#naturebasedsolutions
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Video
youtube
Restoration and Aridity Impact on Grassland Biodiversity #sciencefather #researchawards #soilhealth
🌍🌾 Global evidence: How to reconcile the effect of restoration measures and aridity index on biodiversity and ecosystem multifunctionality in grasslands reveals a crucial step toward sustainable land management. As grasslands face increasing degradation due to climate stress and human activities, restoration measures such as re-vegetation, grazing exclusion, and soil amendments are being widely implemented. 🌱📉 However, their outcomes often vary depending on regional aridity — the balance between rainfall and evaporation. This study integrates global datasets to explore how these restoration efforts interact with the aridity index, uncovering that biodiversity and ecosystem multifunctionality — including productivity, nutrient cycling, and soil health — respond differently across arid to humid gradients. 🌦️🔄 Findings emphasize that tailoring restoration strategies to local climate conditions is essential for optimizing ecological outcomes, ensuring that interventions not only enhance biodiversity 🐞🌿 but also sustain multiple ecosystem services critical for long-term resilience and sustainability. 🌎🔬💚
Natural Scientist Awards
Nomination Link: https://naturalscientist.org/award-nomination/?ecategory=Awards&rcategory=Awardee
Visit Our Website 🌐naturalscientist.org
Contact us [email protected]
Get Connected Here:
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/natural-scientist-466a56357/
Blogger: https://naturalaward.blogspot.com/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/natural_scientist/
Pinterest: https://in.pinterest.com/research2805/_profile/
Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/@NaturalScientistAwards
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/profile.php?id=61574191899176
#youtube#sciencefather#naturalscientistawards#researchawards#globalrestoration#grasslandbiodiversity#ecosystemmultifunctionality#aridityindex#climateimpact#restorationmeasures#sustainablelandmanagement#globalbiodiversity#grasslandrestoration#ecologicalresilience#soilhealth#habitatrestoration#climategradient#environmentalsustainability#ecosystemservices#restorationecology#landdegradation#global#naturebasedsolutions#ecologicalbalance
0 notes
Text
Sustainable Land Management: A Smart Approach for a Greener Future
Know more at https://lamsapp.com/blog/sustainable-land-management-a-smart-approach-for-a-greener-future
As the world continues to urbanize and industrialize rapidly, land resources are facing immense pressure. From deforestation and soil degradation to unsustainable agricultural practices and rapid infrastructure development, our land assets are being stretched beyond capacity. This is where Sustainable Land Management (SLM) steps in — an integrated approach that ensures the responsible use of land resources while maintaining environmental integrity, economic viability, and social equity.
Recommended read https://lamsapp.com/blog/what-is-sustainable-land-management
#economic viability#and social equity.#SustainableLandManagement#SLM#LandManagement#SustainableDevelopment#SmartLandUse#LandUsePlanning#SustainableFarming#SoilConservation#EnvironmentalSustainability#GreenInfrastructure#GISForLandManagement#ClimateSmartAgriculture#LandRestoration#LandGovernance#Agroecology#SustainableAgriculture#SoilHealth#UrbanPlanning#LandRights#EcoFriendlyDevelopment#SDGs#SDG15#ClimateAction#NatureBasedSolutions#SustainabilityMatters#EnvironmentFirst#LandUseChange
0 notes
Text
Let’s plant mangroves everywhere! These climate superheroes protect coastlines, reduce flooding, absorb carbon, and help us adapt to rising seas. 🌊🌱

GIF shows a tree-like plant with roots sticking out above water—yes, it looks like a mangrove, especially a species like the red mangrove (Rhizophora mangle) which has aerial "prop roots" that extend above the water
0 notes
Text
The Water Cycle in the Urban Landscape.
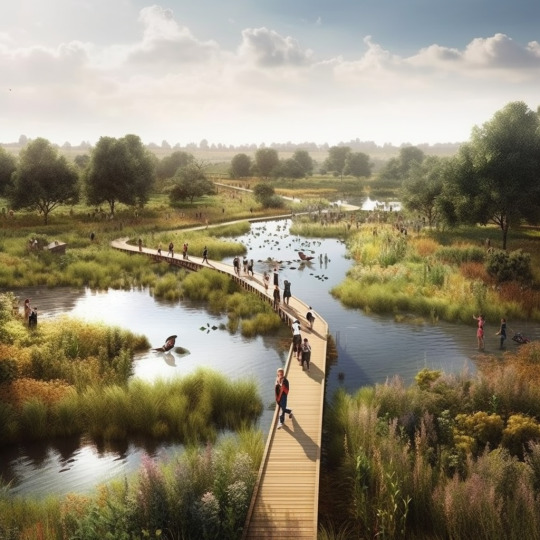

From the sky to the ground, we need to rethink the city as a living sponge. This approach embraces rainfall not as a threat, but as a resource. Through nature-based solutions such as permeable surfaces, green roofs, infiltration zones, and rainwater harvesting systems, we will create resilient cities that absorb, store, and reuse water sustainably.
#cityassponge#urbanhydrology#landscapearchitecture#SustainableCities#greeninfrastructure#NatureBasedSolutions#resilientdesign#RainwaterHarvesting#ClimateAdaptation#ecologicalurbanism#watersensitivedesign#urbanlandscape#spongecityy#bluegreeninfrastructure#CircularWater
0 notes
Text
🌿 Biopolymers and Beyond: Sustainable Materials Redefining Industrial Innovation
By Hafiz Muhammad Husnain Azam Researcher, Brandenburg University of Technology Cottbus-Senftenberg 📘 Published 🔗 Read Full Chapter on Wiley
The Material Revolution Starts with Nature
In an era driven by the urgent need for environmental responsibility, industries across the globe are turning to biopolymers—natural, biodegradable materials derived from plants and microorganisms—as sustainable alternatives to petroleum-based plastics. But biopolymers are no longer limited to raw forms.
In this chapter, we explore the next generation of biopolymer engineering, including:
Blends
Interpenetrating Polymer Networks (IPNs)
Gels
Composites
Nanocomposites
Each form unlocks new levels of functionality, durability, and industrial relevance—setting a new benchmark for sustainable material science.
🔍 What’s Inside the Chapter?
✅ Biopolymer Fundamentals
Derived from natural sources like chitin, starch, and bacterial fermentation, biopolymers offer biodegradability, renewability, and low toxicity—key drivers for their rise in packaging, agriculture, and medical sectors.
✅ Blends & Composites
Blending different biopolymers (e.g., PLA + PBAT) or reinforcing them with natural fibers like hemp and flax creates materials with superior mechanical and thermal properties—ideal for packaging, automotive parts, and construction components.
✅ IPNs (Interpenetrating Polymer Networks)
These materials interlace multiple polymer networks at the molecular level, providing enhanced strength, elasticity, and chemical resistance. Their applications span tissue engineering, drug delivery, and industrial coatings.
✅ Gels & Hydrogels
Engineered for biomedical and pharmaceutical applications, these viscoelastic materials mimic tissue behavior and offer excellent moisture retention, making them useful in wound healing and drug delivery.
✅ Biopolymer-Based Nanocomposites
Infused with graphene oxide, CNTs, and metal nanoparticles, these advanced materials deliver exceptional barrier properties, conductivity, and antimicrobial activity—revolutionizing electronics, sensors, and environmental cleanup systems.
🌍 Applications Across Industries
Sustainable Packaging: Compostable materials replacing traditional plastics
Biomedical Engineering: Smart gels and scaffolds for regenerative medicine
Environmental Remediation: Nanocomposites that adsorb heavy metals and organic toxins
Smart Materials: Biopolymer-based systems with stimuli-responsive behavior
⚠️ Challenges and the Path Forward
Despite immense potential, the commercialization of biopolymer systems is constrained by:
Mechanical performance gaps
Higher production costs
Scalability concerns
Ongoing research focuses on nanofiller optimization, hybrid design, and cost-effective green synthesis to overcome these hurdles. The goal: making sustainable materials mainstream, not niche.
Let’s Redefine the Future of Materials
This chapter is a comprehensive entry point into the world of sustainable, high-performance materials. If you're involved in materials science, product development, environmental policy, or green manufacturing, this research offers actionable insights to guide your innovation pipeline.
📖 Read the full study: Wiley – Biopolymer Blends, IPNs, and Nanocomposites
https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119783473.ch1
https://go.nature.com/4j29x66

#Biopolymers#GreenMaterials#SustainablePackaging#BioComposites#EcoInnovation#Nanocomposites#SmartMaterials#MaterialsScience#CircularEconomy#RenewableResources#GreenEngineering#BiodegradableMaterials#AdvancedPolymers#IPNs#Hydrogels#EcoFriendlyPlastics#SmartPackaging#FutureOfMaterials#EnvironmentalRemediation#TissueEngineering#NaturalPolymers#SustainableDesign#Bioengineering#WasteToWealth#GreenManufacturing#UNSDG12#CleanTechnology#MaterialsInnovation#NatureBasedSolutions#books
1 note
·
View note
Text
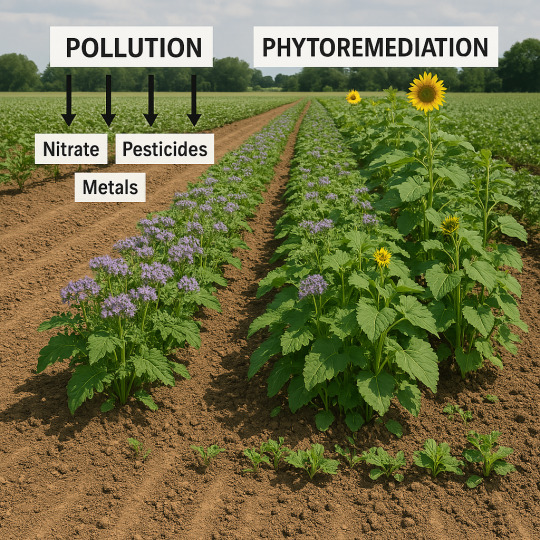
#SoilHealth#Phytoremediation#SustainableFarming#ClimateAction#EnvironmentalProtection#GreenAgriculture#OrganicFarming#PollutionControl#EcoFriendly#SoilRemediation#CleanAgriculture#Agroecology#FarmSustainability#SoilPollution#NatureBasedSolutions#RegenerativeFarming#HealthySoils#CarbonSequestration#EcoFarming#AgTech#ClimateSmart#GreenInnovation#CropDiversity#SoilMicrobiome#Bioremediation#SustainableLandUse#AgriResearch#FutureFarming#SmartAgriculture#EnvironmentalScience
0 notes
Text
Showcasing nature-based solutions in Cobh, Ireland
youtube
Totally forgot to share this project from last year, but looking back on it i'm really quite proud of it. Working in partnership with Glasgow-based arts organisation, WAVEparticle, we made this short documentary for Cork County Council’s Urban design team on using a rain garden (a nature-based solution) to weave nature back into the town with the aim of reducing flood risks, enhancing water quality, fostering biodiversity, and improving the built environment.
1 note
·
View note
Text

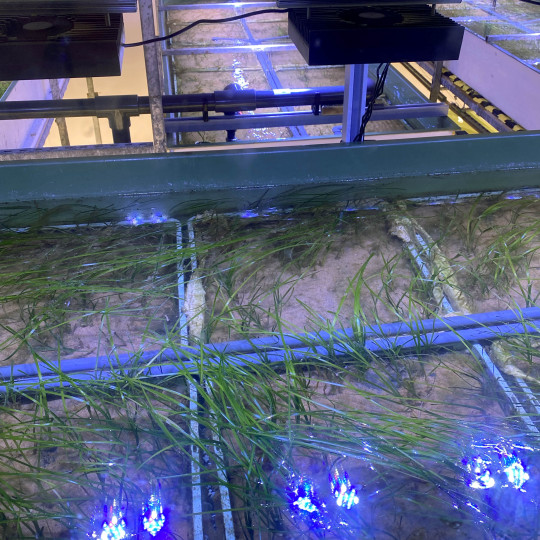






Part 2 of my Plymouth trip!
.
During my MA, my first project explored seagrass—a vital yet often overlooked marine ecosystem. 🌊 Back in 2023, there was significant attention on seagrass decline, but community action and awareness were still limited.
.
🌱 Seagrass meadows combat climate change by absorbing and storing vast amounts of carbon—up to 35 times more efficiently than rainforests of the same size. Despite covering only 0.2% of the ocean floor, seagrasses store 10% of the ocean’s carbon. (Source: Ocean Conservation Trust)
One project that influenced my research was Rosie Sherwood’s “The Seagrass Walk” (slide 3), exhibited in Plymouth. I couldn’t visit at the time, so experiencing it now has brought my own project full circle. It was also fascinating to see the seagrass labs at Plymouth aquarium to, the delicate process of growing such a plant for conservation efforts highlighted the need to conserve these biodiverse areas in situ, such as corals, chalk streams and marsh land. Before they disappear altogether.
.
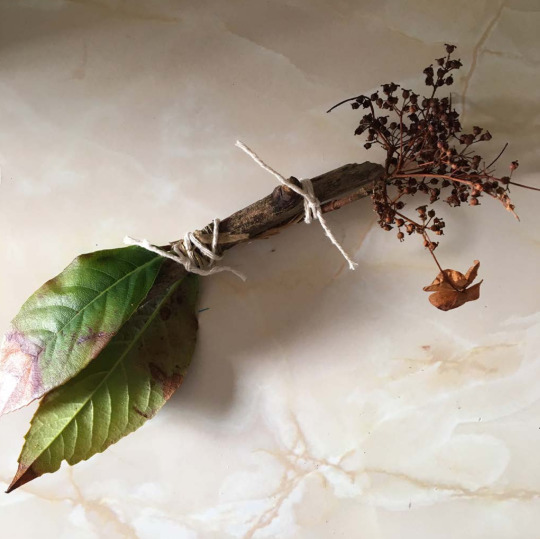
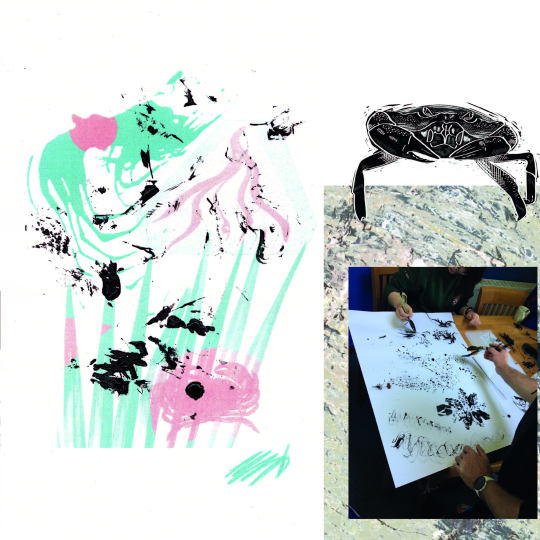
The key research point for my project was inspired by a Cornish research study on the impact of chain moorings on seagrass, specifically how chain width affects seagrass scars. This visual impact led me to explore mark making as a medium.
I began by using secondhand chains to mimic the physical damage to seagrass beds. From there, I incorporated natural materials collected along the coastal path—twigs, seaweed, dried flowers, and grasses—to create custom tools for mark making, connecting the local environment back to the process.
To expand the idea, I developed a workshop prototype, inviting participants to make their own tools and experiment with ink. 🖌️ The hands-on experience fostered creativity and a tangible connection to the issue.
This project not only deepened my understanding of seagrass conservation but also ignited a passion for participatory, community-driven work. I look forward to developing more projects like this in the future!
#seagrassconservation#marineecosystem#oceanconservation#participatorydesign#designresearch#markmaking#ecoart#environmentalart#creativeworkshops#communityart#sustainabledesign#artandecology#conservationdesign#seagrassmeadows#naturebasedsolutions#coastalconservation#visualcommunication#designforchange#graphicdesign#handmadeart#designprocess#visualstorytelling#communityengagement
1 note
·
View note
Text
Role of Climate Data in Assessing Portfolio Risk

Climate-related factors are increasingly being incorporated into financial analysis, with a growing consensus among financial institutions on the importance of understanding the risks and opportunities emanating from climate change. In financial analysis, climate data focuses on metrics that primarily impact asset value, operational costs, and investment returns. These metrics may be qualitative or quantitative, such as greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and targets, extreme weather events tracking, climate scenario analysis, and climate-based regulatory changes and market trends.
Collecting, reporting, and analyzing such climate data is essential for portfolio assessment for the following reasons:
1. Rising Physical Impacts: The number and severity of extreme weather events, such as wildfires, hurricanes, and droughts, have increased over time, especially in the last few years. While financial institutions have limited exposure to physical impacts through their physical assets, they need to consider the indirect effect on their financial assets depending on their exposure and vulnerability to climate hazards.
2. Regulatory Changes: With the rise of policies and regulatory frameworks, such as the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) and Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD), which mandate reporting on the effects of climate change on a company’s operations and vice versa, the need for a strategy to collect and analyze climate data has become more prominent.
3. Investor Demands: There has been a growing demand from investors for more visibility into climate-related variables in their portfolios. While the reasons for investor interest in climate data may range from risk adjustment to sustainability tilts, overall, this trend has resulted in a higher demand for climate data-based analysis, especially from shareholders, debtors, and other stakeholders.
4. Reputational Risk: Public concern about climate change has grown profoundly, and customers and stakeholders are increasingly urging institutions to participate in the transition toward a low-carbon economy. Hence, it is important to incorporate climate data into due diligence practices to avoid any climate-related controversies attracting negative media attention.
These elements have brought climate impact data solutions to the forefront of financial and corporate strategy. As climate risks escalate, the relevance of accounting for climate-related factors in environmental, social, and governance (ESG) portfolio analysis for investors, asset managers, portfolio managers, and financial institutions has grown, along with the need for more comprehensive data reporting.
Recent developments in climate change data reporting standards and frameworks, such as the International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB), Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), CDP, Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB), European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS), etc., have enabled companies to report on their climate change data more effectively. This makes it easier for portfolio managers to incorporate climate data solutions into risk assessment and harmonize portfolios with long-term sustainability goals. This analysis is integral for investors and portfolio managers, as it helps them reduce their exposure to climate risks and identify avenues for opportunities by offering insights into how environmental factors affect future earnings and asset value.
Read More: Role of Climate Data in Assessing Portfolio Risk
#ClimateChange#RiskManagement#SustainableFinance#ImpactInvesting#ClimateAdaptation#GreenEconomy#FinancialSustainability#ClimateDisclosure#InvestmentRisk#NatureBasedSolutions#ClimateAction#CorporateResponsibility#ClimateMetrics#ResilientInvesting#FutureOfFinance#EcoInvesting#ClimateInnovation#SustainableDevelopment#ClimateLeadership
0 notes
Text
Season 3 | Episode 1| The State of Nature Tech with Gilad Goren
youtube
Welcome to Season 3 of The Think Wildlife Podcast. It has been almost two years since I began the Podcast and have had the good fortune of interviewing nearly 100 conservationists around the world. This season consists of another 50 episodes, with topics ranging from nature tech and bioacoustics to conservation filmmaking, the illegal wildlife trade, marine ecology and ecosystem restoration.
#ThinkWildlifePodcast#NatureTech#ConservationPodcast#GiladGoren#EnvironmentalTechnology#WildlifeConservation#NatureBasedSolutions#COP16#Bioacoustics#MarineEcology#EcosystemRestoration#IllegalWildlifeTrade#Sustainability#ConservationFilmmaking#RemoteSensing#AIForNature#ClimateAction#PaidSubscription#ConservationProjects#PodcastCommunity#Youtube
0 notes
Video
youtube
Implementing high-integrity nature-based solutions with Naturebase
0 notes
Video
youtube
Boosting Biodiversity: Education's Role! #sciencefather #biodiversity #scholar
Developing higher education capacity in biodiversity conservation is essential for addressing global environmental challenges and safeguarding the planet’s rich biological diversity 🌍🦋. A key priority is strengthening academic and research institutions in biodiversity-rich, low-resource countries, enabling them to generate local knowledge and solutions 🌱📚. This includes creating interdisciplinary programs that blend ecology, policy, indigenous knowledge, and sustainable development, while fostering global collaborations and knowledge exchange 🤝🌿. Investing in faculty training, infrastructure, and digital access ensures that students and researchers can engage with cutting-edge science and conservation strategies 🧪💻. Additionally, empowering underrepresented communities and promoting inclusivity in conservation education helps build a more equitable and effective global effort to protect biodiversity for future generations 🌺👩🎓🌏.
Natural Scientist Awards
Nomination Link: https://naturalscientist.org/award-nomination/?ecategory=Awards&rcategory=Awardee
Visit Our Website 🌐naturalscientist.org
Contact us [email protected]
Get Connected Here:
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/natural-scientist-466a56357/
Blogger: https://naturalaward.blogspot.com/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/natural_scientist/
Pinterest: https://in.pinterest.com/research2805/_profile/
Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/@NaturalScientistAwards
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/profile.php?id=61574191899176
#youtube#sciencefather#naturalscientistawards#researchawards#biodiversityconservation#highereducation#sustainabledevelopment#conservationeducation#environmentalstudies#climateaction#globalcollaboration#ecological#capacitybuilding#indigenousknowledgesystems#greenfuture#naturebasedsolutions#academic#wildlifepreservation#research#scientist#researcher#scholar
0 notes
Text

IIT Roorkee in association with Department of Science and Technology, Government of India is organising Capacity and Public Policy for Climate and Disaster Resilience: Integrating Nature Based Solutions on 27 November 2023.
0 notes
Text
Living Lab
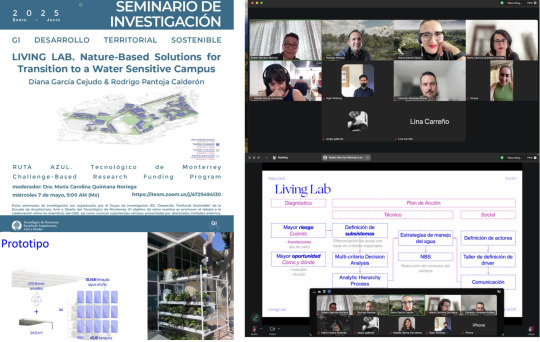
Con gran entusiasmo, el pasado miércoles 7 de mayo compartimos los avances de nuestra investigación “Living Lab: Nature-Based Solutions for the Transition to a Water Sensitive Campus”, cuyo objetivo es reducir en un 20% el consumo de agua en el Tecnológico de Monterrey, Campus Querétaro, en el marco de la Convocatoria Ruta Azul.
Fue un verdadero privilegio presentar este proyecto en colaboración con mis colegas Rubén Garnica, Viviana Barquero y Diana Garcia, y contar con la acertada moderación de la Dra. María Carolina Quintana María Carolina Quintana Noriega.
Agradezco profundamente las valiosas contribuciones del equipo ampliado: Miguel Anaya Díaz, Dany Cn, Claudia Martínez, Luisa Medina y Sergio Rodriguez, así como el acompañamiento y las enriquecedoras sugerencias de los consultores del Centro de Estudios Ambientales y Urbanos urbam EAFITi de la Colombia. Universidad EAFIT en Medellín, Colombia.
La presentación ante el Grupo de Investigación en Desarrollo Territorial Sostenible nos permitió recibir una retroalimentación crítica y propositiva, que sin duda fortalecerá nuestra metodología y enriquecerá la narrativa del proyecto, con miras a implementar estrategias replicables, medibles y orientadas a una transformación sostenible real.
#NatureBasedSolutions#WSC#livinglab#arquitecturadelpaisaje#UrbanismoSostenible#InnovaciónAmbiental#SolucionesbasadasenlaNaturaleza#WaterSensitive#arquitectura#arquitecturamexicana#evolab#evolabarquitectura#paisajismo#landscapearchitecture
0 notes
Text
♻️ Chitosan-Based Nanomaterials: Green Technology for Water Pollution Remediation
By Hafiz Muhammad Husnain Azam Researcher, Brandenburg University of Technology Cottbus-Senftenberg 📘 Published 🔗 Read Full Chapter on ScienceDirect
Tackling the Water Crisis with Bio-Nanotechnology
With industrial discharge, synthetic dyes, and toxic heavy metals increasingly polluting global water systems, conventional treatment methods are falling short. In this chapter, we explore how chitosan-based hybrid nanomaterials offer a sustainable and cost-effective pathway to cleaner, safer water—leveraging the unique power of nature-enhanced with nanotechnology.
Why Chitosan?
Chitosan, a biopolymer derived from chitin (found in crustacean shells), is biodegradable, non-toxic, and naturally adept at binding pollutants. When combined with advanced nanomaterials like graphene oxide, carbon nanotubes, and magnetic nanoparticles, chitosan becomes a versatile, high-performance adsorbent—tailor-made for eco-friendly water purification.
🌊 Key Functional Applications:
Heavy Metal Removal: Efficient adsorption of lead, cadmium, arsenic, and other toxic ions.
Dye and Organic Pollutant Removal: Enhanced capture of synthetic dyes and pharmaceutical residues.
Magnetic Recovery: Easy material recovery post-treatment using magnetic separation—reducing waste and improving reusability.
Why It Matters
Traditional water purification methods often involve toxic chemicals, high energy costs, and non-renewable resources. Chitosan-based nanomaterials address these issues head-on by being:
Eco-friendly and biodegradable
Cost-effective in the long run
Scalable with ongoing innovation
Safe for the environment and human health
The Road Ahead: Opportunities & Challenges
Despite their promise, challenges like pollutant-specific efficiency, scalability, and cost of modification need to be addressed. Our chapter discusses current strategies to optimize chitosan properties for real-world application and highlights ongoing research aimed at:
Improving surface functionality
Reducing synthesis costs
Enhancing performance under variable environmental conditions
Let's Shape the Future of Clean Water
This research opens up critical dialogue around green materials in environmental remediation. Whether you're in nanotech R&D, water resource management, policy, or sustainability, this chapter provides actionable insights for next-gen water treatment technologies.
📖 Dive deeper into the science: Full Chapter on ScienceDirect
https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-443-21891-0.00016-0
https://go.nature.com/4j2lYie

#Chitosan#Nanomaterials#WaterPollution#EcoFriendlyTechnology#WaterTreatment#EnvironmentalRemediation#GreenNanotechnology#SustainableMaterials#HeavyMetalRemoval#WaterPurification#BioNanotechnology#BiodegradableSolutions#SmartWaterSolutions#DyePollution#MagneticNanoparticles#WaterQualityManagement#CleanWaterTech#SustainableDevelopment#EnvironmentalEngineering#PFASRemoval#SmartFiltration#GreenTech#NextGenMaterials#ZeroWasteWater#UNSDG6#NatureBasedSolutions#ScienceForThePlanet#ChemicalEngineering#FutureOfWater#academia
1 note
·
View note
Text
youtube
#SoilHealth#Phytoremediation#SustainableFarming#ClimateAction#EnvironmentalProtection#GreenAgriculture#OrganicFarming#PollutionControl#EcoFriendly#SoilRemediation#CleanAgriculture#Agroecology#FarmSustainability#SoilPollution#NatureBasedSolutions#RegenerativeFarming#HealthySoils#CarbonSequestration#EcoFarming#AgTech#ClimateSmart#GreenInnovation#CropDiversity#SoilMicrobiome#Bioremediation#SustainableLandUse#AgriResearch#FutureFarming#SmartAgriculture#EnvironmentalScience
0 notes