#northern wei dynasty
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text









Relic Prohibited From Displaying Abroad: Northern Wei Dynasty Painting
Painted screen covered with vermilion lacquer from the tomb of Sima Jinlong (司馬金龍).
The outlines are finely drawn in black ink. A dazzling riot of colors distinguishes this specimen from those of previous centuries.
The painting illustrates narratives about female virtues and filial piety from Han dynasty Liu Xiang's (劉向) Confucian classic “Biography of Exemplary Women” (列女傳).
The top section from the well-preserved part in the photo depicts Emperor Shun's story of filial piety.
The second represents Three Queens of Zhou dynasty – Tai Jiang, Tai Ren and Tai Shi – exemplary mothers and wives (whose historicity remains in doubt) included in later collections of moral precepts.
The third section portrays Lushi Chunjiang and Chunjiang’s daughter.
The bottom one illustrates the episode when the Consort Ban (班婕妤) refused to accompany the emperor in a palanquin so as not to distract him from the thoughts about the state welfare.
The screen was unearthed in Shijiazhai (石家寨) village, Datong, Shanxi in 1965. It is surprising that many precious artifacts remained in the burial pit, despite repeated plundering. We can chalk it up to the ignorance of the thieves.
The board is 82 cm long, 40 cm wide and 2.5 cm thick. The two pieces of the lacquer-painted screen are connected by mortise and tenon joint.
Due to its exceptional fragility and value, the panel is not allowed to be exhibited abroad. Despite all the museum care, the second part of the diptych is not so well-preserved. The tomb has been repeatedly flooded over the centuries, and the dampness has taken its toll. The vermilion screen is stored in Datong Museum (大同市博物館), Shanxi. The original is rare on display for several days only, the rest of the time it is replaced by a replica. Pictured is the original.
#ancient china#chinese culture#chinese art#chinese history#chinese painting#painting miniatures#painting on wood#Northern Wei dynasty#lacquer#lacquerware#ancient tomb#tomb art#vermilion#artifact#unique#relic#han dynasty#burial site#burial#chinese customs
68 notes
·
View notes
Photo
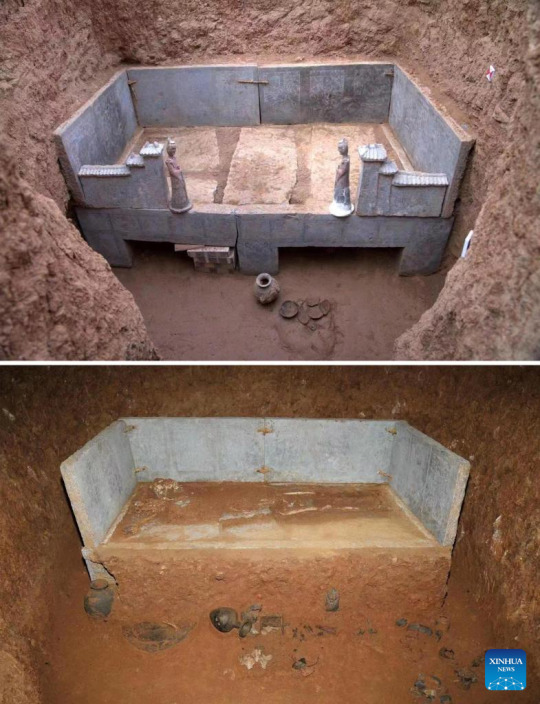
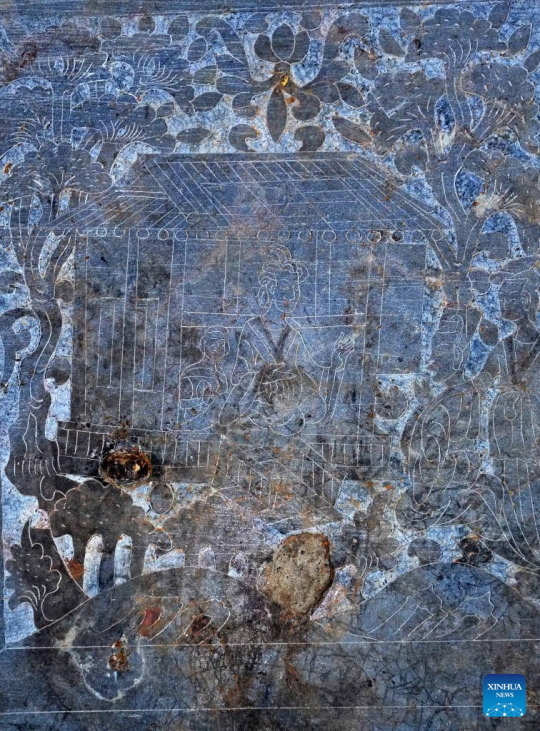








Ancient Tombs Discovered in China's Henan
A cemetery found in Zhucang Village in Mengjin District of Luoyang City, central China's Henan Province. A cemetery consisting of three tombs was recently listed as one of the five key archaeological discoveries in Henan Province in 2022. In the tombs probably built between the late period of the Northern Wei Dynasty (386-534) and the Eastern Wei Dynasty (534-550), large-scale and well-organized stone beds with stone folding screens were found. This is the first time that stone beds dating back to this period have been unearthed in Luoyang City.
#Ancient Tombs Discovered in China's Henan#ancient tombs#ancient graves#ancient artifacts#archeology#archeolgst#history#history news#ancient history#ancient culture#ancient civilizations#ancient china#chinese history#northern wei dynasty#eastern wei dynasty
59 notes
·
View notes
Text
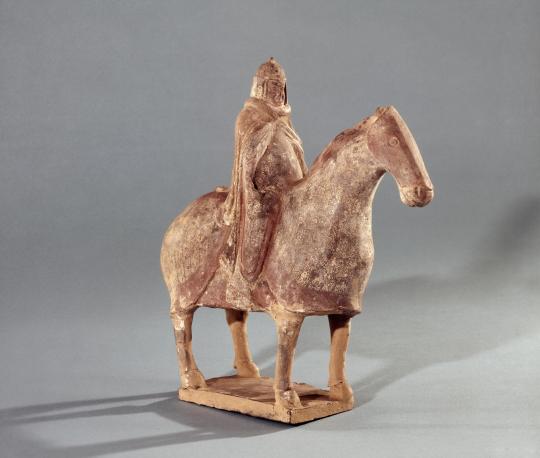

earthenware figure of horse with rider. northern wei dynasty, 386-534.
the british museum only notes that the figure was purchased from private collector george eumorfopoulos; it might have been originally taken from a tomb.
#china#northern and southern dynasties#northern wei dynasty#decorative arts#funereal arts#museum trawling#image source: british museum
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Art from November 2023.

Her name is Jingyi and she's a journalist with a little blog.
#my art#ffvii oc#final fantasy vii#final fantasy vii oc#northern wei dynasty#hanfu#just a one off oc#original character
1 note
·
View note
Text
Mercury was already known to be poisonous by the Northern Wei dynasty.
via @romanceyourdemons
anyways i love the hypothesis that zhao gao was so surnamed because he was from the state of zhao (of brutally destroyed by qin fame) and his whole tenure as an integral part of the qin court was a very very slow and utterly effective revenge campaign
In which Zhao Gao keeps the Qin Emperor isolated and feeds into his ever-growing paranoia. notes: Crown Prince Fusu, eldest son of QSH, was recorded as being popular and kind-hearted. He was exiled to the northern frontier for daring to speak up to his father about the deplorable civil rights of the empire. (Think Prince Zuko from avatar). As far as I know the decision to exile him was all QSH's, very par for the course, no meddling required, but it does strike me as rather lenient for a man of his reputation. he might have genuinely liked Fusu, so wouldn't it be interesting if he expressed regrets about this towards the end of his life, as he lies there isolated, dying, and without a proper heir? if I was Zhao Gao trying to topple the Qin, I would do everything in my power to keep the most experienced, powerful, not to mention popular crown prince (and his loyal war-hero general) far, far away from court, and promote his youngest brother, who is a malleable teenager that i've been grooming for years. "men are naturally inclined to evil" is a corruption of the confucian saying "people are born kind". QSH was the posterboy for legalism, which can be (simplisticly) summed up in Zhao Gao's "might makes right" speech. "strict statues...needful bits" pay tribute to shakespere's measure for measure. mercury was not known to be poisionous until the tang dynasty, so we have to discount Zhao Gao poisioning him on purpose, but Zhao Gao has eyes, and must see that it's definitely not improving QSH's condition. you could also interpret it as him tacitly encouraging QSH to chase after immortality and neglect affairs of state.
20 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Emperor Xiaowen and his entourage worshipping the Buddha, ca.522-23
Northern Wei dynasty, China
From the Central Binyang Cave, Longmen, Henan province
Limestone with traces of pigment
H. 82 in. (208.3 cm); W. 12 ft. 11 in. (393.7 cm)
Together with a companion piece showing an empress and her attendants (now in the Nelson-Atkins Museum of Art, Kansas City), this depiction of an emperor and his entourage once adorned the Central Binyang Cave (also known as Cave 3) in the Longmen complex, near Luoyang, in Henan province. It was positioned centrally on the northeast wall between a group of protective semidivinities above and a narrative debate scene below. Xuanwu commissioned the construction of the Central Binyang Cave in honor of his father, the emperor Xiaowen (r. 471–99), and his mother, the dowager Wenzhou (d. 494); the emperor and empress in the reliefs are therefore believed to refer to his parents. A figure wearing court garments and holding a tasseled baton leads the procession. He is followed by a smaller figure wearing armor and another who stands before the emperor, holding an incense burner. The trees originally indicated the point at which the procession moved around a corner, from the north to the east wall. Several of the attendants hold lotuses or other flowers and offerings, and the entire procession can be understood as making offerings to the Buddhas in the cave, an act of merit making that would continue in perpetuity and improve the future lives of the participants.
Collection of the Metropolitan Museum of Art
#The Met#Metropolitan Museum of Art#Northern Wei dynasty#Northern and Southern dynasties#6th century#relief#religion#art#art history#Chinese#Binyang Caves#Longmen Grottoes#Henan#Xuanwu era#period dress#stone#limestone#portrait
1 note
·
View note
Text
[China Makeup history]The production of concealer powder for women in the Northern Wei Dynasty(386–535)of China 1,500 years ago
The author's experience of the production process is as follows:
1.Concealer powder for women in the Northern Wei Dynasty. After experiencing the entire production process, my first impression: the rice soaked for more than 20 days is really smelly! like the biological weapon my painful expression doesn't require any acting skills, but the rice soaked for many days is very soft and sticky, and it is very convenient to rub or grind it by hand (Women with no strength like me can quickly grind it into pulp in 5 minutes)
2.The process is complicated and the production takes more than 30 days. The resulting "rice powder" is indeed delicate. Although its adhesion cannot compare with today's cosmetics, it is still very good as a basic makeup powder for women more than a thousand years ago.
————————
🧚🏻Production & Model/Makeup:@曾嚼子
🔗 Xiaohongshu:http://xhslink.com/uc8W4S
————————
#chinese hanfu#Northern Wei Dynasty(386–535)#China Makeup history#hanfu#hanfu accessories#chinese traditional clothing#hanfu_challenge#china#chinese#cosmetics#historical makeup#historical fashion#曾嚼子#Concealer powder#漢服#汉服#中華風
216 notes
·
View notes
Text


北魏(鲜卑族)大襟长袍 North Wei (Xianbei tribe) large collared long robe
Because today's garment is from the Xianbei ethnic group, I wanted to give a brief background to its origins.
Some people argue very intensely that "Hanfu" must only come from the Han ethnic group. But clothing isn't restricted by state borders, it's just very natural for people to see clothing they like and take influence from it.
Hanfu has influenced a lot of China's bordering countries, and in return it has also been influenced by them throughout history. There's no shame in that, that's not something negative, it's just a very natural thing that happens. For me, if a garment originated from outside the Han ethnic group but became incorporated into Hanfu, then I'll happily include it while giving credit to where it originated from.
Early Chinese History
I compiled some maps for the early Chinese dynasties to give a better idea of just how much fighting took place between dynasty changes. Sometimes it's difficult to explain because you get dozens of little Kingdoms fighting each other. Even some Chinese people get confused much less trying to explain it to others who're completely new to it all @__@


The Spring/Autumn period (East Zhou), Warring States period (East Zhou), and Sixteen Kingdoms period (East Jin) saw some of the most intense, chaotic fighting.
There's a saying in Chinese; 天下大势,分久必合,合久必分
It translates to: What is long divided shall be unified, What is long unified shall divide, such is the way of the world.
This saying comes from seeing dynasty after dynasty go through the same cycle over and over. The first few emperors of every dynasty are hardworking (they fought for it, they shed blood for it, it's THEIR kingdom), then gradually with each generation things start to deteriorate. Advisors start manipulating, queens and concubines start fighting for power (often with family members in high positions of power), young puppet emperors start being propped up, the court is saturated with internal conflict and the country falls to chaos as local authorities start being assholes to the people. Finally, rebellion. And then a new dynasty starts.


#hanfu#汉服#china#中国#chinese hanfu#culture#history#fashion#clothing#historical clothing#北魏#鲜卑族#南北朝#大襟长袍#North wei#northern southern dynasty#xianbei ethnic group
16 notes
·
View notes
Text

#mdzs#dungeon meshi#wei wuxian#marcille donato#i know mdzs has no specific canonical time period#but mxtx has mentioned her main inspirations were the wei-jin and northern and southern dynasties#so putting wwx's death in 451- 13 years before marcille's birth- isn't much of a stretch#anyway necromancy blorbos go brrrrr
26 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ugh. Why is it so difficult to find info on men's clothing? 90% of the websites I visit are about women's clothing only. Sometimes with a very small paragraph or two on men's clothing. Ugh. Whyyyyyyy.
#hanfu#chinese history#historical fashion#chinese fashion#sui dynasty#tang dynasty#northern and southern dynasties#wei and jin dynasties#history of hanfu
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
Tuoba Tao: Ok, maybe playing ‘whose family is most dysfunctional’ wasn’t the best idea we’ve had. Tuoba Huang's been crying in the bathroom for an hour. We can’t get him out...
#tuoba tao#tuoba huang#incorrect northern wei#this could be any dynasty#or tuoba gui and tuoba si#there was so much daddy issues in northern wei
0 notes
Text
INTERESTING
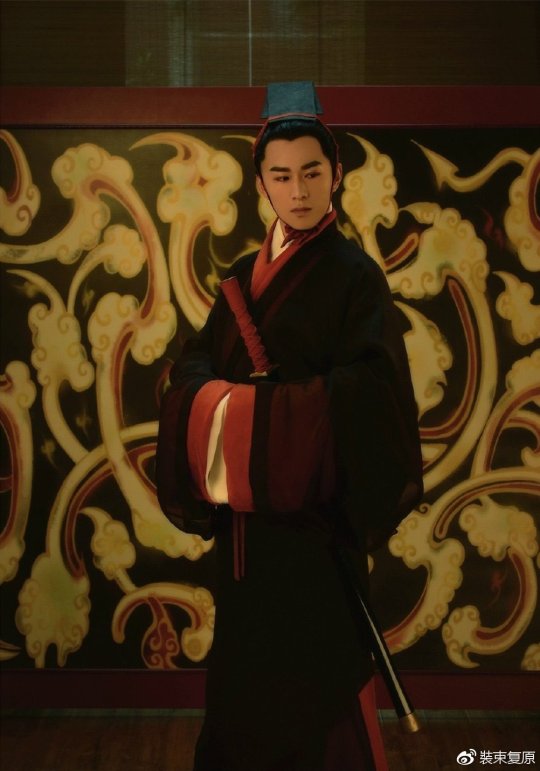
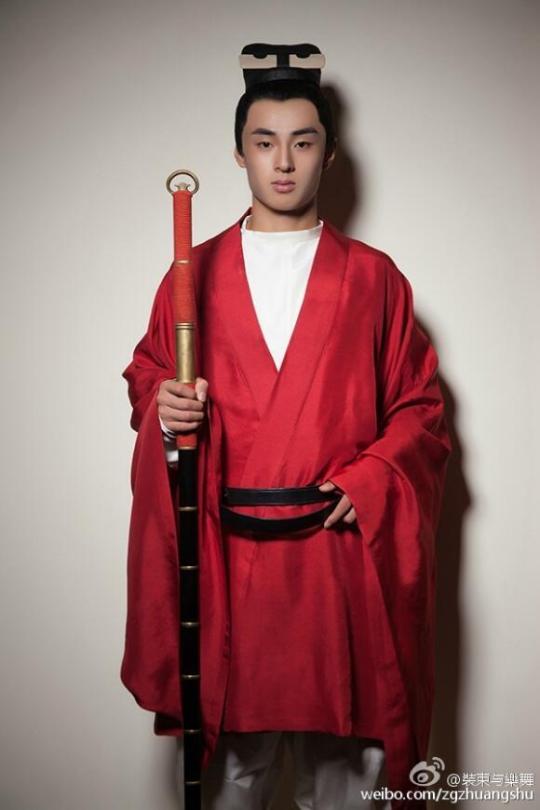










men’s hanfu
line 1 - line 5 :Han Dynasty
line 1 - line 3 : Western Han
line 4 - line 5 :Eastern Han
line 6 : Wei and Jin Dynast
line 7 - line 8 : Northern Song Dynasty
#hanfu#mens hanfu#mens headwear#hats#runway#history#reference#Han dynasty#western han dynasty#Eastern Han dynasty#wei/jin dynasties#Song dynasty#Northern Song#Coser小梦
97 notes
·
View notes
Text










The Cryptic Motif of “Three Hares with Conjoined Ears”
On the Heavenly Palace decorative patterns found in the Mogao Caves at Dunhuang from the late Northern dynasties are images with cryptic patterns, including Buddha's head, the Taotie beast, deer, animals copulating, three hares with conjoined ears, and also writings. This type of decorative pattern is cryptic and difficult to understand and may be closely related to the history of the popular Eastern iconology and divination philosophy from the Han and Wei dynasties and Emperor Wu of Northern Zhou's suppression of Buddhism. They are important references for studying the related history of this period.
#china#motif#three hares with conjoined ears#silk road#culture influenced by buddhism from ancient india#art#reference
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
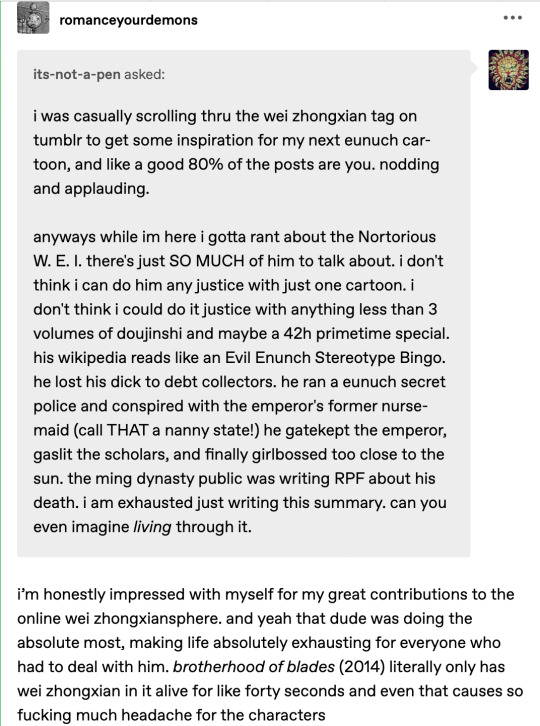
eunuch rating system: part 2 electric boogaloo! part 1 based on the original post by @welcometothejianghu wherein i continue to rate REAL historical chinese eunuchs! this is a non-exhaustive list and there's honestly no metric to it. i just pick the guys i like.
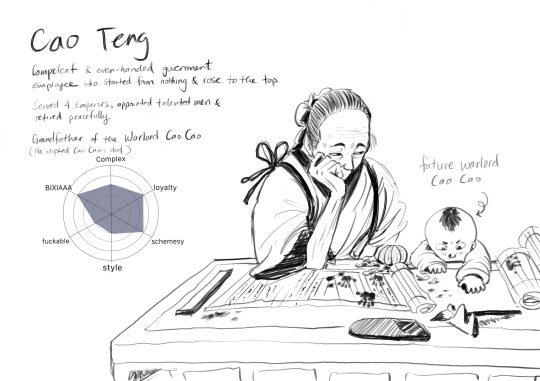
Han Dynasty (yes, again. the Han was like 400 years long lol) Cao Teng was a pretty normal guy whose biggest claim to fame is his extremely infamous grandson, Cao Cao. Because of this, Cao Teng is the only enunch in chinese history to get a royal title; Emperor Gao of Wei, which was granted posthumerously through Cao Cao’s grandson Cao Rui.
Cao Teng was a good judge of character who promoted a bunch of famous people, one of whom was a guy who had even tried to impeach him previously. After 30 years of service, he retired, got married, and adopted a son.
i decided to put him on the list because the common perception of the eunuch is a "mutilated" man living a lonely, unfulfilled life. What is often left out is they are highly motivated people who excel at their jobs, exert a lot of influence, and are able to have families and leave a legacy.
the majority of eunuchs came from poor families, and serving at the palace gave them an opportunity to obtain wealth, status and an education they would otherwise never have access to. it does require an unimaginably painful sacrifice, but that shouldn't be the only thing that defines them.
Cao Teng's hard work benefited his entire clan and lifted them out of poverty. But there was a complex interplay between him being a venerable ancestor, and someone marked by the stigma of castration. I imagine there was something bittersweet here for Cao Teng, knowing that he had done so much for his family, but they would rather he didn't exist.
Cao Cao was able to become a prime minister because of the wealth, connections, and education earned by his grandfather. At the same time, he appeared to resent him. The source of his ancestory was a sore spot which was repeatedly brought up by his political enemies to discredit him, something he never commented directly on or attempted to defend.


ming dynasty
MAKE SOME FUCKING NOISE FOR THE COOLEST PERSON IN THE MING DYNASTY!!!! actually scratch that, MAKE SOME FUCKING NOISE FOR THE COOLEST PERSON IN CHINESE HISTORY, PERIOD.
Zheng He was born Ma He to muslims living in Yunan, which was ruled by Mongols at the time. He was captured by the Ming army between the age of 10-14, castrated, and given to the young Yongle Emperor as a servant. Incredibly enough, he was like "no hard feelings mate" and went on to work in EVERY SINGLE JOB. and kick absolute ass in ALL OF THEM. he started out as a soldier on the northern frontier (the toughest place to serve, that was where all the border conflicts were) and fought in several campaigns with the future emperor, distinguishing himself and earning the emperor's trust.
I originally had him drawn in a more stereotypically "heroic" pose, by all accounts he was a tough guy who "walked like a tiger", and while the main purpose of the Ming voyages were diplomatic, he didn't shy away from violence. (he fought PIRATES. like a fucking shonen protagonist). in the end i decided to go with a picture that showcases less celebrated but equally important leadership qualities like curiosity, patience and discipline. I also want to point out that he wasn't the only eunuch on the trip, around half of the commanding officers were also eunuchs. He wasn't an exception to the rule but rather the face of a largely ignored majority; complicated people who were making the most of a difficult job.
Notes: the giraffe he brought back didn't have a name (at least not on record), but the Ming thought it was a qilin (kinda like a chinese unicorn) and i thought that would be an adorable name for a giraffe.
Ming Dynasty
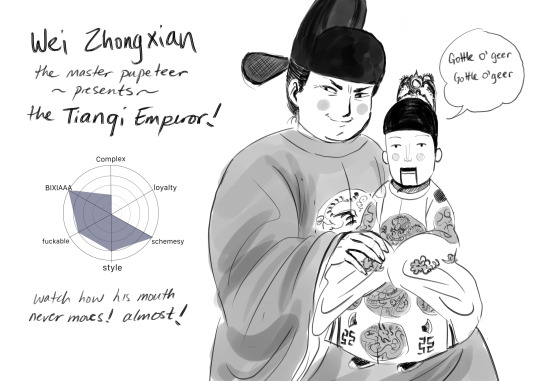
i feel like we've had too much nuance, so lets finish this list off with a properly corrupt and scheming enunch! Wei Zhongxian castrated himself at age 21 to escape his gambling debts, and it unleashed his potiential like Rock Lee removing his leg weights. once inside the palace, he started out as a minor kitchen hand but managed to hustle his way to being the right hand of the emperor, who was an indifferent ruler that prefered woodworking to running a country. for this reason, I decided to make him a ventriloquist dummy.
Wei Zhongxian then proceeded to go on an extravagant and over-compensating ego trip. actually, it was more like a 40-year-long, olympic worthy, ego-long jump. things came to a terrible end when he tried to stage a coup (it failed and he decided not to hang around the capital, and go hang on some rafters instead). by then, decades of corruption had weakened the Ming, the emperor's only son got exploded in horrible incident that also wiped out most of the Ming Dynasty munitions--and what's this? here comes the Qing Dynasty with a steel chair!!!! notes: I decided to make Wei Zhongxian's design a human version of my cat, because he is also an incredibly devious but rather low-wisdom individial.
159 notes
·
View notes
Text



The Ballad of Mulan
an anonymous work of Chinese folklore, is dated from the Northern Wei dynasty (386-534 AD), a period marked by significant Silk Road cultural exchanges and the spread of Buddhism, influenced Chinese art, music, and literature, including Mulan's tale. It was first transcribed in the 6th-century "Musical Records of Old and New" by Guo Maoqian during the Song dynasty.
The ballad embodies key Confucian principles such as Xiao (family devotion) and loyalty (zhong). Confucius (551-479 BC) was a Chinese philosopher whose teachings on ethics and proper conduct, recorded in the "Analects," have profoundly shaped Chinese culture and emphasized social harmony through respect and integrity. These values emphasize respect for family and duty to the state, which are central themes in Mulan’s decision to enlist in the army to protect her aging father.
UNIVERSAL TRUTHS: Filial piety, a key Confucian value, highlights the deep respect and loyalty children owe to their parents and ancestors. Today, filial piety remains crucial in modern Chinese culture, often shown by caring for elderly parents and upholding family obligations. Within your own family, do you see filial piety as a core value? Are you prepared to make personal sacrifices to benefit your family members?
Overcoming Gender barriers: The ballad illustrates that personal empowerment and heroism are not confined by gender. Similar themes appear in historical figures like Joan of Arc, who led French troops, and Deborah Sampson, who fought in the American Revolutionary War disguised as a man. The ballad of Mulan ultimately recognizes Mulan’s merit and contributions based on her abilities rather than her gender, advocating for the value of personal achievement and character over rigid gender stereotypes.
Like this art? It will be in my illustrated book with over 130 other full page illustrations coming in October to kickstarter. to get unseen free hi-hes art subscribe to my email newsletter
Follow my backerkit kickstarter notification page.
Thank you for supporting independent artists! 🤘❤️🏛😁
#Mulan#ChineseFolklore#AncientChina#Confucianism#BalladofMulan#NorthernWeiDynasty#ChineseArt#AsianArt#ArtHistory#TraditionalChinese#ChineseCulture#artists on tumblr
101 notes
·
View notes
Text
April 14, Xi'an, China, Shaanxi History Museum, Qin and Han Dynasties Branch (Part 3 – Innovations and Philosophies):
(Edit: sorry this post came out so late, I got hit by the truck named life and had to get some rest, and this post in itself took some effort to research. But anyway it's finally up, please enjoy!)
A little background first, because this naming might lead to some confusions.....when you see location adjectives like "eastern", "western", "northern", "southern" added to the front of Zhou dynasty, Han dynasty, Song dynasty, and Jin/晋 dynasty, it just means the location of the capital city has changed. For example Han dynasty had its capital at Chang'an (Xi'an today) in the beginning, but after the very brief but not officially recognized "Xin dynasty" (9 - 23 AD; not officially recognized in traditional Chinese historiography, it's usually seen as a part of Han dynasty), Luoyang became the new capital. Because Chang'an is geographically to the west of Luoyang, the Han dynasty pre-Xin is called Western Han dynasty (202 BC - 8 AD), and the Han dynasty post-Xin is called Eastern Han dynasty (25 - 220 AD). As you can see here, in these cases this sort of adjective is simply used to indicate different time periods in the same dynasty.
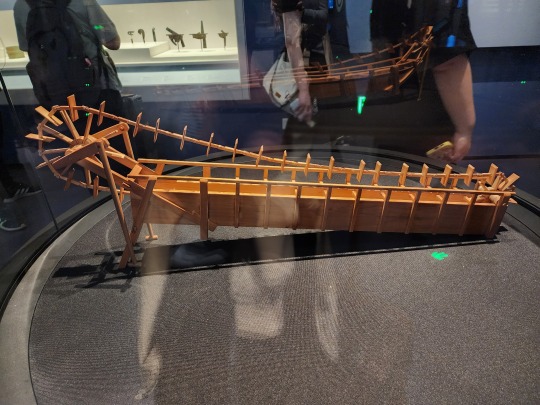
Model of a dragonbone water lift/龙骨水车, Eastern Han dynasty. This is mainly used to push water up to higher elevations for the purpose of irrigation:
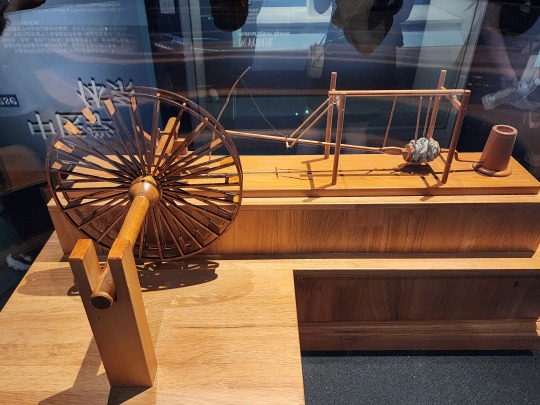
Model of a water-powered bellows/冶铁水排, Eastern Han dynasty. Just as the name implies, as flowing water pushes the water wheel around, the parts connected to the axle will pull and push on the bellows alternately, delivering more air to the furnace for the purpose of casting iron.
The Nine Chapters on the Mathematical Art/《九章算术》, Fangcheng/方程 chapter. It’s a compilation of the work of many scholars from 10 th century BC until 2 nd century AD, and while the earliest authors are unknown, it has been edited and supplemented by known scholars during Western Han dynasty (also when the final version of this book was compiled), then commented on by scholars during Three Kingdoms period (Kingdom of Wei) and Tang dynasty. The final version contains 246 example problems and solutions that focus on practical applications, for example measuring land, surveying land, construction, trading, and distributing taxes. This focus on practicality is because it has been used as a textbook to train civil servants. Note that during Han dynasty, fangcheng means the method of solving systems of linear equations; today, fangcheng simply means equation. For anyone who wants to know a little more about this book and math in ancient China, here’s an article about it. (link goes to pdf)

Diagram of a circle in a right triangle (called “勾股容圆” in Chinese), from the book Ceyuan Haijing/《测圆海镜》 by Yuan-era mathematician Li Ye/李冶 (his name was originally Li Zhi/李治) in 1248. Note that Pythagorean Theorem was known by the name Gougu Theorem/勾股定理 in ancient China, where gou/勾 and gu/股 mean the shorter and longer legs of the right triangle respectively, and the hypotenuse is named xian/弦 (unlike what the above linked article suggests, this naming has more to do with the ancient Chinese percussion instrument qing/磬, which is shaped similar to a right triangle). Gougu Theorem was recorded in the ancient Chinese mathematical work Zhoubi Suanjing/《周髀算经》, and the name Gougu Theorem is still used in China today.

Diagram of the proof for Gougu Theorem in Zhoubi Suanjing. The sentence on the left translates to "gou (shorter leg) squared and gu (longer leg) squared makes up xian (hypotenuse) squared", which is basically the equation a² + b² = c². Note that the character for "squared" here (mi/幂) means "power" today.

This is a diagram of Zhang Heng’s seismoscope, called houfeng didong yi/候风地动仪 (lit. “instrument that measures the winds and the movements of the earth”). It was invented during Eastern Han dynasty, but no artifact of houfeng didong yi has been discovered yet, this is presumably due to constant wars at the end of Eastern Han dynasty. All models and diagrams that exist right now are what historians and seismologists think it should look like based on descriptions from Eastern Han dynasty. This diagram is based on the most popular model by Wang Zhenduo that has an inverted column at the center, but this model has been widely criticized for its ability to actually detect earthquakes. A newer model that came out in 2005 with a swinging column pendulum in the center has shown the ability to detect earthquakes, but has yet to demonstrate ability to reliably detect the direction where the waves originate, and is also inconsistent with the descriptions recorded in ancient texts. What houfeng didong yi really looks like and how it really works remains a mystery.

Xin dynasty bronze calipers, the earliest sliding caliper found as of now (not the earliest caliper btw). This diagram is the line drawing of the actual artifact (right).


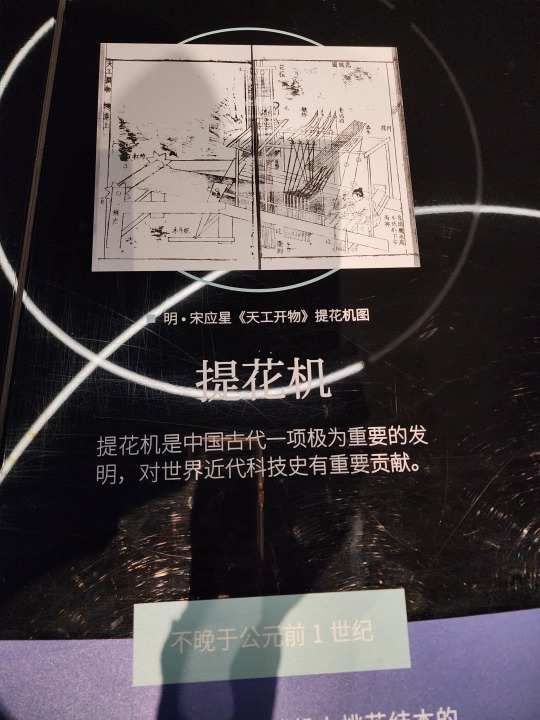
Ancient Chinese "Jacquard" loom (called 提花机 or simply 花机 in Chinese, lit. "raise pattern machine"), which first appeared no later than 1st century BC. The illustration here is from the Ming-era (1368 - 1644) encyclopedia Tiangong Kaiwu/《天工开物》. Basically it's a giant loom operated by two people, the person below is the weaver, and the person sitting atop is the one who controls which warp threads should be lifted at what time (all already determined at the designing stage before any weaving begins), which creates patterns woven into the fabric. Here is a video that briefly shows how this type of loom works (start from around 1:00). For Hanfu lovers, this is how zhuanghua/妆花 fabric used to be woven, and how traditional silk fabrics like yunjin/云锦 continue to be woven. Because it is so labor intensive, real jacquard silk brocade woven this way are extremely expensive, so the vast majority of zhuanghua hanfu on the market are made from machine woven synthetic materials.
Chinese purple is a synthetic pigment with the chemical formula BaCuSi2O6. There's also a Chinese blue pigment. If anyone is interested in the chemistry of these two compounds, here's a paper on the topic. (link goes to pdf)

A list of common colors used in Qin and Han dynasties and the pigments involved. White pigment comes from chalk, lead compounds, and powdered sea shells; green pigment comes from malachite mineral; blue pigment usually comes from azurite mineral; black comes from pine soot and graphite; red comes from cinnabar; ochre comes from hematite; and yellow comes from realgar and orpiment minerals.

Also here are names of different colors and shades during Han dynasty. It's worth noting that qing/青 can mean green (ex: 青草, "green grass"), blue (ex: 青天, "blue sky"), any shade between green and blue, or even black (ex: 青丝, "black hair") in ancient Chinese depending on the context. Today 青 can mean green, blue, and everything in between.

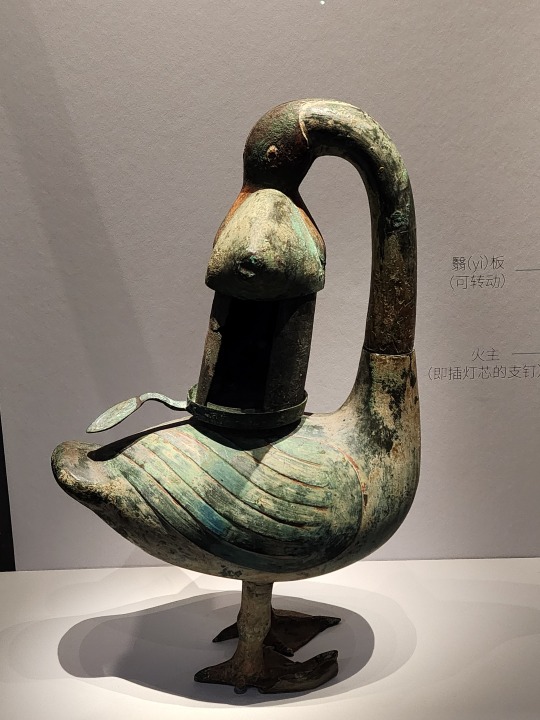
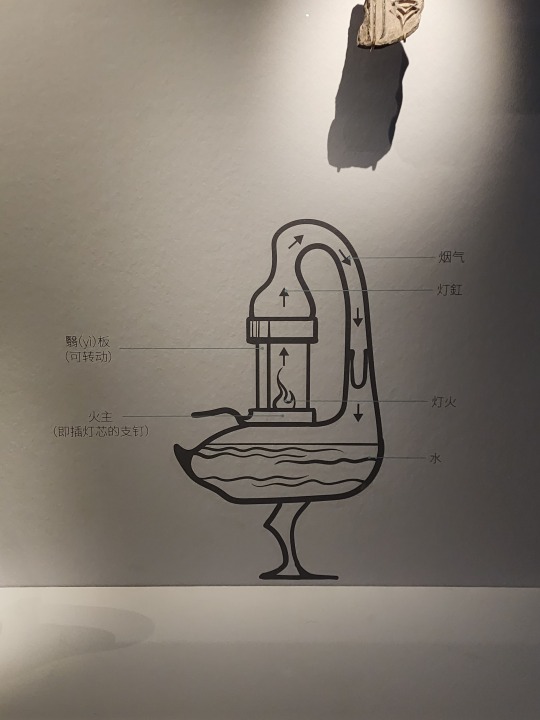
Western Han-era bronze lamp shaped like a goose holding a fish in its beak. This lamp is interesting as the whole thing is hollow, so the smoke from the fire in the lamp (the fish shaped part) will go up into the neck of the goose, then go down into the body of the goose where there's water to catch the smoke, this way the smoke will not be released to the surrounding environment. There are also other lamps from around the same time designed like this, for example the famous gilt bronze lamp that's shaped like a kneeling person holding a lamp.

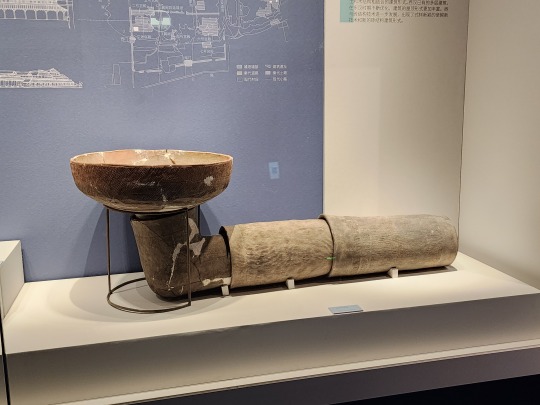
Part of a Qin-era (?) clay drainage pipe system:

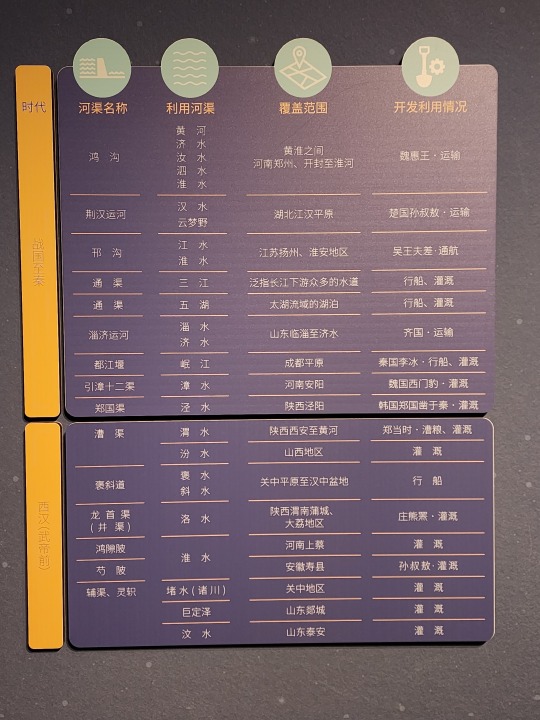
A list of canals that was dug during Warring States period, Qin dynasty, and pre-Emperor Wu of Han Han dynasty (475 - 141 BC). Their purposes vary from transportation to irrigation. The name of the first canal on the list, Hong Gou/鸿沟, has already become a word in Chinese language, a metaphor for a clear separation that cannot be crossed (ex: 不可逾越的鸿沟, meaning "a gulf that cannot be crossed").
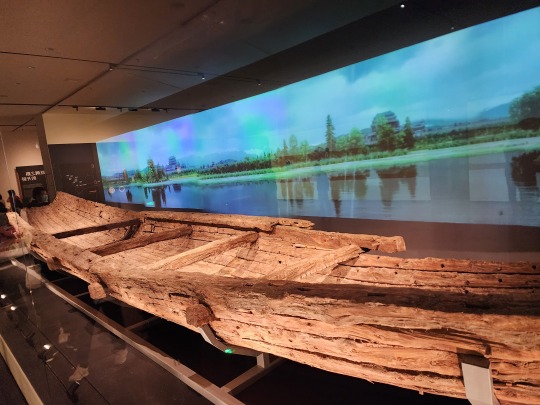
Han-era wooden boat. This boat is special in that its construction has clear inspirations from the ancient Romans, another indication of the amount of information exchange that took place along the Silk Road:

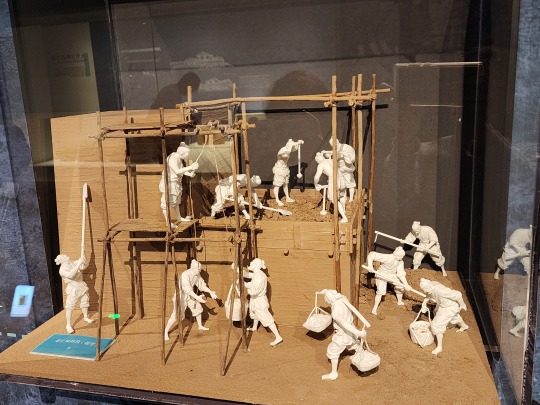
A model that shows how the Great Wall was constructed in Qin dynasty. Laborers would use bamboo to construct a scaffold (bamboo scaffolding is still used in construction today btw, though it's being gradually phased out) so people and materials (stone bricks and dirt) can get up onto the wall. Then the dirt in the middle of the wall would be compressed into rammed earth, called hangtu/夯土. A layer of stone bricks may be added to the outside of the hangtu wall to protect it from the elements. This was also the method of construction for many city walls in ancient China.

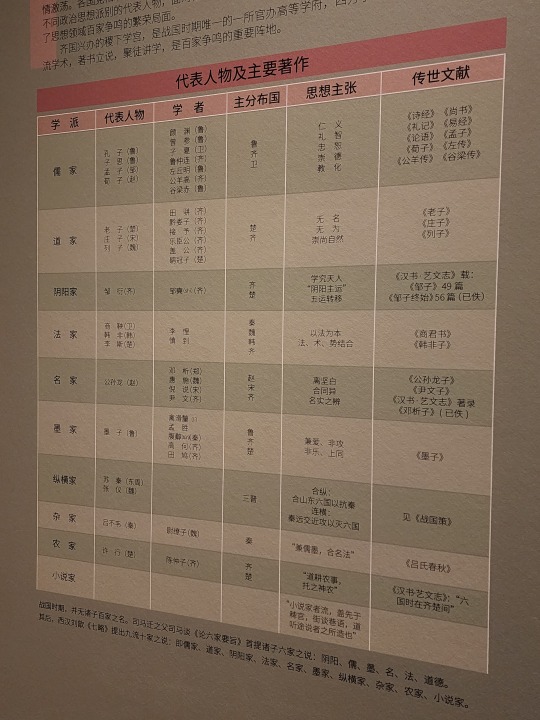
A list of the schools of thought that existed during Warring States period, their most influential figures, their scholars, and their most famous works. These include Confucianism (called Ru Jia/儒家 in Chinese; usually the suffix "家" at the end denotes a school of thought, not a religion; the suffix "教" is that one that denotes a religion), Daoism/道家, Legalism (Fa Jia/法家), Mohism/墨家, etc.
The "Five Classics" (五经) in the "Four Books and Five Classics" (四书五经) associated with the Confucian tradition, they are Shijing/《诗经》 (Classic of Poetry), Yijing/《易经》 (also known as I Ching), Shangshu/《尚书》 (Classic of History), Liji/《礼记》 (Book of Rites), and Chunqiu/《春秋》 (Spring and Autumn Annals). The "Four Books" (四书) are Daxue/《大学》 (Great Learning), Zhongyong/《中庸》 (Doctrine of the Mean), Lunyu/《论语》 (Analects), and Mengzi/《孟子》 (known as Mencius).

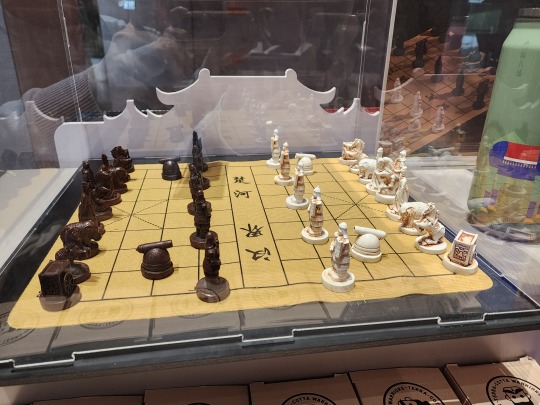
And finally the souvenir shop! Here's a Chinese chess (xiangqi/象棋) set where the pieces are fashioned like Western chess, in that they actually look like the things they are supposed to represent, compared to traditional Chinese chess pieces where each one is just a round wooden piece with the Chinese character for the piece on top:

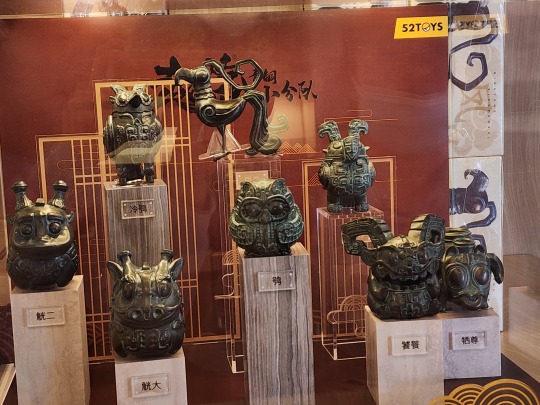
A blind box set of small figurines that are supposed to mimic Shang and Zhou era animal-shaped bronze vessels. Fun fact, in Shang dynasty people revered owls, and there was a female general named Fu Hao/妇好 who was buried with an owl-shaped bronze vessel, so that's why this set has three different owls (top left, top right, and middle). I got one of these owls (I love birds so yay!)
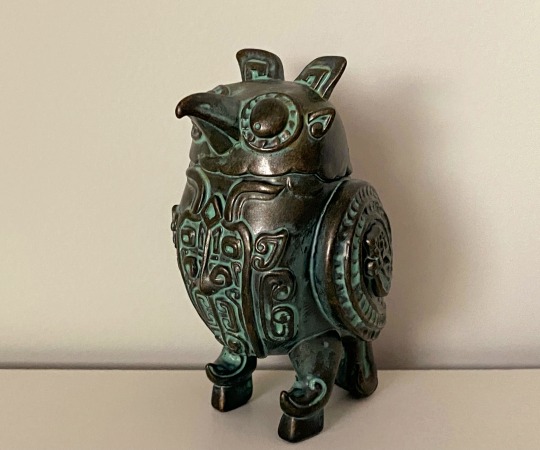


And that concludes the museums I visited while in Xi'an!
#2024 china#xi'an#china#shaanxi history museum qin and han dynasties branch#chinese history#chinese culture#chinese language#qin dynasty#han dynasty#warring states period#chinese philosophy#ancient technology#math history#history#culture#language
90 notes
·
View notes