#new natives
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
"A tribal-led nonprofit is creating a network of native bison ranchers that are restoring ecosystems on the Great Plains, restoring native ranchers’ connections with their ancestral land, and restoring the native diet that their ancestors relied on.
Called the Tanka Fund, they coordinate donors and partners to help ranchers secure grazing land access, funds needed to install and repair fencing, increase their herd sizes, and access markets for bison meat across the country.
That’s the human part of the story. But as Dawn Sherman, executive director of the Tanka Fund, told Native Sun News, they’re “buffalo people” and these four-legged, 2,000 lbs. “cousins” are equal-part-protagonists.
The return of the bison means the return of the prairie, one of the three great grassland ecosystems on the planet, of which just 1% remains as it was when the Mayflower arrived.
“Bringing buffalo back to their ancestral homelands is essential to restoring the ecosystem. We know that the buffalo is a keystone species,” said Dawn Sherman, a member of the Lakota, Delaware, Shawnee, and Cree.
“Bringing the buffalo back to the land and to our people, helps restore the ecosystem and everything it supports from the animals to the plants to the people. It’s come full circle. That’s how we see it.”
As Sherman and the Tanka Fund help native ranchers grow their operations, everyone is well aware of the power of the bison to transform the environment: just as nations across Europe are, who are reintroducing wood bison to various ecosystems, for all the same reasons.
Sherman points out the variety of ways in which buffalo anchor the prairie ecosystem. The almost-extinct black-footed ferret, she points out, lived symbiotically with the bison, and with the latter gone, the former followed—nearly.
The long-billed curlew uses bison dung as a disguise to hide nests from predators. Deer, pronghorn antelope, and elk all rely on bison to plow through deep snows and uncover the grasses that these smaller animals can’t reach.
Everywhere the bison hurls its massive body, life springs in the beast’s wake. When bison roll about on the plains, it creates depressions known as wallows. These fill with rainwater and create enormous puddles where amphibians and insects thrive and reproduce. Certain plants evolved to grow in the wet conditions of the wallows which Native Americans harvested for food and medicine.
Native plants evolved under the trampling hooves of millions of bison, and that constant tamping down of the Earth is a key necessity in the spreading of native wildflower seed.
Indeed, Sherman says some of these native ranchers are bringing bison onto lands still visibly affected by the Dust Bowl, and already the animals are acting like a giant wooly cure-all for the land’s ills.
Since 2020, the Tanka Fund, in partnership with the Inter-Tribal Buffalo Council and the Nature Conservancy, has overseen the transfer of 2,300 bison from Nature Conservancy reserves to lands managed by ranchers within the Tanka Fund network.
“[T]he more animals that we can get the more of that prairie we can restore,” said Sherman. “We can help restore the land that has been plowed and has been leased out to cattle ranchers.”"
youtube
-Article via Good News Network, February 13, 2025. Video via Tanka Fund, July 17, 2024.
#indigenous#indigenous peoples#first nations#native americans#bison#ecology#ecosystem#ecosystem restoration#keystone species#endangered species#environment#prairie#great plains#land back#good news#hope#Youtube
14K notes
·
View notes
Text
Stay Noisy. It works sometimes.
#Pentagon#Navajo Code Talkers#Native veterans#U.S. Marine Corps#Navajo#in World War II#Native American heroes#Censorship#Doversity Ban#Department of Defense#Code Talkers#Iwo Jima flag raiser#Donald Trump#DEI#Ira Hayes#the Gila River#News
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
A caveat to this study: the researchers were primarily looking at insect pollinator biodiversity. Planting a few native wildflowers in your garden will not suddenly cause unusual megafauna from the surrounding hinterlands to crowd onto your porch.
That being said, this study backs up Douglas Tallamy's optimistic vision of Homegrown National Park, which calls for people in communities of all sizes to dedicate some of their yard (or porch or balcony) to native plants. This creates a patchwork of microhabitats that can support more mobile insect life and other small beings, which is particularly crucial in areas where habitat fragmentation is severe. This patchwork can create migration corridors, at least for smaller, very mobile species, between larger areas of habitat that were previously cut off from each other.
It may not seem like much to have a few pots of native flowers on your tiny little balcony compared to someone who can rewild acres of land, but it makes more of a difference than you may realize. You may just be creating a place where a pollinating insect flying by can get some nectar, or lay her eggs. Moreover, by planting native species you're showing your neighbors these plants can be just as beautiful as non-native ornamentals, and they may follow suit.
In a time when habitat loss is the single biggest cause of species endangerment and extinction, every bit of native habitat restored makes a difference.
#nature#wildlife#animals#ecology#environment#conservation#science#scicomm#pollinators#bees#butterflies#hoverflies#insects#native plants#habitat restoration#solarpunk#hopepunk#naturecore#wildflowers#good news
5K notes
·
View notes
Text
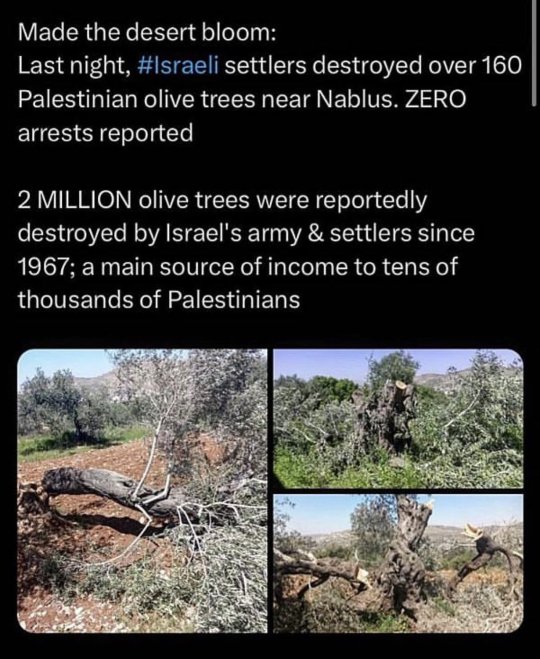


US literally is a teaching guide for war crimes.
#free palestine#politics#news#palestine#west bank#democrats#republicans#trees#botany#nature#native americans#military#woc#poc#women of color#colonialism#colonization#usa
9K notes
·
View notes
Text
Please please please, I’m begging people, start talking about indonesia occupied papua. Over the last 50 years Indonesia has killed over 500,000 native Papuans in their occupation of the west half of the island.
This is also a genocide that should be talked about. It needs to be addressed, but it’s ignored on the global stage.
Free Papua!
#Palestine#native news#indonesia#papua#papua new guinea#west papua#Indonesia occupied Papua#free Palestine#free Papua
5K notes
·
View notes
Text
[Original video. Downloaded for easier access.]
#palestine#from the river to the sea palestine will be free#gaza#free gaza#students for justice in palestine#palestine news#save palestine#free palestine#war on gaza#gaza news#gaza genocide#palestinian genocide#genocide#stop genocide#usa is a terrorist state#usa propaganda#american government#america politics#fuck america#native american#polio#polio vaccine#history#historical women#boycott disney#disney#netflix#boycott#boycott mcdonalds#boycott starbucks
2K notes
·
View notes
Text


The forest king and the postwoman
#artists on tumblr#art#illustration#character design#oc#digital art#SORRY for reposting but I wasn't satisfied with the sketches so I'm making a new post without it#postwoman#the postwoman#adalore#king of the forest#original#original character#Ill draw more of him because I love him#also he is beautiful to any human but for all natives of the world the postwoman lives in he is UGLY AF
12K notes
·
View notes
Text



Source
Is this really satire?
#indigenous people day#politics#us politics#government#the left#native americans#current events#news#satire#activism#the onion#imperialism
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Dandelion News - February 15-21
Like these weekly compilations? Tip me at $kaybarr1735 or check out my Dandelion Doodles!
1. Solar farms managed for nature boost bird abundance and diversity, new study finds

“There were more than twice as many farmland birds in the well-managed solar farms compared with the intensively farmed land, and nearly 16 times as many woodland birds. […] Overall, diversity was 2.5 times higher, while woodland birds were nine times more diverse.”
2. Washington judge blocks Trump’s gender-affirming care ban, says it's unconstitutional in multiple ways

“This marks the second time in a week that a judge has stood in the way of Trump’s attacks on trans kids. [… The ruling grants] a temporary restraining order that halts enforcement of provisions in Trump’s directive that would cut off federal funding to medical institutions that provide gender-affirming care to minors.”
3. Fog harvesting could provide water for arid cities

“17,000 sq m of mesh could produce enough water to meet the weekly water demand of [… the] urban slums. 110 sq m could meet the annual demand for the irrigation of the city's green spaces. Fog water could be used for soil-free (hydroponic) agriculture, with yields of 33 to 44lb (15 to 20kg) of green vegetables in a month.”
4. Audubon Applauds Bipartisan Federal Effort to Protect Delaware River Basin with Critical Reauthorization Bill

“The bill would […] ensure long-term conservation and restoration efforts, expand the official definition of the basin to include Maryland, and prioritize projects that serve small, rural, and disadvantaged communities. […] The watershed provides important year-round habitats and critical migratory stopovers for approximately 400 bird species[….]”
5. mRNA vaccines show promise in pancreatic cancer in early trial
“Half of the people in the study — eight of the participants — responded to the vaccine, producing T cells that targeted their tumors. […] Just two of the patients who had a response to the vaccine had their cancer return during the three-year follow- up, compared to seven of the eight who did not respond to the vaccine treatments.”
6. Minn. Lt. Gov. Flanagan Makes It Official; She's running for U.S. Senate

“[Flanagan has] “championed kitchen-table issues like raising the minimum wage, paid family and medical leave, and free school meals.” If elected, Flanagan, a tribal citizen of the White Earth Nation, would become the first Native American female U.S. senator in history.”
7. Federal Funding Restored for Low-Income Alabama Utility Assistance After Outcry

“A program meant to help low-income Alabamians pay their utility bills has resumed two weeks after it was canceled due to an executive order from President Donald Trump. […] “We can confirm the funds are reaching those affected by the previous pause[….]””
8. Modeling study suggests Amazon rainforest is more resilient than assumed

“[Previous] studies were either conducted with global climate models that used a simplified representation of convection [or were on a regional scale….] According to the computations, mean annual precipitation in the Amazon does not change significantly even after complete deforestation.“
9. States are moving forward with Buy Clean policies despite Trump reversal

““Buy Clean is a great example of how states and other nonfederal actors can continue to press forward on climate action, regardless of what the federal government does,” said Casey Katims, executive director of the U.S. Climate Alliance, a bipartisan coalition of two dozen governors.”
10. The rewilded golf courses teeming with life

“A wildflower meadow, ponds, scrub habitat, coastline and even an area of peat bog can be found on this little 60-acre (24-hectare) plot, which boasts roe deer, otters, lizards, eels and a huge array of insects and birds.”
February 8-14 news here | (all credit for images and written material can be found at the source linked; I don’t claim credit for anything but curating.)
#hopepunk#good news#nature#us politics#solar power#solar panels#solar energy#birds#biodiversity#gender affirming care#transgender#trans rights#trans healthcare#water conservation#habitat#migratory birds#vaccines#vaccination#mrna vaccine#pancreatic cancer#cancer#native american#alabama#low income#amazon rainforest#rainforest#executive orders#climate action#golf course#habitat restoration
980 notes
·
View notes
Note
I know this happened last year, but Illinois has its first reservation! The Department of the Interior placed 130 acres of land in DeKalb County near Shabbona State Park into trust for the Prairie Band Potawatomi.
!!! That's huge! I had no idea!! Congratulations to be Prairie Band Potawatomi!!!
"Nearly 200 years after Native Americans were forced out of Illinois, the Prairie Band Potawatomi Nation has become the first federally recognized tribal nation in the state after a decision from the U.S. Department of the Interior last week.
The move represents the first victory in the tribe’s larger effort to regain the approximately 1,280 acres of its ancestral land in Illinois via legislation in both the General Assembly and Congress.
But the tribe first had to spend $10 million over the last 20 years to repurchase the first 130 acres of the Shab-eh-nay Reservation, located in what is now DeKalb County, that the federal government illegally sold out from under Chief Shab-eh-nay around 1850.
Nearly two centuries later, Prairie Band Chairman Joseph “Zeke” Rupnick – a fourth-great grandson of Chief Shab-eh-nay – signed paperwork on Friday that allows the Department of the Interior to place those 130 acres into a trust, which gives the tribe sovereignty over the land.
Rupnick said he’d heard the story of his ancestral land in Illinois “ever since I was a child” from his grandparents, and said his mother started the push to reclaim the Prairie Band’s land three decades ago when she was the tribe’s chairperson.
“For me to actually get it accomplished and signed, honestly, words couldn't describe the feeling that I had that, you know, when I actually completed that task,” he told Capitol News Illinois on Monday, adding that the credit should be shared with his entire counsel and tribal membership more broadly. “And now the real work begins.”"
-via NPR Illinois, April 30, 2024
#zackprincebooks#ask#ask game#indigenous#first nations#native american#prairie band potawatomi#indigenous peoples#potawatomi#land back#illinois#north america#good news#hope#hopepunk#hope posting
1K notes
·
View notes
Text


February 19, 2025 - Leonard Peltier is finally out of prison! If you happen to be near Belcourt, North Dakota, you can welcome him home today. [link]
#leonard peltier#american indian movement#ndn#indigenous resistance#free leonard peltier#2025#indigenous#native american#political prisoners#usa#good news#aim
685 notes
·
View notes
Text

Central Park West, New York, 1975-78 by Helmut Newton.
#helmut newton#nyc#1970s#central park west#native new yorker#vintage#retro#fashion#editorial#vogue#vintage vogue
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
So this is a really creative solution to a pernicious ecological problem! The short version is that arid ecosystems like deserts are quite fragile. For example, many have soil that is covered in a thin biocrust that can be damaged just by walking or driving on it. And because life needs water to grow and recover, these super-dry ecosystems may not be able to repair a footprint or tire track for over a century.
However, arid ecosystems are often some of the least understood because they can be difficult to access. And they suffer from P.R. issues because deserts are often seen as "bad" ecosystems full of death and nothingness, and because we do legitimately want to avoid the desertification of other native habitats.
In order to raise awareness and appreciation of these landscapes, biological surveys that tally the living beings found there help show how biodiverse they can be. And when we know more about how abundant or scarce a given species there is, it gives us more impetus to protect them, especially those that are at risk of extinction.
These paramotorists were able to fly across Peru's lomas (coastal fog deserts), which primarily receive scant amounts of moisture from mist. They collected plant samples to take back to scientists, carefully recording where they were found. And because they were able to fly long distances, they could minimize the amount of time their feet were on the ground and therefore minimize their impact on the local ecology.
At a time where it seems every interaction between motorized technology and nature is a negative one, this is a pleasant departure. yes, of course we wish we weren't in a place where we have to be worried about increasing extinction and other ecological woes. But let's take the wins where we can; the morale boost is crucial to being able to keep looking toward a better future.
#desert#lomas#ecology#botany#plants#native plants#science#scicomm#nature#endangered species#extinction#environment#conservation#biology#hopepunk#good news#paramotor#paragliding
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Biden creates a new national monument near the Grand Canyon - https://www.npr.org/2023/08/08/1192622716/biden-national-monument-grand-canyon-arizona
The move protects lands that are sacred to indigenous peoples and permanently bans new uranium mining claims in the area. It covers nearly 1 million acres.
—
"It will help protect lands that many tribes referred to as their eternal home, a place of healing and a source of spiritual sustenance," she said. "It will help ensure that indigenous peoples can continue to use these areas for religious ceremonies, hunting and gathering of plants, medicines and other materials, including some found nowhere else on earth. It will protect objects of historic and scientific importance for the benefit of tribes, the public and for future generations."
—
The new national monument will be called Baaj Nwaavjo I'tah Kukveni Grand Canyon National Monument. According to the Grand Canyon Tribal Coalition that drafted a proposal for the monument, "Baaj Nwaavjo" means "where tribes roam" in Havasupai, and "I'tah Kukveni" translates to "our ancestral footprints" in Hopi.
all land is sacred (and should be returned) but this is good news.
#indigenous#native american#ndn#arizona#grand canyon#climate change#nature#good news#land conservation and preservation#hopi#havasupai
7K notes
·
View notes
Text


I miss my fuck buddies🤤🤤
#native women#ndn#sexy native#navajo#navajogirl#nativebigtity navajo#n8tive#n8vgirls#nativebaddiez#Shiprock#farmington#new mexico#native#native beauty#native girls
475 notes
·
View notes
Photo






Māori rights protests in New Zealand draw tens of thousands : NPR
800 notes
·
View notes