#plant based diet covid
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
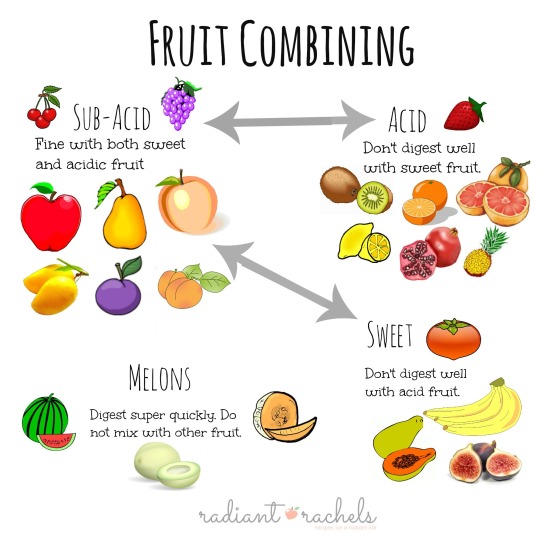
I like to re post this every now and again because it's good advice I frequently forget.
Also I post it in part because I'm laying in bed with Covid (for the first time) at the moment and eating as much fruit as I can to expedite recovery. I grabbed a banana and orange, ate the banana and asked myself if this was a good combo or not. Glad I checked, because it was not. The last thing I need is indigestion.
But because it's me, my main focus has been doubling down on nutrition and observing my own results. I was eating plant based before, but sometimes I went a little too hard on the peanut butter trail mix, breads, or other sweet treats.
My doctor said rest and hydrate, but I took it a step further and since testing positive have cut out wheat, sugar, and any kind of dairy or processed foods. I figure nothing that could make inflammation worse. I've been consuming tons of herbs like cinnamon, ginger, echinacea, and turmeric while eating fresh citrus fruits like lemon, orange, strawberry, and pineapple daily.
Now I did a bit of tooling about the internet to see if any studies had been done over the last four years regarding a plant based diet and it's effects on Covid. The results were hopeful.
I found one study that said,
"Merino et al revealed that healthy plant-based foods could decrease the risk and severity of COVID-19.21 In this large survey, it was shown that as the quality of the diet rises, the risk of disease COVID-19 (HR 0.91) and severe COVID-19 (HR 0.59) diminishes.
Which gave me hope so I kept digging.
Another one stated, "Compared with an omnivorous Western diet, plant-based diets containing mostly fruits, vegetables, grains, legumes, nuts and seeds, with restricted amounts of foods of animal origin, are associated with reduced risk and severity of COVID-19. "
And I can tell you that has been my experience thus far. I developed a fever that went away after 24 hours and didn't go over 100.4. My only other symptom has been a stuffy nose with sinus pressure. Im definitely tired and need to limit activity but I can still taste and smell, breathe through my nose a decent amount of the time, and I'm not coughing. I'm lucky in that I have time off from work and for that I am grateful, as rest is another key component.
And why would a plant based diet be so beneficial for mitigating Covid symptoms? Because, "plant-based dietary patterns are rich in antioxidants, phytosterols and polyphenols which positively affect several cell types implicated in immune function and exhibit direct antiviral properties."
The full study can be found if you pop this into Google::
Acosta-Navarro JC, Dias, LF, de Gouveia LAG et al. Vegetarian and plant based diets associated with lower incidence of COVID-19. BMJ Nutr Prev Health 2024:e000629. doi:10.1136/bmjnph-2023-000629
I was really scared at first and this information helped me feel more empowered in my health and recovery. It's not a substitute for any medical attention or prevention like vaccines, hand washing, and mask wearing- all things I was doing regularly prior to getting sick which may have also been variables in keeping my symptoms down. A little help goes a long way.
Has any other plant based person had a similar experience? Let me know.
#food#vegan#foodie#healthy#health#vegetarian#fitness#diet#nutrition#plant based#plant based diet covid#covid conscious#covid recovery#covid vegan#study#herbology#herbs#inflammation#fitblr#healthy lifestyle#long covid
42 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
#recovery#ed recovery#eating disorders#disordered eating#eating disorder recovery#eating disorder#covid#covid 19#being sick#sick#sick in bed#i feel sick#stuck at home#what vegans eat#what i eat in a day#food diaries#vegan diet#health and fitness#fitness#rest day#gym life#vegan#diet#nutrition#health#plant based#healthy living#hobbies#sewing#vitamin c
0 notes
Text
FAFO applied to the carnivore diet community
I want to make an observation about MAGA + carnivore diet in these trying times. Stay with me.
Very briefly, the carnivore diet is an elimination diet: you eat just meat for 90 days, after which you slowly start reintroducing foods, one at a time, back into your diet and gauging your body's reaction.
Some people find that after this purification they can still eat most of everything without getting symptoms, some find they are intolerant/allergic to some of the foods everybody's typically allergic to (peanuts, dairy, gluten, etc). Some find they're allergic to everything but meat and these are usually autoimmune patients, meaning they have a leaky gut which translates to lots and lots of food allergies. Some people who found they can eat whatever nonetheless stick to eating carnivore regardless because they just feel better this way.
Carnivore displeases mainstream medicine that still labours under the delusion created by bad and corrupt science that diet is irrelevant to your overall health, or that for health purposes you can never be too vegetarian. And carnivores are typically accused of being right-wing conspiracy believing ignoramuses, when in reality most are elderly people who only late in life arrived at this way of eating after decades of obediently listening to their doctors and following the dietary guidelines... with disastrous consequences to their health. They're not eating meat because Trump says so - Trump eats and drinks sugar all day long and all you have to do is look at him to know that this is true. They eat meat because it heals.
End preamble.
Having said that, it is very true that carnivore has formed an association with fascists like Joe Rogan and Jordan Peterson, much like vegetarianism is associated with Socialism and "soy boys" and eco warriors. Most carnivores don't wear either their politics or religion on their sleeve at all, but those who do never identify as, say, Muslim or left-wing, they're always right-wing and Christian.
And yet the paradox is you will never find a more radically anti-consumerist, minimalist, anti-capitalist move than going full carnivore. I know it's never going to happen but in theory if everyone became a carnivore it would be a complete and unmitigated disaster for the world's economy. Think of all those crops and plants that would suddenly become pointless for anything other than feeding them to farm animals. A hamburger joint like MacDonald's, whose food offer is actually 90% plants and a sliver of meat, would be screwed. Add to that the fact that most carnivores practice OMAD (one meal a day) and fast the rest of the time and eat their one meal mostly at home and every restaurant is closed, every supermarket too.
Even if the transition from an omnivore, plant-based diet to a carnivore diet took place very gradually it would still mean that entire food empires that are dependent on stuffing you with seed oils, gluten and sugar every couple of hours would collapse. All those billionaires would go broke.
If the transition took place carefully it'd be brilliant for the world's health - but the food industry that makes you sick and the medical and pharmacological industry that depend on the money they make from unsuccessfully treating you for preventable diseases would lose an immense fortune, forever.
Which brings me to my point: MAGA guys, I know you. I know you wish the food pyramid were turned upside down. For years I've been hearing you decry the ignorance of doctors and the criminal greed of Big Pharma. I agree, it's bad. And I know, even though youtube won't let you say it and you only say it on Rumble, that you think Covid was created by a bat in a Chinese lab and was transmitted to people through vaccines. You're challenged.
And now you believe it's great that Trump has appointed Robert Kennedy Jr. to be his health secretary, because he's a psychopath who drove his ex-wife to commit suicide and because he's an antivaxxer - just like you. All the while you pointedly ignore that Trump also picked up Dr. Oz, famous plant-based diet guru who made Oprah fatter and sicker than ever.
But I know none of these appointments mean anything. Trump only follows the money, not some sort of higher calling to serve the people. So I know that whatever happens in the future will not be determined by these guys...
... but rather by whatever the money people, i.e. Big Pharma, mainstream medicine and the food industry, have to say on the matter.
For instance, it is possible that Big Pharma will allow Trump to get rid of vaccines. But only if they do the math and conclude that the money they lose by not selling those vaccines they'll more than make up by "taking care" of the sick. If that doesn't add up then Trump/Kennedy won't be allowed by that super powerful mega-billionaire industry to do a goddamn thing.
Prepare to see during the next years ahead the official guidelines change from telling kids to eat more fruit like Michelle Obama wanted (which is no good) to eating breakfast cereal every five seconds (which is worse).
You know I'm right.
I would agree that it's true enough that you wouldn't be any closer to your carnivore dreams if you had voted for Kamala instead. I don't even know what her diet is, except that she doesn't stuff herself every five minutes like Trump does, nor has she ever raped anyone. But at least your kids would still have Obamacare aka ACA - which should really have mattered to doctors in the carnivore sphere, who instead remained silent and did not use their platform to warn their viewers; and your kids would not be in danger of dying from the measles and other diseases preventable by vaccines. And under Kamala you would still be allowed to stuff them all you like with stakes.
But you couldn't suffer to have a woman of colour as your president. It all boils down to that. So you fucked around and now you're going to find out. I don't feel sorry for you but I do feel sorry for your victims.
#racism#health#carnivore diet#fascism#donald trump#robert kennedy jr#misogyny#feminism#obama#kamala harris#fuck around and find out#fafo#joe rogan#jordan peterson#capitalism#minimalism#religion#anti vaxxers#rumble#covid#dr. oz#vegetarianism
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Similar problems arise with Vettese and Pendergrass’s contention that “the easiest—and perhaps only—way to achieve large-scale reforestation and feed the world at the same time is through widespread veganism.” They defend this contention by feeding into their model per capita estimates of land requirements for different dietary regimes based on agricultural figures within the coterminous United States and multiplying these by global population numbers. Notably, even the article from which these estimates are drawn observes that a smaller total number of people can be supported by a vegan diet than a vegetarian or low-meat mixed one, as the former is unable to use land suitable to grazing. Although this may be less of a problem in the context of the United States—as even the lowest estimate of the maximum population fed by U.S. agriculture is 1.3 times the size of the 2010 U.S. population—it becomes a much more dangerous assumption when applied to more arid regions, such as parts of Africa, Latin America, and Asia, where attempts to impose sedentary agriculture on Indigenous populations have undermined pastoral livelihoods with disastrous social and ecological consequences. It also runs counter to the nonprofit organization GRAIN’s contentions that struggles around agriculture and sustainability need to start from the premise that “farming communities should also be able to decide by and for themselves, and without pressure, the type of land tenure they want to practice”—a sentiment echoed by movements such as La Vía Campesina and in the Marseille Manifesto. These complexities do not negate the fact that shifting that portion of the world’s population presently consuming large quantities of industrially produced meat to a more vegetable-based diet would have numerous health, ecological, and ethical benefits. Rather, a more comprehensive ecological approach suggests that there are problems with assuming that experiences and conditions based on a single U.S. metropolitan view are directly translatable into global realities. As Rob Wallace and Max Ajl point out in response to a piece co-authored by Vettese that advocates Half-Earth Socialism, planetary veganism, and synthetic meat in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, many vegan criticisms of the social-ecological effects and suffering inflicted by industrial animal husbandry are valid. Nevertheless, they lose their moral and empirical backing when they adopt a series of settler-colonial biases that facilitate the careful drawing of distinctions between industrial and sustainable cultivation of plants while treating industrial and peasant animal husbandry as an undifferentiated whole. That is, the differences between peasant and pastoral animal husbandry practiced by countless peoples around the world and industrial livestock operations are as great as those that Vettese and Pendergrass recognize between industrial and organic agriculture, in terms of their ecological consequences, their contributions to and imbrications with cultural identities, and the amount of harm inflicted on the animals involved. In this sense, Vettese and Pendergrass’s universal condemnation of all “animal husbandry as one of the most consequential and dangerous ways humans shape life on Earth” is both inaccurate and reflects what Wallace and Ajl refer to as “specific values, specific devaluations, and pathological externalizations” undergirding a project “that consents to the brute confiscation and erasure of peasant and pastoral particularisms in the name of ‘universal’ ideals: rewilding Earth upon the bones of supposedly atavistic peoples poor and brown.”
41 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
Study shows plant-based eaters experience less severe COVID-19 symptoms
A survey of over 2,800 frontline medical workers in six countries revealed that those following a plant-based diet had a 73% lower chance of developing a moderate to severe COVID-19 infection.
Plus, a second study of almost 600,000 people found that diets with the most plant foods were linked to a reduced risk of a COVID-19 infection altogether.
Vegan: cuz we want 2 b healthy n strong.
For more details and free downloads, please visit SupremeMasterTV.com/be-veg
3 notes
·
View notes
Note
pls tell us ur thoughts on veganism (#2 from the ask thing)
my thoughts are good! i've been exclusively plant based before for years and i had a largely good experience with it, and i think it's a great thing to do for people who want to and are able but i also completely understand not wanting to. i also think it very often gets made out to be something it's not, but every diet and lifestyle has adherents who are kinda...deranged and misrepresent it. there are people who hate vegans for very stupid reasons and there are also vegans who are very hateable for very good reasons that are not their diet (usually extremely problematic influencers) but like, vegans aren't monolithic so it can all get pretty frustrating and exhausting to witness the media try to come to some singular conclusion about a huge movement and massive number of people based on a really myopic view of very loud and bad examples.
like anti-vegan raw meat fitness bros and shithead podcasters who antagonise vegans are putrid but so are the vegans who view themselves as morally bulletproof for loving animals while being very privileged, out of touch and racist, wearing plastic fur and leather, shaming people in food deserts or referring to sustainable and traditional practices of indigenous cultures as "barbaric".
it's also not a miracle cure or protective spell against cancer and people who tout it as one are fucking cunts. there's a few public figures here in australia who have done a lot to make vegans look completely insane, saying it will cure anything from covid to brain cancer or smearing themselves in blood and shrieking at people in restaurants. but then there are also always people who are eager to denigrate everyday vegans for nothing at all.
but in my own experience i've never really gotten into any irl discourse with anyone about it, every vegan i've known personally was very normal about it and so was i when it was a part of my life. the people who make asses out of themselves on either side duking it out online and in the media in some kind of eternal hot take battle clearly have bigger issues than what they do or don't put in their mouths and on their bodies. they mostly have a lot of misplaced anger or shame or really any combination of vitriol and distress and this is one of the hills they've chosen to loudly die on as a coping mechanism. at the end of the day their main issue is that they haven't made peace with the limits of their own influence and their sphere of control and it's broken their brains so the anti-vegans hatefully obsess over people not eating bacon and the unhinged self-appointed ambassadors of veganism do reprehensible shit like comparing eating animals to the holocaust. like when piers morgan interviewed tash peterson i wanted the studio to collapse and kill them both lol
in my own experience, my own circle and my own day to day life it has been a primarily positive thing. the main negative i've experienced and the reason i'm not currently exclusively plant based (or exclusively anything) is that following any kind of specific or rule based diet has triggered a relapse into disordered eating for me in the past. that's a whooooole different conversation for another time lol but i'll just say that the vast majority of what i eat now is plant based, and when it comes to the fraction of my diet that isn't, i'm not going to guilt myself over it. while i can't claim to be doing EVERYTHING i can, i'm doing as much as i can while prioritising my mental health and enjoyment of life and i'm a lot healthier now doing that, physically and mentally, than i was when i was a raw vegan letting the concepts of morality and purity and right and wrong in regards to food trigger me into a greenwashed relapse.
i also have the awareness to know that my subjective experience with that pitfall is not the fault of vegan philosophy, just a distortion of it peddled by "wellness" culture that i was particularly susceptible to given my past experiences. and besides, charlatans are not exclusive to veganism, the people on tiktok spruiking raw liver diets and borax smoothies also claim to be doing it in the pursuit of some nebulous ideal of "wellness" so....
basically in conclusion i still personally see the value in being as plant based as i can feasibly and comfortably be, but my relationship to food has been so complex and difficult in the past that i'm ok with pursuing something i see as worthwhile without allowing shame or pursuit of perfection to factor in. and i've also got enough going on with my own relationship to food that i don't really care what anyone else puts in their mouths. if you're vegan or not, just do what you feel is right and what works for you and makes you happy. regardless of my own feelings on veganism and my own history and future with it, everyone and anyone else's diet is firmly outside of my jurisdiction and none of my business. we've seen how trying to dictate the dietary choices of other people has made both pro and anti vegan people become crazy assholes so let's just focus on our own choices because that's all any of us can really control.
(oh my god i didn't mean to write you a novel but all these thoughts just spilled out lol, sorry for the text wall and thank u for asking! <3<3)
#turns out i had a lot more thoughts on it than i knew lol#but yeah your diet is your business eat a cheeseburger or don't idc about anyone's diet but my own we're all gonna die anyway lol#p
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Eat your garbage
First in New York City, and now in Connecticut, I’ve learned a lot from my garbage. Not the trash itself, of course, but food waste and compost.
Over the last seven years, I have maintained a plant-based diet and have committed to compositing or repurposing our household food waste. I will spare you an exhortation on less complicated eating and head right to the compost pile. Learning what is compostable and watching how everything breaks down has reinforced my perspective on diet.
Water required. Whether you are adding in enough fruit and vegetable remnants that contain moisture, or sprinkling the pile when it dries out, just enough water keeps the process going. Too much or too little and you won’t get the results you want. Pro tip: Melon rinds, pumpkins, and gourds really help the pile stay hydrated. Drink up.
Go for flesh and seeds. Fruits, vegetables, and nuts are really the core of a plant-based diet. Peels, cores, leaves, and more jump right into the pile and integrate. Tomatoes, peppers, onions, melons, beans, and gourds also come back months later as volunteers to plant in the garden.
Avoid animal products. While commercial composting facilities accept animal products, at home, meat, fish, poultry, cheese, bones, and animal fat attract vermin.
Minimize salt, refined sugar, and excessive oils. Added salt, sugar, and fat provide little to no value to the compost outcome…so keep them low as an input.
Cut down on baked goods. Flour, water, salt. We all learned to make sourdough during the height of COVID-19, but, when you watch the pile, bread and other baked goods break down slower than other foods.
No chemicals. Natural and organic waste promote healthy compost. Chemicals, including alcohol and artificial sweeteners, do not. Pass.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Healthy forests, healthy planet, healthy humans.
youtube

Forests are often called the lungs of the planet, because they absorb harmful carbon dioxide and produce life-giving oxygen so it’s no exaggeration to equate healthy forests with healthy people, the theme of this year’s International Day of Forests.
Covering 31 per cent of Earth’s land and providing a home to 80 per cent of all land-based species, forests are crucial to human health and well-being, but their loss across the planet is threatening people everywhere.
Here are five things you need to know about the age-old and ever-growing interlinked relationship between forests and human health.

CityAdapt - Forests are key to building climate resilience.
1. Carbon sinks combat climate change
Forest ecosystems keep the planet healthy by regulating the climate, rainfall patterns, and watersheds and crucially provide the oxygen which is essential to human existence.
Healthy forests help to keep climate change in check by acting as “carbon sinks”, which annually absorb about two billion tonnes of carbon dioxide, the gas which is contributing to climate change and the increase of temperatures globally.
The rapidly changing climate is threatening the very existence of people in many different ways: through death and illness due to extreme weather events, the disruption of food systems, and the increase in diseases. Simply put, without healthy forests, people around the world, especially in the world’s most vulnerable countries, will struggle to lead healthy lives and maybe even to survive.

UN-REDD Forest products are processed into medicine in Viet Nam.
2. Nature’s pharmacies: from masks to medicine cabinets
From masks to medicines, forest products are used around the world every day. As many as 80 per cent of developing nations and one quarter of developed countries depend on plant-based medicinal drugs.
Forests contain about 50,000 plant species used for medicinal purposes by both local communities and multinational pharmaceutical companies. For millennia, forest dwellers have treated a range of ailments using products they have harvested. At the same time, many common pharmaceutical medicines are rooted in forest plants, including cancer-treating drugs from the Madagascar periwinkle and malaria medication, quinine, from cinchona trees.
The One Health approach, launched as part of the UN response to the COVID-19 pandemic, recognizes that the health of humans, animals, plants, and the wider environment, including forests, are closely linked and interdependent.

© FAO/ A woman carries goods through Uluguru Nature Forest Reserve in Morogoro, Tanzania.
3. Dinner for 1 billion people
Nearly one billion people globally depend on harvesting wild food such as herbs, fruits, nuts, meat, and insects for nutritious diets. In some remote tropical areas, the consumption of wild animals is estimated to cover between 60 and 80 per cent of daily protein needs.
A study from 43,000 households across 27 countries in Africa found that the dietary diversity of children exposed to forests was at least 25 per cent higher than those who were not.
In 22 countries in Asia and Africa, including both industrialized and developing countries, researchers found that indigenous communities use an average of 120 wild foods per community, and in India, an estimated 50 million households supplement their diets with fruits gathered from wildland forests and surrounding bushland.

UNDP Timor-Leste / Communities in Timor-Leste are helping to restore mangrove forests.
4. Forests are crucial for sustainable development
Forests provide goods and services, employment, and income to perhaps 2.5 billion people worldwide; that’s around one third of the global population.
Keeping forests – and humans – healthy is also at the heart of sustainable development and the 2030 Agenda. Woodlands play a key role in advancing progress across the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), including:
SDG 3 Well-being: Woodlands feel good. Studies show that spending time in forests can boost immune systems while elevating positive emotions and lowering stress, blood pressure, depression, fatigue, anxiety, and tension. Human health and well-being depend on the natural environment, which provides such essential benefits as clean air, water, healthy soils, and food.
SDG 6 Water: Forests play a filtering role in providing freshwater. About 75 per cent of the world’s accessible freshwater comes from forested watersheds. By feeding rivers, forests supply drinking water for nearly half of the world’s largest cities. Threats to forests could trigger water shortages and put global freshwater resources at risk for people across the world, which are among urgent issues addressed at the forthcoming UN 2023 Water Conference.
SDG 13 Climate action: The woods buffer the impacts of storms and floods, protecting human health and safety during extreme weather events. For centuries, forests have acted as nature’s socio-economic safety nets in times of crisis. Sustainably managed and protected forests mean enhanced health and safety for all.

Deforestation continues despite international calls to protect forests.
5. Forests need protecting
The wide-ranging benefits of forests are well known, but that doesn’t mean they are offered the protection that they perhaps deserve. Fire, insect-damage and deforestation have accounted for up to 150 million hectares of forest loss in certain years over the last decade, that’s more than the landmass of a country like Chad or Peru. The production of agricultural commodities alone, including palm oil, beef, soy, timber, and pulp and paper, drives around 70 per cent of tropical deforestation.
Many governments have adopted forest-friendly policies, and others have increased investment in woodlands and trees. Local communities and actors are making their own strides, sometimes one tree at a time. The UN established the Decade for Ecosystem Restoration (2021-2023) and its agencies are harnessing partnerships with local to global stakeholders to better protect forests, from planting three million trees in Peru to empowering young women to work as community forest rangers to protect illegal fauna trafficking in Indonesia.
Established in 2008, UN-REDD is the flagship UN knowledge and advisory partnership on forests and climate, supporting 65 partner countries. Building on the expertise of the UN Environment Programme (UNEP), UN Development Programme, and the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), the initiative has, among other things, seen member countries reduce forest emissions at levels equivalent to taking 150 million cars off the road for a year, ushering in a lot of more fresh air.
For guidance on creating an enabling environment in which people can benefit from all woodlands have to offer, FAO offers recommendations alongside a closer look at many key interlinkage between forest and human health in its report, Forests for human health and well-being
#UN-REDD#FAO#UNDP#UNEP#International Day of Forests#21 march#Forests and health#sdg13#SDG15#intlforestday#vegetation#forestry#Youtube
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
SURPRISING WAYS TO HELP THE ENVIRONMENT
1. EATING A PLANT-BASED DIET
37% of the carbon emissions produced worldwide��are related to food production. FAO estimates that just meat and dairy account for 14.5% of the total. Particularly, the production of beef generates 20 times higher emissions per calorie than the majority of plant-based proteins. The number of individuals eating plant-based diets might greatly cut world emissions.
2. WORKING REMOTELY
Given that the transportation industry is accountable for over 25% of global emissions, commutes to work significantly increase carbon emissions. The discovery that many people are able to work remotely may be one benefit of the Covid-19 pandemic We might observe a decline in commuting traffic and fewer emissions as a result of more professionals working from home.

2 notes
·
View notes
Text
A Deep Dive into the Fats and Oils Market: Trends, Challenges, and Opportunities
The global fats and oils market is a cornerstone of the food and agriculture industries, supporting a wide array of applications beyond cooking, including biofuels, cosmetics, and industrial uses. This blog explores the current state of the market, key growth drivers, challenges, and the evolving trends shaping its future.
Market Overview
The fats and oils market has seen steady growth due to rising demand from various end-use industries. With the expanding global population, increasing disposable incomes, and growing awareness of the health benefits of certain fats and oils, the market is expected to maintain its upward trajectory.
Key Drivers of Growth:
Surging Food Demand: The use of fats and oils in cooking and food preparation is a primary driver of the market, particularly in emerging economies with growing middle-class populations.
Health and Wellness Trends: The rising popularity of healthy oils like olive oil, avocado oil, and coconut oil aligns with consumer preferences for natural and organic products.
Biofuel Production: The use of fats and oils, particularly vegetable oils, in biodiesel production has seen a sharp rise due to global sustainability initiatives.
Industrial Applications: Fats and oils are essential in manufacturing soaps, cosmetics, and lubricants, contributing to market growth.
Market Segmentation
The fats and oils market is diverse, segmented by type, source, application, and region.
By Type:
Vegetable Oils: Includes palm oil, soybean oil, sunflower oil, and others. Palm oil dominates the segment due to its versatile applications and high yield.
Animal Fats: Includes tallow, lard, and butter.
Specialty Fats: Such as margarine, cocoa butter substitutes, and shortening.
By Source:
Plant-Based Oils: Derived from seeds, nuts, and fruits.
Animal-Based Fats: Derived from livestock and marine sources.
By Application:
Food and Beverage: Cooking oils, bakery products, snacks, and confectionery.
Industrial: Biofuels, soaps, detergents, and lubricants.
Cosmetics: Used in skincare and haircare products.
By Region:
Asia-Pacific: The largest consumer, driven by high demand for palm oil and soybean oil in India, China, and Indonesia.
North America: Witnessing growth due to rising biofuel production and consumer preferences for healthy oils.
Europe: Focused on sustainability, with a growing market for organic and non-GMO oils.
Rest of the World: Includes Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa, showing potential due to expanding agricultural activities.
Emerging Trends
Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing: Consumers are increasingly seeking sustainably produced and ethically sourced fats and oils, particularly in the case of palm oil.
Rise of Functional Oils: Oils enriched with omega-3 fatty acids and other nutrients are gaining popularity for their health benefits.
Alternative Fats: The demand for plant-based and vegan fats is on the rise, driven by the global shift towards plant-based diets.
Technological Advancements: Innovations in extraction and refining processes are enhancing the quality and yield of fats and oils.
Challenges
Environmental Concerns: Palm oil production, in particular, has faced criticism for deforestation and habitat destruction.
Price Volatility: Fluctuations in raw material prices due to weather conditions and geopolitical factors can impact market stability.
Health Concerns: The consumption of trans fats and saturated fats has raised health concerns, leading to regulatory interventions in some regions.
Supply Chain Disruptions: The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted vulnerabilities in global supply chains, affecting production and distribution.
Competitive Landscape
The fats and oils market is highly competitive, with key players focusing on innovation, sustainability, and strategic partnerships. Major players include:
Archer Daniels Midland Company
Cargill, Incorporated
Wilmar International Ltd.
Bunge Limited
IOI Corporation Berhad
Future Outlook
The fats and oils market is poised for robust growth, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of X% projected from 2023 to 2030. The rising demand for sustainable and health-focused products, combined with technological advancements, will continue to shape the market’s trajectory.
Key Opportunities:
Expansion into Emerging Markets: Companies can tap into the growing demand in regions like Africa and Latin America.
Innovation in Health-Focused Products: Developing oils with enhanced nutritional profiles can cater to health-conscious consumers.
Investments in Sustainable Practices: Adopting eco-friendly production methods and sourcing can build consumer trust and loyalty.
Conclusion
The global fats and oils market is a dynamic and essential component of the food, agriculture, and industrial sectors. With evolving consumer preferences and advancements in production technologies, the market is set to witness transformative growth. Businesses must adapt to changing trends and invest in sustainability to remain competitive in this vibrant market.
0 notes
Text
Explosive Growth Ahead for Pea Protein: $2.1 Billion in 2024 to $3.7 Billion by 2029
The global pea protein market is on track for remarkable growth, with an anticipated value of USD 2.1 billion in 2024 and a forecasted expansion to USD 3.7 billion by 2029, driven by a strong compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.0%. This upward trend underscores the increasing consumer preference for health-focused, plant-based, and eco-friendly dietary solutions.
Health & Wellness Trends Propel Pea Protein Market Growth
Rising awareness around health and wellness is a key driver behind the demand for pea protein. Consumers are gravitating towards products that support muscle growth, assist with weight management, and provide a sense of fullness. Pea protein, rich in essential nutrients, easily digestible, and free from common allergens such as soy and dairy, aligns perfectly with these preferences. Its clean-label appeal, characterized by minimal processing and natural origins, enhances consumer trust and loyalty.
This versatility makes pea protein a valuable component in plant-based foods and beverages, catering especially to vegan and vegetarian diets. The COVID-19 pandemic further accelerated the adoption of plant-based lifestyles, with Europe leading the market in 2024 due to its economic stability and heightened demand for clean-label, plant-based products.
Get PDF Copy: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/pdfdownloadNew.asp?id=36916504
Environmental Benefits Fuel Popularity
The environmental advantages of pea protein are another significant factor driving its adoption. As consumers increasingly prioritize reducing their carbon footprints, plant-based proteins emerge as sustainable alternatives to animal-based options. With lower resource requirements and reduced greenhouse gas emissions, pea protein is a compelling choice for environmentally conscious individuals and aligns seamlessly with global sustainability goals.
Leading Innovators in the Market
Several prominent pea protein manufacturers are shaping the future of the industry through innovation and expansion:
Roquette Frères (France): A global leader in plant-based ingredients, Roquette offers pea protein under its NUTRALYS brand. Renowned for its binding, thickening, and texturizing properties, NUTRALYS is a preferred ingredient in food formulations promoting weight management, muscle development, and blood glucose regulation.
ADM (USA): With a century-long legacy, ADM provides a diverse portfolio of nutritional solutions, including pea protein, reinforcing its strong international presence.
Ingredion (USA): Known for its range of pea protein products—isolates, concentrates, and flours—Ingredion serves various dietary needs across global markets.
Kerry Group (Ireland): Specializing in taste and nutrition, Kerry delivers innovative pea protein solutions tailored to meet the growing demand for plant-based ingredients in the food and beverage sector.
Glanbia PLC (Ireland): Offering high-quality pea protein with exceptional functional qualities like flavor and solubility, Glanbia supports a wide spectrum of nutrition-focused manufacturers.
Schedule a call with our Analysts to discuss your business needs
A Promising Outlook for Pea Protein
The future of the pea protein market looks bright, driven by consumer demand for healthier and more sustainable food options. Key factors like wellness trends, environmental consciousness, and the rise of plant-based diets are solidifying pea protein’s role as a cornerstone ingredient in modern nutrition. Manufacturers are responding with innovative products and broader offerings, ensuring the market remains dynamic and responsive to evolving consumer needs.
As the global shift toward plant-based, sustainable diets continues, pea protein is set to remain a pivotal force, not just as a trend but as a transformative element in the food industry.
0 notes
Text
Pistachio Market Trends: The Impact of Product Innovation on Consumer Preferences and Market Growth
The pistachio market has seen notable growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer demand for healthy snacks and a heightened awareness of the nutritional benefits of pistachios. This article explores the key trends shaping the pistachio market, analyzing the factors contributing to its growth, evolving consumer preferences, and future projections.

1. Rising Health Consciousness Fuels Demand for Pistachios
One of the primary drivers of the pistachio market is the growing awareness of health and wellness. Pistachios are packed with essential nutrients like protein, fiber, and healthy fats. They are a source of antioxidants, and studies have shown that they may help reduce cholesterol levels and improve heart health. As consumers increasingly lean towards healthier snack alternatives, pistachios are emerging as a popular choice. This shift in consumer preferences is expected to continue to propel the market’s growth.
2. Innovations in Product Offerings
Product diversification plays a significant role in the pistachio market's growth. Manufacturers are introducing innovative pistachio-based products to cater to the tastes and dietary preferences of a broader consumer base. From pistachio butter and pistachio milk to flavored pistachios and confectioneries, the market has witnessed a wave of new products. These innovations not only cater to the growing demand for plant-based foods but also provide consumers with various options to incorporate pistachios into their diets.
3. Expansion of Pistachio Production
To meet the rising demand for pistachios, global production is on the rise. Countries like the United States, Iran, and Turkey are the leading producers of pistachios, but other regions are seeing an increase in cultivation as well. The expansion of pistachio orchards and advancements in agricultural technology are making it easier to grow pistachios in a variety of climates. This trend is expected to continue, contributing to the global availability of pistachios and keeping prices relatively stable.
4. The Role of E-Commerce in Pistachio Distribution
E-commerce has significantly transformed the way consumers purchase pistachios. Online grocery shopping, in particular, has gained popularity, especially after the COVID-19 pandemic. Many consumers are now purchasing pistachios from online stores, which offer a wide range of products, competitive prices, and the convenience of home delivery. The rise of e-commerce platforms is not only benefiting consumers but also creating new opportunities for pistachio producers and suppliers to reach global markets.
5. Sustainability and Ethical Practices in Pistachio Farming
As sustainability becomes a growing concern across industries, the pistachio market is also experiencing shifts towards more eco-friendly farming practices. Consumers are increasingly concerned about the environmental impact of agricultural activities, which is leading to a demand for sustainably produced pistachios. Pistachio farmers are adopting organic farming methods, reducing water usage, and minimizing the carbon footprint of their operations. Certifications like Fair Trade and organic labels are becoming more common as ethical sourcing practices gain traction.
Market Outlook and Future Trends
Looking ahead, the pistachio market is poised to continue its upward trajectory. The demand for healthy and sustainable snack options is expected to grow, driven by the shift in consumer dietary preferences and an increasing interest in plant-based products. Technological advancements in pistachio production, coupled with a continued focus on sustainable farming practices, will likely shape the future of the industry. The pistachio market's growth is not just a passing trend but rather a reflection of broader consumer behavior shifts towards health-conscious and sustainable choices.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the pistachio market is undergoing significant transformations driven by health-conscious consumers, product innovation, expanding production, e-commerce growth, and a focus on sustainability. These trends suggest that the pistachio industry will continue to thrive in the coming years, with new opportunities for producers, suppliers, and consumers alike.
0 notes
Text
UHT Dairy Market Exploring Supply Chain and Regulatory Vulnerabilities
The UHT (Ultra-High Temperature) dairy products market has experienced significant growth in recent years, offering extended shelf life and convenience to consumers globally. However, despite its many advantages, the market faces several vulnerabilities that could impact its continued success. These vulnerabilities stem from a range of challenges, including environmental concerns, supply chain disruptions, regulatory pressures, and evolving consumer preferences. Addressing these vulnerabilities is crucial for the market's long-term sustainability and growth.
1. Environmental Impact and Sustainability Concerns
The environmental impact of UHT dairy production is one of the most significant vulnerabilities facing the market. While UHT dairy products offer convenience and long shelf life, the packaging used for these products, such as tetra packs and plastic containers, contributes to plastic waste and environmental degradation. The demand for eco-friendly packaging is on the rise, as consumers become more conscious of the environmental impact of their purchases. Manufacturers in the UHT dairy products market are increasingly under pressure to adopt sustainable packaging solutions and reduce their carbon footprints. Failure to respond to this demand for sustainability could result in consumer backlash and regulatory challenges, undermining the market's growth potential.
2. Supply Chain Disruptions and Raw Material Sourcing
Supply chain vulnerabilities also pose a significant challenge to the UHT dairy products market. The dairy industry relies heavily on a steady supply of raw materials, such as milk, which can be affected by various external factors, including weather conditions, disease outbreaks in livestock, and geopolitical instability. Additionally, transportation and logistics disruptions, such as those caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, can result in delays and increased costs for UHT dairy manufacturers.
For instance, any fluctuations in milk supply or quality can directly impact the production of UHT dairy products, potentially leading to price increases or shortages in the market. The rising costs of raw materials and transportation can reduce the profitability of UHT dairy products and challenge the market’s ability to keep prices competitive.
3. Health and Wellness Trends
While UHT dairy products are widely appreciated for their convenience, the increasing consumer preference for plant-based diets and healthier alternatives poses a vulnerability to traditional dairy products. As more consumers opt for non-dairy substitutes like almond milk, oat milk, and soy milk, the demand for UHT dairy products could face a decline, particularly in regions where plant-based alternatives are gaining traction.
Moreover, concerns over the high sugar content in flavored UHT dairy beverages and concerns regarding the environmental impact of animal agriculture have led some consumers to seek healthier and more sustainable options. UHT dairy manufacturers may need to adapt to these evolving consumer preferences by offering low-sugar, organic, and plant-based UHT options to maintain market share.
4. Regulatory Pressures and Labeling Standards
The regulatory environment surrounding the dairy industry is another vulnerability that could impact the growth of the UHT dairy products market. Different countries have varying regulations and standards for food safety, labeling, and marketing, which can create challenges for UHT dairy manufacturers, particularly those involved in international trade.
In many regions, there is increasing scrutiny over labeling practices, with consumers demanding more transparency regarding product ingredients, sourcing, and production methods. UHT dairy products, particularly those that contain preservatives or artificial additives, may face more stringent regulations and scrutiny. Non-compliance with these regulatory standards can result in reputational damage, loss of consumer trust, and legal consequences, impacting market growth.

5. Competition from Local and Regional Dairy Products
In many emerging markets, UHT dairy products face strong competition from local and regional dairy products, which are often perceived as fresher and more authentic. While UHT products have a longer shelf life, consumers in some regions may still favor locally produced dairy due to cultural preferences or the perception that locally produced dairy is healthier and of higher quality.
For example, in countries with a rich dairy culture, such as India, China, and parts of Europe, fresh milk and dairy products may be preferred over UHT alternatives. Additionally, in regions with a strong emphasis on traditional farming practices, there is often a preference for dairy that has not undergone industrial processing methods like UHT. This cultural preference can hinder the growth of UHT dairy products in specific markets.
6. Price Sensitivity and Economic Factors
Economic factors, such as inflation, fluctuations in disposable income, and changes in consumer spending behavior, can affect the UHT dairy products market. While UHT products are generally cost-effective due to their long shelf life and efficient production methods, price sensitivity in some regions could influence purchasing decisions.
In developing economies, where consumers are more price-conscious, the higher cost of UHT dairy products compared to locally sourced fresh dairy could deter some customers from choosing UHT options. As competition in the dairy sector intensifies, UHT dairy producers may be forced to reduce prices, which could erode profitability and impact market growth.
Conclusion
The UHT dairy products market is undoubtedly a growing and lucrative segment in the global dairy industry. However, it is not without vulnerabilities. Environmental concerns, supply chain disruptions, shifting consumer preferences, and regulatory pressures are all factors that could influence the future of the UHT dairy market. Manufacturers and stakeholders in the market must address these vulnerabilities proactively by adopting sustainable practices, diversifying product offerings, and adhering to evolving regulations. By doing so, they can ensure the continued growth and success of UHT dairy products in an increasingly competitive and dynamic global market.
0 notes
Text
Fruit Smoothies Market Financial Health in 2025: Growth Prospects, Innovations, and Economic Challenges Ahead
The fruit smoothies market has experienced a significant surge in recent years, driven by changing consumer preferences, growing health awareness, and the increased demand for convenient, nutritious beverages. As a result, the industry’s financial health is in a dynamic phase, with both opportunities and challenges affecting market growth.

Market Overview and Growth Drivers
The global fruit smoothies market, which was valued at approximately $10 billion in 2020, is projected to grow at a robust compound annual growth rate (CAGR). The increasing popularity of plant-based diets, the rise in vegan and vegetarian lifestyles, and a heightened awareness of the benefits of a balanced diet are key factors contributing to the market's expansion. Fruit smoothies have become an essential part of many people's diets due to their ability to offer a healthy dose of fruits, vegetables, vitamins, and essential nutrients all in one convenient drink.
Moreover, the shift toward on-the-go lifestyles is also fueling the demand for portable, ready-to-consume health products, including fruit smoothies. Additionally, a steady rise in the number of health-conscious millennials, coupled with innovations in blending and product offerings, is giving brands a competitive edge in the market. The introduction of superfood smoothie blends and protein-rich smoothies, often targeted toward fitness enthusiasts, is helping cater to a wide consumer base.
Financial Performance of Leading Players
Financial health within the fruit smoothies market can largely be seen through the performance of leading companies in the sector, such as Jamba Juice, Naked Juice, and Smoothie King. These brands have maintained strong financial performance, primarily by tapping into consumer trends toward healthier and plant-based foods. They also benefit from the ongoing trend of delivery and food subscription services, enhancing their reach and ensuring a consistent stream of revenue.
A variety of strategies, including offering seasonal flavors, experimenting with new product lines, and leveraging partnerships with health-focused retailers and delivery platforms, have allowed these companies to thrive. Despite growing competition, the financial resilience of industry giants remains robust due to their extensive market presence, established brand names, and ability to adapt to evolving health and wellness trends.
Economic Factors Influencing Market Growth
Like any industry, the financial health of the fruit smoothies market is not immune to macroeconomic factors. The COVID-19 pandemic brought both challenges and opportunities, as demand for healthier products rose while also imposing disruptions in supply chains and retail operations. However, the surge in at-home consumption as a result of lockdowns, coupled with increased consumer interest in immune-boosting ingredients like citrus and ginger, benefitted the market during these turbulent times.
Supply chain disruptions have also been a cause of concern for smoothie makers. Global logistics bottlenecks, along with a lack of availability of key ingredients such as exotic fruits or protein powders, have raised costs for production. Brands are increasingly looking for ways to mitigate these challenges through direct relationships with farmers and suppliers, vertical integration, and sustainable sourcing models. Despite these obstacles, the overarching outlook for the market remains promising, owing to the continual consumer demand for healthy, convenient products.
Emerging Trends and Financial Outlook
Financially speaking, the future of the fruit smoothies market looks optimistic, with several emerging trends continuing to gain momentum. For instance, plant-based and dairy-free smoothies are on the rise as consumers seek alternatives to traditional dairy options. Additionally, eco-friendly packaging and sustainability are influencing purchasing decisions, with customers increasingly opting for brands that offer compostable or recyclable packaging.
Technology, too, is playing a significant role in the industry's evolution, with some brands adopting artificial intelligence to analyze consumer preferences and streamline inventory management. Moreover, expanding the online presence through e-commerce channels and digital ordering systems has proven to be a crucial aspect of driving market growth and financial stability.
Challenges and Potential Roadblocks
The financial success of the fruit smoothies market will ultimately depend on the ability of brands to navigate several key challenges. Increasing health and wellness trends in the food and beverage market mean heightened competition and the pressure to differentiate oneself from competitors. Additionally, rising raw material costs, changes in consumer demand, and regulatory constraints around labeling, advertising, and food safety are all factors companies must manage to safeguard their market share and financial health.
Despite these challenges, the resilience and adaptability of leading companies ensure that the market can withstand economic pressures. A continuous focus on innovation, consumer-driven product development, and strategic marketing efforts can mitigate the financial impacts of industry disruptions, paving the way for future success.
Conclusion
In summary, the fruit smoothies market stands at a crossroads of financial opportunity and challenge. With growing consumer demand, technological advancements, and innovative product offerings, the market is set for continued growth. However, to maintain financial health, companies must address external challenges, evolving consumer tastes, and operational hurdles to secure a prosperous future. Ultimately, those that can deliver on both health-conscious, sustainable products and cater to ever-changing market dynamics will be the leaders of the pack.
0 notes
Text
The Canned Vegetables Market is projected to grow from USD 24166.3 million in 2024 to an estimated USD 33585.5 million by 2032, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.2% from 2024 to 2032.The global canned vegetables market is witnessing significant growth, driven by increasing consumer demand for convenient, long-lasting, and nutritious food options. Canned vegetables, preserved through heat processing, offer a practical solution for modern lifestyles that prioritize time-saving and cost-effective food choices. Their ability to retain essential nutrients and provide year-round availability of seasonal produce has further solidified their appeal across diverse demographics. From urban consumers seeking ready-to-eat meals to rural regions with limited access to fresh produce, canned vegetables cater to a wide spectrum of needs. Additionally, advancements in canning technology, sustainable packaging, and growing health awareness have contributed to the market’s expansion.
Browse the full report https://www.credenceresearch.com/report/canned-vegetables-market
Market Drivers and Trends
One of the primary drivers of the canned vegetables market is the rising demand for convenience foods. As urbanization accelerates and dual-income households become more prevalent, consumers are seeking food products that are easy to prepare, require minimal effort, and provide consistent quality. Canned vegetables, with their extended shelf life and ready-to-use nature, fit perfectly into this narrative. The growing awareness about food wastage has also played a pivotal role in driving demand, as canned vegetables minimize spoilage and waste compared to fresh produce.
Moreover, the increasing focus on health and wellness has led manufacturers to innovate and introduce low-sodium, organic, and preservative-free canned vegetables. These healthier options appeal to health-conscious consumers, addressing concerns about added preservatives and excessive sodium content typically associated with canned foods. The inclusion of plant-based diets and vegan trends further supports the market, as consumers incorporate canned vegetables like beans, peas, and tomatoes into their meals.
The market has also seen significant influence from sustainability trends. Companies are adopting eco-friendly packaging solutions, such as recyclable metal cans and BPA-free linings, to align with global environmental goals and cater to environmentally conscious consumers. Innovations in canning technology have improved the preservation of texture, flavor, and nutrients, ensuring that canned vegetables compete effectively with fresh and frozen alternatives.
Key Players and Competitive Landscape
The canned vegetables market is highly competitive, with major players focusing on product innovation, sustainable practices, and strategic partnerships to gain a competitive edge. Prominent companies like Del Monte Foods, Bonduelle Group, Green Giant, Conagra Brands, and General Mills are leading the market with diverse product portfolios and strong distribution networks.
These companies are investing in marketing campaigns to highlight the nutritional benefits and convenience of canned vegetables. Additionally, partnerships with retail chains and online platforms have enhanced product accessibility, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic, which saw a spike in demand for shelf-stable food products.
Future Outlook
The canned vegetables market is poised for steady growth, driven by evolving consumer preferences and technological advancements. As sustainability becomes a core focus, the adoption of environmentally friendly packaging and energy-efficient production processes will become increasingly important. Innovations in flavor preservation, reduced sodium content, and organic offerings will cater to health-conscious consumers, further expanding the market's reach.
Moreover, as e-commerce platforms continue to flourish, the accessibility of canned vegetables will improve, particularly in emerging economies. With urbanization, changing dietary patterns, and increased awareness of food preservation benefits, the canned vegetables market is set to play a pivotal role in the global food industry, meeting the needs of both convenience-driven and health-conscious consumers.
Key Player Analysis:
365 by WFM
Cento
Del Monte Foods, Inc
Farmer’s Market Foods
Good & Gather
Goya
Great Value
Green Giant
Libby’s
Native Forest
Nature’s Greatest Foods
Old El Paso
Reese
Rosarita
Rotel
Whole Foods Market
Segmentation:
By Nature:
Organic
Conventional
By Canning Type:
Canned in Water
Canned in Oil
Canned in Juice
By Vegetable Type:
Corn
Peas
Beans
Carrots
Potatoes
Tomatoes
Spinach
Mixed Vegetables
Other Vegetables
By Vegetable Group:
Leafy Vegetables
Cruciferous
Marrows
Roots
Others (Stems, Alliums, etc)
By End User
Household
Foodservice
Industrial
By Distribution Channel
Supermarkets and hypermarkets
Convenience stores
Online retailers
Specialty stores
Direct sales
By Region
North America
U.S.
Canada
Mexico
Europe
Germany
France
U.K.
Italy
Spain
Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
China
Japan
India
South Korea
South-east Asia
Rest of Asia Pacific
Latin America
Brazil
Argentina
Rest of Latin America
Middle East & Africa
GCC Countries
South Africa
Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Browse the full report https://www.credenceresearch.com/report/canned-vegetables-market
Contact:
Credence Research
Please contact us at +91 6232 49 3207
Email: [email protected]
Website: www.credenceresearch.com
0 notes
Text
Top 5 Key Factors Driving Consumer Behavior in Profitable Restaurants: Premium Design and Build Strategies for Success
Before we start talking about the current trends in consumer behaviour, let us first understand the basics of the food and beverage industry. Well, the first thing you need to know is that it is massive. It encompasses everything at once, like- bars, cafes, restaurants, manufacturers and even food transportation. Did you know that the F&B industry serves the livelihoods of about 7.3 million people in India, according to ET Hospitality World, making it one of the most significant sectors in the country? It also acts as a catalyst for various other sectors, like- retail, agriculture and transportation.
When COVID-19 hit, all major outlets suffered a setback; restaurants, cafes, and all public spaces went silent. It affected every business. But perhaps the most affected industry was the food and beverage industry. Consumers went from hanging out at cafes to ordering in and even ordering groceries online. Fortunately, this wouldn’t last for long as the world recovers. We have witnessed the resurgence of in-person dining as a result of revenge dining, which is making the best of every situation when people lacked the chance to go out during COVID-19.

The design has been the central theme of every restaurant and cafe designers as it attracts consumers. Ambience plays an important role in this venture. The amalgamation of comfort and safety caters to new consumer preferences. From outdoor seating to flexible indoor layouts, the new outdoor dining experience has everything. Consumers are also placing more value on sustainable and eco-friendly products, showing a willingness to switch to different food and beverage brands to align with their new criteria. According to changing consumer behaviour, factors affecting them also evolve. Let us get into these factors at length.
1. Adding Value to Nutrition
We all know that when it comes to food, taste, flavour and smell are the catalysts that drive consumers to satisfy their cravings. What if we told you that these factors have become limited over time and have been replaced by nutritional weightage? A survey conducted by the International Food Information Council in 2020 found that approximately 54% of consumers consider the healthfulness of food when making purchase decisions. The percentage was more inclined towards the younger generation. Thanks to the information provided on social media, the population is now becoming increasingly aware of their health choices. The rise of new consumerism has, therefore, triggered reactions from restaurants and food brands that are currently making room for healthier menus, transparent lists of ingredients, and nutritional information. They have also emphasized the sustainable and organic ingredients that conform to this growing demand for clean eating.
These businesses stand to gain in the changing landscape of increasing healthful food options and straightforward, honest communication of information between companies and customers. This shift can lead to improvements not only in meeting consumer demand but also in promoting a generally healthier society.

2. Environmental Concerns
To minimize their carbon footprints, many environmentally-conscious consumers are now opting for a plant-based diet. Food that is sustainably sourced is now gaining traction and becoming increasingly popular. It is now becoming very common to have plant-based menus at cafes and restaurants.
Restaurants adopting these trends are not only catering to a growing demographic but also leading toward a more sustainable and ethically sourced food industry. Putting plant-based and responsibly sourced foods on their menus not only promotes better brand images but also broadens customer bases while making a positive mark on the planet.
3. Clean- Labelling practices
One more thing attributed to changing consumer behaviour is clean labelling practices. The simpler, the better, is their mantra. Do you ever see the ingredient lists, and it makes you more confused than ever? Well, clean labelling eliminates this practice. It focuses mainly on natural and minimally processed ingredients that customers can easily understand. Clean labels appeal to those looking to make educated decisions supporting their wellness objectives. Customers profit from this trend, pushing producers to use more sustainable and transparent production methods. Clean labelling goes beyond marketing to regulatory compliance, product quality, consumer trust, and ethical production practices. It is a space that, as the trend evolves, will likely shape significant parts of the future food industry into more sustainable and friendly practices for consumers globally.

4. Culture
Culture is a significant drive in determining what and how we eat—food choice, taste preference, and views on food. This is due to different cultural food traditions and beliefs. For instance, people will have more or less willingness to venture into trying new foods: it all depends on their cultural background, the policies of their country, or the prevailing social environment. In a connected world like today, food companies need to understand cultural differences to be able to cater to diverse tastes. In other words, people’s perception and acceptance of foods are culturally determined, which includes familiarity with the foods, the language under which food marketing is done, and the environment of the foods as part of their culture. From premium restaurants to street food vendors, everyone is now heavily influenced by ramen and Japanese cuisine, leading us to believe that cultural ties are strengthened through food.
5. The Ambience
The experience and ambience of a restaurant make the very first impression and foster an experience. This means that lighting, decor, and music all come into play, which controls the mood and the customer’s expectations; on the other hand, a unique ambience will usher in memorable moments that complement the culinary delights. Not only does such an ambience add to the taste of the meal, but it also provokes the diners to share the experience with others, making this restaurant more attractive for business. Furthermore, a restaurant space can reflect the identity and ethos of the restaurant, introducing layers of complexity to the dining experience. It also assures returning customers about the quality and experience they will get, building great loyalty and, hence, an excellent brand reputation.

Conclusion
The food and beverage sector is experiencing major changes due to new technologies and changing customer expectations. Consumers are increasingly demanding thorough information about sourcing, production processes, and ethical standards, therefore, transparency and sustainability have become critical. These developments do, however, carry some inherent dangers, which require strict quality controls, aggressive regulatory compliance, and strong risk management.
To remain competitive, firms must embrace a holistic strategy that integrates cutting-edge technologies, moral sourcing, and quick response to market shifts. Through the implementation of creative solutions and a focus on transparency, brands may establish consumer loyalty and trust, guaranteeing adherence to changing regulations and attaining steady expansion and a competitive edge in a constantly changing marketplace. Innovation and tradition, efficiency and sustainability—all need to be balanced for the food and beverage industry to grow and become a reliable, vibrant sector that caters to the demands and values of contemporary consumers.
Head to our website to know more: https://sprint-co.com/
1 note
·
View note