#respiration
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
“Heard the bass ride out
Like an ancient mating call”

#black star#mos def#talib kweli#common#respiration#hip hop#rap videos#rap#embassyposts#90s hip hop#Spotify
1K notes
·
View notes
Text

Alors, alors je respire..
#alors#respira#natalia doco#gofloresgo#flores#drawing#go flores go#amores#draw#illustration#angels#breath#roses#ahora respira#aprender a respirar#yoga#budismo#yogainspiration#girls in yoga pants#yogadaily#argentina#pluie#respiro#respiration#ciel#viento#armonia
49 notes
·
View notes
Text
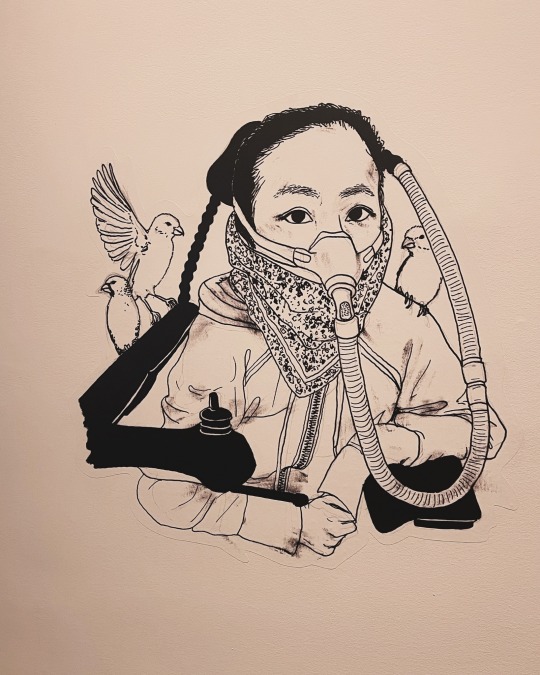

Portrait of Alice Wong by Georgia Webber
Contemporary Calgary, Mohkinstis, Canada
As part of the exhibition “Resistance & Respiration”
January 2024
#art#artist#artists#artists on tumblr#artwork#digital gallery#artsy#original art#art gallery#art museum#contemporaryart#contemporary art#contemporary Calgary#resistance#respiration#Georgia Webber#Alice Wong#disabled artist#disabled art#resistance & respiration#vinyl#drawing#illustration#portrait#modern art#art show#art exhibition#exhibition
93 notes
·
View notes
Photo

EXPRESSION | Suer d'ahan ➽ https://tinyurl.com/Expression-Suer-Ahan C’est se donner une grande peine, une fatigue extraordinaire
#expression#suer#ahan#peine#fatigue#cri#respiration#bûcheron#origine#étymologie#racines#langue#française#français#linguistes#lexicologie#lexicologues#usage
7 notes
·
View notes
Text







Experiments with Plants
-The Universe 1873
54 notes
·
View notes
Text

Factors Affecting Population Size
#biology#igcse#science#study notes#study tips#studyblr#gcse#gcse studyblr#population#growth#population growth#food#disease#temperature#oxygen#respiration#photosynthesis#abiotic factor#animals#humans#people
8 notes
·
View notes
Text

Breathe
#breathing#ocean#beach#atlantic coast#sunset#clouds#cote sauvage#west coast#charente-maritime#ile lumineuse#IO#IOMN#lumiere du soir#light#lumiere#plage#ile d'oleron#respiration#breathe#il faut que tu respires
54 notes
·
View notes
Text
Comment calmer les crises d’angoisses :
Dans ta tête, il y a ce qu’on appelle le nerf sympathique et le nerf parasympathique.
Quand tu te sens submergé.e par pleins de choses, le nerf sympathique s’active : le rythme de ton cœur s’accélère, tu transpire, t’arrive plus trop à respirer…
Le nerf parasympathique, lui, fait en sorte que tes muscles se détendent et que tu ai une bonne respiration.
Ses deux nerfs ne peuvent pas s’activer en même donc quand tu te sens mal il faut essayer d’activer le nerf parasympathique.
Pour ça il faut que tu calme ta respiration, essaie de passer le même temps à inspirer qu’à expirer, et puis tu peux aussi t’entourer d’une personne que t’apprécie. Cette personne peut te rassurer.
Le but, c’est vraiment d’avoir la respiration la plus lente, même si c’est dur.
Sur ce, je te souhaite une bonne journée 😘❤️✨
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Greater Ventilation than Perfusion

Patreon
#studyblr#notes#medblr#medical notes#med notes#mcat biology#mcat#mcat bio#bio#bio notes#biology#biology notes#physiology#physiology notes#human physiology#animal physiology#anatomy and physiology#health science#biochemistry#biochem#organic chemistry#biochemistry notes#ventilation#perfusion#respiration#respiratory system#airways#circulatory system#cardiovascular system
2 notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
Black Star - Respiration ft. Common
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Stomata in Plants
The stomata plays a key role in the respiration of plants. The stomata are pores found on the epidermis of leaves. However stomata can also be found on the stem on some plants. Stomata are multiple stomas. The image below shows stomata under a microscope, and the one below that is an image of stoma found on the web.
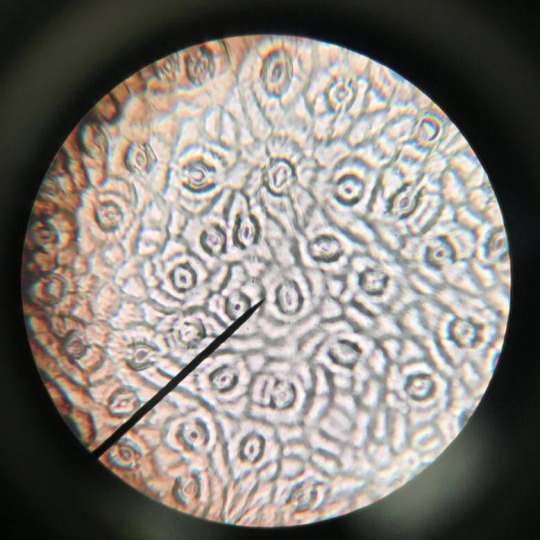

The stoma is made up of guard cells (the sausage like shape in the image above) and is surrounded by the epidermal cell and the subsidiary cell.
These guard cells open when the stomata have taken in a lot of water (this is called the turgid state). They close when the opposite happens (this is called the flacid state).
Stomata open to for the uptake of carbon dioxide and release of oxygen. They close for the uptake of oxygen and release of carbon dioxide.
A problem that plants face is the loss of water. To prevent this as much as possible, the stomata open for a short amount of time before closing.

4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Le Magnétisme : Profiter du Moment Présent avec l'Énergie

Photo by Frames For Your Heart on Unsplash Le magnétisme est un sujet fascinant qui suscite de nombreuses questions. Que ce soit par curiosité ou par scepticisme, il est indéniable que les énergies et leurs impacts sur notre bien-être méritent d’être explorés. Dans cet article, nous allons plonger dans les concepts du magnétisme et de l'énergie, tout en découvrant comment ces éléments peuvent enrichir notre expérience de vie. Qu'est-ce que le Magnétisme ? Le magnétisme est souvent perçu comme une force mystérieuse. Il est lié à l'idée que tout dans notre univers est constitué d'énergie, et q... Read more : https://opensynaps.com/decouvrir-le-magnetisme-et-l-energie/?feed_id=206&_unique_id=671974040e467&utm_source=Tumblr #alternative #anxiété #bien_être #ia #méditation #respiration #scientifique #stress #Anxiété #Bien_être #Médecine_alternative #Méditation_guidée #Scientifique
#Anxiété#Bien_être#Médecine_alternative#Méditation_guidée#Scientifique#alternative#anxiété#bien_être#ia#méditation#respiration#scientifique#stress
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
What is the Difference Between Breathing and Respiration?
Breathing, also known as pulmonary ventilation, is how air is moved into and out of the lungs. This physical act involves two main phases: inhalation (or inspiration) and exhalation (or expiration).
Inhalation: When you inhale, the diaphragm tightens and shifts downward, increasing the chest cavity’s size. At the same time, the intercostal muscles between the ribs contract, causing the rib cage to expand. This expansion lowers the pressure within the lungs compared to the external atmosphere, allowing air to flow into the lungs.
Exhalation: Exhalation involves pushing air out of the lungs. This happens when the diaphragm and intercostal muscles relax, decreasing the volume of the chest cavity. The pressure inside the lungs then becomes higher than the outside atmosphere, driving air out through the respiratory passages.
Breathing is an essential process for delivering oxygen to the body and removing carbon dioxide, a waste product of cellular metabolism. Without breathing, cells would not receive the oxygen necessary for survival, and carbon dioxide would accumulate to toxic levels.
What is Respiration?
Respiration, on the other hand, is a biochemical process within the cells. It involves the conversion of glucose and oxygen into energy, carbon dioxide, and water. This process is vital for producing the energy required for various cellular activities.
Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration can be broken down into three main stages:
Glycolysis: This occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell, where glucose is split into two molecules of pyruvate, generating a small amount of energy (ATP) and producing NADH.
Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle): This takes place in the mitochondria. The pyruvate is further broken down, producing more NADH and FADH2, and releasing carbon dioxide as a byproduct.
Electron Transport Chain (ETC): Also in the mitochondria, the NADH and FADH2 generated in the previous steps donate electrons to the ETC, creating a flow of protons that drives the production of a large amount of ATP. Oxygen acts as the final electron acceptor and combines with protons to form water.
Aerobic vs Anaerobic Respiration
Respiration can be either aerobic or anaerobic. Aerobic respiration requires oxygen and produces a significant amount of ATP. Anaerobic respiration, which occurs when oxygen is scarce, produces less ATP and results in byproducts like lactic acid or ethanol.
Difference between Breathing and Respiration
While both breathing and respiration are crucial for sustaining life, they serve different functions and occur in different locations within the body. Here’s a detailed comparison:
Breathing
Definition: Breathing, or ventilation, is the physical process of moving air in and out of the lungs.
Involves: The respiratory muscles, particularly the diaphragm and the intercostal muscles, which help in the expansion and contraction of the chest cavity.
Purpose: To bring oxygen into the lungs and remove carbon dioxide from the body.
Phases:
Inhalation (Inspiration): The process of taking air into the lungs. The diaphragm contracts and moves downward, while the rib cage expands, creating a vacuum that pulls air into the lungs.
Exhalation (Expiration): The process of expelling air from the lungs. The diaphragm relaxes and moves upward, and the rib cage contracts, pushing air out of the lungs.
Control: Can be voluntary or involuntary. While we can control our breathing rate and depth consciously, it is primarily regulated involuntarily by the respiratory center in the brainstem in response to the body's needs.
Respiration
Definition: Respiration is a biochemical process that occurs in cells to produce energy.
Involves: Cellular organelles called mitochondria are often referred to as the cell's powerhouses.
Purpose: To convert glucose and oxygen into energy (ATP), carbon dioxide, and water.
Types:
Aerobic Respiration: Requires oxygen and produces a large amount of energy. The overall reaction can be summarized as: Glucose+Oxygen→Carbon Dioxide+Water+Energy (ATP)\text{Glucose} + \text{Oxygen} \rightarrow \text{Carbon Dioxide} + \text{Water} + \text{Energy (ATP)}Glucose+Oxygen→Carbon Dioxide+Water+Energy (ATP)
Anaerobic Respiration: Occurs without oxygen and produces less energy. This type of respiration results in byproducts such as lactic acid (in animals) or ethanol and carbon dioxide (in yeast and some plants).
Stages:
Glycolysis: Occurs in the cytoplasm, where glucose is broken down into pyruvate, producing a small amount of ATP.
Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle): Takes place in the mitochondria, where pyruvate is further broken down, producing electron carriers and a small amount of ATP.
Electron Transport Chain: Occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane, where the electron carriers are used to produce a large amount of ATP.
Respiration vs Breathing – Overview
Breathing and respiration are interconnected processes essential for maintaining life. Breathing is the mechanical process that facilitates oxygen intake and carbon dioxide expulsion. Respiration is the cellular process that uses the oxygen delivered by breathing to produce energy, which powers all bodily functions. Together, they form a vital system ensuring that cells receive the oxygen they need and remove the carbon dioxide they produce.
Understanding the distinction between breathing and respiration is fundamental in biology. Breathing is the external, mechanical process of moving air into and out of the lungs, while respiration is the internal, biochemical process of generating energy at the cellular level. Both processes are crucial for life, supporting each other to maintain the body’s overall function.
Were you looking for clear and easy-to-understand explanations like the one provided? Check out the Tutoroot Blog section for simplified learning experiences. Enhance your understanding of biology and get your questions answered with TutorootBiology Online Tuition. Start your journey with Tutoroot’s online home tuition by scheduling a FREE DEMO session today.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
THE RESPIRATION SYSTEM:
part 2: aerobic & anaerobic respiration
part 1 | part 2 | part 3 coming soon
what is aerobic respiration?
aerobic respiration is a chemical reaction that happens in your body.
it requires oxygen
produces a lot of energy.
when does it happen?
happens when there is plenty of oxygen available (so when you're doing normal, everyday activities
just normally breathing

what is anaerobic respiration?
anaerobic respiration does not need/ require oxygen
produces lesser energy than aerobic respiration.
when does it happen?
happens when the body has no oxygen/ has run out (so during strenuous exercise like running or sports which make you tired)
#thesciencegirl#respiration#the respiration system#the respiration system series#the respiration system part 2#anaerobic respiration#aerobic respiration#lungs#breathing#biology#science about the body
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
Breathing guide, breathing with a 5-2-5-2 rate Inspiration 5 seconds - Hold 2 seconds - Expires 5 seconds - Hold 2 seconds For 6 minutes. The video is guided with animation and sounds to assist in the exercise. Let us guide you. Cardiac coherence is a breathing technique that can help reduce stress and promote relaxation. This involves breathing deeply and regularly following a specific rhythm. It is a simple but effective method to calm the mind and body.
2 notes
·
View notes
Photo

(via Épinglé sur Le Yoga || Curated with love by yogadaily)
#pourquoifaireduyoga#meditation#respiration#ekapadaurdhvadharunasana#beachyoga#beach#seaside#seasideyoga#tropical#troplicalbeach#tropicalyoga#yoga#yogi#yogini#yogainspiration#yogaaesthetic#aesthetic#inspiration#inspire#motivation#yogamotivation#yogaposes#asanas#asana#manifestation#manifest#manifesting#fitness#Health & Fitness#yogaeverywhere
8 notes
·
View notes