow). I've been wanting to do this post for months, but life got in the way and I eventually forgot about it. But hey: better late than never, right?
Now, to the post.
In this foreword, I do want to address the nature of my resources. In fact, I am not writing all of this off of articles or academic works, but off of a questionnaire I had published back in July 2023. The answers given by fellow pagans are the main resources for this blog, whose objective is that of determining the main characteristics of two different approaches to lost practices: reconstructionism and revivalism.
Why choose such a peculiar approach to resources? Reconstructionism and revivalism are part of a spectrum, which can be intended and defined differently by different practitioners. Every pagan will have a slightly different idea of these terms. That means that these labels do not have a universal meaning - there is no institution recognised worldwide that gives us the requirements to be a revivalist or a reconstructionist: it is up to the practitioner and their understanding of the term. This is the reason why I've decided to opt for a form rather than articles as a resource. After all, who, better than a pagan who lives and practices paganism daily, can instruct us about paganism-related terms?
One last important thing I want to do is introduce you to our “cast”* - the wonderful pagans who took the time to compile the form, that is:
➳ anonymous contibutor (revivalist)
➳ Dead (revivalist)
➳ Guenevere (reconstructionist)
➳ Magpie (reconstructionist)
I do feel like thanking the people above is the least I can do. For this reason, I thank all of those who participated from the bottom of my heart: this post wouldn't exist without you.
*The "cast" is formed by aquaintances from a closed Amino community.

On paganism
In order to understand the definition of paganism-related labels, we must first define paganism. My personal research led me to two definitions I will provide you with:
An umbrella-term that indicates non-Abrahamic religions*;
An umbrella-term that indicates religions that are not main world religions**.
The options above might seem similar - if not identical. However, the subtle difference between them is extremely important.
According to Dr. Angela Puca¹, pagan beliefs/religions show the following characteristics:
A polytheistic and animistic approach to spirituality;
A direct relationship with the divine - which sometimes translates with little interest to scriptures and interactions in a non-institutionalised way;
The belief of immanence - the belief that the divine is everywhere and, thus, is not external to the natural world but within the same;
As a consequence of (3.), the reverence for everything as everything holds divine power.
For the reasons above, pagans are very likely to believe in magick - if not practice it. Quoting Dr. Puca, one could say that some of the most popular beliefs that fall under paganism are “Wicca/Witchcraft, Druidry, Heathernry, Asatrù, Goddess worship, ethnic reconstructions and other animist earth-based traditions��.
Now that we have defined, very broadly, what paganism is, let us get to reconstructionism and revivalism.
*Abrahamic religions include Judaism, Christianity and Islam.
**Main world religions include, among the others, Judaism, Christianity, Islam, Buddhism and Hinduism.
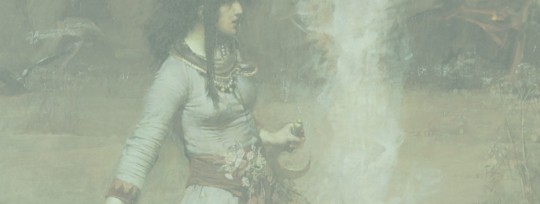
On reconstructionism
“Reconstructionism is about recreating an ancient or dead religion as closely as possible to the original source. This means learning about, understanding, and incorporating historical traditions. Being a Reconstructionist involves a lot of time and research.” - Magpie
“A reconstructionist seeks to find the historic pieces of practice and remain true to that as best they can.” - Guevevere
As the two members of the cast above already said ever-so-clearly, reconstructionism puts a lot of emphasis on historical accuracy - which revivalism also does but to a lesser extent, as we will see later on. The key characteristic of this approach to pagan traditions is the will to practice a dead religion as it was by ancient peoples.
For example: a modern Hellenic polytheist who considers themselves a reconstructionist will do a ritual as a 3rd century BCE Hellenic polytheist would have - if that is indeed the era they mean to reconstruct: the same pagan religion can show different characteristics depending on the century.
The modern reconstructionist practitioner will not alter the rituals and, sometimes, nor will they attempt to fill the gaps with their own UPG*². For this reason, many reconstructionists affirm that it takes a lot of time and research for them to add new practices to their own, as they must research thoroughly the subject and reconstruct it exclusively thanks to historical accounts - for this reason, they rely on academical and primary resources**. Sometimes, if gaps make it impossible to reconstruct a, say, ritual, reconstructionists might decide not to include it in its entirety - in place of, as said before, use any UPG to fill said gaps.
*Unverified Personal Gnosis: a belief that is not backed up by mythos and is exclusively theorized/recognised by the single practitioner.
**Primary resources: texts that were written in the historical period that one is researching. Eg: Saint Augustine of Hippo's texts are a primary resource to those who are researching 4th/5th century Christianity.

On revivalism
“Revivalism is a sort of subcategory of Reconstruction. It has the same goals and also has an emphasis on historical accuracy but tends to be on the less strict side and not as culturally focused*. While Recon. as a whole would include people that expect near-total adherence to historically or culturally attested practices, Revivalism is more theologically focused and has more room for adaptation to one's existing culture and environment. *cultural context is still important, revivalism just doesn't expect participation/membership to a specific culture.” - Dead
“Revivalists keep a sense of tradition within their practice but still allow room for UPG/SPG* and modern practices while still keeping it within the religion.” - anonymous contributor
As we anticipated before, revivalism, too, heavily focuses on historical accuracy. However, there is more room to add one's personal beliefs and/or alter some parts of the practice. This is the very big - and very important - difference between the two approaches: while reconstructionism hardly accepts UPG or SPG to fill the gaps - and, so, adjust part of a practice to one's needs/beliefs -, revivalism is much more flexible on that bit.
For example: a modern Gaulish polytheist who considers themselves a revivalist might decide to fill the gaps given by the little - and biased - resources on their practice by adding their own UPG to what is already historically attested.
Just because revivalism accepts UPG and SPG, it doesn't mean that it is a less-demanding approach than reconstructionism. In fact, it does require the same amount of research and of digging into academic and primary texts. Revivalism is about *adapting* an historical practice; it is not about eradicating it from its original historical and/or cultural context, which has to be researched nonetheless. One could say that revivalists want to reconstruct ancient practices as if they were never destroyed in the first place, taking into account the evolutions such practices would have gone through in the contemporary world. Thus, using one of the examples above, if I am a revivalist I am not practicing Hellenic polytheism as a 3rd century BCE polytheist would have, but I am practicing it as a potential 2024 Hellenic polytheist would have after all of the probable changes religion could have gone through.
To better explain the difference between reconstructionism and revivalism: Roman deities used to be offered incense and wine. If I were to use a reconstructionist approach, I might want to stick to these offerings as they are two of the few offerings that are historically attested. If I were to use a revivalist approach, I might prefer using incense or wine, but I could opt for a strawberry beverage from time to time.
*Shared Personal Gnosis: a belief that is not backed up by mythos and is exclusively theorized/recognised by a group of practitioners.
Conclusion
I personally, to this day, do not know whether to consider myself a reconstructionist or a revivalist. That is because, depending on the pagan community you're interacting with, the "requirements" to label yourself as reconstructionist or revivalist might change - and this is something I already mentioned in the foreword. What I - and the other contributors - tried to do is give you some very broad guidelines in order to let you establish whether you fall under one or the other category.
If you do not find any of these two approaches fitting for you, there is no need to worry: as I stated in the foreword, we are talking about a spectrum. Some people lean towards one of the two extremes of this spectrum and there might be people who find themselves outside of it, which is valid nonetheless.
This being said, I thank you all for reading this blog. Let me know in the comments whether you describe yourself as a reconstructionist, a revivalist or something else entirely!
Wish you a pleasant day/evening/night.
The Silly Sybil
Resources
Informative
¹ Dr. Angela Puca's video on paganism
² Dead's post on UPG and SPG
Paintings
¹ "Priestess of Delphi" by John Collier
² "Magic Circle" by John William Waterhouse
³ "Roman Woman Lighing a Lamp at the Home Altar" by Stephan Wladilawowitsch Bakalowicz
#silly-sybil-informs#all-things-pagan::🌿#roman pagan#pagan community#paganblr#paganism#pagan#roman polytheist#roman polytheism#roman pantheon#roman paganism#religio romana#hellenic polytheism#hellenic deities#greek paganism#gaulish paganism#polytheism#deity work#norse paganism#upg#spg#reconstructionist#reconstructionism#revivalist#revivalism#cultus deorum
36 notes
·
View notes
Text
Connecting with a lesser-known deity was something I never expected to feel so special.
Like don't get me wrong, my bonds with other deities are just as special and I cherish them deeply--
but there was something about having to dig endlessly to find information on Belisama after she reached out to me. There was something about having to intensely look and search and discern until I was 100% certain it was her. There was something about the fact that I've been drawn to thematic light/sunlight since I was a child and there was something about how I always felt a calling whenever I visited large bodies of water.
Especially because she was the first goddess to reach out to me in a very long time, it felt holy in a weird way? Like... after years of wondering why I never seemed to connect with goddesses... after years of worrying that I somehow offended them or caused them to hate me... she found me and she helped me learn how to connect with other goddesses.
#paganism#pagan#paganblr#celtic pagan#celtic paganism#gaulish paganism#Belisama#Belesama#pagans of tumblr#deity worship#deity work#Belisama deity#lesser known deities
26 notes
·
View notes
Text

⚡️Taranis ☀️ Celtic god of thunder and weather
#sketchbook#sketch#my art#fanart#art#paganism#deity#digitalart#celtic gods#god#pagan gods#gaulish#gaul#gaulish polytheism#taranis#taranis god#Zeus#jupiter#mythology
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
A great way to honor the metaphor of Cernunnos is to not use AI art!
#paganism#gaulish paganism#cernunnos deity#cernunnos#celtic paganism#yes I'm referencing a particular post#stares at the camera like the Office
20 notes
·
View notes