#renin-angiotensin system
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Link
See also:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36762752/
SIBO ("Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth") is a novel pathology of COVID-19 [1-4]. SIBO is thought to be related to the dysfunction of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) [5], which can be induced by infection with the SARS-CoV-2 virus or by the vaccine Spike protein (Spike protein from the COVID-19 vaccines) [6-8]. The RAS is a ubiquitous physiological and hormonal system in the human body, involved in renal, pulmonary, and cardiovascular autonomic functions, and its dysfunction is responsible for COVID-19 diseases [7].
Interestingly, RAS also controls renal, pulmonary, and cardiovascular autonomic functions, as well as innate immunity and various microbiota, including the intestinal microbiota. The intestinal microbiota is made up of about 10,000 billion microorganisms (bacteria, fungi, and yeasts) living as specific communities and establishing a powerful symbiosis with our body. About 160 bacterial species have been identified. This microbiota plays a crucial role in digestion, cellular metabolism, and immunity (the intestinal microbiota actively participates in the proper functioning of our immune system). In our opinion, SIBO, the etiology of which is still a mystery, is an intestinal dysbiosis mediated by the dysfunction of the RAS. Dysbiosis is an imbalance of the intestinal microbiota, resulting from a decrease in the number of "good" bacteria or an increase in "bad" bacteria or both
Under normal conditions, the colon of an individual harbors low numbers of aerobic Gram-positive bacteria, while the small intestine contains high numbers of anaerobic Gram-negative bacteria. The aerobic bacteria in the small intestine are beneficial because they participate in the digestion of food and the absorption of nutrients (they also allow the production of vitamins K, B8, B9, and B12, as well as short-chain fatty acids, while regulating the absorption of calcium, magnesium, and fatty acids). These bacteria promote the mobility of ingested food in the intestinal tract. The bacterial balance in the small intestine is maintained by the Ileocecal valve (which prevents retrograde translocation of bacteria from the colon to the small intestine), gastric acids (killing microorganisms, including pathogenic bacteria) produced by gastric cells, and the presence of immunoglobulin A in the intestinal tract [10, 11]
SIBO results from the migration of bacteria from the colon to the small intestine, where they excessively multiply (a pullulation of bacteria from the colon into the small intestine). While the function of the small intestine is the absorption of food, the function of the colon is the subsequent fermentation of the non-digestible food residues or wastes produced.
Thus, during SIBO, an early and abnormal fermentation of food is initiated directly in the small intestine by the anaerobic bacteria of the colon, causing more or less severe digestive disorders associated with various potentially highly disabling pathologies
In neurological disorders, intestinal dysbiosis is observed among patients suffering from depression or anxiety, Alzheimer's or Parkinson's disease, schizophrenia, and other autistic or bipolar disorders. All of these pathologies are associated with RAS dysfunction (and overactivation of the AT1R receptor)
In the end, cooperation between specialists from different scientific or medical disciplines is desirable for the benefit of patients. Subsequently, there is no doubt that SARS-CoV-2, COVID-19, and RAS are at the interface of various disciplines, such as virology, immunology, pharmacology, endocrinology, and physiology.
0 notes
Note
Is your url an ACE inhibitor pun? That’s my headcanon when you pop up on my dash
noooo haha it was originally intended to be “stuck in april” (a username w sentimental meaning to me) but a lot of ppl have sent me asks saying they thought it was “stuck in a pril”/an ACE inhibitor pun (for those of u who don’t know, most ACE inhibitors have the suffix -pril). I’m lowly starting to love it as a pre-med biochemistry major SO…. at this point I’m willing to run w either interpretation
#I say stuck in april basically but it’s up to interpretation 😍 and I’m good w either one#the timing of this ask is incredible btw bc I was JUST reviewing my flash cards on the renin angiotensin aldosterone system#I love that this username is an unintentional scientific pun… I think I rly won w this one#ask
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
Also preserved in our archive (Daily updates!)
As part of the COVID-19 International Research Team, researchers at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center, Children's Hospital of Philadelphia, the University of Pittsburgh and Weill Cornell Medicine discovered a novel cause of cytokine storm -; the extreme inflammatory response associated with increased risk of death in COVID-19 infection.
Their findings were reported Nov. 27 in the online issue of Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
In an intensive genomic search for causes of cytokine storm, the research team used autopsy samples obtained from 40 patients who died from COVID-19. They performed genome analysis on samples taken from multiple sites, including the lung, heart, liver, kidney, lymph nodes in the chest that initially filter the virus, and the nasal cavity where the virus enters the body.
They zeroed in on some 50 upregulated immune genes in the samples obtained from nasal swabs and followed through in the genomics for the autopsy tissues.
Stephen Baylin, M.D., Virginia and D.K. Ludwig Professor for Cancer Research and co-senior author, and first author Michael Topper, Ph.D., Evelyn Grollman Glick Scholar and instructor in oncology, were
familiar with many of the genes as part of the inflammasome, a protein signaling network they helped define that is activated to rid the body of virus or bacteria-infected cells.
"Some of the same genes involved in overactivation of the inflammasome appear to be key immune gene regulators of the hyperinflammatory process that leads to a new view of how these subsequently activate the "cytokine storm syndrome" and severely damage multiple tissues, says Topper.
The genes should turn on and off, Baylin explains, but when they stay on, it results in cytokine storm, the very severe inflammation that can be lethal to patients with COVID.
Essentially, immune genes in the nasal cavity, where the virus enters, send signals downstream through a system called renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) to initiate cytokine storm.
RAAS, a hormone system that normally turns on and off to help regulate blood pressure, body fluids and electrolytes, is the spark that pushes the immune response into overdrive, the researchers found, compromising the infection-fighting function of lymph nodes and causing severe damage to the lungs, kidneys, heart, liver and other organs.
The researchers also believe their findings may have implications for long COVID, a chronic condition following COVID-19 infection that is characterized by a wide range of symptoms, including fever, fatigue, coughing, chest pain, heart palpitations, headaches, joint and muscle pain, gastrointestinal issues and more. This is a focus of ongoing research, Topper and Baylin say.
In addition to Baylin and Topper, other researchers participating in the investigation are co-first author Joseph W. Guarnieri and co-corresponding authors with Baylin: Afshin Behesti (leader of COVIRT) and Douglas C. Wallace, Simon Pollett, Deanne Taylor, Eve Syrkin Wurtele, Robert E. Schwartz, Christopher E. Mason, Jeffrey A. Haltom, Amy Chadburn, Henry Cope, Justin Frere, Julia An, Alain Borczuk, Saloni Sinha, JangKeun Kim, Jiwoon Park, Daniel Butler, Cem Meydan, Jonathan Foox, Yaron Bram, Stephanie A. Richard, Nusrat J. Epsi, Brian Agan, Josh G. Chenoweth, Mark P. Simons, David Tribble, Timothy Burgess, Clifton Dalgard, Mark T. Heise, Nathaniel J. Moorman, Victoria K. Baxter, Emily A. Madden, Sharon A. Taft-Benz, Elizabeth J. Anderson, Wes A. Sanders, Rebekah J. Dickmander, Katherine Beigel, Gabrielle A. Widjaja, Kevin A. Janssen, Timothy Lie, Deborah G. Murdock, Alessia Angelin, Yentli E. Soto Albrecht, Arnold Z. Olali, Zimu Cen, Joseph Dybas, Waldemar Priebe, Mark R. Emmett, Sonja M. Best, Maya Kelsey Johnson, Nidia S. Trovao, Kevin B. Clark, Victoria Zaksas, Robert Meller, Peter Grabham, Jonathan C. Schisler, and Pedro M. Moraes-Vieira.
This researach was supported by the Division of Intramural Research, NIAID, NIH grant to Sonja Best, and DOD W81XWH-21-1-0128 grant awarded to Douglas Wallace, the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation Grant INV-046722 awarded to Douglas Wallace, Adelson Medical Research Foundation, Hodson Scholar Foundation, Glick scholar awards and Samuel Waxman Research Foundation awarded to Stephen Baylin from the Defense Health Program (HU00012020067 and HU00012120103), the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease (HU00011920111), and the USU RESPONSE award (HU00012020070).
Source: Johns Hopkins Medicine
Journal reference: Topper, M. J., et al. (2024). Lethal COVID-19 associates with RAAS-induced inflammation for multiple organ damage including mediastinal lymph nodes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2401968121.
Study link: www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.2401968121
#mask up#public health#wear a mask#pandemic#wear a respirator#covid#covid 19#still coviding#coronavirus#sars cov 2#long covid#covid is not over
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
The pathophysiology of hypertension
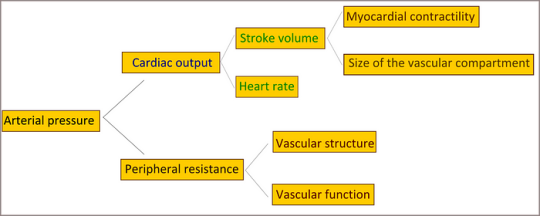
Introduction
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a complex medical condition affecting a significant proportion of the global population. Despite its prevalence, there remains uncertainty regarding its pathophysiology, with essential hypertension constituting a substantial portion where no single identifiable cause is found. This comprehensive discussion aims to delve into the physiological mechanisms involved in the development of hypertension, exploring factors such as cardiac output, peripheral resistance, the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, the autonomic nervous system, endothelial dysfunction, genetic factors, and intrauterine influences.
Cardiac Output and Peripheral Resistance
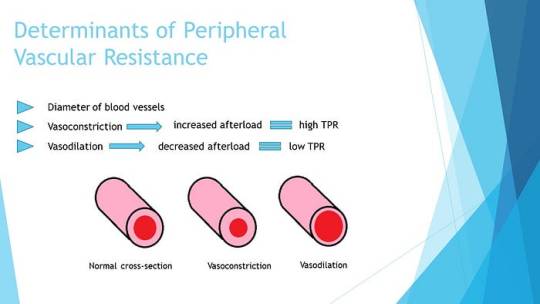
Maintaining normal blood pressure relies on the delicate balance between cardiac output and peripheral vascular resistance. Essential hypertension often involves a normal cardiac output but elevated peripheral resistance, primarily determined by small arterioles. The role of smooth muscle cells, calcium concentration, and structural changes in arteriolar vessel walls contribute to the irreversible rise in peripheral resistance.
Renin-Angiotensin System
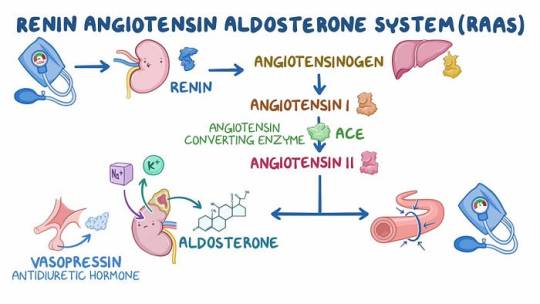
The renin-angiotensin system plays a crucial role in blood pressure regulation. Renin, released in response to various stimuli, initiates the conversion of angiotensinogen to angiotensin I, which is then converted to the vasoconstrictor angiotensin II. This system also stimulates aldosterone release, promoting sodium and water retention. While the circulating system may not be directly responsible for essential hypertension, local renin-angiotensin systems in organs like the kidney, heart, and arterial tree gain significance in regulating regional blood flow.
Autonomic Nervous System
Sympathetic nervous system stimulation affects arteriolar constriction and dilation, playing a pivotal role in maintaining normal blood pressure. Although the exact role of epinephrine and norepinephrine in hypertension etiology remains unclear, drugs blocking the sympathetic nervous system demonstrate therapeutic efficacy.
Endothelial Dysfunction
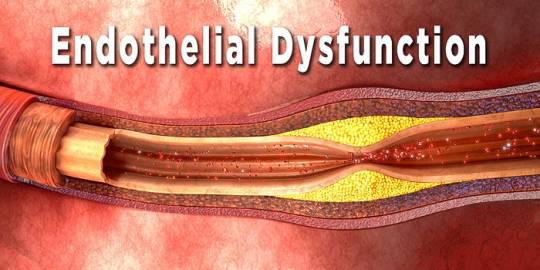
Vascular endothelial cells, producing vasoactive agents like nitric oxide and endothelin, play a key role in cardiovascular regulation. Endothelial dysfunction, implicated in essential hypertension, involves impaired production of nitric oxide. This dysfunction, once established, becomes irreversible, highlighting its primary nature in hypertension.
Vasoactive Substances

Various vasoactive substances, such as bradykinin, endothelin, atrial natriuretic peptide, and ouabain, influence sodium transport and vascular tone. These substances contribute to the delicate balance in maintaining normal blood pressure.
Genetic Factors
Genetic predisposition significantly contributes to hypertension, with specific mutations linked to disorders like Liddle’s syndrome, glucocorticoid-remediable aldosteronism, and others. The intricate interplay of multiple genes makes it challenging to pinpoint individual contributions.
Intrauterine Influences
Fetal influences, particularly birth weight, emerge as determinants of adult blood pressure. The Barker hypothesis suggests a link between low birth weight, metabolic abnormalities, and hypertension in later life. However, the role of genetic factors in this relationship requires further exploration.
Diastolic Dysfunction

Hypertensive left ventricular hypertrophy leads to impaired diastolic relaxation, affecting ventricular input during exercise. This dysfunction contributes to increased atrial pressure, pulmonary congestion, atrial fibrillation, and potential complications like pulmonary edema.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the pathophysiology of hypertension involves a multifaceted exploration of various physiological mechanisms. While essential hypertension remains a complex and often multifactorial condition, advancements in research shed light on factors such as cardiac output, peripheral resistance, the renin-angiotensin system, the autonomic nervous system, endothelial dysfunction, genetic influences, and intrauterine factors. A comprehensive understanding of these elements is crucial for developing effective therapeutic strategies and preventive measures against the global burden of hypertension.
We hope this helps in improving our comprehension of the Hypertension condition. All the best in your journey in the medical field.
Incase of any challenges' and in need of professional guidance, contact;
Expert Academic Assignment Help at;
#fullmetal alchemist#healthcare#medical students#assignment help#aesthetic#puppies#kittens#ratblr#fourteenth doctor#tenth doctor#doctor who#14th doctor#medicine#medicare#medication#nursing school#nursing student#nurses#nurse#pharmercy#pets#health tips#health and wellness#online pharmacy#pharmacy student#pharmacy technician#pharmacy colleges#phar
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hormones (Fluid Regulation Balance) RAAS Thirst Mechanism Quiz
This quiz will test your knowledge on the hormones in fluid regulation balance. Hormones play a very vital role in balancing fluid levels in the body. The thirst mechanism and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) work to try to correct fluid volume deficits. Hormones you want to be familiar with in fluid regulation include: aldosterone, antidiuretic hormone, atrial natriuretic peptide…

View On WordPress
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
literally sick and tired of renin angiotensin aldosterone system can i like read some fiction please
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
I had long COVID with terrible post-exertional malaise and I overcame it.
I had to completely relearn how to pace myself. I have recovered from many past illnesses in the past, including 3 bouts of flu, mono, bronchitis, and lots of other more routine illnesses like colds. These illnesses were easier to recover from because I would feel tired and weak until I didn't, and I could just listen to my body in the default way, pushing myself as I was able, and I'd be tired, but I'd eventually bounce back.
Long COVID was a different beast in that I would feel like I was energetic enough to do a certain level of exercise, and then I'd do it, and I'd feel awful. Like, disproportionately awful, both in intensity and duration. Once after carrying groceries up the steps, my heart rate started racing and I had to lie down for 2 hours before it calmed down, and then I felt somewhat off all day long and took like over a day to fully recover to my (not great) baseline before carrying the groceries.
One thing I learned over time was that I was better able to tolerate increased duration of exercise, than increased intensity. I had to be very careful to avoid increased intensity, but if I kept the intensity low, I could exercise more.
When I realized this I was able to start down a path to recovery that actually worked for me. I took some baby steps. One day I went down the steps and just sat outside in the courtyard in the sun for like 45 minutes. Then I went back up and lay down and rested. That was all I could do.
I realized I was then able to go on long, slow, walks. I would not increase my pace, I would instead just increase the duration. I started going first around the block, then two blocks, then a half mile. Eventually I got to where I could comfortably walk two miles, but I was going at a slow pace and I was listening very carefully to my body. It was very nonlinear. There were some days I tried to go around the block and I couldn't even do that.
In my apartment, I did low-intensity stuff. I would do Qigong warmup exercises every day but I would usually not do any forms. I eventually got to where I would do like one form, sometimes. Usually I just did the warmups.
The thing was, when I was able to be more active within the confines of what I could do, I started to actually recover. It felt really good to be able to go on long, slow walks. Doing the warmup exercises very gently helped me feel better.
I don't know what was going on in my body and I don't know if we'll ever fully know, but my theory was that there was probably some sort of dysfunction like referenced in the article, possibly caused by microclots and/or mitochrondrial dysfunction. And then when I got some exercise, especially increased duration, it got the blood flowing and helped my body to eventually flush out whatever was wrong, heal, and rebuild.
Some theories that support this included that drinking fenugreek tea and taking aspirin seemed to make me feel better, and these both are blood thinners. Also taking niacin seemed to help, and niacin is known to treat NAD+ depletion in mitochondria.
I also think my ACE/ACE2 (angiotensin-renin) system was out-of-whack especially during the first 3 months. Evidence supporting this conclusion was that I felt much more thirsty than normal, and my blood pressure was elevated, and I seemed to have a variety of signs of chronic inflammation. I also felt better after drinking hibiscus tea, which acts as an ACE inhibitor. Normally, when I am healthy, I feel worse after drinking hibiscus tea and I avoid it.
I also had to figure out a lot of stuff I need to change. During the worst of long COVID I became carb-intolerant and I had to be very careful about my carb intake. I also had to figure out how to tolerate certain treatments, like I found taking niacin helped but it also caused flushing which I found very unpleasant, but I figured out that consuming it together with an unripe banana reduced my symptoms, which was a delicate balance because bananas are high in carbs. I had very little appetite, but I'd feel even worse if I didn't eat. I sought out nutrient-dense, calorie-dense, protein-rich foods that I was able to get down and that didn't trigger symptom relapses, and ate as much as possible...small fatty fish, citrus, bell pepper, nuts, sheep/goat cheese. There wasn't a lot of leeway but I found it and figured out how to get by.
After the fact I discovered some interesting things that reinforced that I had been self-medicating. For example sheep and goat cheese contain an ACE inhibitor which probably was helping me similarly to how the hibiscus tea did. Fish oil has a blood thinning effect so eating all that fatty fish was probably doing something to address microclots, assuming I had that.
Eventually, I was able to increase the intensity of exercise. Very gradually. Much slower than I had increased the duration. I remember one day I was feeling unusually good and I tried just a very light jog, just for a distance of maybe 25 feet or so. Then I stopped and waited for my heart to calm down. I was really surprised when I didn't feel worse. I didn't want to overdo it so I just went back in. But it never came, I never felt worse. And then it started looking up even more. I would go on vigorous walks and push myself and I'd feel better for once, not worse.
I forget how long it was, over a year out, maybe closer to two (it's all a blur sometimes), but I remember there was this overpass near my home and I remember one day I sprinted up it. I got to the top, and I felt great. I wasn't out of breath, my heart rate went up but it went up a normal amount, it wasn't racing for an inordinate amount of time afterwards, it calmed down pretty soon after. I am crying writing this. I can't even put into words how amazing this felt after what I had been through.
I got there, but like...I had to adjust my expectations and pacing, both relative to my own expectations, and to what doctors and health authorities were telling me.
If you are struggling with long COVID, it is very important both to listen to your body and not push yourself more than you can handle, but also, not to give up hope of a full recovery. In those first 3 months I could not imagine a full recovery. I really feared I was going to be disabled the rest of my life, because I kept feeling worse again, I'd feel better, then worse. Some setbacks left me feeling worse than the original illness had.
But I did fully recover.
You need to be stubborn and determined. Don't let people tell you what to do with your body. Don't give in to the pressure to take it too fast. If your body tells you to take it much slower than people tell you, listen. But also, don't let the illness or society tell you you can't recover. Be persistent. Try to find ways to increase your activity level or at least maintain some activity level. Experiment. Find treatments that work. Find food or drink that makes you feel better. Find a way to exercise that doesn't wear you down, or better yet some sort of activity that somehow makes you feel better. Then lean into those things. Do what works.
I also found visualization was really helpful. Back when I couldn't exercise vigorously, I would go on a slow walk and then when I felt discouraged, I would sit down and rest, or even lie down, and then I would visualize, as vividly as I had, something in the past I had done when healthier, like running or biking up a hill and feeling really good when I got to the top of the hill. I would tell myself: "I've done that before, I'm going to do it again. It doesn't matter if it's not today." and that took a lot of the anxiety and fear out. I wasn't insisting that I would recover immediately or even any time soon.
And then I would feel better and walk back slowly, not overdoing it. You have to maintain hope and a positive attitude while also respecting your body's limits.
Full Transcript at the link; 3-minute listen.
Quote:
By taking biopsies from long COVID patients before and after exercising, scientists in the Netherlands constructed a startling picture of widespread abnormalities in muscle tissue that may explain this severe reaction to physical activity.
Among the most striking findings were clear signs that the cellular power plants, the mitochondria, are compromised and the tissue starved for energy.
"We saw this immediately and it's very profound," says Braeden Charlton, one of the study's authors at Vrije University in Amsterdam.
The tissue samples from long COVID patients also revealed severe muscle damage, a disturbed immune response, and a buildup of microclots.
"This is a very real disease," says Charlton. "We see this at basically every parameter that we measure."
30K notes
·
View notes
Text
Mediterranean Fish Vaccine Market Company Profiles, Segments, Landscape, Demand and Trends by Forecast to 2030
The Mediterranean fish vaccine market size is expected to reach US$ 2,09,030.80 million by 2030 from US$ 96,323.46 million in 2022; it is estimated to record a CAGR of 10.2% from 2022 to 2030.
Consumers are becoming aware of the nutritious value of animal protein. The demand for healthy, sustainable, high-quality meat products with fewer or no drugs is also increasing rapidly. The growing demand for food products derived from aquatic animals (oil, caviar, protein powders, meat, etc.) encourages farmers to undertake vaccinations to safeguard aquaculture and attain high profitability.
📚 𝐃𝐨𝐰𝐧𝐥𝐨𝐚𝐝 𝐒𝐚𝐦𝐩𝐥𝐞 𝐏𝐃𝐅 𝐂𝐨𝐩𝐲@ https://www.businessmarketinsights.com/sample/BMIRE00028804
Regular fish consumption is widely promoted as a part of a healthy diet. Fishes have a high protein content compared to terrestrial animal meat, which is evident through lower feed conversion rates (FCR) than land animals. Moreover, fish proteins are highly digestible and rich in essential amino acids, unlike animal-sourced proteins that have low essential amino acid content. Fish and shellfish consumption has been associated with a decreased risk of heart disease, inflammation, and arthritis through different research studies. The health benefits of fish are mainly linked to the presence of long-chain omega 3 (n-3) polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA).
📚𝐅𝐮𝐥𝐥 𝐑𝐞𝐩𝐨𝐫𝐭 𝐋𝐢𝐧𝐤 @ https://www.businessmarketinsights.com/reports/mediterranean-fish-vaccine-market
In addition, fish proteins are enriched with bioactive peptides, which offer many health benefits if consumed in appropriate concentrations that support their optimal bioavailability within the human body. Other health benefits of fish consumption include the control of blood pressure through the inhibition of enzymes within the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS); maintenance of bone health; control of inflammation (antioxidant peptides); and maintenance of mental health through the action of opioid peptides and platelet-activating factor acetyl-hydrolase (PAF-AH) inhibitory peptides; and so on. Thus, the tremendous health benefits of aquatic animal-derived proteins indicate the need for healthy breeding of these animals, which propels the demand for fish vaccines in the Mediterranean region.
Enhancing Vaccine Delivery and Addressing Emerging Threats
Beyond novel vaccine design, two crucial areas are driving further innovation:
Mucosal Vaccines: The development of effective mucosal vaccines, designed to stimulate immunity at mucosal surfaces (gills, gut, skin), is critical for aquatic animals. Optimized administration methods, such as immersion or oral delivery, simplify large-scale vaccination and minimize stress.
Autogenous Vaccines: The effective use of emergency (autogenous) vaccines, prepared from pathogens isolated from specific disease outbreaks, provides a rapid and tailored response to emerging threats. This is essential for addressing novel or rapidly evolving pathogens.
These developments are expected to accelerate the adoption of regular fish vaccination processes in Mediterranean aquaculture businesses.
Market Segmentation: Understanding the Dynamics
The Mediterranean fish vaccine market is diverse and can be segmented based on several factors:
Vaccine Type:
Inactivated vaccines
Live-attenuated vaccines
Toxoid vaccines
Subunit vaccines
𝐀𝐛𝐨𝐮𝐭 𝐔𝐬: Business Market Insights is a market research platform that provides subscription service for industry and company reports. Our research team has extensive professional expertise in domains such as Electronics & Semiconductor; Aerospace & Defense; Automotive & Transportation; Energy & Power; Healthcare; Manufacturing & Construction; Food & Beverages; Chemicals & Materials; and Technology, Media, & Telecommunications
𝐀𝐮𝐭𝐡𝐨𝐫’𝐬 𝐁𝐢𝐨: 𝐬𝐭𝐞𝐩𝐡𝐞𝐧 𝐣𝐨𝐡𝐧𝐬𝐨𝐧 𝐒𝐞𝐧𝐢𝐨𝐫 𝐌𝐚𝐫𝐤𝐞𝐭 𝐑𝐞𝐬𝐞𝐚𝐫𝐜𝐡 𝐄𝐱𝐩𝐞𝐫𝐭
0 notes
Text
Mediterranean Fish Vaccine Market Company Profiles, Segments, Landscape, Demand and Trends by Forecast to 2030
The Mediterranean fish vaccine market size is expected to reach US$ 2,09,030.80 million by 2030 from US$ 96,323.46 million in 2022; it is estimated to record a CAGR of 10.2% from 2022 to 2030.
Consumers are becoming aware of the nutritious value of animal protein. The demand for healthy, sustainable, high-quality meat products with fewer or no drugs is also increasing rapidly. The growing demand for food products derived from aquatic animals (oil, caviar, protein powders, meat, etc.) encourages farmers to undertake vaccinations to safeguard aquaculture and attain high profitability.
📚 𝐃𝐨𝐰𝐧𝐥𝐨𝐚𝐝 𝐒𝐚𝐦𝐩𝐥𝐞 𝐏𝐃𝐅 𝐂𝐨𝐩𝐲@ https://www.businessmarketinsights.com/sample/BMIRE00028804
Regular fish consumption is widely promoted as a part of a healthy diet. Fishes have a high protein content compared to terrestrial animal meat, which is evident through lower feed conversion rates (FCR) than land animals. Moreover, fish proteins are highly digestible and rich in essential amino acids, unlike animal-sourced proteins that have low essential amino acid content. Fish and shellfish consumption has been associated with a decreased risk of heart disease, inflammation, and arthritis through different research studies. The health benefits of fish are mainly linked to the presence of long-chain omega 3 (n-3) polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA).
📚𝐅𝐮𝐥𝐥 𝐑𝐞𝐩𝐨𝐫𝐭 𝐋𝐢𝐧𝐤 @ https://www.businessmarketinsights.com/reports/mediterranean-fish-vaccine-market
In addition, fish proteins are enriched with bioactive peptides, which offer many health benefits if consumed in appropriate concentrations that support their optimal bioavailability within the human body. Other health benefits of fish consumption include the control of blood pressure through the inhibition of enzymes within the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS); maintenance of bone health; control of inflammation (antioxidant peptides); and maintenance of mental health through the action of opioid peptides and platelet-activating factor acetyl-hydrolase (PAF-AH) inhibitory peptides; and so on. Thus, the tremendous health benefits of aquatic animal-derived proteins indicate the need for healthy breeding of these animals, which propels the demand for fish vaccines in the Mediterranean region.
The Mediterranean Fish Vaccine Market: A Fertile Ground for Growth
The Mediterranean region, with its thriving aquaculture industry, presents a significant opportunity for the development and deployment of novel fish vaccines.
Disease Prevalence: The region's diverse aquaculture practices and environmental conditions create a breeding ground for various infectious diseases.
Economic Impact: Disease outbreaks can cause substantial economic losses, impacting fish farmers, related industries, and food security.
Sustainability Concerns: The need to reduce antibiotic usage and promote sustainable aquaculture practices is driving demand for effective vaccines.
Key Drivers of Market Growth:
Investment in R&D: The growing recognition of the importance of novel vaccines is encouraging investment in research and development.
Technological Advancements: Continued advancements in genomics, immunoproteomics, and vaccine delivery technologies are driving innovation.
Regulatory Support: Governments and regulatory agencies are increasingly supporting the development and adoption of safe and effective vaccines.
Demand for Sustainable Aquaculture: Consumers and industry stakeholders are demanding sustainable aquaculture practices, including the use of preventive measures like vaccination.
𝐀𝐛𝐨𝐮𝐭 𝐔𝐬: Business Market Insights is a market research platform that provides subscription service for industry and company reports. Our research team has extensive professional expertise in domains such as Electronics & Semiconductor; Aerospace & Defense; Automotive & Transportation; Energy & Power; Healthcare; Manufacturing & Construction; Food & Beverages; Chemicals & Materials; and Technology, Media, & Telecommunications
𝐀𝐮𝐭𝐡𝐨𝐫’𝐬 𝐁𝐢𝐨: 𝐕𝐚𝐢𝐛𝐡𝐚𝐯 𝐆𝐡𝐚𝐫𝐠𝐞 𝐒𝐞𝐧𝐢𝐨𝐫 𝐌𝐚𝐫𝐤𝐞𝐭 𝐑𝐞𝐬𝐞𝐚𝐫𝐜𝐡 𝐄𝐱𝐩𝐞𝐫𝐭
0 notes
Text
Mediterranean Fish Vaccine Market Statistics, Trends, Size, Share, Regional Analysis by Key Players
The Mediterranean fish vaccine market size is expected to reach US$ 2,09,030.80 million by 2030 from US$ 96,323.46 million in 2022; it is estimated to record a CAGR of 10.2% from 2022 to 2030.
Consumers are becoming aware of the nutritious value of animal protein. The demand for healthy, sustainable, high-quality meat products with fewer or no drugs is also increasing rapidly. The growing demand for food products derived from aquatic animals (oil, caviar, protein powders, meat, etc.) encourages farmers to undertake vaccinations to safeguard aquaculture and attain high profitability.
📚 𝐃𝐨𝐰𝐧𝐥𝐨𝐚𝐝 𝐒𝐚𝐦𝐩𝐥𝐞 𝐏𝐃𝐅 𝐂𝐨𝐩𝐲@ https://www.businessmarketinsights.com/sample/BMIRE00028804
Regular fish consumption is widely promoted as a part of a healthy diet. Fishes have a high protein content compared to terrestrial animal meat, which is evident through lower feed conversion rates (FCR) than land animals. Moreover, fish proteins are highly digestible and rich in essential amino acids, unlike animal-sourced proteins that have low essential amino acid content. Fish and shellfish consumption has been associated with a decreased risk of heart disease, inflammation, and arthritis through different research studies. The health benefits of fish are mainly linked to the presence of long-chain omega 3 (n-3) polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA).
📚𝐅𝐮𝐥𝐥 𝐑𝐞𝐩𝐨𝐫𝐭 𝐋𝐢𝐧𝐤 @ https://www.businessmarketinsights.com/reports/mediterranean-fish-vaccine-market
In addition, fish proteins are enriched with bioactive peptides, which offer many health benefits if consumed in appropriate concentrations that support their optimal bioavailability within the human body. Other health benefits of fish consumption include the control of blood pressure through the inhibition of enzymes within the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS); maintenance of bone health; control of inflammation (antioxidant peptides); and maintenance of mental health through the action of opioid peptides and platelet-activating factor acetyl-hydrolase (PAF-AH) inhibitory peptides; and so on. Thus, the tremendous health benefits of aquatic animal-derived proteins indicate the need for healthy breeding of these animals, which propels the demand for fish vaccines in the Mediterranean region.
The Mediterranean Fish Vaccine Market: An Opportunity for Innovation
The Mediterranean Fish Vaccine Market presents a significant opportunity for companies to invest in the development of novel vaccines. The growing demand for sustainable aquaculture practices and the increasing awareness of the economic and environmental costs of disease outbreaks are driving the need for effective and safe vaccines.
Key factors driving the growth of the Mediterranean Fish Vaccine Market include:
Increasing Aquaculture Production: The demand for seafood is increasing globally, and aquaculture is playing a vital role in meeting this demand.
Disease Outbreaks: The prevalence of infectious diseases in aquaculture is a major challenge, creating a need for effective vaccines.
Consumer Demand for Safe Seafood: Consumers are increasingly concerned about the safety and quality of seafood, driving demand for sustainable aquaculture practices.
Government Regulations: Governments are implementing stricter regulations regarding the use of antibiotics in aquaculture, promoting the adoption of alternative disease management strategies.
Technological Advancements: The development of novel vaccine technologies, such as chimeric multiepitope vaccines, is driving innovation in the market.
𝐀𝐛𝐨𝐮𝐭 𝐔𝐬: Business Market Insights is a market research platform that provides subscription service for industry and company reports. Our research team has extensive professional expertise in domains such as Electronics & Semiconductor; Aerospace & Defense; Automotive & Transportation; Energy & Power; Healthcare; Manufacturing & Construction; Food & Beverages; Chemicals & Materials; and Technology, Media, & Telecommunications
𝐀𝐮𝐭𝐡𝐨𝐫’𝐬 𝐁𝐢𝐨: 𝐒𝐡𝐫𝐞𝐲𝐚 𝐏𝐚𝐰𝐚𝐫 𝐒𝐞𝐧𝐢𝐨𝐫 𝐌𝐚𝐫𝐤𝐞𝐭 𝐑𝐞𝐬𝐞𝐚𝐫𝐜𝐡 𝐄𝐱𝐩𝐞𝐫𝐭
0 notes
Text
Mediterranean Fish Vaccine Market Company Profiles, Segments, Landscape, Demand and Trends by Forecast to 2030
The Mediterranean fish vaccine market size is expected to reach US$ 2,09,030.80 million by 2030 from US$ 96,323.46 million in 2022; it is estimated to record a CAGR of 10.2% from 2022 to 2030.
Consumers are becoming aware of the nutritious value of animal protein. The demand for healthy, sustainable, high-quality meat products with fewer or no drugs is also increasing rapidly. The growing demand for food products derived from aquatic animals (oil, caviar, protein powders, meat, etc.) encourages farmers to undertake vaccinations to safeguard aquaculture and attain high profitability.
📚 𝐃𝐨𝐰𝐧𝐥𝐨𝐚𝐝 𝐒𝐚𝐦𝐩𝐥𝐞 𝐏𝐃𝐅 𝐂𝐨𝐩𝐲@ https://www.businessmarketinsights.com/sample/BMIRE00028804
Regular fish consumption is widely promoted as a part of a healthy diet. Fishes have a high protein content compared to terrestrial animal meat, which is evident through lower feed conversion rates (FCR) than land animals. Moreover, fish proteins are highly digestible and rich in essential amino acids, unlike animal-sourced proteins that have low essential amino acid content. Fish and shellfish consumption has been associated with a decreased risk of heart disease, inflammation, and arthritis through different research studies. The health benefits of fish are mainly linked to the presence of long-chain omega 3 (n-3) polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA).
📚𝐅𝐮𝐥𝐥 𝐑𝐞𝐩𝐨𝐫𝐭 𝐋𝐢𝐧𝐤 @ https://www.businessmarketinsights.com/reports/mediterranean-fish-vaccine-market
In addition, fish proteins are enriched with bioactive peptides, which offer many health benefits if consumed in appropriate concentrations that support their optimal bioavailability within the human body. Other health benefits of fish consumption include the control of blood pressure through the inhibition of enzymes within the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS); maintenance of bone health; control of inflammation (antioxidant peptides); and maintenance of mental health through the action of opioid peptides and platelet-activating factor acetyl-hydrolase (PAF-AH) inhibitory peptides; and so on. Thus, the tremendous health benefits of aquatic animal-derived proteins indicate the need for healthy breeding of these animals, which propels the demand for fish vaccines in the Mediterranean region.
The Persistent Threat of Infectious Diseases in Aquaculture
The Mediterranean region, with its diverse aquaculture practices and valuable fish species, is particularly susceptible to the impact of infectious diseases. Intensive farming practices, coupled with environmental stressors and the introduction of new pathogens, create fertile ground for disease outbreaks. These outbreaks not only result in direct mortality and reduced growth rates but also necessitate increased antibiotic usage, contributing to antimicrobial resistance and raising concerns about environmental contamination.
Common diseases affecting Mediterranean aquaculture include:
Viral Diseases: Viral hemorrhagic septicemia (VHS), infectious pancreatic necrosis (IPN), viral nervous necrosis (VNN), and lymphocystis disease pose significant threats to various fish species, including sea bass, sea bream, and turbot.
Bacterial Diseases: Vibriosis, caused by various Vibrio species, is a prevalent bacterial infection leading to septicemia and high mortality. Photobacteriosis, caused by Photobacterium damselae subsp. piscicida, is another major bacterial disease affecting sea bass and sea bream.
Parasitic Diseases: Parasitic infestations, such as those caused by myxozoan parasites (e.g., Ceratomyxa shasta) and copepods (e.g., Caligus spp.), can severely compromise fish health and productivity.
The economic consequences of these diseases are substantial, impacting not only fish farmers but also related industries such as feed suppliers, processing plants, and seafood retailers. Moreover, the reliance on antibiotics to control bacterial infections raises concerns about the development of antibiotic resistance, which poses a significant threat to both animal and human health.
𝐀𝐛𝐨𝐮𝐭 𝐔𝐬: Business Market Insights is a market research platform that provides subscription service for industry and company reports. Our research team has extensive professional expertise in domains such as Electronics & Semiconductor; Aerospace & Defense; Automotive & Transportation; Energy & Power; Healthcare; Manufacturing & Construction; Food & Beverages; Chemicals & Materials; and Technology, Media, & Telecommunications
𝐀𝐮𝐭𝐡𝐨𝐫’𝐬 𝐁𝐢𝐨: 𝐏𝐫𝐚𝐠𝐚𝐭𝐢 𝐏𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐥 𝐒𝐞𝐧𝐢𝐨𝐫 𝐌𝐚𝐫𝐤𝐞𝐭 𝐑𝐞𝐬𝐞𝐚𝐫𝐜𝐡 𝐄𝐱𝐩𝐞𝐫𝐭
0 notes
Text
Mediterranean Fish Vaccine Market Insights, Future Trends, On-going Demand, Opportunities, Segmentation, and Forecast till 2030
The Mediterranean fish vaccine market size is expected to reach US$ 2,09,030.80 million by 2030 from US$ 96,323.46 million in 2022; it is estimated to record a CAGR of 10.2% from 2022 to 2030.
Consumers are becoming aware of the nutritious value of animal protein. The demand for healthy, sustainable, high-quality meat products with fewer or no drugs is also increasing rapidly. The growing demand for food products derived from aquatic animals (oil, caviar, protein powders, meat, etc.) encourages farmers to undertake vaccinations to safeguard aquaculture and attain high profitability.
📚 𝐃𝐨𝐰𝐧𝐥𝐨𝐚𝐝 𝐒𝐚𝐦𝐩𝐥𝐞 𝐏𝐃𝐅 𝐂𝐨𝐩𝐲@ https://www.businessmarketinsights.com/sample/BMIRE00028804
Regular fish consumption is widely promoted as a part of a healthy diet. Fishes have a high protein content compared to terrestrial animal meat, which is evident through lower feed conversion rates (FCR) than land animals. Moreover, fish proteins are highly digestible and rich in essential amino acids, unlike animal-sourced proteins that have low essential amino acid content. Fish and shellfish consumption has been associated with a decreased risk of heart disease, inflammation, and arthritis through different research studies. The health benefits of fish are mainly linked to the presence of long-chain omega 3 (n-3) polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA).
📚𝐅𝐮𝐥𝐥 𝐑𝐞𝐩𝐨𝐫𝐭 𝐋𝐢𝐧𝐤 @ https://www.businessmarketinsights.com/reports/mediterranean-fish-vaccine-market
In addition, fish proteins are enriched with bioactive peptides, which offer many health benefits if consumed in appropriate concentrations that support their optimal bioavailability within the human body. Other health benefits of fish consumption include the control of blood pressure through the inhibition of enzymes within the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS); maintenance of bone health; control of inflammation (antioxidant peptides); and maintenance of mental health through the action of opioid peptides and platelet-activating factor acetyl-hydrolase (PAF-AH) inhibitory peptides; and so on. Thus, the tremendous health benefits of aquatic animal-derived proteins indicate the need for healthy breeding of these animals, which propels the demand for fish vaccines in the Mediterranean region.
Market Segmentation: Understanding the Landscape
The Mediterranean fish vaccine market is diverse and can be effectively analyzed through various segmentation strategies:
Vaccine Type:
Inactivated vaccines: Traditional vaccines using killed pathogens.
Live-attenuated vaccines: Vaccines using weakened live pathogens.
Toxoid vaccines: Vaccines targeting bacterial toxins.
Subunit vaccines: Vaccines using specific pathogen proteins.
Conjugate vaccines: Vaccines linking polysaccharides to proteins.
Recombinant vector vaccines: Vaccines using harmless viruses or bacteria to deliver pathogen genes.
Species:
Turbot
European anchovy and seabass
Salmon
Mediterranean sea bass
Common dentex and common pandora
Sea bream (Sparus aurata)
Rainbow wrasse
Trout
Mediterranean swordfish and bluefin tuna
Grouper and amberjack
Others
𝐀𝐛𝐨𝐮𝐭 𝐔𝐬: Business Market Insights is a market research platform that provides subscription service for industry and company reports. Our research team has extensive professional expertise in domains such as Electronics & Semiconductor; Aerospace & Defense; Automotive & Transportation; Energy & Power; Healthcare; Manufacturing & Construction; Food & Beverages; Chemicals & Materials; and Technology, Media, & Telecommunications
𝐀𝐮𝐭𝐡𝐨𝐫’𝐬 𝐁𝐢𝐨: 𝐒𝐰𝐢𝐭𝐢 𝐏𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐥 𝐒𝐞𝐧𝐢𝐨𝐫 𝐌𝐚𝐫𝐤𝐞𝐭 𝐑𝐞𝐬𝐞𝐚𝐫𝐜𝐡 𝐄𝐱𝐩𝐞𝐫𝐭
0 notes
Text
Mediterranean Fish Vaccine Market Key Details and Outlook by Top Companies till 2030
The Mediterranean fish vaccine market size is expected to reach US$ 2,09,030.80 million by 2030 from US$ 96,323.46 million in 2022; it is estimated to record a CAGR of 10.2% from 2022 to 2030.
Consumers are becoming aware of the nutritious value of animal protein. The demand for healthy, sustainable, high-quality meat products with fewer or no drugs is also increasing rapidly. The growing demand for food products derived from aquatic animals (oil, caviar, protein powders, meat, etc.) encourages farmers to undertake vaccinations to safeguard aquaculture and attain high profitability.
📚 𝐃𝐨𝐰𝐧𝐥𝐨𝐚𝐝 𝐒𝐚𝐦𝐩𝐥𝐞 𝐏𝐃𝐅 𝐂𝐨𝐩𝐲@ https://www.businessmarketinsights.com/sample/BMIRE00028804
Regular fish consumption is widely promoted as a part of a healthy diet. Fishes have a high protein content compared to terrestrial animal meat, which is evident through lower feed conversion rates (FCR) than land animals. Moreover, fish proteins are highly digestible and rich in essential amino acids, unlike animal-sourced proteins that have low essential amino acid content. Fish and shellfish consumption has been associated with a decreased risk of heart disease, inflammation, and arthritis through different research studies. The health benefits of fish are mainly linked to the presence of long-chain omega 3 (n-3) polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA).
📚𝐅𝐮𝐥𝐥 𝐑𝐞𝐩𝐨𝐫𝐭 𝐋𝐢𝐧𝐤 @ https://www.businessmarketinsights.com/reports/mediterranean-fish-vaccine-market
In addition, fish proteins are enriched with bioactive peptides, which offer many health benefits if consumed in appropriate concentrations that support their optimal bioavailability within the human body. Other health benefits of fish consumption include the control of blood pressure through the inhibition of enzymes within the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS); maintenance of bone health; control of inflammation (antioxidant peptides); and maintenance of mental health through the action of opioid peptides and platelet-activating factor acetyl-hydrolase (PAF-AH) inhibitory peptides; and so on. Thus, the tremendous health benefits of aquatic animal-derived proteins indicate the need for healthy breeding of these animals, which propels the demand for fish vaccines in the Mediterranean region.
The Role of Genomics, Immunoproteomics, and Bioinformatics
The development of chimeric multiepitope vaccines relies heavily on the integration of genomics, immunoproteomics, and bioinformatics.
Genomics: Whole genome sequencing of pathogens allows researchers to identify potential vaccine targets, such as virulence factors and surface antigens.
Immunoproteomics: This field enables the identification of immunogenic proteins and epitopes that are recognized by the fish's immune system.
Bioinformatics: Bioinformatics tools are used to analyze genomic and proteomic data, predict potential epitopes, and design chimeric multiepitope vaccines.
The decreasing cost of whole genome sequencing and the increasing availability of bioinformatics tools have made it more feasible to develop species-specific vaccines tailored to the unique immune responses of different fish species.
𝐀𝐛𝐨𝐮𝐭 𝐔𝐬: Business Market Insights is a market research platform that provides subscription service for industry and company reports. Our research team has extensive professional expertise in domains such as Electronics & Semiconductor; Aerospace & Defense; Automotive & Transportation; Energy & Power; Healthcare; Manufacturing & Construction; Food & Beverages; Chemicals & Materials; and Technology, Media, & Telecommunications
𝐀𝐮𝐭𝐡𝐨𝐫’𝐬 𝐁𝐢𝐨: 𝐀𝐤𝐚𝐬𝐡𝐚 𝐆𝐡𝐚𝐫𝐠𝐞 𝐒𝐞𝐧𝐢𝐨𝐫 𝐌𝐚𝐫𝐤𝐞𝐭 𝐑𝐞𝐬𝐞𝐚𝐫𝐜𝐡 𝐄𝐱𝐩𝐞𝐫𝐭
0 notes
Text
Also preserved in our archive
Severe COVID-19 has been considered an inflammatory “cytokine storm” condition.
Severe COVID-19 arises in part from the SARS-CoV-2 virus’s impact on mitochondria, tiny oxygen-burning power plants in cells, which can help trigger a cascade of organ- and immune system-damaging events, suggests a study by investigators at Weill Cornell Medicine, Johns Hopkins Medicine, Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, and the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, along with other members of the COVID-19 International Research Team.
Severe COVID-19 has been considered an inflammatory “cytokine storm” condition in which the immune response to a viral infection becomes excessive, flooding the bloodstream and tissues with immune signaling proteins at levels that cause lung-impairing inflammation and other signs and symptoms.
The new study, published Nov. 27 in PNAS, extends the scientific understanding of the molecular pathways driving this storm. By using RNA sequencing and other laboratory techniques on patient and animal model tissue samples, the investigators were able to examine these processes in great detail. Weill Cornell Medicine researchers, led by Dr. Robert Schwartz, associate professor of medicine, provided much of the deidentified patient material, including nasopharyngeal swabs and autopsied organ samples, as well as COVID-19 animal models, and contributed to their analysis.
The teams’ findings show that SARS-CoV-2 virus infection can cause significant damage to mitochondria in infected cells—damage that activates the immune system, contributing to the storm of inflammatory and other responses.
Prominent among these responses, the researchers noted, is the overactivation of a blood-pressure-regulating system called the renin-angiotensin-activation-system (RAAS). The overactive RAAS is associated with abnormal blood clotting—a striking feature of severe COVID-19—and, the researchers noted, with scarring-like abnormalities in lymph nodes, and dysfunctions of the immune cells found within them. The latter, the researchers say, may account for the impaired immune function that is also seen in severe COVID-19.
“One of the suggestions of these findings is that there is, early in the process, profound mitochondrial dysfunction and damage, which is then driving RAAS overactivation, which in turn contributes to the multi-organ damage of severe COVID-19,” said Dr. Schwartz, who is also a hepatologist at NewYork-Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medical Center. “In addition, we’re concerned that these processes underlying acute COVID-19 may not always return to normal afterwards.”
The researchers are currently investigating this possibility in cases of “long COVID,” a syndrome that features lingering inflammation as well as immune cell dysfunction.
Reference: Topper MJ, Guarnieri JW, Haltom JA, et al. Lethal COVID-19 associates with RAAS-induced inflammation for multiple organ damage including mediastinal lymph nodes. PNAS. 2024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2401968121
www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.2401968121
#mask up#public health#wear a mask#pandemic#wear a respirator#covid#covid 19#still coviding#coronavirus#sars cov 2#long covid#covid is not over
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Does alcohol raise blood pressure
Yes, alcohol can raise blood pressure, especially when consumed in large amounts or over a prolonged period. Short-term drinking can cause a temporary increase in blood pressure, and heavy or chronic alcohol consumption is associated with long-term hypertension (high blood pressure)
Here's a more detailed explanation of how alcohol affects blood pressure:
1. Short-Term Effects
When you drink alcohol, it can cause a temporary increase in blood pressure. This is due to the immediate effect alcohol has on your body's cardiovascular system. The alcohol acts as a vasodilator, meaning it relaxes and widens blood vessels for a short period. Initially, this may lower blood pressure slightly, but the body compensates by increasing heart rate and constricting blood vessels, which can raise blood pressure.
However, once the alcohol begins to be metabolized, your body responds by constricting the blood vessels, which can lead to an increase in blood pressure.
2. Long-Term Effects
Chronic alcohol consumption has a more significant and lasting effect on blood pressure. Long-term heavy drinking (more than 2 drinks per day for men or 1 drink per day for women) can increase your risk of developing hypertension, which is high blood pressure. This occurs through several mechanisms:
Sympathetic Nervous System Activation: Alcohol stimulates the sympathetic nervous system, which controls the "fight or flight" response. This causes your heart to beat faster and your blood vessels to constrict, both of which increase blood pressure.
Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS): Chronic alcohol use can activate the RAAS, a hormone system that regulates blood pressure. Activation of this system increases sodium retention, which leads to water retention, increasing blood volume and raising blood pressure.
Structural Changes to the Heart and Blood Vessels: Long-term alcohol abuse can lead to changes in the structure and function of the heart, causing left ventricular hypertrophy (thickening of the heart muscle), which can contribute to elevated blood pressure.
Hormonal Disruptions: Alcohol affects the balance of hormones such as cortisol, insulin, and adrenaline, all of which can influence blood pressure.
3. Moderate Drinking and Blood Pressure
Even moderate alcohol consumption has been shown to raise blood pressure in some individuals, especially those who are already at risk of hypertension or who have other cardiovascular issues. Studies suggest that regular moderate drinking, such as one or two drinks a day, can still have a cumulative effect on blood pressure over time.
4. Alcohol and Other Factors
The relationship between alcohol and blood pressure is influenced by several factors:
Genetics: Some people may be more sensitive to the blood pressure-raising effects of alcohol due to genetic predispositions.
Diet: A diet high in salt and low in potassium, combined with alcohol consumption, can have a more pronounced effect on raising blood pressure.
Weight: Alcohol can contribute to weight gain, and excess weight is a significant risk factor for hypertension.
Other Health Conditions: Conditions such as diabetes, kidney disease, or cardiovascular disease can be worsened by alcohol consumption, leading to an increased risk of high blood pressure.
5. Blood Pressure and Alcohol Withdrawal
For people who regularly drink large amounts of alcohol, stopping suddenly or withdrawing from alcohol can also temporarily elevate blood pressure. This is part of withdrawal symptoms and can be especially dangerous for individuals with a history of high blood pressure or heart disease.
Lowering Blood Pressure: Fildena is a phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitor. By inhibiting PDE5, it causes blood vessels to dilate, which can lower blood pressure. For most people, this effect is not dramatic, but it can be more pronounced in some individuals, especially when combined with other blood pressure-lowering medications.
Interactions with Blood Pressure Medications: If you are taking medications for high blood pressure, combining them with Cenforce can cause a significant drop in blood pressure, leading to dizziness, fainting, or even more severe complications in rare cases.
When alcohol and Sildenafil are used together, the effects on blood pressure can be unpredictable and potentially risky:
Alcohol's Effect on Blood Pressure: As mentioned, alcohol can raise blood pressure, but the effect might be temporary.
Effect on Blood Pressure: Sildenafil tends to lower blood pressure by dilating blood vessels.
Combining the two can cause a conflict between these opposing effects. In some cases, alcohol can dampen the effectiveness of Sildenafil, and it can increase the risk of side effects like:
Moderation is Key: Limiting alcohol intake is a preventive measure. The CDC defines moderate drinking as up to one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for men.
Blood Pressure Monitoring: If you're concerned about your blood pressure, it's crucial to monitor it regularly, especially if you drink alcohol. In some cases, reducing or eliminating alcohol consumption may be necessary.
Consulting a Doctor: If you have high blood pressure or other cardiovascular risk factors, it’s important to talk to a healthcare provider about your alcohol intake. They can help you develop a strategy for managing both blood pressure and alcohol consumption.
By understanding these factors, you can better manage the potential risks of alcohol when it comes to your blood pressure and overall heart health.

1 note
·
View note