#peptide receptor
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
PRRT is a molecular technique in which a radioisotope which is labeled with a small body that actually targets a particular receptor which is known as the somatostatin receptors is used to treat a specific kind of tumor known as a Neuroendocrine Tumor.
#prrt therapy#Actinium Ac 225 Alpha PRRT#PRRT in India#Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy in India#Nuclear Medicine Expert in India#PRRT Treatment for Neuroendocrine Tumors#PRRT Therapy Side Effects#PRRT Therapy#PRRT Treatment#PRRT in Neuroendocrine Tumors#Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy#PRRT
0 notes
Text

In recent years, a breakthrough in diabetes management has emerged in the form of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) analogs. These innovative medications have revolutionized the treatment landscape by providing improved glycemic control and additional benefits for individuals with type 2 diabetes.
Read More: https://cmibloggers.blogspot.com/2023/06/understanding-glucagon-like-peptide-1.html
#coherent market insights#Healthcare Industry#Pharmaceutical#Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 analogs Market#GLP-1 receptor agonists#Diabetes management#Type 2 diabetes#Glycemic control#Blood sugar regulation#Insulin therapy
0 notes
Link
The market opportunities for key players to enter into this market are high owing to less competition and increasing demand for peptide receptor radionuclide therapy in the Italy market. Moreover, increasing incidence of cancer in Italy is directly contributing to demand for PRRT therapy. These factors are creating growth opportunities for companies to focus on research and development of new drugs. As per the Italian Association of Medical Oncology’s report, in April 2019, 71,000 new cases were diagnosed with new additional cancer cases.
0 notes
Text
Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy (PRRT) Market end-user demand, trend, new innovations, global forecast to 2032

This Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy market study offers a comprehensive analysis of the business models, key strategies, and respective market shares of some of the most prominent players in this landscape. Along with an in-depth commentary on the key influencing factors, market statistics in terms of revenues, segment-wise data, region-wise data, and country-wise data are offered in the full study. This study is one of the most comprehensive documentation that captures all the facets of the evolving Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy Prrt market.
Advancement and growing researches in the medical industry leads to a dramatic surge in the availability of new cancer treatment options. Radiation therapies and targeted therapy is showing significant promise in cancer treatment. For example, peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) had recently approved the neuroendocrine tumors and projecting significant growth in the cancer treatment market. Peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) is radioisotope or molecular therapy used to treat neuroendocrine tumors (NETs).
Get Sample Report@ https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/reports/sample/rep-gb-10376
Peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) is recommended for the somatostatin receptor-positive gastroenteropancreatic NETs affected patients. Peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) is a targeted therapy designed to slow the progression of gastroenteropancreatic NET and limiting radiation exposure to healthy tissue. Lutathera (lutetium Lu 177 Oxodotreotide) was the first drug approved for the peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) for the treatment of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (GEP-NETs). In September 2017, the European Commission approved Lutathera peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) drug manufactured by Advanced Accelerator Applications S.A. Although, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) was approved LUTATHERA in January 2018. Growing clinical trials and development activities to create therapeutic radiopharmaceuticals expected to surge the growth of the peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) market over the forecast period.
Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy (PRRT) Market: Drivers and Restraints-
Increasing prevalence of the neuroendocrine tumors expected to impel the demand for peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) as an increasing number of the patient pool. Establishment of reimbursement policies for Lutathera favors the demand for peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT). A temporary insurance/billing code was used for the peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) till 2018. Moreover, increasing clinical trials for the new radiopharmaceuticals drugs approval for cancer therapy expected to surge the growth of the peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) market.
Increasing government and private organizations funding for cancer drugs and therapy development is another major factor expected to propel the growth of the peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) market. Moreover, growing manufacturer’s interest in the radiopharmaceutical and cancer market flourish the growth of the peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) market. Side effects such as the transient decrease in blood counts, nausea and others associated with PRRT expected to hamper the growth of the peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) market.
Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy (PRRT) Market: Overview
Peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) a special type of radiopharmaceutical which injected into the patients’ bloodstream. This radiopeptide travels and binds to neuroendocrine tumor cells and provide a high dose of radiation directly to the cancer cell. Big pharmaceutical market players are focusing to enter in the radiopharmaceutical market. For instance, In October 2017, Novartis AG acquired Advanced Accelerator Applications (AAA) for $3.9 billion to expand oncology portfolio. This acquisition was valuable for Lutathera radiopharmaceutical candidates which were under FDA review in 2018.
Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy (PRRT) Market: Region-wise Outlook
North America and Europe region are expected to grebe more than half of the market share for peptide receptor radionuclide therapy. Increasing clinical trials for radiopharmaceuticals and growing demand for the targeted therapy for cancer are the major factors driving the growth of the peptide receptor radionuclide therapy market in the U.S. and European countries. The Asia pacific peptide receptor radionuclide therapy market expected to grow with significant growth rate as growing demand for advance treatment option and comparatively high prevalence of cancer in India and China.
Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy (PRRT) Market: Key Market Participants
Example of some market players participants in global peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) market find across the value chain are Advanced Accelerator Applications (AAA) (Novartis AG) and others.
The research report presents a comprehensive assessment of the market and contains thoughtful insights, facts, historical data, and statistically supported and industry-validated market data. It also contains projections using a suitable set of assumptions and methodologies. The research report provides analysis and information according to market segments such as geographies, application, and industry.
The report covers exhaust analysis on:
Market Segments
Market Dynamics
Market Size
Supply & Demand
Current Trends/Issues/Challenges
Competition & Companies involved
Technology
Value Chain
Regional analysis includes:
North America (U.S., Canada)
Latin America (Mexico. Brazil)
Western Europe (Germany, Italy, France, U.K, Spain)
Eastern Europe (Poland, Russia)
Asia Pacific (India, China ASEAN, Australia & New Zealand)
Japan
Middle East and Africa (GCC Countries, S. Africa, Northern Africa)
The report is a compilation of first-hand information, qualitative and quantitative assessment by industry analysts, inputs from industry experts and industry participants across the value chain. The report provides in-depth analysis of parent market trends, macro-economic indicators and governing factors along with market attractiveness as per segments. The report also maps the qualitative impact of various market factors on market segments and geographies.
Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy (PRRT) Market: Segmentation
On the basis of indication, peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) market can be segmented as:
Foregut Neuroendocrine Tumors
Midgut Neuroendocrine Tumors
Hindgut Neuroendocrine Tumors
On the basis of end user, peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) market can be segmented as:
Hospitals
Ambulatory Surgical Centers
Cancer Care Centers
For in-depth insights, Download a PDF Brochure – https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/reports/brochure/rep-gb-10376
Report highlights:
Detailed overview of parent market
Changing market dynamics in the industry
In-depth market segmentation
Historical, current and projected market size in terms of volume and value
Recent industry trends and developments
Competitive landscape
Strategies of key players and products offered
Potential and niche segments, geographical regions exhibiting promising growth
A neutral perspective on market performance
Must-have information for market players to sustain and enhance their market footprint
#Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy (PRRT) Market Market#Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy (PRRT) Market Market Size#Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy (PRRT) Market Market Growth
0 notes
Text
Vydura gains positive CHMP nod for migraine, but faces tough competition ahead
Vydura will turn into the primary CGRP receptor adversary accessible in Europe whenever supported by the European Meds Organization (EMA).
On February 25, Biohaven and Pfizer declared that Vydura (rimegepant) had gotten a positive assessment from the European Drugs Organization's (Ema's) Panel for Restorative Items for Human Use (CHMP) in the intense and protection therapy of headache. Whenever endorsed by the EMA, Vydura, which is marketed in the US as Nurtec, will turn into the primary oral calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) type -1 receptor adversary to open up in Europe. Notwithstanding, the medication's market passage will be followed intently by AbbVie's CGRP receptor bad guy, Qulipta (atogepant), which will end up being a savage rival in the headache prophylaxis space.
In spite of a logical first-to-market advantage for Vydura in Europe, GlobalData expects the medication will confront powerful contest from AbbVie's Qulipta, as would be considered normal to enter European markets in 2023. Key assessment pioneers (KOLs) talked with by GlobalData were dazzled with Qulipta's excellent headache avoidance rates and commended its accessibility in three qualities for simple portion titration. Contrasted with Qulipta, Vydura has the additional advantage of both intense and safeguard therapy signs. Notwithstanding, KOLs noticed that gepants had restricted utility in the intense therapy of headache. They made sense of that gepants are generally very delayed in their beginning of activity, and are subsequently less ideal for intense relief from discomfort, especially when contrasted with reasonable generic triptans. In light of these variables, GlobalData gauges Vydura and Qulipta to arrive at deals of $35.4 million and $57.1 million, separately, by 2030 in the five significant European markets (5EU) (France, Germany, Italy, Spain, and the UK).
For more CALCRL Pipeline Products Market mechanisms of action insights, download a free report sample
Across the seven significant pharmaceutical markets (7MM) (US, 5EU, and Japan), GlobalData expects headache market deals of $652.1 million for Nurtec/Vydura in 2030, addressing almost 22% of complete deals inside the developing oral CGRP inhibitor class. Probable in a bid to separate it from contenders, Biohaven has plans for Nurtec/Vydura beyond the nervous system science space. In January 2021, as a team with Weill Cornell Clinical School , the organization began a Stage II pilot investigation of Nurtec in the treatment of plaque psoriasis. All the more as of late, the organization reported the beginning of another Stage II/III preliminary (NCT05248997) of Nurtec in the therapy of persistent rhinosinusitis. These two illness markets are sizeable and could enormously expand Nurtec's range in the event that the medication is viewed as solid.
0 notes
Text
"A team at Northwestern University has come up with the term “dancing molecules” to describe an invention of synthetic nanofibers which they say have the potential to quicken the regeneration of cartilage damage beyond what our body is capable of.
The moniker was coined back in November 2021, when the same team introduced an injection of these molecules to repair tissues and reverse paralysis after severe spinal cord injuries in mice.
Now they’ve applied the same therapeutic strategy to damaged human cartilage cells. In a new study, published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, the treatment activated the gene expression necessary to regenerate cartilage within just four hours.
And, after only three days, the human cells produced protein components needed for cartilage regeneration, something humans can’t do in adulthood.
The conceptual mechanisms of the dancing molecules work through cellular receptors located on the exterior of the cell membrane. These receptors are the gateways for thousands of compounds that run a myriad of processes in biology, but they exist in dense crowds constantly moving about on the cell membrane.
The dancing molecules quickly form synthetic nanofibers that move according to their chemical structure. They mimic the extracellular matrix of the surrounding tissue, and by ‘dancing’ these fibers can keep up with the movement of the cell receptors. By adding biological signaling receptors, the whole assemblage can functionally move and communicate with cells like natural biology.
“Cellular receptors constantly move around,” said Northwestern Professor of Materials Sciences Samuel Stupp, who led the study. “By making our molecules move, ‘dance’ or even leap temporarily out of these structures, known as supramolecular polymers, they are able to connect more effectively with receptors.”
The target of their work is the nearly 530 million people around the globe living with osteoarthritis, a degenerative disease in which tissues in joints break down over time, resulting in one of the most common forms of morbidity and disability.
“Current treatments aim to slow disease progression or postpone inevitable joint replacement,” Stupp said. “There are no regenerative options because humans do not have an inherent capacity to regenerate cartilage in adulthood.”
In the new study, Stupp and his team looked to the receptors for a specific protein critical for cartilage formation and maintenance. To target this receptor, the team developed a new circular peptide that mimics the bioactive signal of the protein, which is called transforming growth factor beta-1 (TGFb-1).
Northwestern U. Press then reported that the researchers incorporated this peptide into two different molecules that interact to form supramolecular polymers in water, each with the same ability to mimic TGFb-1...
“With the success of the study in human cartilage cells, we predict that cartilage regeneration will be greatly enhanced when used in highly translational pre-clinical models,” Stupp said. “It should develop into a novel bioactive material for regeneration of cartilage tissue in joints.”
“We are beginning to see the tremendous breadth of conditions that this fundamental discovery on ‘dancing molecules’ could apply to,” Stupp said. “Controlling supramolecular motion through chemical design appears to be a powerful tool to increase efficacy for a range of regenerative therapies.”"
-via Good News Network, August 5, 2024
#nanotechnology#osteoarthritis#arthritis#medical news#science news#cell biology#molecular biology#cartilage#good news#hope
710 notes
·
View notes
Text
A drug commonly used to treat type 2 diabetes could also effectively protect against colorectal cancer (CRC), based on a new analysis by researchers in the US. The drug in question is a class of medications known as glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists – more easily referred to as GLP-1 RAs. These medications, which include the widely-known 'wonder drug' sold under the commercial name Wegovy, have also previously been linked to weight loss and reducing the risk of cardiovascular problems.
Continue Reading.
76 notes
·
View notes
Text
Propaganda!


Sertoli cells are a type of sustentacular "nurse" cell found in human testes which contribute to the process of spermatogenesis (the production of sperm) as a structural component of the seminiferous tubules. They are activated by follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) secreted by the adenohypophysis and express FSH receptor on their membranes.
Insulin is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the insulin (INS) gene. It is the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and protein by promoting the absorption of glucose from the blood into cells of the liver, fat, and skeletal muscles.
#sertoli cells#insulin#tournament poll#polls#wikipedia#cells of the human body#science tournament#biochemistry
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
Also preserved in our archive (Daily updates!)
There've been a lot of studies showing vitamin D deficiency in people with mild to severe covid cases. A new meta-analysis probes into the possible connections and effects of vitamin D during acute covid infections.
By Dr. Liji Thomas, MD
New study suggests vitamin D supplementation may lower ICU and intubation rates in COVID-19 patients, with greater benefits seen in older and severe cases.
The impact of vitamin D on the progression of COVID-19 remains uncertain. A recent meta-analysis in Nutrients reviewed studies on vitamin D supplementation in COVID-19 patients to assess its effectiveness in reducing disease severity across various health metrics.
Why is vitamin D important? Vitamin D is essential for bone health, but its influence extends far beyond, as its receptor is present in all nucleated human cells. This receptor regulates nearly 4% of human genes, impacting many physiological processes, including cancer development, muscle function, cardiovascular health, glucose balance, and immune response to infections and autoimmune reactions.
With the onset of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, there was significant interest in whether vitamin D could reduce the severity or spread of COVID-19. Vitamin D plays a role in immunity by lowering the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, boosting antimicrobial peptides, supporting epithelial barriers, and modulating T-cell activity—mechanisms that may help prevent the severe hyperinflammation associated with critical COVID-19 cases and high mortality.
This study investigates the protective effects of vitamin D supplementation during COVID-19, used alongside standard treatments like glucocorticoids, anticoagulants, and antivirals, as recommended in current care guidelines.
About the study The researchers included 21 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and eight analytical studies in the meta-analysis. Of these, mortality rates were examined in 19 RCTs and seven analytical studies, intensive care unit (ICU) admissions in 14 and five, respectively, intubation rates in nine and three, respectively, and the length of hospital stay (LOS) only in RCTs.
Vitamin D dosage varied considerably between studies, both in intervention and control groups.
Vitamin D and ICU admissions In the randomized controlled trials (RCTs), vitamin D supplementation demonstrated a stronger protective effect at higher doses compared to lower doses. Specifically, higher doses were associated with a 63% reduction in ICU admission rates compared to lower doses.
ICU admissions decreased by 57% among patients aged 65 or older and by 44% among those under 65. Patients with severe disease did not show a significant response to vitamin D, while those with non-severe disease experienced 33% fewer ICU admissions.
Intubation rates Intubation rates fell by 50% in RCTs. The lack of effect in analytical studies may have been because they were carried out only in non-severe older COVID-19 patients and were limited in number.
The tendency towards significance strengthens the hypothesis of the benefit of vitamin D in reducing the need for intubation during COVID-19.
Mortality rates Mortality rates showed significant differences in the vitamin D supplementation group but only in analytical studies, with a fall of 55%. This might indicate a tendency to bias in analytical studies.
Despite the overall lack of significance, age-stratified analysis of the RCTs showed a 42% reduction in mortality in older patients but not those <65 years. The authors suggested that the overall analysis might have failed to reveal these more granular effects.
Another interesting effect was that vitamin D supplementation had a more marked mortality-reducing impact in the early months of the pandemic, up to May 2020, than later on.
Finally, the most ill patients had a 50% mortality reduction benefit, but not the less severely ill patients. Thus, mortality analyses in the RCTs present a complex picture, with significant protective effects observable in some subgroups but not in the overall analysis.
LOS Among non-severe COVID-19 patients, vitamin D supplementation was associated with a -0.95-day difference in hospital length of stay. Potential benefits could exist in other groups, but this awaits validation from future research.
The variations between studies should be interpreted as accounting for the forms of vitamin D in use, such as calcifediol or cholecalciferol.
The latter is faster-acting than the former, which may make a difference in acute severe COVID-19, especially as evidence indicates that active vitamin D is used up in the acute response to the infection.
However, broad differences were noted across the studies, including baseline vitamin D levels, dosages, and duration of symptoms before vitamin D supplementation. Still, the findings agree with some previous analyses, with a more nuanced conclusion.
Conclusions The findings do indicate that vitamin D supplementation could be of benefit in COVID-19 treatment, reducing ICU admissions, mortality, and intubation requirements. All studies showed fewer ICU admissions in the intervention group.
“The differing effects based on age, disease severity, and possibly baseline vitamin D status highlight the need for a nuanced approach to vitamin D supplementation in COVID-19 management.”
The greatest effect seems to be in reducing ICU admissions. Still, with differences in the evidence across various patient subgroups and for different outcomes, there is a need for larger trials with a better design that adjusts for baseline vitamin D levels and uses standardized dosages and regimens, as well as compensating for patient characteristics.
Journal reference: Sartini, M., Puente, F. D., Carbone, A., et al. (2024). The Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation Post COVID-19 Infection and Related Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients. doi: doi.org/10.3390/nu16223794. www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/16/22/3794.
#mask up#covid#pandemic#public health#wear a mask#wear a respirator#covid 19#coronavirus#still coviding#sars cov 2#vitamin d
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
Neuroendocrine Tumors often present with large volume Liver Metastases and because these are relatively Indolent Tumors the patient often does not know that he has a Neuroendocrine Tumors specially those who have non-functioning Neuroendocrine Tumors.
#Transarterial Radioembolisation#Transarterial Radioembolisation in India#Side Effects of TARE#TACE vs TARE#PRRT#PRRT in India#PRRT in Neuroendocrine Tumors#PRRT Therapy#PRRT Therapy Side Effects#PRRT Treatment#PRRT Treatment Cost in India#PRRT Treatment for Neuroendocrine Tumors#PRRT Treatment in India#Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy#Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy in India#Nuclear Medicine Expert in India#Nuclear Medicine Therapy#Nuclear Medicine Therapy in India#Dr. Ishita B. Sen
0 notes
Text
Two cool migraine-related papers i found today:
CGRP has a direct biochemical effect on anxiety. Relevant because migraine patients (sometimes! there are multiple pathologies involved in migraine and not everyone is the same) have significantly elevated serum CGRP compared to healthy controls
2. Migraine patients on CGRP antibody treatments see improvements in depressive symptoms independent of the effect on their migraines
The second study is a small group and the numbers aren't super impressive but it matches up with my experience from the patient side and pretty cool to see work being done on this!
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
By Peter A. McCullough, MD, MPH
Glucagon-like peptide receptor agonists (GLP-1 RA) are the current financial rainmakers for BIG PHARMA.
Shi et al from Harvard reported recently in JAMA Cardiology.
Rapidly increasing uptake of semaglutide made it the top-selling drug in the US in 2023, with net sales of $13.8 billion. Quantifying the number of US adults eligible for semaglutide may guide future policies for this high-cost therapy and clarify potential implications for pharmaceutical spending.
The authors conclude that approximately 137 million adults or half the of the US population could have a clinical indication for once weekly GLP-1 RA drugs. This budget breaking conclusion no doubt will have to be addressed by the incoming HHS administration led by Robert F. Kennedy, Jr.Shi I, Khan SS, Yeh RW, Ho JE, Dahabreh IJ, Kazi DS. Semaglutide Eligibility Across All Current Indications for US Adults. JAMA Cardiol. Published online November 18, 2024. doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2024.4657
GLP-1 RAs mimic the actions of the GLP-1 hormone, which is released in the gut after eating. This stimulates the release of insulin and reduces blood sugar levels.
BenefitsGLP-1 RAs can help with:
Blood sugar: GLP-1 RAs are effective at lowering blood sugar levels after meals and during fasting. They are also unlikely to cause hypoglycemia (low blood sugar).
Weight: GLP-1 RAs can help with weight reduction.
Heart health: GLP-1 RAs may have benefits for heart health, including reducing the risk of heart attacks.
Kidney function: GLP-1 RAs may have benefits for kidney function.
Thus there are significant benefits, however the effect on weight reduction is transient and about two thirds regain the weight that is lost after stopping the shots.
11 notes
·
View notes
Text

Cool Heads Prevail
What do head injuries, strokes and seizures have in common? They can all cause brain damage. Urgent cooling of the brain, triggering hypothermia, protects against this. Physical cooling comes with complications so instead triggering hypothermia with a drug called neurotensin is now being investigated. But it only works if administered directly into the brain as it can’t cross the blood–brain barrier (BBB). So researchers engineered neurotensin with extra bits of protein (peptides) that aid BBB crossing and tested it in a mouse model of epilepsy. Modified neurotensin triggered hypothermia, reduced seizures and reduced inflammation in part of the brain (hippocampus) responsible for learning and memory that shrinks in humans after repeated seizures. Treated mice also performed better in learning and memory tests. The team investigated whether these effects were possible due to neurotensin receptors in the hippocampus, and sure enough fluorescence microscopy of hippocampal neurons (pictured, blue) grown from brain slices revealed they were indeed (red).
Written by Lux Fatimathas
Image from work by Lotfi Ferhat and colleagues
Aix-Marseille Université, CNRS, Inst Neurophysiopathol, UMR 7051, Marseille, France
Image originally published with a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0)
Published in eLife (reviewed preprint), September 2024
You can also follow BPoD on Instagram, Twitter and Facebook
#science#biomedicine#immunofluorescence#neuroscience#brain#biology#hyopthermia#brain injury#blood-brain barrier#hippocampus
11 notes
·
View notes
Note
hey! would you mind answering a more general genetics question? i’m still pretty new to genetics and the terminology but it’s very interesting so far! i really appreciate you taking the time to explain these concepts in a way even someone like me can understand!
i noticed that people will refer to genes like KIT or PAX3 occurring in different animals, such as in your posts about KIT being found to affect coat colours in both cats and rabbits. Does this mean that the KIT gene (or any other example) is exactly the same in both species? As in, do they both have a string of the exact same DNA? Does KIT act the same/change the same things in both species? If they’re not the same, why do we call them both KIT?
thanks in advance!
Yes, it's pretty much the same. Maybe not the exact sequence base-by-base, but the difference is small, they code the same peptide, and that peptide has the same function (so their mutations can have similar effects too). I think pigment production is a pretty universal process in mammals, so they all have basically the same genes about it.
The human KIT gene (KIT proto-oncogene, receptor tyrosine kinase) has studied orthologs in all these species:

(Source: HGNC)
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
endorphins
ɛnˈdɔrfɪnz
noun
: any of a group of endogenous peptides (such as enkephalin) found especially in the brain that bind chiefly to opiate receptors and produce some pharmacological effects (such as pain relief) like those of opiates
Example sentence:
Moving in the same way, and at the same time, as others triggers a release of endorphins.
Washington Post, 21 Jan. 2020
So does watching the synchronized movements of these two.
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
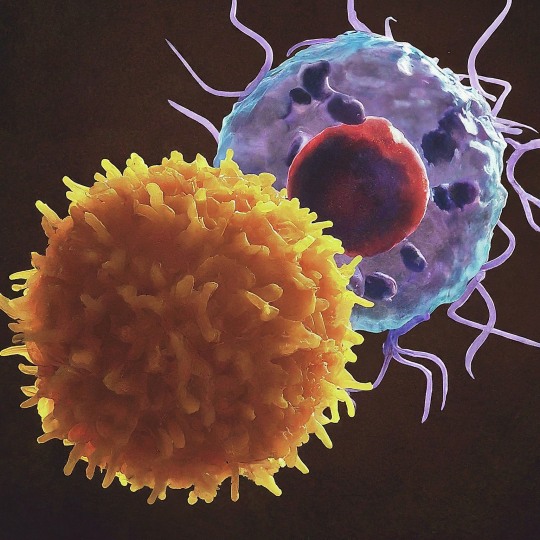
The T Cell Landscape
T cells, a critical component of the adaptive immune system, stand as the body's elite force in combatting infections and diseases. These specialized lymphocytes boast remarkable diversity, each type playing a distinct role in orchestrating a targeted and effective immune response.
T cells, like all blood cells, originate from hematopoietic stem cells residing in the bone marrow. However, their training ground lies within the thymus, a specialized organ located in the chest. Here, they undergo a rigorous selection process known as thymocyte education. During this process, immature T cells, called thymocytes, are presented with self-antigens (molecules unique to the body) by special cells. Thymocytes that bind too strongly to these self-antigens are eliminated, preventing them from attacking healthy tissues later. Only thymocytes that demonstrate the ability to recognize foreign invaders while exhibiting tolerance to self are released into the bloodstream as mature T cells.
Following this rigorous training, mature T cells exit the thymus and embark on their patrol, circulating throughout the bloodstream and lymphatic system. They remain vigilant, constantly scanning for their specific targets – antigens. Antigens are foreign molecules, such as fragments of viruses, bacteria, or even cancerous cells, that trigger the immune response.
The hallmark of a T cell is its T cell receptor (TCR), a highly specialized protein complex embedded on its surface. This receptor acts like a lock, uniquely shaped to fit a specific antigen, the "key." Each T cell develops a unique TCR capable of recognizing only a single antigen, enabling a highly specific immune response.
But how do T cells encounter these hidden antigens lurking within infected or cancerous cells? This critical role is played by antigen-presenting cells (APCs). APCs, such as macrophages and dendritic cells, engulf pathogens or abnormal cells, break them down into smaller fragments (peptides), and present them on their surface complexed with major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules. MHC molecules act as identification tags, allowing T cells to distinguish between "self" and "non-self." When a T cell's TCR encounters its specific antigen bound to an MHC molecule on an APC, a dance of activation begins. The T cell becomes stimulated, and a cascade of signaling events is triggered. This leads to the T cell's proliferation, producing an army of clones specifically tailored to combat the recognized threat.
T cells are not a single, monolithic entity. They comprise a diverse population, each type with a specialized function:
Helper T Cells (Th Cells):
Helper T cells, often abbreviated as Th cells, play a central role in coordinating immune responses. They express the CD4 surface marker and can recognize antigens presented by major histocompatibility complex class II (MHC-II) molecules. Subtypes of helper T cells include Th1, Th2, Th17, and regulatory T cells (Tregs), each with distinct functions and cytokine profiles.
Th1 cells mediate cellular immunity by activating macrophages and cytotoxic T cells, crucial for defense against intracellular pathogens.
Th2 cells are involved in humoral immunity, promoting B cell activation and antibody production, thus aiding in defense against extracellular parasites.
Th17 cells contribute to the immune response against extracellular bacteria and fungi, producing pro-inflammatory cytokines. Regulatory T cells (Tregs) maintain immune tolerance and prevent autoimmunity by suppressing excessive immune responses.
Cytotoxic T Cells (Tc Cells):
Cytotoxic T cells, also known as Tc cells or CD8+ T cells, are effector cells responsible for directly killing infected or aberrant cells. They recognize antigens presented by MHC class I molecules on the surface of target cells. Upon activation, cytotoxic T cells release perforin and granzymes, inducing apoptosis in target cells and eliminating the threat.
Memory T Cells:
Memory T cells are a long-lived subset of T cells that persist after the clearance of an infection. They provide rapid and enhanced immune responses upon re-exposure to the same antigen, conferring immunological memory. Memory T cells can be either central memory T cells (TCM), residing in lymphoid organs, or effector memory T cells (TEM), circulating in peripheral tissues.
γδ T Cells:
Unlike conventional αβ T cells, γδ T cells express a distinct T cell receptor (TCR) composed of γ and δ chains. They recognize non-peptide antigens, such as lipids and metabolites, and are involved in immune surveillance at epithelial barriers and responses to stress signals.
Beyond the Battlefield: The Expanding Roles of T Cells: The remarkable capabilities of T cells have opened doors for several groundbreaking applications in medicine:
Vaccines: By presenting weakened or inactivated forms of pathogens, vaccines "train" the immune system to generate memory T cells. This prepares the body to recognize and rapidly eliminate the real pathogen upon future exposure, preventing disease.
Cancer immunotherapy: CAR T-cell therapy, a revolutionary approach, genetically engineers a patient's own T cells to express chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) that recognize and target specific cancer cells. These "supercharged" T cells are then reintroduced into the patient, unleashing a potent attack against the tumor.
Autoimmune disease treatment: Researchers are exploring ways to manipulate T cells to suppress harmful immune responses that underlie autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis.
The diverse array of T cells underscores the immune system's complexity and adaptability in mounting tailored responses against a myriad of threats. From orchestrating immune reactions to maintaining tolerance and establishing long-term immunity, T cells play multifaceted roles in safeguarding the body's health. Understanding the intricacies of T cell biology not only sheds light on immune-mediated diseases but also paves the way for developing novel therapeutic strategies harnessing the power of the immune system.
T cells represent a fascinating aspect of immunology, with their diversity and specificity driving the complexity of immune responses. As research advances, further insights into T cell biology promise to revolutionize immunotherapy and enhance our ability to combat diseases ranging from infections to cancer. By understanding and harnessing their power, we can unlock new avenues for protecting and improving human health.
#science sculpt#life science#science#molecular biology#biology#biotechnology#artists on tumblr#t cells#T helper cells#autoimmune#autoimmunity#helathcare#immunology#immunotherapy#medical care#cancer#human health#research#scientific research#the glass scientists#scientific illustration#research scientist
11 notes
·
View notes